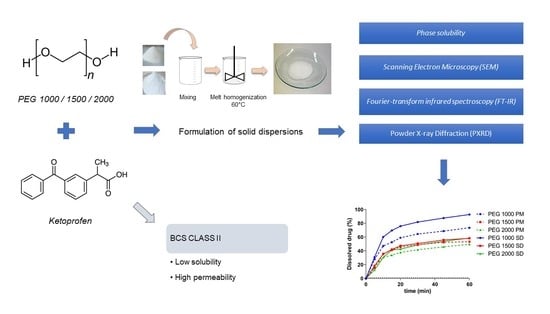
Effect of Molecular Weight on the Dissolution Profiles of PEG Solid Dispersions Containing Ketoprofen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Phase Solubility
2.2.2. Preparation of Solid Dispersions and Physical Mixtures
2.2.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.2.4. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.6. In Vitro Dissolution Test
3. Results
3.1. Phase Solubility
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.3. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.5. In Vitro Dissolution Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kantor, T.G. Ketoprofen: A Review of Its Pharmacologic and Clinical Properties. Pharmacotherapy 1986, 6, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Atzeni, F.; Lanata, L.; Bagnasco, M.; Colombo, M.; Fischer, F.; D’Imporzano, M. Pain and Ketoprofen: What Is Its Role in Clinical Practice? Reumatismo 2010, 62, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbanti, P.; Grazzi, L.; Egeo, G. Pharmacotherapy for Acute Migraines in Children and Adolescents. Expert Opin. Pharm. 2019, 20, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziesenitz, V.C.; Welzel, T.; van Dyk, M.; Saur, P.; Gorenflo, M.; Anker, J.N.V.D. Efficacy and Safety of NSAIDs in Infants: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature of the Past 20 Years. Paediatr. Drugs 2022, 24, 603–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczyńska, J.; Pawlak, A.; Nieradko-Iwanicka, B. The Comparison of Dexketoprofen and Other Painkilling Medications (Review from 2018 to 2021). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, F.; Masala, I.F.; Bagnasco, M.; Lanata, L.; Mantelli, F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Comparison of Efficacy of Ketoprofen and Ibuprofen in Treating Pain in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetge, E.; du Plessis, J.; Müller, D.G.; Goosen, C.; van Rensburg, F.J. The Influence of the Physicochemical Characteristics and Pharmacokinetic Properties of Selected NSAID’s on Their Transdermal Absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 193, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guan, Y.; Tian, Q.; Shi, X.; Fang, L. Transdermal Enhancement Strategy of Ketoprofen and Teriflunomide: The Effect of Enhanced Drug-Drug Intermolecular Interaction by Permeation Enhancer on Drug Release of Compound Transdermal Patch. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsume, Y.; Mudie, D.M.; Langguth, P.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. The Biopharmaceutics Classification System: Subclasses for in Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Methodology and IVIVC. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangishetty, H.; Eedara, B.B.; Bandari, S. Development of Ketoprofen Loaded Proliposomal Powders for Improved Gastric Absorption and Gastric Tolerance: In Vitro and in Situ Evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2015, 20, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Cano-Cebrián, M.-J.; Olander, T.; Hedeland, M.; Sjöblom, M.; Lennernäs, H. Regional Intestinal Drug Permeability and Effects of Permeation Enhancers in Rat. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elezović, A.; Marić, A.; Biščević, A.; Hadžiabdić, J.; Škrbo, S.; Špirtović-Halilović, S.; Rahić, O.; Vranić, E.; Elezović, A. In Vitro PH Dependent Passive Transport of Ketoprofen and Metformin. ADMET DMPK 2020, 9, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.D.; Rathod, V.; Haware, R.V.; Stagner, W.C. Optimized L-SNEDDS and Spray-Dried S-SNEDDS Using a Linked QbD-DM3 Rational Design for Model Compound Ketoprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 631, 122494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuse, M.; Tagami, T.; Ogawa, K.; Ozeki, T. Contamination-Free Milling of Ketoprofen Nanoparticles Using Mannitol Medium and Hoover Automatic Muller: Optimization of Effective Design of Experiment. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, R.; Aramini, A.; Boccella, S.; Bagnasco, M.; Cattani, F.; Ferrari, M.P.; Goisis, G.; Minnella, E.M.; Allegretti, M.; Pace, V. Ketoprofen Lysine Salt Has a Better Gastrointestinal and Renal Tolerability than Ketoprofen Acid: A Comparative Tolerability Study in the Beagle Dog. Biomed. Pharm. 2022, 153, 113336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Obi, N. Studies on Absorption of Eutectic Mixture. I. A Comparison of the Behavior of Eutectic Mixture of Sulfathiazole and That of Ordinary Sulfathiazole in Man. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1961, 9, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tambe, S.; Jain, D.; Meruva, S.K.; Rongala, G.; Juluri, A.; Nihalani, G.; Mamidi, H.K.; Nukala, P.K.; Bolla, P.K. Recent Advances in Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Preformulation, Formulation Strategies, Technological Advancements and Characterization. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, W.L.; Riegelman, S. Pharmaceutical Applications of Solid Dispersion Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971, 60, 1281–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, S.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N. Investigating the Physicochemical Properties of Solid Dispersions Based on Semicrystalline Carriers: A Case Study with Ketoprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 632, 122576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duong, T.; Van den Mooter, G. The Role of the Carrier in the Formulation of Pharmaceutical Solid Dispersions. Part I: Crystalline and Semi-Crystalline Carriers. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Harris, M.T.; Taylor, L.S. Modification of Crystallization Behavior in Drug/Polyethylene Glycol Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.V.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Van den Mooter, G. Crystallization Kinetics of Indomethacin/Polyethylene Glycol Dispersions Containing High Drug Loadings. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, R.; Budhwar, V.; Kaushik, D. An Overview on Recent Patents and Technologies on Solid Dispersion. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. 2020, 14, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boghra, R.J.; Kothawade, P.C.; Belgamwar, V.S.; Nerkar, P.P.; Tekade, A.R.; Surana, S.J. Solubility, Dissolution Rate and Bioavailability Enhancement of Irbesartan by Solid Dispersion Technique. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Shi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Pei, Y. Enhancing the Bioavailability of Cyclosporine A Using Solid Dispersion Containing Polyoxyethylene (40) Stearate. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2006, 32, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.L.; Stewart, A.F.; Dubois, J.-L. The Properties of Solid Dispersions of Indomethacin or Phenylbutazone in Polyethylene Glycol. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 28, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, M.J.; Mcginty, J.W.; Martin, A. Combined Water-Soluble Carriers for Coprecipitates of Tolbutamide. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serajuddin, A.T.M.; Mufson, D.; Bernstein, D.F.; Sheen, P.-C.; Augustine, M.A. Effect of Vehicle Amphiphilicity on the Dissolution and Bioavailability of a Poorly Water-Soluble Drug from Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 1988, 77, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, W.L.; Riegelman, S. Preparation and Dissolution Characteristics of Several Fast-Release Solid Dispersions of Griseofulvin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1969, 58, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betageri, G.V.; Makarla, K.R. Enhancement of Dissolution of Glyburide by Solid Dispersion and Lyophilization Techniques. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 126, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguiano-Igea, S.; Otero-Espinar, F.J.; Vila-Jato, J.L.; Blanco-Méndez, J. The Properties of Solid Dispersions of Clofibrate in Polyethylene Glycols. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1995, 70, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordunoo, S.K.; Ford, J.L.; Rubinstein, M.H. Physical Stability of Solid Dispersions Containing Triamterene or Temazepam in Polyethylene Glycols. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1997, 49, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, P.; Faucci, M.T.; Manderioli, A.; Bramanti, G.; Parrini, P. Thermal Behavior and Dissolution Properties of Naproxen From Binary and Ternary Solid Dispersions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1999, 25, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, I.S.; Nada, A.; Zaghloul, A.-A. Physicochemical Characterization of Gliclazide–Macrogol Solid Dispersion and Tablets Based on Optimized Dispersion. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapani, G.; Franco, M.; Latrofa, A.; Pantaleo, M.R.; Provenzano, M.R.; Sanna, E.; Maciocco, E.; Liso, G. Physicochemical Characterization and in Vivo Properties of Zolpidem in Solid Dispersions with Polyethylene Glycol 4000 and 6000. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 184, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, U.P.; Bhat, H.R.; Mazumder, B. Physicochemical Characterization and in Vitro Dissolution Studies of Solid Dispersions of Ketoprofen with PVP K30 and D-Mannitol. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schachter, D.M.; Xiong, J.; Tirol, G.C. Solid State NMR Perspective of Drug-Polymer Solid Solutions: A Model System Based on Poly(Ethylene Oxide). Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 281, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, P.; Moyano, J.R.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Rabasco-Alvaréz, A.M.; Cirri, M.; Maestrelli, F. Characterization and Dissolution Properties of Ketoprofen in Binary and Ternary Solid Dispersions with Polyethylene Glycol and Surfactants. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2005, 31, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vueba, M.L.; Batista de Carvalho, L.A.E.; Veiga, F.; Sousa, J.J.; Pina, M.E. In Vitro Release of Ketoprofen from Hydrophilic Matrix Tablets Containing Cellulose Polymer Mixtures. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.N.; Majumdar, S.; Singh, A.; Deng, W.; Murthy, N.S.; Pinto, E.; Tewari, D.; Durig, T.; Repka, M.A. KlucelTM EF and ELF Polymers for Immediate-Release Oral Dosage Forms Prepared by Melt Extrusion Technology. Aaps PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haimhoffer, Á.; Vas, A.; Árvai, G.; Fenyvesi, É.; Jicsinszky, L.; Budai, I.; Bényei, A.; Regdon, G.; Rusznyák, Á.; Vasvári, G.; et al. Investigation of the Drug Carrier Properties of Insoluble Cyclodextrin Polymer Microspheres. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, T.S.; Acharya, F. Optimizing Similarity Factor of in Vitro Drug Release Profile for Development of Early Stage Formulation of Drug Using Linear Regression Model. J. Math. Ind. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic Modeling on Drug Release from Controlled Drug Delivery Systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samaha, D.; Shehayeb, R.; Kyriacos, S. Modeling and Comparison of Dissolution Profiles of Diltiazem Modified-Release Formulations. Dissolution Technol. 2009, 16, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Shah, S.; Patel, J. Solid Dispersion Technology as a Formulation Strategy for the Fabrication of Modified Release Dosage Forms: A Comprehensive Review. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 30, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.-Y.; Toh, S.-M.; Khan, N.H.; Chung, Y.-Y.; Cheah, X.-Z. The Improved Dissolution Performance of a Post Processing Treated Spray-Dried Crystalline Solid Dispersion of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1800–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, E.; Charifou, R.; Worku, Z.A.; Babu, R.P.; Healy, A.M. Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Ketoprofen and Poly-Vinyl Polymers Prepared via Electrospraying and Spray Drying: A Comparison of Particle Characteristics and Performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-kasmi, B.; Alsirawan, M.H.D.B.; Paradkar, A.; Nattouf, A.-H.; El-Zein, H. Aqueous and PH Dependent Coacervation Method for Taste Masking of Paracetamol via Amorphous Solid Dispersion Formation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.-L.; Zheng, S.-D.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Cui, W.-Q.; Hao, M.-Q.; God’spower, B.-O.; Chen, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-H. Albendazole Solid Dispersions Prepared Using PEG6000 and Poloxamer188: Formulation, Characterization and in Vivo Evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, A.; Mahmoodian, R.; Abdullah, B.J.J.; Abdullah, H.; Hamdi, M.; Abu Kasim, N.H. Low-Melting-Point Polymeric Nanoshells for Thermal-Triggered Drug Release under Hyperthermia Condition. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermans, A.; Milsmann, J.; Li, H.; Jede, C.; Moir, A.; Hens, B.; Morgado, J.; Wu, T.; Cohen, M. Challenges and Strategies for Solubility Measurements and Dissolution Method Development for Amorphous Solid Dispersion Formulations. AAPS J 2022, 25, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.D.; Wen, H.; Taylor, L.S. Non-Sink Dissolution Conditions for Predicting Product Quality and In Vivo Performance of Supersaturating Drug Delivery Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Purohit, H.S.; Taylor, L.S. Phase Separation Kinetics in Amorphous Solid Dispersions Upon Exposure to Water. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Kjoller, K.; Dillon, E.; Purohit, H.S.; Taylor, L.S. Phase Separation in Surfactant-Containing Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Orthogonal Analytical Methods to Probe the Effects of Surfactants on Morphology and Phase Composition. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 619, 121708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vippagunta, S.R.; Maul, K.A.; Tallavajhala, S.; Grant, D.J.W. Solid-State Characterization of Nifedipine Solid Dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 236, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Yin, T.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. A Comparative Study on in Vitro and in Vivo Characteristics of Enzalutamide Nanocrystals versus Amorphous Solid Dispersions and a Better Prediction for Bioavailability Based on “Spring-Parachute” Model. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 628, 122333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hens, B.; Brouwers, J.; Corsetti, M.; Augustijns, P. Supersaturation and Precipitation of Posaconazole Upon Entry in the Upper Small Intestine in Humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vippagunta, S.R.; Wang, Z.; Hornung, S.; Krill, S.L. Factors Affecting the Formation of Eutectic Solid Dispersions and Their Dissolution Behavior. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoulonche, F.; Chauvet, A.; Masse, J.; Egea, M.A.; Garcia, M.L. An Investigation of FB Interactions with Poly(Ethylene Glycol) 6000, Poly(Ethylene Glycol) 4000, and Poly-Epsilon-Caprolactone by Thermoanalytical and Spectroscopic Methods and Modeling. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjökvist, E.; Nyström, C. Physicochemical Aspects of Drug Release. VI. Drug Dissolution Rate from Solid Particulate Dispersions and the Importance of Carrier and Drug Particle Properties. Int. J. Pharm. 1988, 47, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Ahmed, F.; Shuma, M.L.; Azad, M.A.K.; Kabir, E.R. Impact of Drying on Dissolution Behavior of Carvedilol-Loaded Sustained Release Solid Dispersion: Development and Characterization. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.K.; Shukla, M.; Shrivastava, V. Development and in Vitro Evaluation of Ibuprofen Mouth Dissolving Tablets Using Solid Dispersion Technique. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Publication | API | PEG | Relationship of Molecular Weight and Percentage of Released Drug |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford et al. [26] | indomethacin, phenylbutazone | 1500, 4000, 6000, 20,000 | Inverse proportionality |
| Miralles et al. [27] | tolbutamide | 4000, 6000 | Inverse proportionality |
| Serajuddin et al. [28] | α-Pentyl-3-(2-quinolinylmethoxy)benzene methanol | 1000, 1450, 8000 | Inverse proportionality |
| Chiou and Riegelman [29] | griseofulvin | 4000, 20,000 | Proportional |
| Betageri and Makarla [30] | glyburide | 4000, 6000 | Proportional |
| Anguiano-Igea et al. [31] | clofibrate | 10,000, 20,000, 35,000 | Proportional |
| Dordunoo and Rubinstein [32] | triamterene, temazepam | 1500, 2000, 4000, 6000 | Proportional |
| Mura et al. [33] | naproxen | 4000, 6000, 20,000 | None |
| Khattab et al. [34] | gliclazide | 4000, 10,000, 20,000 | None |
| Trapani et al. [35] | zolpidem | 4000, 6000 | None |
| Model Name | Equations [43,44] | GRAPHIC |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-order | The graphic of the drug-dissolved fraction versus time is linear. | |
| First-order | The graphic of the decimal logarithm of the released amount of drug versus time is linear. | |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas model | The graphic of the released drug versus the square root of time should form a straight line. |
| Concentration (w/w%) | ΔG0tr (J/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PEG 1000 | PEG 1500 | PEG 2000 | |
| 1 | −3316 | −1445 | −1166 |
| 5 | −1342 | −1316 | −1491 |
| 10 | −2420 | −2585 | −2731 |
| 20 | −4911 | −4901 | −5042 |
| Comparison of Compositions | f1 | f2 |
|---|---|---|
| PEG 1000 PM vs. SD | 29.80 | 39.84 |
| PEG 1500 PM vs. SD | 5.00 | 76.78 |
| PEG 2000 PM vs. SD | 10.84 | 59.19 |
| PEG 1000 SD vs. PEG 1500 SD | 38.27 | 25.74 |
| PEG 1000 SD vs. PEG 2000 SD | 42.30 | 27.59 |
| PEG 1500 SD vs. PEG 2000 SD | 6.54 | 71.39 |
| Type of Kinetics Profile | Zero-Order Model | First-Order Model | Korsmeyer–Peppas Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical mixture | PEG 1000 | 0.8440 | 0.8854 | 0.9321 |
| PEG 1500 | 0.8371 | 0.7104 | 0.7859 | |
| PEG 2000 | 0.8588 | 0.8715 | 0.9109 | |
| Solid dispersions | PEG 1000 | 0.8416 | 0.9469 | 0.9592 |
| PEG 1500 | 0.8547 | 0.8242 | 0.8710 | |
| PEG 2000 | 0.8823 | 0.8543 | 0.8444 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Khanh, H.P.; Haimhoffer, Á.; Nemes, D.; Józsa, L.; Vasvári, G.; Budai, I.; Bényei, A.; Ujhelyi, Z.; Fehér, P.; Bácskay, I. Effect of Molecular Weight on the Dissolution Profiles of PEG Solid Dispersions Containing Ketoprofen. Polymers 2023, 15, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071758
Le Khanh HP, Haimhoffer Á, Nemes D, Józsa L, Vasvári G, Budai I, Bényei A, Ujhelyi Z, Fehér P, Bácskay I. Effect of Molecular Weight on the Dissolution Profiles of PEG Solid Dispersions Containing Ketoprofen. Polymers. 2023; 15(7):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071758
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Khanh, Ha Pham, Ádám Haimhoffer, Dániel Nemes, Liza Józsa, Gábor Vasvári, István Budai, Attila Bényei, Zoltán Ujhelyi, Pálma Fehér, and Ildikó Bácskay. 2023. "Effect of Molecular Weight on the Dissolution Profiles of PEG Solid Dispersions Containing Ketoprofen" Polymers 15, no. 7: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071758
APA StyleLe Khanh, H. P., Haimhoffer, Á., Nemes, D., Józsa, L., Vasvári, G., Budai, I., Bényei, A., Ujhelyi, Z., Fehér, P., & Bácskay, I. (2023). Effect of Molecular Weight on the Dissolution Profiles of PEG Solid Dispersions Containing Ketoprofen. Polymers, 15(7), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071758