Multi-Material 3D Printing of Biobased Epoxy Resins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Photocured Formulations
2.3. Characterisation Methods
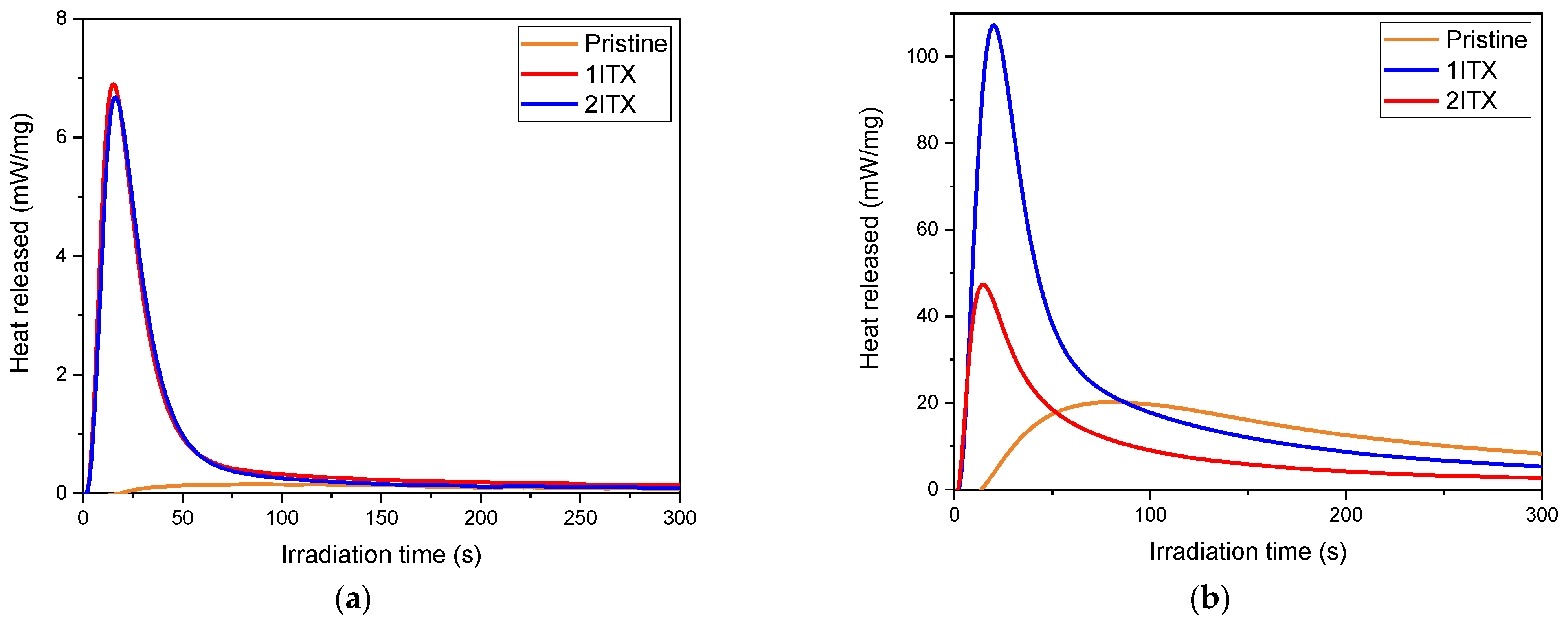
2.3.1. Photo Dynamic Scanning Calorimetry (Photo-DSC)
2.3.2. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
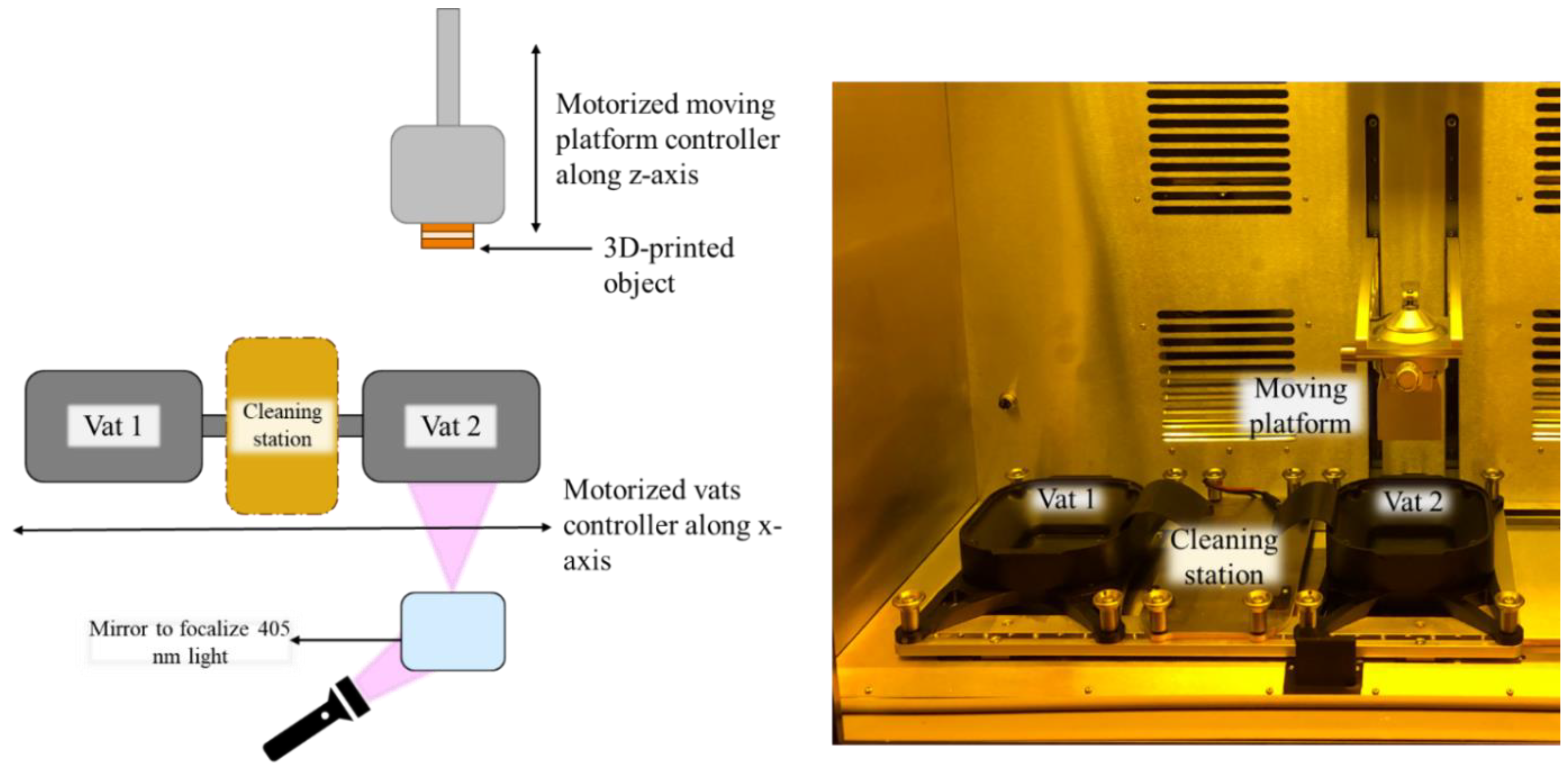
2.4. Dual-Vat Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D Printing
2.4.1. Single-Material DLP 3D Printing
2.4.2. Multi-Material DLP 3D Printing
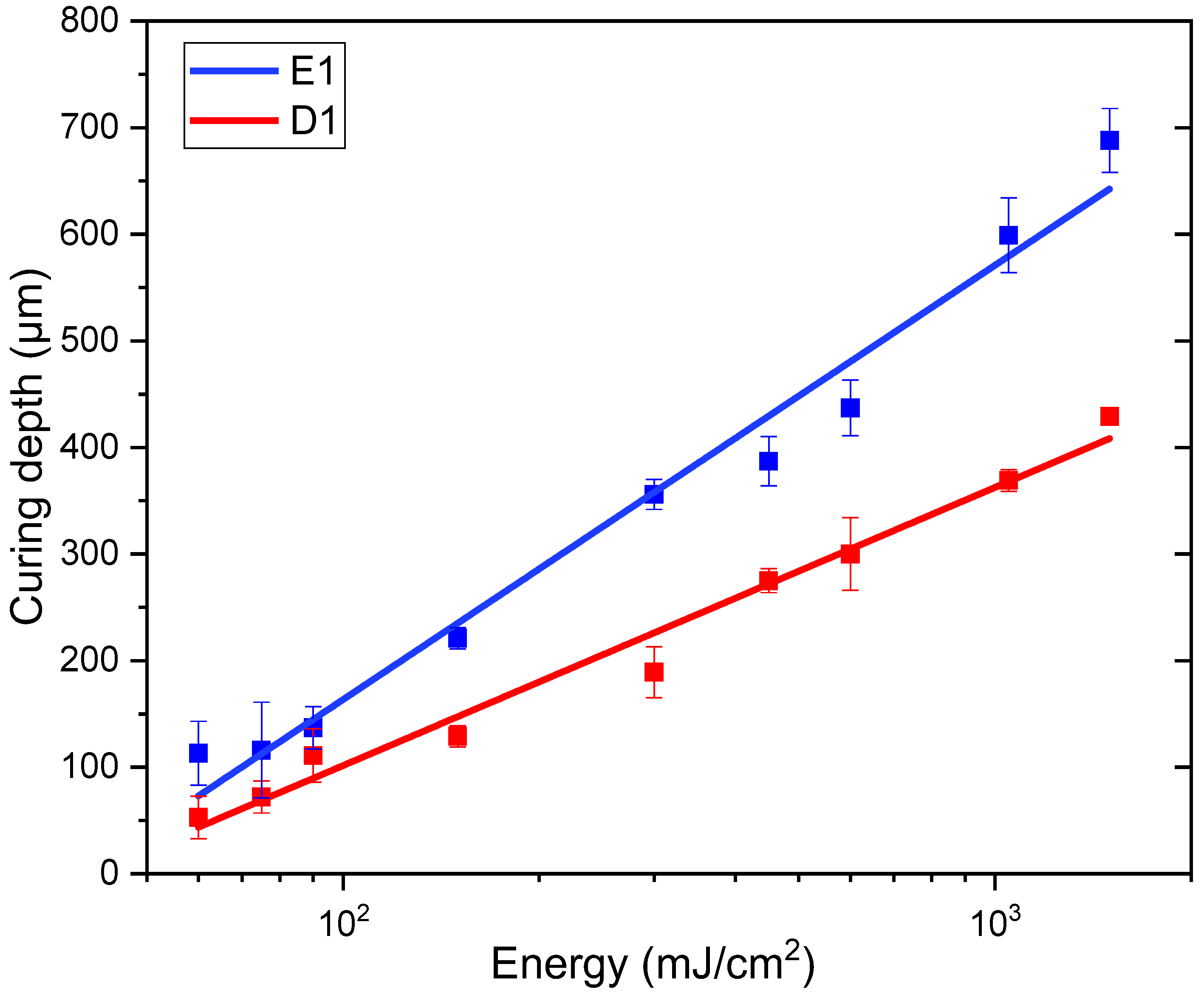
2.5. Jacobs Working Curves
2.6. Mechanical and Thermomechanical Properties
2.7. Shape Memory Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Photo-Curing Process
3.2. Single-Material DLP 3D Printing
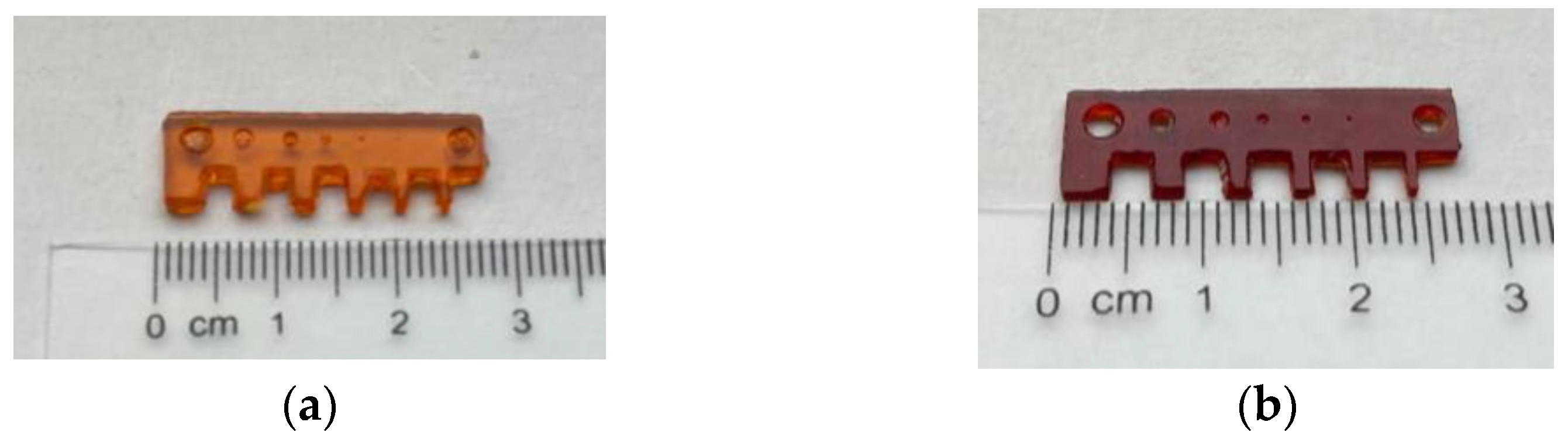
3.3. Multi-Material DLP 3D Printing
3.4. Characterisation Tests
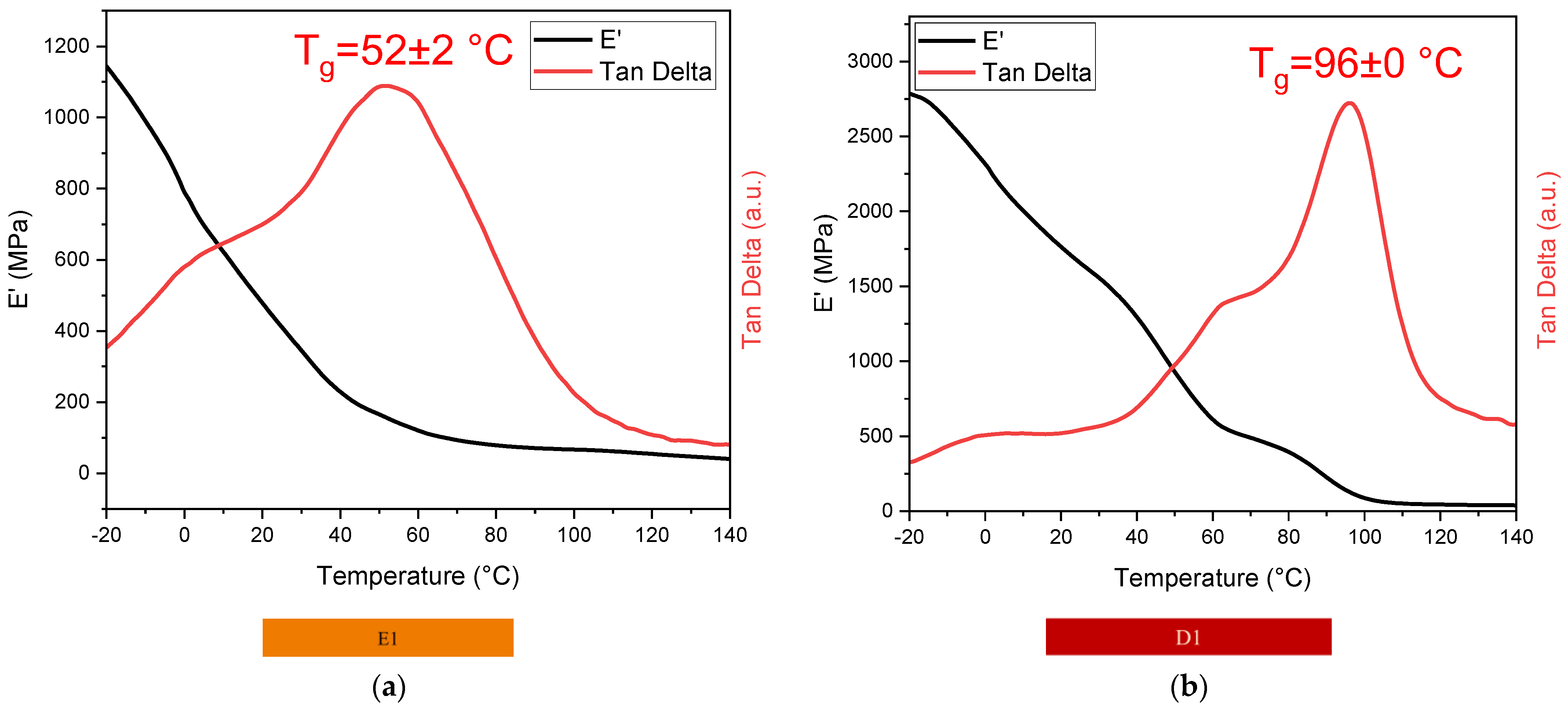
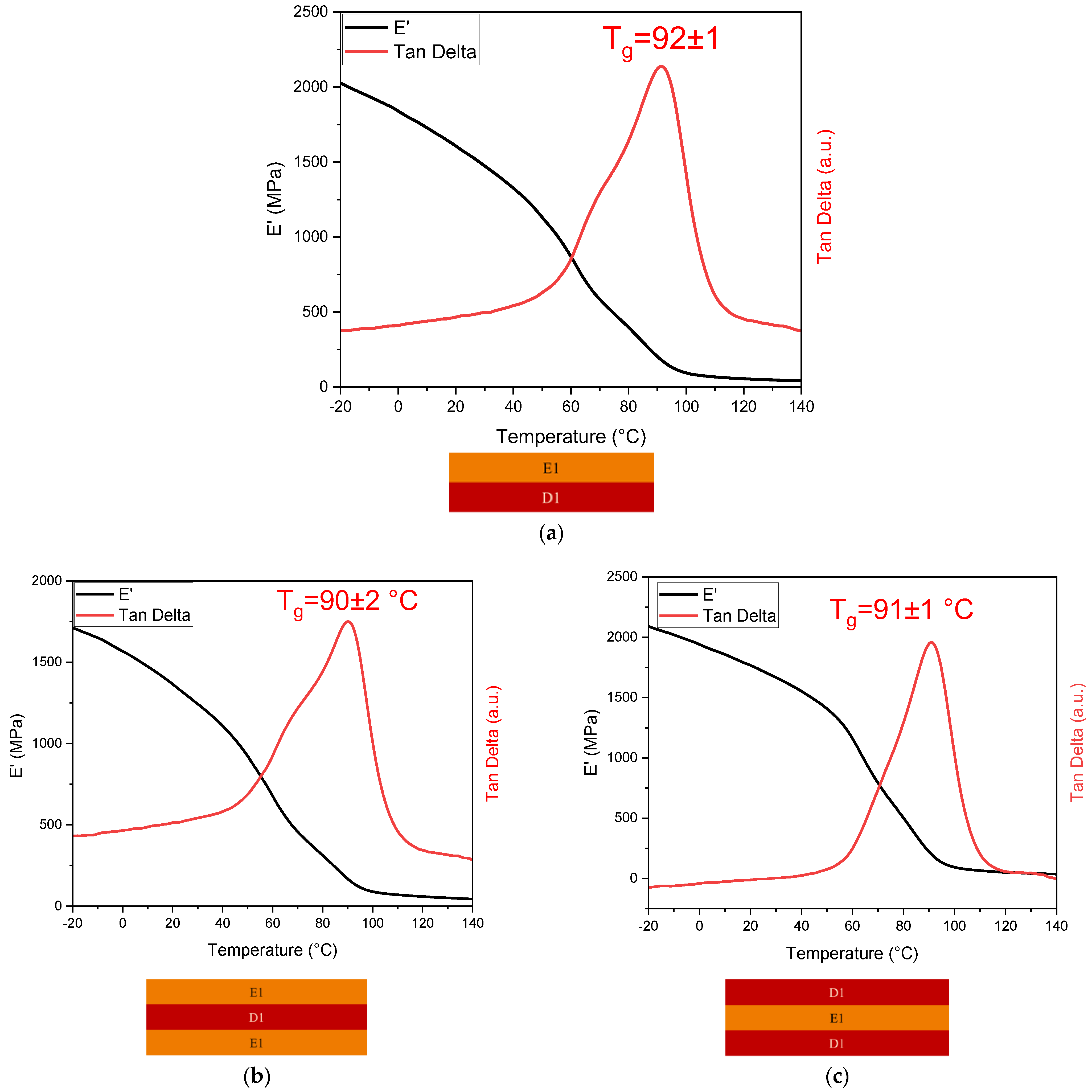
3.4.1. DMTA
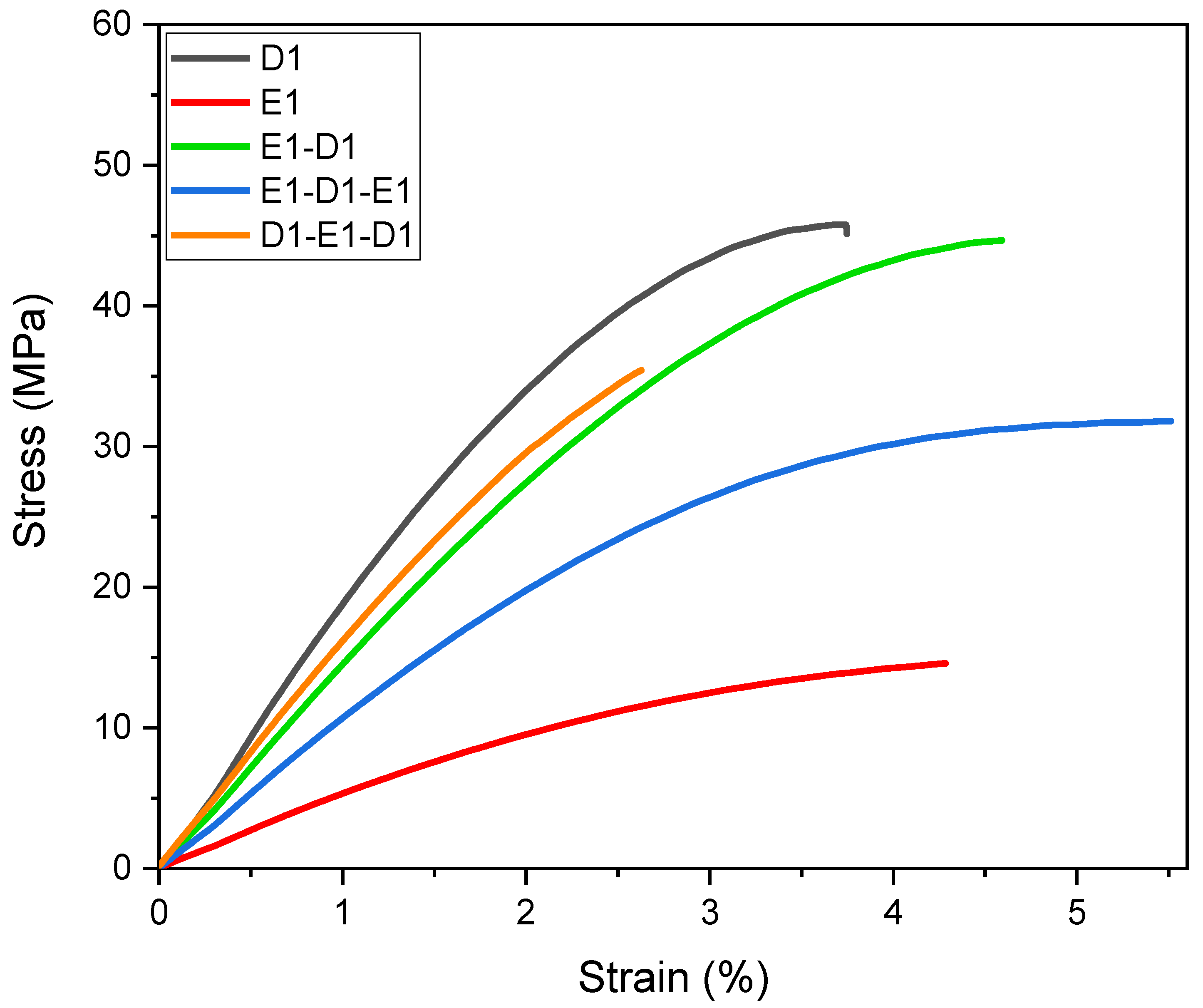
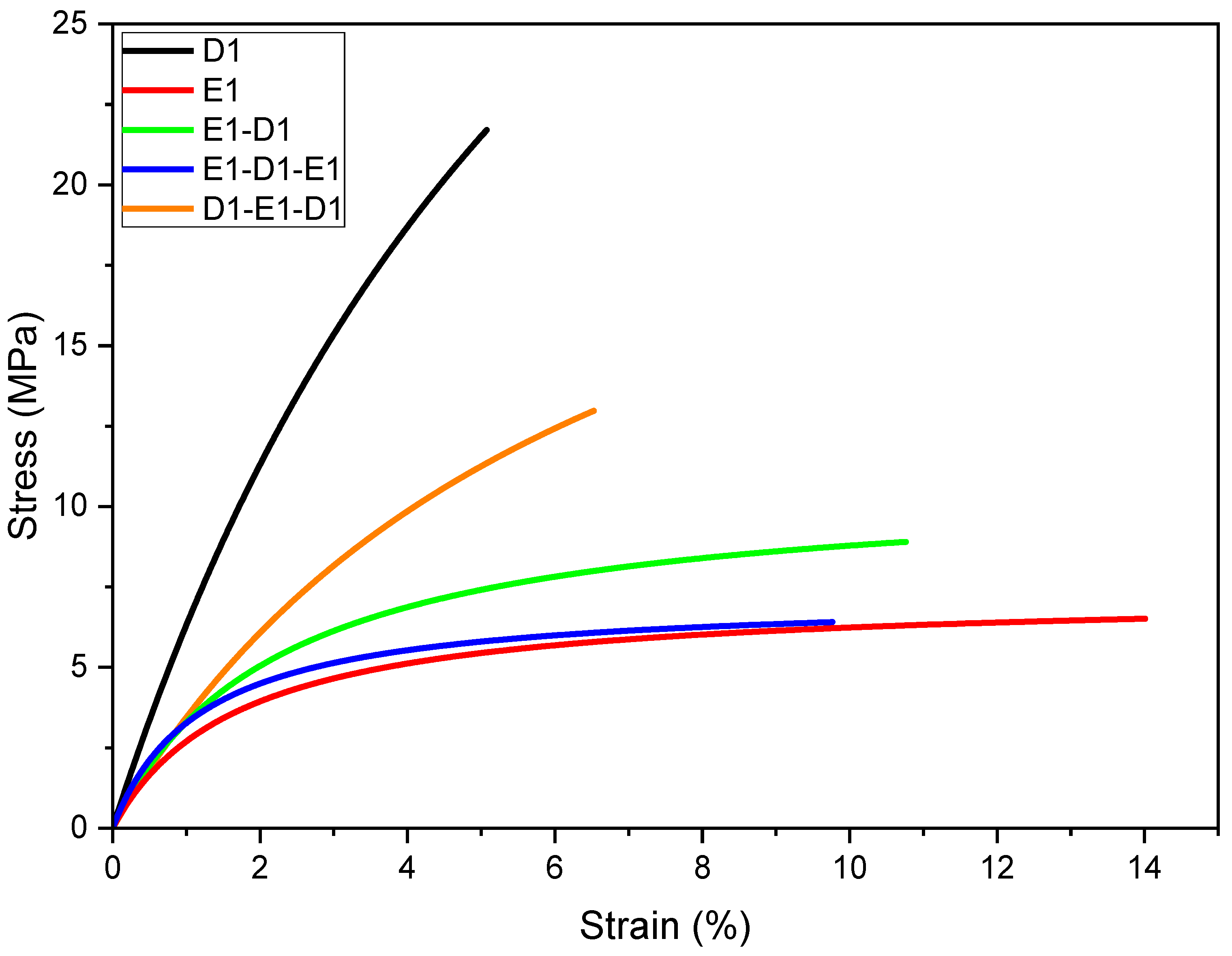
3.4.2. Mechanical Tests
3.4.3. TGA
3.5. Shape Memory
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ligon, S.C.; Liska, R.; Stampfl, J.; Gurr, M.; Mülhaupt, R. Polymers for 3D Printing and Customized Additive Manufacturing. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10212–10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): A Review of Materials, Methods, Applications and Challenges. Compos. B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Leu, M.C. Additive Manufacturing: Technology, Applications and Research Needs. Front. Mech. Eng. 2013, 8, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Liu, P.; Mokasdar, A.; Hou, L. Additive Manufacturing and Its Societal Impact: A Literature Review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 67, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofail, S.A.M.; Koumoulos, E.P.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bose, S.; O’Donoghue, L.; Charitidis, C. Additive Manufacturing: Scientific and Technological Challenges, Market Uptake and Opportunities. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truby, R.L.; Lewis, J.A. Printing Soft Matter in Three Dimensions. Nature 2016, 540, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; An, J.; Chua, C.K. Fundamentals and Applications of 3D Printing for Novel Materials. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 7, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandoush, P.; Lin, D. A Review on Additive Manufacturing of Polymer-Fiber Composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 182, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagac, M.; Hajnys, J.; Ma, Q.-P.; Jancar, L.; Jansa, J.; Stefek, P.; Mesicek, J. A Review of Vat Photopolymerization Technology: Materials, Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends of 3D Printing. Polymers 2021, 13, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Jin, J. Photopolymerization in 3D Printing. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Morsali, M.; Moreno, A.; Sipponen, M.H.; Hakkarainen, M. Lignin Nanoparticle-Enhanced Biobased Resins for Digital Light Processing 3D Printing: Towards High Resolution and Tunable Mechanical Properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 194, 112146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Fabbri, P.; Leoni, E.; Mazzanti, F.; Akbari, R.; Antonini, C. Additive Manufacturing by Digital Light Processing: A Review. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 8, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, A.; Falster, V.; Doest, M.B.; Ribo, M.M.; Eiriksson, E.R.; Pedersen, D.B.; Frisvad, J.R. Microstructure Control in 3D Printing with Digital Light Processing. Comput. Graph. Forum 2020, 39, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Zheng, K.; Chen, S.; Li, N.; Shang, X.; Wang, F.; Liang, J.; Khan, S.B.; Shen, Y.; Lu, B.; et al. Additive Manufacturing of High Solid Content Lunar Regolith Simulant Paste Based on Vat Photopolymerization and the Effect of Water Addition on Paste Retention Properties. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 71, 103607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Regulation of the Interface Compatibility of the 3D-Printing Interpenetration Networks Toward Reduced Structure Anisotropy and Enhanced Performances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 32984–32992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergoglio, M.; Najmi, Z.; Cochis, A.; Miola, M.; Vernè, E.; Sangermano, M. UV-Cured Bio-Based Acrylated Soybean Oil Scaffold Reinforced with Bioactive Glasses. Polymers 2023, 15, 4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-Basteiro, P.; Reviriego, F.; Martínez-Campos, E.; Reinecke, H.; Elvira, C.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Gallardo, A. Vat Photopolymerization 3D Printing of Hydrogels with Re-Adjustable Swelling. Gels 2023, 9, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazin, I.; Gleirscher, M.O.; Fleisch, M.; Berer, M.; Sangermano, M.; Schlögl, S. Spatially Controlling the Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Objects by Dual-Wavelength Vat Photopolymerization. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 57, 102977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrello, J.; Nasser, P.; Iatridis, J.C.; Costa, K.D. 3D Printing a Mechanically-Tunable Acrylate Resin on a Commercial DLP-SLA Printer. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 23, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.; Renner, M.; Griesbeck, A.G.; Büsgen, T. From 3D to 4D Printing: A Reactor for Photochemical Experiments Using Hybrid Polyurethane Acrylates for Vat-Based Polymerization and Surface Functionalization. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 15161–15164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D. 3D Printing of Polymer Matrix Composites: A Review and Prospective. Compos. B Eng. 2017, 110, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Shou, W.; Makatura, L.; Matusik, W.; Fu, K. (Kelvin) 3D Printing of Polymer Composites: Materials, Processes, and Applications. Matter 2022, 5, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerzada, M.; Abbasi, S.; Lau, K.T.; Hameed, N. Additive Manufacturing of Epoxy Resins: Materials, Methods, and Latest Trends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 6375–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qatatsheh, A.; Peerzada, M.; Salim, N.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Hameed, N. Introduction to Rapidly Cured Epoxy Resins and Composites. In Rapid Cure Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai, A.; Kadiyala, A.K.; Ó Brádaigh, C.M. Introduction to Epoxy/Synthetic Fiber Composites. In Handbook of Epoxy/Fiber Composites; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cain, M.L. Epoxy Resins: Synthesis, Applications and Recent Developments; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yan, J.; Wu, Z. Room-to-Low Temperature Thermo-Mechanical Behavior and Corresponding Constitutive Model of Liquid Oxygen Compatible Epoxy Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 245, 110357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, R.; Luo, Y.; Sheng, X.; Xie, D.; Mei, Y. Construction of Polyphosphazene-Functionalized Ti3C2TX with High Efficient Flame Retardancy for Epoxy and Its Synergetic Mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sha, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Li, J. Deterministic Manipulation of Heat Flow via Three-Dimensional-Printed Thermal Meta-Materials for Multiple Protection of Critical Components. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 39354–39363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Argine, C.; Hochwallner, A.; Klikovits, N.; Liska, R.; Stampf, J.; Sangermano, M. Hot-Lithography SLA-3D Printing of Epoxy Resin. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, L.K.; Thapliyal, P.C.; Karade, S.R. Anticorrosive Properties of the Epoxy–Cardanol Resin Based Paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 2007, 59, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J. Research Progress on Bio-based Thermosetting Resins. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, S.; Markle, T.; Thompson, S.; Wallace, E. Bisphenol A Exposure, Effects, and Policy: A Wildlife Perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 104, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundouri, P.; Devves, S.; Plataniotis, A. Alignment of the European Green Deal, the Sustainable Development Goals and the European Semester Process: Method and Application. Theor. Econ. Lett. 2021, 11, 743–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, X.; Ye, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J.; Han, X. Recent Progress of Biomass in Conventional Wood Adhesives: A Review. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 10304–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noè, C.; Hakkarainen, M.; Malburet, S.; Graillot, A.; Adekunle, K.; Skrifvars, M.; Sangermano, M. Frontal-Photopolymerization of Fully Biobased Epoxy Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fache, M.; Auvergne, R.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. New Vanillin-Derived Diepoxy Monomers for the Synthesis of Biobased Thermosets. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noè, C.; Hakkarainen, M.; Sangermano, M. Cationic UV-Curing of Epoxidized Biobased Resins. Polymers 2020, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesia, R.; Cardone, A.G.; Ferraris, S.; Spriano, S.; Sangermano, M. Exploitation of Tannic Acid as Additive for the Adhesion Enhancement of UV-Curable Bio-Based Coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 189, 108311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergoglio, M.; Reisinger, D.; Schlögl, S.; Griesser, T.; Sangermano, M. Sustainable Bio-Based UV-Cured Epoxy Vitrimer from Castor Oil. Polymers 2023, 15, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzana, L.; Melilli, G.; Guigo, N.; Sbirrazzuoli, N.; Sangermano, M. Cross-Linking of Biobased Monofunctional Furan Epoxy Monomer by Two Steps Process, UV Irradiation and Thermal Treatment. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2023, 224, 2200012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.G.; Chow, W.S. Curing Characteristics and Thermal Properties of Epoxidized Soybean Oil Based Thermosetting Resin. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzana, L.; Wolff, R.; Stampfl, J.; Liska, R.; Sangermano, M. High Temperature Vat Photopolymerization 3D Printing of Fully Bio-Based Composites: Green Vegetable Oil Epoxy Matrix & Bio-Derived Filler Powder. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 79, 103929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzana, L.; Wolff, R.; Melilli, G.; Guigo, N.; Sbirrazzuoli, N.; Stampfl, J.; Liska, R.; Sangermano, M. Hot-Lithography 3D Printing of Biobased Epoxy Resins. Polymer 2022, 254, 125097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Mantha, S.N.; Crowder, D.C.; Chinchilla, S.; Shah, K.N.; Yun, Y.H.; Wicker, R.B.; Choi, J.-W. Microstereolithography and Characterization of Poly(Propylene Fumarate)-Based Drug-Loaded Microneedle Arrays. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, D.; Truong, V.; Neitzke, C.C.; Guo, S.; Walsh, P.J.; Monat, J.R.; Meng, F.; Park, S.H.; Dutton, J.R.; Parr, A.M.; et al. 3D Printed Stem-Cell Derived Neural Progenitors Generate Spinal Cord Scaffolds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terryn, S.; Roels, E.; Brancart, J.; Van Assche, G.; Vanderborght, B. Self-Healing and High Interfacial Strength in Multi-Material Soft Pneumatic Robots via Reversible Diels–Alder Bonds. Actuators 2020, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, A.D.; Busbee, T.A.; Boley, J.W.; Raney, J.R.; Chortos, A.; Kotikian, A.; Berrigan, J.D.; Durstock, M.F.; Lewis, J.A. Hybrid 3D Printing of Soft Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, U.; Rossegger, E.; Schlögl, S. A Review of Multi-Material 3D Printing of Functional Materials via Vat Photopolymerization. Polymers 2022, 14, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, U.; Thalhamer, A.; Rossegger, E.; Schlögl, S. Dual-Vat Photopolymerization 3D Printing of Vitrimers. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 79, 103930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossegger, E.; Strasser, J.; Höller, R.; Fleisch, M.; Berer, M.; Schlögl, S. Wavelength Selective Multi-Material 3D Printing of Soft Active Devices Using Orthogonal Photoreactions. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 44, 2200586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-D.; Hong, J.-W. UV-Initiated Free Radical and Cationic Photopolymerizations of Acrylate/Epoxide and Acrylate/Vinyl Ether Hybrid Systems with and without Photosensitizer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J. Measuring UV Curing Parameters of Commercial Photopolymers Used in Additive Manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 18, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEN-EN-ISO 527-2:2012; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- BS-EN-ISO-178-2019; Plastics—Determination of Flexural Properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Pezzana, L.; Emanuele, A.; Sesana, R.; Delprete, C.; Malmström, E.; Johansson, M.; Sangermano, M. Cationic UV-Curing of Isosorbide-Based Epoxy Coating Reinforced with Macadamia Nut Shell Powder. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 185, 107949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivello, J.V.; Lam, J.H.W. Diaryliodonium Salts. A New Class of Photoinitiators for Cationic Polymerization. Macromolecules 1977, 10, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, J.; Arbeiter, F.; Kolednik, O.; Pinter, G. Influence of Layer Architecture on Fracture Toughness and Specimen Stiffness in Polymer Multilayer Composites. Mater. Des. 2022, 219, 110828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, J.; Kaineder, H.; Kolednik, O.; Arbeiter, F. Optimization of Mechanical Properties and Damage Tolerance in Polymer-Mineral Multilayer Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; Wiener, J.; Arbeiter, F.; Pinter, G.; Kolednik, O. Application of the Material Inhomogeneity Effect for the Improvement of Fracture Toughness of a Brittle Polymer. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 224, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waly, C.; Petersmann, S.; Arbeiter, F. Multimaterial Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing of Compliant Crack Arrester: Influence of Interlayer Length, Thickness, and Applied Strain Rate. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2101703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbeiter, F.J.; Petersmann, S.; Wiener, J.; Oesterreicher, F.; Spoerk, M.; Pinter, G. Using Compliant Interlayers as Crack Arresters in 3-D-Printed Polymeric Structures. Mater. Perform. Charact. 2020, 9, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stögerer, J.; Baumgartner, S.; Hochwallner, A.; Stampfl, J. Bio-Inspired Toughening of Composites in 3D-Printing. Materials 2020, 13, 4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaiger, M.; Waly, C.; Huszar, M.; Oreski, G.; Feuchter, M.; Arbeiter, F.; Resch-Fauster, K. Bioinspired Fracture Toughness Enhancement of a Fully Bio-Based Epoxy Resin. Polym. Test. 2023, 124, 108098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Formulation ID | Biobased Monomer | Photoinitiator (phr) | ITX (phr) | Sudan II (phr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | ELO | 2 | From 0 to 2 | 0.02 |
| D1 | DGEVA | 2 | From 0 to 2 | 0.02 |
| E1 | Peak (s) | Heat Released (mW/mg) | Area (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine | 87 ± 2 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 54 ± 5 |
| 1ITX | 16 ± 1 | 6.7 ± 0.3 | 224 ± 2 |
| 2ITX | 15 ± 2 | 6.8 ± 0.14 | 231 ± 12 |
| D1 | |||
| Pristine | 84 ± 8 | 2.0 ± 0.0 | 487 ± 2 |
| 1ITX | 18 ± 0 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 457 ± 31 |
| 2ITX | 12 ± 0 | 5.0 ± 0.8 | 415 ± 10 |
| Sample | Glass Transition Temperature Tg (°C) |
|---|---|
| E1 | 52 ± 2 |
| D1 | 96 ± 0 |
| E1-D1 double-layer | 92 ± 1 |
| E1-D1-E1 triple-layer | 90 ± 0 |
| D1-E1-D1 triple-layer | 91 ± 1 |
| Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | 505 ± 46 | 15.4 ± 1.2 | 4.7 ± 0.7 |
| D1 | 1615 ± 132 | 33.3 ± 7.0 | 2.7 ± 0.7 |
| E1-D1 double-layer | 1312 ± 102 | 33.2 ± 10.9 | 3.0 ± 1.4 |
| E1-D1-E1 triple-layer | 1105 ± 96 | 32.3 ± 0.5 | 4.2 ± 1.2 |
| D1-E1-D1 triple-layer | 1589 ± 67 | 28.4 ± 5.4 | 1.9 ± 0.5 |
| Flexural Modulus (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | 523 ± 25 | 7.1 ± 0.5 | 15.1 ± 01.0 |
| D1 | 1422 ± 331 | 18.4 ± 1.8 | 6.4 ± 1.4 |
| E1-D1 | 490 ± 140 | 8.9 ± 0.1 | 12.2 ± 0.5 |
| E1-D1-E1 | 523 ± 5 | 7.4 ± 1.0 | 11.6 ± 1.2 |
| D1-E1-D1 | 1217 ± 250 | 13.6 ± 0.5 | 7.2 ± 1.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bergoglio, M.; Rossegger, E.; Schlögl, S.; Griesser, T.; Waly, C.; Arbeiter, F.; Sangermano, M. Multi-Material 3D Printing of Biobased Epoxy Resins. Polymers 2024, 16, 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111510
Bergoglio M, Rossegger E, Schlögl S, Griesser T, Waly C, Arbeiter F, Sangermano M. Multi-Material 3D Printing of Biobased Epoxy Resins. Polymers. 2024; 16(11):1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111510
Chicago/Turabian StyleBergoglio, Matteo, Elisabeth Rossegger, Sandra Schlögl, Thomas Griesser, Christoph Waly, Florian Arbeiter, and Marco Sangermano. 2024. "Multi-Material 3D Printing of Biobased Epoxy Resins" Polymers 16, no. 11: 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111510
APA StyleBergoglio, M., Rossegger, E., Schlögl, S., Griesser, T., Waly, C., Arbeiter, F., & Sangermano, M. (2024). Multi-Material 3D Printing of Biobased Epoxy Resins. Polymers, 16(11), 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111510








