Preparation of Quick-Dissolving Nanofiber Face Masks Based on Needleless Electrostatic Spinning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
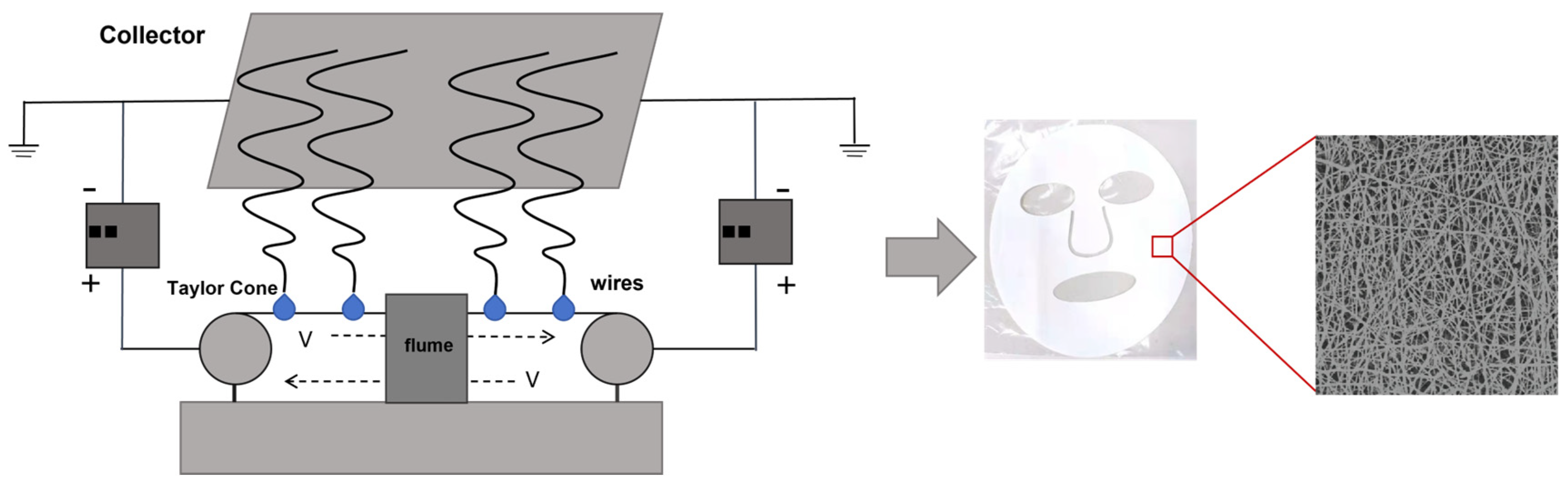
3. Preparation of Nanofiber Facial Mask
4. Characterization Method
5. Results and Discussion
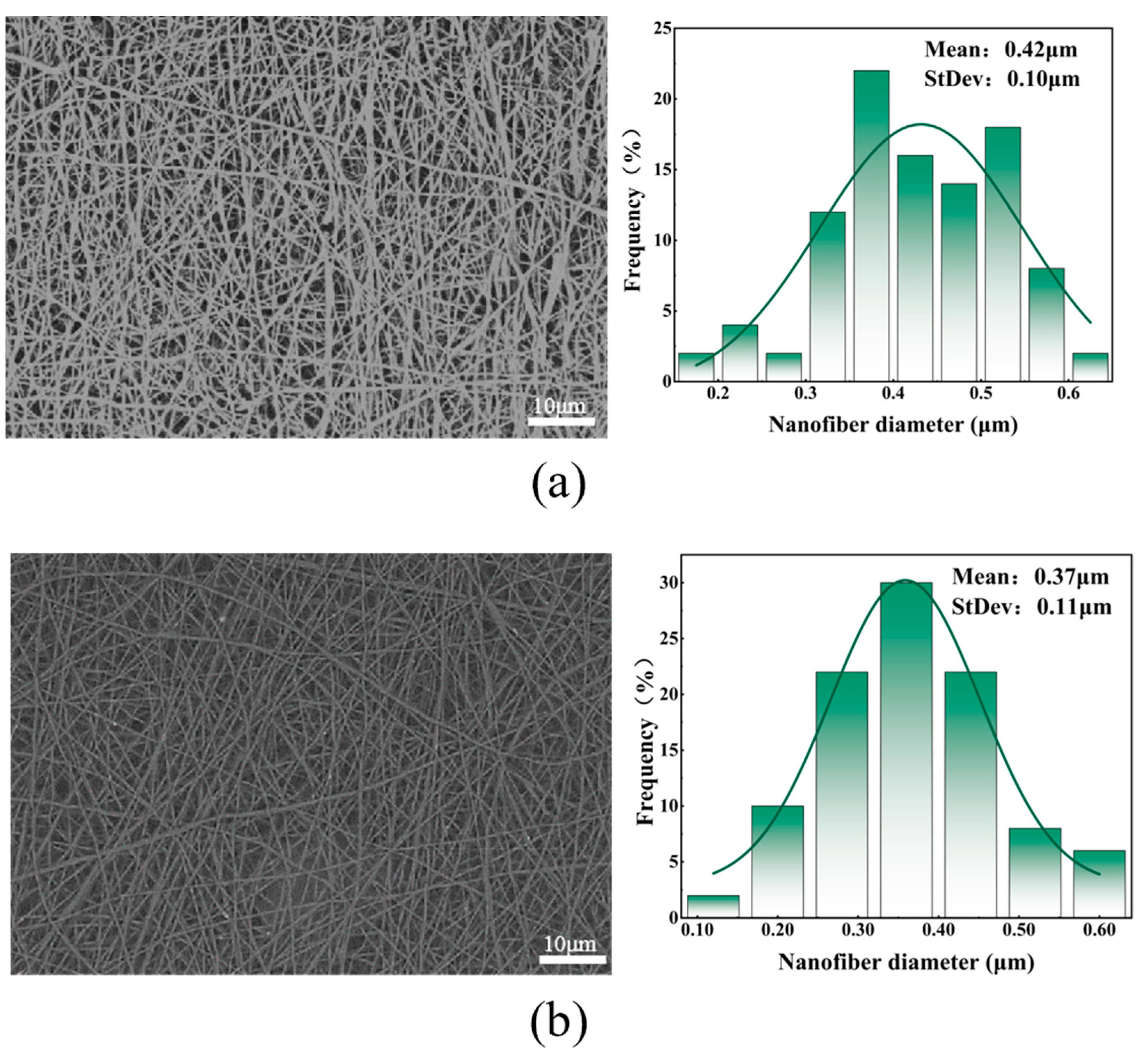
5.1. Effect of Different Mixing Ratios of PEO/Collagen Peptide Solutions on Fiber Morphology
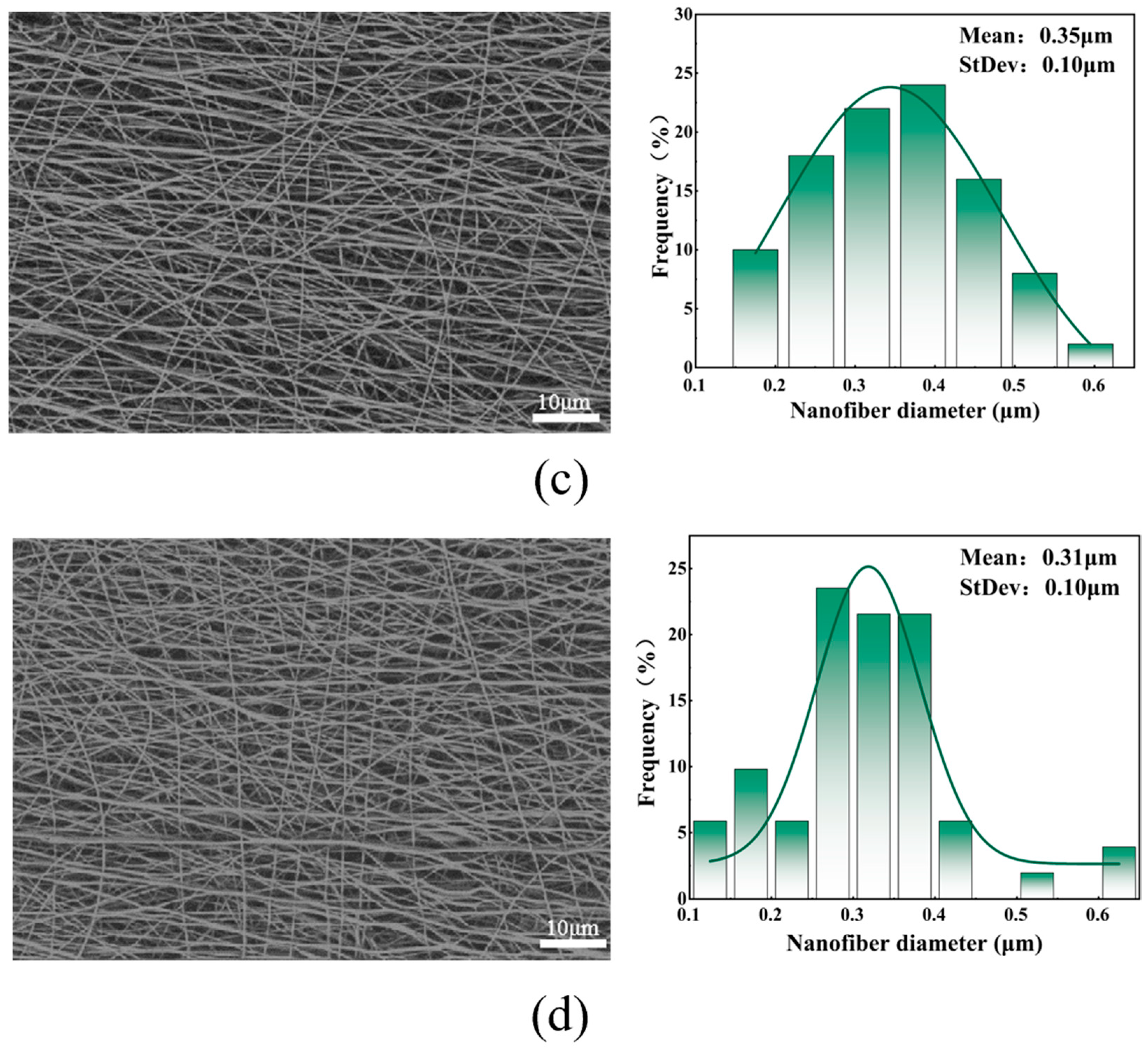
5.2. Effect of Different Spinning Voltages on Fiber Morphology
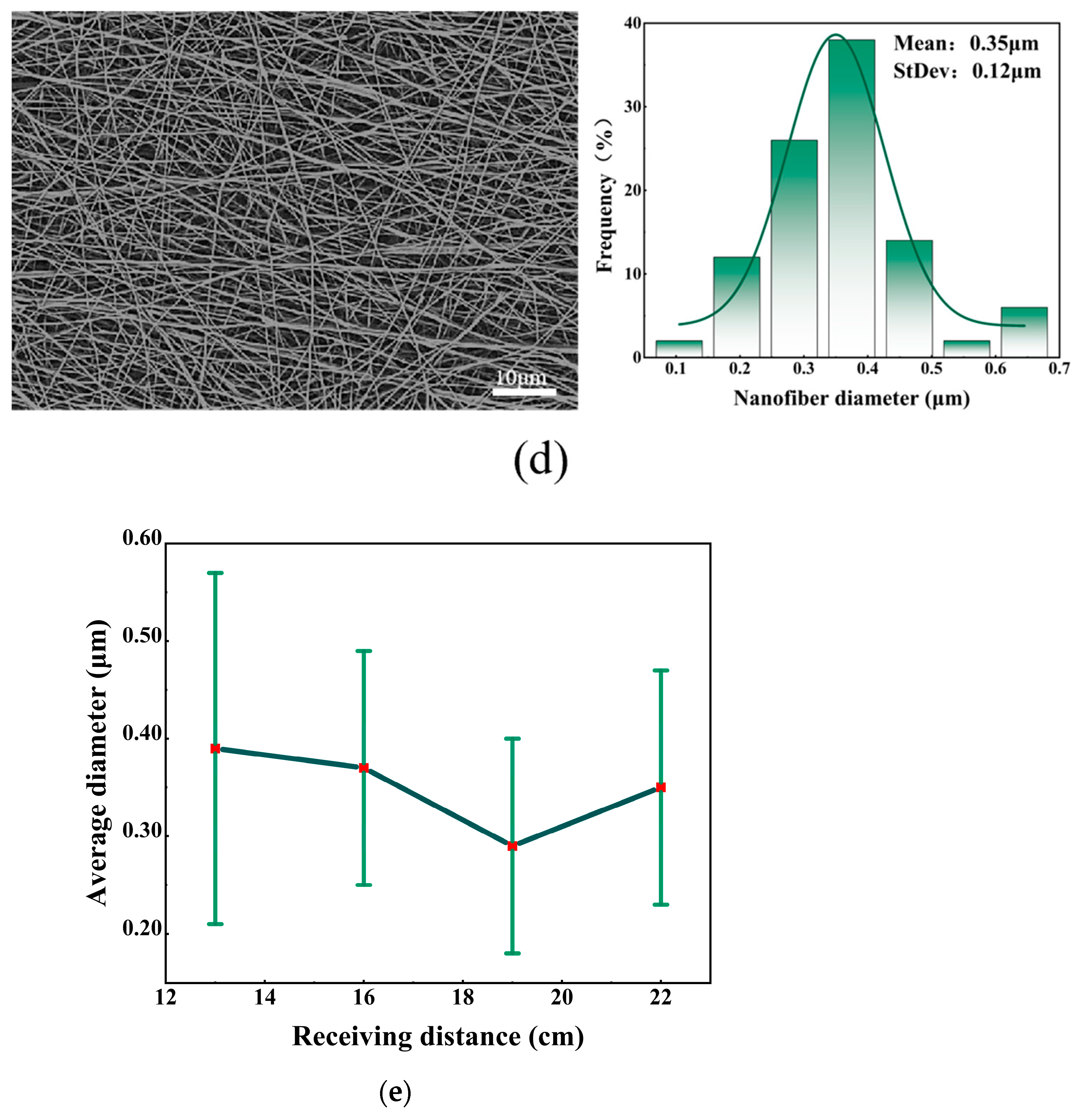
5.3. Effect of Different Receiving Distances on Fiber Morphology
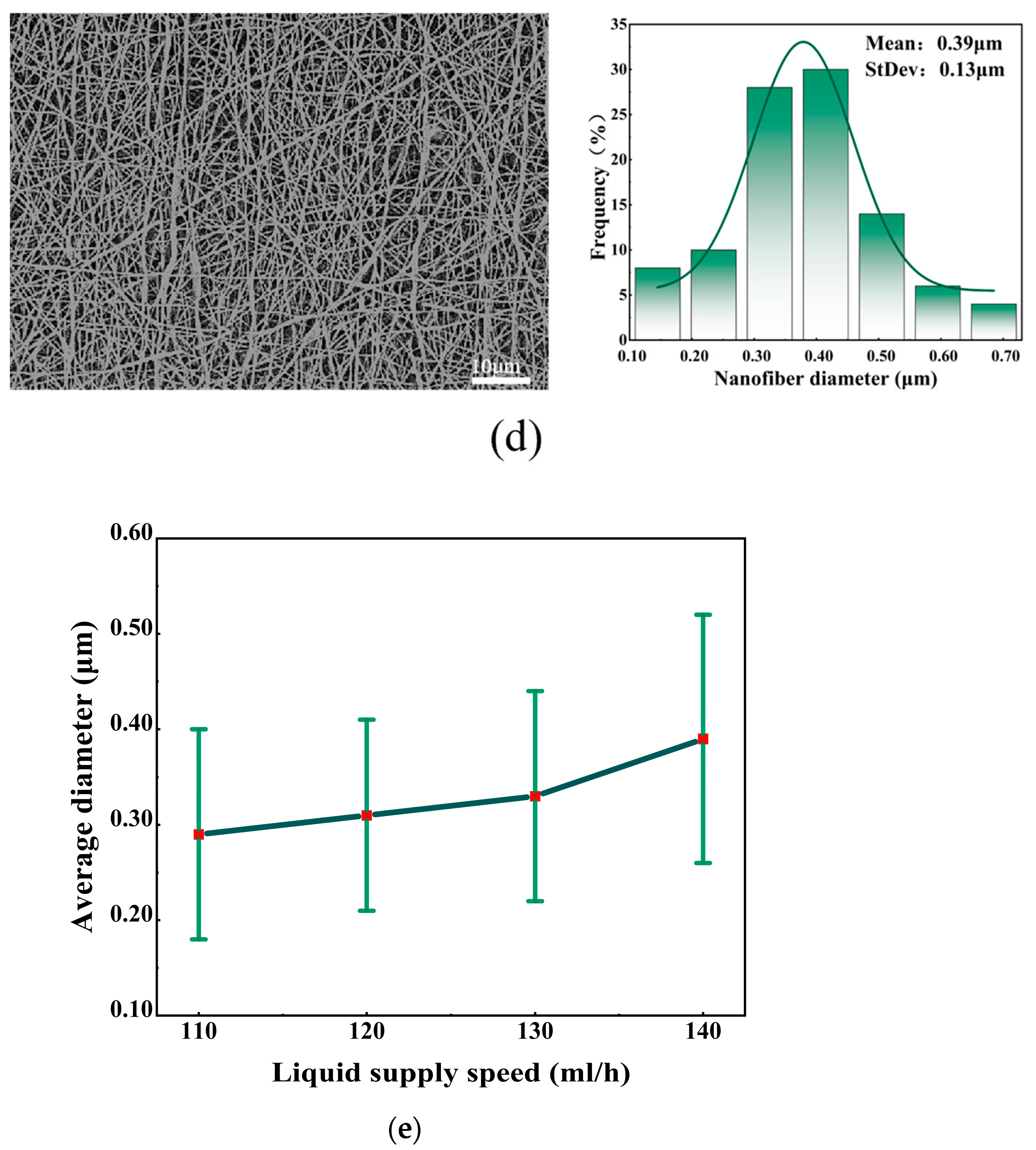
5.4. Effect of Different Liquid Supply Speeds on Fiber Morphology
6. Performance Analysis of Needleless Electrospinning Nano-Mask
6.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Measurement
6.2. Moisturizing Performance Experimental Design
- Expose the target skin area to the air for 10 min at room temperature (25 °C), and then use an instrument to measure the moisture content and oil content of the skin at that time.
- Apply five groups of PEO/collagen peptide nanofiber masks with different ratios evenly to the skin test site, and use a spray bottle containing deionized water to apply to the mask to melt and be absorbed by the skin. Then, gently massage the skin area, and after 10 min, measure the moisture content and oil content of the mask area. (Before each experiment, a certain period of time should be allowed to pass and the skin’s moisture content and oil content should be re-measured).
- As a control experiment, while performing step 2, spray deionized water on the adjacent parts of the skin where the mask is applied, and massage gently. After 10 min, measure the skin moisture and oil content of the area at the same time.
6.3. Quick-Dissolving Performance Experimental Design
7. Experimental Results and Analysis
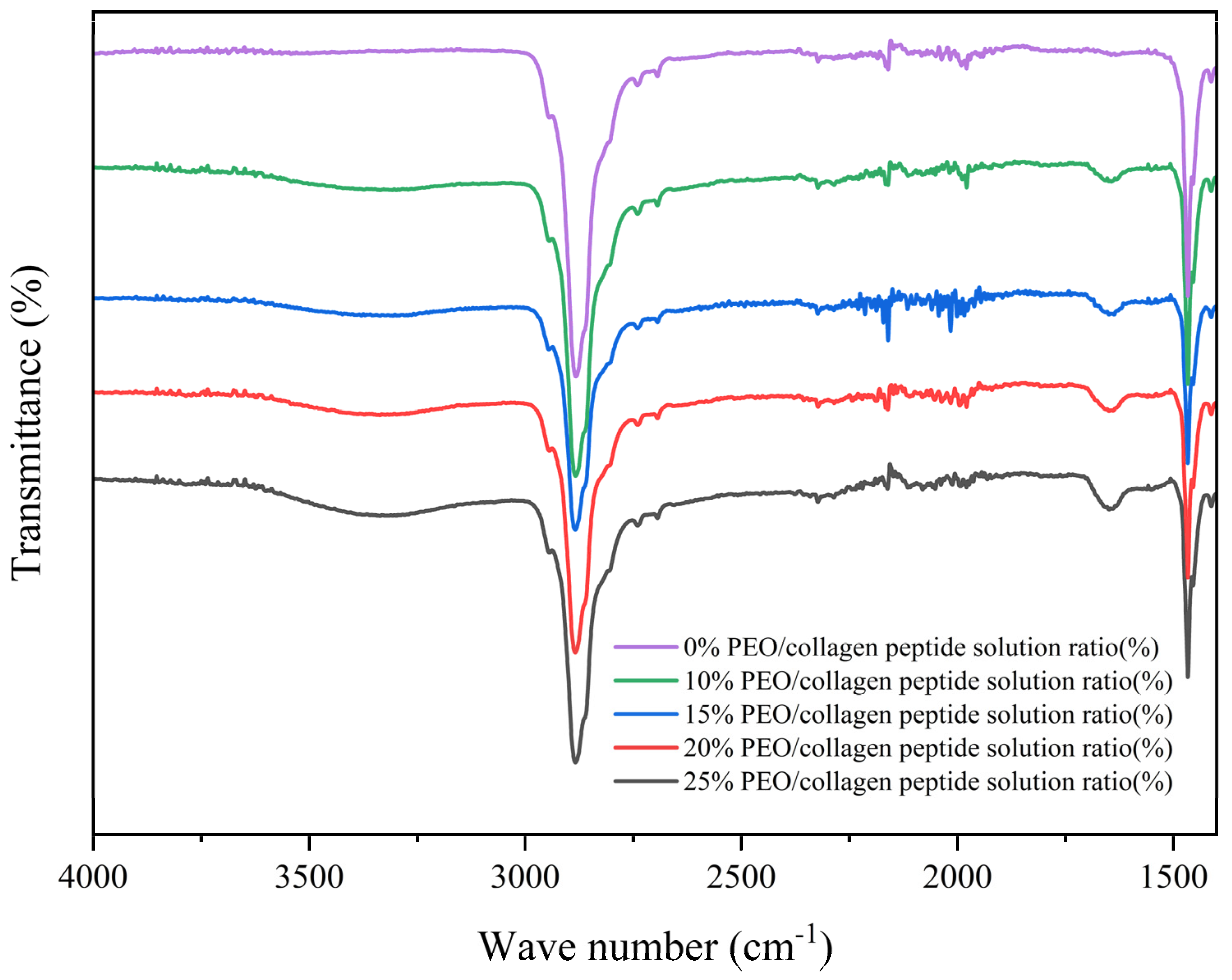
7.1. Infrared Spectral Analysis
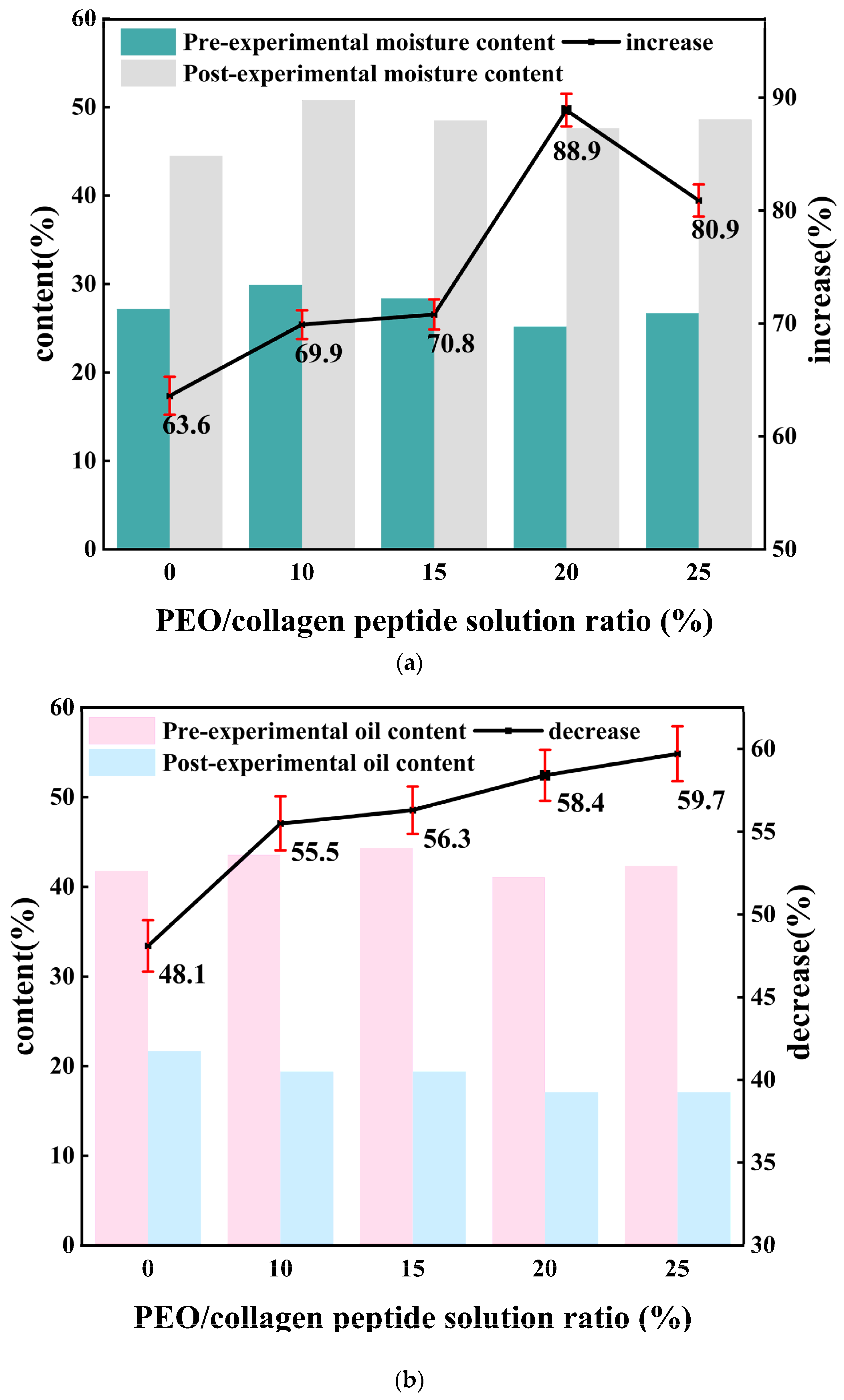
7.2. Moisturizing Performance Analysis
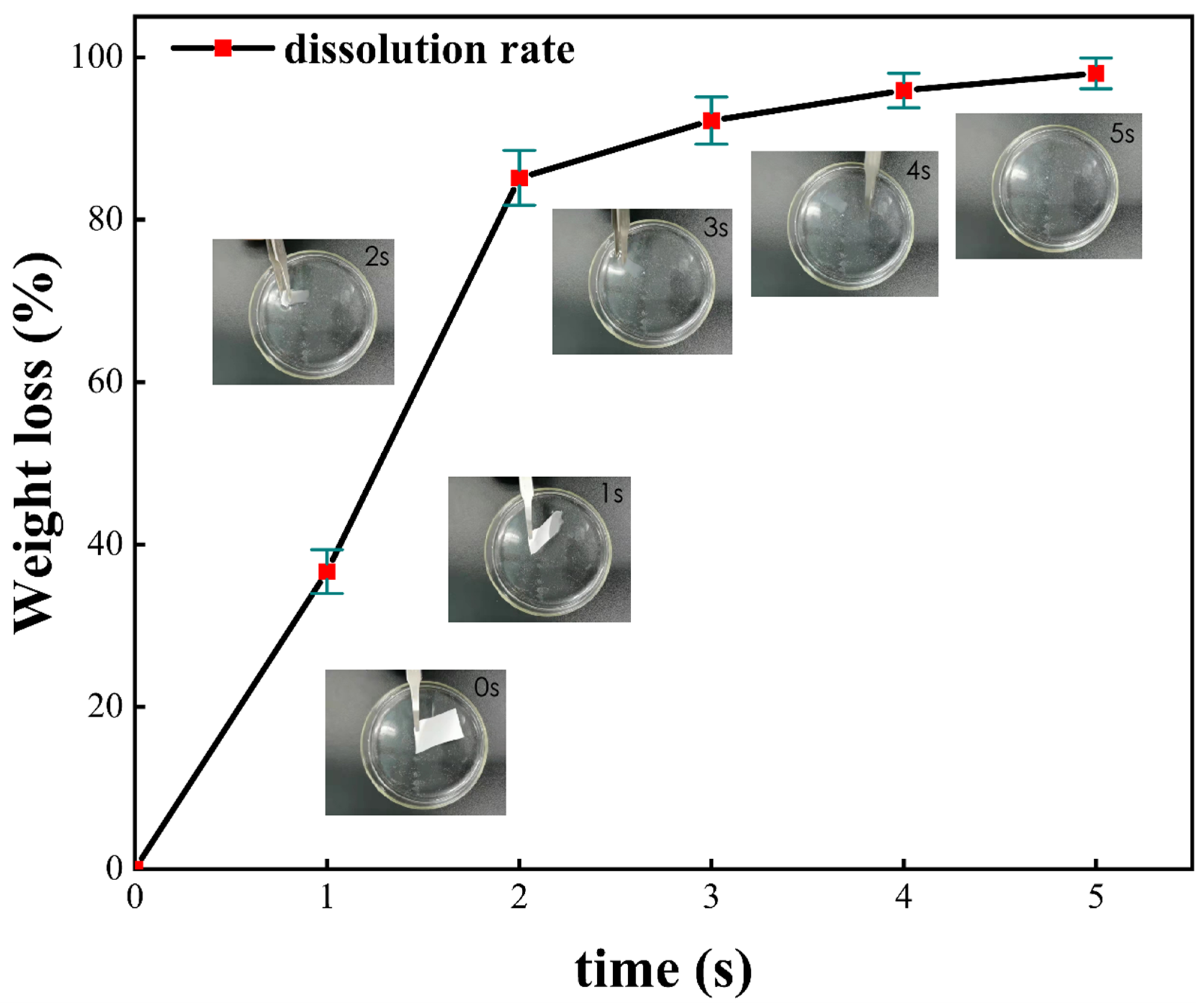
7.3. Quick-Dissolving Performance Analysis
8. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fathi-Azarbayjani, A.; Qun, L.; Chan, Y.W.; Chan, S.Y. Novel Vitamin and Gold-Loaded Nanofiber Facial Mask for Topical Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, D.; Singh, N.; Afreen, S.; Talreja, N.; Ashfaq, M.; Sankararamakrishnan, N.; Chaudhary, G.R. A thermoresponsive CA-PNIPAM-based electrospun nanofibrous membrane for oil/water separation. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 18984–18989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, T.; Bhat, G.S.; Tock, R.W.; Parameswaran, S.; Ramkumar, S.S. Electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 96, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Chen, X.; Du, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, P. Controllable Direct-Writing of Serpentine Micro/Nano Structures via Low Voltage Electrospinning. Polymers 2015, 7, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shen, J.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Tjong, S.C. Development and Antibacterial Performance of Novel Polylactic Acid-Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanoparticle Hybrid Nanocomposite Mats Prepared By Electrospinning. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.-T.; Wu, P.-S.; Huang, T.-Y. Osteogenic differentiation of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth on poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofibers containing strontium phosphate. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.T.; Liu, Y.J.; Huang, T.Y. Nanofibers promote HepG2 aggregate formation and cellular function. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, gmr.15038993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, M.; Kim, G.H. Anisotropically Aligned Cell-Laden Nanofibrous Bundle Fabricated via Cell Electrospinning to Regenerate Skeletal Muscle Tissue. Small 2018, 14, 1803491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, K.Y.; Na, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, J.; Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.H. Fabrication of a multi-walled carbon nanotube-deposited glass fiber air filter for the enhancement of nano and submicron aerosol particle filtration and additional antibacterial efficacy. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4132–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Y. Recent advances in energy materials by electrospinning. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1825–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinatra, N.R.; Ranzani, T.; Vlassak, J.J.; Parker, K.K.; Wood, R.J. Nanofiber-reinforced soft fluidic micro-actuators. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 084002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsasulak, S.; Patapeejumruswong, M.; Weiss, J.; Supaphol, P.; Yoovidhya, T. Electrospinning of food-grade nanofibers from cellulose acetate and egg albumen blends. J. Food Eng. 2010, 98, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Venugopal, J.; Huang, Z.-M.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Crosslinking of the electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2006, 47, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.-T.; Hsu, M.-S. Nanofiber Mask Fabrication by Electrospun and Its Application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1637, 012102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Kannan, B.; Chand, N.A.; Blake, A.; Chong, J.; Hosie, I.; Lepe, P. Chapter 9—ActiVLayr nanofiber technology. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Manufacturing Applications; Hussain, C.M., Ed.; In Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, R.; Albargi, H.B.; Ahmad, A.; Qadir, M.B.; Khaliq, Z.; Nazir, A.; Khalid, T.; Batool, M.; Arshad, S.N.; Jalalah, M.; et al. Development of Sustainable Hydrophilic Azadirachta indica Loaded PVA Nanomembranes for Cosmetic Facemask Applications. Membranes 2023, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, J.; Jia, R.; Nawaz, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. Multifunctional Cellulose Ester Containing Hindered Phenol Groups with Free-Radical-Scavenging and UV-Resistant Activities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 4302–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, H. Fabrication and Characterization of Multiple Herbal Extracts-loaded Nanofibrous Patches for Topical Treatment of Acne Vulgaris. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-B.; Won, B.; Yang, S.; Kim, D.-H. Asterias pectinifera derived collagen peptide-encapsulating elastic nanoliposomes for the cosmetic application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, O.M.; Iacob, A.T.; Mignon, A.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Baican, M.; Danu, M.; Ibănescu, C.; Simionescu, N.; Profire, L. Design, preparation and in vitro characterization of biomimetic and bioactive chitosan/polyethylene oxide based nanofibers as wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Fu, Y.; Dai, H.; Wang, Q.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Y. Recent progress in preventive effect of collagen peptides on photoaging skin and action mechanism. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, W. Fabrication and properties of carboxymethyl chitosan/polyethylene oxide composite nonwoven mats by centrifugal spinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saatchi, A.; Arani, A.R.; Moghanian, A.; Mozafari, M. Synthesis and characterization of electrospun cerium-doped bioactive glass/chitosan/polyethylene oxide composite scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadehie, F.S.; Dehkordi, A.H.; Zafari, M.; Bagheri, M.; Yousefiasl, S.; Pourmotabed, S.; Mahmoodnia, L.; Validi, M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zare, E.N.; et al. Lawsone-encapsulated chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibrous mat as a potential antibacterial biobased wound dressing. Eng. Regen. 2021, 2, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, J.; Mai, R.; Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, T. Preparation of Quick-Dissolving Nanofiber Face Masks Based on Needleless Electrostatic Spinning. Polymers 2024, 16, 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111602
Hu J, Chen X, Jiang J, Mai R, Wang H, Xu Q, Zhang T. Preparation of Quick-Dissolving Nanofiber Face Masks Based on Needleless Electrostatic Spinning. Polymers. 2024; 16(11):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111602
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jingyi, Xiaojie Chen, Jianmin Jiang, Renbiao Mai, Han Wang, Qiming Xu, and Ting Zhang. 2024. "Preparation of Quick-Dissolving Nanofiber Face Masks Based on Needleless Electrostatic Spinning" Polymers 16, no. 11: 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111602
APA StyleHu, J., Chen, X., Jiang, J., Mai, R., Wang, H., Xu, Q., & Zhang, T. (2024). Preparation of Quick-Dissolving Nanofiber Face Masks Based on Needleless Electrostatic Spinning. Polymers, 16(11), 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111602





