An Oxalato-Bridged Cu(II)-Based 1D Polymer Chain: Synthesis, Structure, and Adsorption of Organic Dyes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Crystallographic Measurements
2.2. Thermal Analysis
2.3. Adsorption Batch Experiments
2.4. Synthesis of {[Cu(C2O4)(C10H8N2)]·H2O·0.67(CH3OH)]}n (1)
3. Results
3.1. Structural Description
3.2. Adsorption Parameter Study
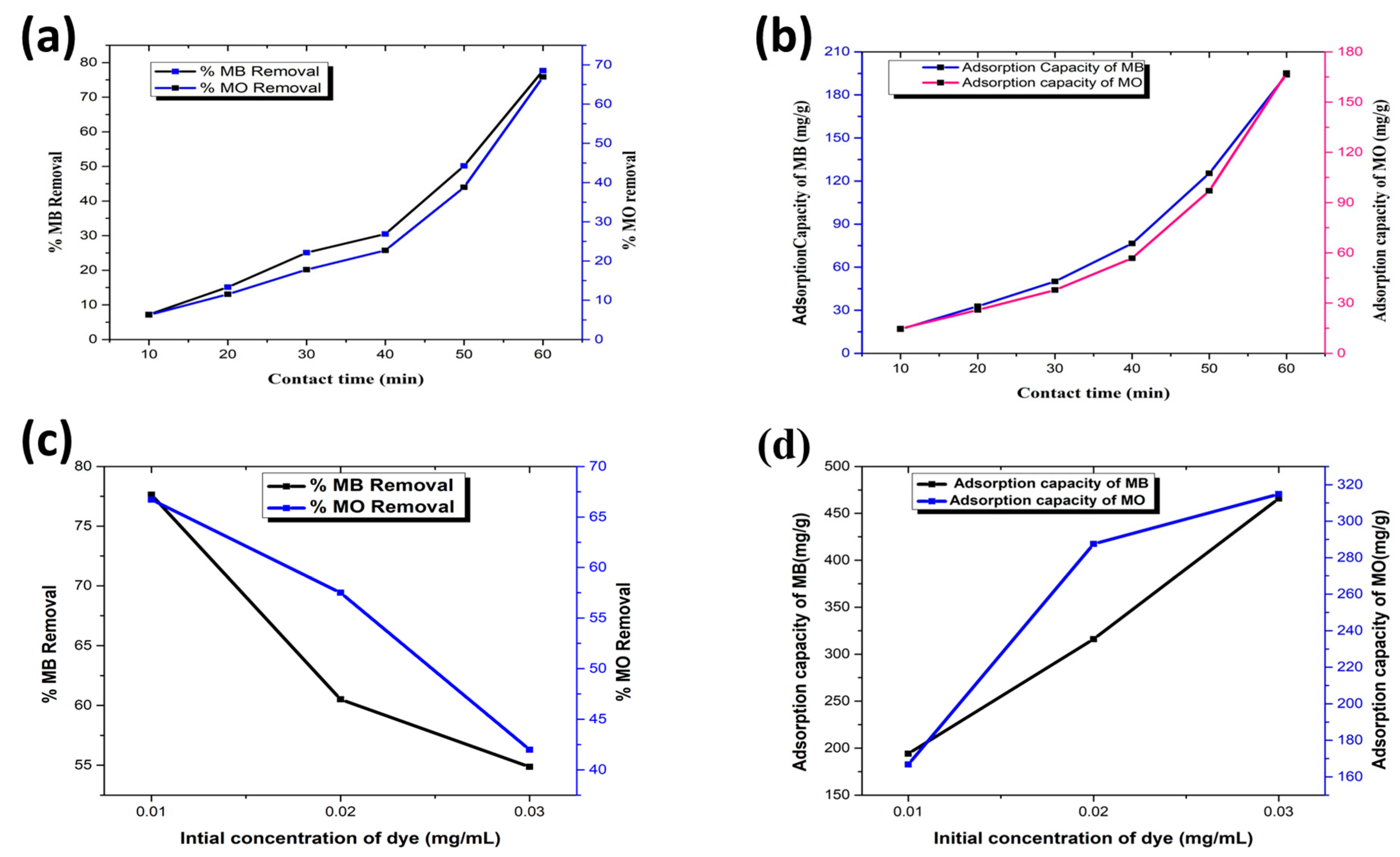
3.3. Effect of Contact Time
3.4. Effect of Initial Concentration
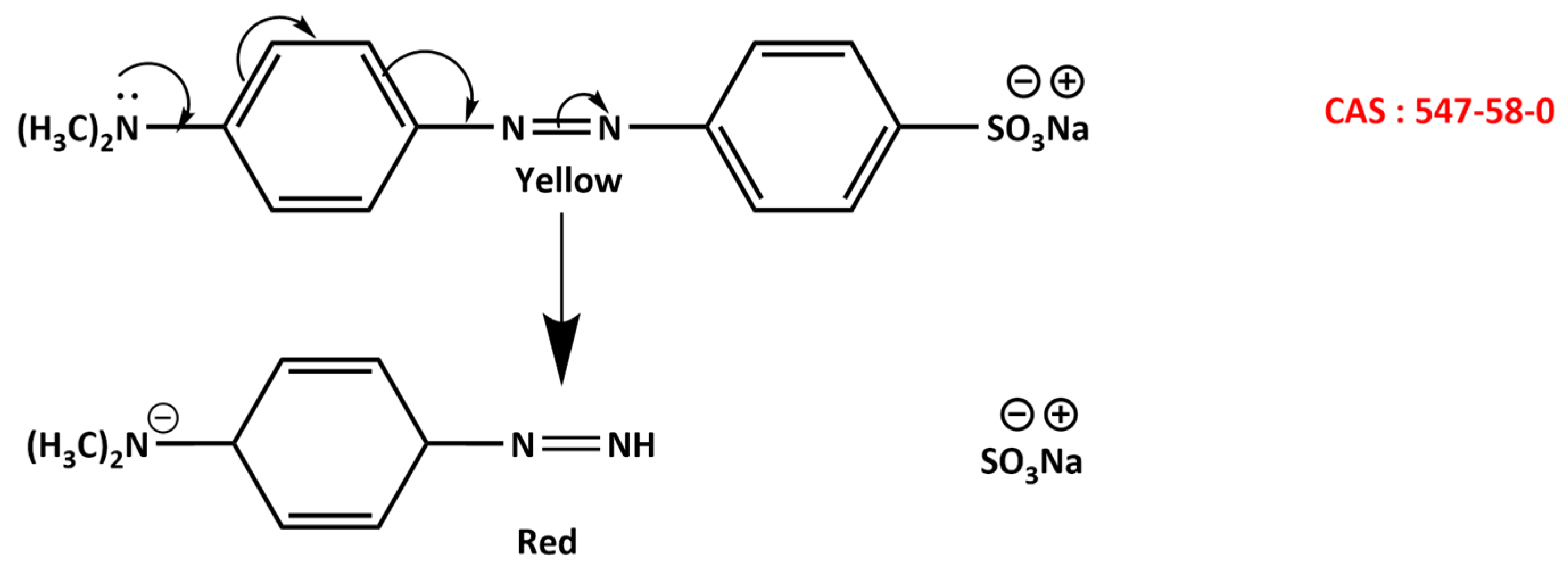
3.5. Effect of pH
3.6. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
3.7. Effect of Temperature
3.8. Adsorption Kinetics
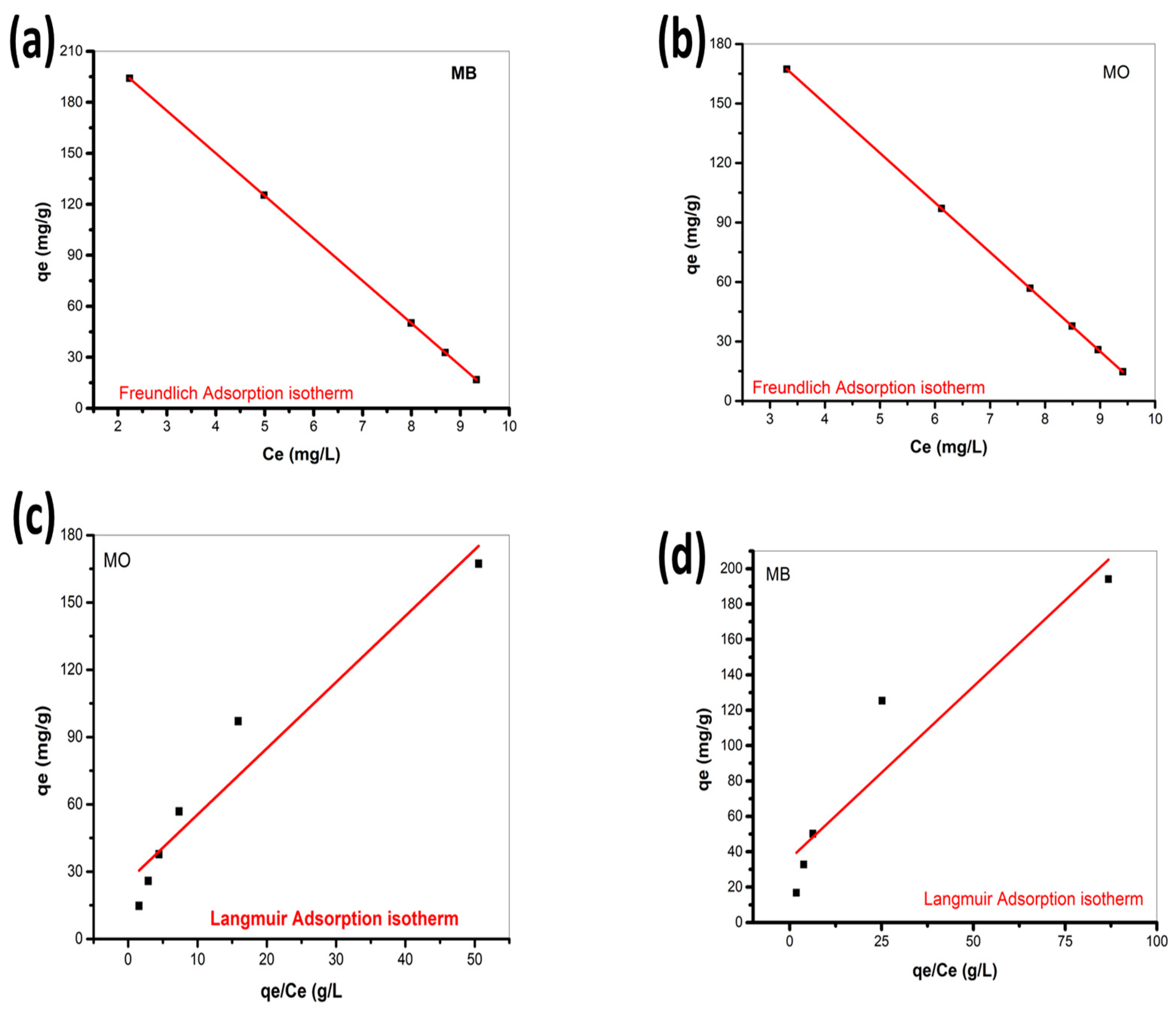
3.9. Adsorption Isotherm
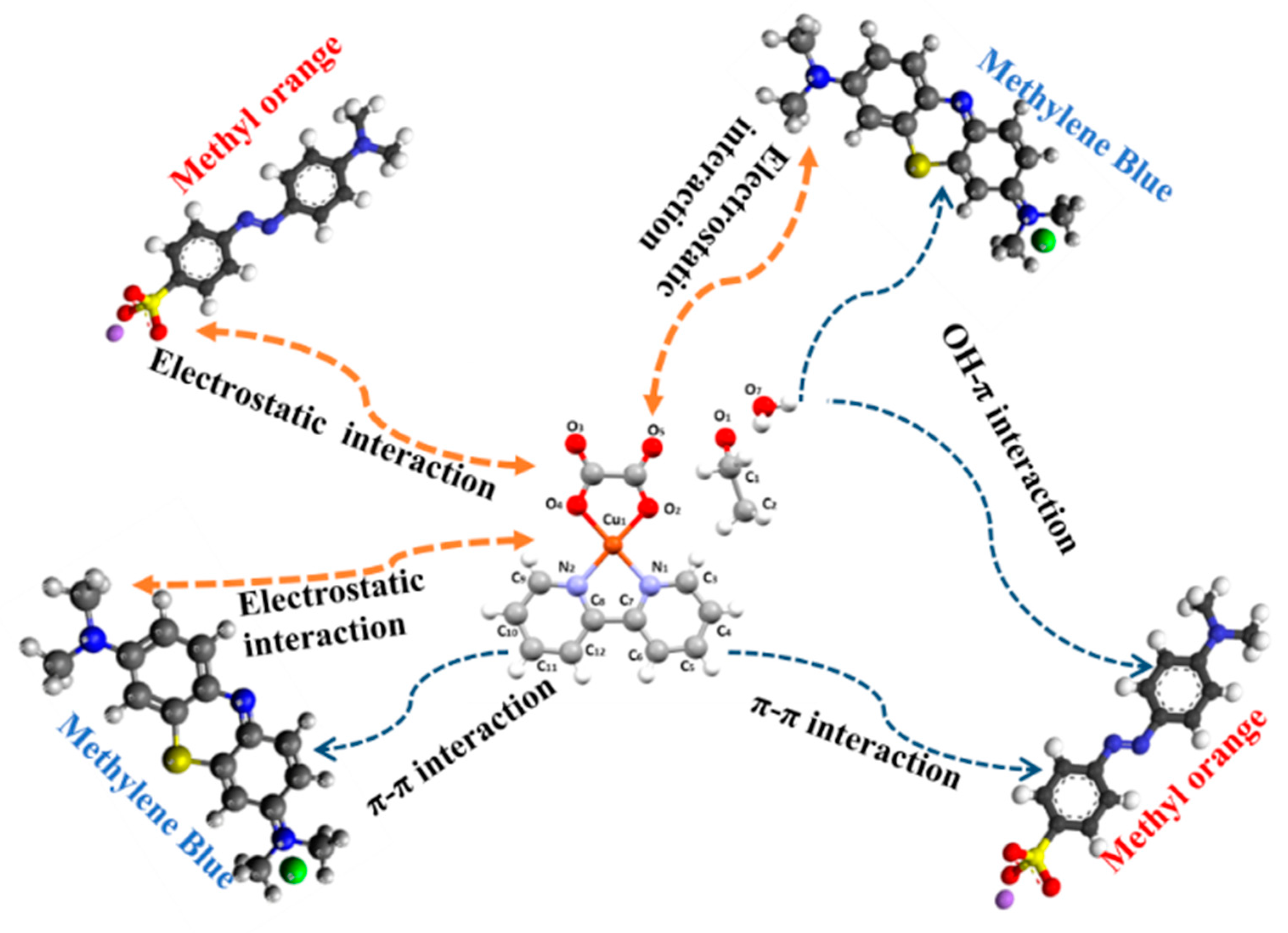
3.10. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Reusability
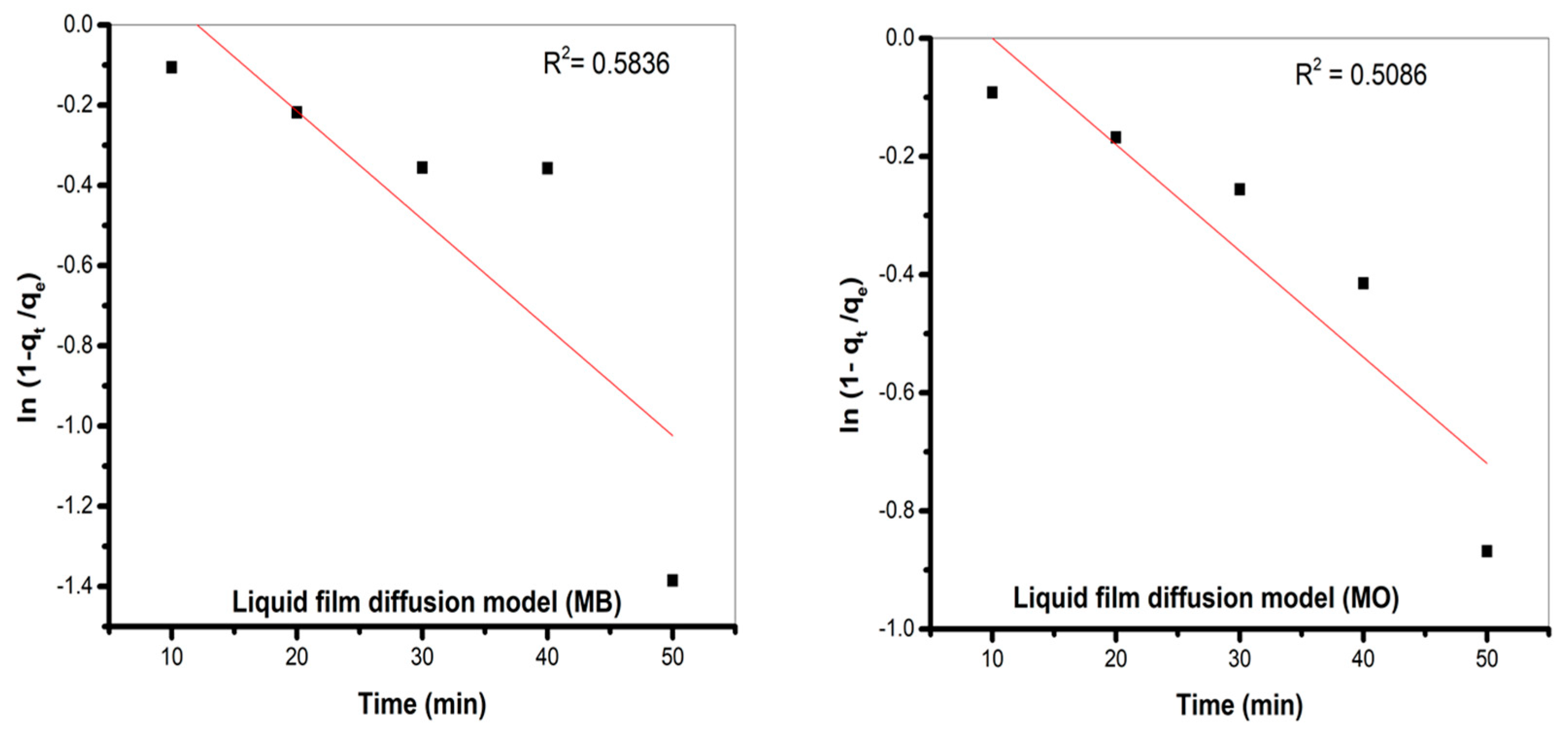
Liquid Film Diffusion Model
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sriram, G.; Bendre, A.; Mariappan, E.; Altalhi, T.; Kigga, M.; Ching, Y.C.; Jung, H.-Y.; Bhaduri, B.; Kurkuri, M. Recent trends in the application of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for the removal of toxic dyes and their removal mechanism—A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 31, e00378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, B.; Saravanan, A.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Thamarai, P.; Shaji, A.; Rangasamy, G. A review on algae biosorption for the removal of hazardous pollutants from wastewater: Limiting factors, prospects and recommendations. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthigadevi, G.; Manikandan, S.; Karmegam, N.; Subbaiya, R.; Chozhavendhan, S.; Ravindran, B.; Chang, S.W.; Awasthi, M.K. Chemico-nanotreatment methods for the removal of persistent organic pollutants and xenobiotics in water—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 324, 124678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudhoo, A.; Ramasamy, D.L.; Bhatnagar, A.; Usman, M.; Sillanpää, M. An analysis of the versatility and effectiveness of composts for sequestering heavy metal ions, dyes and xenobiotics from soils and aqueous milieus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, G.; Thakur, A. Distinct approaches of removal of dyes from wastewater: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solayman, H.M.; Hossen, M.; Abd Aziz, A.; Yahya, N.; Hon, L.; Ching, S.; Monir, M.; Zoh, K.-D. Performance Evaluation of Dye Wastewater Treatment Technologies: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Krishnan, V.; Koner, R.R. Trifunctional metal–organic platform for environmental remediation: Structural features with peripheral hydroxyl groups facilitate adsorption, degradation and reduction processes. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonai, G.; Guelli Souza, S.; Oliveira, D.; Souza, A. The application of textile sludge adsorbents for the removal of Reactive Red 2 dye. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 168, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisi, S.D.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M. Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 9, 10–40. [Google Scholar]
- Younas, F.; Mustafa, A.; Ur, Z.; Farooqi, Z.U.; Xiukang, W.; Younas, S.; Mohy-Ud-Din, W.; Hameed, M.; Abrar, M.M.; Maitlo, A.L.I.; et al. Current and Emerging Adsorbent Technologies for Wastewater Treatment: Trends, Limitations, and Environmental Implications. Water 2021, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Adsorption of anionic MO or cationic MB from MO/MB mixture using polyacrylonitrile fiber hydrothermally treated with hyperbranched polyethylenimine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Cheng, T.; Lin, Q. A novel mesoporous carbon nanospheres-based adsorbent material with desirable performances for dyes removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Suhas. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-J.; Wang, C.-C.; Fu, H.-F.; Cui, J.-R.; Xu, P.; Guo, J.; Li, J.-R. High-performance adsorption and separation of anionic dyes in water using a chemically stable graphene-like metal–organic framework. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 10197–10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Mantasha, I.; Shahid, M.; AlDamen, M.A.; Khalid, M.; Akram, M. Cationic dye adsorption and separation at discrete molecular level: First example of an iron cluster with rapid and selective adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous system. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, K.M.A.; Khan, S.; Fitta, M.; Akhtar, M.N.; AlDamen, M.A.; Shahid, M.; Saleh, H.A.M.; Ahmad, M. A new {Cu3–Gd2} cluster as a two-in-one functional material with unique topology acting as a refrigerant and adsorbent for cationic dye. CrystEngComm 2022, 24, 5215–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Abazari, R.; Tahir, M.; Fan, W.K.; Kumar, A.; Kalhorizadeh, T.; Kirillov, A.M.; Amani-Ghadim, A.R.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y. Trimetallic metal–organic frameworks and derived materials for environmental remediation and electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 461, 214505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.A.M.; Mantasha, I.; Qasem, K.M.A.; Shahid, M.; Akhtar, M.N.; AlDamen, M.A.; Ahmad, M. A two dimensional Co(II) metal–organic framework with bey topology for excellent dye adsorption and separation: Exploring kinetics and mechanism of adsorption. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2020, 512, 119900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chauhan, C.; Kumar, R.; Kalra, N.; Saini, A.; Sharma, S.; Singh, A. Concomitant role of metal clusters and ligands in the synthesis and control of porosity in Metal-Organic Frameworks: A literature review. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejsmont, A.; Andreo, J.; Lanza, A.; Galarda, A.; Macreadie, L.; Wuttke, S.; Canossa, S.; Ploetz, E.; Goscianska, J. Applications of reticular diversity in metal–organic frameworks: An ever-evolving state of the art. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 430, 213655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.V.; Sharma, S.; Let, S.; Ghosh, S.K. N-donor linker based metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Advancement and prospects as functional materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 395, 146–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Chen, Y.-C.; AlDamen, M.A.; Tong, M.-L. 3D oxalato-bridged lanthanide(III) MOFs with magnetocaloric, magnetic and photoluminescence properties. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, R. Selective anionic dye adsorption, topology and luminescence study of structurally diverse cadmium(II) coordination polymers. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of hazardous materials using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, G.; Liu, J.; Bao, F.; Wei, Y.; Wang, H. Amide-functionalized ionic indium–organic frameworks for efficient separation of organic dyes based on diverse adsorption interactions. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Z.; Shi, J.Y.; Chen, P.Y.; Tian, L.; Chen, J. Two 3D Cobalt(II) Metal–Organic Frameworks with Micropores for Selective Dye Adsorption. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Nabil, G.; Khalifa, M.; El-Mallah, N.; Hassouba, H. Effective Removal of Crystal Violet and Methylene Blue Dyes from Water by Surface Functionalized Zirconium Silicate Nanocomposite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.K.; Amin, M.K.; Ahmed, J.; Elias, M.; Mahiuddin, M. Removal of toxic methyl orange by a cost-free and eco-friendly adsorbent: Mechanism, phytotoxicity, thermodynamics, and kinetics. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 40, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.-W.; Liu, J.-M.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Zhao, N.; Wang, S. Simultaneous adsorption of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution using amino functionalized Zr-based MOFs. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 282, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, E.M.; Petit, C. Towards the use of metal–organic frameworks for water reuse: A review of the recent advances in the field of organic pollutants removal and degradation and the next steps in the field. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22484–22506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Din, A.T.M.; Ahmad, A.L. Adsorption of methylene blue onto bamboo-based activated carbon: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, L.; Zhang, C.; Meng, L. Adsorption of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solution on Hydrothermal Synthesized Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.Z.; Zhang, L.M. Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by adsorption onto sodium humate/polyacrylamide/clay hybrid hydrogels. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2182–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamil, M.; Akhtar, M.N.; Imran, M.; Javaid, A.; Zafar, H.; Sohail, M.; AlDamen, M.; Fitta, M.; Khanfar, M.; Al-Qawasmeh, R. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye and electrocatalytic water oxidation over copper(II) complex with mixed ligands. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 446, 115095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, S.; Saleem, H.; Akhtar, M.N.; Imran, M.; Javaid, A.; AlDamen, M.A.; Bikas, R.; Khanfar, M.A. A Zn-based Zig-Zag 1D chain type coordination polymer for removal of methylene blue dye from an aqueous solution. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2024, 559, 121756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Stalke, D. SADABS 2016/2. J. Appl. Cryst. 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O.; Bourhis, L.; Gildea, R.; Howard, J.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71 Pt 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.L.; Yang, G.Y. Two Copper(II) Complexes Built from a Novel Redox-Active Bipyridinium Dimer Ligand and Oxalate Anions: Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 2004, 3837–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androš, L.; Jurić, M.; Planinić, P.; Žilić, D.; Rakvin, B.; Molčanov, K. New mononuclear oxalate complexes of copper(II) with 2D and 3D architectures: Synthesis, crystal structures and spectroscopic characterization. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinehart, D.F. The Beer-Lambert Law. J. Chem. Educ. 1962, 39, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, X.; Feng, P.; Chai, H.; Huang, Y. ZIF-67 derived hollow cobalt sulfide as superior adsorbent for effective adsorption removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V. Linear and non-linear regression analysis for the sorption kinetics of methylene blue onto activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 derived nanoporous carbon as an effective and recyclable adsorbent for removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotics from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amooey, A.A. A New Film Diffusion Controlling Kinetic Model for Adsorption at the Solid/Solution Interface. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2020, 39, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, O.; Luque, A.; Iglesias, S.; Guzmán-Miralles, C.; Román, P. A novel one-dimensional oxalato-bridged copper(II) complex with 2,2′-bipyridine. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2001, 4, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanižaj, L.; Šenjug, P.; Pajić, D.; Pavic, L.; Molcanov, K.; Jurić, M. Magnetic and Electrical Behaviors of the Homo- and Heterometallic 1D and 3D Coordination Polymers Based on the Partial Decomposition of the [Cr(C2O4)3]3−Building Block. Materials 2020, 13, 5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Gao, E.; Bu, W.; Liao, D.; Yan, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, G. Synthesis and crystal structure of oxalato-bridged dicopper(II) complex with hydrogen bonds [Cu2(µ-C2O4)(bpy)2(H2O)2(NO3)2]. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 525, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, M.; Pajić, D.; Žilić, D.; Rakvin, B.; Milić, D.; Planinić, P. Synthesis, crystal structures and magnetic properties of the oxalate-bridged single CuIICuII and cocrystallized CuIIZnII systems. Three species (CuCu, CuZn, ZnZn) in the crystalline lattice. Polyhedron 2015, 98, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totti, F. An Oxalate-Bridged Copper(II) Complex Combining Monodentate Benzoate, 2,2′-bipyridine and Aqua Ligands: Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Investigation of Magnetic Properties. Molecules 2020, 25, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, S.; Okubo, T.; Kawata, S.; Kondo, M.; Katada, M.; Kobayashi, H. An oxalate-linked copper(II) coordination polymer, [Cu2(oxalate)2(pyrazine)3]n, constructed with two different copper units: X-ray crystallographic and electronic structures. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 4790–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Lee, G.-H.; Tsai, H.-L. Syntheses, structures, and magnetic properties of two 1D, mixed-ligand, metal coordination polymers, [M(C4O4)(dpa)(OH2)] (M = CoII, NiII, and ZnII; dpa = 2,2′-dipyridylamine) and [Cu(C4O4)(dpa)(H2O)]2·(H2O). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 2005, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, R.; Fernández-Hermida, N.; Lago, A.B.; Vázquez-López, E.M. A new [Cu(ox)(Im)2] complex resulting from the oxidation of chelidonate to oxalate. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 968, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, R.; Oliveira, T.; Martins, F.; Ellena, J.; Lloret, F.; Julve, M.; Cangussu, D. Synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic properties of the helical oxalate-bridged copper(II) chain {[(CH3)4N]2[Cu(C2O4)2]·H2O}n. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2012, 15, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnic, E.; Kravtsov, V.; Krämer, K.; Leusen, J.; Decurtins, S.; Liu, S.-X.; Kögerler, P.; Baca, S. Versatility of copper(II) coordination compounds with 2,3-bis(2-pyridyl)pyrazine mediated by temperature, solvents and anions choice. Solid State Sci. 2018, 82, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslim, M.; Ali, A.; Ahmad, M.; Alarifi, A.; Afzal, M.; Sepay, N.; Dege, N. A zinc(II) metal–organic complex based on 2-(2-aminophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole ligand: Exhibiting high adsorption capacity for aromatic hazardous dyes and catecholase mimicking activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadijokani, F.; Mohammadkhani, R.; Ahmadipouya, S.; Shokrgozar, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Molavi, H.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Arjmand, M. Superior chemical stability of UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for selective dye adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, H.; Yildiz, I.; Yasmeen, F.; Munawar, K.S.; Ashfaq, M.; Abbas, M.; Ahmed, M.; Younus, H.A.; Zhang, S.; Ahmad, N. Synthesis of a 2D copper(II)-carboxylate framework having ultrafast adsorption of organic dyes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 602, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, E.; Lee, J.E.; Jang, I.T.; Hwang, Y.K.; Chang, J.S.; Jegal, J.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution with metal-organic frameworks, porous chromium-benzenedicarboxylates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liua, P.; Yao, Z.; Zhoua, I.; Yanga, Z.; Kong, L.B. Small magnetic Co-doped NiZn ferrite/graphene nanocomposites and their dual-region microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 9738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Abdullahi, S.S.; Habibu, S.; Jagaba, A.H.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.I.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Tabassum Parveen, T.; Umar, K. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue cationic dye in aqueous solution using polypyrrole-polyethylenimine nano-adsorbent. Polymers 2022, 14, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ruan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Su, M.; Diao, Z.; Chen, D.; Hou, L.; Lee, P.H.; Shih, K.; Kong, L. Solvent-free hydrothermal synthesis of gamma-aluminum oxide nanoparticles with selective adsorption of Congo red. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 536, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadi, R.; Saadi, Z.; Fazaeli, R.; Elmi Fard, N. Monolayer and multilayer adsorption isotherm models for sorption from aqueous media. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.; Naushad, M.; Alothman, Z.; Ahamad, T. Adsorptive performance of MOF nanocomposite for methylene blue and malachite green dyes: Kinetics, isotherm and mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Long, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, C.; Hu, B.; Lu, P.; Chen, J. Hydrogen Bond and π-π Stacking Interaction: Stabilization Mechanism of Two Metal Cyclo-N5–Containing Energetic Materials. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 6627–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.; Kwak, C.; Yang, J.; Kim, J.; Ryu, S.Y.; Lee, J. Role of electrostatic interactions in the adsorption of dye molecules by Ti3C2-MXenes. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 6201–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, G.E.; Adamson, A.W.; Myers, L.S. The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solutions by organic zeolites II kinetics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munawar, F.; Khalid, M.; Imran, M.; Qasim, M.N.; Waseem, S.; AlDamen, M.A.; Ashfaq, M.; Imran, M.; Akhtar, M.N. An Oxalato-Bridged Cu(II)-Based 1D Polymer Chain: Synthesis, Structure, and Adsorption of Organic Dyes. Polymers 2024, 16, 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121742
Munawar F, Khalid M, Imran M, Qasim MN, Waseem S, AlDamen MA, Ashfaq M, Imran M, Akhtar MN. An Oxalato-Bridged Cu(II)-Based 1D Polymer Chain: Synthesis, Structure, and Adsorption of Organic Dyes. Polymers. 2024; 16(12):1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121742
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunawar, Fouzia, Muhammad Khalid, Muhammad Imran, Muhammad Naveed Qasim, Shazia Waseem, Murad A. AlDamen, Muhammad Ashfaq, Muhammad Imran, and Muhammad Nadeem Akhtar. 2024. "An Oxalato-Bridged Cu(II)-Based 1D Polymer Chain: Synthesis, Structure, and Adsorption of Organic Dyes" Polymers 16, no. 12: 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121742
APA StyleMunawar, F., Khalid, M., Imran, M., Qasim, M. N., Waseem, S., AlDamen, M. A., Ashfaq, M., Imran, M., & Akhtar, M. N. (2024). An Oxalato-Bridged Cu(II)-Based 1D Polymer Chain: Synthesis, Structure, and Adsorption of Organic Dyes. Polymers, 16(12), 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121742






