Cellulose Acetate Microparticles Synthesized from Agave sisalana Perrine for Controlled Release of Simvastatin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Vegetable Raw Material
2.3. Cellulose Extraction Process I: Elimination of Soluble Compounds
2.4. Cellulose Extraction Process II: Obtention of Holocellulose
2.5. Extraction of Cellulose
2.6. Production Cellulose Acetate
2.7. Determination of the Yield of the Extraction Process
2.8. Determination of the Degree of Substitution of Cellulose Acetate
2.8.1. Chemical Route
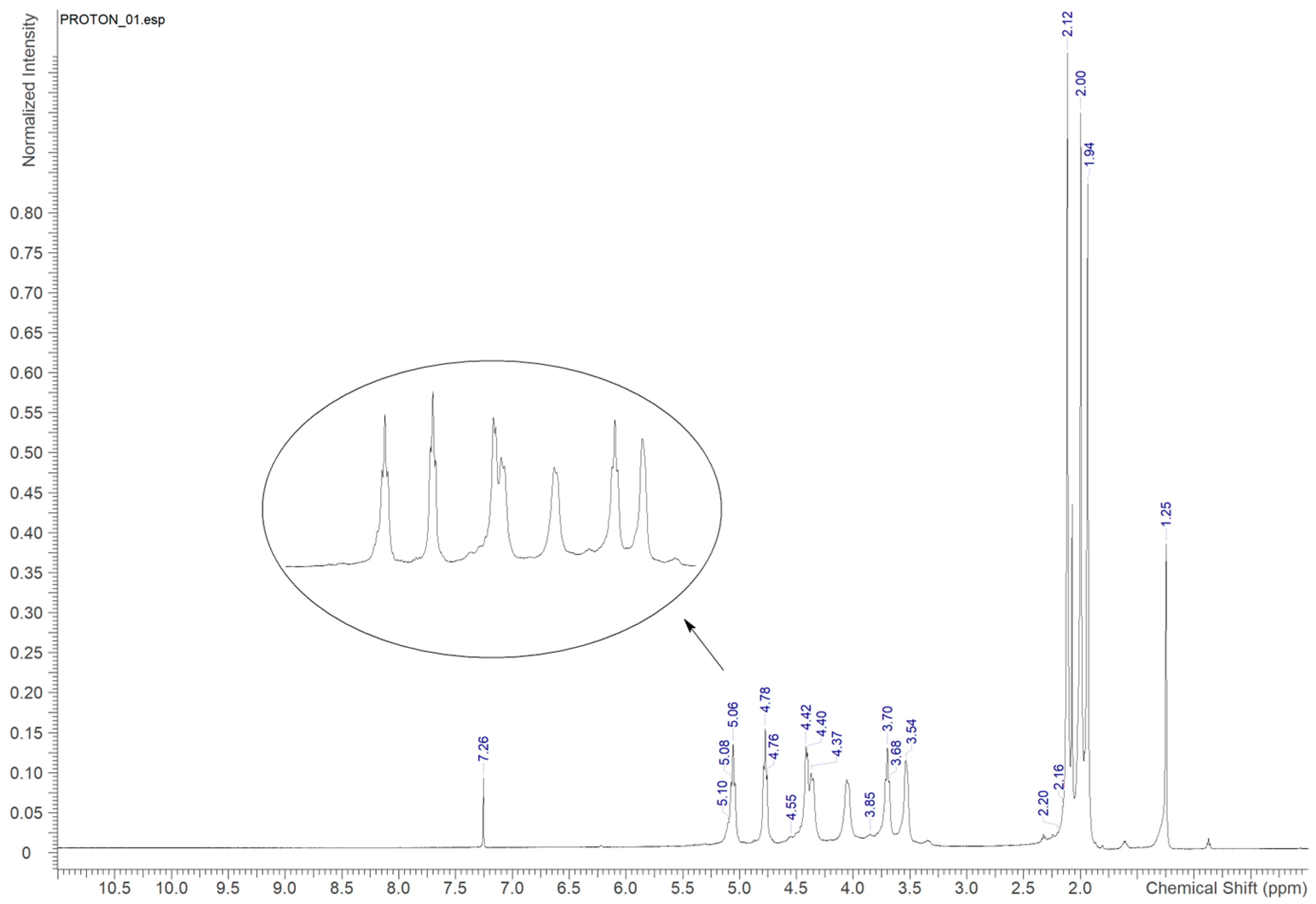
2.8.2. 1H-NMR Spectrometry
2.9. Microparticles Preparation
2.10. Physicochemical Characterization
2.10.1. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index, Zeta Potential and Encapsulation Efficiency
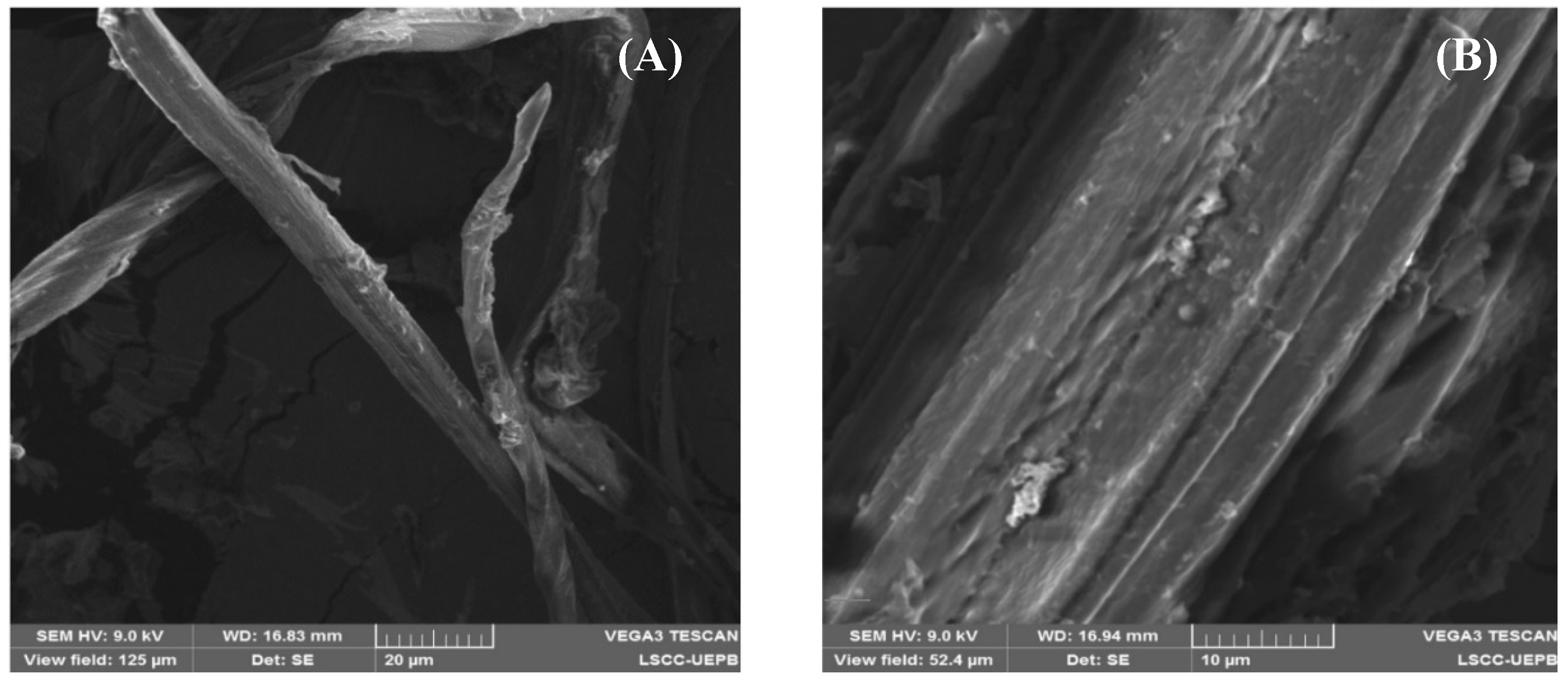
2.10.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
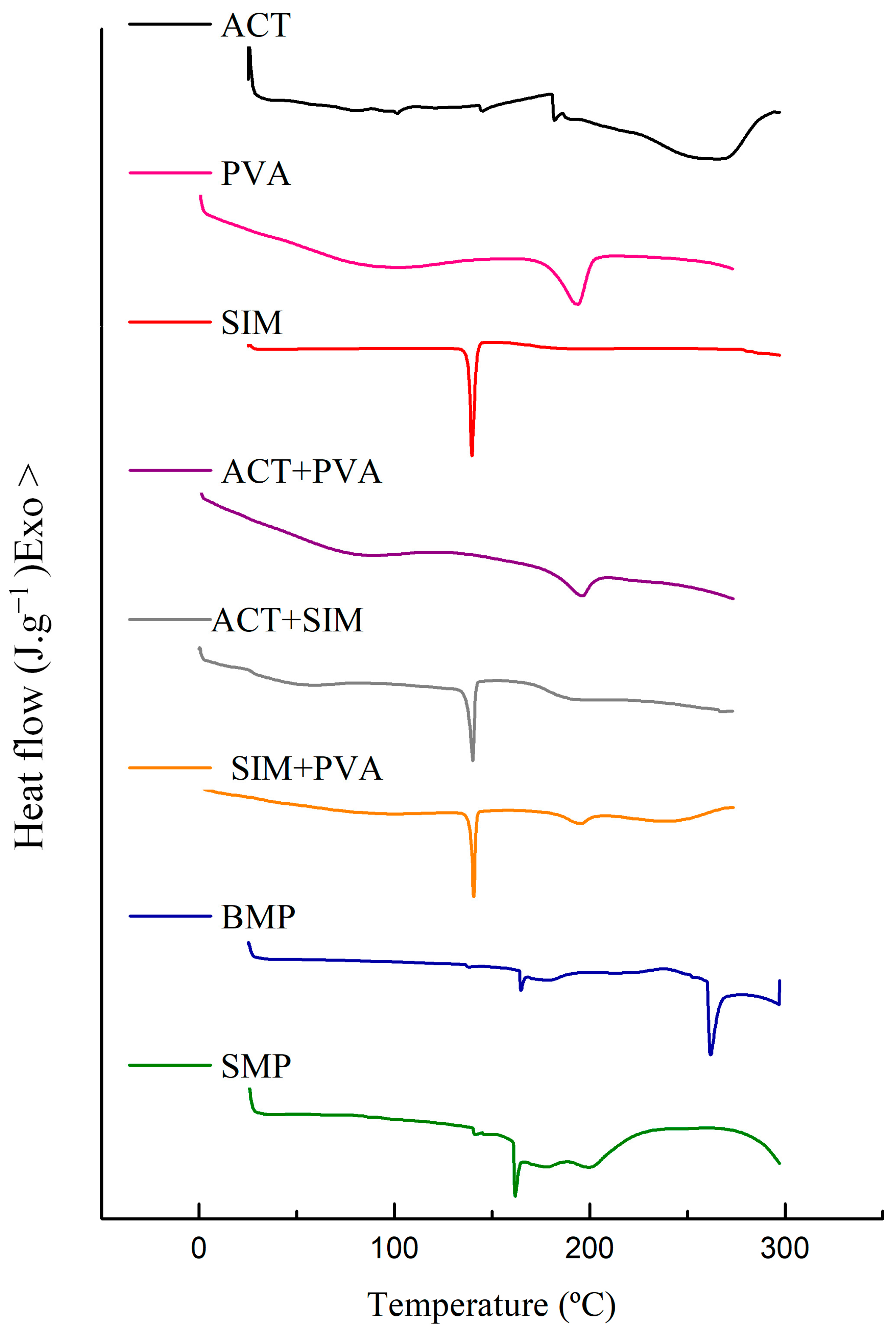
2.10.3. Thermal Analysis
2.10.4. X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
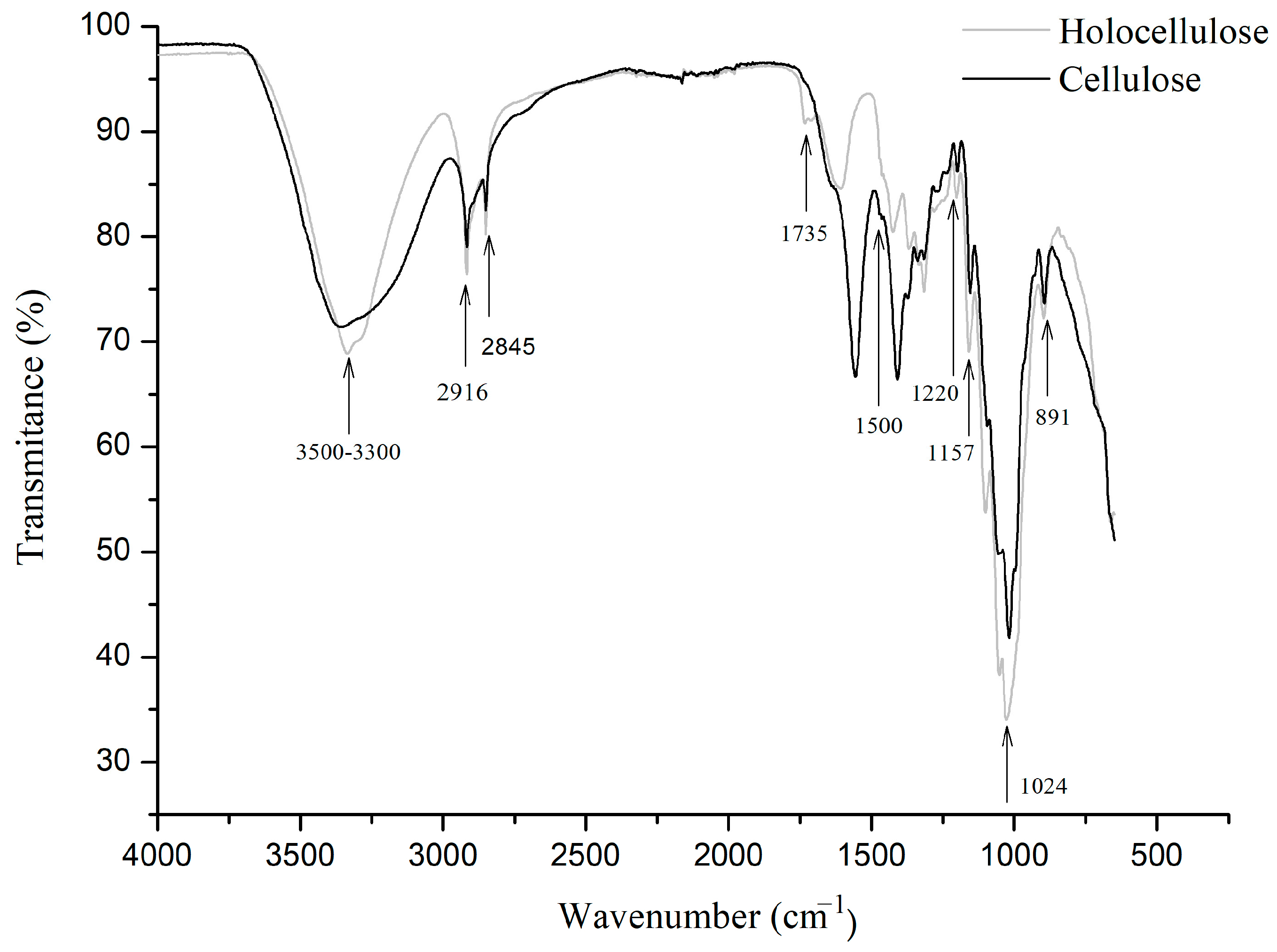
2.10.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.10.6. In Vitro SMP Release
2.10.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Extraction of Cellulose and Cellulose Acetate from Agave sisalana Perrine
3.2. Degree of Substitution of Cellulose Acetate
3.2.1. Chemical Route
3.2.2. H-NMR
3.3. Characterizations of Microparticles
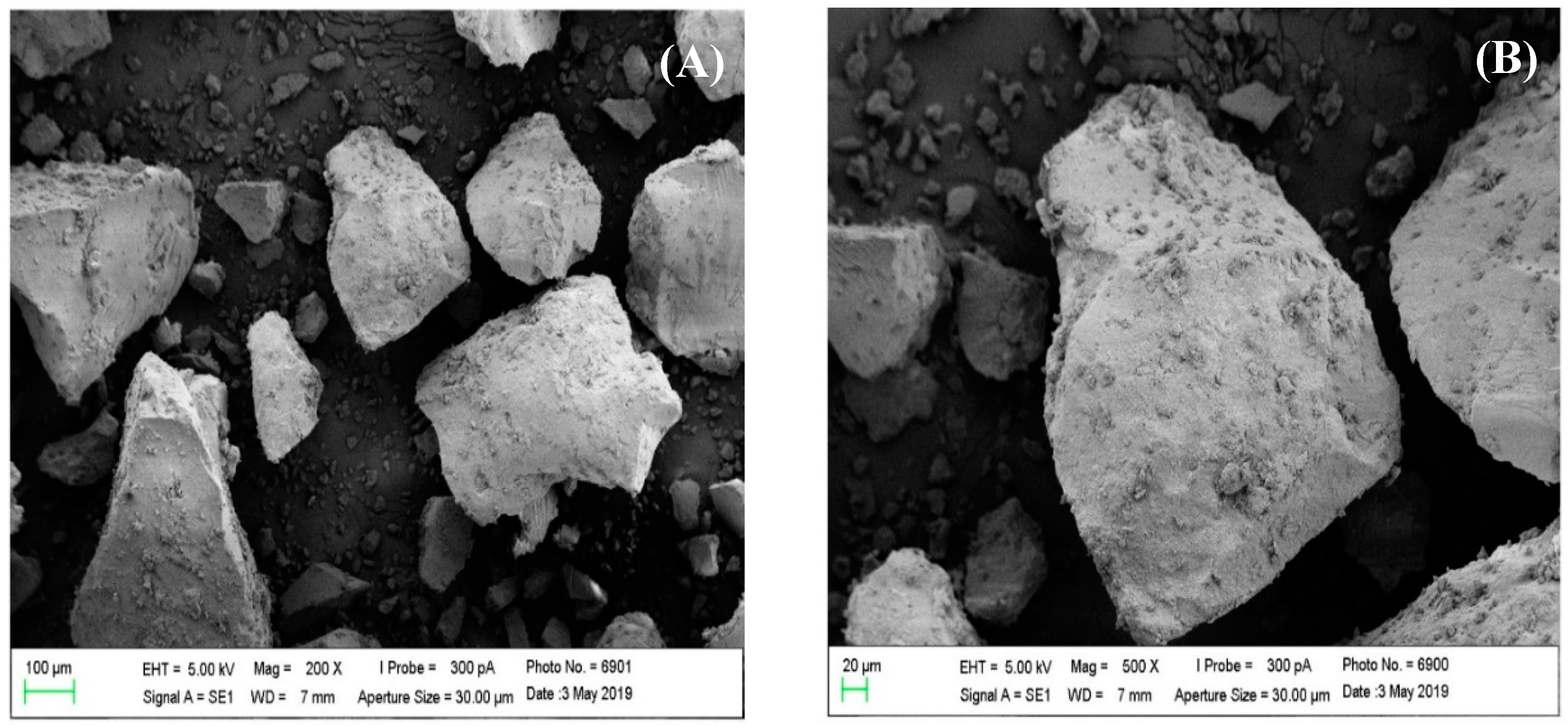
3.3.1. Morphological Analysis
3.3.2. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index, Zeta Potential and Encapsulation Efficiency
3.3.3. Thermal Analysis
3.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
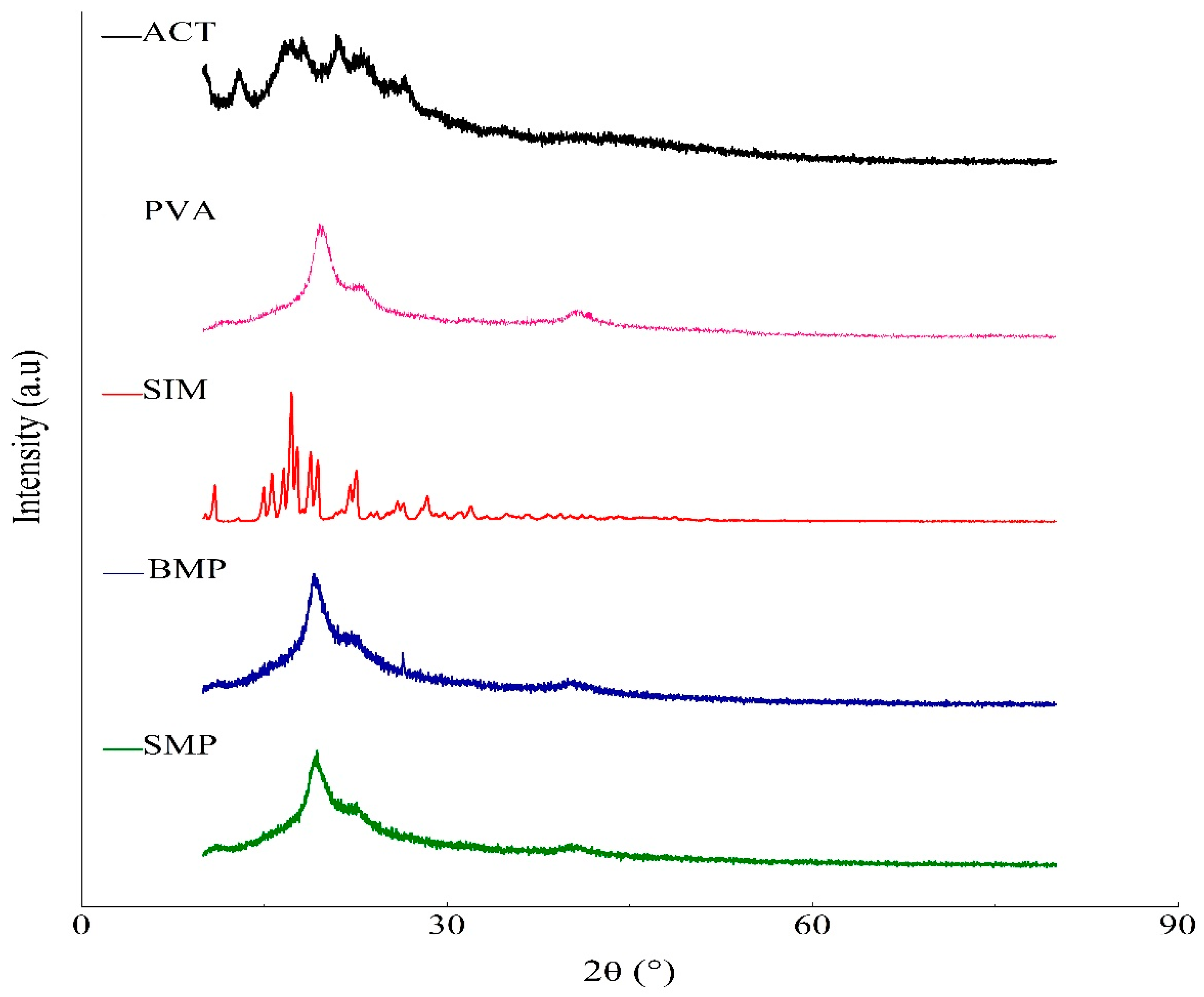
3.3.5. X-ray Diffraction
3.3.6. In Vitro SMP Release
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Assis, A.C.L.; Alves, L.P.; Malheiro, J.P.T.; Barros, A.R.A.; Pinheiro-Santos, E.E.; de Azevedo, E.P.; Alves, H.d.S.; Oshiro-Junior, J.A.; Damasceno, B.P.G.d.L. Opuntia Ficus-Indica L. Miller (Palma Forrageira) as an Alternative Source of Cellulose for Production of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Biomaterials: Extraction and Characterization. Polymers 2019, 11, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.L.; O'Connor, R.T. Nelson Relation of Certain Infrared Bands to Cellulose Crystallinity and Crystal Lattice Type. Part II. A New Infrared Ratio for Estimation of Crystallinity in Celluloses I and II. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1964, 8, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendjeffal, H.; Djebli, A.; Mamine, H.; Metidji, T.; Dahak, M.; Rebbani, N.; Bouhedja, Y. Effect of the Chelating Agents on Bio-Sorption of Hexavalent Chromium Using Agave Sisalana Fibers. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschuk, J.J.; Lacerda, T.M.; Frollini, E. Investigating Effects of High Cellulase Concentration on the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of the Sisal Cellulosic Pulp. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, H.R.; Cipriano, D.F.; Santos, M.S.; Schettino, M.A.; Ferreti, J.V.T.; Meirelles, C.S.; Pereira, V.S.; Cunha, A.G.; Emmerich, F.G.; Freitas, J.C.C. Production of High-Purity Cellulose, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose-Silica Composite from Babassu Coconut Shells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 210, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, M.; Das, A.M. Synthesis and Characterization of a Biodegradable Cellulose Acetate-Montmorillonite Composite for Effective Adsorption of Eosin Y. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cruz, A.C.; Da Silva Meireles, C.; Ribeiro, S.D.; Filho, G.R.; De Assunção, R.M.N.; Cerqueira, D.A.; Zeni, M.; Poletto, P. Utilização Do Acetato de Celulose Produzido a Partir Da Celulose Extraída Do Caroço de Manga Como Matriz Para Produção de Sistemas Microparticulados. Quim. Nova 2011, 34, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, I.L.; D’autilia, F.; Garzoni, A.; Bonferoni, C.; Scarpellini, A.; Brunetti, V.; Carzino, R.; Bianchini, P.; Pompa, P.P.; Athanassiou, A. All Natural Cellulose Acetate—Lemongrass Essential Oil Antimicrobial Nanocapsules. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 510, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo Brites, M.; Cerón, A.A.; Costa, S.M.; Oliveira, R.C.; Ferraz, H.G.; Catalani, L.H.; Costa, S.A. Bromelain Immobilization in Cellulose Triacetate Nanofiber Membranes from Sugarcane Bagasse by Electrospinning Technique. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 132, 109384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, R.G.; Godoy, G.G.; Gonçalves, A. Characterization and Application of Cellulose Acetate Synthesized from Sugarcane Bagasse. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, M.; Gellerstedt, G.; Henriksson, G. Wood Chemistry and Biotechnology; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Lim, L.T.; Manickavasagan, A. Imaging and Spectroscopic Techniques for Microstructural and Compositional Analysis of Lignocellulosic Materials: A Review. Biomass Convers. Biorefin 2023, 13, 499–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos-Jr, F.E.; Comunian, T.A.; Thomazini, M.; Favaro-Trindade, C.S. Effect of Feed Preparation on the Properties and Stability of Ascorbic Acid Microparticles Produced by Spray Chilling. LWT 2017, 75, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Sun, X.; Gong, T.; Liu, J.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, Z.R. Inhalable Microparticles as Carriers for Pulmonary Delivery of Thymopentin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, E.F.; Paula, H.C.B.; Paula, R.C.M. de Alginate/Cashew Gum Nanoparticles for Essential Oil Encapsulation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, I.; Rocha, S.; Gomes, J.; Morais, S.; Pereira, M.C.; Coelho, M. Preservation of Catechin Antioxidant Properties Loaded in Carbohydrate Nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassesco, M.E.; Fuciños, P.; Pastrana, L.; Picó, G. Development of Alginate Microparticles as Efficient Adsorption Matrix for Protein Recovery. Process Biochem. 2019, 80, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Woo, M.W.; Selomulya, C. Modification of Molecular Conformation of Spray-Dried Whey Protein Microparticles Improving Digestibility and Release Characteristics. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, F.; Pontes, J.F.; Rosa da Costa, A.M.; Grenha, A. Spray-Drying of Konjac Glucomannan to Produce Microparticles for an Application as Antitubercular Drug Carriers. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopalco, A.; Ali, H.; Denora, N.; Rytting, E. Oxcarbazepine-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles: Development and Permeability Studies across in Vitro Models of the Blood–Brain Barrier and Human Placental Trophoblast. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1985–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honary, S.; Zahir, F. Effect of Zeta Potential on the Properties of Nano-Drug Delivery Systems-A Review (Part 1). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Y.; Mu, W. Effects of Simvastatin-loaded PLGA Microspheres on Treatment of Rats with Intervertebral Disk Degeneration and on 6-K-PGF1α and HIF-1α. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 19, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasasvini, S.; Anusa, R.S.; VedhaHari, B.N.; Prabhu, P.C.; RamyaDevi, D. Topical Hydrogel Matrix Loaded with Simvastatin Microparticles for Enhanced Wound Healing Activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 72, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragagni, M.; Gil-Alegre, M.E.; Mura, P.; Cirri, M.; Ghelardini, C.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L. Improving the Therapeutic Efficacy of Prilocaine by PLGA Microparticles: Preparation, Characterization and in Vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Neves, J.K.; Apolinário, A.C.; Alcantara Saraiva, K.L.; da Silva, D.T.C.; de Freitas Araújo Reis, M.Y.; de Lima Damasceno, B.P.G.; Pessoa, A.; Moraes Galvão, M.A.; Soares, L.A.L.; Veiga Júnior, V.F.d.; et al. Microemulsions Containing Copaifera Multijuga Hayne Oil-Resin: Challenges to Achieve an Efficient System for β-Caryophyllene Delivery. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, M.; Rodomonte, A.; Antoniella, E.; Minelli, G.; Bertocchi, P. Hydrate Modifications of the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Diclofenac Sodium: Solid-State Characterisation of a Trihydrate Form. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, G.; Capasso, G.; Maestrelli, F.; Cirri, M.; Mura, P. Physical-Chemical Characterization of Binary Systems of Metformin Hydrochloride with Triacetyl-β-Cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.A.; Yoshida, M.I.; Gomes, E.C.L.; Mussel, W.N. Análise Térmica Aplicada à Caracterização Da Sinvastatina Em Formulações Farmacêuticas. Quim. Nova 2010, 33, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderHart, D.L.; Hyatt, J.A.; Atalla, R.H.; Tirumalai, V.C.S.-S. 13C NMR and Raman Studies of Cellulose Triacetate: Oligomers, Polymorphism, and Inferences about Chain Polarity. Macromol. 1996, 29, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harisa, G.I.; Badran, M.M. Simvastatin Nanolipid Carriers Decreased Hypercholesterolemia Induced Cholesterol Inclusion and Phosphatidylserine Exposure on Human Erythrocytes. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 208, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, V.; de Siqueira Ferreira, D.; Barreto, P.L.M.; Weiss-Angeli, V.; Vanderlinde, R. Preparation and Characterization of Microparticles of β-Cyclodextrin/Glutathione and Chitosan/Glutathione Obtained by Spray-Drying. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Yu, W.; Li, Z. Analysis of Structural Changes in Jute Fibers after Peracetic Acid Treatment. J. Eng. Fiber Fabr. 2017, 12, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, Q.; Shi, Z.; Ye, J. Interactions between Wheat Starch and Cellulose Derivatives in Short-Term Retrogradation: Rheology and FTIR Study. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, P.; Kundu, S.; Patel, S.; Parthasarathy, R.; Pramanik, B.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Shah, K. TGA-FTIR Study on the Slow Pyrolysis of Lignin and Cellulose-Rich Fractions Derived from Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid Pre-Treatment of Sugarcane Straw. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 200, 112067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barud, H.S.; de Araújo Júnior, A.M.; Santos, D.B.; de Assunção, R.M.N.; Meireles, C.S.; Cerqueira, D.A.; Rodrigues Filho, G.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Messaddeq, Y.; Ribeiro, S.J.L. Thermal Behavior of Cellulose Acetate Produced from Homogeneous Acetylation of Bacterial Cellulose. Thermochim. Acta 2008, 471, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho Eufrásio Pinto, M.; David Da Silva, D.; Amorim Gomes, A.L.; Leite, V.d.S.A.; Fialho, E.; Moraes, A.R.; Ferreira de Novais, R.; Tronto, J.; Pinto, F.G. Film Based on Magnesium Impregnated Biochar/Cellulose Acetate for Phosphorus Adsorption from Aqueous Solution. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5620–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pshezhetskii, V.S.; Rakhnyanskaya, A.A.; Gaponenko, I.M.; Nalbandyan, Y.E. A Differential Scanning Calorimetry Study of Polyvinyl Alcohol. Polym. Sci. U.S.S.R. 1990, 32, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M.M.; Hugenschmidt, C.; Dickmann, M.; Abdel-Hady, E.E.; Mohamed, H.F.M.; Abdel-Hamed, M.O. Crosslinked PVA/SSA Proton Exchange Membranes: Correlation between Physiochemical Properties and Free Volume Determined by Positron Annihilation Spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 28287–28299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Chiang, C.Y.; Wang, H.Z.; Yang, C.C. Two Step Modification of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) by UV Radiation with 2-Hydroxy Ethyl Methacrylate and Sol-Gel Process for the Application of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 341, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanjeri, V.N.; Goudar, N.; Kasai, D.; Masti, S.P.; Chougale, R.B. Thermal and Tensile Properties Study of 4-Hydroxycoumarin Doped Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Blend Films. Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 23, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matijašić, G.; Gretić, M.; Kezerić, K.; Petanjek, J.; Vukelić, E. Preparation of Filaments and the 3D Printing of Dronedarone HCl Tablets for Treating Cardiac Arrhythmias. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villela Martinez, L.M.; Beltran, B.E.; Candelaria, M.; Ramirez, A.F.; Torres Viera, M.; Oliver, C.; Quintero, H.I.; perez-Jacobo, F.; Robles Rodriguez, A.; Perini, G.F.; et al. Validating the Systemic Inmmune-Inflamation Index (SII) As a Prognostic Biomarker of Overall Survival in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Retrospective Analyses by the Gruppo De Estudio Latinoamericano De Linfoproliferativos (GELL). Blood 2023, 142, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzar, N.; Mirza, M.A.; Anwer, K.; Khuroo, T.; Alshetaili, A.S.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Meena, J.; Hasan, N.; Talegaonkar, S.; Panda, A.K.; et al. Preparation, Evaluation and Pharmacokinetic Studies of Spray Dried PLGA Polymeric Submicron Particles of Simvastatin for the Effective Treatment of Breast Cancer. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, R.; Padilam, S. In Vitro Permeation and Stability Studies on Developed Drug-in-Adhesive Transdermal Patch of Simvastatin. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2018, 56, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.F.; Do Couto, R.O.; Sinisterra, R.D.; Jensen, C.E. de M. Novel Eudragit®-Based Polymeric Nanoparticles for Sustained Release of Simvastatin. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 56, e18363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandele, A.M.; Neacsu, P.; Cimpean, A.; Staras, A.I.; Miculescu, F.; Iordache, A.; Voicu, S.I.; Thakur, V.K.; Toader, O.D. Cellulose Acetate Membranes Functionalized with Resveratrol by Covalent Immobilization for Improved Osseointegration. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 438, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, R.; de Almeida Carvalho, V.; da Silva, L.G.; de Magalhães, D.; Ferreira, J.A.; de Menezes, H.H.M.; de Melo, P.G.; Naves, M.M. Study of in Vitro Degradation of Cellulose Acetate Membranes Modified and Incorporated with Tetracycline for Use as an Adjuvant in Periodontal Reconstitution. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 72, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhu, M.; Fan, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, Z. All-Cellulose Composites Based on Jute Cellulose Nanowhiskers and Electrospun Cellulose Acetate (CA) Fibrous Membranes. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Mani, M.P.; Jaganathan, S.K. Development and Blood Compatibility Assessment of Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol Blended with Metallocene Polyethylene and Plectranthus Amboinicus (PVA/MPE/PA) for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2777–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Sun, L.; Gao, S. PVA/CS and PVA/CS/Fe Gel Beads’ Synthesis Mechanism and Their Performance in Cultivating Anaerobic Granular Sludge. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balata, G.F.; Zidan, A.S.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Essa, E.A. Rapid Disintegrating Tablets of Simvastatin Dispersions in Polyoxyethylene-Polypropylene Block Copolymer for Maximized Disintegration and Dissolution. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2016, 10, 3211–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasaei, M.; Khakbiz, M.; Ghasemi, E.; Zamanian, A. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnAl-NO 3 (-CO 3) Layered Double Hydroxide: A Novel Structure for Intercalation and Release of Simvastatin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljun, A.; Benians, T.A.S.; Goubet, F.; Meulewaeter, F.; Knox, J.P.; Blackburn, R.S. Comparative Analysis of Crystallinity Changes in Cellulose i Polymers Using ATR-FTIR, X-Ray Diffraction, and Carbohydrate-Binding Module Probes. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4121–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, F.; Colom, X.; Suñol, J.J.; Saurina, J. Structural FTIR Analysis and Thermal Characterisation of Lyocell and Viscose-Type Fibres. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, H.A.; Allam, A.; Elsabahy, M.; Fetih, G.; El-Badry, M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Improved Oral Delivery and Prolonged Antihyperlipidemic Effect of Simvastatin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 162, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, F.; Santos, L. Inclusion of Hydroxytyrosol in Ethyl Cellulose Microparticles: In Vitro Release Studies under Digestion Conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavini, V.; Konijeti, S.; Nagaraju, S.T. Formulation and Chatacterization of Controlled Release Bioadhesive Nanoparticles Encapsulated with Neostigmine Bromide. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 6, 3501–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, R.R.M.; Senna, A.M.; Botaro, V.R. Influence of Degree of Substitution on Thermal Dynamic Mechanical and Physicochemical Properties of Cellulose Acetate. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolinário, A.C.; de Carvalho, E.M.; de Lima Damasceno, B.P.G.; da Silva, P.C.D.; Converti, A.; Pessoa, A.; da Silva, J.A. Extraction, Isolation and Characterization of Inulin from Agave Sisalana Boles. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 108, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Daud, W.R.; Djuned, F.M. Cellulose Acetate from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch via a One Step Heterogeneous Acetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, K.; Cao, X.; Sun, R. Cellulose Acetate Fibers Prepared from Different Raw Materials with Rapid Synthesis Method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elashmawi, I.S.; Menazea, A.A. Different Time’s Nd:YAG Laser-Irradiated PVA/Ag Nanocomposites: Structural, Optical, and Electrical Characterization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Sun, X.; Tian, H.; Maiti, S.; Ma, Z. Effects of Cellulose Nanofibrils on the Structure and Properties on PVA Nanocomposites. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukala, P.K.; Palekar, S.; Patki, M.; Patel, K. Abuse Deterrent Immediate Release Egg-Shaped Tablet (Egglets) Using 3D Printing Technology: Quality by Design to Optimize Drug Release and Extraction. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Du, B.; Huang, X.; Pang, L.; Zhou, Z. Silk Fibroin-Coated PLGA Dimpled Microspheres for Retarded Release of Simvastatin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 158, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moangella Andrade de Assis, K.; Maísa da Silva Leite, J.; Ferreira de Melo, D.; Cordeiro Borges, J.; Matheus Barreto Santana, L.; Maria Lucas dos Reis, M.; Martins Moreira, V.; Rainny Vieira da Rocha, W.; Mayer Ramalho Catão, R.; Golzio dos Santos, S.; et al. Bicontinuous Microemulsions Containing Melaleuca Alternifolia Essential Oil as a Therapeutic Agent for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1748–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, A.L.M.; Reis, M.Y.F.A.; Silva, G.C.L.; Ramalho, Í.M.M.; Guimarães, G.P.; Silva, J.A.; Saraiva, K.L.A.; Damasceno, B.P.G.L. Microemulsion for Topical Application of Pentoxifylline: In Vitro Release and in Vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, K.J.; Buchanan, C.M.; Debenham, J.S.; Rundquist, P.A.; Seiler, B.D.; Shelton, M.C.; Tindall, D. Advances in Cellulose Ester Performance and Application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1605–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.B.; Rathi, S.; Jyothi, V.G.S.S.; Shastri, N.R. Cellulose Based Polymers in Development of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau Costa, K.M.; Sato, M.R.; Barbosa, T.L.A.; Rodrigues, M.G.F.; Medeiros, A.C.D.; Damasceno, B.P.G.d.L.; Oshiro-Júnior, J.A. Curcumin-Loaded Micelles Dispersed in Ureasil-Polyether Materials for a Novel Sustained-Release Formulation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djekic, L.; Primorac, M.; Filipic, S.; Agbaba, D. Investigation of Surfactant/Cosurfactant Synergism Impact on Ibuprofen Solubilization Capacity and Drug Release Characteristics of Nonionic Microemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 433, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.; Patel, S.; Devkar, R.; Patel, A. Camptothecin Encapsulated into Functionalized MCM-41: In Vitro Release Study, Cytotoxicity and Kinetics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, J.; Zhou, W.; Liang, X.; Zhou, G.; Han, C.C.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y. Mechanism of a Long-Term Controlled Drug Release System Based on Simple Blended Electrospun Fibers. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Qiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Ai, M.; Yang, Y.; Sui, L.; Zhou, Z. Polymeric Non-Spherical Coarse Microparticles Fabricated by Double Emulsion-Solvent Evaporation for Simvastatin Delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 199, 111560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Nandagiri, V.K.; Daly, J.; Chiono, V.; Mattu, C.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Ciardelli, G.; Ramtoola, Z. Localised Controlled Release of Simvastatin from Porous Chitosan-Gelatin Scaffolds Engrafted with Simvastatin Loaded PLGA-Microparticles for Bone Tissue Engineering Application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaeli, R.; Kashi, T.S.J.; Dinarvand, R.; Tahriri, M.; Rakhshan, V.; Esfandyari-Manesh, M. Preparation, Characterization and Evaluation of Drug Release Properties of Simvastatin-Loaded PLGA Microspheres. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2016, 15, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diba, F.S.; Boden, A.; Thissen, H.; Bhave, M.; Kingshott, P.; Wang, P.Y. Binary Colloidal Crystals (BCCs): Interactions, Fabrication, and Applications. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2018, 261, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, J.P.F.; Silva, A.C.Q.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R.; Vilela, C. Spherical Cellulose Micro and Nanoparticles: A Review of Recent Developments and Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhou, X.; Jin Hur, S.; Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Xue, C. Hydrogel/Microcarrier Cell Scaffolds for Rapid Expansion of Satellite Cells from Large Yellow Croakers: Differential Analysis between 2D and 3D Cell Culture. Food Res. Int. 2024, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, T.; Fujiwara, S.; Ishioka, S.; Urakubo, T.; Suzawa, T. Isolation of Recombinant Human Antithrombin Isoforms by Cellufine Sulfate Affinity Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed Life Sci. 2018, 1095, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | BMP | SMP |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size (nm) | 1842.74 ± 4.1 | 1857.36 ± 1.30 |
| PDI | 0.229 ± 0.042 | 0.278 ± 0.008 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −3.79 ± 0.26 | −4.45 ± 1.12 |
| EE (%) DL (%) | - | 98.92% ± 2.60 6.2% |
| Substrate | LOI (1420/893 cm−1) | TCI (1375/2900 cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Holocellulose | 1.11 | 0.93 |
| Cellulose | 0.90 | 0.98 |
| Samples | O-H | C-H | C-O | C=O | C-O-C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACT | 3552 | 2917 | 1035 | 1745 | 1033 |
| PVA | 3305 | 2945 | 1095 | 1722 | - |
| SIM | 3548 | 3008 | 1043 | 1700 | 1273 |
| BMP | 3299 | 2945 | 1087 | 1715 | - |
| SMP | 3309 | 2943 | 1087 | 1715 | - |
| Kinetic Model | Equation | Line Equation | Determination Coefficient (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-order | Q0 = Qt + K0.t | y = 1.5957x + 8.4063 | 0.9784 |
| First order | ln Qt = ln Q0 + K1.t | y = 0.0171x + 1.0522 | 0.6958 |
| Higuchi | Qt = KH.t1/2 | y = 14.66x − 12.807 | 0.9917 |
| Korsmeyer-Peppas | Mt/M∞ = K.tn | y = 0.8194x + 1.436 | 0.9752 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves, L.P.; Oliveira, K.d.S.; Santos, A.C.G.d.; Melo, D.F.d.; Moreira, L.M.C.d.C.; Oshiro Junior, J.A.; Silva, D.T.C.d.; Cavalcanti, A.L.d.M.; Damasceno, B.P.G.d.L. Cellulose Acetate Microparticles Synthesized from Agave sisalana Perrine for Controlled Release of Simvastatin. Polymers 2024, 16, 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131898
Alves LP, Oliveira KdS, Santos ACGd, Melo DFd, Moreira LMCdC, Oshiro Junior JA, Silva DTCd, Cavalcanti ALdM, Damasceno BPGdL. Cellulose Acetate Microparticles Synthesized from Agave sisalana Perrine for Controlled Release of Simvastatin. Polymers. 2024; 16(13):1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131898
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves, Larissa Pereira, Kevin da Silva Oliveira, Ana Cláudia Gonçalves dos Santos, Demis Ferreira de Melo, Lívia Maria Coelho de Carvalho Moreira, João Augusto Oshiro Junior, Dayanne Tomaz Casimiro da Silva, Airlla Laana de Medeiros Cavalcanti, and Bolívar Ponciano Goulart de Lima Damasceno. 2024. "Cellulose Acetate Microparticles Synthesized from Agave sisalana Perrine for Controlled Release of Simvastatin" Polymers 16, no. 13: 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131898
APA StyleAlves, L. P., Oliveira, K. d. S., Santos, A. C. G. d., Melo, D. F. d., Moreira, L. M. C. d. C., Oshiro Junior, J. A., Silva, D. T. C. d., Cavalcanti, A. L. d. M., & Damasceno, B. P. G. d. L. (2024). Cellulose Acetate Microparticles Synthesized from Agave sisalana Perrine for Controlled Release of Simvastatin. Polymers, 16(13), 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131898











