Factorial Analysis and Thermal Kinetics of Chemical Recycling of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Aided by Neoteric Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Chemical Recycling of PET
2.3. Statistical Design of Experiments
2.4. Analytical Techniques
2.5. Thermal Kinetic Analysis of the Glycolysis of PET
3. Results and Discussion
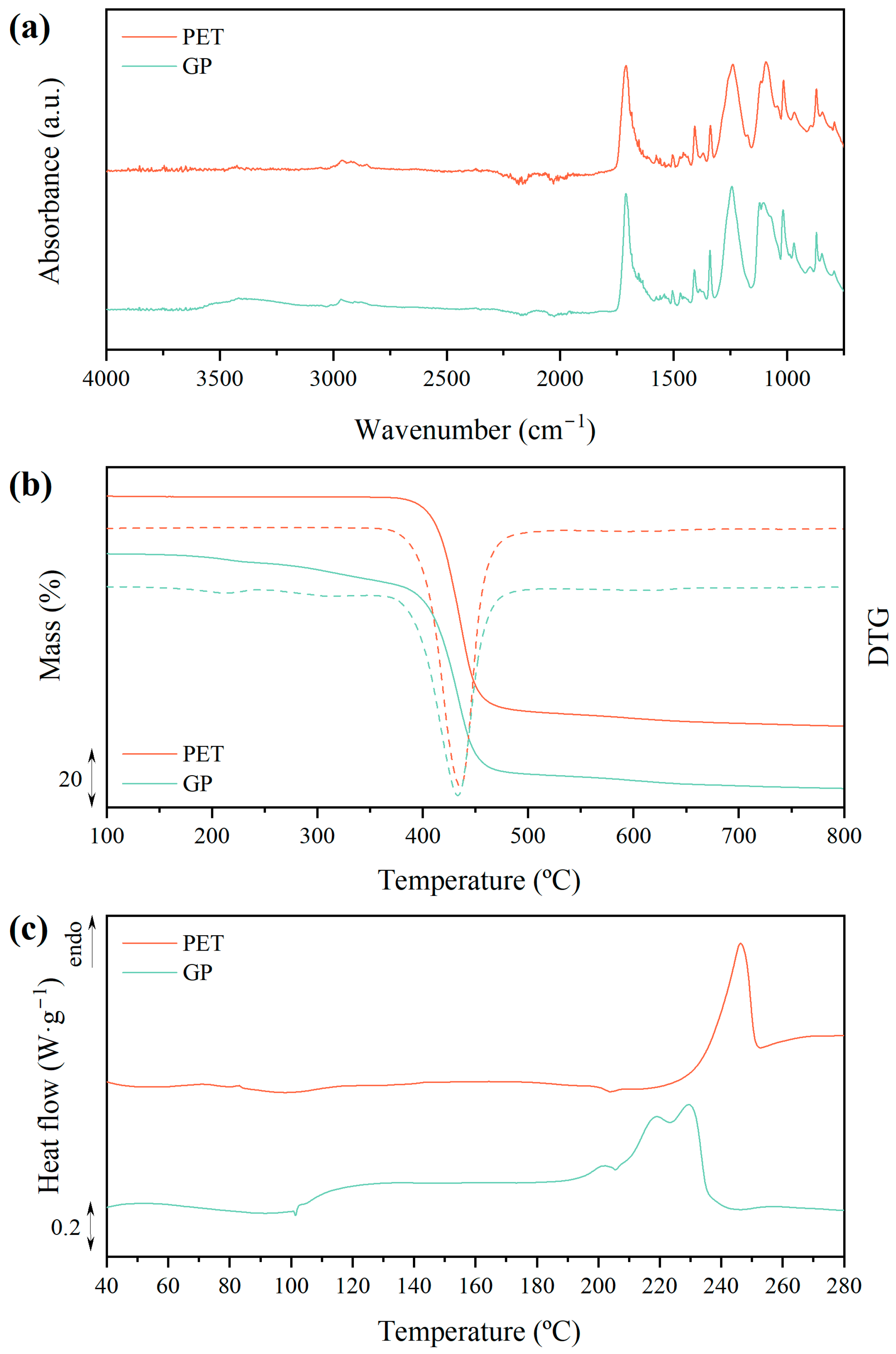
3.1. Glycolysis of PET to Obtain BHET
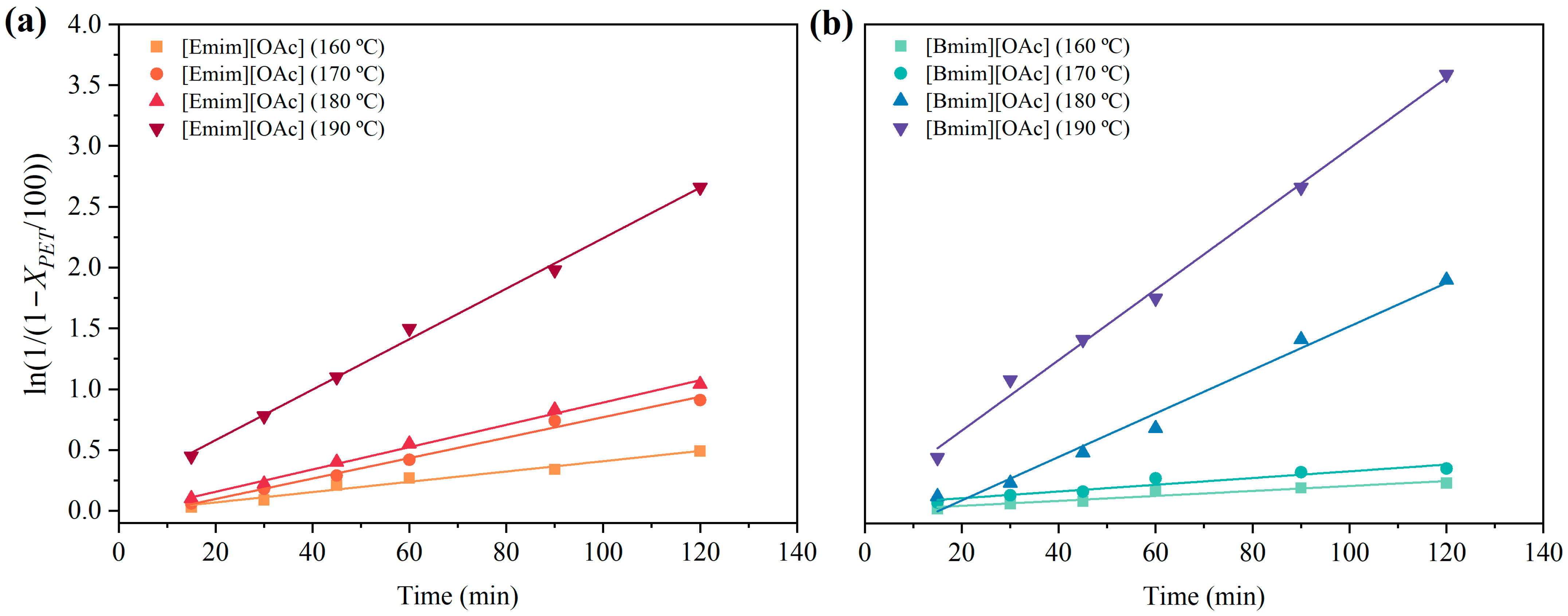
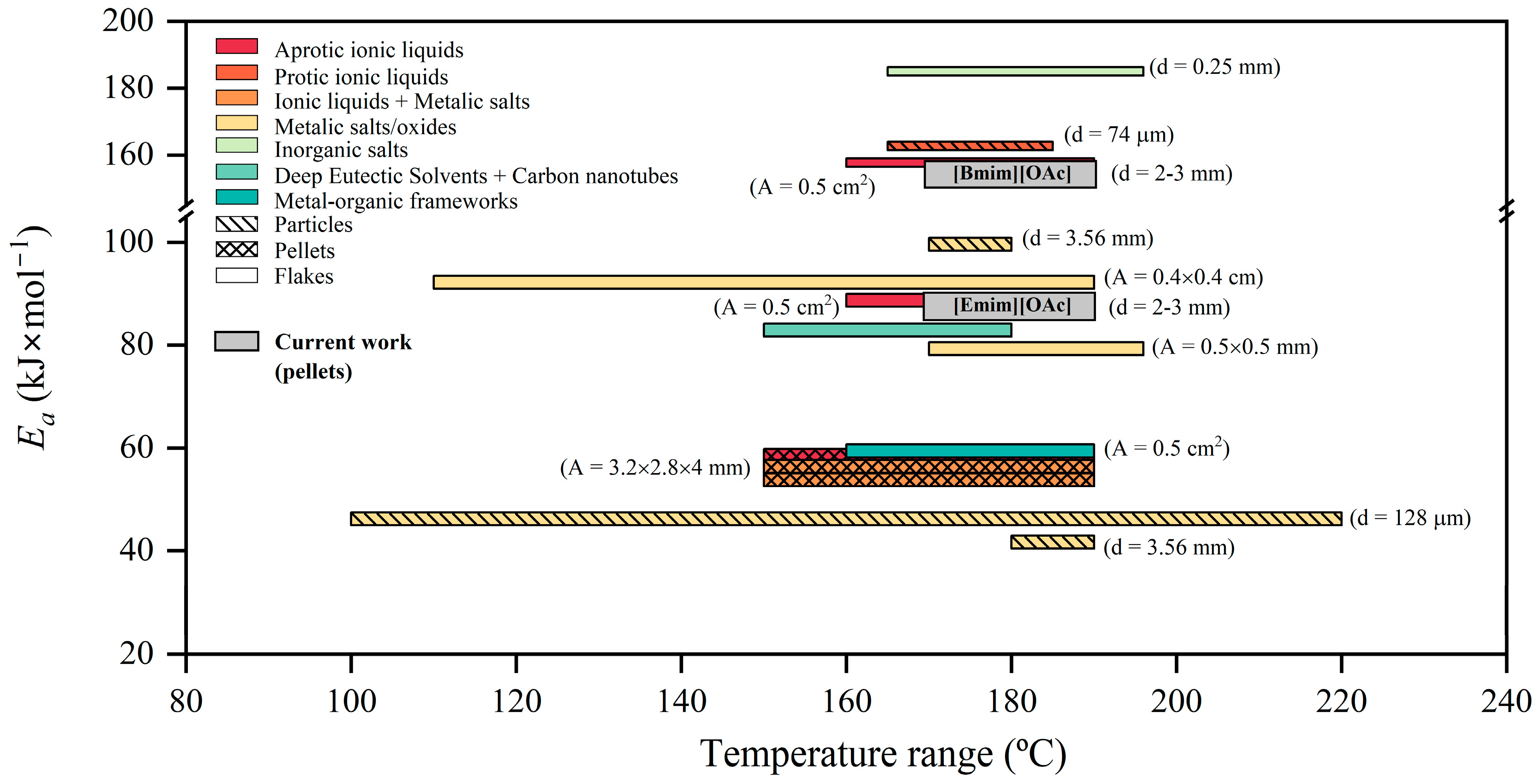
3.2. Thermal Kinetics of the Glycolysis of PET Using [Emim][OAc] and [Bmim][OAc] as Catalytic Co-Solvents
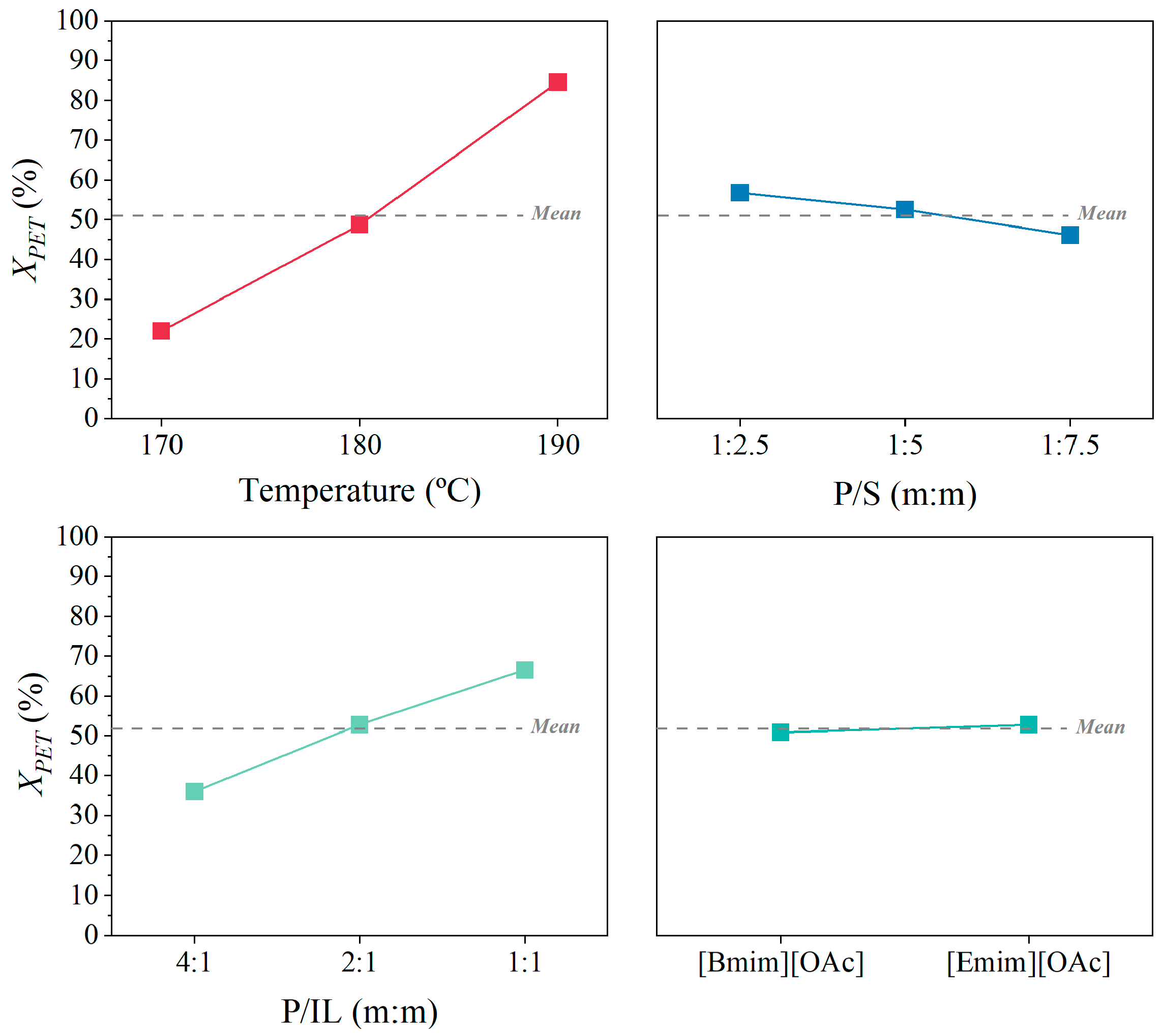
3.3. Individual and Interaction Effects on the Glycolysis of PET
3.4. Maximization of Glycolysis of PET Using [Bmim][OAc] and [Emim][OAc] as Catalytic Co-Solvents
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plastics Europe. The Circular Economy for Plastics: A European Analysis. 2024. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/the-circular-economy-for-plastics-a-european-analysis-2024/ (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Nisticò, R. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) in the Packaging Industry. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, A.K.; Muruganandam, M.; Imran, M.; Gill, R.; Vasudeva Reddy, M.R.; Shkir, M.; Sayed, M.A.; AlAbdulaal, T.H.; Algarni, H.; Arif, M.; et al. A Study on Managing Plastic Waste to Tackle the Worldwide Plastic Contamination and Environmental Remediation. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 139979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouloumpis, V.; Pell, R.S.; Correa-Cano, M.E.; Yan, X. Potential Trade-Offs between Eliminating Plastics and Mitigating Climate Change: An LCA Perspective on Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Bottles in Cornwall. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybaczewska-Blazejowska, M.; Mena-Nieto, A. Circular Economy: Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Fossil Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Its Recycled and Bio-Based Counterparts. Manag. Prod. Eng. Rev. 2020, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Gao, Y.; Tang, Y. Sustainable Developments in Polyolefin Chemistry: Progress, Challenges, and Outlook. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2023, 143, 101713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Sadeghi, K.; Seo, J. Chain-Extending Modification for Value-Added Recycled PET: A Review. Polym. Rev. 2022, 62, 860–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hsu, T.G.; Wang, J. Mechanochemical Degradation and Recycling of Synthetic Polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202300768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Vilaplana, F.; Karlsson, S.; Ribes-Greus, A. Thermal Analysis as a Quality Tool for Assessing the Influence of Thermo-Mechanical Degradation on Recycled Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Test. 2009, 28, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Martinez-Felipe, A.; Santonja-Blasco, L.; Ribes-Greus, A. Thermal and Thermo-Oxidative Stability of Reprocessed Poly(ethylene terephthalate). J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 99, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, R.P.; Cunha, J.M.; Sousa, S.F. Perspectives on the Role of Enzymatic Biocatalysis for the Degradation of Plastic Pet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhu, L. Recent Advances and Challenges in Enzymatic Depolymerization and Recycling of PET Wastes. ChemBioChem 2023, 25, e202300578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Lopez-Lorenzo, X.; Fang, Y.; Bäckström, E.; Capezza, A.J.; Vanga, S.R.; Furó, I.; Hakkarainen, M.; Syrén, P.O. Fast Depolymerization of PET Bottle Mediated by Microwave Pre-Treatment and an Engineered PETase**. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202300742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckström, E.; Odelius, K.; Hakkarainen, M. Ultrafast Microwave Assisted Recycling of PET to a Family of Functional Precursors and Materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 151, 110441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi Kalali, E.; Lotfian, S.; Entezar Shabestari, M.; Khayatzadeh, S.; Zhao, C.; Yazdani Nezhad, H. A Critical Review of the Current Progress of Plastic Waste Recycling Technology in Structural Materials. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 40, 100763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Ribes-Greus, A. Mechanical Recycling of Polylactide, Upgrading Trends and Combination of Valorization Techniques. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 84, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations (UN). Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development|Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- United Nations (UN). Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- El Mejjatti, A.; Harit, T.; Riahi, A.; Khiari, R.; Bouabdallah, I.; Malek, F. Chemical Recycling of Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Application to the Synthesis of Multiblock Copolyesters. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Nayak, C. Recent Advances in Chemical Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate Waste into Value Added Products for Sustainable Coating Solutions-Hope vs. Hype. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1974–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikles, D.E.; Farahat, M.S. New Motivation for the Depolymerization Products Derived from Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) Waste: A Review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2005, 290, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.; Patel, M.R.; Patel, J.V. PET Waste Management by Chemical Recycling: A Review. J. Polym. Env. 2010, 18, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Naveed, M.; Aayanifard, Z.; Rabnawaz, M. Efficient Chemical Recycling of Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 187, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Banerjee, S.L.; Kumari, K.; Kundu, P.P. Recent Innovations in Chemical Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate Waste: A Circular Economy Approach toward Sustainability. In Handbook of Solid Waste Management; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1149–1176. ISBN 10.1007/9789811. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Huang, R.; Jaffery, Q.Z.; Yan, D.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, J.; Lu, X. Progress in the Catalytic Glycolysis of Polyethylene Terephthalate. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Adolfsson, E.; Tam, P.L. Nanostructured Micro Particles as a Low-Cost and Sustainable Catalyst in the Recycling of PET Fiber Waste by the Glycolysis Method. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis, S.F.; Verdejo, E.; Gil-Castell, O.; Ribes-Greus, A. Partial Glycolytic Depolymerisation of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) in the Solid State: Modelling the Contribution of Time and Temperature. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 221, 110695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Ballesteros-Garrido, R.; Gamir-Cobacho, A.; Gil-Castell, O.; Cháfer, A. Chemical Recycling of Post-Consumer Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) Driven by the Protic Ionic Liquid 2-HEAA: Performance, Kinetics and Mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, D.; Cao, G.; D’Angeli, C. Chemical Recycling of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) by Hydrolysis and Glycolysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguado, A.; Martínez, L.; Becerra, L.; Arieta-araunabeña, M.; Arnaiz, S.; Asueta, A.; Robertson, I. Chemical Depolymerisation of PET Complex Waste: Hydrolysis vs. Glycolysis. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2014, 16, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, A.; Sebastian, J. Pyrolysis Process to Produce Fuel from Different Types of Plastic—A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 396, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.; Wen, L.; Frazão, C.J.R.; Walther, T. Next-Generation Feedstocks Methanol and Ethylene Glycol and Their Potential in Industrial Biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 69, 108276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.W.; Iborra, S.; Corma, A. Synthesis of Transportation Fuels from Biomass: Chemistry, Catalysts, and Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheel, A.; Pant, D. Chemical Depolymerization of PET Bottles via Glycolysis. In Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate Bottles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, P.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Cao, M.; He, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J. Solar Thermal Catalysis for Sustainable and Efficient Polyester Upcycling. Matter 2022, 5, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Chu, M.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, W.; Cao, M.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Highly Efficient Photothermal Catalytic Upcycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate via Boosted Localized Heating. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 49, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, F.; Moreno-Marrodán, C.; Barbaro, P. Valorisation of Plastic Waste via Metal-Catalysed Depolymerisation. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 589–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Yehia, F.Z.; Eshaq, G.; Rabie, A.M.; ElMetwally, A.E. Greener Routes for Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.H.; Hunt, A.; Topi, C.; Paggiola, G.; Sherwood, J. Sustainable Solvents: Perspectives from Research, Business and International Policy; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-78262-335-9. [Google Scholar]
- Paparella, A.N.; Perrone, S.; Salomone, A.; Messa, F.; Cicco, L.; Capriati, V.; Perna, F.M.; Vitale, P. Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Plastic Depolymerization. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoff-Tempesta, T.; Epps, T.H. Ionic-Liquid-Mediated Deconstruction of Polymers for Advanced Recycling and Upcycling. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, A.J.; Jacquemin, J.; Hardacre, C. Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Liu, W.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, H.P. Do We Understand the Recyclability of Ionic Liquids? Chemistry 2009, 15, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zheng, X.; Yao, X.; Song, K.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, C.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Xin, J.; El Sayed, I.E.-T.; et al. Light-Colored RPET Obtained by Nonmetallic TPA-Based Ionic Liquids Efficiently Recycle Waste PET. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 11851–11861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Degradation of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Using Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.F.; Yang, H.G.; Zhang, M.L.; Bai, X.F. Metal-Containing Ionic Liquids: Highly Effective Catalysts for Degradation of Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 454756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- e Silva, F.; Sousa, A.; Freire, M.; Coutinho, J. Waste Valorisation Using Ionic Liquids; Green Chemistry Series; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-83916-399-9. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, K.S.; Tan, X.; Ooi, C.W.; Chew, K.W.; Leong, W.H.; Chai, Y.H.; Ho, S.H.; Show, P.L. How Does Ionic Liquid Play a Role in Sustainability of Biomass Processing? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Cui, X.; Yu, S.; Li, Z.; Ge, X. Hydrolysis Reaction of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Using Ionic Liquids as Solvent and Catalyst. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3561–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.S.; Vieira Da Silva, M.J.; Cristina Da Silva, D.; Freitas, A.D.R.; Rosa, F.A.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. PET Depolymerisation in Supercritical Ethanol Catalysed by [Bmim][BF4]. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 20308–20316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoonkari, M.; Haghighi, A.H.; Sefidbakht, Y.; Shekoohi, K.; Ghaderian, A. Chemical Recycling of PET Wastes with Different Catalysts. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 124524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Yehia, F.Z.; Eissa, A.-M.M.F.; Moustafa, M.E.; Eshaq, G.; Rabie, A.-R.M.; ElMetwally, A.E. Glycolysis of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Catalyzed by the Lewis Base Ionic Liquid [Bmim][OAc]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18443–18451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Yehia, F.Z.; Eissa, A.M.F.; Moustafa, M.E.; Eshaq, G.; Rabie, A.M.; ElMetwally, A.E. Cu- and Zn-Acetate-Containing Ionic Liquids as Catalysts for the Glycolysis of Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, I.; Martin, C.; Fernandes, J.A.; Lodge, R.W.; Dupont, J.; Casado-Carmona, F.A.; Lucena, R.; Cardenas, S.; Sans, V.; de Pedro, I. Paramagnetic Ionic Liquid-Coated SiO2@Fe3O4 Nanoparticles—The next Generation of Magnetically Recoverable Nanocatalysts Applied in the Glycolysis of PET. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 260, 118110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.F.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, L.N.; Ni, Y.; Jin, Y.X. Glycolysis of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) Using Basic Ionic Liquids as Catalysts. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoukos, S.; Becker, J.; Dobre, A.; Fan, Z.; Othman, F.; Philippi, F.; Smith, G.J.; Welton, T. Synthesis of Aprotic Ionic Liquids. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.E.S.J.; Prydderch, H.; Spulak, M.; Shimizu, S.; Walker, A.J.; Gathergood, N. Green Profiling of Aprotic versus Protic Ionic Liquids: Synthesis and Microbial Toxicity of Analogous Structures. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 7, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, X.; Gao, G. Anion–Cation Cooperative Catalysis by Ionic Liquids. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, A.; Shiramatsu, Y.; Kawamoto, T. Depolymerization of Polyamide 6 in Hydrophilic Ionic Liquids. Green Energy Environ. 2019, 4, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, P.; Nikjoo, D.; Warna, J.; Irgum, K.; Mikkola, J.P.; Khokarale, S.G. Sustainable, Highly Selective, and Metal-Free Thermal Depolymerization of Poly-(3-hydroxybutyrate) to Crotonic Acid in Recoverable Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 4130–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Yu, S.; Liu, S. Hydrolysis of Poly(lactic acid) into Calcium Lactate Using Ionic Liquid [Bmim][OAc] for Chemical Recycling. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Yu, S.; Liu, S. Methanolysis of Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) Catalyzed by Ionic Liquids. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2760–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goje, A.S.; Mishra, S. Chemical Kinetics, Simulation, and Thermodynamics of Glycolytic Depolymerization of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Waste with Catalyst Optimization for Recycling of Value Added Monomeric Products. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2003, 288, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H. Study of Glycolysis of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Recycled from Postconsumer Soft-Drink Bottles. III. Further Investigation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 2004–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, A. Polymorphism of Bis-β-Hydroxyethyl Terephthalate. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1957, 30, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Peng, Y.K.; Lee, H.L.; Pratama, D.E. Chemical Recycling Development of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) by Glycolysis and Cooling Crystallization with Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 19873–19883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, X.; Yao, H.; Zhou, Q.; Xin, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Degradation of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Catalyzed by Metal-Free Choline-Based Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 3122–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shen, C.; Yu, G.; Chen, X. The Upcycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate Using Protic Ionic Liquids as Catalyst. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 203, 110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.V.G.; da Silva Filho, E.A.; Uliana, F.; de Jesus, L.F.R.; de Melo, C.V.P.; Barthus, R.C.; Rodrigues, J.G.A.; Vanini, G. PET Glycolysis Optimization Using Ionic Liquid [Bmin]ZnCl3 as Catalyst and Kinetic Evaluation. Polímeros 2018, 28, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermanaki Farahani, S.; Zolgharnein, J. Removal of Alizarin Red S by Calcium-Terephthalate MOF Synthesized from Recycled PET-Waste Using Box-Behnken and Taguchi Designs Optimization Approaches. J. Solid. State Chem. 2022, 316, 123560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Strömberg, E.; Ribes-Greus, A.; Karlsson, S. A Statistical Design of Experiments for Optimizing the MALDI-TOF-MS Sample Preparation of Polymers. An Application in the Assessment of the Thermo-Mechanical Degradation Mechanisms of Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 692, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Kittikorn, T.; Strömberg, E.; Santonja-Blasco, L.; Martínez-Felipe, A.; Ribes-Greus, A.; Ek, M.; Karlsson, S. Water Absorption and Hydrothermal Performance of PHBV/Sisal Biocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujjala, L.K.S.; Kundu, D.; Dutta, D.; Kumar, A.; Bal, M.; Kumar, A.; Singh, E.; Mishra, R.; Kumar, S.; Vo, D.V.N. Advances in Ionic Liquids: Synthesis, Environmental Remediation and Reusability. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 396, 123896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dołżonek, J.; Kowalska, D.; Maculewicz, J.; Stepnowski, P. Regeneration, Recovery, and Removal of Ionic Liquids. Encycl. Ion. Liq. 2020, 15, 1992–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerachanchai, P.; Lee, J.M. Recyclability of an Ionic Liquid for Biomass Pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Ouyang, X.; Huang, L.; Ni, Y.; Chen, L. Cellulase Pretreatment for Enhancing Cold Caustic Extraction-Based Separation of Hemicelluloses and Cellulose from Cellulosic Fibers. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Polymer | Cationic Species | Anionic Species | Solvent | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) | [Emim]+ | [Terephthalic acid]− | Ethylene glycol | [44] |
| Polyamide 6 (PA6) | [Emim]+ | [BF4]− | - | [59] |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) | [Emim]+ | [OAc]− | - | [60] |
| Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) | [Bmim]+ | [OAc]− | Ethylene glycol | [52] |
| Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) | [Bmim]+ | [Cl]− [HCO3]− [Br]− [OH]− | Ethylene glycol | [55] |
| Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | [Bmim]+ | [OAc]− | Water | [61] |
| Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | [Bmim]+ | [OAc]− | Methanol | [62] |
| Parameter | Variable (Unit) | Coded and Experimental Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| T | Temperature (°C) | 170 | 180 | 190 |
| P/IL | PET:IL (m:m) {mass IL} (g) | 4:1 {0.5} | 2:1 {1} | 1:1 {2} |
| P/S | PET:EG (m:m) {mass EG} (g) | 1:2.5 {5} | 1:5 {10} | 1:7.5 {15} |
| IL | Ionic liquid type | [Emim][OAc] | - | [Bmim][OAc] |
| Ionic Liquid | T (°C) | k × 103 (min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Emim][OAc] | 160 | 4.07 | 0.9965 |
| 170 | 7.51 | 0.9978 | |
| 180 | 8.87 | 0.9918 | |
| 190 | 22.82 | 0.9909 | |
| [Bmim][OAc] | 160 | 2.07 | 0.9984 |
| 170 | 3.40 | 0.9758 | |
| 180 | 14.56 | 0.9739 | |
| 190 | 29.98 | 0.9763 |
| Solution | T (°C) | P/IL (m:m) | P/S (m:m) | XPET (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Emim][OAc] | E1 | 190 | 2:1 | 1:2.5 | 93 |
| * E2 | 1:1 | 1:2.5 | 100 | ||
| E3 | 1:1 | 1:5 | 96 | ||
| E4 | 180 | 1:1 | 1:7.5 | 61 | |
| E5 | 1:1 | 1:2.5 | 72 | ||
| * E6 | 1:1 | 1:5 | 80 | ||
| [Bmim][OAc] | B1 | 190 | 2:1 | 1:2.5 | 95 |
| * B2 | 1:1 | 1:2.5 | 100 | ||
| B3 | 1:1 | 1:5 | 97 | ||
| B4 | 180 | 1:1 | 1:2.5 | 61 | |
| B5 | 1:1 | 1:7.5 | 63 | ||
| * B6 | 1:1 | 1:5 | 78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gil-Castell, O.; Jiménez-Robles, R.; Gálvez-Subiela, A.; Marco-Velasco, G.; Cumplido, M.P.; Martín-Pérez, L.; Cháfer, A.; Badia, J.D. Factorial Analysis and Thermal Kinetics of Chemical Recycling of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Aided by Neoteric Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. Polymers 2024, 16, 2451. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172451
Gil-Castell O, Jiménez-Robles R, Gálvez-Subiela A, Marco-Velasco G, Cumplido MP, Martín-Pérez L, Cháfer A, Badia JD. Factorial Analysis and Thermal Kinetics of Chemical Recycling of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Aided by Neoteric Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. Polymers. 2024; 16(17):2451. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172451
Chicago/Turabian StyleGil-Castell, Oscar, Ramón Jiménez-Robles, Alejandro Gálvez-Subiela, Gorka Marco-Velasco, M. Pilar Cumplido, Laia Martín-Pérez, Amparo Cháfer, and Jose D. Badia. 2024. "Factorial Analysis and Thermal Kinetics of Chemical Recycling of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Aided by Neoteric Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids" Polymers 16, no. 17: 2451. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172451
APA StyleGil-Castell, O., Jiménez-Robles, R., Gálvez-Subiela, A., Marco-Velasco, G., Cumplido, M. P., Martín-Pérez, L., Cháfer, A., & Badia, J. D. (2024). Factorial Analysis and Thermal Kinetics of Chemical Recycling of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Aided by Neoteric Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. Polymers, 16(17), 2451. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172451








