Carbon Nanotube Sheets/Elastomer Bilayer Harvesting Electrode with Biaxially Generated Electrical Energy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials for CNT Sheets/Elastomer Bilayer
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Characterization of Harvesting Performance for CBHE
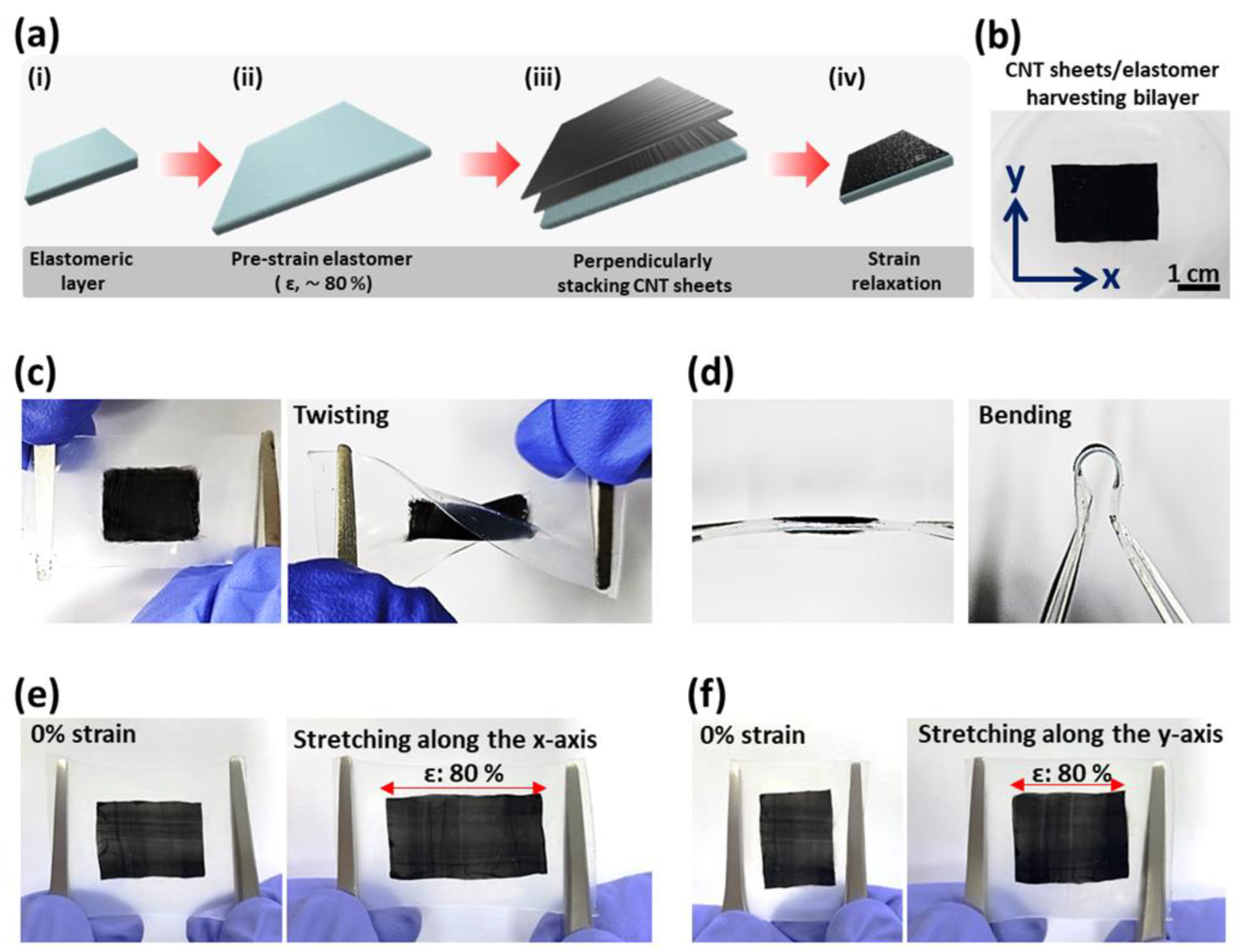
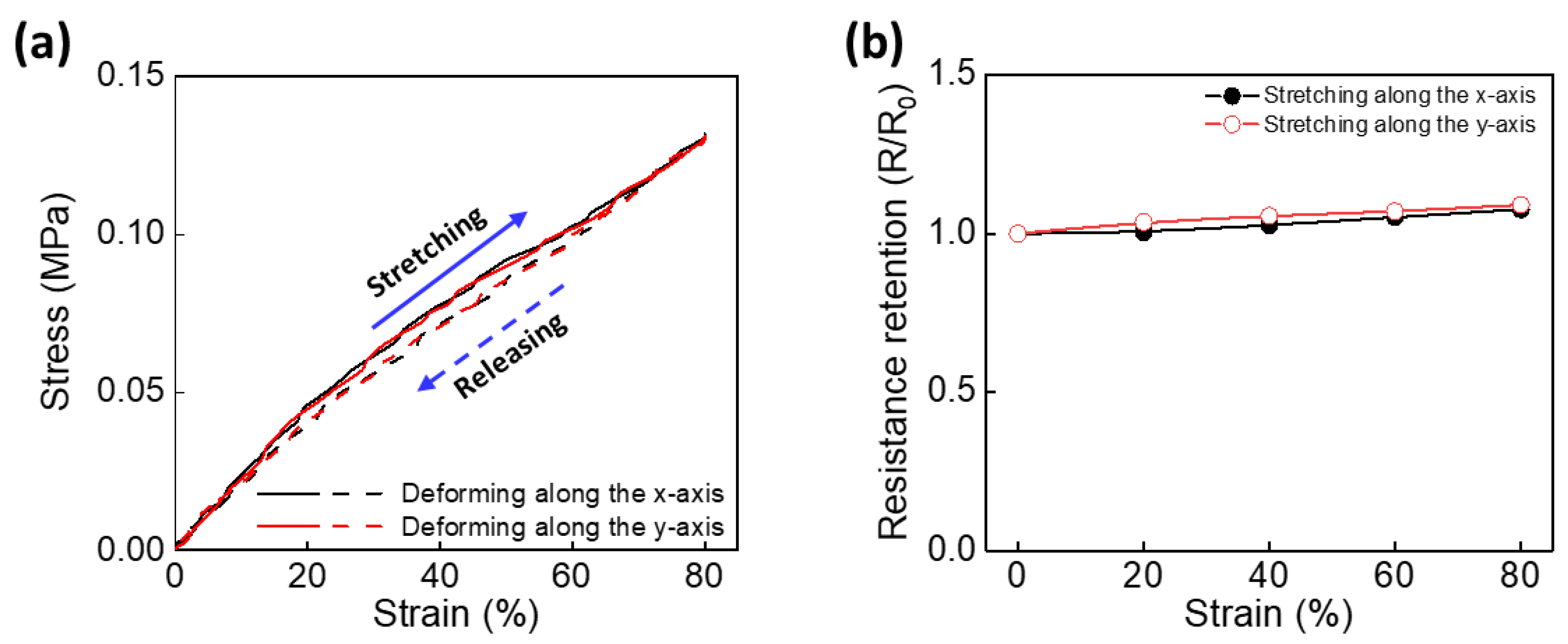
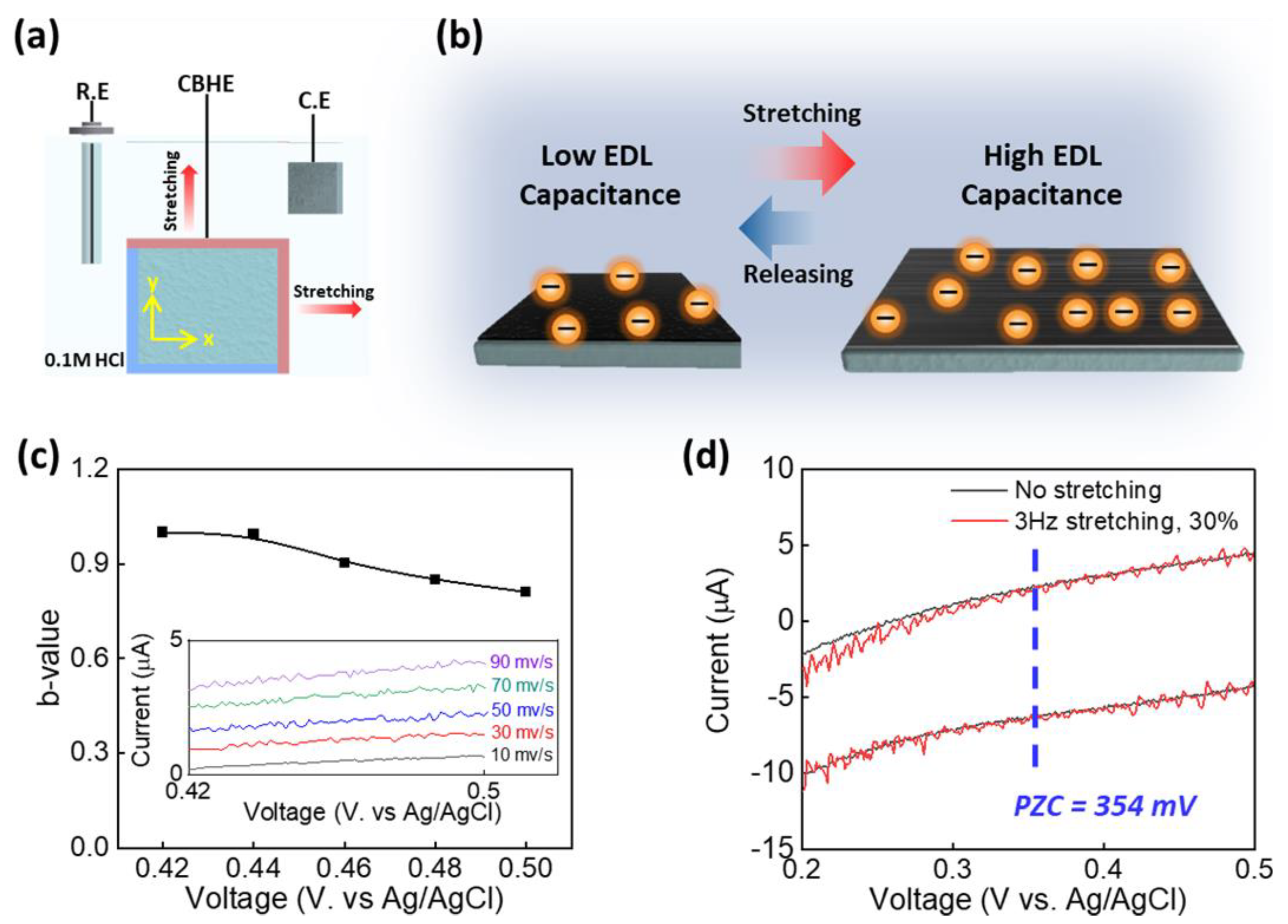
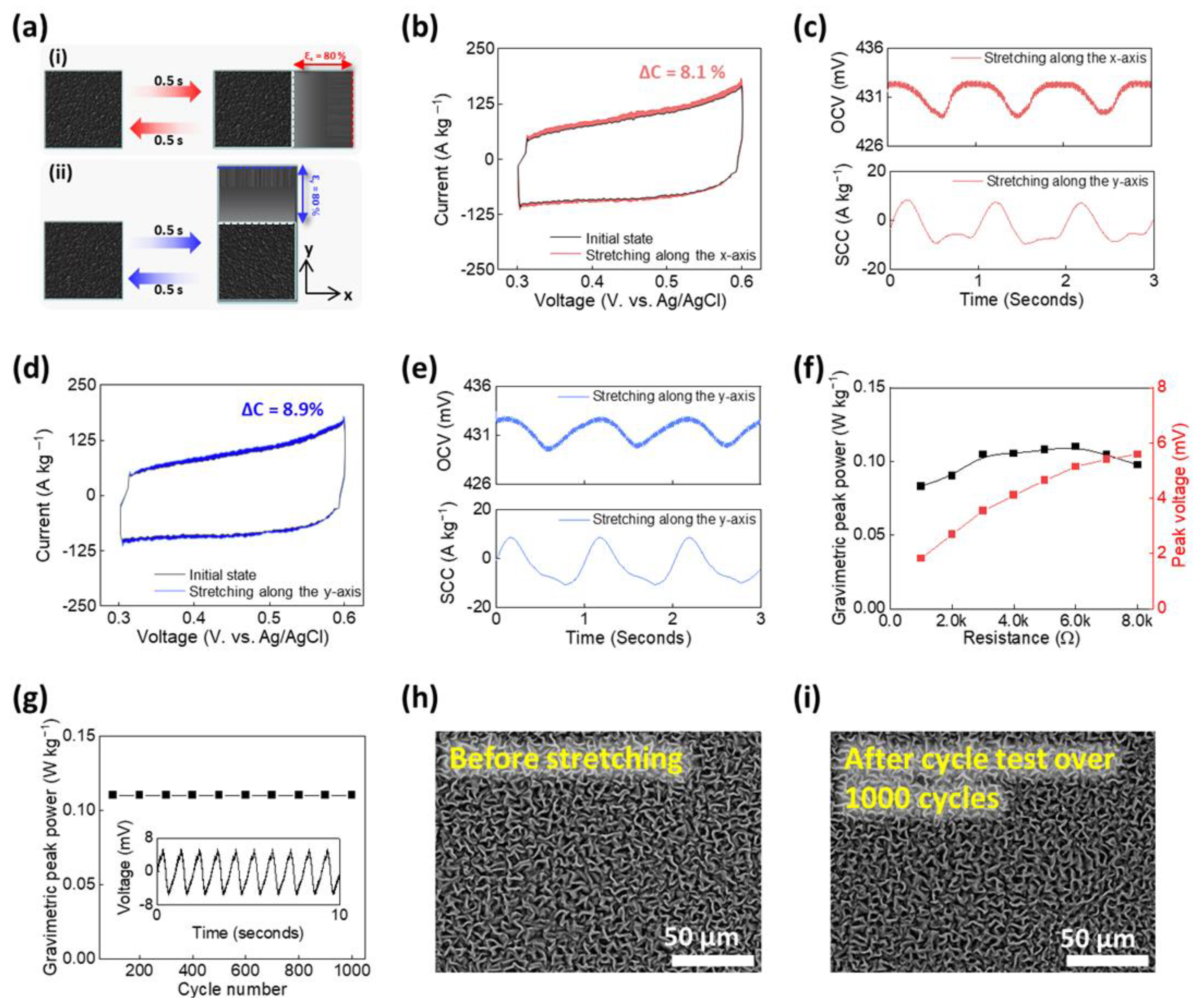
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hinchet, R.; Kim, S.-W. Wearable and Implantable Mechanical Energy Harvesters for Self-Powered Biomedical Systems. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7742–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Song, Y.; Han, M.; Zhang, H. Portable and wearable self-powered systems based on emerging energy harvesting technology. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, F.; Wang, X.; Niu, S.; Li, S.; Yin, Y.; Dai, K.; Zhang, G.; Lin, L.; Wen, Z.; Guo, H. A highly shape-adaptive, stretchable design based on conductive liquid for energy harvesting and self-powered biomechanical monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Liu, T.; Meng, X.; Luo, B.; Yuan, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cai, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, J. Wearable triboelectric visual sensors for tactile perception. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhparwar, A.; Osswald, A.; Kim, H.; Wakili, R.; Müller, J.; Pizanis, N.; Al-Rashid, F.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.; Rassaf, T.; Kim, S.J. Implanted Carbon Nanotubes Harvest Electrical Energy from Heartbeat for Medical Implants. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2313688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Xu, Z.; Duan, J.; Huang, L.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Piezoelectrets for wearable energy harvesters and sensors. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.J.; Sim, H.J.; Kim, B.-J.; Park, J.W.; Baughman, R.H.; Ruhparwar, A.; Kim, S.J. Self-powered coiled carbon-nanotube yarn sensor for gastric electronics. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2893–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cai, W.; Wang, Z.; Fang, S.; Zhang, R.; Lu, H.; Aliev, A.E.; Zakhidov, A.A.; Huynh, C.; Gao, E. Mechanical energy harvesters with tensile efficiency of 17.4% and torsional efficiency of 22.4% based on homochirally plied carbon nanotube yarns. Nat. Energy 2023, 8, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, M.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H. Design, manufacturing and applications of wearable triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Cui, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Parida, K.; Lin, M.-F.; Lee, P.S. Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proto, A.; Penhaker, M.; Conforto, S.; Schmid, M. Nanogenerators for human body energy harvesting. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 610–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zohair, M.; Moyer, K.; Eaves-Rathert, J.; Meng, C.; Waugh, J.; Pint, C.L. Continuous energy harvesting and motion sensing from flexible electrochemical nanogenerators: Toward smart and multifunctional textiles. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2308–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, N.; Li, M.; Carter, R.E.; Galioto, N.; Pint, C.L. Ultralow frequency electrochemical–mechanical strain energy harvester using 2D black phosphorus nanosheets. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Son, W.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-K.; Kim, S.J.; Oh, J.-M.; Choi, C. Synergistic effect of microscopic buckle and macroscopic coil for self-powered organ motion sensor. Nano Energy 2024, 128, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairagi, S.; Shahadat, M.; Mulvihill, D.M.; Ali, W. Mechanical energy harvesting and self-powered electronic applications of textile-based piezoelectric nanogenerators: A systematic review. Nano Energy 2023, 111, 108414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatua, D.K.; Kim, S.-J. Perspective on the development of high performance flexible piezoelectric energy harvesters. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 2905–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SKim, H.; Haines, C.S.; Li, N.; Kim, K.J.; Mun, T.J.; Choi, C.; Di, J.; Oh, Y.J.; Oviedo, J.P.; Bykova, J. Harvesting electrical energy from carbon nanotube yarn twist. Science 2017, 357, 773–778. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Kim, K.J.; Goh, B.; Park, C.L.; Lee, G.D.; Shin, S.; Lim, S.; Kim, E.S.; Yoon, K.R.; Choi, C. Chemo-Mechanical Energy Harvesters with Enhanced Intrinsic Electrochemical Capacitance in Carbon Nanotube Yarns. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2203767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y.; Park, C.L.; Song, Y.C.; Lee, H.; Kim, E.S.; Suh, D.; Lim, S.C.; Kim, H. Understanding Piezoionic Effects in Chemo–Mechanical Energy Harvesting by Carbon Nanotube Yarn Twists. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2303343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, S.; Nie, J.; Fei, P.; Aliev, A.E.; Baughman, R.H.; Xu, M. Self-powered, electrochemical carbon nanotube pressure sensors for wave monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mun, T.J.; Machado, F.M.; Moon, J.H.; Fang, S.; Aliev, A.E.; Zhang, M.; Cai, W.; Mu, J.; Hyeon, J.S. More powerful twistron carbon nanotube yarn mechanical energy harvesters. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.; Park, C.L.; Oh, J.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, H. Integrated Electrostimulation Cell Culture Systems Driven by Chemically Modified Twistron Mechanical Energy Harvesting Electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2315279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Son, W.; Jeon, G.; Kim, J.; You, J.; Ko, S.; Choi, C. Electromechanical stability, electrochemical energy storage, and mechano-electrochemical energy harvesting of carbon nanotube buckles. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 256, 110664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.J.; Choi, C. Microbuckled Mechano-electrochemical Harvesting Fiber for Self-Powered Organ Motion Sensors. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 8695–8703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Di, J.; Baughman, R.H. Twistable and stretchable sandwich structured fiber for wearable sensors and supercapacitors. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7677–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, A.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Guan, L. Multi-Functional Eutectic Hydrogel for 3D Printable Flexible Omnidirectional Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2301123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xue, Y.; Ren, S.; Wang, F. Sensor-Based wearable systems for monitoring human motion and posture: A review. Sensors 2023, 23, 9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, S.; Zakhidov, A.A.; Lee, S.B.; Aliev, A.E.; Williams, C.D.; Atkinson, K.R.; Baughman, R.H. Strong, transparent, multifunctional, carbon nanotube sheets. Science 2005, 309, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Li, Q.; Fan, S. Spinning continuous carbon nanotube yarns. Nature 2002, 419, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, W.; Chun, S.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, Y.; Park, J.; Suh, D.; Lee, D.W.; Jung, H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, Y. Highly twisted supercoils for superelastic multi-functional fibres. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezesinski, T.; Wang, J.; Polleux, J.; Dunn, B.; Tolbert, S.H. Templated nanocrystal-based porous TiO2 films for next-generation electrochemical capacitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Bag, M. Quantifying capacitive and diffusion-controlled charge storage from 3D bulk to 2D layered halide perovskite-based porous electrodes for efficient supercapacitor applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 16946–16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z.; Mu, J.; Li, N.; Zhou, X.; Fang, S.; Haines, C.S.; Park, J.W.; Qin, S. Unipolar stroke, electroosmotic pump carbon nanotube yarn muscles. Science 2021, 371, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, S.H. Carbon Nanotube Sheets/Elastomer Bilayer Harvesting Electrode with Biaxially Generated Electrical Energy. Polymers 2024, 16, 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172477
Oh S, Kim HJ, Lee S, Kim KJ, Kim SH. Carbon Nanotube Sheets/Elastomer Bilayer Harvesting Electrode with Biaxially Generated Electrical Energy. Polymers. 2024; 16(17):2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172477
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Seongjae, Hyeon Ji Kim, Seon Lee, Keon Jung Kim, and Shi Hyeong Kim. 2024. "Carbon Nanotube Sheets/Elastomer Bilayer Harvesting Electrode with Biaxially Generated Electrical Energy" Polymers 16, no. 17: 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172477
APA StyleOh, S., Kim, H. J., Lee, S., Kim, K. J., & Kim, S. H. (2024). Carbon Nanotube Sheets/Elastomer Bilayer Harvesting Electrode with Biaxially Generated Electrical Energy. Polymers, 16(17), 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172477






