Modified Cellulose-Based Waste for Enhanced Adsorption of Selected Heavy Metals from Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Characterization
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
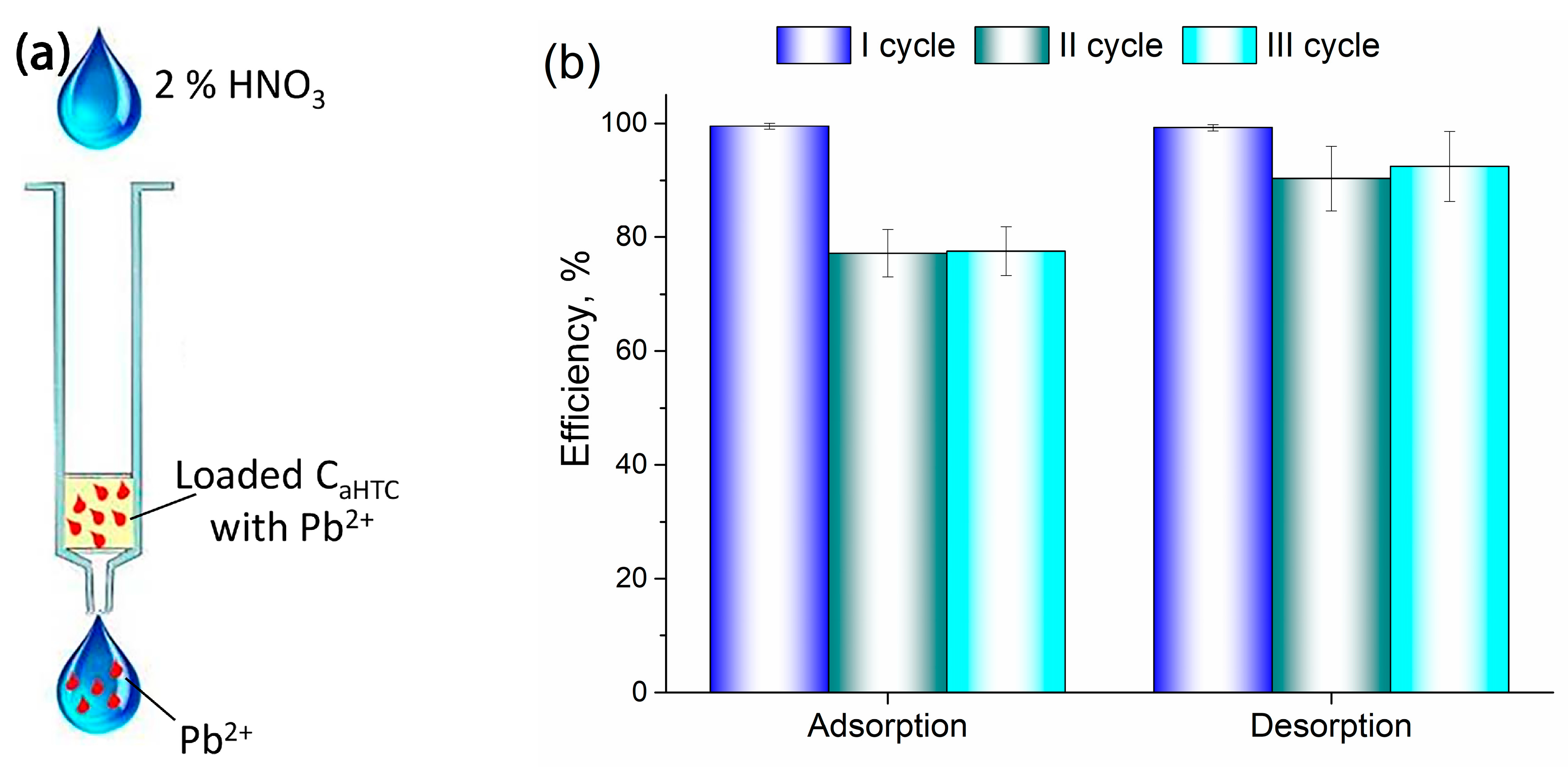
3.3. Adsorption/Desorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panigrahi, T.; Santhoskumar, A.U. Adsorption process for reducing heavy metals in Textile Industrial Effluent with low cost adsorbents. Prog. Chem. Biochem. Res. 2020, 3, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asadi, S.T.; Al-Qaim, F.F.; Al-Saedi, H.F.S.; Deyab, I.F.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S. Adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using low-cost adsorbent: Kinetic, isotherm adsorption, and thermodynamic studies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minelgaitė, A.; Liobikienė, G. Waste problem in European Union and its influence on waste management behaviours. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Anandjiwala, R.D. Recent developments in chemical modification and characterization of natural fiber-reinforced composites. Polym. Composite 2008, 29, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.S.A.; Naveed, M.; Jost, N. Polysaccharides; Classifcation, Chemical Properties, and Future Perspective Applications in Fields of Pharmacology and Biological Medicine (A Review of Current Applications and Upcoming Potentialities). J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltzer, M.A.; Salvay, A.G.; Delgado, J.F.; Wagner, J.R. Use of edible films and coatings for functional foods developments: A review. In Functional Foods: Sources, Health Effects and Future Perspectives; Nelson, D.L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishing: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Textile Exchange. Available online: https://textileexchange.org/app/uploads/2021/08/Textile-Exchange_Preferred-Fiber-and-Materials-Market-Report_2021.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Bediako, J.K.; Apalangya, V.; Hodgson, I.O.A.; Anugwom, I.; Repo, E. Adsorbents for water decontamination: A recycling alternative for fiber precursors and textile fiber wastes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 171000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, D.S.; Bosomoiu, M.; Stefan, M. Methods for Natural and Synthetic Polymers Recovery from Textile Waste. Polymers 2022, 1419, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli, A.; Rodrigue, D. Sustainable Reuse of Waste Tire Textile Fibers WTTF, as Reinforcements. Polymers 2022, 1419, 3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichola, P.; Witthayolankowit, K.; Sukyai, P.; Sampoompuang, C.; Lobyam, K.; Kampakun, P.; Toomtong, R. Recycling of Nanocellulose from Polyester–Cotton Textile Waste for Modification of Film Composites. Polymers 2023, 1515, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Qi, R.; Zhang, D.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, M.; Chen, W. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of cotton textile waste and polyvinyl chloride waste for the production of solid fuel: Interaction mechanisms and combustion behaviors. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Zhao, P. Hydrothermal pretreatment of cotton textile wastes: Biofuel characteristics and biochar electrocatalytic performance. Fuel 2022, 316, 123327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvanimoghaddama, K.; Czech, B.; Wiącek, A.E.; Ćwikła-Bundyra, W.; Naebe, M. Sustainable carbon microtube derived from cotton waste for environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolfsson, K.H.; Yadav, N.; Hakkarainen, M. Cellulose-derived hydrothermally carbonized materials and their emerging applications. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 23, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Sako, K.; Ogata, T.; Tanabe, K. Environmentally friendly, hydrothermal treatment of mixed fabric wastes containing polyester, cotton, and wool fibers: Application for HMF production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 11, 100478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Tang, J.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, H. Characterization of potassium hydroxide (KOH) modified hydrochars from different feedstocks for enhanced removal of heavy metals from water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Feng, X.; Gao, L.; Tang, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, S. Hydrolysis and carbonization of reactive dyes/cotton fiber in hydrothermal environment. Waste Manag. 2020, 103, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soffian, M.S.; Halim, F.Z.A.; Aziz, F.; Rahman, M.A.; Amin, M.A.M.; Chee, D.N.A. Carbon-based material derived from biomass waste for wastewater treatment. Environ. Adv. 2022, 9, 100259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, P.S.; Spessato, L.; Crespo, L.H.S.; Yokoyama, J.T.C.; Fonseca, J.M.; Bedin, K.C.; Ronix, A.; Cazetta, A.L.; Silva, T.L.; Almeida, V.C. Activated carbon fibers prepared from cellulose and polyester–derived residues and their application on removal of Pb2+ ions from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 289, 111150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmakoğlu, E.Ü.; Cxay, A.; Yanik, J. Valorization of Solid Wastes from Textile Industry as an Adsorbent Through Activated Carbon Production. AATCC J. Res. 2023, 10, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediako, J.K.; Wei, W.; Yun, Y.-S. Conversion of waste textile cellulose fibers into heavy metal adsorbents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 43, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racho, P.; Waiwong, W. Modified textile waste for heavy metals removal. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Vaccari, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Amrane, A.; Rtimi, S. Mechanisms and adsorption capacities of biochar for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from industrial wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3273–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, Z.; Yi, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, A.; Wang, L. Impacts of pyrolysis temperature on lead adsorption by cotton stalk-derived biochar and related mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.-P.; Shi, S.; Hou, W.-S.; Yan, Z.-F.; Dan, J.-M. Hydrolysis and carbonization mechanism of cotton fibers in subcritical water. New Carbon Mater. 2018, 33, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Cotton-Based Activated Carbon Fiber with High Specific Surface Area Prepared by Low-Temperature Hydrothermal Carbonization with Urea Enhancement. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 8744–8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Ahmed, G.; Vedika, S.; Kumar, P.; Chaturvedi, S.K.; Rai, S.N.; Vamanu, E.; Kumar, A. Toxic heavy metal ions contamination in water and their sustainable reduction by eco-friendly methods: Isotherms, thermodynamics and kinetics study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayuo, J.; Rwiza, M.J.; Choi, J.W.; Mtei, K.M.; Bandegharaei, A.H.; Sillanpa, M. Adsorption and desorption processes of toxic heavy metals, regeneration and reusability of spent adsorbents: Economic and environmental sustainability approach. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2024, 329, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husien, S.; El-taweel, R.M.; Salim, A.I.; Fahim, I.S.; Said, L.A.; Radwan, A.G. Review of activated carbon adsorbent material for textile dyes removal: Preparation, and modelling. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Al Mushaiqri, N.R.S.; Al Subhi, H.M.; Yoo, K.; Al Sadeq, H. Low-cost activated carbon production from organic waste and its utilization for wastewater treatment. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azharul Islam, M.; Benhouria, A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Methylene blue adsorption on factory-rejected tea activated carbon prepared by conjunction of hydrothermal carbonization and sodium hydroxide activation processes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 52, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babeker, T.M.A.; Chen, Q. Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater by Adsorption with Hydrochar Derived from Biomass: Current Applications and Research Trends. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2021, 7, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, S.; Radonić, J.; Trifunović, S.; Adamović, D.; Mihajlović, I.; Vojinović Miloradov, M.; Turk Sekulić, M. Evaluation of the adsorption potential of eco-friendly activated carbon prepared from cherry kernels for the removal of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Pandey, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Kumar, P. Adsorption potential of hydrochar derived from hydrothermal carbonization of waste biomass towards the removal of methylene blue dye from wastewater. Biomass. Convers. Biorefin. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur the oriedersogennanten adsorption geloesterstoffe, Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Bio-Chem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Adsorption in solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 384–410. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Xiang, Z.; Mo, L. Research on cellulose nanocrystals produced from cellulose sources with various polymorphs. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, G.; Tan, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cui, L.; Choi, S.W.; Li, M.-X. Preparation of Y2O3/TiO2-Loaded Polyester Fabric and Its Photocatalytic Properties under Visible Light Irradiation. Polymers 2022, 14, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.-M.; White, R.J.; Falco, C.; Sevilla, M. Black perspectives for a green future: Hydrothermal carbons for environment protection and energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amen, R.; Bashir, H.; Bibi, I.; Shaheen, S.M.; Niazi, N.K.; Shahid, M.; Hussain, M.M.; Antoniadis, V.; Shakoor, M.B.; Al-Solaimani, S.G.; et al. A critical review on arsenic removal from water using biochar-based sorbents: The significance of modification and redox reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, C.E.S.; Sheng, K.; Zhang, X. Effect of swelling pretreatment on properties of cellulose-based hydrochar. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10821–10829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, S. Characterization of biofuel production from hydrothermal treatment of hyperaccumulator waste (Pteris vittata L.) in sub- and supercritical water. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2160–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharrazi, S.M.; Mirghaffari, N.; Dastgerdi, M.M.; Soleimani, M. A novel post-modification of powdered activated carbon prepared from lignocellulosic waste through thermal tension treatment to enhance the porosity and heavy metals adsorption. Powder Technol. 2020, 366, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalijadis, A.; Đorđević, J.; Trtić-Petrović, T.; Vukčević, M.; Popović, M.; Maksimović, V.; Rakočević, Z.; Laušević, Z. Preparation of boron-doped hydrothermal carbon from glucose for carbon paste electrode. Carbon 2015, 95, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, B.; Wang, S.; Fang, J.; Xue, Y.; Yang, K. Removal of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by biochar derived from KMnO4 treated hickory wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, U. Enhanced adsorption of metal ions onto Vetiveriazizanioides biochar via batch and fixed bed studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhu, N.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Lang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Jiao, W. Enhanced adsorption of Pb(II) onto modified hydrochar: Modeling and mechanism analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbouy, R.; Lejiu, R.; Takahashi, F.; Yoshikawa, K. Effect of acid-assisted hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) process of tree branches using nitric acid on cadmium adsorption. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 67, 03033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Yao, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, D.; Lv, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, N.; Zhong, M.E. Effect of pyrolysis condition on the adsorption mechanism of lead, cadmium and copper on tobacco stem biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using carbon-based adsorbents: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Pashalidis, I.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Robalds, A.; Usman, M.; Escudero, L.B.; Zhou, Y.; Colmenares, J.C.; Núńez-Delgado, A.; et al. Agricultural biomass/waste as adsorbents for toxic metal decontamination of aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 295, 111684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.S.; Salehi, E. Adsorption of cations on nanofiltration membrane: Separation mechanism, isotherm confirmation and thermodynamic analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Zhao, C.; Xu, J. Enhanced adsorption of Cd (II) from aqueous solution by a shrimp bran modified Typha orientalis biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 37092–37100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakta, J.N.; Majumdar, P.B.; Munekage, Y. Development of Activated Carbon from Cotton Fibre Waste as Potential Mercury Adsorbent: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 1, 176483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosa, A.A.; El-Ghamry, A.; Al-Zahrani, H.; Selim, E.M.; El-Khateeb, A. Chemically Modified Biochar Derived from Cotton Stalks: Characterization And Assessing Its Potential for Heavy Metals Removal from Wastewater. Environ. Biodivers. Soil Secur. 2017, 1, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

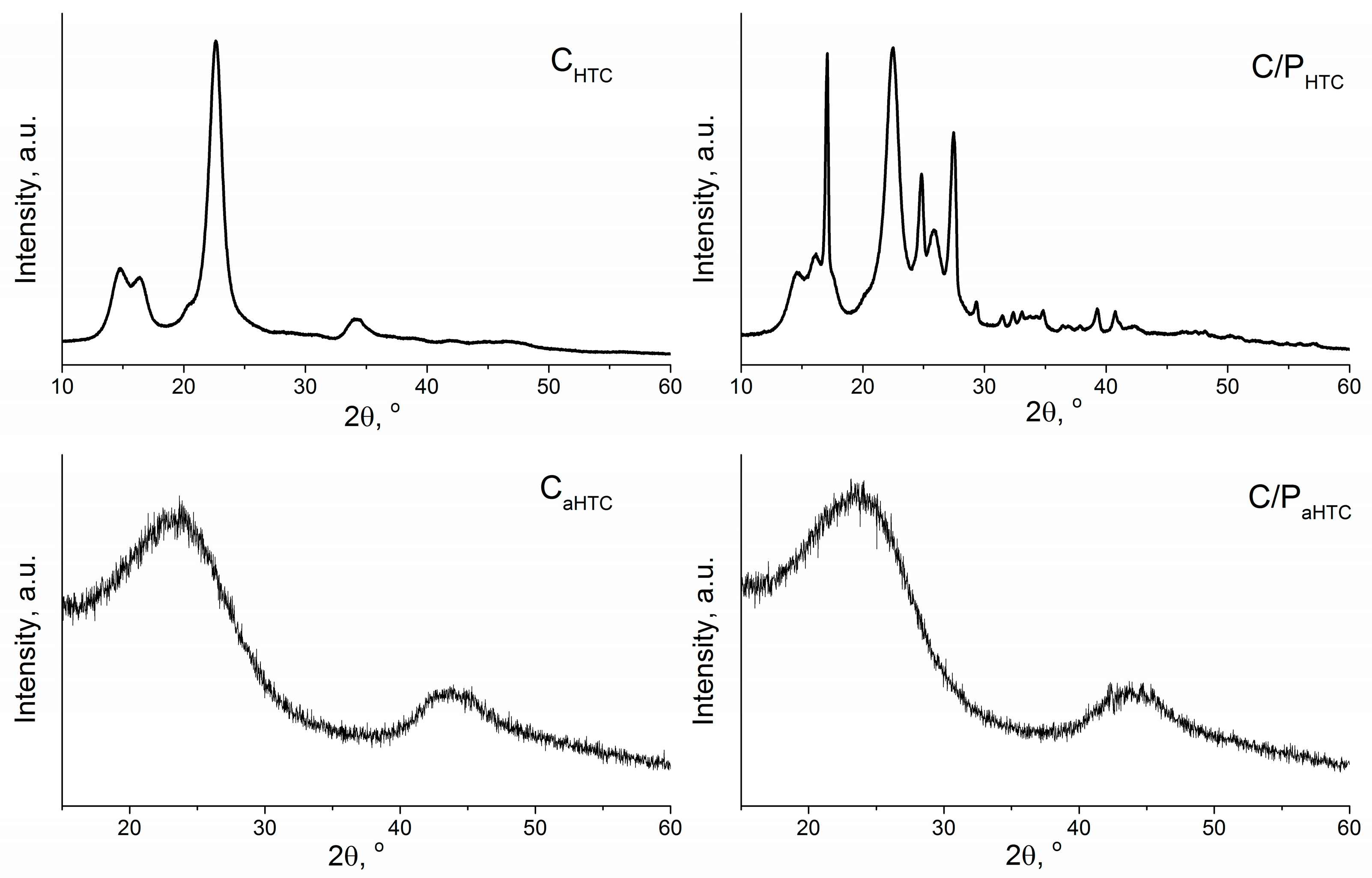

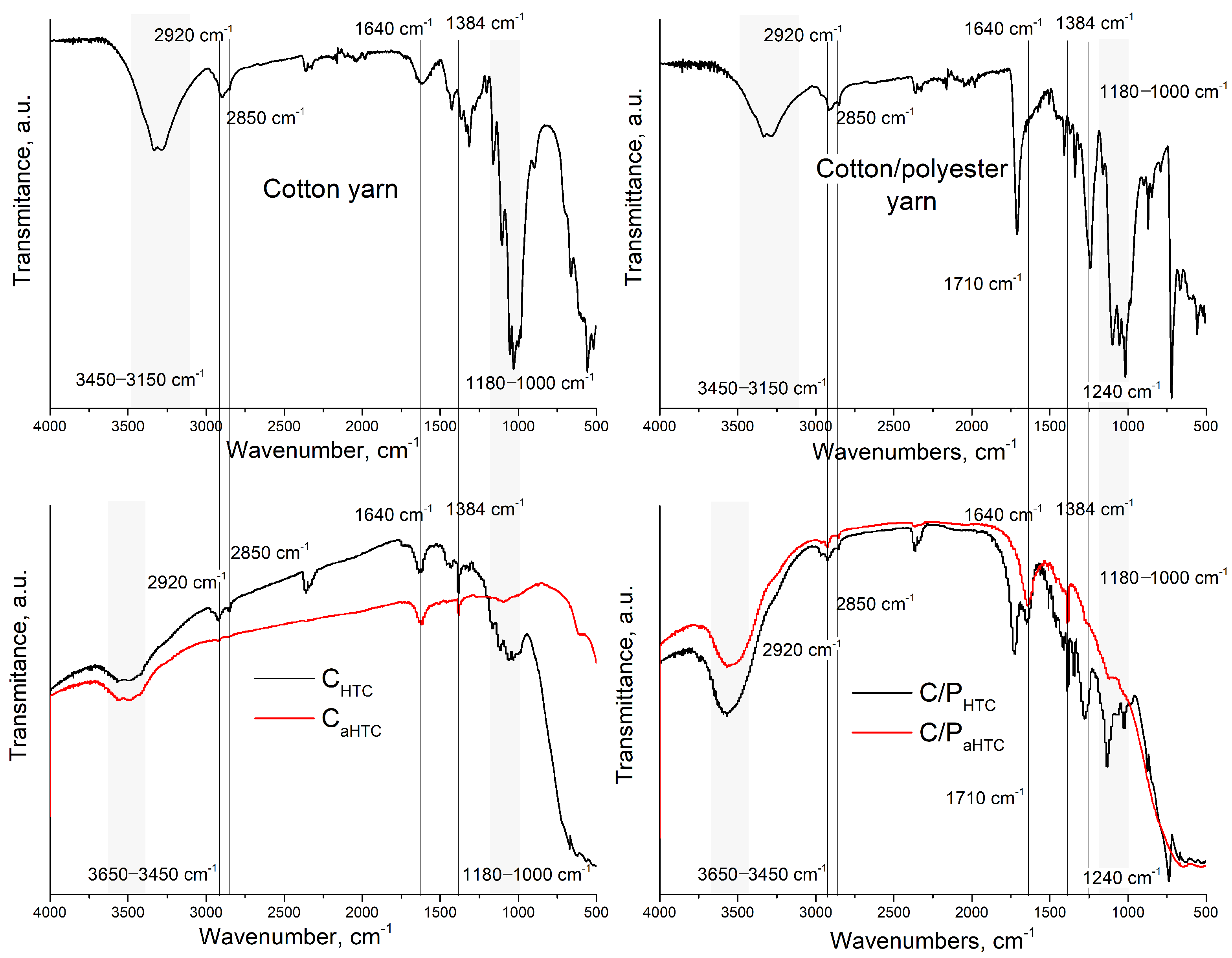
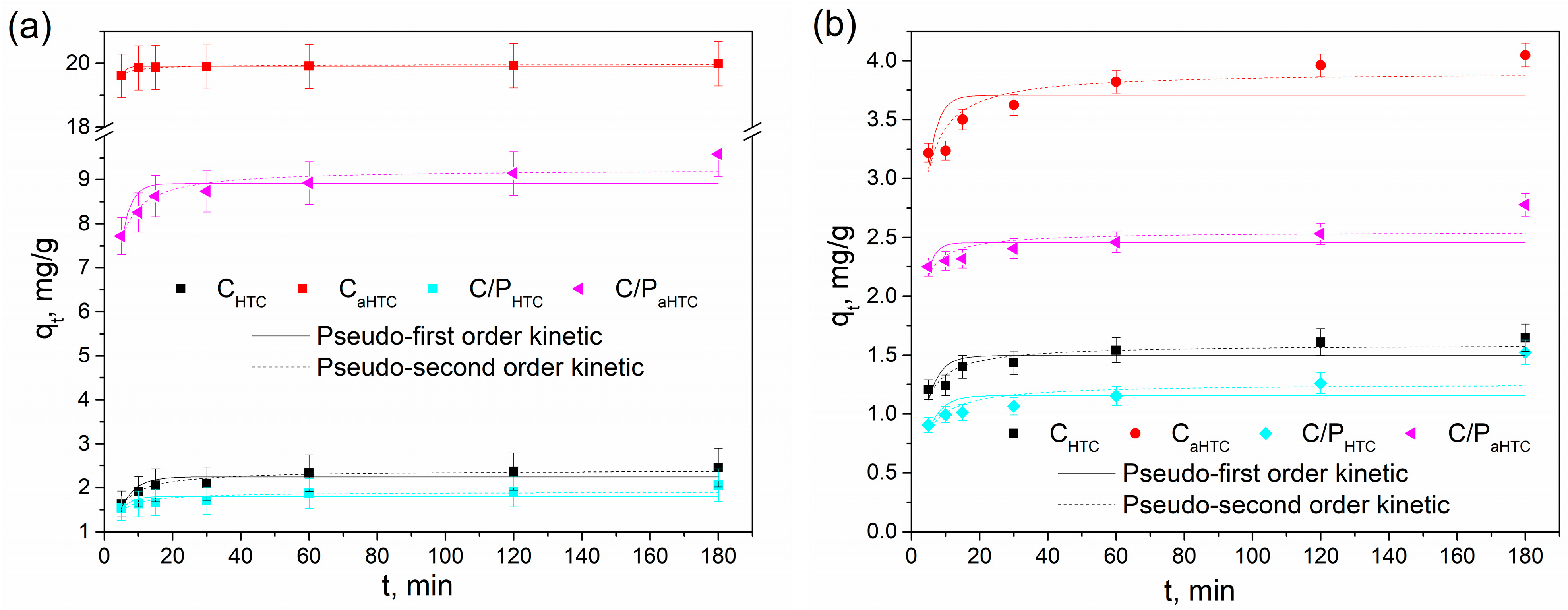
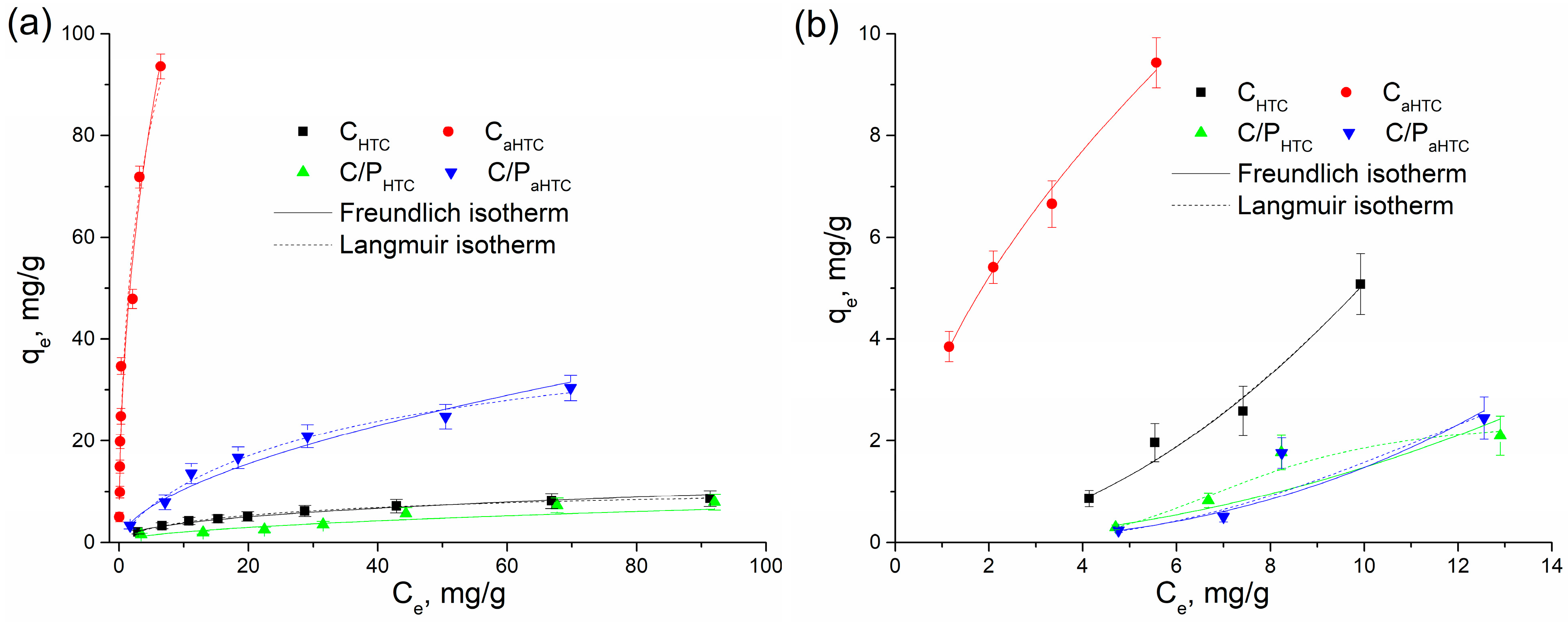
| Sample | SBET, m2/g | Sext, m2/g | Smicro, m2/g | Vtotal, cm3/g | Vmicro, cm3/g | Dm, nm | Amount of Surface Oxygen Groups, mmol/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | Acidic | Total | |||||||
| CHTC | 0.003 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.983 ± 0.020 | 3.782 ± 0.017 | 4.765 ± 0.037 |
| C/PHTC | 0.64 | 0.122 | 0.516 | 0.01 | 4 × 10−4 | 28.75 | 0.345 ± 0.015 | 4.866 ± 0.012 | 5.211 ± 0.027 |
| CaHTC | 872.2 | 386.1 | 486 | 0.532 | 0.269 | 4.82 | 2.134 ± 0.008 | 3.940 ± 0.025 | 6.074 ± 0.033 |
| C/PaHTC | 21.75 | 19.03 | 2.72 | 0.035 | 0.002 | 8.93 | 2.333 ± 0.010 | 4.811 ± 0.015 | 7.144 ± 0.025 |
| Metal Ion | Sample | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | k1 (1/min) | qe,mod (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/(mg min)) | qe,mod (mg/g) | qe,exp (mg/g) | ||
| Pb(II) | CHTC | 0.71124 | 0.216 | 2.28 | 0.94000 | 0.159 | 2.42 | 2.46 |
| C/PHTC | 0.28953 | 0.325 | 1.83 | 0.70164 | 0.325 | 1.93 | 2.06 | |
| CaHTC | 0.85576 | 0.842 | 19.91 | 0.91098 | 0.607 | 19.96 | 19.98 | |
| C/PaHTC | 0.54732 | 0.372 | 8.95 | 0.86901 | 0.100 | 9.26 | 9.59 | |
| Cd(II) | CHTC | 0.47925 | 0.255 | 1.52 | 0.85098 | 0.295 | 1.61 | 1.65 |
| C/PHTC | 0.23811 | 0.212 | 1.22 | 0.56231 | 0.243 | 1.31 | 1.52 | |
| CaHTC | 0.31121 | 0.337 | 3.75 | 0.78406 | 0.175 | 3.93 | 4.05 | |
| C/PaHTC | 0.10068 | 0.446 | 2.48 | 0.50107 | 0.417 | 2.57 | 2.78 | |
| Metal Ion | Sample | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg/g) | b (dm3/mg) | R2 | Kf ((mg/g)/(mg/dm3)1/n) | 1/n | R2 | ||
| Pb(II) | CHTC | 260.8 | 0.006 | 0.99999 | 1.683 | 0.372 | 0.98237 |
| C/PHTC | 81.6 | 0.004 | 0.94043 | 0.361 | 0.694 | 0.92571 | |
| CaHTC | 3345.0 | 0.012 | 0.99999 | 40.596 | 0.448 | 0.95892 | |
| C/PaHTC | 49.7 | 0.046 | 0.98189 | 3.634 | 0.501 | 0.97498 | |
| Cd(II) | CHTC | 1357.0 | 4.62 × 10−5 | 0.93807 | 0.063 | 1.906 | 0.96911 |
| C/PHTC | 2.2 | 1.01 × 10−6 | 0.92372 | 0.086 | 1.275 | 0.71281 | |
| CaHTC | 843.4 | 0.00414 | 0.97853 | 3.480 | 0.573 | 0.98945 | |
| C/PaHTC | 2.4 | 4.81 × 10−13 | 0.94990 | 0.026 | 1.807 | 0.76007 | |
| Material | Modification | Initial Concentration, mg/dm3 | Heavy Metal | Adsorption Capacity qmax, mg/g | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton fabric | Pyrolysis + Activation H3PO4 | 80–500 | Pb(II) | 361.54 | [20] |
| Cotton/polyester fabric 75:25 | 80–500 | 385.77 | |||
| Cotton fibre | Microwave-assisted carbonization | 0.05–0.4 | Hg(II) | 169.2 | [58] |
| Cotton stalk | Pyrolysis | 100–500 | Pb(II) | 146.78 | [25] |
| Cotton stalk | Hydrothermal carbonization + Activation KOH | 5–300 | Cd(II) | 30.40 | [17] |
| Cotton stalk | Pyrolysis | 10–80 | Pb(II) | 42.55 | [59] |
| 0.1–1.0 | Cd(II) | 0.53 | |||
| 1.0–10 | Ni(II) | 5.25 | |||
| 0.1–1.0 | Co(II) | 0.54 | |||
| Pyrolysis + H2SO4 | 10–80 | Pb(II) | 38.76 | ||
| 0.1–1.0 | Cd(II) | 0.53 | |||
| 1.0–10 | Ni(II) | 2.21 | |||
| 0.1–1.0 | Co(II) | 0.52 | |||
| Pyrolysis + NaOH | 10–80 | Pb(II) | 37.59 | ||
| 0.1–1.0 | Cd(II) | 0.51 | |||
| 1.0–10 | Ni(II) | 2.05 | |||
| 0.1–1.0 | Co(II) | 0.50 | |||
| Pyrolysis + H2C2O4 | 10–80 | Pb(II) | 44.64 | ||
| 0.1–1.0 | Cd(II) | 0.65 | |||
| 1.0–10 | Ni(II) | 6.20 | |||
| 0.1–1.0 | Co(II) | 0.52 | |||
| Waste cotton yarns | Hydrothermal carbonization | 5–100 | Pb(II) | 260.8 | This study |
| Waste cotton/polyester yarns | 5–100 | 81.6 | |||
| Waste cotton yarns | 5–15 | Cd(II) | 3345.0 | ||
| Waste cotton/polyester yarns | 5–15 | 49.7 | |||
| Waste cotton yarns | Hydrothermal carbonization + Activation KOH | 5–100 | Pb(II) | 1357.0 | |
| Waste cotton/polyester yarns 50:50 | 5–100 | 2.2 | |||
| Waste cotton yarns | 5–15 | Cd(II) | 843.4 | ||
| Waste cotton/polyester yarns 50:50 | 5–15 | 2.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trivunac, K.; Mihajlović, S.; Vukčević, M.; Maletić, M.; Pejić, B.; Kalijadis, A.; Perić Grujić, A. Modified Cellulose-Based Waste for Enhanced Adsorption of Selected Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Polymers 2024, 16, 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182610
Trivunac K, Mihajlović S, Vukčević M, Maletić M, Pejić B, Kalijadis A, Perić Grujić A. Modified Cellulose-Based Waste for Enhanced Adsorption of Selected Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Polymers. 2024; 16(18):2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182610
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrivunac, Katarina, Snežana Mihajlović, Marija Vukčević, Marina Maletić, Biljana Pejić, Ana Kalijadis, and Aleksandra Perić Grujić. 2024. "Modified Cellulose-Based Waste for Enhanced Adsorption of Selected Heavy Metals from Wastewater" Polymers 16, no. 18: 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182610
APA StyleTrivunac, K., Mihajlović, S., Vukčević, M., Maletić, M., Pejić, B., Kalijadis, A., & Perić Grujić, A. (2024). Modified Cellulose-Based Waste for Enhanced Adsorption of Selected Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Polymers, 16(18), 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182610






