Performance Investigation of PSF-nAC Composite Ultrafiltration Membrane for Protein Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Fabrication
2.3. Water Contact Angle Test
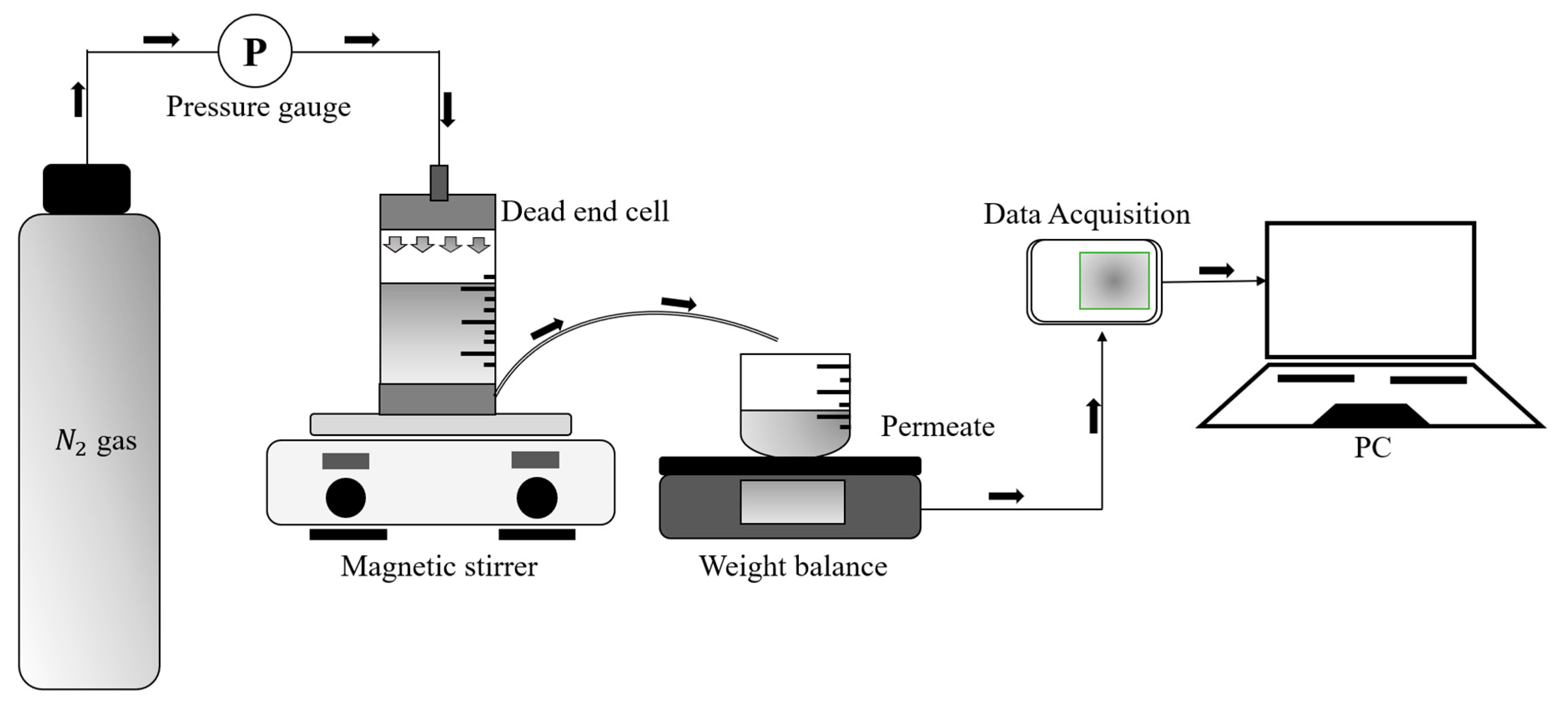
2.4. Filtration Experiments
2.4.1. Water Flux Test
2.4.2. Protein Separation
2.5. Membrane Porosity
2.6. Average Pore Size
2.7. Molecular Weight Cutoff (MWCO)
3. Results
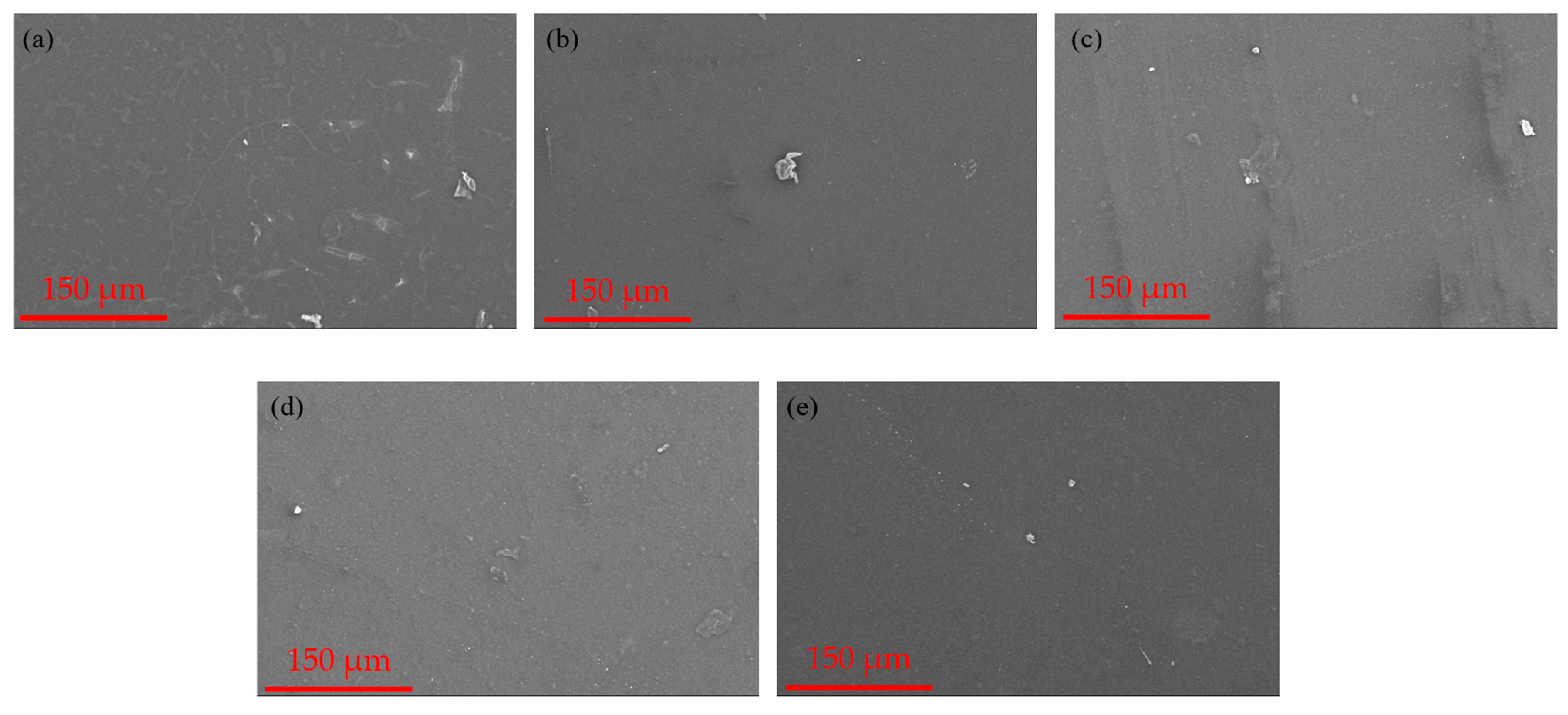
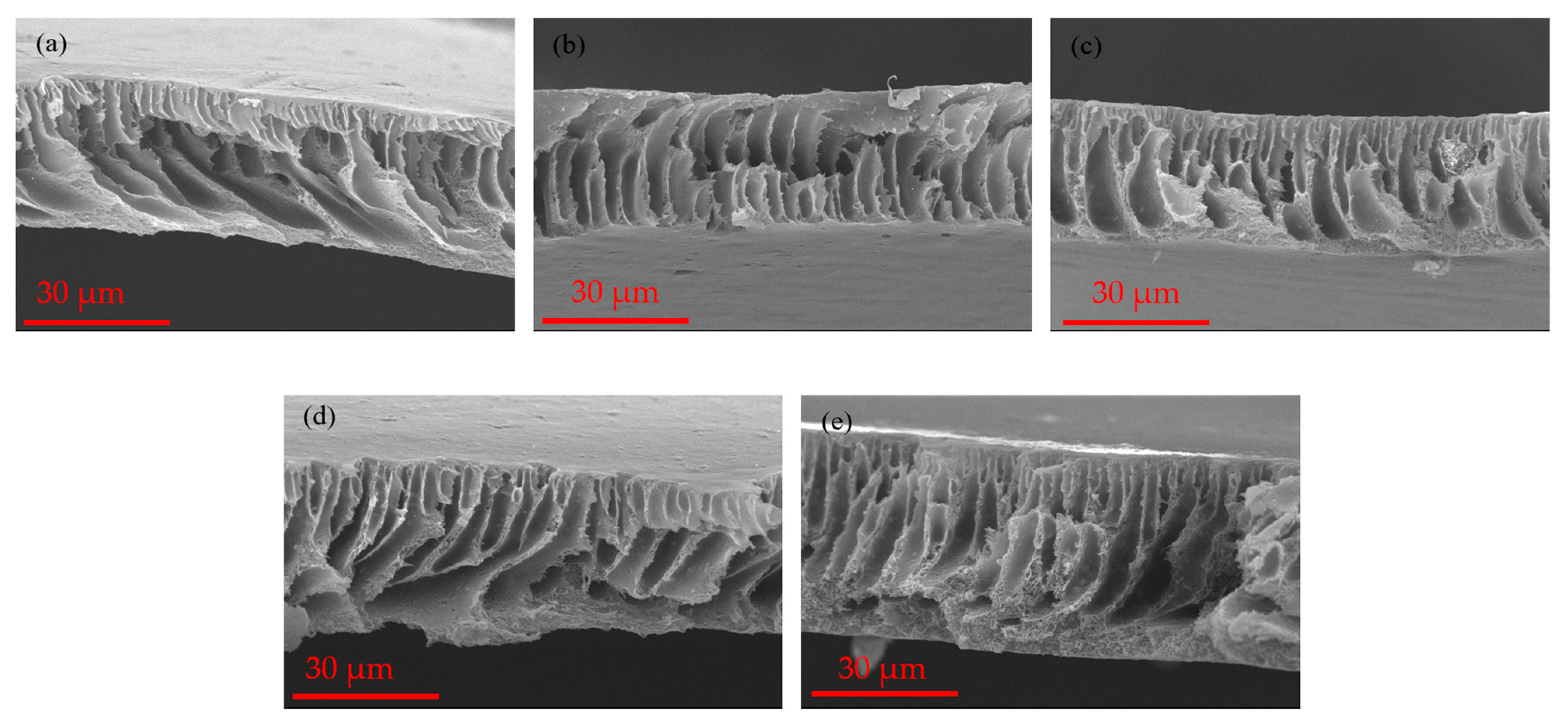
3.1. Membrane Morphology
3.2. Contact Angle Analysis
3.3. Pure Water Flux Test Experiments
3.4. Effect of nAC on Protein Rejection
3.5. Porosity
3.6. Measurement of Average Pore Size
3.7. Molecular Weight Cutoff Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakrabarty, T.; Kumar, M.; Shahi, V.K. Effective Adsorption and Separation of Lysozyme with Magnetite/Isinglass Composite Nanoparticles: Investigation of the Operational Parameters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3015–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Ahn, C.Y.; Lee, J. Amino acid side chain-like surface modification on magnetic nanoparticles for highly efficient separation of mixed proteins. Talanta 2012, 93, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Khataee, A.; Vatanpour, V. High-flux PVDF mixed matrix membranes embedded with size-controlled ZIF-8 nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Khataee, A.; Safarpour, M. A review on the applications of ultrasonic technology in membrane bioreactors. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, A.; Bellare, J. Efficient separation of biological macromolecular proteins by polyethersulfone hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes modified with Fe3O4 nanoparticles-decorated carboxylated graphene oxide nanosheets. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 35, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arockiasamy, D.L.; Alhoshan, M.; Alam, J.; Muthumareeswaran, M.R.; Figoli, A.; Kumar, S.A. Separation of proteins and antifouling properties of polyphenylsulfone based mixed matrix hollow fiber membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, H.; Stahra, N.; Ulbricht, M. High performance polyethersulfone microfiltration membranes having high flux and stable hydrophilic property. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 342, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeva, P.D.; Knoche, T.; Pieper, T. Cross-flow ultrafiltration of protein solutions through unmodified and surface functionalized polyethersulfone membranes—Effect of process conditions on separation performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 92, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheydaei, M.; Zangouei, M.; Vatanpour, V. Coupling visible light sono-photocatalysis and sono-enhanced ultrafiltration processes for continuous flow degradation of dyestuff using N-doped titania nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2019, 143, 107631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, J.; Othman, M.H.D.; Matsuura, T. Polymeric membranes for desalination using membrane distillation: A review. Desalination 2020, 490, 114530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashov, S.; Demirel, E.; Suvaci, E. Tailoring microstructure of polysulfone membranes via novel hexagonal ZnO particles to achieve improved filtration performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 651, 120462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Electrospun polyethersulfone@MOF composite membranes for air cleaning and oil-water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Han, W.; Yang, X. Electrospun polyetherimide/zeolitic imidazolate framework nanofibrous membranes for enhanced air filtration performance under high temperature and high humidity conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhong, Q. Preparation and filtration performance of antibacterial PVDF/SiO2/Ag composite nanofiber membrane. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 74, 106864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovar, Z.; Babanzadeh, S.; Mehdipour-Ataei, S. Polysulfone/sepiolite nanocomposites and disulfonated polysulfone as de-salination membranes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 198, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, M.; Goswami, R.; Borah, A. Functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube thin-layered hollow fiber membrane for enantioselective permeation of racemic β-substituted-α-amino acids. J. Chem. Sci. 2022, 134, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, M.; Fadali, O.A.; Lim, B.-H. Super-hydrophilic and highly stable in oils polyamide-polysulfone composite membrane by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2015, 138, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Zhao, Y. Bio-inspired modification of superhydrophilic iPP membrane based on polydopamine and gra-phene oxide for highly antifouling performance and reusability. Mater. Lett. 2019, 255, 126573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Soulegani, S.; Sherafat, Z.; Rasouli, M. Morphology, physical, and mechanical properties of potentially applicable coe-lectrospun polysulfone/chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol fibrous membranes in water purification. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 49933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shi, F.; Ma, J. Effect of PEG additive on the morphology and performance of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 2011, 272, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Vatanpour, V.; Khataee, A. Contra-diffusion synthesis of ZIF-8 layer on polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membranes for improved water purification. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 73, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S.; Asghari, A.; Vatanpour, V. Fabrication and characterization of a novel polyvinyl alcohol-graphene oxide-sodium alginate nanocomposite hydrogel blended PES nanofiltration membrane for improved water purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.; Leo, C.P. Polymeric membranes incorporated with metal/metal oxide nanoparticles: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2013, 308, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, P. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets functionalized composite membrane with self-cleaning and antibacterial performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Hu, J.; Sun, W. Graphene oxide-polyethylene glycol incorporated PVDF nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane with enhanced hydrophilicity, permeability, and antifouling performance. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, F.; Dilshad, M.R.; Islam, A. Synthesis, characterization and desalination study of polyvinyl chloride-co-vinyl acetate/cellulose acetate membranes integrated with surface modified zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 309, 110579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavabari, E.S.; Goudarzi, A.; Shahrousvand, M. Preparation of novel polyurethane/activated carbon/cellulose nano-whisker nanocomposite film as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue and basic violet 16 dyes from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalhy, Q.F.; Al-Ani, F.H.; Al-Najar, A.E. A study of the effect of embedding ZnO-NPs on PVC membrane performance use in actual hospital wastewater treatment by membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. Process. 2018, 130, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cheng, P.; Ye, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Biological performance and fouling mitigation in the biochar-amended anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) treating pharmaceutical wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Jegal, J.; Kim, W.N. Fabrication and characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/polymer blend membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathi, M.S.; Rana, R.; Alwarappan, S.; Gowrishankar, S.; Kanimozhia, P.; Nagendran, A. Cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes customized with bio-inspired polydopamine coating and in situ immobilization of silver nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 4216–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, P.; Nagendran, A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Neelakandan, S.; Malarvizhi, K. Effects of Polyvinylpyrrolidone on the permeation and fouling-resistance properties of Polyetherimide ultrafiltration membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4832–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manorma; Ferreira, I.; Alves, P.; Gil, M.H.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M. Lignin separation from black liquor by mixed matrix polysulfone nanofiltration membrane filled with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 260, 118231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbolouki, M.N. A general diagram for estimating pore size of ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1982, 17, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, R.; Malaisamy, R.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Mohan, D. Cellulose acetate-poly(ether sulfone) blend ultrafiltration membranes. II. Application studies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 3659–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Volli, V.; Lohani, L.; Purkait, M.K. Polymeric ultrafiltration membranes modified with fly ash-based carbon nanotubes for thermal stability and protein separation. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 4, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Purkait, M.K. Role of poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid) in the modification of polysulfone membranes for ultrafiltration. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Yadav, V.S.K.; Purkait, M.K. Cu2O photocatalyst modified antifouling polysulfone mixed matrix membrane for ultrafiltration of protein and visible light driven photocatalytic pharmaceutical removal. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, A.K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Understanding and guiding the phase inversion process for synthesis of solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.A.; Wong, L.Y.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Ng, S.L. Development of hybrid polymeric polyerthersulfone (PES) membrane incorporated with powdered activated carbon (PAC) for palm oil mill effluent (POME) treatment. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2018, 10, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihandana, G.S.; Ito, H.; Sanada, I.; Nishinaka, Y.; Kanno, Y.; Miki, N. Permeability and blood compatibility of nanoporous parylene film-coated polyethersulfone membrane under long-term blood diffusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40024–40030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheripour, E.; Moghadassi, A.R.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ray, M.B.; Parvizian, F.; Van der Bruggen, B. Highly hydrophilic and antifouling nanofiltration membrane incorporated with water-dispersible composite activated carbon/chitosan nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 132, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayab, S.S.; Abbas, M.A.; Mushtaq, S.; Khan Niazi, B.; Batool, M.; Shehnaz, G.; Ahmad, N.; Ahmad, N.M. Anti-foulant ultrafiltration polymer composite membranes incorporated with composite activated carbon/chitosan and activated carbon/thiolated chitosan with enhanced hydrophilicity. Membranes 2021, 11, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimpour, A.; Jahanshahi, M.; Rajaeian, B.; Rahimnejad, M. TiO2 entrapped nano-composite PVDF/SPES membranes: Preparation, characterization, antifouling and antibacterial properties. Desalination 2011, 278, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, B.; Naziri Mehrabani, S.A.; Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Orhun Teber, O.; Khataee, A.; Orooji, Y.; Koyuncu, I. Development of Ti2AlN MAX phase/cellulose acetate nanocomposite membrane for removal of dye, protein and lead ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 296, 119913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, M.N.Z.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Othman, M.H.D.; Hasbullah, H.; Said, N.; Kadir, S.H.S.A.; Kamal, F.; Abdullah, M.S.; Ng, B.C. Development of biocompatible and safe polyethersulfone hemodialysis membrane incorporated with functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Kumar, V.V. Polymeric membranes customized with super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for effective separation of pentachlorophenol and proteins in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1284, 135449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.Y.; Ahmad, A.L.; Zaulkiflee, N.D. Antifouling and antibacterial evaluation of ZnO/MWCNT dual nanofiller polyethrsulfone mixed matrix membrane. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpatova, A.; Kim, E.S.; Sun, X.; Hwang, G.; Liu, Y.; Gamal El-Din, M. Fabrication of porous polymeric nanocomposite membranes with enhanced anti-fouling properties: Effect of casting composition. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 444, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraei, P.; Madaeni, S.S.; Ghaemi, N.; Salehi, E.; Khadivi, M.A.; Moradian, R.; Astinchap, B. Novel polyethersulfone nano-composite membrane prepared by PANI/Fe3O4 nanoparticles with enhanced performance for Cu(II) removal from water. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Amini, S.H.; Khodabakhshi, A.R.; Bagheripour, E.; Van der Bruggen, B. Activated carbon nanoparticles entrapped mixed matrix polyethersulfone based nanofiltration membrane for sulfate and copper removal from water. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 82, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Feng, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Luan, J.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Z.; Wang, G. Combined strategy of blending and surface modification as an effective route to prepare antifouling ultrafiltration membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Al-Juhani, A.A.; Al-Hamaouz, O.C.; Laoui, T.; Khan, Z.; Atieh, M.A. Preparation and properties of nanocomposite polysulfone/multi-walled carbon nanotubes membranes for desalination. Desalination 2015, 367, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benally, C.; Li, M.; El-Din, M.B. The effect of carboxyl multiwalled carbon nanotubes content on the structure and performance of polysulfone membranes for oil sands process affected water treatment. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatkhah, F.; Mohammadi, T.; Tofighy, M.A. Polysulfone hollow fiber membrane containing charcoal-carbon nano-material for wastewater treatment in membrane bioreactor. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2022, 50, 103222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ke, J.; Duan, F.; Chen, J. Preparation and application of novel multi-walled carbon nanotubes/polysulfone nanocomposite membrane for chiral separation. Desal. Water Treat. 2017, 87, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sianipar, M.; Kim, S.H.; Min, C.; Tijing, L.D.; Shon, H.K. Potential and performance of a polydopamine-coated multi-walled carbon nanotube/polysulfone nanocomposite membrane for ultrafiltration application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 34, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Z.W.; Tan, Y.Y.; Chong, W.C.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mohammad, A.W.; Teoh, H.C.; Sim, L.C.; Koo, C.H. Preparation of a novel polysulfone membrane by incorporated with carbon dots grafted silica from rice husk for dye removal. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2021, 40, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Membrane Code | Polysulfone (wt.%) | nAC (wt.%) | NMP (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSF-nAC0 | 20 | 0 | 80 |
| PSF-nAC2 | 20 | 2 | 78 |
| PSF-nAC4 | 20 | 4 | 76 |
| PSF-nAC6 | 20 | 6 | 74 |
| PSF-nAC8 | 20 | 8 | 72 |
| Membrane Code | Porosity (%) | Pore Radius, | MWCO (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSF-nAC0 | 57.8 | 40.43 | 69 |
| PSF-nAC2 | 52.2 | 41.76 | 69 |
| PSF-nAC4 | 34.3 | 19.57 | 14 |
| PSF-nAC6 | 34.5 | 22.22 | 35 |
| PSF-nAC8 | 27.8 | 29.76 | 35 |
| Modifier | PWF (LMH/bar) | BSA Rejection (%) | WCA | Porosity, (%) | Pore Radius, | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP + multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) | 12.8 | - | 59 | 54.57 | 3.015 | [53] |
| Carboxyl MWCNT (mMWCNT) | 48 | - | 73 | - | 2.55 | [54] |
| PVP + carbon–charcoal nanomaterial | 196.3 | 95.8 | 69.6 | 91 | 13 | [55] |
| Carboxilated MWCNT (β-CD-cMWCNTs) | 320 | 67.5 | - | 87 | 10.1 | [56] |
| MWCNT coated with polydopamine | 174 | 99.21 | 42.85 | 35.7 | - | [57] |
| PVP + carbon dots + silica | 7.4 | - | 75.6 | 89.88 | 6.5 | [58] |
| Nano-activated carbon | 428 | 92.1 | 59 | 34.3 | 1.95 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prihandana, G.S.; Mahardika, M.; Arifvianto, B.; Baskoro, A.S.; Whulanza, Y.; Sriani, T.; Yusof, F. Performance Investigation of PSF-nAC Composite Ultrafiltration Membrane for Protein Separation. Polymers 2024, 16, 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182654
Prihandana GS, Mahardika M, Arifvianto B, Baskoro AS, Whulanza Y, Sriani T, Yusof F. Performance Investigation of PSF-nAC Composite Ultrafiltration Membrane for Protein Separation. Polymers. 2024; 16(18):2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182654
Chicago/Turabian StylePrihandana, Gunawan Setia, Muslim Mahardika, Budi Arifvianto, Ario Sunar Baskoro, Yudan Whulanza, Tutik Sriani, and Farazila Yusof. 2024. "Performance Investigation of PSF-nAC Composite Ultrafiltration Membrane for Protein Separation" Polymers 16, no. 18: 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182654
APA StylePrihandana, G. S., Mahardika, M., Arifvianto, B., Baskoro, A. S., Whulanza, Y., Sriani, T., & Yusof, F. (2024). Performance Investigation of PSF-nAC Composite Ultrafiltration Membrane for Protein Separation. Polymers, 16(18), 2654. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16182654






