Blue Laser for Production of Carbon Dots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
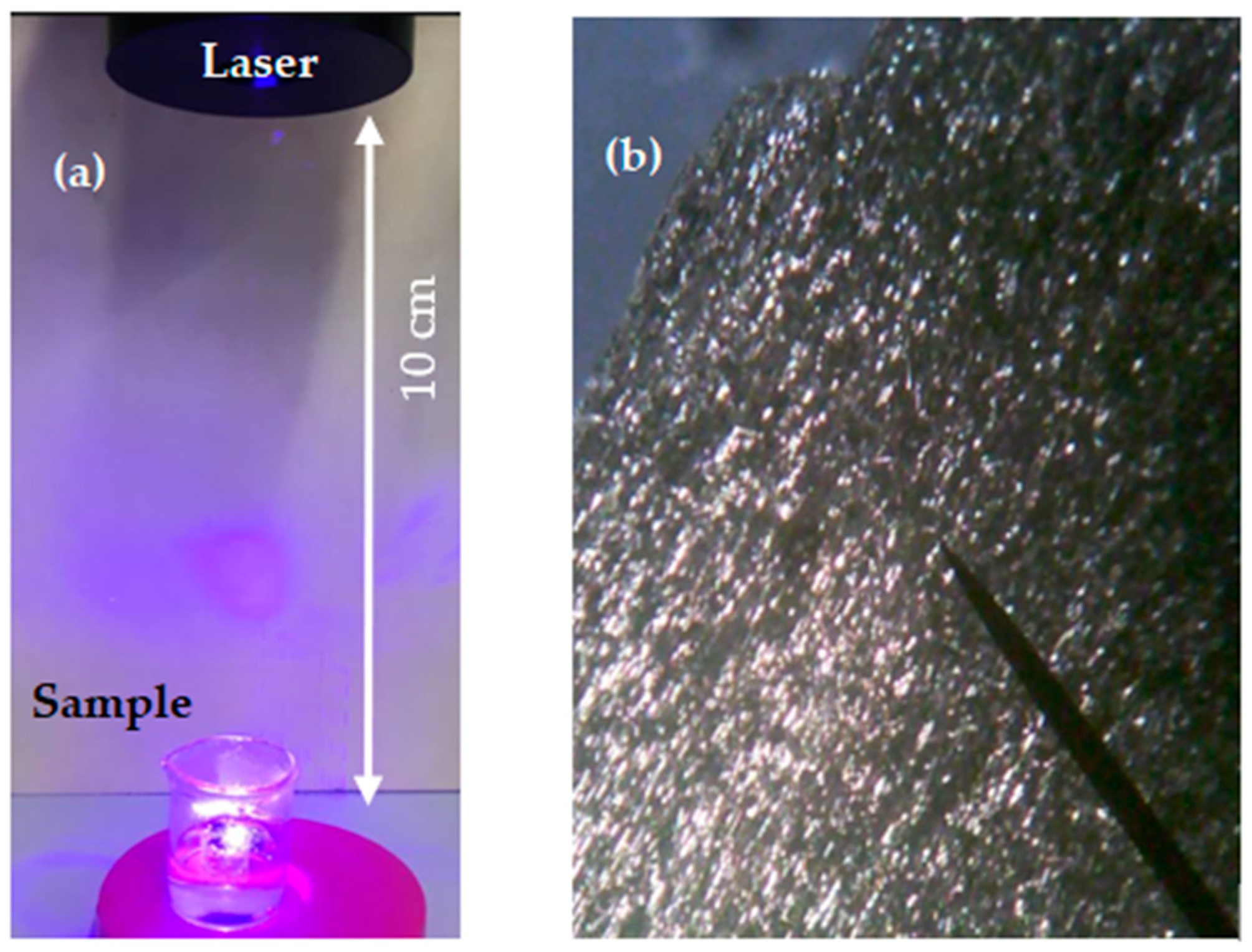
2.1. Process of Laser Ablation in Liquid
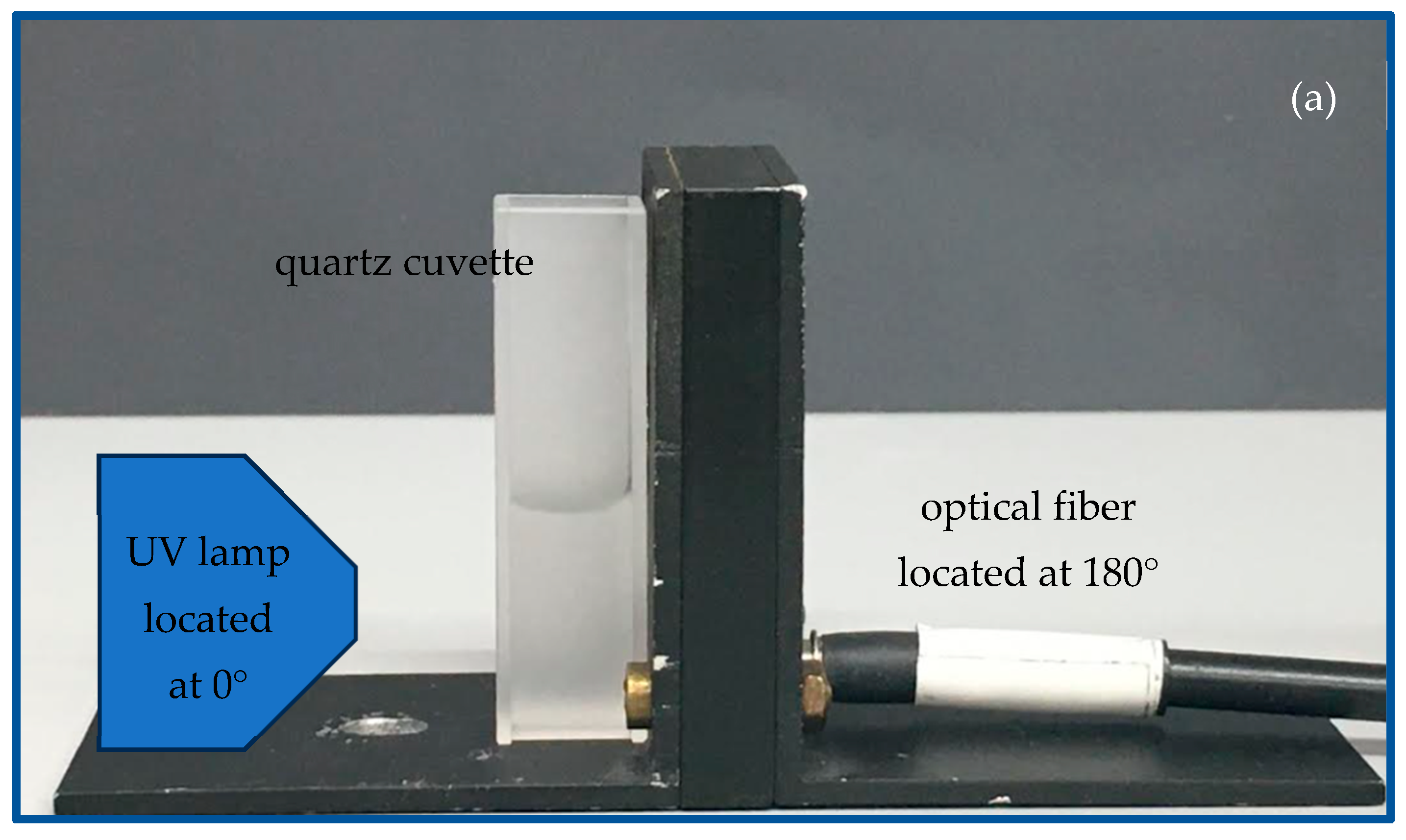
2.2. Characterization of the Produced CDs and the PCL + CDs Composites
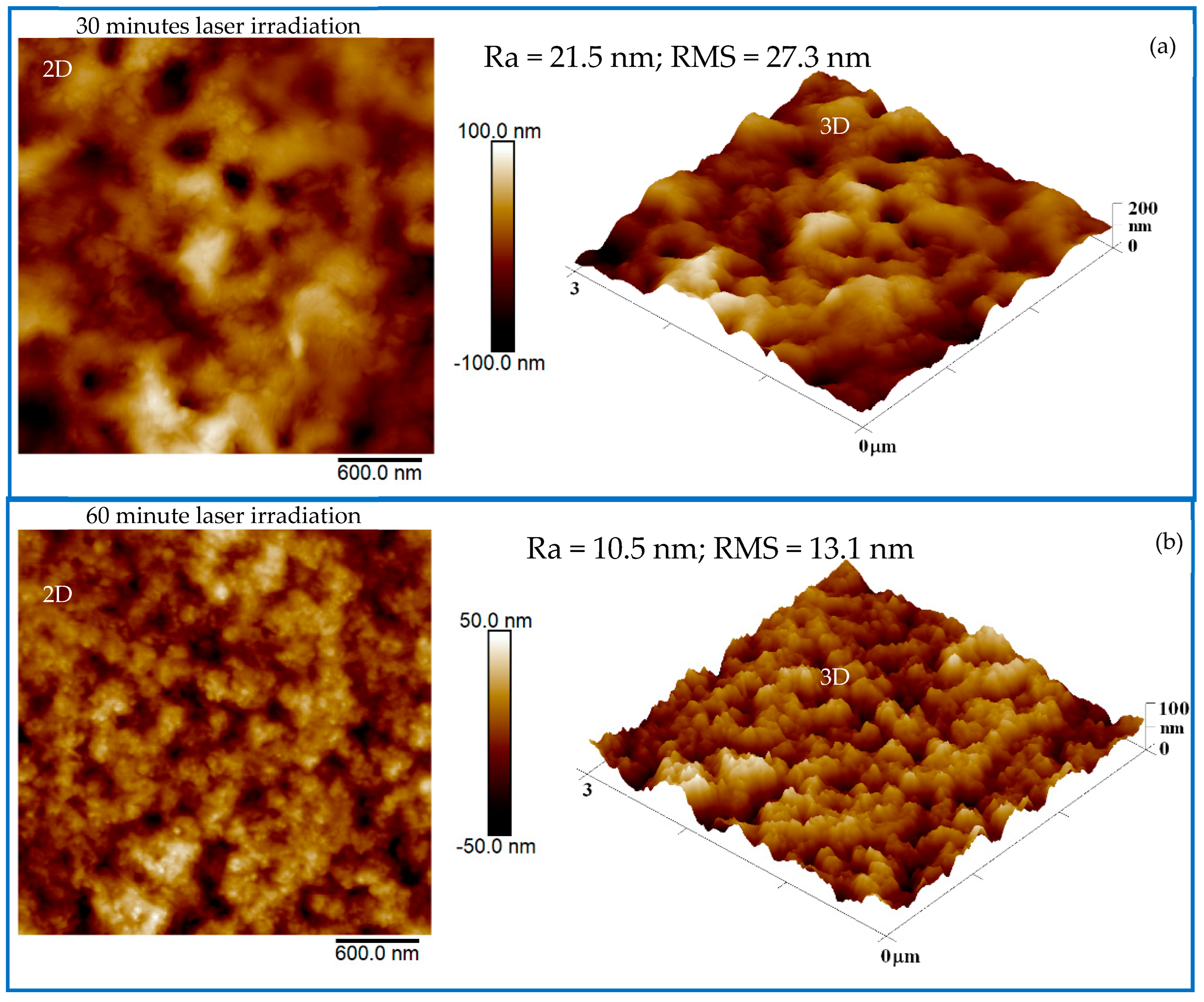
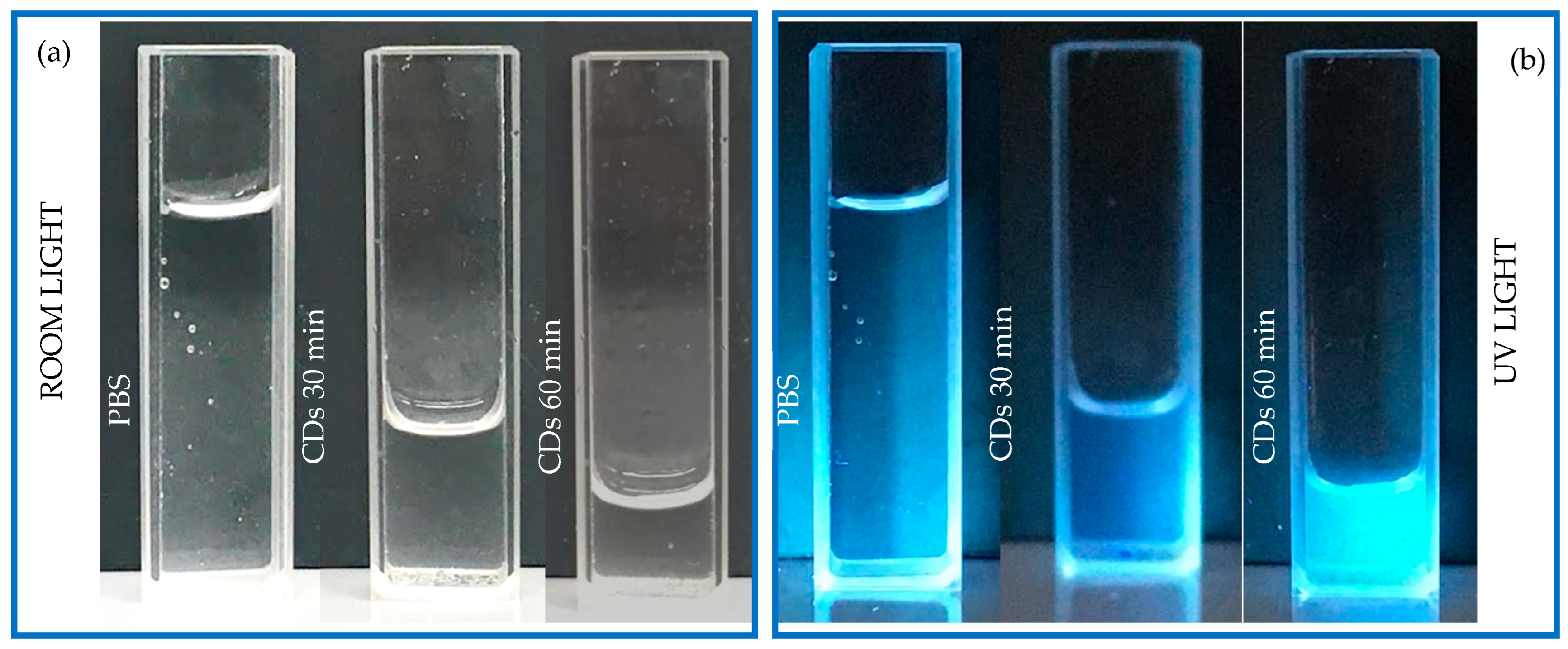
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek, A.; Hoffman, J.; Morgiel, J.; Mościcki, T.; Stobiński, L.; Szymański, Z.; Małolepszy, A. Luminescent Carbon Dots Synthesized by the Laser Ablation of Graphite in Polyethylenimine and Ethylenediamine. Materials 2021, 14, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalet, X.; Pinaud, F.F.; Bentolila, L.A.; Tsay, J.M.; Doose, S.; Li, J.J.; Sundaresan, G.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Weiss, S. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 2005, 307, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovric, J.; Cho, S.J.; Winnik, F.M.; Maysinger, D. Unmodified cadmium telluride quantum dots induce reactive oxygen species formation leading to multiple organelle damage and cell death. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Meziani, M.J.; Sahu, S.; Sun, Y.P. Photoluminescence Properties of Graphene versus Other Carbon Nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y.; Qi, B.; Pang, D.-W. Electrochemical Tuning of Luminescent Carbon Nanodots: From Preparation to Luminescence Mechanism. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5801–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Wen, X.; Toh, Y.-R.; Tang, J. Temperature-Dependent Fluorescence in Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 25552–25557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kalytchuk, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Kershaw, S.V.; Rogach, A.L. Thickness-dependent full-color emission tunability in a flexible carbon dot ionogel. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Chi, Y.W.; Dong, Y.Q.; Lin, J.P.; Wang, B.B. Electrochemiluminescence of water-soluble carbon nanocrystals released electrochemically from graphite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4564–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Ji, J.; Fei, R.; Wang, C.Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.R.; Jiang, L.P.; Zhu, J.J. A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlinos, A.B.; Stassinopoulos, A.; Anglos, D.; Zboril, R.; Karakassides, M.; Giannelis, E.P. Surface functionalized carbogenic quantum dots. Small 2008, 4, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.-H.; Chi, Y.; Yang, H.-H.; Yu, T. Luminescence origin of carbon-based dots obtained from citric acid and amino group containing molecules. Carbon 2017, 118, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Cutroneo, M. Alluminium plasma production at high laser intensity. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 083105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutroneo, M.; Havranek, V.; Mackova, A.; Malinsky, P.; Silipigni, L.; Slepicka, P.; Fajstavr, D.; Torrisi, L. Synthesis of porous polydimethylsiloxane gold nanoparticles composites by a single step laser ablation process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Cutroneo, M.; Ceccio, G. Effect of metallic nanoparticle in thin foils for laser ion acceleration. Phys. Scr. 2015, 90, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Cutroneo, M.; Silipigni, L.; Barreca, F.; Fazio, B.; Restuccia, N.; Kovacik, L. Gold nanoparticles produced by laser ablation in water and in graphene oxide suspension. Phil. Mag. 2018, 98, 2205–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, M.; Liu, X. Zinc oxide porous nano-cages fabricated by laser ablation of Zn in ammonium hydroxide. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 18707–18714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asl, P.M.; Dorranian, D. Effect of liquid medium temperature on the production rate and quality of graphene nanosheets produced by laser ablation. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2016, 48, 535. [Google Scholar]
- Małolepszy, A.; Błoński, S.; Chrzanowska-Giżyńska, J.; Wojasiński, M.; Płociński, T.; Stobiński, Z.; Szymański, Z. Fluorescent carbon and graphene oxide nanoparticles synthesized by the laser ablation in liquid. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beikzadeh, S.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mofid, V.; Ramezani, S.; Ghorbani, M.; Ehsani, A.; Mortazavian, A.M. Electrospun ethyl cellulose/poly caprolactone/gelatin nanofibers: The investigation of mechanical, antioxidant, and antifungal properties for food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeong, W.Y.; Sudarmadji, N.; Yu, H.Y.; Chua, C.K.; Leong, K.F.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Boey, Y.C.F.; Tan, L.P. Porous polycaprolactone scaffold for cardiac tissue engineering fabricated by selective laser sintering. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, N. Thermally exfoliated graphene oxide reinforced polycaprolactone-based bactericidal nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Mater. Technol. 2022, 37, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezati, P.; Rhim, J.-W. Pectin/carbon quantum dots fluorescent film with ultraviolet blocking property through light conversion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 219, 112804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezati, P.; Rhim, J.-W.; Molaei, R.; Priyadarshi, R.; Han, S. Cellulose nanofiber-based coating film integrated with nitrogen-functionalized carbon dots for active packaging applications of fresh fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 186, 111845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M. Highly Fluorescent Polycaprolactones with Tunable Light Emission Wavelengths across Visible to NIR Spectral Window. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, N.; Fukumura, D.; Gralla, O.; Au, P.; Schechner, J.S.; Jain, R.K. Creation of long-lasting blood vessels. Nature 2004, 428, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, H.J.; Wang, K.; Long, H.Y.; Wang, M.; Chew, S.Y. Highly fluorescent and photostable polymeric nanofibers as scaffolds for cell interfacing and long-term tracking. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2016, 5, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsakowski, S.; Santagata, A.; Dell’aglio, M.; de Giacomo, A.; Barcikowski, S.; Wagener, P.; Gökce, B. High productive and continuous nanoparticle fabrication by laser ablation of a wire-target in a liquid jet. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 403, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Torrisi, A.; Cutroneo, M. Intense continuous wave laser to synthesize luminescent solution of carbon dots. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2024, 32, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Torrisi, A.; Cutroneo, M. Luminescence enhancement of carbon dots synthesized by intense CW laser at 450 nm irradiating biocompatible solutions. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindivan, F.; Göktaş, M. The green synthesis of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) and characterization of polycaprolactone (PCL/CQDs) films. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 677, 132446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, N.; Ahmadi, S.; Alghoul, M.A.; Hammadi, F.Y.; Saeedfar, K.; Sopian, K. Research and Development Aspects on Chemical Preparation Techniques of Photoanodes for Dye Sensitized Solar Cells. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 518156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, L.; Lee, C.-S. Oxygen/nitrogen-related surface states controlled carbon nanodots with tunable full-color luminescence: Mechanism and bio-imaging. Carbon 2020, 160, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich, Phosphate Buffer Saline, Actual Website 2024. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/IT/it/substance/phosphatebufferedsaline1234598765 (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Acqua-calc.com, Density of Charcoal (Material), Actual Website 2024: Density of Charcoal in 285 Units of Density (aqua-calc.com). Available online: https://www.aqua-calc.com/page/density-table/substance/charcoal (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Tumuluru, J.S.; Hess, J.R.; Boardman, R.D.; Wright, C.T.; Westover, T.L. Formulation, Pretreatment, and Densification Options to Improve Biomass Specifications for Co-Firing High Percentages with Coal. Ind. Biotechnol. 2012, 8, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemons, R.V.; Baaijens, L. An Innovative Carbonisation Report: Technology and Environmental Impact. Termotehnika 2012, XXXVIII, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, J.; Chrzanowska, J.; Mościcki, T.; Radziejewska, J.; Stobiński, L.; Szymański, Z. Plasma generated during underwater pulsed laser processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 417, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G. Laser ablation in liquids: Applications in the synthesis of nanocrystals. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2007, 52, 648–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xue, S.; Sun, L.; Zong, X.; An, L.; Qu, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Formation and fluorescent mechanism of red emissive carbon dots from o-phenylenediamine and catechol system. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmaleki, A.; Mohamadi, Z. Acidic ionic liquids catalyst in homo and graft polymerization of ε-caprolactone. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkaddour, A.; Jradi, K.; Robert, S.; Daneault, C. Grafting of Polycaprolactone on Oxidized Nanocelluloses by Click Chemistry. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, K.; Guerrero, B.; Leblanc, R. Photoinduced Electron Transfer in Carbon Dots with Long-Wavelength Photoluminescence. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 29507–29515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Ehrat, F.; Urban, P.; Teves, R.; Wyrwich, R.; Döblinger, M.; Feldmann, J.; Urban, A.S.; Stolarczyk, J.K. Effect of nitrogen atom positioning on the trade-off between emissive and photocatalytic properties of carbon dots. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventrella, A.; Camisasca, A.; Fontana, A.; Giordani, S. Synthesis of green fluorescent carbon dots from carbon nano-onions and graphene oxide. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 36404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backes, E.H.; Harb, S.V.; Beatrice, C.A.G.; Shimomura, K.M.B.; Passador, F.R.; Costa, L.C.; Pessan, L.A. Polycaprolactone usage in additive manufacturing strategies for tissue engineering applications: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 1479–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, W.; Bartolo, P. Investigation of polycaprolactone for bone tissue engineering scaffolds: In vitro degradation and biological studies. Mater. Des. 2022, 216, 110582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Khoshkalampour, A.; Ghorbani, M.; Ramezani, S.; Ghasempour, Z.; Ghareaghajlou, N. Development of active packaging material based on polycaprolactone/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose nanofibers containing carbon dot nanoparticles for meat preservation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 197, 115913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
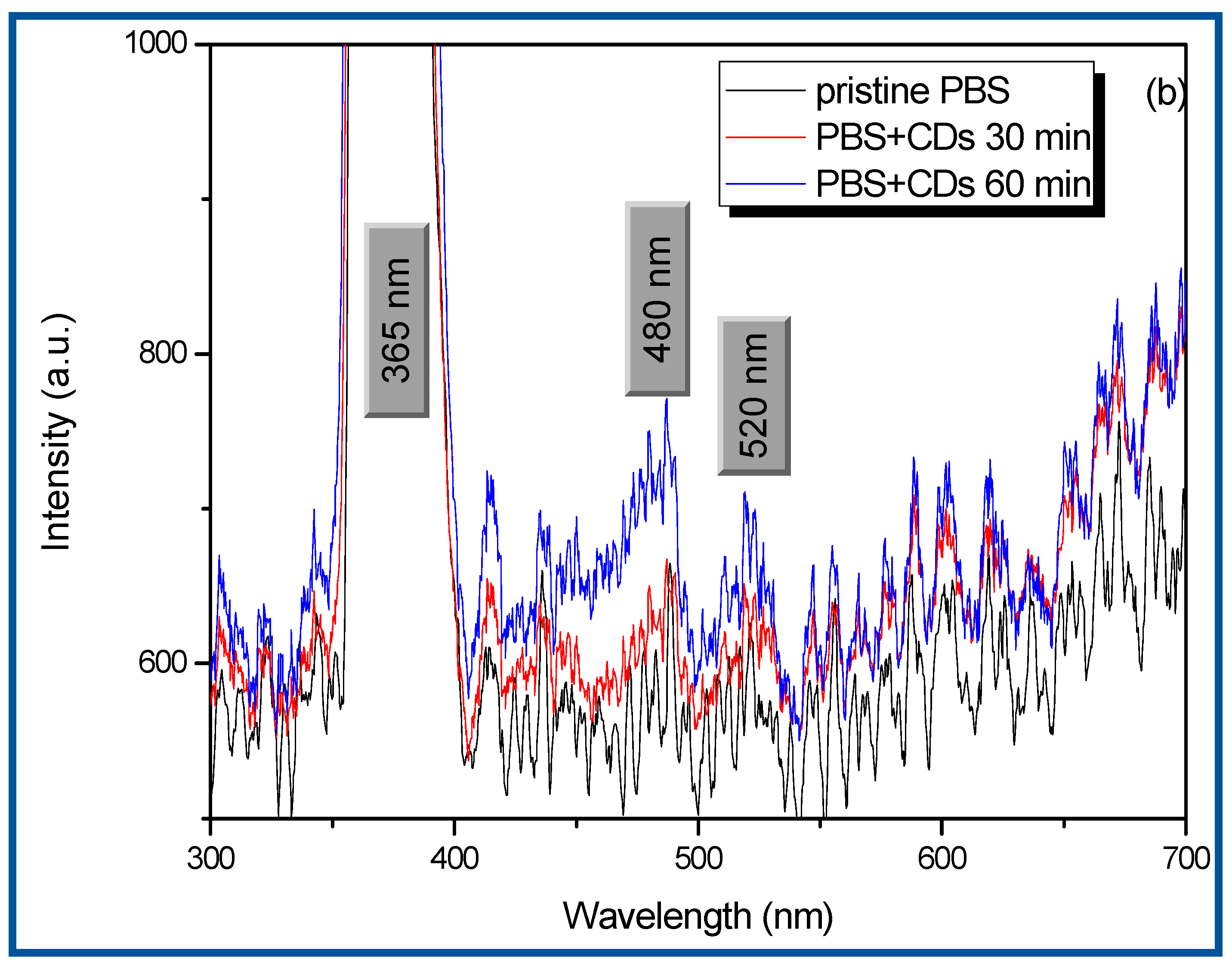
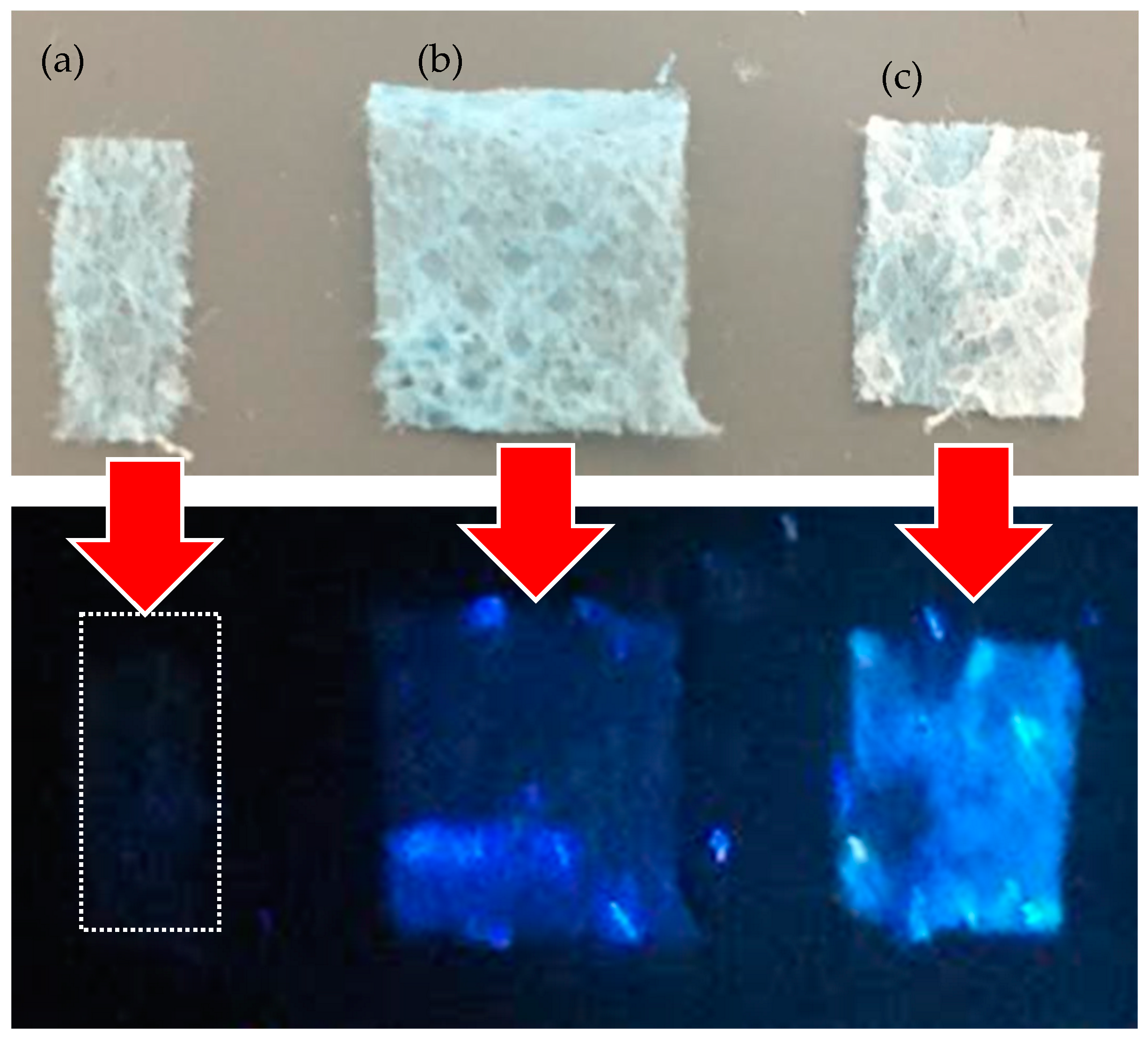
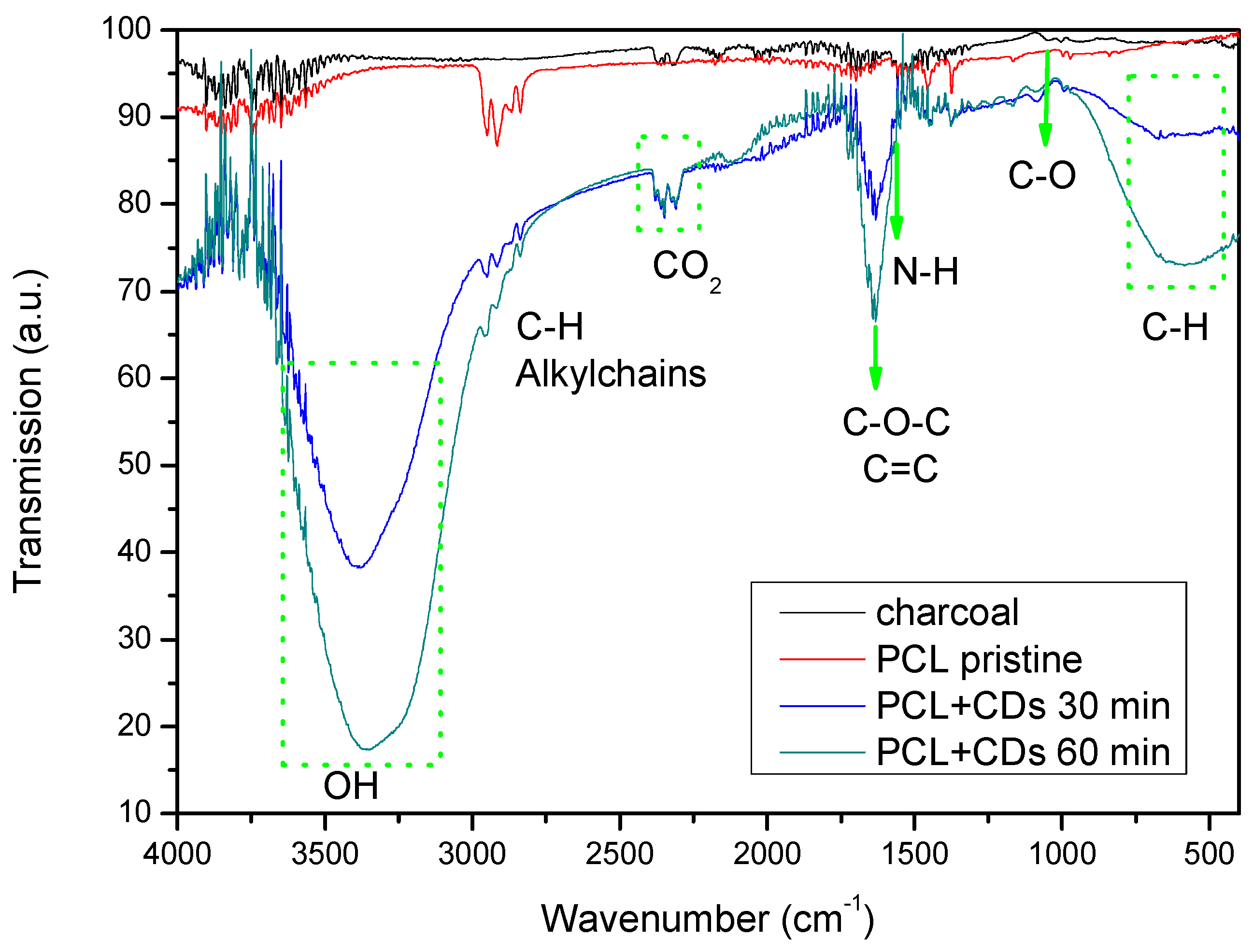
| Advantage | Disadvantage | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical method [32] | It avoids the use of both expensive beginning materials and energy systems. | The use of strong acids such as nitric acid in large quantities. |
| Carbonization of molecular precursors such as glucose, sucrose, glycerol, citric acid, ascorbic acid, and biowaste | It produces fluorescent CQDs. | CDs obtained from natural sources using chemicals for modification can lead to CD toxicity; this is a multi-step process. |
| Hydrothermal method [33] | It is performed in a single environment and it is economically advantageous. | It requires expensive autoclaves and involves safety issues during the reaction process. |
| Laser ablation technique | It is very fast and easily implemented. | It is not economically advantageous, it is complex, and it requires the use of reactants and a subsequent purification process [34]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cutroneo, M.; Malinsky, P.; Slepicka, P.; Torrisi, L. Blue Laser for Production of Carbon Dots. Polymers 2024, 16, 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192801
Cutroneo M, Malinsky P, Slepicka P, Torrisi L. Blue Laser for Production of Carbon Dots. Polymers. 2024; 16(19):2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192801
Chicago/Turabian StyleCutroneo, Mariapompea, Petr Malinsky, Petr Slepicka, and Lorenzo Torrisi. 2024. "Blue Laser for Production of Carbon Dots" Polymers 16, no. 19: 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192801
APA StyleCutroneo, M., Malinsky, P., Slepicka, P., & Torrisi, L. (2024). Blue Laser for Production of Carbon Dots. Polymers, 16(19), 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16192801







