Enhanced Impact Resistance, Oxygen Barrier, and Thermal Dimensional Stability of Biaxially Processed Miscible Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) Thin Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Biaxially Processed PLA/PBS and PLA/PBS/SA Thin Films
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
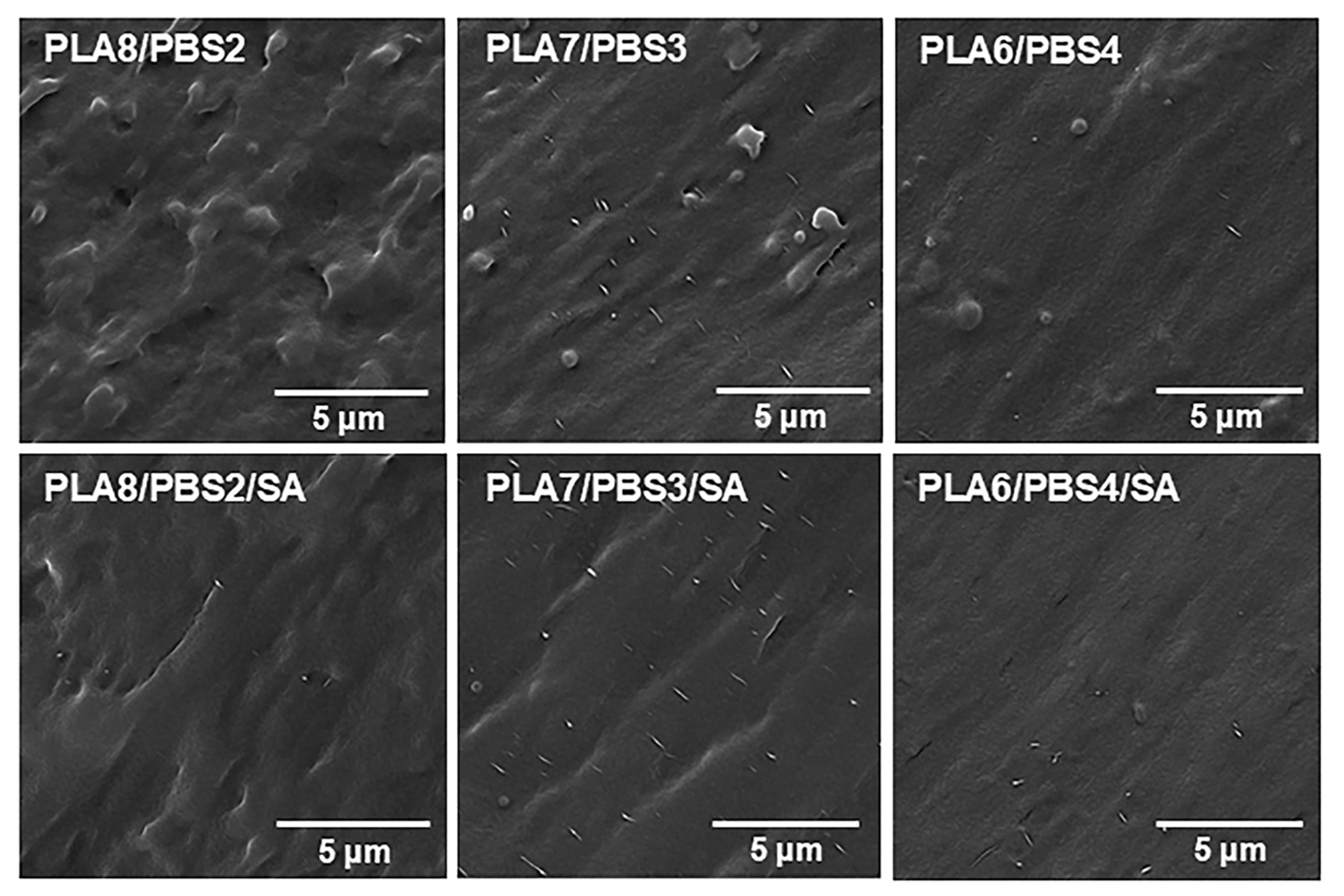
3.1. Morphological Observation of PLA/PBS and PLA/PBS/SA Blends
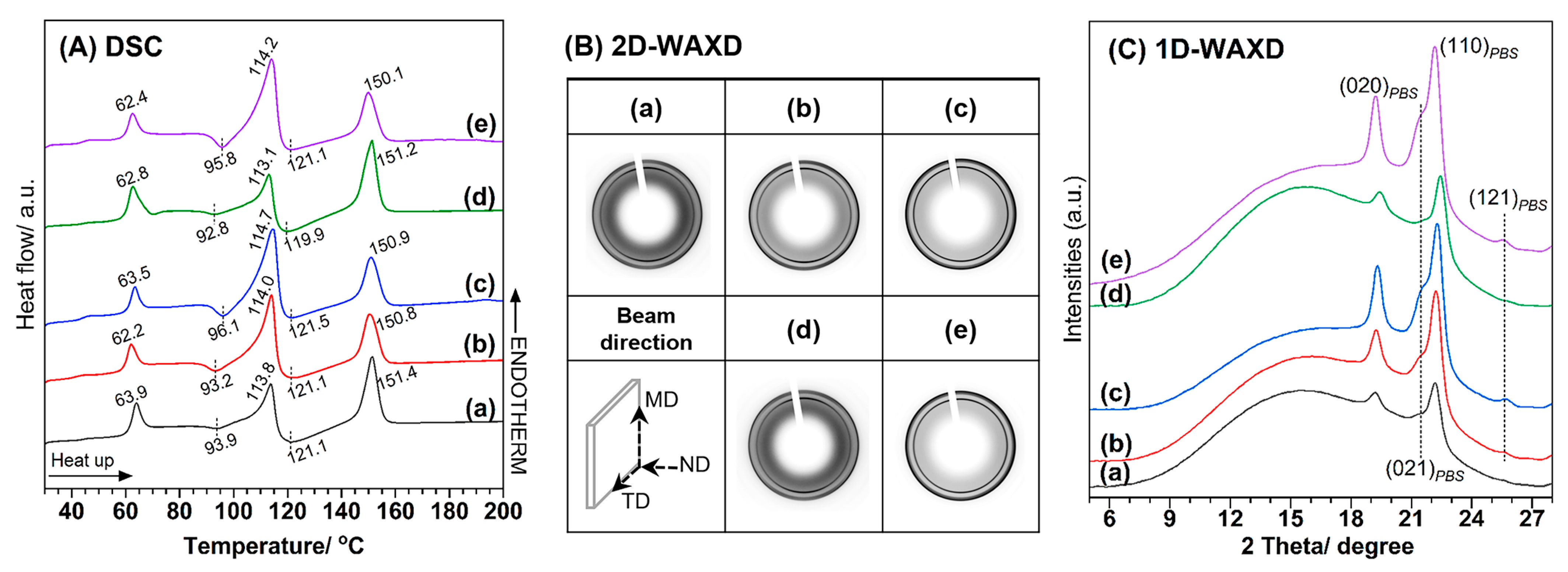
3.2. Thermal Properties and Crystallization of PLA/PBS and PLA/PBS/SA Blends
3.3. Thermal Properties and Crystallization of Biaxially Processed PLA/PBS and PLA/PBS/SA Thin Films
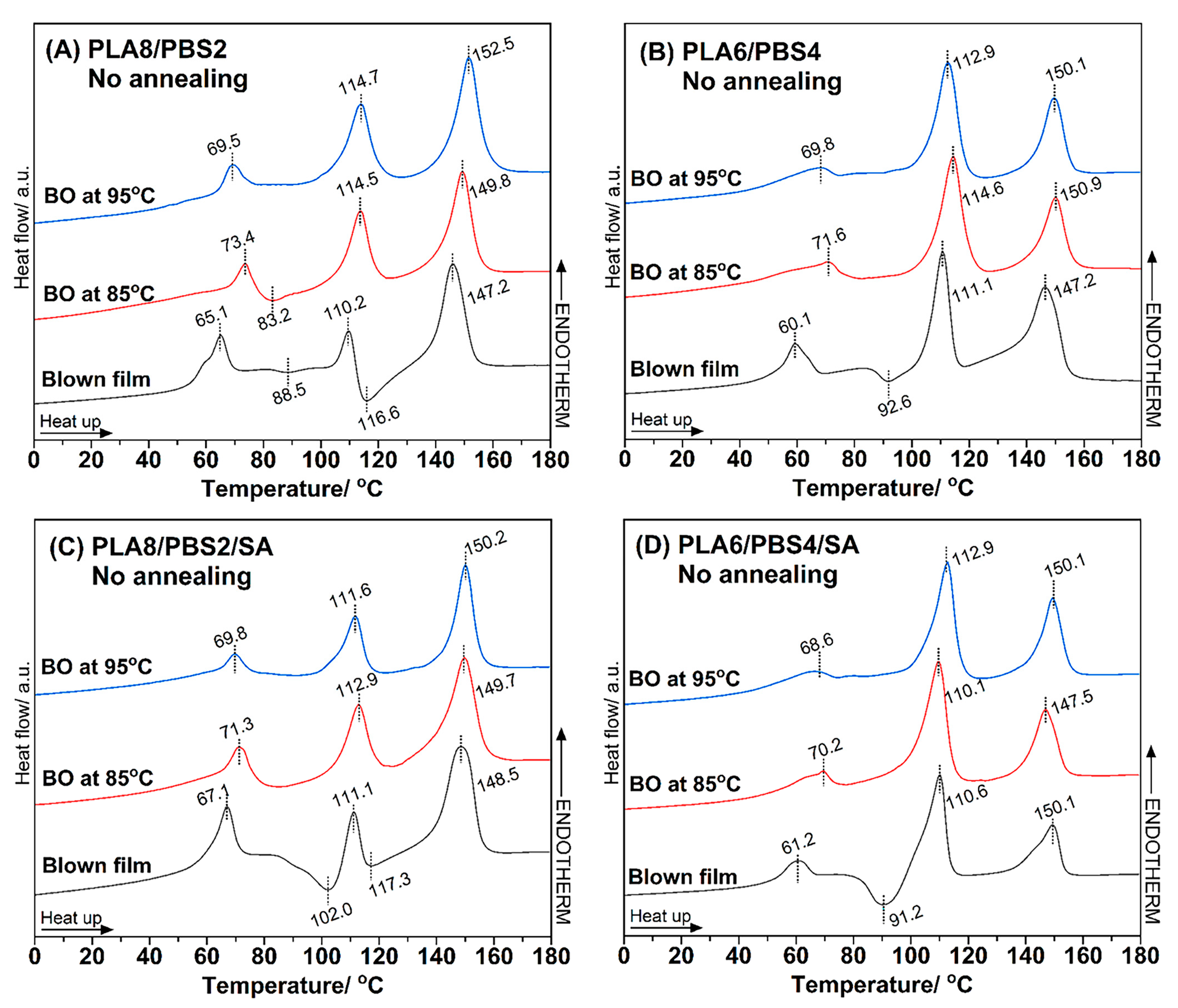
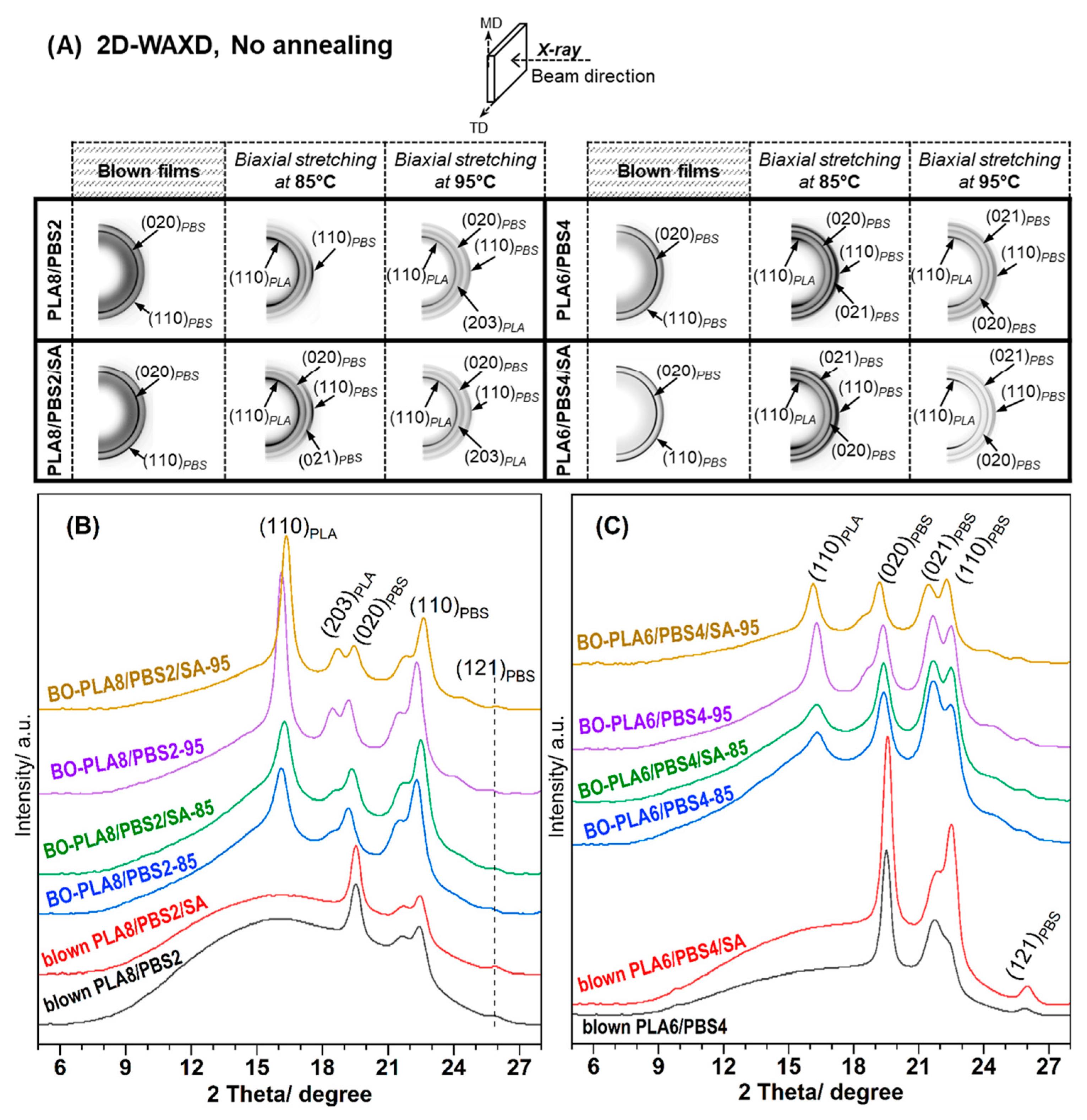
3.3.1. No Annealing Condition
3.3.2. Annealing Conditions
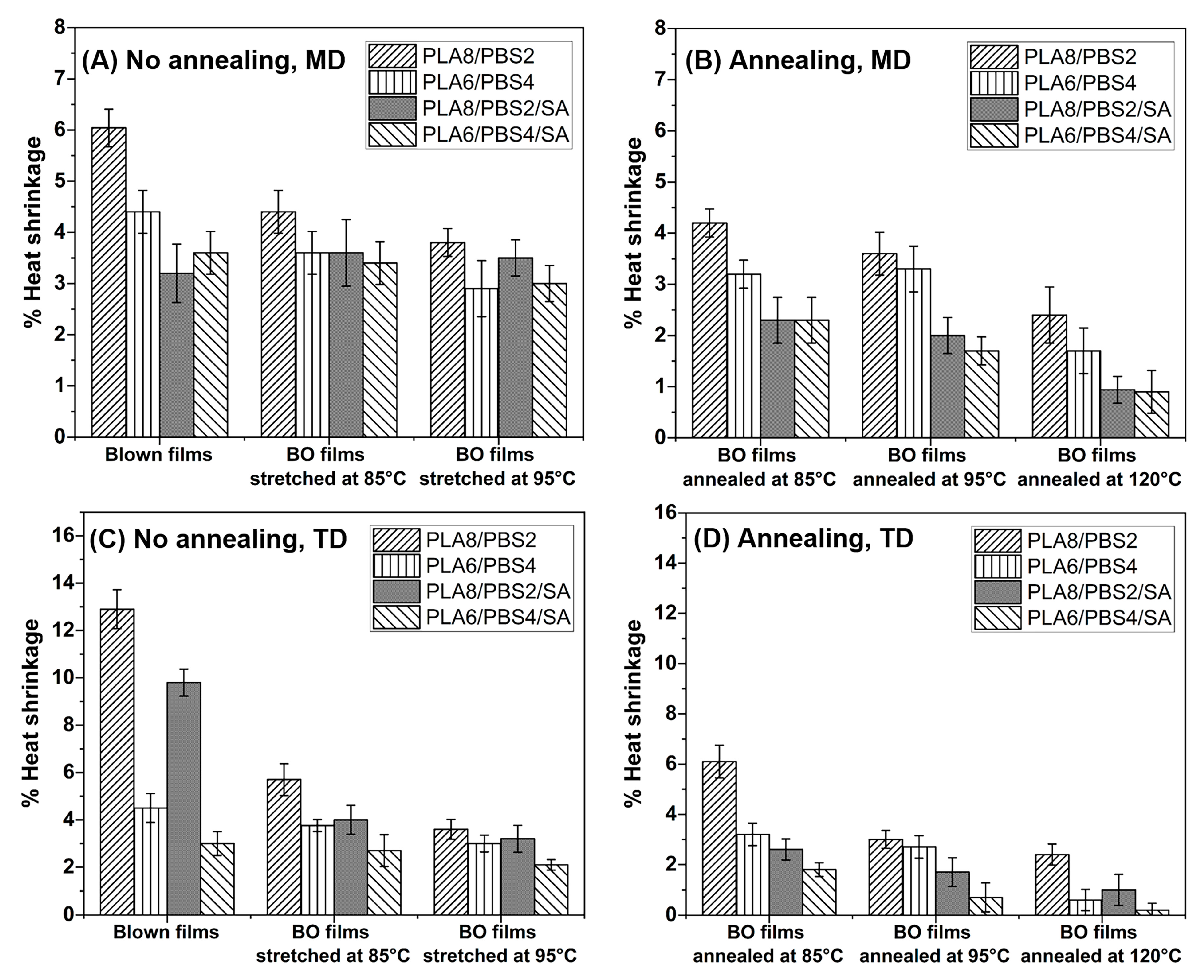
3.3.3. Thermal Shrinkage
3.4. Mechanical Properties and Oxygen Permeation of Biaxially Processed PLA/PBS and PLA/PBS/SA Thin Films
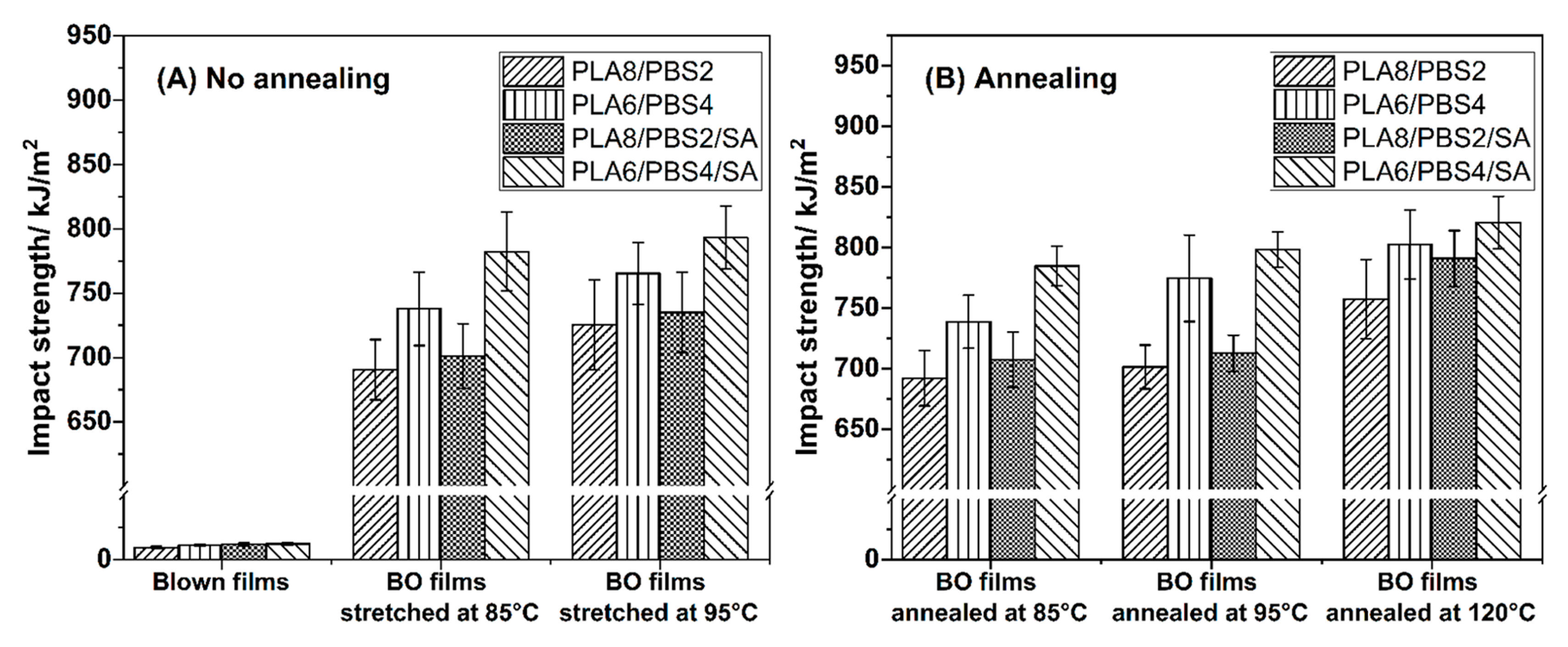
3.4.1. Impact Strength
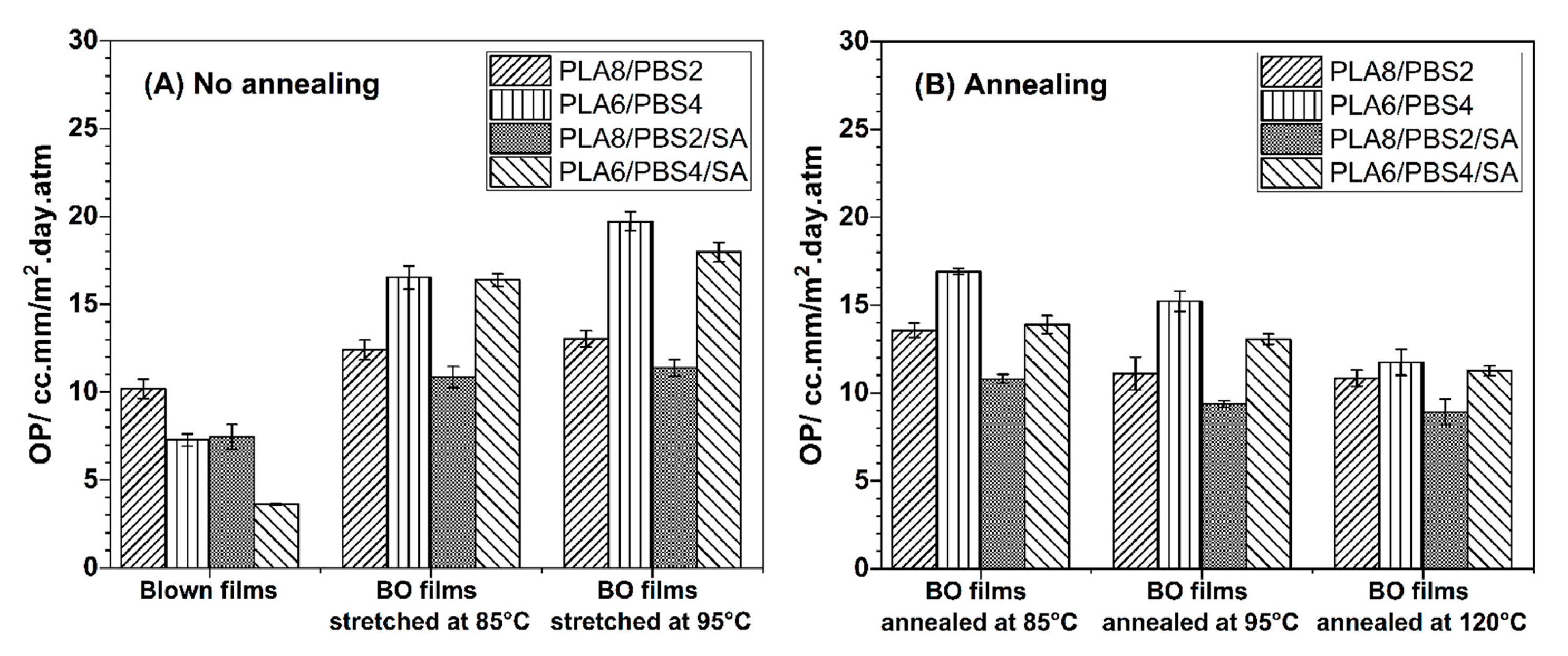
3.4.2. Oxygen Permeation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amulya, K.; Katakojwala, R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mohan, S.V. Low carbon biodegradable polymer matrices for sustainable future. Compos. Part C Open 2021, 4, e100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Leeke, G.A.; Moretti, C.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Mu, L.; et al. Replacing Traditional Plastics with Biodegradable Plastics: Impact on Carbon Emissions. Engineering 2024, 32, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, T.A.; Swetha, T.A.; Bora, A.; Mohanrasu, K.; Balaji, P.; Raja, R.; Ponnuchamy, K.; Muthusamy, G.; Arun, A. A comprehensive review on polylactic acid (PLA)–Synthesis, processing and application in food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, e123715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, D.H.; Ebrahimi, F. Synthesis, properties, and applications of polylactic acid-based polymers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 22–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Huang, C.; Xiu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Toughening of poly(l-lactide) with poly(ε-caprolactone): Combined effects of matrix crystallization and impact modifier particle size. Polymer 2013, 54, 5257–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostafinska, A.; Fortelný, I.; Hodan, J.; Krejčíková, S.; Nevoralová, M.; Kredatusová, J.; Kruliš, Z.; Kotek, J.; Šlouf, M. Strong synergistic effects in PLA/PCL blends: Impact of PLA matrix viscosity. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 69, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Rho, J.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Hwang, T.; Kim, K.J. Mechanical properties and cytotoxicity of PLA/PCL films. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2018, 8, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Kuo, M.T.; Chiang, T.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Wang, Y.H. Heat treatment effects on the mechanical properties and morphologies of poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 1, e951696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zou, B.; Ma, P.; Liu, W.; Zhou, X.; Shi, D.; Ni, Z.; Chen, M. Influence of phthalic anhydride and bioxazoline on the mechanical and morphological properties of biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/poly[(butylene adipate)-co-terephthalate] blends. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayshbeyn, L.I.; Mastalygina, E.E.; Olkhov, A.A.; Podzorova, M.V. Poly(lactic acid)-Based Blends: A Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, e5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, W.; Zhang, S.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Bian, J.; Zhang, H. Thermal, crystallization, and mechanical properties of polylactic acid (PLA)/poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) blends. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 2481–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, V.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Perspective on polylactic Acid (PLA) based sustainable materials for durable applications: Focus on toughness and heat resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2899–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.L. Poly(L-lactic Acid)/poly(butylene succinate) biobased biodegradable blends. Polym. Rev. 2021, 61, 457–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liang, X.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S. Strategies and techniques for improving heat resistance and mechanical performances of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) biodegradable materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 218, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokohara, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Structure and properties for biomass-based polyester blends of PLA and PBS. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yuan, L.; Laredo, E.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, W. Interfacial properties, viscoelasticity, and thermal behaviors of poly(butylene succinate)/polylactide blend. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Seo, H.J.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, J.; Lim, S.K. Effects of polybutylene succinate content on the rheological properties of polylactic acid/polybutylene succinate blends and the characteristics of their fibers. Materials 2024, 17, e662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Yu, S.; Zhou, H.; Peng, S. Recent advances in compatibility and toughness of poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate) blends. e-Polymers 2021, 21, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, C.; Ma, P. Toughening modification of PLLA/PBS blends via in situ compatibilization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cao, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Bao, J. Extraordinary toughness and heat resistance enhancement of biodegradable PLA/PBS blends through the formation of a small amount of interface-localized stereocomplex crystallites during melt blending. Polymer 2022, 262, e125454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, P.; Niu, D.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Ma, P. Biodegradable reactive compatibilizers for efficient in-situ compatibilization of poly (lactic acid)/poly (butylene adipate-terephthalate) blends. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, e130029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Reactive compatibilization: Formation of double-grafted copolymers by in situ binary grafting and their compatibilization effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 33091–33099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias da Silva, J.M.; Soares, B.G. Epoxidized cardanol-based prepolymer as promising biobased compatibilizing agent for PLA/PBAT blends. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, e106889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, H.; Pan, H.; Zhang, H.; Ran, X. Heat resistant and mechanical properties of biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate) blends crosslinked by polyaryl polymethylene isocyanate. Polym. Plast.Technol. 2018, 57, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Song, G.; Tang, G. Novel biodegradable polylactide/poly(butylene succinate) composites via cross-linking with methylene diphenyl diisocyanate. Polym. Plast. Technol. 2013, 52, 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetwarotai, W.; Maneechot, H.; Kalkornsurapranee, E.; Phusunti, N. Thermal behaviors and characteristics of polylactide/poly(butylene succinate) blend films via reactive compatibilization and plasticization. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwutthinan, P.; Leejarkpai, T.; Kashima, D.P.; Chuayjuljit, S. Poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate) blends filled with epoxy functionalised polymeric chain extender. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 664, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, B.; Bian, X.; Li, G.; Chen, X. High melt strength and high toughness PLLA/PBS blends by copolymerization and in situ reactive compatibilization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, J.; Pan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Bian, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, H. Super-tough polylactic acid (PLA)/poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) materials prepared through reactive blending with epoxy-functionalized PMMA-GMA copolymer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, e126150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Liu, Z.; Lan, X.; Wu, F.; Xie, B.; Yang, M. Morphology, rheology, crystallization behavior, and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate)/dicumyl peroxide reactive blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, e39580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimalanon, P.; Prapagdee, B.; Markpin, T.; Sombatsompop, N. Effects of DCP as a free radical producer and HPQM as a biocide on the mechanical properties and antibacterial performance of in situ compatibilized PBS/PLA blends. Polym. Test. 2018, 67, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Su, T.; Li, P.; Wang, Z. Blending modification of PBS/PLA and its enzymatic degradation. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariyasakoolroj, P.; Makyarm, K.; Klairasamee, K.; Sane, A.; Jarupan, L. Crystallization behavior analysis and reducing thermal shrinkage of poly(lactic acid) miscibilized with poly(butylene succinate) film for food packaging. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Yen, M.S.; Wu, C.P.; Li, C.H.; Kuo, M.C. Effect of biaxial stretching on thermal properties, shrinkage and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid) films. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariyasakoolroj, P.; Tashiro, K.; Wang, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Chinsirikul, W.; Kerddonfag, N.; Chirachanchai, S. Isotropically small crystalline lamellae induced by high biaxial-stretching rate as a key microstructure for super-tough polylactide film. Polymer 2015, 68, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchiar, S.; Stoclet, G.; Cabaret, C.; Addad, A.; Gloaguen, V. Effect of biaxial stretching on thermomechanical properties of polylactide based nanocomposites. Polymer 2016, 99, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Tahon, J.F.; De-Waele, I.; Stoclet, G.; Gaucher, V. Brittle-to-ductile transition of PLA induced by macromolecular orientation. Express Polym. Lett. 2020, 14, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Itry, R.; Lamnawar, K.; Maazouz, A.; Billon, N.; Combeaud, C. Effect of the simultaneous biaxial stretching on the structural and mechanical properties of PLA, PBAT and their blends at rubbery state. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 68, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mo, Z.; Cui, L.; Yu, C.; Zou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Tan, J. Effect of biaxial stretching on the microstructure evolution, optical, mechanical and oxygen barrier properties of biodegradable poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, e126976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions. Kolloid-Z. Z. Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correlo, V.M.; Boesel, L.F.; Bhattacharya, M.; Mano, J.F.; Neves, N.M.; Reis, R.L. Hydroxyapatite reinforced chitosan and polyester blends for biomedical applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2005, 290, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.L. The Scherrer formula for X-Ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Thomas, N.L. Blending poly(butylene succinate) with poly(lactic acid): Ductility and phase inversion effects. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 71, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supthanyakul, R.; Kaabbuathong, N.; Chirachanchai, S. Random poly(butylene succinate-co-lactic acid) as a multi-functional additive for miscibility, toughness, and clarity of PLA/PBS blends. Polymer 2016, 105, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Shi, J.; Ye, H.; Zhou, Q. Distinctive tensile properties of the blends of poly(l-lactic acid) (PLLA) and poly(butylene succinate) (PBS). J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Bai, Z.; Su, T.; Wang, Z. Selective enzymatic degradation and porous morphology of poly(butylene succinate)/poly(lactic acid) blends. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, W.; Nie, H.; Li, F.; He, X. Novel poly(butylene succinate-co-lactic acid) copolyesters: Synthesis, crystallization, and enzymatic degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, P.; Hong, J.; Liu, J.; Ji, J.; Chu, P.K. Copolymer P(BS-co-LA) enhanced compatibility of PBS/PLA composite. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilsouk, M.; Raihane, M.; Rhouta, B.; Meri, R.M.; Zicans, J.; Vecstaudža, J.; Lahcini, M. The relationship of structure, thermal and water vapor permeability barrier properties of poly(butylene succinate)/organomodified beidellite clay bionanocomposites prepared by in situ polycondensation. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37314–37326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, L. Multiple melting behavior of poly(butylene succinate). Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3163–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, M.C.; Di Lorenzo, M.L.; Cavallo, D.; Müller, A.J.; Gazzano, M. Structural evolution of poly(butylene succinate) crystals on heating with the formation of a dual lamellar population, as monitored by temperature-dependent WAXS/SAXS analysis. Polymer 2023, 268, e125711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Xiao, Y.J.; Duan, J.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.L. Accelerated hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactic acid) achieved by adding poly(butylene succinate). Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 1067–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariyasakoolroj, P.; Klairasamee, K.; Kumsang, P.; Phattarateera, S.; Kerddonfag, N. Effect of biaxial orientation on gas permeability and remarkably enhanced toughness of poly(butylene succinate)-based films. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 2551–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gan, Z.; Schultz, J.M.; Yan, S. A morphological study of poly(butylene succinate)/poly(butylene adipate) blends with different blend ratios and crystallization processes. Polymer 2008, 49, 2342–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivsa-Art, W.; Fujii, K.; Nomura, K.; Aso, Y.; Ohara, H.; Yamane, H. Isothermal crystallization kinetics of talc-filled poly(lactic acid) and poly(butylene succinate) blends. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.C.; Qu, J.P. Characterization of poly(butylene succinate)/poly(lactic acid) blends with in-situ sub-micron fibers and intercalation structure manufacturing by volumetric pulsating elongation flow. Polym. Test. 2019, 77, e105889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, Y.; Kojio, K. Crystallization behavior of biodegradable poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA)/poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) blends based on in situ simultaneous wide-angle x-ray diffraction/small-angle x-ray scattering techniques and thermal analyses. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajji, A.; Zhang, X.; Elkoun, S. Biaxial orientation in HDPE films: Comparison of infrared spectroscopy, X-ray pole figures and birefringence techniques. Polymer 2005, 46, 3838–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Liao, G.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Cui, L.; Liu, Y. Relaxation behavior of biaxially stretched PLA film during the heat setting stage. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, e1241104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shan, G.; Bao, Y.; Wang, W.; Pan, P. Stretch-induced crystalline structural evolution and cavitation of poly(butylene adipate-ran-butylene terephthalate)/poly(lactic acid) immiscible blends. Polymer 2020, 188, e122121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Huang, S.; Meng, Y.; Christiansen, J.; Yu, D.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, S. Thermal strain-induced cold crystallization of amorphous poly(lactic acid). Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2016, 18, 3237–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.L.; Cocca, M.; Malinconico, M. Crystal polymorphism of poly(L-lactic acid) and its influence on thermal properties. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 522, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, B.; Han, W.; Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Lin, J. Tailoring the thermal and mechanical properties of injection-molded poly (lactic acid) parts through annealing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e49648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, A.; Pantani, R. Poly(Lactic Acid): Flow-Induced Crystallization. In Thermal Properties of Bio-Based Polymers; Di Lorenzo, M.L., Androsch, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 87–117. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Deng, C.; Hong, R.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, J. Effect of thermal annealing on crystal structure and properties of PLLA/PCL blend. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkraled, L.; Zennaki, A.; Zair, L.; Arabeche, K.; Berrayah, A.; Barrera, A.; Bouberka, Z.; Maschke, U. Effect of plasticization/annealing on thermal, dynamic mechanical, and rheological properties of poly(lactic acid). Polymers 2024, 16, e974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Han, J.I.; Heo, J.W. Endotherm just above glass transition in uniaxially drawn poly(lactic acid)s films with various d-isomer contents. Polymer 2013, 54, 3624–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska, J.; Sadurski, W.; Paluch, M.; Tyński, P.; Bogusz, J. The effect of poly(butylene succinate) content on the structure and thermal and mechanical properties of its blends with polylactide. Polym. Int. 2019, 68, 271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrosanto, A.; Apicella, A.; Scarfato, P.; Incarnato, L.; Di Maio, L. Development of novel blown shrink films from poly(lactide)/poly(butylene-adipate-co-terephthalate) blends for sustainable food packaging applications. Polymers 2022, 14, e2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Wu, R.-J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Li, S.-C.; Siao, Y.-Y.; Kong, D.-C.; Jang, G.-W. Crystallinity and dimensional stability of biaxial oriented poly(lactic acid) films. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seier, M.; Archodoulaki, V.-M.; Koch, T.; Duscher, B.; Gahleitner, M. Polyethylene terephthalate based multilayer food packaging: Deterioration effects during mechanical recycling. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, e100890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Oliveros, R.; Balart, R.; Ivorra-Martinez, J.; Gomez-Caturla, J.; Montanes, N.; Quiles-Carrillo, L. Improvement of impact strength of polylactide blends with a thermoplastic elastomer compatibilized with biobased maleinized linseed oil for applications in rigid packaging. Molecules 2021, 26, e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Qu, J. Simultaneously achieving super toughness and reinforcement of immiscible high-density polyethylene/poly(ethylene terephthalate) composite via oriented spherical crystal structure. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 163, e107186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuniarto, K.; Wett, B.A.; Purwanto, A.; Purwadaria, H.K.; Abdellatief, A.; Sunarti, T.C.; Purwanto, S. Effect of plasticizer on oxygen permeability of cast polylactic acid (PLA) films determined using dynamic accumulation method. J. Appl. Packag. Res. 2014, 6, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, P.P.; Ni, S.H.; Xu, L.; Lin, H.; Zhong, G.J.; Huang, H.D.; Li, Z.M. Superior ductile and high-barrier poly(lactic acid) films by constructing oriented nanocrystals as efficient reinforcement of chain entanglement network and promising barrier wall. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 40, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drieskens, M.; Peeters, R.; Mullens, J.; Franco, D.; Lemstra, P.J.; Hristova-Bogaerds, D.G. Structure versus properties relationship of poly(lactic acid). I. Effect of crystallinity on barrier properties. J. Polym. Sci. 2009, 47, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample Code | Composition | BO Film Preparation Conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA (wt.%) | PBS (wt.%) | SA (phr) | Stretching Temperature (°C) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | |
| PLA8/PBS2 | 80 | 20 | - | - | - |
| PLA7/PBS3 | 70 | 30 | - | - | - |
| PLA6/PBS4 | 60 | 40 | - | - | - |
| PLA8/PBS2/SA | 80 | 20 | 5 | - | - |
| PLA7/PBS3/SA | 70 | 30 | 5 | - | - |
| PLA6/PBS4/SA | 60 | 40 | 5 | - | - |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-85 | 80 | 20 | - | 85 | - |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-85 | 60 | 40 | - | 85 | - |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-85 | 80 | 20 | 5 | 85 | - |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-85 | 60 | 40 | 5 | 85 | - |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-95 | 80 | 20 | - | 95 | - |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-95 | 60 | 40 | - | 95 | - |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-95 | 80 | 20 | 5 | 95 | - |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-95 | 60 | 40 | 5 | 95 | - |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-AN85 | 80 | 20 | - | 85 | 85 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-AN85 | 60 | 40 | - | 85 | 85 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-AN85 | 80 | 20 | 5 | 85 | 85 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-AN85 | 60 | 40 | 5 | 85 | 85 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-AN95 | 80 | 20 | - | 85 | 95 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-AN95 | 60 | 40 | - | 85 | 95 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-AN95 | 80 | 20 | 5 | 85 | 95 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-AN95 | 60 | 40 | 5 | 85 | 95 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-AN120 | 80 | 20 | - | 85 | 120 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-AN120 | 60 | 40 | - | 85 | 120 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-AN120 | 80 | 20 | 5 | 85 | 120 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-AN120 | 60 | 40 | 5 | 85 | 120 |
| Sample Code | DSC Thermograms | 1D-WAXD Patterns | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xc,PBS (%) | Xc,PLA (%) | Xc,WAXD (%) | <L>(020)PBS (nm) | <L>(021)PBS (nm) | <L>(110)PBS (nm) | |
| PLA8/PBS2 | 40.4 | 7.7 | 6.3 | 18.4 | - | 14.9 |
| PLA7/PBS3 | 40.7 | 9.0 | 7.9 | 16.0 | 6.2 | 17.9 |
| PLA6/PBS4 | 40.6 | 13.3 | 15.9 | 22.5 | 11.3 | 18.1 |
| PLA8/PBS2/SA | 36.8 | 7.9 | 7.6 | 17.2 | - | 20.6 |
| PLA6/PBS4/SA | 39.4 | 12.2 | 17.9 | 21.0 | 7.6 | 22.4 |
| Sample | DSC Thermograms | 1D-WAXD Patterns | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xc,PBS (%) | Xc,PLA (%) | Xc,WAXD (%) | <L>(110)PLA (nm) | <L>(203)PLA (nm) | <L>(020)PBS (nm) | <L>(021)PBS (nm) | <L>(110)PBS (nm) | |
| blown PLA8/PBS2 | 14.9 | 20.1 | 7.4 | - | - | 20.2 | 6.7 | 23.1 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-85 | 50.1 | 25.2 | 18.4 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 17.6 | 15.0 | 15.4 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-95 | 59.5 | 26.8 | 26.3 | 19.4 | 25.5 | 19.7 | 13.3 | 15.1 |
| blown PLA8/PBS2/SA | 23.6 | 20.2 | 7.8 | - | - | 23.0 | 11.7 | 18.2 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-85 | 43.2 | 32.1 | 18.8 | 12.6 | 13.5 | 18.1 | 12.7 | 13.0 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-95 | 59.4 | 34.1 | 29.1 | 19.8 | 19.2 | 16.7 | 15.4 | 18.5 |
| blown PLA6/PBS4 | 28.6 | 24.0 | 18.7 | - | - | 24.7 | 13.5 | 15.8 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-85 | 54.3 | 31.4 | 17.7 | 9.0 | - | 15.1 | 12.0 | 15.9 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-95 | 58.4 | 30.2 | 24.1 | 17.8 | 4.4 | 15.2 | 11.8 | 16.4 |
| blown PLA6/PBS4/SA | 30.7 | 23.4 | 23.6 | - | - | 19.7 | 6.7 | 23.1 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-85 | 55.5 | 30.1 | 20.6 | 8.7 | - | 16.3 | 11.6 | 15.7 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-95 | 63.6 | 34.7 | 25.3 | 18.1 | 5.7 | 16.3 | 13.4 | 17.6 |
| Sample | DSC Thermograms | 1D-WAXD Patterns | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xc,PBS (%) | Xc,PLA (%) | Xc,WAXD (%) | <L>(110)PLA (nm) | <L>(203)PLA (nm) | <L>(020)PBS (nm) | <L>(021)PBS (nm) | <L>(110)PBS (nm) | |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-AN85 | 39.7 | 21.5 | 21.0 | 14.4 | 14.9 | 17.4 | 15.2 | 15.4 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-AN95 | 54.3 | 27.1 | 25.5 | 17.7 | 16.0 | 20.7 | 15.6 | 16.5 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2-AN120 | 59.0 | 29.4 | 31.6 | 20.0 | 16.9 | 24.1 | 15.6 | 18.8 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-AN85 | 59.3 | 30.6 | 22.9 | 15.5 | 15.0 | 16.4 | 13.3 | 14.0 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-AN95 | 57.0 | 31.2 | 27.0 | 17.2 | 16.4 | 18.8 | 16.2 | 16.8 |
| BO-PLA8/PBS2/SA-AN120 | 52.6 | 31.2 | 32.9 | 20.7 | 17.8 | 23.7 | 15.8 | 19.1 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-AN85 | 62.0 | 30.1 | 20.4 | 12.6 | - | 14.0 | 12.3 | 15.7 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-AN95 | 62.2 | 30.3 | 22.5 | 15.9 | 5.0 | 18.8 | 12.9 | 16.0 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4-AN120 | 64.4 | 31.0 | 28.6 | 17.6 | 9.4 | 23.5 | 14.1 | 19.4 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-AN85 | 57.8 | 29.6 | 21.5 | 13.8 | - | 14.5 | 12.8 | 16.6 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-AN95 | 66.8 | 35.1 | 23.3 | 14.7 | 6.9 | 23.3 | 13.4 | 17.5 |
| BO-PLA6/PBS4/SA-AN120 | 61.7 | 33.6 | 32.9 | 16.9 | 8.3 | 31.7 | 11.1 | 22.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jariyasakoolroj, P.; Kumsang, P.; Phattarateera, S.; Kerddonfag, N. Enhanced Impact Resistance, Oxygen Barrier, and Thermal Dimensional Stability of Biaxially Processed Miscible Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) Thin Films. Polymers 2024, 16, 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213033
Jariyasakoolroj P, Kumsang P, Phattarateera S, Kerddonfag N. Enhanced Impact Resistance, Oxygen Barrier, and Thermal Dimensional Stability of Biaxially Processed Miscible Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) Thin Films. Polymers. 2024; 16(21):3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213033
Chicago/Turabian StyleJariyasakoolroj, Piyawanee, Pramote Kumsang, Supanut Phattarateera, and Noppadon Kerddonfag. 2024. "Enhanced Impact Resistance, Oxygen Barrier, and Thermal Dimensional Stability of Biaxially Processed Miscible Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) Thin Films" Polymers 16, no. 21: 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213033
APA StyleJariyasakoolroj, P., Kumsang, P., Phattarateera, S., & Kerddonfag, N. (2024). Enhanced Impact Resistance, Oxygen Barrier, and Thermal Dimensional Stability of Biaxially Processed Miscible Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) Thin Films. Polymers, 16(21), 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213033






