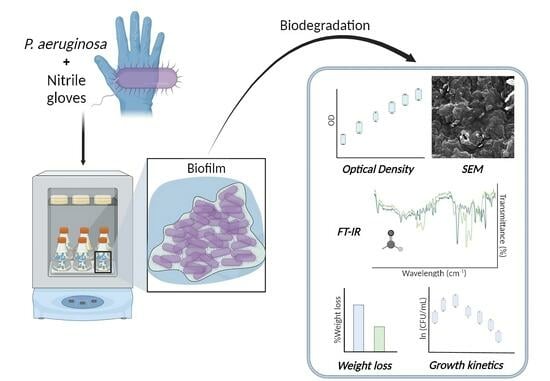
Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves as Sole Carbon Source of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Liquid Culture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Nitrile Glove Samples
2.2. P. aeruginosa Cultivation
2.3. Adaptation of P. aeruginosa with 1% (w/v) Nitrile Gloves
2.4. Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves at 3% and 5% (w/v)
2.5. Growth Kinetics of P. aeruginosa Using Nitrile Gloves as Sole Carbon Source
2.6. Optical Density (OD 600 nm) Data for Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves
2.7. Weight Loss of Nitrile Gloves
2.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.9. Microscopic Analysis of Surface Changes in Nitrile Gloves
2.10. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results
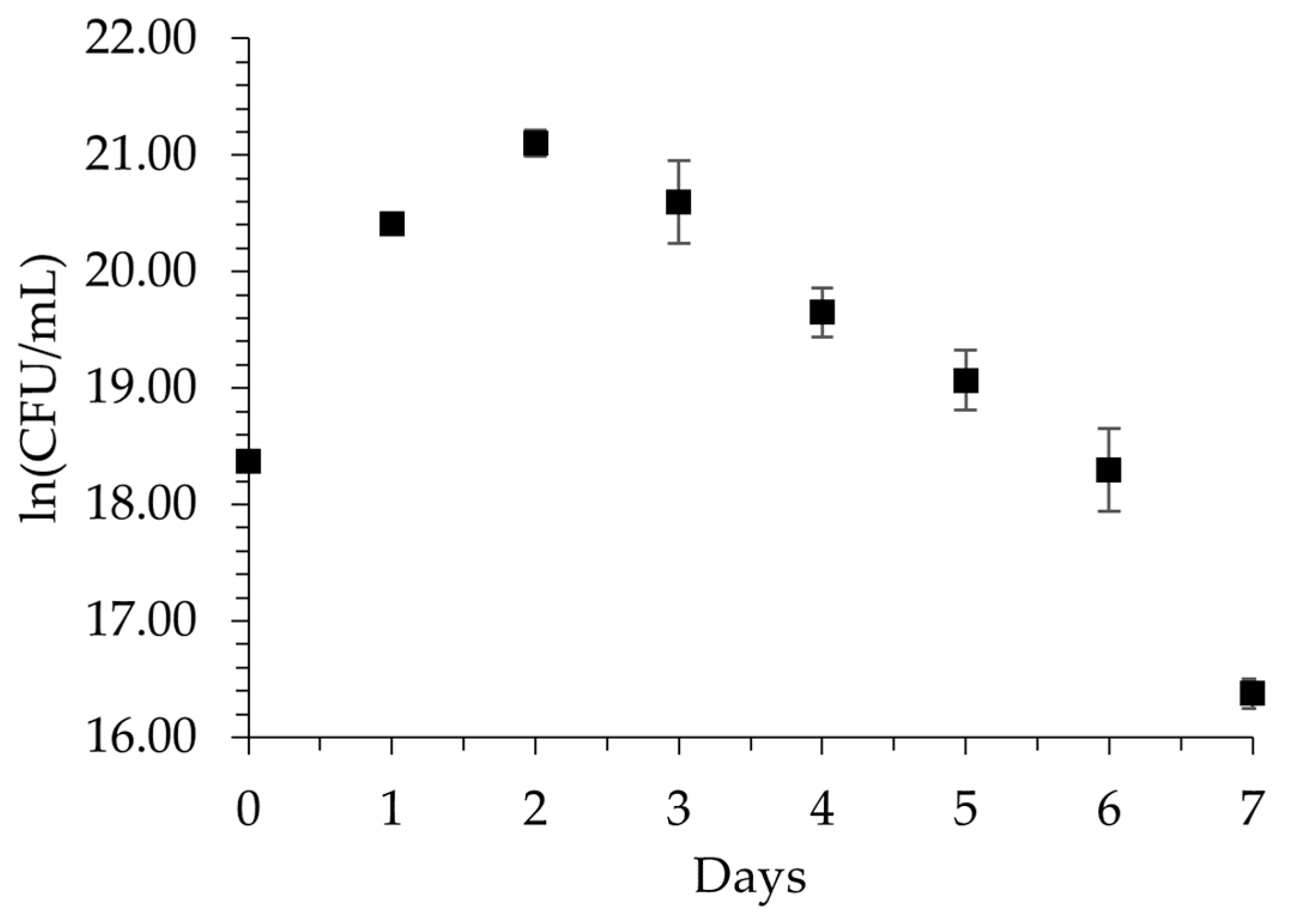
3.1. Growth Kinetics of P. aeruginosa Using Nitrile Gloves as Sole Carbon Source
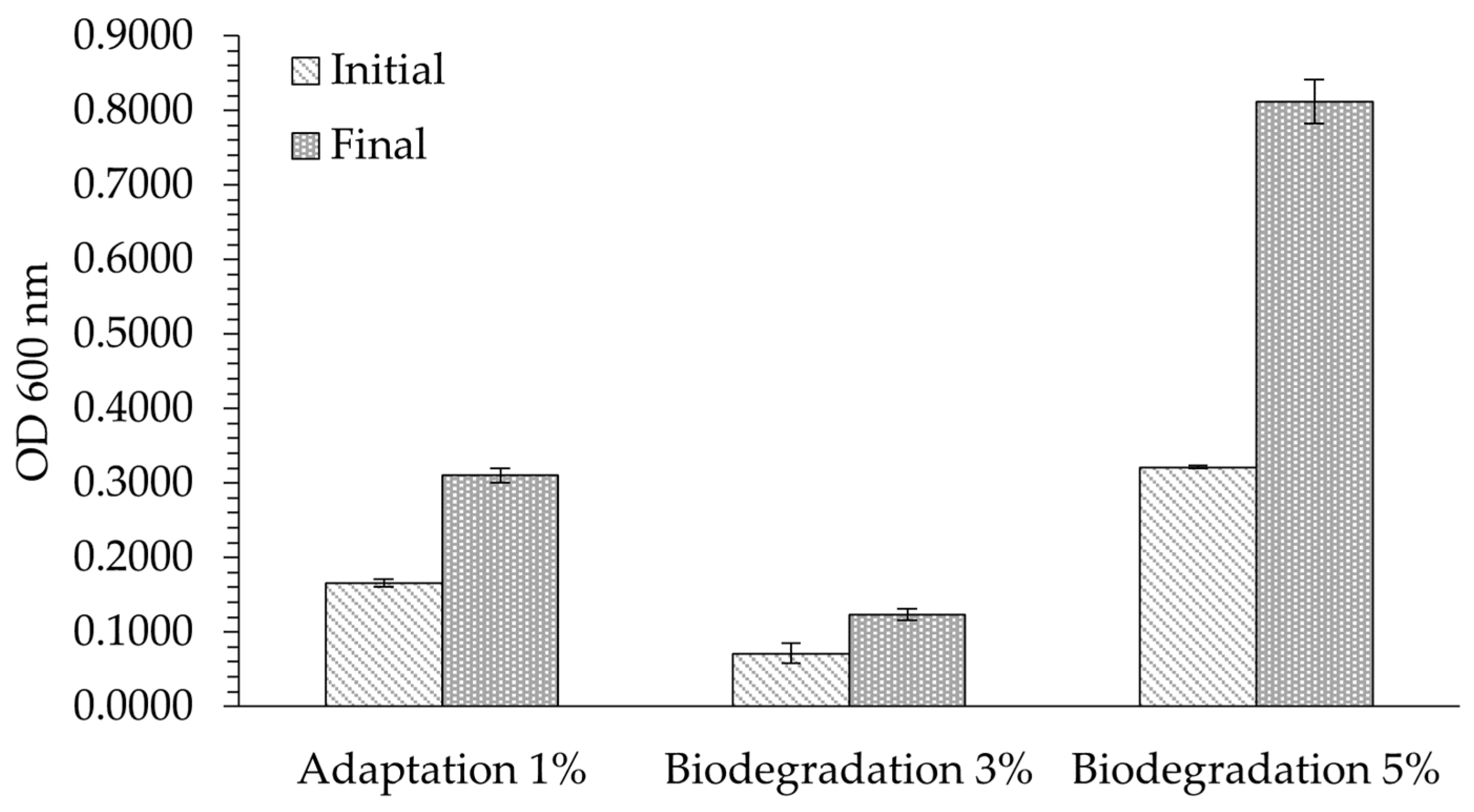
3.2. Optical Density (OD 600 nm) Data for Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves
3.3. Weight Loss of Nitrile Gloves
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
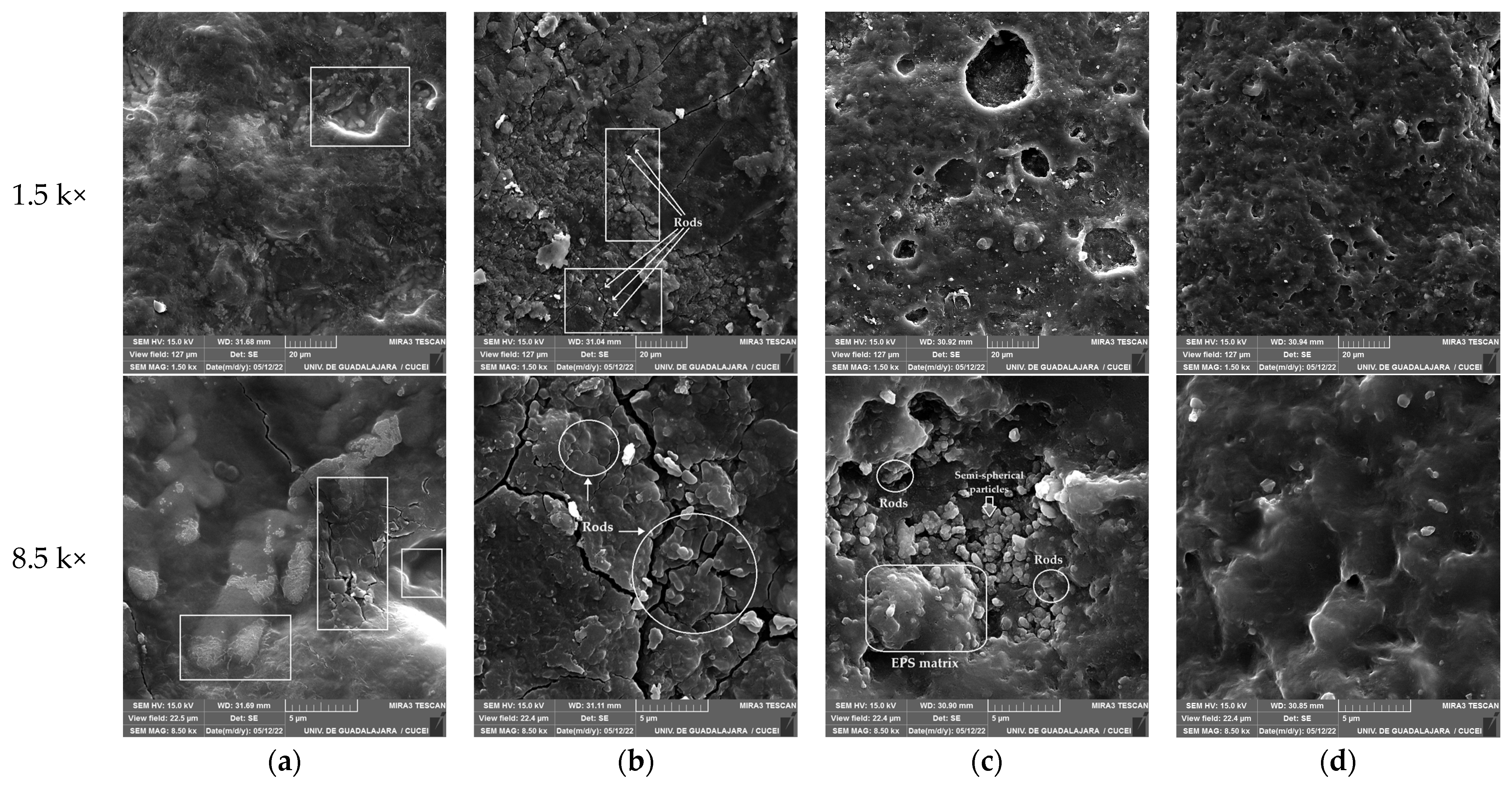
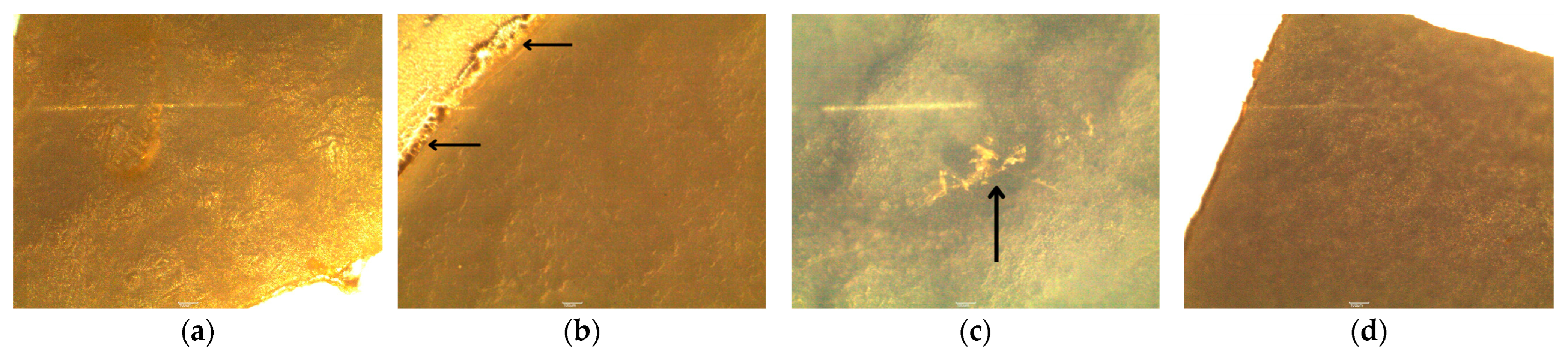
3.5. Microscopic Analysis of Surface Changes on Nitrile Gloves
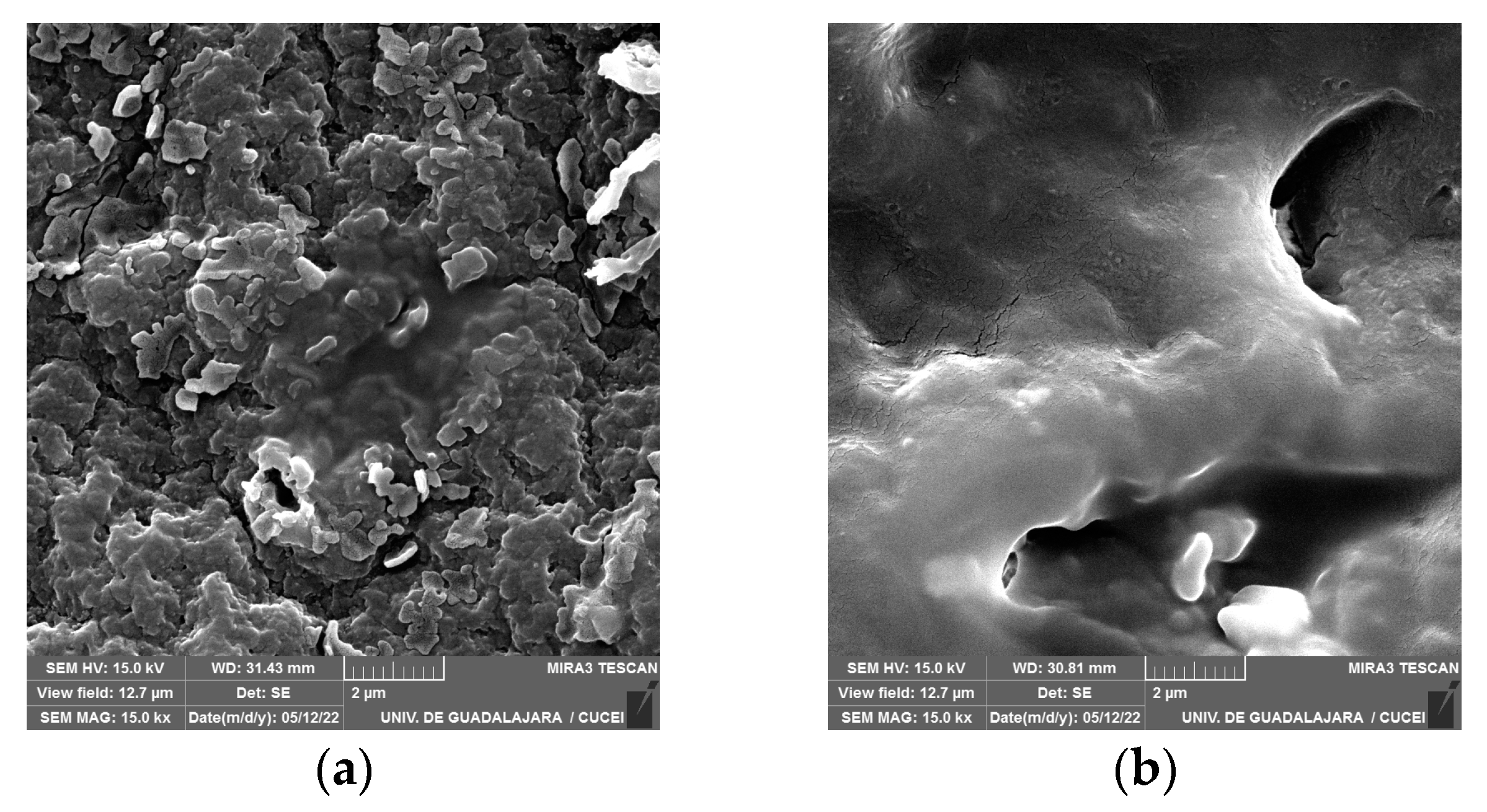
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jędruchniewicz, K.; Ok, Y.S.; Oleszczuk, P. COVID-19 Discarded Disposable Gloves as a Source and a Vector of Pollutants in the Environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 125938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, Z.H.; Teo, Y.Y.; Ang, D.T.C. Recent Development of Biodegradable Synthetic Rubbers and Bio-Based Rubbers Using Sustainable Materials from Biological Sources. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 34028–34052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilmartin-Lynch, S.; Roychand, R.; Saberian, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Application of COVID-19 Single-Use Shredded Nitrile Gloves in Structural Concrete: Case Study from Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayeemasae, N.; Masa, A.; Ahmad, H.S.; Shuib, R.K.; Ismail, H.; Surya, I. Sustainable Recycling of Waste from Nitrile Gloves: Prolonging the Life Span by Designing Proper Curing Systems. Polymers 2022, 14, 4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, J. Microplastics in Soils during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Sources, Migration and Transformations, and Remediation Technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Saberian, M.; Perera, S.T.A.M.; Roychand, R.; Li, J.; Wang, G. Reusing COVID-19 Disposable Nitrile Gloves to Improve the Mechanical Properties of Expansive Clay Subgrade: An Innovative Medical Waste Solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovato, M.J.; del Valle, L.J.; Puiggalí, J.; Franco, L. Performance-Enhancing Materials in Medical Gloves. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, B.R.; Lecka, J.; Pulicharla, R.; Brar, S.K. Microplastic Pollution and Associated Health Hazards: Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 34, 100480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrawoot, S.; Tran, T.; Arunchaiya, M.; Somsongkul, V.; Chisti, Y.; Hansupalak, N. Environmental Impacts of Examination Gloves Made of Natural Rubber and Nitrile Rubber, Identified by Life-cycle Assessment. SPE Polym. 2021, 2, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempel, G.L.; Wang, H. Nitrile Rubber Latex Blends: Preparation, Characterization and Applications. In Rubber Nano Blends; Markovic, G., Visakh, P.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 67–88. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.S.; Lu, Z.M.; Li, H.; Shi, J.S.; Zhou, Z.M.; Xu, Z.H. Nitrilases in Nitrile Biocatalysis: Recent Progress and Forthcoming Research. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, V.K.; Arfi, T.; Kumar, V.; Shukla, P. Bioengineering of Nitrilases Towards Its Use as Green Catalyst: Applications and Perspectives. Indian. J. Microbiol. 2017, 57, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pippo, F.; Bocci, V.; Amalfitano, S.; Crognale, S.; Levantesi, C.; Pietrelli, L.; Di Lisio, V.; Martinelli, A.; Rossetti, S. Microbial Colonization Patterns and Biodegradation of Petrochemical and Biodegradable Plastics in Lake Waters: Insights from a Field Experiment. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1290441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badoei-Dalfard, A.; Ramezani-Pour, N.; Karami, Z. Production and Characterization of a Nitrilase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa RZ44 and Its Potential for Nitrile Biotransformation. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shartooh, S.M.; Najeeb, L.M.; Sirhan, M.M. Biological Treatment of Carcinogenic Acrylonitrile Using Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Basra City. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 18, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Egelkamp, R.; Zimmermann, T.; Schneider, D.; Hertel, R.; Daniel, R. Impact of Nitriles on Bacterial Communities. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berekaa, M.M.; Linos, A.; Reichelt, R.; Keller, U.; Steinbüchel, A. Effect of Pretreatment of Rubber Material on Its Biodegradability by Various Rubber Degrading Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 184, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali Shah, A.; Hasan, F.; Shah, Z.; Kanwal, N.; Zeb, S. Biodegradation of Natural and Synthetic Rubbers: A Review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 83, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Mandal, S. Microbial Degradation of Natural and Synthetic Rubbers. In Microbial Bioremediation & Biodegradation; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–550. ISBN 9789811518126. [Google Scholar]
- Nawong, C.; Umsakul, K.; Sermwittayawong, N. Rubber Gloves Biodegradation by a Consortium, Mixed Culture and Pure Culture Isolated from Soil Samples. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatenh, E.; Gizaw, B.; Tsegaye, Z.; Wassie, M. The Role of Microorganisms in Bioremediation- A Review. Open J. Environ. Biol. 2017, 2, 38–046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.; Martínez, I.; Quer, A.; Fonseca, C.; Varrone, C. Microbial Degradation of Plastics: New Plastic Degraders, Mixed Cultures and Engineering Strategies. In Soil Microenvironment for Bioremediation and Polymer Production; Jamil, N., Kumar, P., Batool, R., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing: Salem, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 213–238. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, P.R.; McCulloch, J.A.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Lincopan, N. Pseudomonas: Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology: Second Edition; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 253–260. ISBN 9780123847331. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Li, X. Klebsiella Pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In Molecular Medical Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1547–1564. ISBN 9780123971692. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes, R.A.; Aristilde, L. Degradation and Metabolism of Synthetic Plastics and Associated Products by Pseudomonas sp.: Capabilities and Challenges. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The Biofilm Matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahto, K.U.; Das, S. Microscopic Techniques to Evaluate the Biofilm Formation Ability of a Marine Bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa PFL-P1 on Different Substrata. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2021, 84, 2451–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kiely, P.D.; Kibbee, R.; Ormeci, B. Effect of Polymeric Support Material on Biofilm Development, Bacterial Population, and Wastewater Treatment Performance in Anaerobic Fixed-Film Systems. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estepa Pedregosa, J. Degradación Bacteriana de Cianuro y Compuestos Nitrogenados Tóxicos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Córdoba, Córdoba, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Muriel-Millán, L.F.; Rodríguez-Mejía, J.L.; Godoy-Lozano, E.E.; Rivera-Gómez, N.; Gutierrez-Rios, R.M.; Morales-Guzmán, D.; Trejo-Hernández, M.R.; Estradas-Romero, A.; Pardo-López, L. Functional and Genomic Characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain Isolated From the Southwestern Gulf of Mexico Reveals an Enhanced Adaptation for Long-Chain Alkane Degradation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.M. Navneet Review on the Current Status of Polymer Degradation: A Microbial Approach. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2017, 4, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Kim, H.R.; Jeon, E.; Yu, H.C.; Lee, S.; Li, J.; Kim, D.H. Evaluation of the Biodegradation Efficiency of Four Various Types of Plastics by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from the Gut Extract of Superworms. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.V.; Das, M.; Banerjee, R.; Bhowmick, A.K. Comparative Studies on Crosslinked and Uncrosslinked Natural Rubber Biodegradation by Pseudomonas sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2485–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazer, Z.; Najafi, M.B.H.; Levin, D.B. Challenges with Verifying Microbial Degradation of Polyethylene. Polymers 2020, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, J.; Ruan, Y.; Cai, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H. Degradation of Polypropylene by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains LICME WZH-4 and WGH-6. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 3949–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.K.; Devi, D. Characteristics Investigation on Biofilm Formation and Biodegradation Activities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain ISJ14 Colonizing Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) Surface. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Xi, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, T.; Liu, T.; Qu, W.; Lin, Y.B. Biodegradability of Polyethylene Mulching Film by Two Pseudomonas Bacteria and Their Potential Degradation Mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tania, M.; Anand, V. The Implementation of Microbes in Plastic Biodegradation. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci. 2023. Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C.A.; Larcher, L.I.; Acosta, C.A.; Cardona, A.; Storti, M.; Zuppa San Luis, C. Determinación de Parámetros de Crecimiento de Microorganismos Usando Autómatas Celulares. Mecánica Comput. 2008, XXVII, 3283–3298. [Google Scholar]
- Thierie, J. A Method for Exploring Suspended Particles Interactions by Means of Optical Density Measurements: Application to Bacterial Floc and Solid Nutrients. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2014, 6, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, H.M.; Yu, H.C.; Jeon, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.H. Rapid Biodegradation of Polyphenylene Sulfide Plastic Beads by Pseudomonas sp. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corral Dávalos, L. Estadística y Técnicas Experimentales Para La Investigación Biológica, 1st ed.; Universidad Politécnica Salesiana: Quito, Ecuador, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vinches, L.; Hallé, S.; Peyrot, C.; Wilkinson, K.J. Which Gloves Are Efficient to Protect Against Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles In Work Conditions? Int. J. Theor. Appl. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, T.; Ogawa, T. Prediction of the Lifetime of Nitrile-Butadiene Rubber by FT-IR. Anal. Sci. 2005, 21, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gregoriou, A.G. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of Polymers. In Applied Polymer Science: 21st Century; Craver, C.D., Carraher, C.E., Jr., Eds.; Elsevier Science Ltd: Kidlington, UK, 2000; pp. 709–757. [Google Scholar]
- Pretsch, E.; Bühlmann, P.; Badertscher, M. Structure Determination of Organic Compounds: Tables of Spectral Data; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; ISBN 9783540938095. [Google Scholar]
- Mondragón Cortez, P. Espectroscopia de Infrarrojo Para Todos…y 51 Espectros de Alimentos Consumidos En México, 1st ed.; Centro de Investigación y Asistencia en Tecnología y Diseño del Estado de Jalisco, A.C.: Zapopan, México, 2017; ISBN 978-607-97548-4-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ammineni, S.P.; Nagaraju, C.; Raju, D.L. Modal Performance Degradation of Naturally Aged NBR. Polym. Test. 2022, 115, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.A. Biodegradation of Inorganic Nitrogen Compounds. In Biochemistry of Microbial Degradation; Ratledge, C., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 487–512. [Google Scholar]
- Debbarma, P.; Suyal, D.C.; Kumar, S.; Zaidi, M.G.H.; Goel, R. Comparative E-Waste Plastics Biodegradation Efficacy of Monoculture Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain PE10 and Bacterial Consortium under in Situ Condition. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1277186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpa; Basak, N.; Meena, S.S. Biodegradation of Low-Density Polythene (LDPE) by a Novel Strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa WD4 Isolated from Plastic Dumpsite. Biodegradation 2023. Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.; Niese, B.; Redman, W.; Vanderpool, E.; Gordon, V.; Rumbaugh, K.P. Contribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Exopolysaccharides Pel and Psl to Wound Infections. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 835754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichhardt, C. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Matrix Protein CdrA Has Similarities to Other Fibrillar Adhesin Proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2023, 205, e0001923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarian-Saravi, N.; Basar, I.A.; Margoto, O.H.; Abdollahi, G.N.; Crawford, B.; Magel, B.; Gharibnavaz, M.; Eskicioglu, C.; Milani, A.S. Characterization of the Mechanical, Biodegradation, and Morphological Properties of NBR/Biopolymer Blend, Integrated with a Risk Evaluation. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 9256–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoodley, P.; Toelke, N.; Schwermer, C.; de Beer, D. Bioenergetics of Simultaneous Oxygen and Nitrate Respiration and Nitric Oxide Production in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Agar Colony Biofilm. Biofilm 2024, 7, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemke, A.C.; D’Amico, E.J.; Torres, A.M.; Carreno-Florez, G.P.; Keeley, P.; DuPont, M.; Kasturiarachi, N.; Bomberger, J.M. Bacterial Respiratory Inhibition Triggers Dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0110123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.; Golia, V.; Overland, M.; Stoller, M.; Chatterjee, K. Mechanobactericidal Nanotopography on Nitrile Surfaces toward Antimicrobial Protective Gear. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


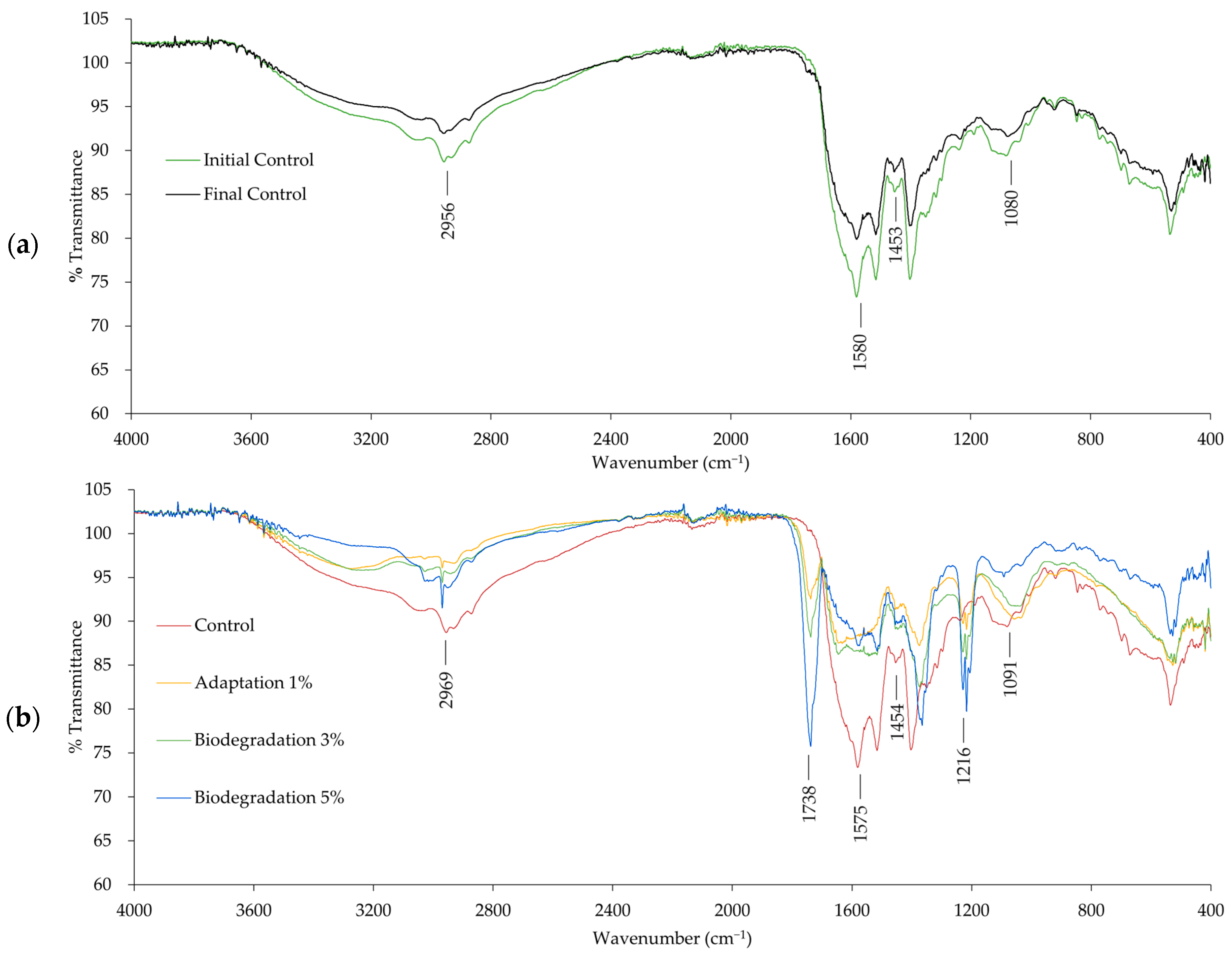

| FT-IR Peak (cm−1) | Region (cm−1) | Functional Group | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2969 | 3000–2840 | Alkane (C-H stretch) | [18,33,45,46,47] |
| 1575 | 1560–1640 | Primary amine (N-H) | |
| 1454 | 1475–1450 | Alkane (C-H bend) | |
| 1092 | 1020–1220 | Aliphatic amines (C-N) | |
| 1738 | 1720–1740 | Aldehydes (C=O) | |
| 1216 | 1020–1220 | Aliphatic amines (C-N) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delgado-Nungaray, J.A.; Grajeda-Arias, D.; Reynaga-Delgado, E.; Gonzalez-Reynoso, O. Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves as Sole Carbon Source of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Liquid Culture. Polymers 2024, 16, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081162
Delgado-Nungaray JA, Grajeda-Arias D, Reynaga-Delgado E, Gonzalez-Reynoso O. Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves as Sole Carbon Source of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Liquid Culture. Polymers. 2024; 16(8):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081162
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelgado-Nungaray, Javier Alejandro, David Grajeda-Arias, Eire Reynaga-Delgado, and Orfil Gonzalez-Reynoso. 2024. "Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves as Sole Carbon Source of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Liquid Culture" Polymers 16, no. 8: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081162
APA StyleDelgado-Nungaray, J. A., Grajeda-Arias, D., Reynaga-Delgado, E., & Gonzalez-Reynoso, O. (2024). Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves as Sole Carbon Source of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Liquid Culture. Polymers, 16(8), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081162