Effect of Ultra-High Temperature Degradation on the Physical Properties and Chemical Structure of an AMPS-Based Copolymer Oil-Well Cement Additive PADIM in Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.1.1. Materials
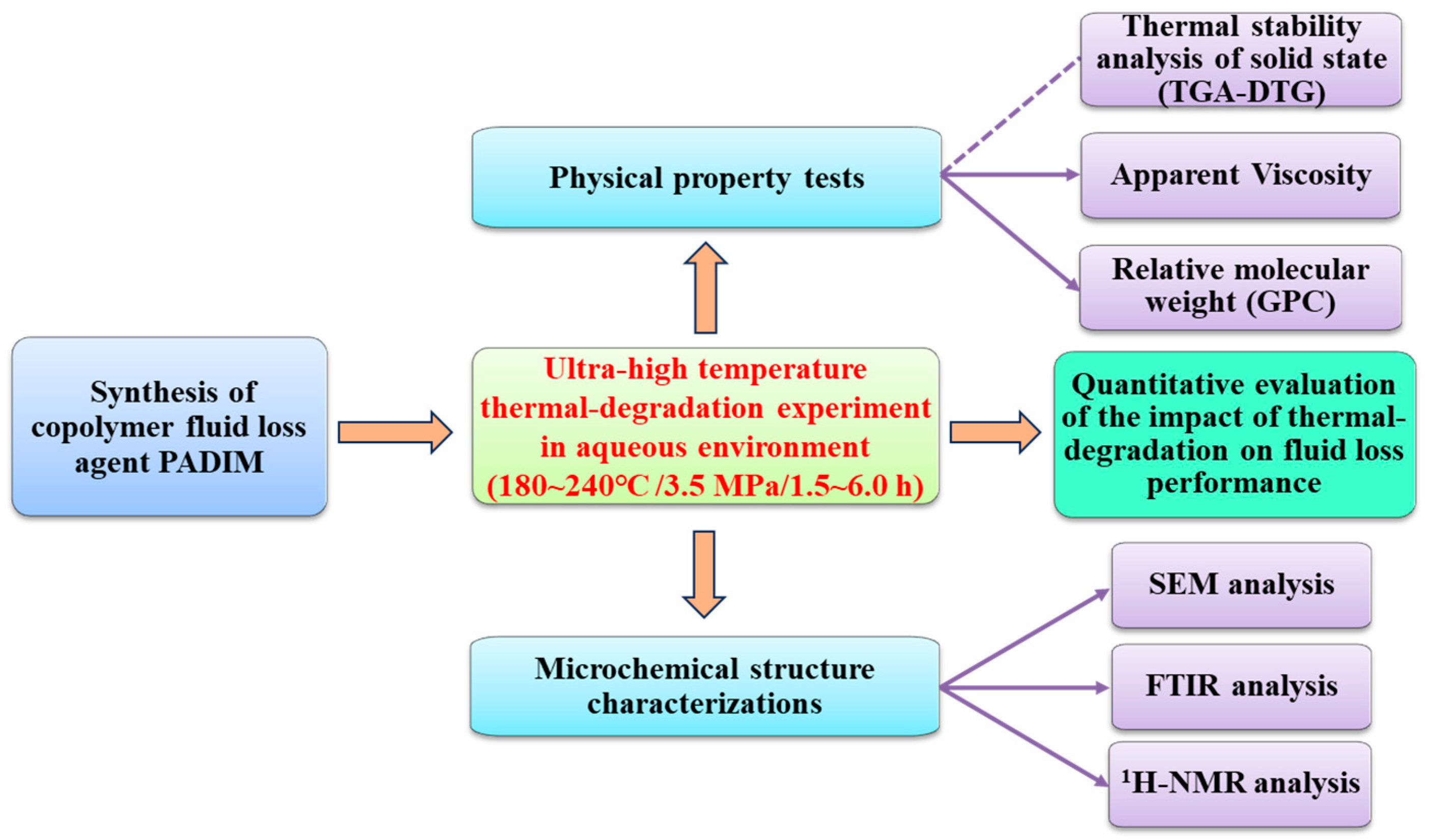
2.1.2. Research Methodology
2.2. Tests and Characterizations
2.2.1. Synthesis of the Copolymer PADIM
2.2.2. Ultra-High Temperature Thermal Degradation Experiments
2.2.3. Physical Property Tests
2.2.4. Microchemical Characterizations
2.2.5. Static Fluid Loss Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evolution Mechanism of Physical Properties
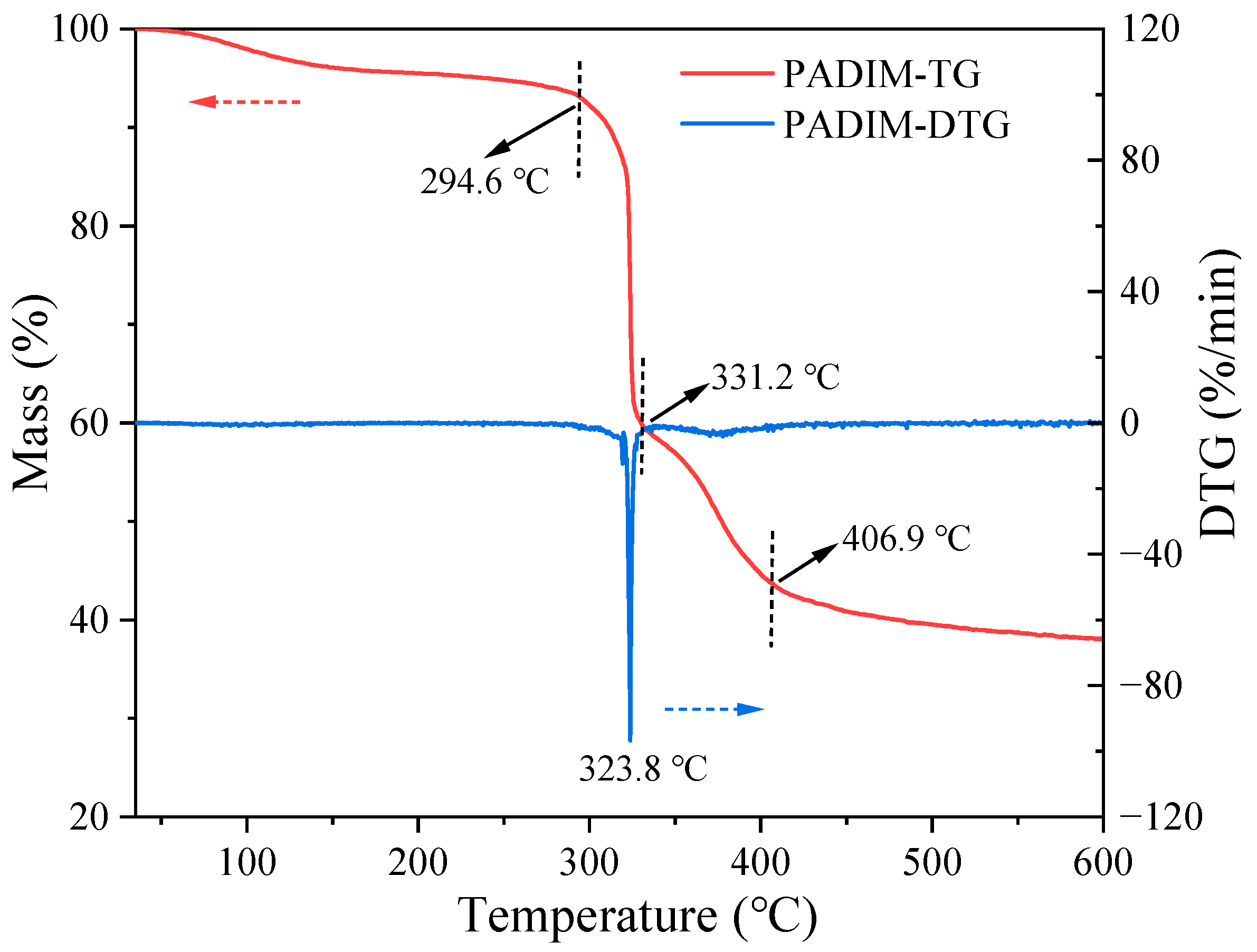
3.1.1. Thermal Stability Analysis
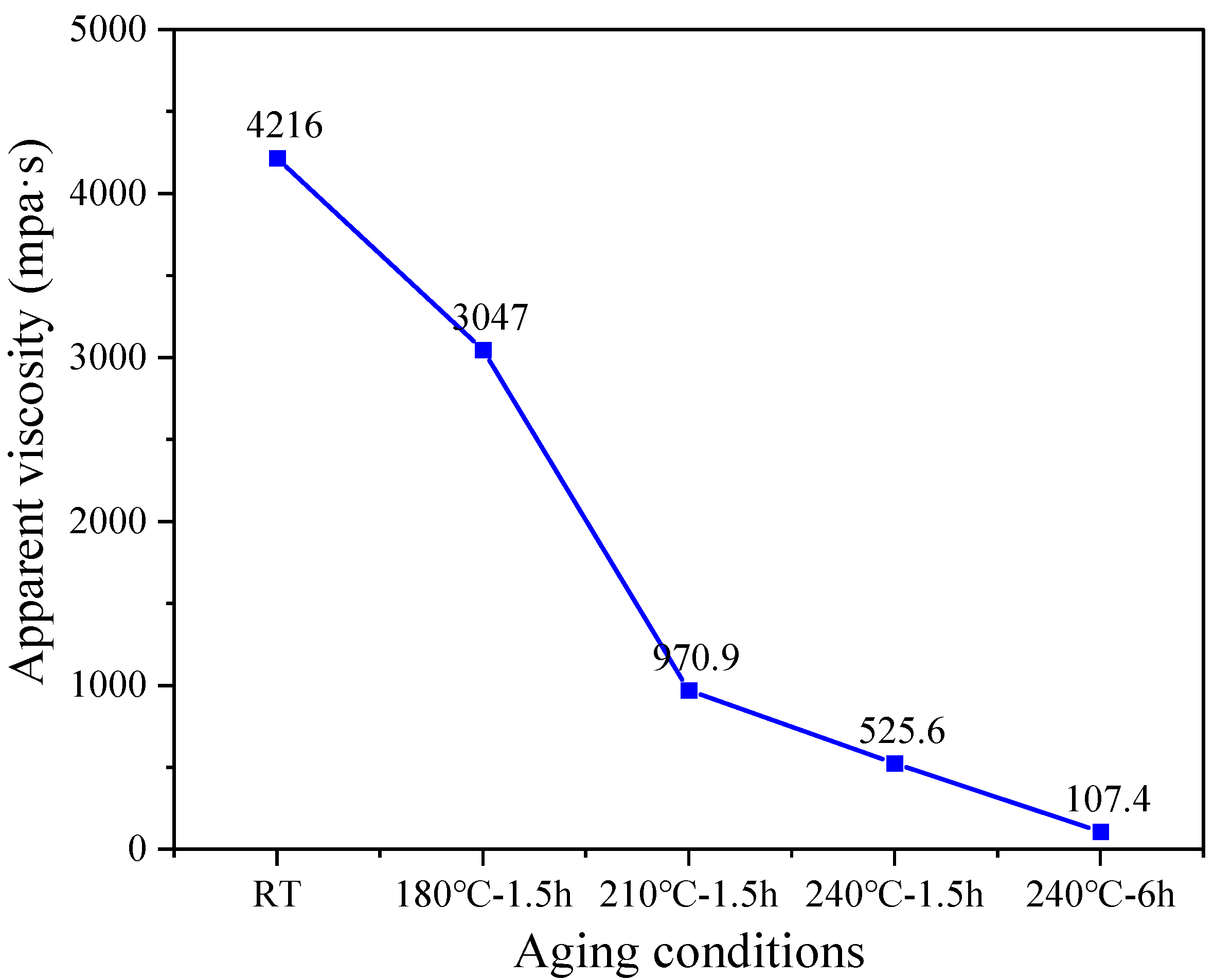
3.1.2. Apparent Viscosity Analysis
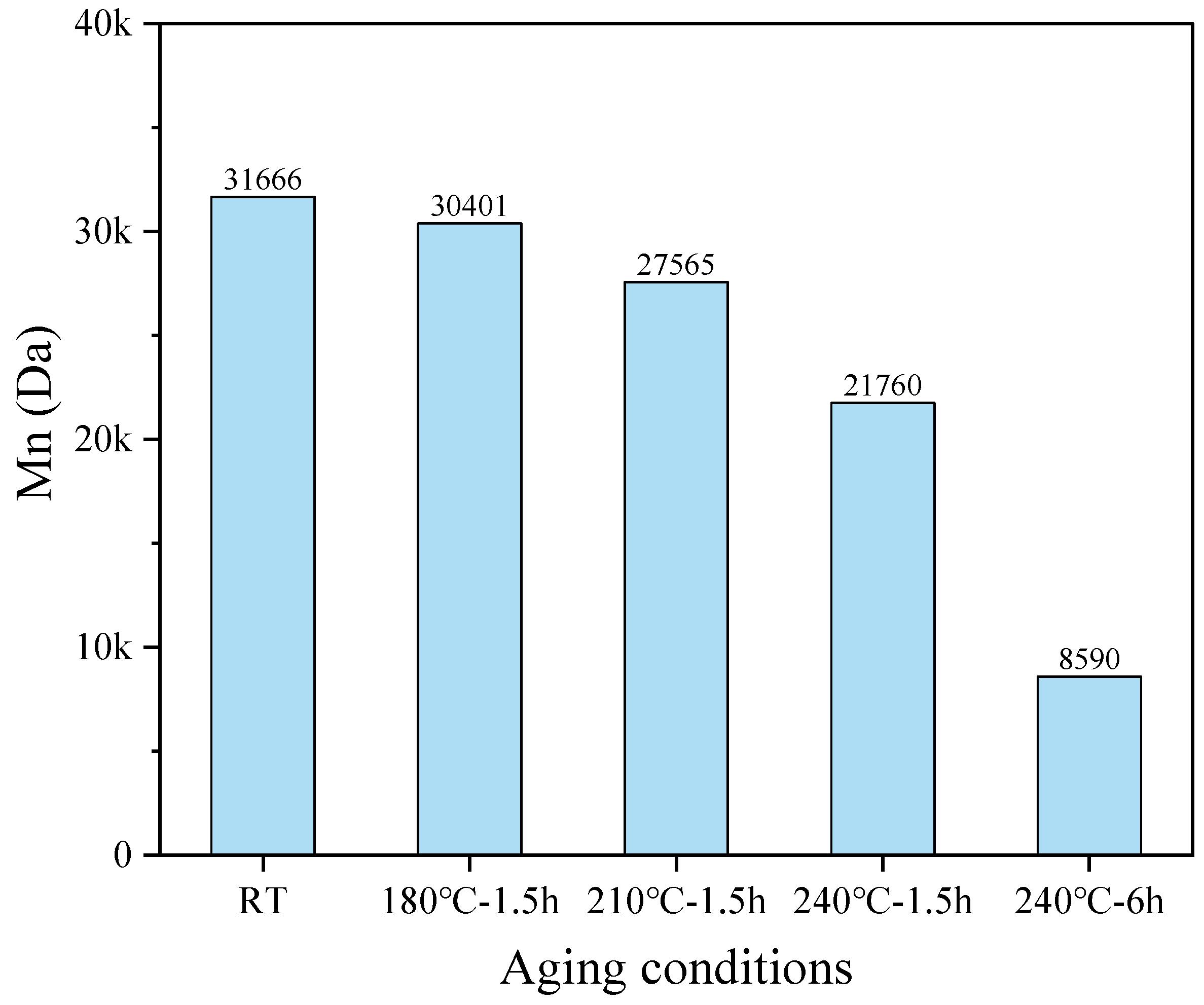
3.1.3. Relative Molecular Weight (Mn) Analysis
3.2. Evolution Mechanism of Microchemical Structure
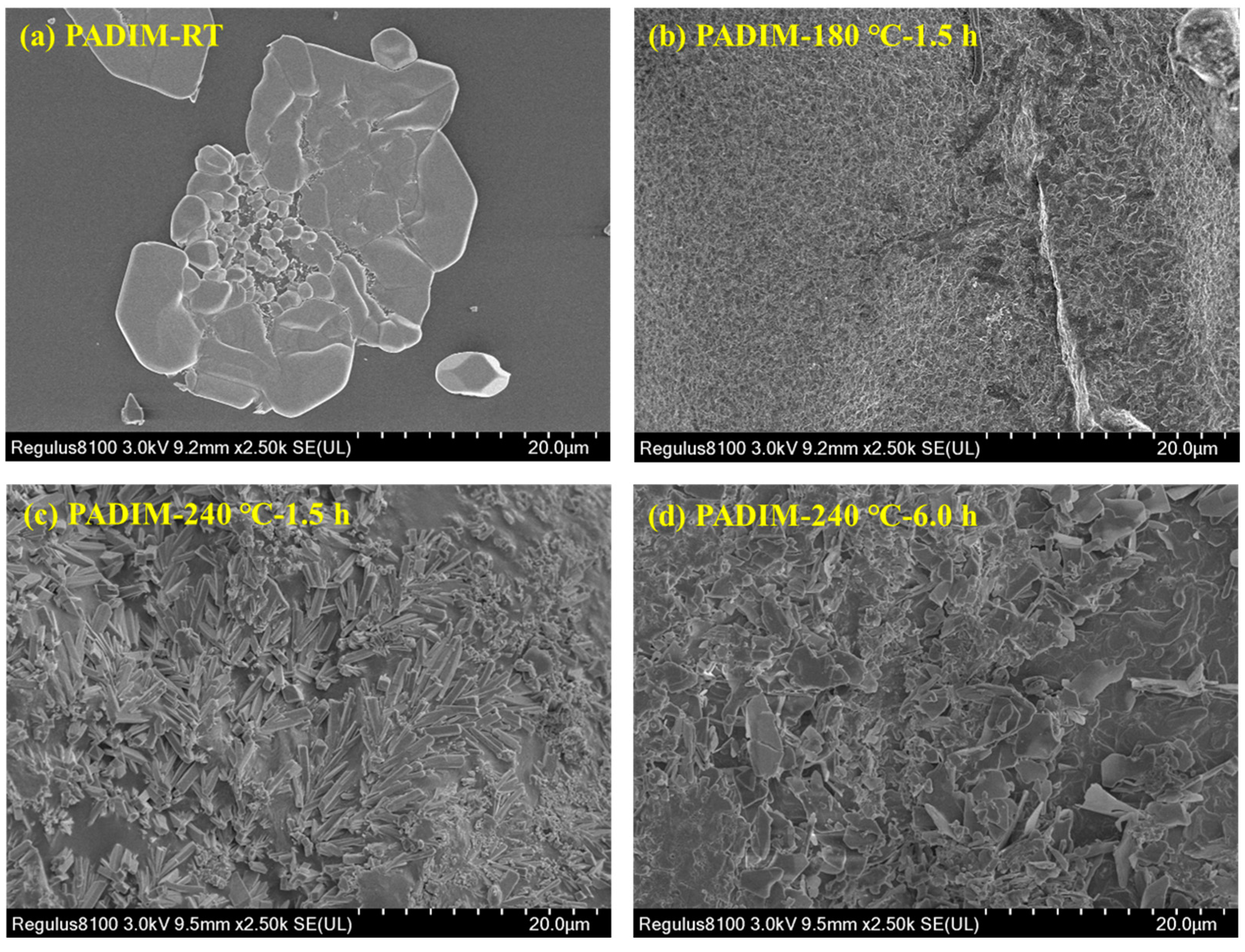
3.2.1. SEM Micro-Morphology Analysis
3.2.2. FTIR Analysis
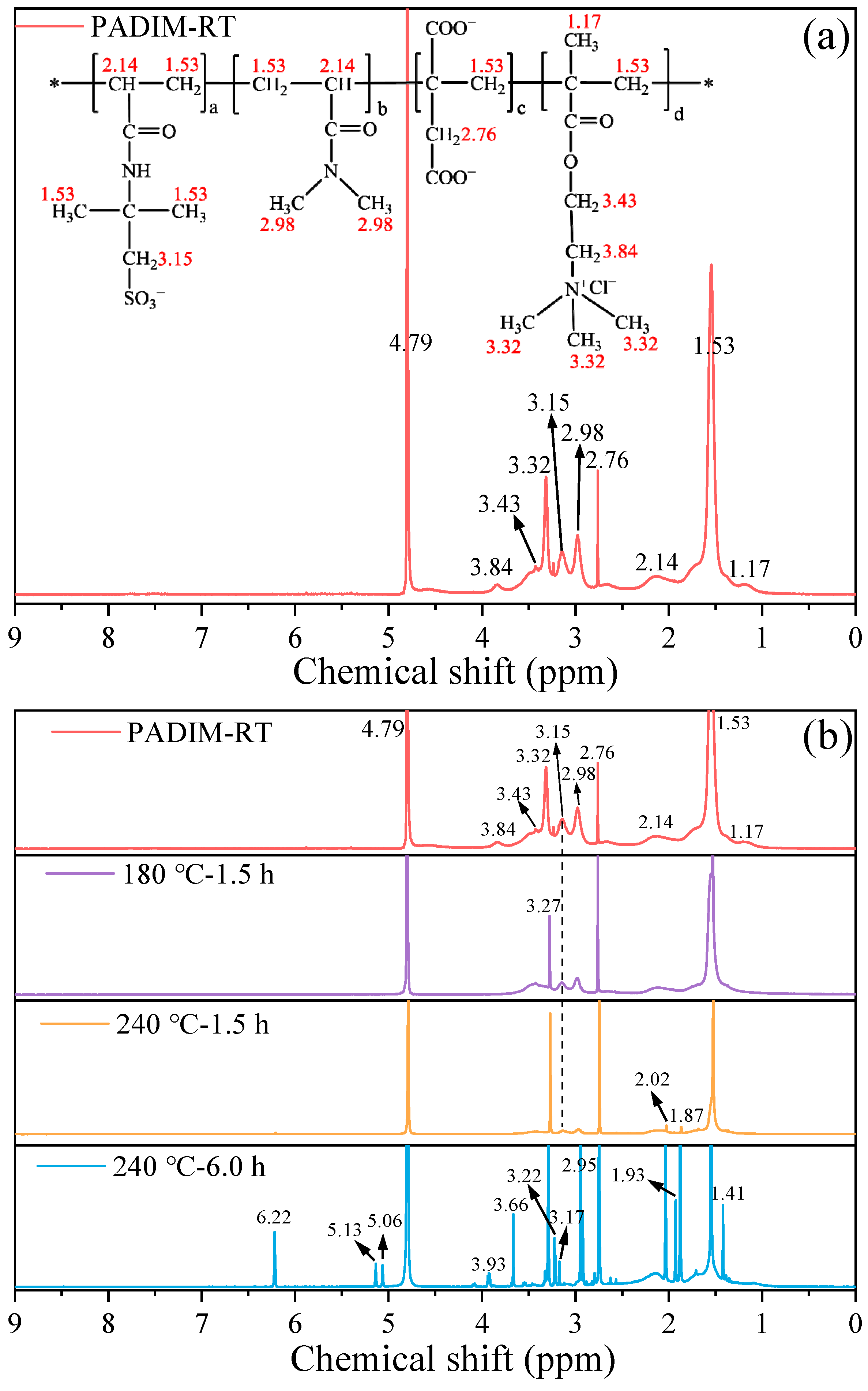
3.2.3. 1H-NMR Analysis
3.3. Evolution Tendency of Fluid Loss Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, D.; Jia, C.; Zhao, W.; Xu, F.; Luo, X.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y.; Gao, S.; Zheng, X.; Li, D.; et al. Research progress and key issues of ultra-deep oil and gas exploration in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, O.T.; Plank, J. Preparation and properties of a dispersing fluid loss additive based on humic acid graft copolymer suitable for cementing high temperature (200 °C) oil wells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2544–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, R.; Sun, J.; Qu, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, L. Comb polymer/layered double hydroxide (LDH) composite as an ultrahigh temperature filtration reducer for water-based drilling fluids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 645, 158884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Liu, G.; Dong, Z.; Miao, X.; Hu, M.; Guo, J. Effect of poly(AMPS/DMAA/IA/SSS) intercalated Mg/Al layered double hydroxides on reducing fluid loss at 240 °C and improving early strength of oil well cement. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 229, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, C.; Hu, M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, M.; Xia, X.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, J. Nanosilica interface graft copolymer for improving the suspension stability and filtration performance of oil-well cement slurry. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 404, 124894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Brandl, A.; Lummer, N.R. Effect of different anchor groups on adsorption behavior and effectiveness of poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-Ca 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonate) as cement fluid loss additive in presence of acetone-formaldehyde-sulfite dispersant. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 3889–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemeyer, C.; Plank, J. Synthesis, characterization, and working mechanism of a synthetic high temperature (200 °C) fluid loss polymer for oil well cementing containing allyloxy-2-hydroxy propane sulfonic (AHPS) acid monomer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.Y.; Li, M.; Xie, D.B. Salt-Tolerance Performance of Oil Well Cement Fluid Loss Additive SSS/HAM/IA. Mater. Sci. Forum 2020, 993, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Feng, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, S.; Jin, J.; Yu, Y. Zwitterionic copolymer for controlling fluid loss in Oilwell cementing: Preparation, characterization, and working mechanism. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017, 57, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xie, D.; Guo, Z.; Lu, Y.; Guo, X. A Novel Terpolymer as Fluid Loss Additive for Oil Well Cement. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017, 3940394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülichen, D.; Plank, J. Role of colloidal polymer associates for the effectiveness of hydroxyethyl cellulose as a fluid loss control additive in oil well cement. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, E25–E34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Zheng, L.; Ji, D.; Yi, Y.; Fan, C.; Ding, F.; Lai, Z. Preparation and evaluation of fluid loss reducer of heat-resistant and environment friendly modified starch. J. China Univ. Petroleum. Ed. Natrual Sci. 2010, 35, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, P.; Guo, J. Synthesis and working mechanism of fluid loss additive by freeze-drying method. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Lv, K.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J. Hydrophobic-associated polymer-based laponite nanolayered silicate composite as filtrate reducer for water-based drilling fluid at high temperature. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 137, 48608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Luo, X.; Yu, X.; Han, W.; Luo, Y. Synthesis and performance evaluation of a micron-size silica-reinforced polymer microsphere as a fluid loss agents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 130, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.B.; Mathad, S.N.; Patil, A.Y.; Khan, A.; Hussein, M.A.; Alosaimi, A.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Manikandan, A.; Khan, M.M.A. Functional Properties of Grapefruit Seed Extract Embedded Blend Membranes of Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Starch: Potential Application for Antiviral Activity in Food Safety to Fight Against COVID-19. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 31, 2519–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, M.; Hunasikai, S.G.; Mathad, S.N.; Patil, A.Y.; Hegde, C.G.; Sudeept, M.A.; Amshumali, M.K.; Elgorban, A.M.; Wang, S.; Wong, L.S.; et al. Enhanced O2/N2 separation by QuaternizedMatrimid/Multiwalled carbon nanotube mixed-matrix membrane. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoodi, S.; Al-Shargabi, M.; Wood, D.A.; Rukavishnikov, V.S. Recent advances in polymers as additives for wellbore cementing applications: A review. Fuel 2024, 357, 129692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Pu, X.; Wang, X. Synthesis, characterization, and performance evaluation of the AM/AMPS/DMDAAC/SSS quadripolymer as a fluid loss additive for water-based drilling fluid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Jin, J.; Yu, Y. The novel fluid loss additive HTF-200C for oil field cementing. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2012, 39, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, M.; Li, P.; Liu, M.; Yu, Y.; Xia, X.; Liu, H.; Guo, J. Covalently bonded AMPS-based copolymer-C-S-H hybrid as a fluid loss additive for oilwell saline cement slurry in UHT environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 378, 131177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, P.; Jin, J.; Yu, Y. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of a copolymer used as fluid loss additive in oil well cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurnaus, T.; Plank, J. Synthesis, characterization and performance of a novel phosphate-modified fluid loss additive useful in oil well cementing. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2016, 36, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Guo, J.; Feng, Y.; Chen, D.; Yu, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, S. Hydrophobic associated polymer “grafted onto” nanosilica as a multi-functional fluid loss agent for oil well cement under ultrahigh temperature. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 91728–91740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Jiang, G.; He, Y. New structure found in a filter cake with the addition of an amphoteric polymer fluid loss additive. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Xue, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jin, J.; Wang, R. A novel thermo-thickening viscosity modifying admixture to improve settlement stability of cement slurry under high temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ran, Y.; Jiang, P.; Pei, H. A Study on the Thermal Degradation of an Acrylamide and 2-Acrylamido-2-Methylpropanesulfonic Acid Copolymer at High Temperatures. Polymers 2023, 15, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunxiang, L.; Ling, L.; Wenke, Y.; Xin, L.; Han, G.; Hongji, L. Degradation mechanism of P(AA/AMPS) and P(AM/AA/AMPS) aqueous solutions at high temperature. Oilfield Chem. 2022, 39, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Peng, W.; Yang, F.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, M.; Wu, T.; Fu, Q. Investigation on thermal degradation mechanism of poly(phenylene sulfide). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 197, 109863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, C.; Lacuve, M.; Haller, S.; Espuche, E.; Colin, X. Influence of thermo-oxidative aging on the structure and the water transport properties of sulfur-crosslinked EPDM. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2025, 234, 111210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- API. API Recommended Practice 10B-2 “Recommended Practice for Testing Well Cements”; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, A. Synthesis and characterization of SSS/HAM/AA terpolymer as a fluid loss additive for oil well cement. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Dai, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J. Novel lignosulfonate/N,N-dimethylacrylamide/γ-methacryloxypropyl trimethoxy silane graft copolymer as a filtration reducer for water-based drilling fluids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 137, 48274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lu, H.; Hu, M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, M.; Xia, X.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, J. Performance comparison and adsorption mechanism analysis of polyanionic and zwitterionic copolymer fluid loss additives for oil-well cement paste: An experimental and computational study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 415, 134955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Wang, C.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, F.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Z. Nano-enhancing polymer as a fluid loss additive for ultra-high temperature cementing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, D.; Dai, J.; Zhang, R.; Niu, M.; Huang, Y. Enhancing the resistance against oxidation of polyphenylene sulphide fiber via incorporation of nano TiO2-SiO2 and its mechanistic analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 129, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y. Structural Characterization and Molecular Model Construction of Lignite: A Case of Xianfeng Coal. Energies 2024, 17, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lin, L.; Guo, Y.; Luo, P.; Xiong, G.; Li, Z.; Ao, H. Study on high-temperature degradation of acrylamide-based polymer ZP1 in aqueous solution. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 217, 110533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bu, Y.; Ma, R.; Guo, W. Improve the practicability of calcium aluminate phosphate cement as well cement: The application of amphoteric ion polymer as retarder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 199, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandengen, K.; Widerøe, H.C.; Nurmi, L.; Hanski, S. Hydrolysis kinetics of ATBS polymers at elevated temperature, via 13 C NMR spectroscopy, as basis for accelerated aging tests. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 158, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, H.; Yang, G.; Jiang, C.; Ji, M.; Yu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, C.; Xu, J. Cyclization mechanism and kinetics of poly(acrylonitrile-co-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid) copolymer investigated by FTIR spectroscopy. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, M.; Xu, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Guo, J. Inhibitory effects of functionalized polycarboxylate retarder on aberrant thickening phenomena of oil well cement at high temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Hui, B.; Feng, Y.; Hu, M.; Guo, J. Terpolymer with rigid side chain as filtrate reducer for water-based drilling fluids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 138, 50237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejo-Dávila, A.S.; Moya-Quevedo, M.A.; Chávez-Flores, D.; Vega-Rios, A.; Zaragoza-Contreras, E.A. Role of the Anilinium Ion on the Selective Polymerization of Anilinium 2-Acrylamide-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonate. Polymers 2021, 13, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Xu, W. Synthesis and performance study of amphoteric ion fluid loss additive SSS/AM/FA/DMDAAC. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, C.; Yao, X.; Song, W.; Zou, Y. Effect of a 2-Acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic Acid-Based Fluid Loss Additive on the Hydration of Oil Well Cement. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 9090–9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Preparation and properties of a new type of temperature-resistant and salt-resistant fluid loss additive ADIM for oil well cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 457, 139447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


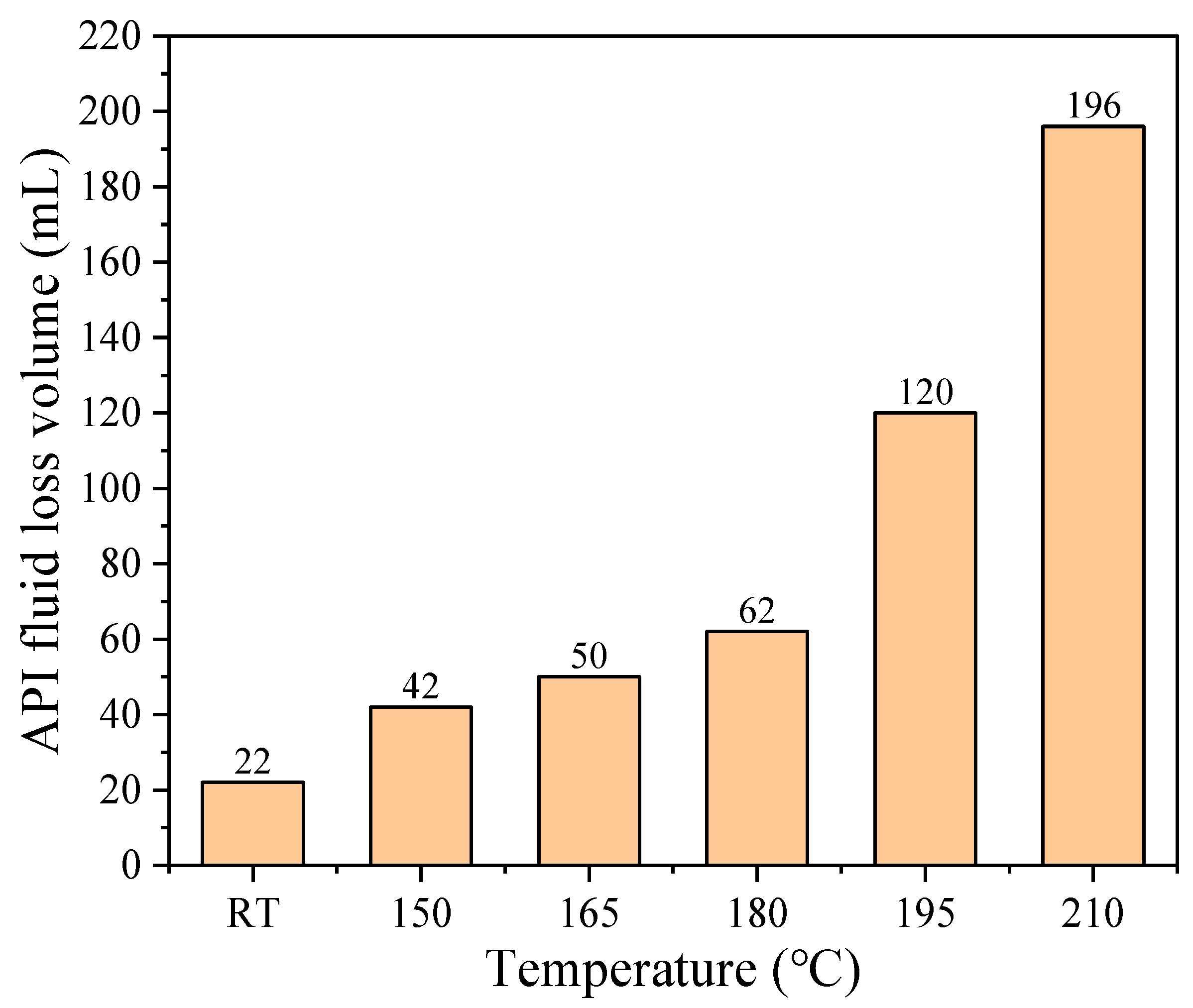
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, M.; Guo, J. Effect of Ultra-High Temperature Degradation on the Physical Properties and Chemical Structure of an AMPS-Based Copolymer Oil-Well Cement Additive PADIM in Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2025, 17, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050591
Yu Y, Zhang H, Xu P, Zhang X, Wang H, Hu M, Guo J. Effect of Ultra-High Temperature Degradation on the Physical Properties and Chemical Structure of an AMPS-Based Copolymer Oil-Well Cement Additive PADIM in Aqueous Solution. Polymers. 2025; 17(5):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050591
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yongjin, Hang Zhang, Pu Xu, Xinyang Zhang, Haige Wang, Miaomiao Hu, and Jintang Guo. 2025. "Effect of Ultra-High Temperature Degradation on the Physical Properties and Chemical Structure of an AMPS-Based Copolymer Oil-Well Cement Additive PADIM in Aqueous Solution" Polymers 17, no. 5: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050591
APA StyleYu, Y., Zhang, H., Xu, P., Zhang, X., Wang, H., Hu, M., & Guo, J. (2025). Effect of Ultra-High Temperature Degradation on the Physical Properties and Chemical Structure of an AMPS-Based Copolymer Oil-Well Cement Additive PADIM in Aqueous Solution. Polymers, 17(5), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050591






