Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Beads: Developments, Applications, and Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
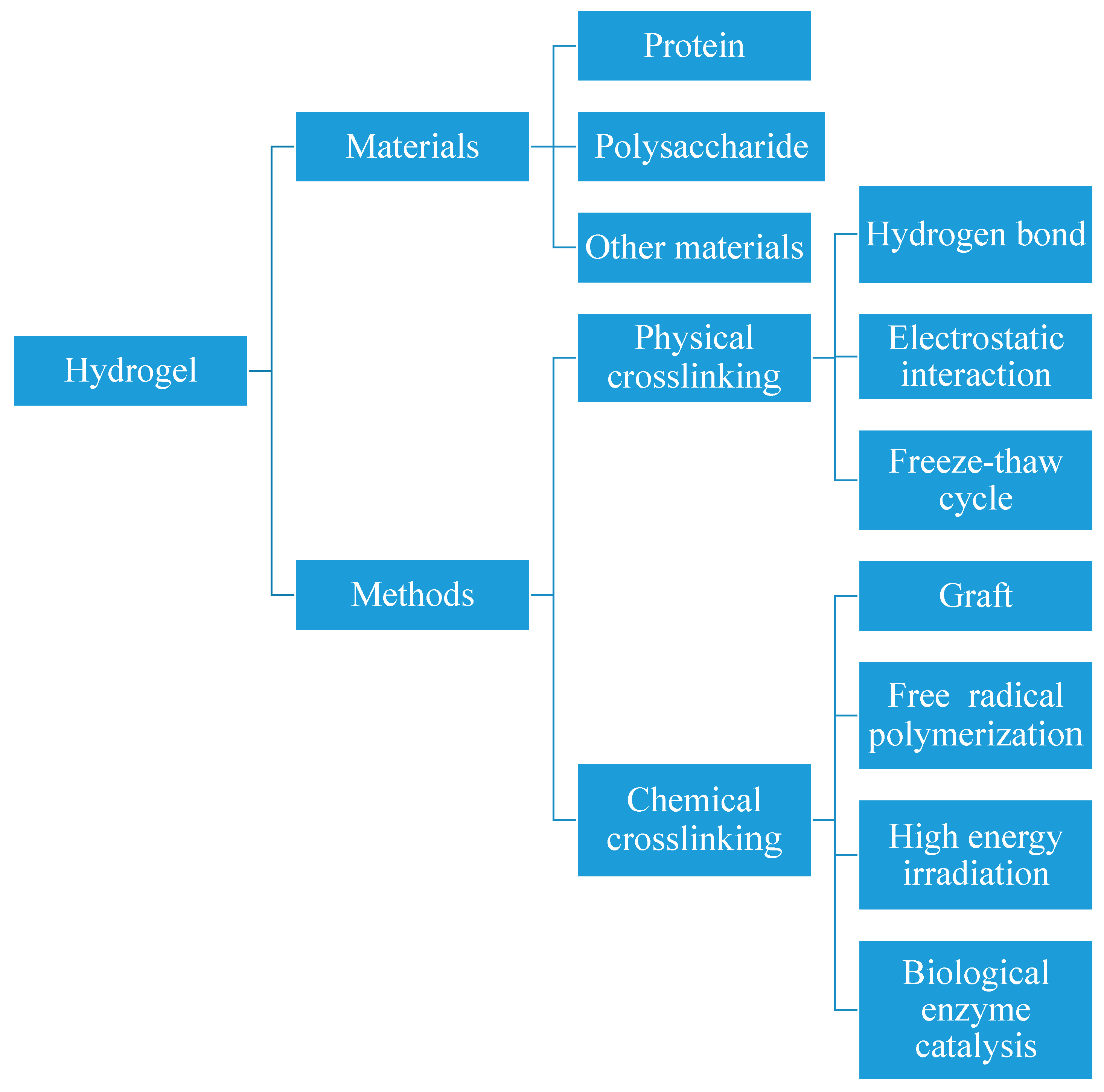
2. Research Progress of CS-Based Hydrogel Beads
2.1. Research Progress in Preparation of CS-Based Hydrogel Beads
2.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Preparation Methods
3. Application of CS-Based Hydrogel Beads
3.1. Application of CS-Based Hydrogel Beads in Food
3.1.1. Application of CS-Based Hydrogel Beads in Fruit Preservation
3.1.2. Application of CS-Based Hydrogel Beads in Meat Preservation
3.2. Application of CS-Based Hydrogel Beads in Medicine
3.3. Application of CS-Based Hydrogel Beads in Environmental Treatment
3.3.1. CS-Based Hydrogel Beads Adsorbed Heavy Metal Ions in Wastewater
3.3.2. CS-Based Hydrogel Beads Adsorbed Dyes and Drugs in Wastewater
4. Prospects and Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shitrit, Y.; Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Bianco-Peled, H. Shear thinning pectin hydrogels physically cross-linked with chitosan nanogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Yang, F.; Hu, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, J. Construction of polysaccharide based physically crosslinked double-network antibacterial hydrogel. Mater. Lett. 2022, 316, 132048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q. Preparation, characterization and release kinetics of a multilayer encapsulated Perilla frutescens L. essential oil hydrogel bead. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 249, 124776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Gao, X. Development of antioxidant sodium alginate gel beads encapsulating curcumin/gum Arabic/gelatin microcapsules. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 152, 109901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, P.; Xu, M.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, W. Fabrication of black wolfberry anthocyanin-based hydrogels for monitoring freshness and extending shelf-life of Dolang lamb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, C.; Kopečková, P.; Kopeček, J. Hybrid Hydrogels Self-Assembled from HPMA Copolymers Containing Peptide Grafts. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Este, M.; Alini, M.; Eglin, D. Single step synthesis and characterization of thermoresponsive hyaluronan hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, T.; Borsa, J.; Takács, E.; Wojnárovits, L. Synthesis of cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogels by high-energy irradiation in the presence of crosslinking agent. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 118, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, S.; Xu, C.; Li, X. Bienzymatically crosslinked gelatin/hyaluronic acid interpenetrating network hydrogels: Preparation and characterization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Song, W.; Wu, N.; Tong, J.; Ren, L. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/polyvinyl porous alcohol aerogel microspheres with stable physicochemical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Zeng, K.; Ming, J.; Lei, X. Chitosan-based emulsion gel beads developed on the multiple-unit floating delivery system for gastric sustained release of proanthocyanidins. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 159, 110704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, N.A.; Hefni, H.H.H.; Abd-Elaal, A.A.A.; Badr, E.A.; Abou Kana, M.T.H. Advancement on modification of chitosan biopolymer and its potential applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 681–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, H.; Hameed, B.H. Chitosan and chitosan composites for oil spills treatment: Review of recent literature. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, D.; Chang, Z. Preparation and characterization of porous chitosan microspheres and adsorption performance for hexavalent chromium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konwar, A.; Gogoi, N.; Majumdar, G.; Chowdhury, D. Green chitosan–carbon dots nanocomposite hydrogel film with superior properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.N.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.P.; Wang, A.Q.; Wei, Q. Swelling characteristics and drug delivery properties of nifedipine-loaded pH sensitive alginate–chitosan hydrogel beads. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 86B, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Huang, X.; Du, X.; Mo, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, H. Facile synthesis of pH-responsive sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel beads promoted by hydrogen bond. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Luo, Y. Chitosan-based hydrogel beads: Preparations, modifications and applications in food and agriculture sectors—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jacquier, J.-C. Preparation of novel chitosan iron microgel beads for fortification applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Gong, L.; Li, Q.; Fan, B.; Ma, C.; He, Y.-C. Preparation of a biobased polyelectrolyte complex from chitosan and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and its antibacterial characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiranpattanakul, P.; Jongjitpissamai, T.; Aungwerojanawit, S.; Tachaboonyakiat, W. Fabrication of a chitin/chitosan hydrocolloid wound dressing and evaluation of its bioactive properties. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4913–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chu, L.; Xia, Q. Liposome-chitosan hydrogel bead delivery system for the encapsulation of linseed oil and quercetin: Preparation and in vitro characterization studies. LWT 2020, 117, 108615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Jia, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Cao, W.; Yan, J.; Gong, X.; Lian, X.; Li, W.; Fan, Y.-Y. In vitro and in vivo release of diclofenac sodium-loaded sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan-ZnO hydrogel beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Ji, S.; Xia, Q. Pickering emulsions-chitosan hydrogel beads carrier system for loading of resveratrol: Formulation approach and characterization studies. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 169, 105074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, S.; Pandit, A.H.; Nadeem, M.; Pandit, A.H.; Rizvi, M.M.A.; Rattan, S. γ-Radiation induced L-glutamic acid grafted highly porous, pH-responsive chitosan hydrogel beads: A smart and biocompatible vehicle for controlled anti-cancer drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C.; Liang, Y. Polyacrylamide modified kaolin enhances adsorption of sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel beads for copper ions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 180, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, A.; Shahid, F.; Pervez, S. Exploration of a three-dimensional matrix as micro-reactor in the form of reactive polyaminosaccharide hydrogel beads using multipoint covalent interaction approach. Biotechnol. Lett. 2022, 44, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, W. The Neutral Protease Immobilization: Physical Characterization of Sodium Alginate-Chitosan Gel Beads. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2269–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-G.; Cao, Q.; Dai, S.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Y.-J.; Zhao, C.-Z.; Yang, Z.-H.; Sun, Y.-X.; Yue, T.; Sang, K.-X.; et al. Bio-Based aerogel beads with multistage pore network structure for Cr(VI) removal using ice template method. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 159983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, L. Formation of pH-responsive hydrogel beads and their gel properties: Soybean protein nanofibers and sodium alginate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 329, 121748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y. Chitosan-gellan gum polyelectrolyte hydrogel beads containing tea tree oil microcapsules: Preparation, characterization and application. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Son, S.U.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Lim, J.; Seo, S.B.; Kang, B.; Kang, T.; Jung, J.; Seo, S.; et al. Polydiacetylene-based hydrogel beads as colorimetric sensors for the detection of biogenic amines in spoiled meat. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Fei, P. Acylating blueberry anthocyanins with fatty acids: Improvement of their lipid solubility and antioxidant activities. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tikunov, Y.; Schouten, R.E.; Marcelis, L.F.M.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bovy, A. Anthocyanin Biosynthesis and Degradation Mechanisms in Solanaceous Vegetables: A Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, M.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Sepidname, M.; Negahdarifar, M.; Li, P. Development of a novel colorimetric sensor based on alginate beads for monitoring rainbow trout spoilage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Dong, T. Colorimetric porous microspheres of natural sodium alginate for chilled pork visual monitoring. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Application of glycyrrhiza polysaccharide nanofibers loaded with tea tree essential oil/ gliadin nanoparticles in meat preservation. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhong, Z. Preparation and characterization of long-term antibacterial and pH-responsive Polylactic acid/Octenyl succinic anhydride-chitosan @ tea tree oil microcapsules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 1318–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Yu, K.; Yu, W.; Jiang, H.; Zhong, J.; Zou, L.; Liu, W. Effect of sustained-release tea tree essential oil solid preservative on fresh-cut pineapple storage quality in modified atmospheres packaging. Food Chem. 2023, 417, 135898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torpol, K.; Sriwattana, S.; Sangsuwan, J.; Wiriyacharee, P.; Prinyawiwatkul, W. Optimising chitosan–pectin hydrogel beads containing combined garlic and holy basil essential oils and their application as antimicrobial inhibitor. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2064–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Han, W.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, T.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Q. Preparation of Perilla frutescens L. essential oil hydrogel beads and preservation application research in strawberry. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichembach, L.H.; de Oliveira Petkowicz, C.L.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Pectin and pectin/chitosan hydrogel beads as coffee essential oils carrier systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadalinejhad, S.; Jensen, I.-J.; Kurek, M.; Lerfall, J. Novel colorimetric indicators based on alginate hydrogel beads containing anthocyanin for visual freshness monitoring of shrimp and minced chicken. LWT 2024, 199, 116127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, M.; Essabir, H.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A.e.k. Edible thermochromic beads from flavonoid, fatty acid, and lecithin for smart packaging. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal-Ozturk, A.; Karal-Yilmaz, O.; Akguner, Z.P.; Aksu, S.; Tas, A.; Olmez, H. Sponge-like chitosan-based nanostructured antibacterial material as a topical hemostat. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. A review on chitosan and its nanocomposites in drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntum, T.; Kiti, K.; Surassmo, S.; Thanomsilp, C.; Suwantong, O. Enhancing wound dressing performance with hydrogel-embedded longan seed extract-loaded alginate/chitosan beads. Polymer 2024, 300, 127002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belščak-Cvitanović, A.; Komes, D.; Karlović, S.; Djaković, S.; Špoljarić, I.; Mršić, G.; Ježek, D. Improving the controlled delivery formulations of caffeine in alginate hydrogel beads combined with pectin, carrageenan, chitosan and psyllium. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Huang, H. Review on Magnetic Natural Polymer Constructed Hydrogels as Vehicles for Drug Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2574–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavinia, G.R.; Etemadi, H.; Soleymani, F. Magnetic/pH-responsive beads based on caboxymethyl chitosan and κ-carrageenan and controlled drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 128, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, T.S.A.; de Souza, J.F.; Fajardo, A.R. Magnetic microspheres based on pectin coated by chitosan towards smart drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 265, 118013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, F. Effective removal of Cu(II) from water by three-dimensional composite microspheres based on chitosan/sodium alginate/silicon dioxide: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Peng, X.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Meng, X.; Yu, G. Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by ion-imprinted tetraethylenepentamine modified chitosan beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Liu, A.; Liu, G.; Jiang, S.; Guo, Y.; Liu, W. Deep removal of phosphate from electroplating wastewater using novel Fe-MOF loaded chitosan hydrogel beads. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 357, 120725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xia, N.; Wan, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, S. Selective capture of toxic anionic dyes of a novel prepared DMDAAC-grafted chitosan/genipin/cellulose hydrogel beads with antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.A.; Dar, A.A.; Banday, J.A. Rheological, morphological and swelling properties of dysprosium-based composite hydrogel beads of alginate and chitosan: A promising material for the effective cationic and anionic dye removal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 663, 131046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, M.; Cegłowski, M.; Kurczewska, J. Hybrid chitosan/molecularly imprinted polymer hydrogel beads doped with iron for selective ibuprofen adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.Z.; Hameed, S.; Mohiuddin, M.; Abbasi, A. Simultaneous adsorptive removal of three fluoroquinolones using humic acid modified hydrogel beads. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 24398–24407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, S.; Qiao, J.; Kołodyńska, D.; Ju, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cai, M.; Deng, D.; Dionysiou, D.D. Malic acid-enhanced chitosan hydrogel beads (mCHBs) for the removal of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
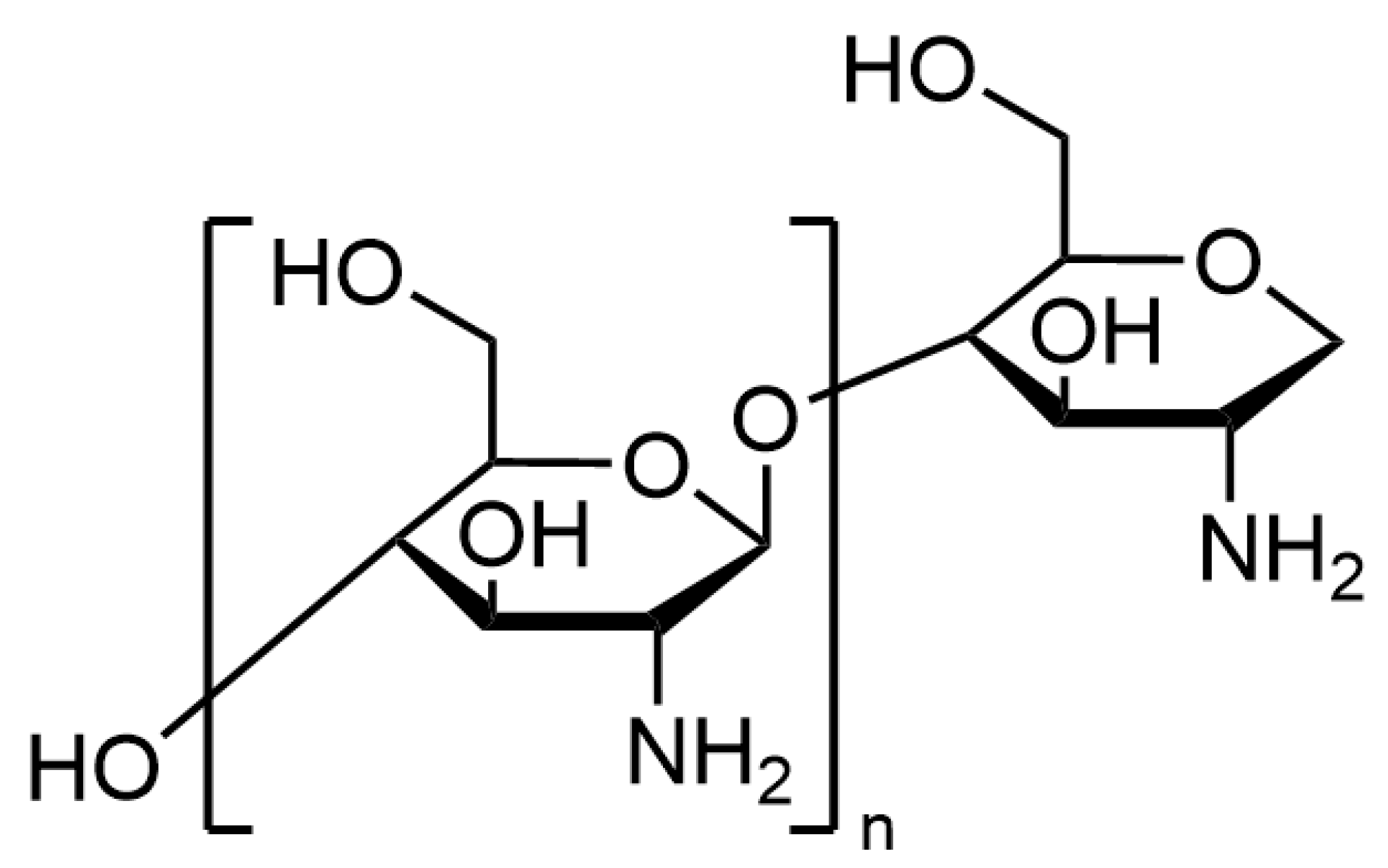


| Samples | Apply | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Application in strawberry preservation | 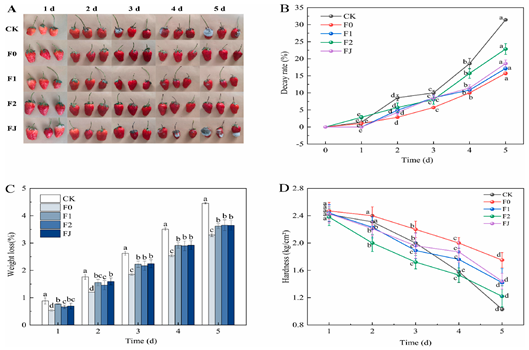 | [41] Note: A represents the freshness of strawberries in different groups, and B–D represents the decay rate, weight loss and hardness of strawberries respectively |
| Hydrogel beads act as carriers of proanthocyanidins | 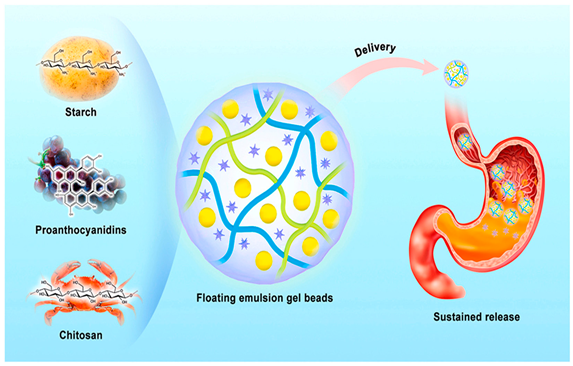 | [11] |
| Hydrogel beads adsorb copper ions |  | [59] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Qin, R.; Xue, J.; Lin, C.; Jiang, L. Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Beads: Developments, Applications, and Challenges. Polymers 2025, 17, 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070920
Li Z, Qin R, Xue J, Lin C, Jiang L. Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Beads: Developments, Applications, and Challenges. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070920
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ziao, Ruoran Qin, Jiayi Xue, Congyu Lin, and Longwei Jiang. 2025. "Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Beads: Developments, Applications, and Challenges" Polymers 17, no. 7: 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070920
APA StyleLi, Z., Qin, R., Xue, J., Lin, C., & Jiang, L. (2025). Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Beads: Developments, Applications, and Challenges. Polymers, 17(7), 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070920








