The Development of a Coaxial Electrospinning Formula Using Fish Gelatin/PBS as the Core for Structurally Intact Liposome Loading and Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solution Preparation
2.3. Set-Up
2.3.1. Coaxial Formula Optimization
2.3.2. Coaxial Fiber Encapsulate and Release Liposomes and FITC
2.3.3. Coaxial Fiber Characterization
2.3.4. In Vitro Evaluation
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Coaxial Formula Development
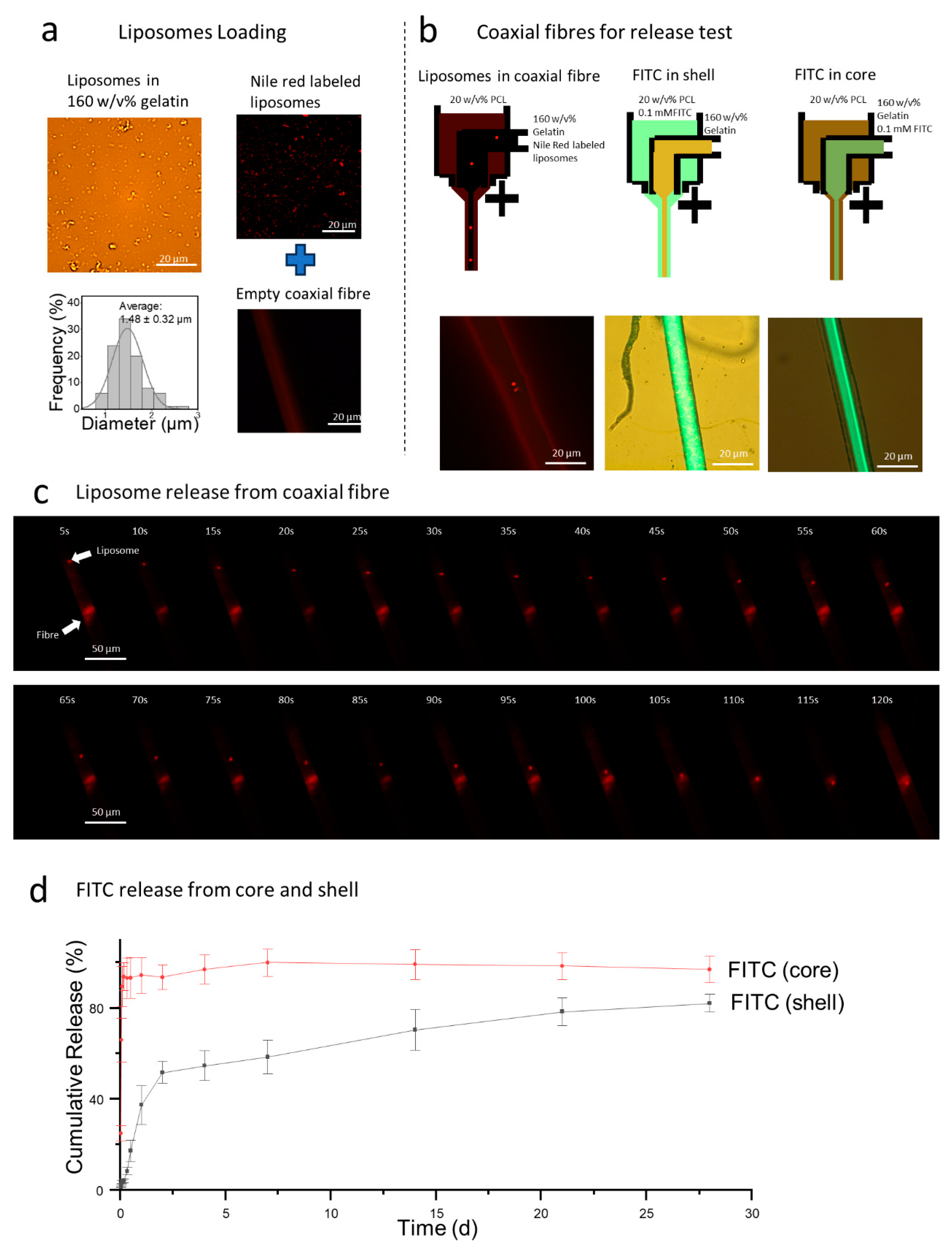
3.1.1. Release Profiles
3.1.2. Liposomes Loaded Coaxial Fiber Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, H.; Li, G.; Cho, H.; Jiang, M.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X. Developments of advanced electrospinning techniques: A critical review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100410. [Google Scholar]
- Heydarkhan-Hagvall, S.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Dhanasopon, A.P.; Rofail, F.; Smith, H.; Wu, B.M.; Shemin, R.; Beygui, R.E.; MacLellan, W.R. Three-dimensional electrospun ECM-based hybrid scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2907–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politi, S.; Carotenuto, F.; Rinaldi, A.; Di Nardo, P.; Manzari, V.; Albertini, M.C.; Araneo, R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Teodori, L. Smart ECM-based electrospun biomaterials for skeletal muscle regeneration. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeller, J.; Itel, F.; Wuertz-Kozak, K.; Fortunato, G.; Rossi, R.M. pH-responsive electrospun nanofibers and their applications. Polym. Rev. 2022, 62, 351–399. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Song, Z.; Nie, X.; Guo, K.; Gu, Y. A smart scaffold composed of three-dimensional printing and electrospinning techniques and its application in rat abdominal wall defects. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Biodegradable polymer electrospinning for tendon repairment. Polymers 2023, 15, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, F.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Advanced Electrospun Nanofibrous Stem Cell Niche for Bone Regenerative Engineering. Regen. Eng. Transl. Med. 2023, 9, 165–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chachlioutaki, K.; Karavasili, C.; Adamoudi, E.; Bouropoulos, N.; Tzetzis, D.; Bakopoulou, A.; Fatouros, D.G. Silk sericin/PLGA electrospun scaffolds with anti-inflammatory drug-eluting properties for periodontal tissue engineering. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 133, 112723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Santos, H.A.; Cui, W. Programmable immune activating electrospun fibers for skin regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3218–3230. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Werning, L.V.; Singh, B.; Johannessen, M.; Engstad, R.E.; Holsæter, A.M. Antimicrobial liposomes-in-nanofiber wound dressings prepared by a green and sustainable wire-electrospinning set-up. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 657, 124136. [Google Scholar]
- Casula, L.; Zidar, A.; Kristl, J.; Jeras, M.; Kralj, S.; Fadda, A.M.; Zupančič, Š. Development of nanofibers with embedded liposomes containing an immunomodulatory drug using green electrospinning. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Xiang, L.; Chen, J.; Qu, H.; Wan, Y.; Xiang, D. PLGA-liposome electrospun fiber delivery of miR-145 and PDGF-BB synergistically promoted wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 129951. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, F.; Santos, J.F.; Bitoque, D.; Silva, G.A.; Marletta, A.; Nunes, V.A.; Ribeiro, P.A.; Silva, J.C.; Raposo, M. Polycaprolactone/gelatin nanofiber membranes containing EGCG-loaded liposomes and their potential use for skin regeneration. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4790–4800. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, N.; Martins, A.; Pires, R.; Faria, S.; Fonseca, N.A.; Moreira, J.N.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Immobilization of bioactive factor-loaded liposomes on the surface of electrospun nanofibers targeting tissue engineering. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, N.; Martins, M.; Martins, A.; Fonseca, N.A.; Moreira, J.N.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Antibacterial activity of chitosan nanofiber meshes with liposomes immobilized releasing gentamicin. Acta Biomater. 2015, 18, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mickova, A.; Buzgo, M.; Benada, O.; Rampichova, M.; Fisar, Z.; Filova, E.; Tesarova, M.; Lukas, D.; Amler, E. Core/shell nanofibers with embedded liposomes as a drug delivery system. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 952–962. [Google Scholar]
- Karakas, C.Y.; Ustundag, C.B.; Sahin, A.; Karadag, A. Co-axial electrospinning of liposomal propolis loaded gelatin-zein fibers as a potential wound healing material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54683. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Kang, H.; Che, N.; Liu, Z.; Li, P.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Cao, C.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y. 27 Controlled release of liposome-encapsulated Naproxen from core-sheath electrospun nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 2014, 111, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kang, H.; Li, Q.; Che, N.; Liu, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y. Ultrathin core–sheath fibers for liposome stabilization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 630–637. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanbegloo, K.; Banihashem, S.; Dizaji, B.F.; Bybordi, S.; Farrokh-Eslamlou, N.; Abadi, P.G.-s.; Jazi, F.S.; Irani, M. Paclitaxel-loaded liposome-incorporated chitosan (core)/poly (ε-caprolactone)/chitosan (shell) nanofibers for the treatment of breast cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123380. [Google Scholar]
- Kordbacheh, H.; Bahmani, E.; Bybordi, S.; Rezaee, A.; Dehghanian, Z.; Ehsanfar, N.; Goleij, P.; SharifianJazi, F.; Irani, M. Co-delivery of Bcl-2 siRNA and doxorubicin using liposome-incorporated poly (ε-caprolactone)/chitosan nanofibers for the treatment of lung cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 99, 105994. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, W.F.; Rao, N.V. Collagen structure in solution. I. Kinetics of helix regeneration in single-chain gelatins. Biochemistry 1970, 9, 3714–3724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, B.C.; Cadinoiu, A.N.; Popa, M.; Desbrieres, J.; Peptu, C.A. Modulated release from liposomes entrapped in chitosan/gelatin hydrogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 43, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Justine, R.Y.; Janssen, M.; Liang, B.J.; Huang, H.-C.; Fisher, J.P. A liposome/gelatin methacrylate nanocomposite hydrogel system for delivery of stromal cell-derived factor-1α and stimulation of cell migration. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- DiTizio, V.; Karlgard, C.; Lilge, L.; Khoury, A.E.; Mittelman, M.W.; DiCosmo, F. Localized drug delivery using crosslinked gelatin gels containing liposomes: Factors influencing liposome stability and drug release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2000, 51, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Elkhoury, K.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, L.; Lavrador, P.; Almeida, R.; Gaspar, V.; Kahn, C.; Cleymand, F.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Mano, J.F. Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) nanocomposite hydrogels embedding bioactive naringin liposomes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Boanini, E.; Panzavolta, S.; Roveri, N. Biomimetic growth of hydroxyapatite on gelatin films doped with sodium polyacrylate. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 752–756. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Shi, B. Physicochemical properties of collagen, gelatin and collagen hydrolysate derived from bovine limed split wastes. J. -Soc. Leather Technol. Chem. 2006, 90, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Sajkiewicz, P.; Kołbuk, D. Electrospinning of gelatin for tissue engineering–molecular conformation as one of the overlooked problems. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, W.T.; Zou, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, W.; Gould, O.E.; Kratz, K.; Ma, N.; Lendlein, A. Coaxial electrospinning of PEEU/gelatin to fiber meshes with enhanced mesenchymal stem cell attachment and proliferation. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2020, 74, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, P.; Santos, P.; Alves, P.; Miguel, S.P.; Carvalho, M.P.; de Sá, K.D.; Correia, I.; Ferreira, P. Coaxial electrospun PCL/Gelatin-MA fibers as scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, I.H.; Ayres, E.; Averous, L.; Schlatter, G.; Hebraud, A.; Mendes, S.T.O.; Oréfice, R.L. Elaboration and Characterization of Coaxial Electrospun Poly (ε-Caprolactone)/Gelatin Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2014, 33, 21475. [Google Scholar]
- Gualandi, C.; Torricelli, P.; Panzavolta, S.; Pagani, S.; Focarete, M.L.; Bigi, A. An innovative co-axial system to electrospin in situ crosslinked gelatin nanofibers. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 11, 025007. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, K.; Kamilah, H.; Karim, A.A.; Ariffin, F. Enhancing the functional properties of fish gelatin mats by dual encapsulation of essential oils in β-cyclodextrins/fish gelatin matrix via coaxial electrospinning. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108324. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, W.F.; von Hippel, P.H. Formation and stabilization of the collagen-fold. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 92, 100–113. [Google Scholar]
- Von Hippel, P.H.; Harrington, W.F. Enzymic studies of the gelatin → collagen-fold transition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1959, 36, 427–447. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, H.W.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Yun, H.; Song, D.W.; Yang, Y.; Shin, B.-S.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, K.H. Fabrication of an ultrafine fish gelatin nanofibrous web from an aqueous solution by electrospinning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, B.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J. Drug delivery applications of core-sheath nanofibers prepared by coaxial electrospinning: A review. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, B.S.; Yu, W.R. Recent progress in coaxial electrospinning: New parameters, various structures, and wide applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704765. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Fassihi, R. Examination of drug solubility, polymer types, hydrodynamics and loading dose on drug release behavior from a triple-layer asymmetric configuration delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 155, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baadani, M.A.; Yie, K.H.R.; Al-Bishari, A.M.; Alshobi, B.A.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, K.; Dai, B.; Shen, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, J. Co-electrospinning polycaprolactone/gelatin membrane as a tunable drug delivery system for bone tissue regeneration. Mater. Des. 2021, 209, 109962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Ahmad, T.; Zain, N.M.; Awang, S.R. Identification of bovine, porcine and fish gelatin signatures using chemometrics fuzzy graph method. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayati, D.; Sabiyla, G.R.; Prasetyo, E.N.; Sa’adah, N.N.; Kurniawan, F. The characteristic of gelatin extracted from the skin of adult and sub-adult striped catfish (pangasius hypophthalmus) using acid-base pretreatment: pH and FTIR. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 755, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipson, K.; Hay, J.; Jenkins, M. Thermal analysis FTIR spectroscopy of poly (ε-caprolactone). Thermochim. Acta 2014, 595, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramnezhad, M.; Akbari, B.; Akbari, M.; Kharaziha, M. Effect of surface modification on physical and cellular properties of PCL thin film. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, X.; Qi, Q.; Liu, W. Interaction of DPPC liposomes with cholesterol and food protein during in vitro digestion using Dynamic Light Scattering and FTIR spectroscopy analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Tian, S. Effect of phospholipids on membrane characteristics and storage stability of liposomes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 81, 103155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, D.; Xia, D.; Liang, C.; Li, N.; Xu, R. Synergistic effect of co-delivering ciprofloxacin and tetracycline hydrochloride for promoted wound healing by utilizing coaxial PCL/gelatin nanofiber membrane. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Q.; Sun, W. Coaxial electrospinning biopolymer with living cells. In Proceedings of the ASME 2010 First Global Congress on NanoEngineering for Medicine and Biology, Houston, TX, USA, 7–10 February 2010; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, J.H.; Peard, G.T. The surface tension of gelatin solutions. Biochem. J. 1925, 19, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choktaweesap, N.; Arayanarakul, K.; Aht-Ong, D.; Meechaisue, C.; Supaphol, P. Electrospun gelatin fibers: Effect of solvent system on morphology and fiber diameters. Polym. J. 2007, 39, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Ueberreiter, K. Surface tension of aqueous gelatin solutions, 1. Concentration dependence. Die Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1979, 180, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Wu, T.-F.; Tsao, H.-K. Interfacial dynamics of a gelatin solution with surfactant. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 8786–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likos, C.; Vaynberg, K.; Löwen, H.; Wagner, N. Colloidal stabilization by adsorbed gelatin. Langmuir 2000, 16, 4100–4108. [Google Scholar]
- Akbulut, M.; Reddy, N.K.; Bechtloff, B.; Koltzenburg, S.; Vermant, J.; Prud’homme, R.K. Flow-induced conformational changes in gelatin structure and colloidal stabilization. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9636–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Dutta, J.; Dutta, P.; Koh, J. A systematic study on chitosan-liposome based systems for biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 470–481. [Google Scholar]
- Reise, M.; Kranz, S.; Guellmar, A.; Wyrwa, R.; Rosenbaum, T.; Weisser, J.; Jurke, A.; Schnabelrauch, M.; Heyder, M.; Watts, D.C. Coaxial electrospun nanofibers as drug delivery system for local treatment of periodontitis. Dent. Mater. 2023, 39, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Cardenas, R.; Wei, S.; Wujcik, E.K.; Guo, Z. Coaxial electrospun fibers: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 654–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Coaxial electrospinning formation of complex polymer fibers and their applications. ChemPlusChem 2019, 84, 1453–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Rasheed, A.; Dong, H.; Carr, W.W.; Dadmun, M.D.; Kumar, S. Electrospun Micro-and Nanostructured Polymer Particles. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2008, 209, 2390–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
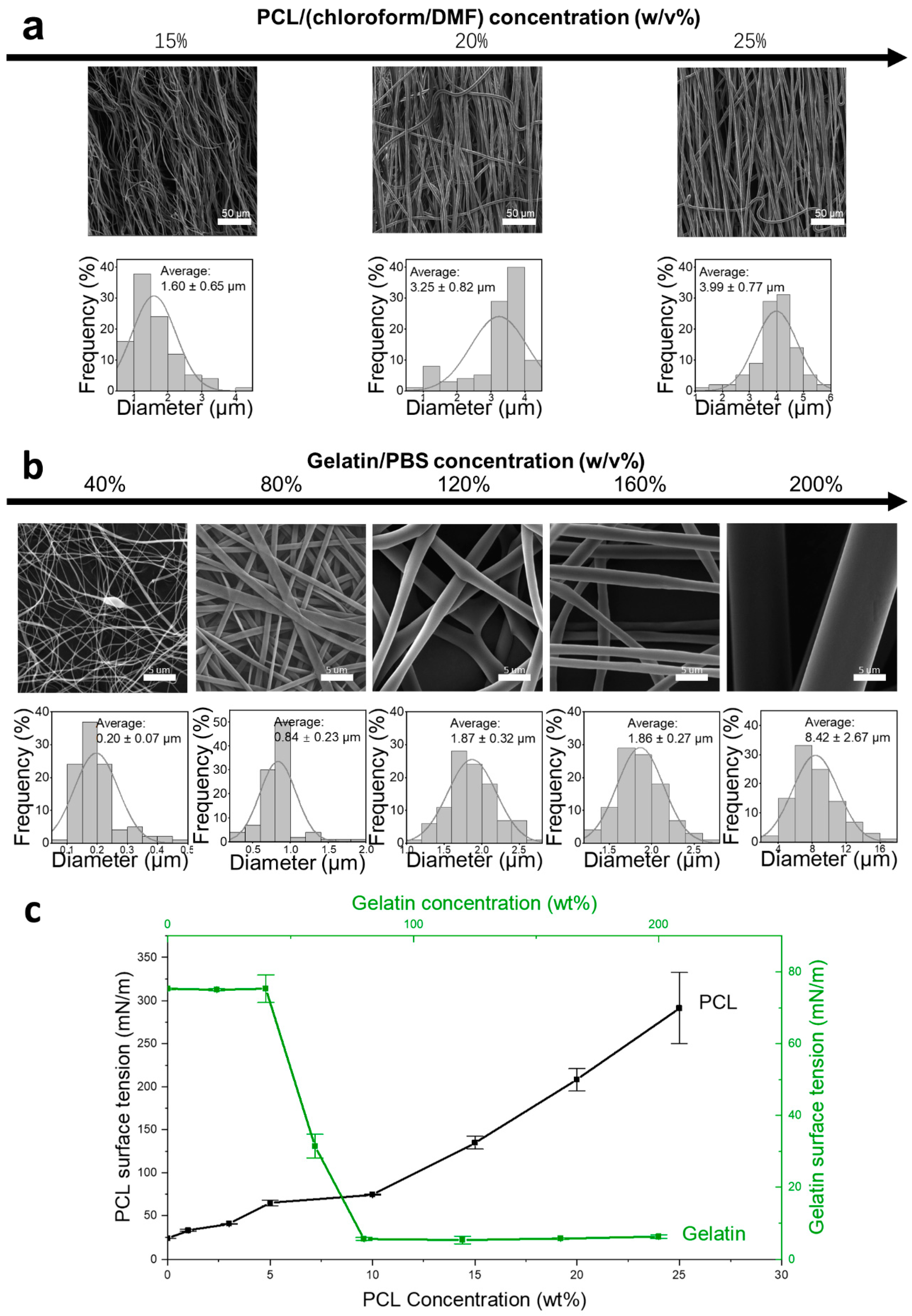



| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 |
|---|---|---|
| PCL Concentration (w/v%) | Gelatin Concentration (w/v%) | Feed Ratio (Gelatin/PCL, v/v) |
| 15 | 120 | 1/1 |
| 20 | 160 | 1/2.5 |
| 25 | 200 | 1/5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Xia, R.; Zhou, M.; Williams, G.R.; Amler, E.; Zhou, F.-L.; Tamaddon, M.; Liu, C. The Development of a Coaxial Electrospinning Formula Using Fish Gelatin/PBS as the Core for Structurally Intact Liposome Loading and Release. Polymers 2025, 17, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070944
Wang H, Xia R, Zhou M, Williams GR, Amler E, Zhou F-L, Tamaddon M, Liu C. The Development of a Coaxial Electrospinning Formula Using Fish Gelatin/PBS as the Core for Structurally Intact Liposome Loading and Release. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070944
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haoyu, Runnan Xia, Mo Zhou, Gareth R. Williams, Evzen Amler, Feng-Lei Zhou, Maryam Tamaddon, and Chaozong Liu. 2025. "The Development of a Coaxial Electrospinning Formula Using Fish Gelatin/PBS as the Core for Structurally Intact Liposome Loading and Release" Polymers 17, no. 7: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070944
APA StyleWang, H., Xia, R., Zhou, M., Williams, G. R., Amler, E., Zhou, F.-L., Tamaddon, M., & Liu, C. (2025). The Development of a Coaxial Electrospinning Formula Using Fish Gelatin/PBS as the Core for Structurally Intact Liposome Loading and Release. Polymers, 17(7), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070944







