Chiral Polymers Based on Vinyl[2.2]paracyclophane and Their Application as CPL Emitters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Remarks
2.2. Reaction Monitoring
2.3. Melting Point
2.4. Optical Rotation
2.5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
2.6. Infrared Spectroscopy (IR)
2.7. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
2.8. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
2.9. Optical Spectroscopy
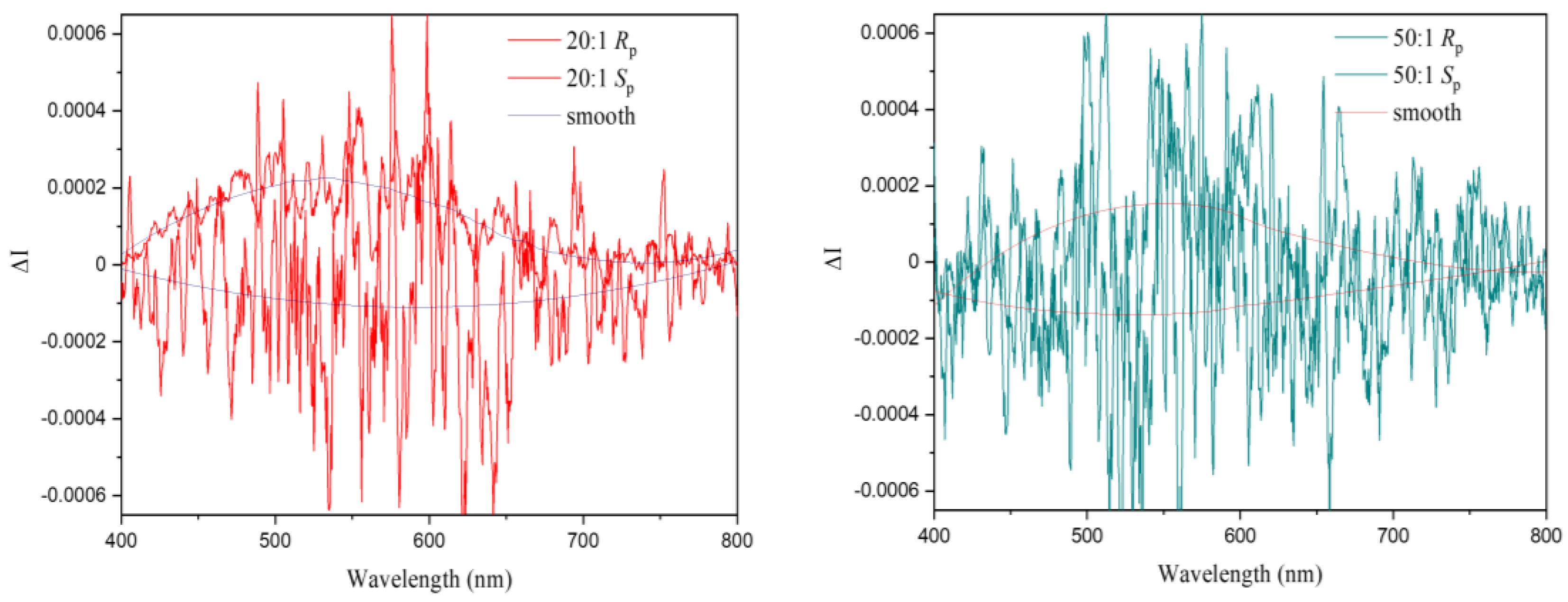
2.10. Electronic Circular Dichroism (ECD) and Circularly Polarized Luminescence (CPL)
2.11. Synthetic Procedures
3. Results
4. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naaman, R.; Paltiel, Y.; Waldeck, D.H. Chiral induced spin selectivity and its implications for biological functions. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2022, 51, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zang, S.-Q.; Chen, X. Stereospecific interactions between chiral inorganic nanomaterials and biological systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2481–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shi, L.; Yue, H.; Gao, X. Recognition at chiral interfaces: From molecules to cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 195, 111268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholl, D.S.; Gellman, A.J. Developing chiral surfaces for enantioselective chemical processing. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 2484–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P. Current status of chirality in agrochemicals. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2389–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, J.; Kim, M.; Yang, Y.; Badloe, T.; Ni, J.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, C.-W.; Rho, J. Electromagnetic chirality: From fundamentals to nontraditional chiroptical phenomena. Light. Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Okamoto, Y. Efficient separation of enantiomers using stereoregular chiral polymers. Chem. Rev. 2015, 116, 1094–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.W.Y.; Toy, P.H. Chiral auxiliaries in polymer-supported organic synthesis. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2004, 15, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wu, Q.-L.; Zhou, L.; Hou, X.-H.; Liu, N.; Wu, Z.-Q. Chiral recognition and resolution based on helical polymers. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 39, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshchi, R.; Ramsteiner, M.; Herfort, J.; Tahraoui, A.; Grahn, H.T. Optical communication of spin information between light emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 162508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Kawai, T.; Yuasa, J. A smart sensing method for object identification using circularly polarized luminescence from coordination-driven self-assembly. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 8973–8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedeon, C.; Del Rio, N.; Furlan, F.; Taddeucci, A.; Vanthuyne, N.; Gregoriou, V.G.; Fuchter, M.J.; Siligardi, G.; Gasparini, N.; Crassous, J.; et al. Rational design of new conjugated polymers with main chain chirality for efficient optoelectronic devices: Carbo[6]Helicene and indacenodithiophene copolymers as model compounds. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2314337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.; Zysman-Colman, E.; Lahann, J.; Bräse, S. From Molecules to Materials: Collaborative Research at the Chemistry—Materials Science Interface and Lessons Learned in Cyclophane Chemistry. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2403365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradies, J. [2.2]Paracyclophane derivatives: Synthesis and application in catalysis. Synthesis 2011, 2011, 3749–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, H.; Jin, Y.; Chen, S.; Duan, P.; Liu, Y. Enantioselective effect of chiral small molecules in sars-cov-2 vaccine-induced immune response. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202301085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisaki, Y.; Chujo, Y. Planar chiral [2.2]paracyclophanes: Optical resolution and transformation to optically active π-stacked molecules. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Spuling, E.; Mattern, C.M.; Li, W.; Fuhr, O.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Adachi, C.; Bräse, S.; Samuel, I.D.W.; Zysman-Colman, E. Turn on of sky-blue thermally activated delayed fluorescence and circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) via increased torsion by a bulky carbazolophane donor. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6689–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hafeez, H.; Seibert, J.; Wu, S.; Ortiz, J.S.O.; Crassous, J.; Bräse, S.; Samuel, I.D.W.; Zysman-Colman, E. [2.2]Paracyclophane-substituted chiral multiresonant thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters for efficient organic light-emitting diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.; Varadharajan, D.; Zippel, C.; Begum, S.; Lahann, J.; Bräse, S. Design strategies for structurally controlled polymer surfaces via cyclophane-based CVD polymerization and Post-CVD fabrication. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2201761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.J.; Zheng, T.; Runowski, M.; Wozny, P.; Martín, I.R.; Soler-Carracedo, K.; Piñero, C.E.; Lebedkin, S.; Fuhr, O.; Bräse, S. Constructing [2.2]paracyclophane-based ultrasensitive optical fluorescent-phosphorescent thermometer with cucurbit[8]uril supramolecular assembly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2313517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, H. [2.2]Paracyclophanes in polymer chemistry and materials science. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 9808–9812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuki, S.; Itoh, T.; Kubo, M.; Okuno, H. Synthesis and polymerization of 4-vinyl [2.2]paracyclophane. Polym. Bull. 1994, 32, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippel, C.; Hassan, Z.; Parsa, A.Q.; Hohmann, J.; Bräse, S. Multigram-scale kinetic resolution of 4-acetyl[2.2]paracyclophane via ru-catalyzed enantioselective hydrogenation: Accessing [2.2]paracyclophanes with planar and central chirality. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 2861–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-L.; Huang, M.-H.; Lee, W.-K.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Pan, K.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Ting, H.-C.; Sarma, M.; Ho, Y.-Y.; Hu, H.-C.; et al. A versatile thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitter for both highly efficient doped and non-doped organic light emitting devices. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 13662–13665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Weng, C.; Ruan, Y.; Li, K.; Cai, G.; Song, C.; Lin, Q. An optical chiral sensor based on weak measurement for the real-time monitoring of sucrose hydrolysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, R.W.; Karamertzanis, P.G.; Hulme, A.T.; Tocher, D.A.; Lewis, T.C.; Price, S.L. The polymorphism of progesterone: Stabilization of a ’disappearing’ polymorph by co-crystallization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 3419–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavely, H.E.; Bergmann, W. The chemistry of unsaturated steroids. Ii. The preparation and properties of 2, 4-cholestadiene. J. Org. Chem. 1937, 1, 575–579. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, T.; Wong, K. Perspective on Host Materials for Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Organic Light Emitting Diodes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
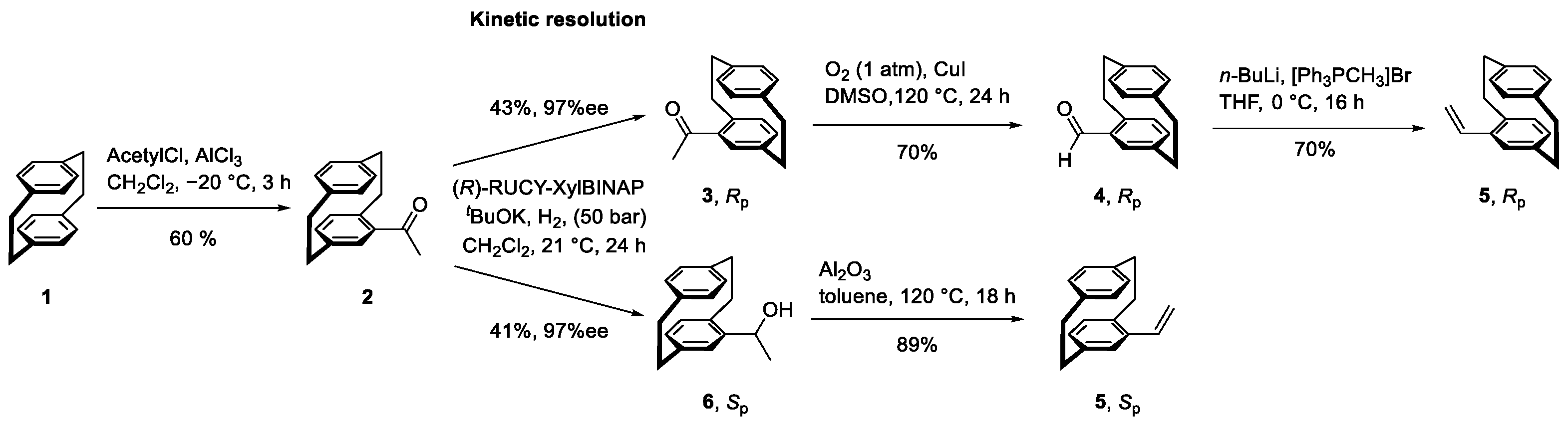

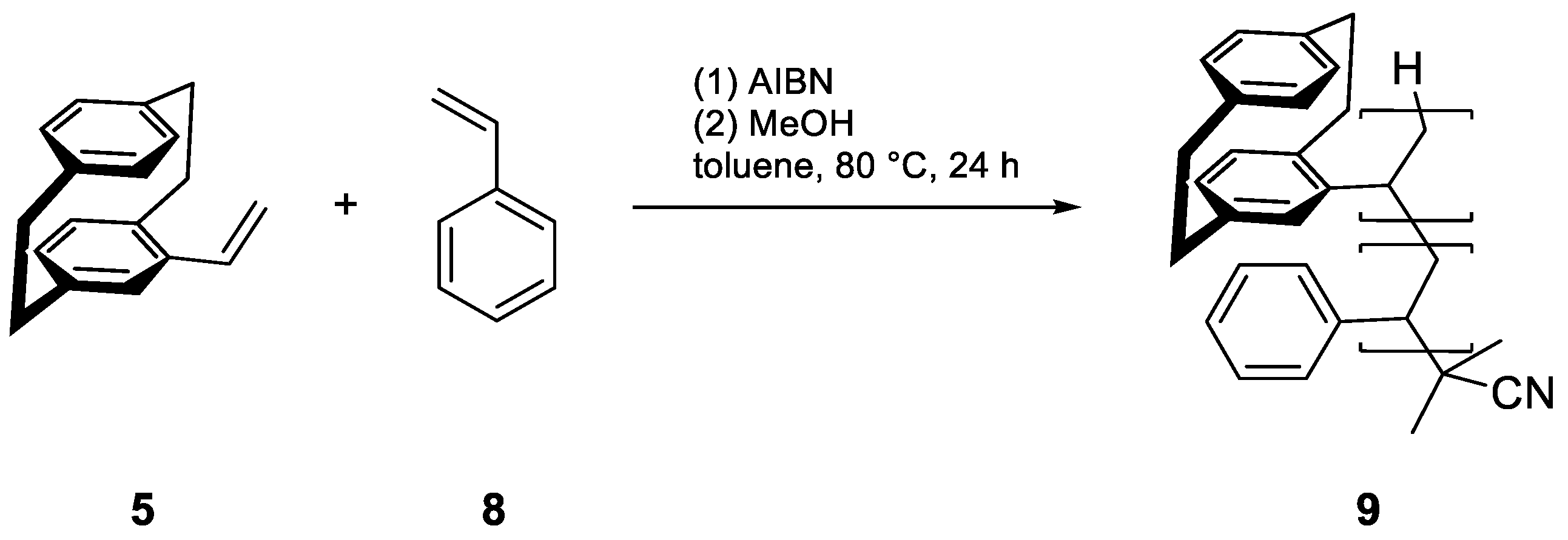

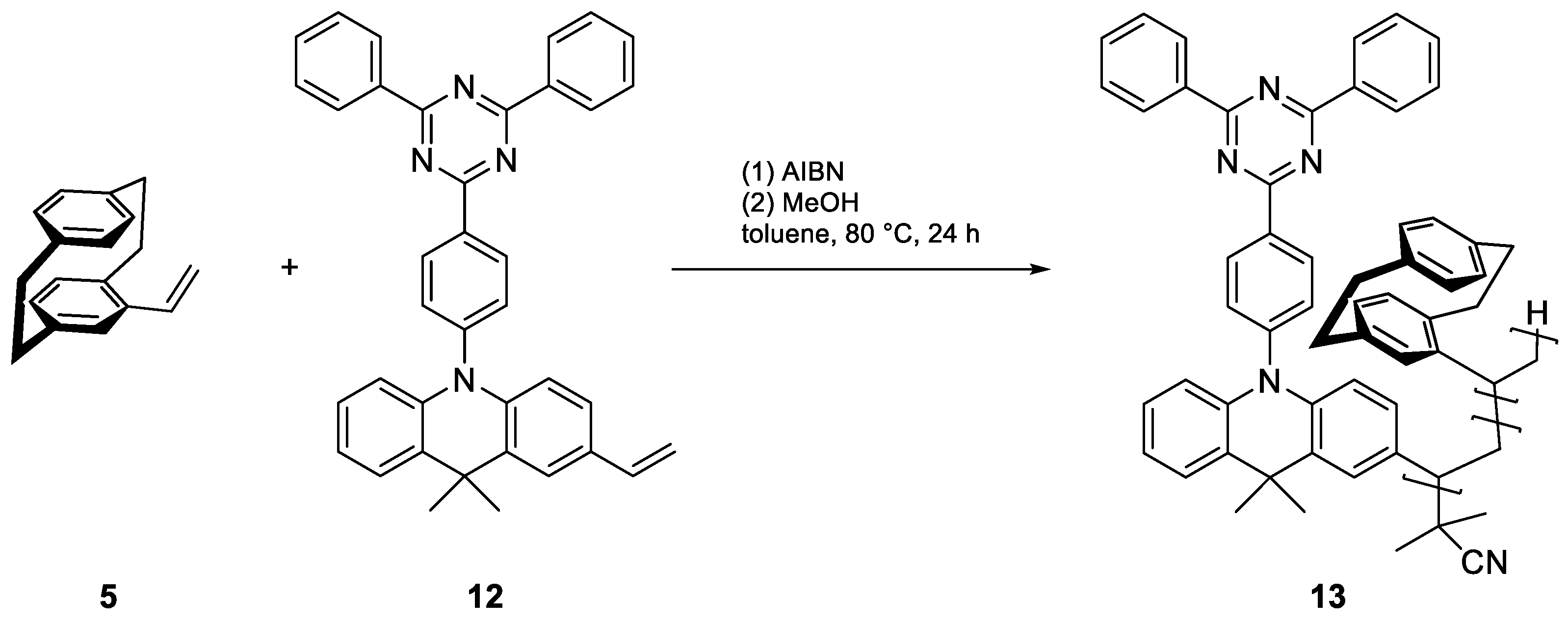
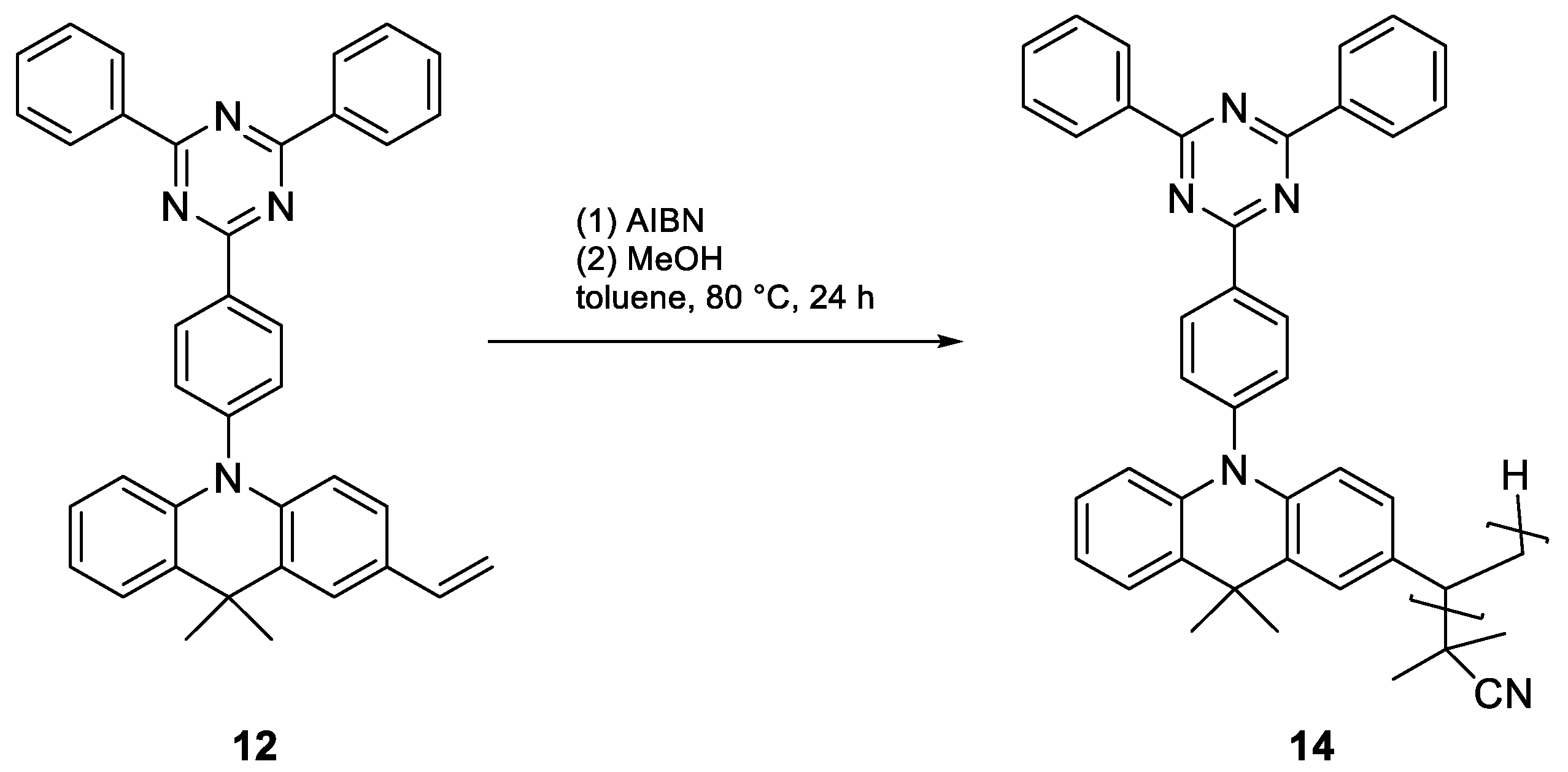


| Enantiomer | Conditions | Mn [kDa] | Mw [kDa] | D | Conversion [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp | 10 mol% tBuLi, toluene, 0 °C, 24 h | 1.78 | 2.03 | 1.14 | 93 |
| Rp | 10 mol% tBuLi, toluene, 0 °C, 24 h | 1.01 | 3.25 | 3.21 | 92 |
| Sp | 1 mol% tBuLi, toluene, 0 °C, 24 h | N/A | N/A | N/A | 97 1 |
| Sp | 10 mol% BF3OEt2, toluene, 0 °C, 24 h | 0.58 | 0.79 | 1.36 | 68 |
| Sp | 10 mol% AIBN, toluene, 60 °C, 24 h | 1.66 | 1.89 | 1.14 | 4 |
| Rp | 10 mol% AIBN, toluene, 60 °C, 24 h | 0.78 | 1.38 | 1.77 | 9 |
| Sp | 2 × 10 mol% AIBN, toluene, 60 °C, 48 h | 1.72 | 2.74 | 1.60 | 18 |
| Sp | 1 mol% AIBN, bulk, 60 °C, 24 h | N/A | N/A | N/A | 34 1 |
| Sample | PCP–Styrene Ratio Determined by 1H NMR Spectroscopy | Mn [kDa] | Mw [kDa] | D | Conversion [%] | Specific Rotation αD20 [(deg*mL)/(g*dm)] Comparison: Vinyl Monomer ± 284 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCP–styrene 1:1 | 1:1.0 | 4.79 | 10.5 | 2.18 | 37 | 102.1 |
| PCP–styrene 1:10 | 1:9.6 | 2.56 | 13.9 | 5.44 | 66 | 51.9 |
| PCP–styrene 1:25 | 1:26.7 | 4.68 | 10.6 | 2.27 | 57 | 14.6 |
| PCP–styrene 1:50 | 1:45.1 | 6.02 | 13.7 | 2.28 | 85 | 7.9 |
| Sample | PCP–DMAC-TRZ Ratio Determined by 1H NMR | Mn [kDa] | Mw [kDa] | D | Conversion [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(vinyl-DMAC-TRZ) (14) | 0:1 | 1.46 | 2.71 | 1.86 | 33 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 10:1 Rp | 3.7:1 | 1.17 | 6.57 | 5.63 | 20 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 20:1 Rp | 6.7:1 | 2.43 | 15.7 | 6.46 | 32 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 50:1 Rp | 11.1:1 | 0.89 | 3.98 | 4.47 | 30 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 100:1 Rp | 18.1:1 | 0.51 | 1.96 | 3.85 | 23 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 20:1 Sp | 7.8:1 | 0.73 | 2.19 | 2.99 | 56 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 50:1 Sp | 17.7:1 | 0.76 | 2.27 | 3.00 | 28 |
| Sample | λmax at 370 nm Excitation (nm) | PLQY in N2 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Poly(vinyl-DMAC-TRZ) (14) | 526 | 26.8 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 10:1 Rp | 525 | 29.1 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 20:1 Rp | 513 | 40.8 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 50:1 Rp | 510 | 47.2 |
| PCP–DMAC-TRZ 100:1 Rp | 513 | 38.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tappert, H.; Puttock, E.V.; Oviedo Ortiz, J.S.; Zysman-Colman, E.; Crassous, J.; Bräse, S. Chiral Polymers Based on Vinyl[2.2]paracyclophane and Their Application as CPL Emitters. Polymers 2025, 17, 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081070
Tappert H, Puttock EV, Oviedo Ortiz JS, Zysman-Colman E, Crassous J, Bräse S. Chiral Polymers Based on Vinyl[2.2]paracyclophane and Their Application as CPL Emitters. Polymers. 2025; 17(8):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081070
Chicago/Turabian StyleTappert, Henrik, Emma V. Puttock, Jhon Sebastian Oviedo Ortiz, Eli Zysman-Colman, Jeanne Crassous, and Stefan Bräse. 2025. "Chiral Polymers Based on Vinyl[2.2]paracyclophane and Their Application as CPL Emitters" Polymers 17, no. 8: 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081070
APA StyleTappert, H., Puttock, E. V., Oviedo Ortiz, J. S., Zysman-Colman, E., Crassous, J., & Bräse, S. (2025). Chiral Polymers Based on Vinyl[2.2]paracyclophane and Their Application as CPL Emitters. Polymers, 17(8), 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081070






