Surface Modification of Polydopamine Particles with Polyethyleneimine Brushes for Enhanced Stability and Reduced Fragmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Pdop Particles
2.3. Synthesis of Pdop/(PEI/PSS)3 and Pdop/(PAH/PSS)3 Multilayers
2.4. Synthesis of Pdop/L-PEI or S-PEI Brushes
2.5. Characterization
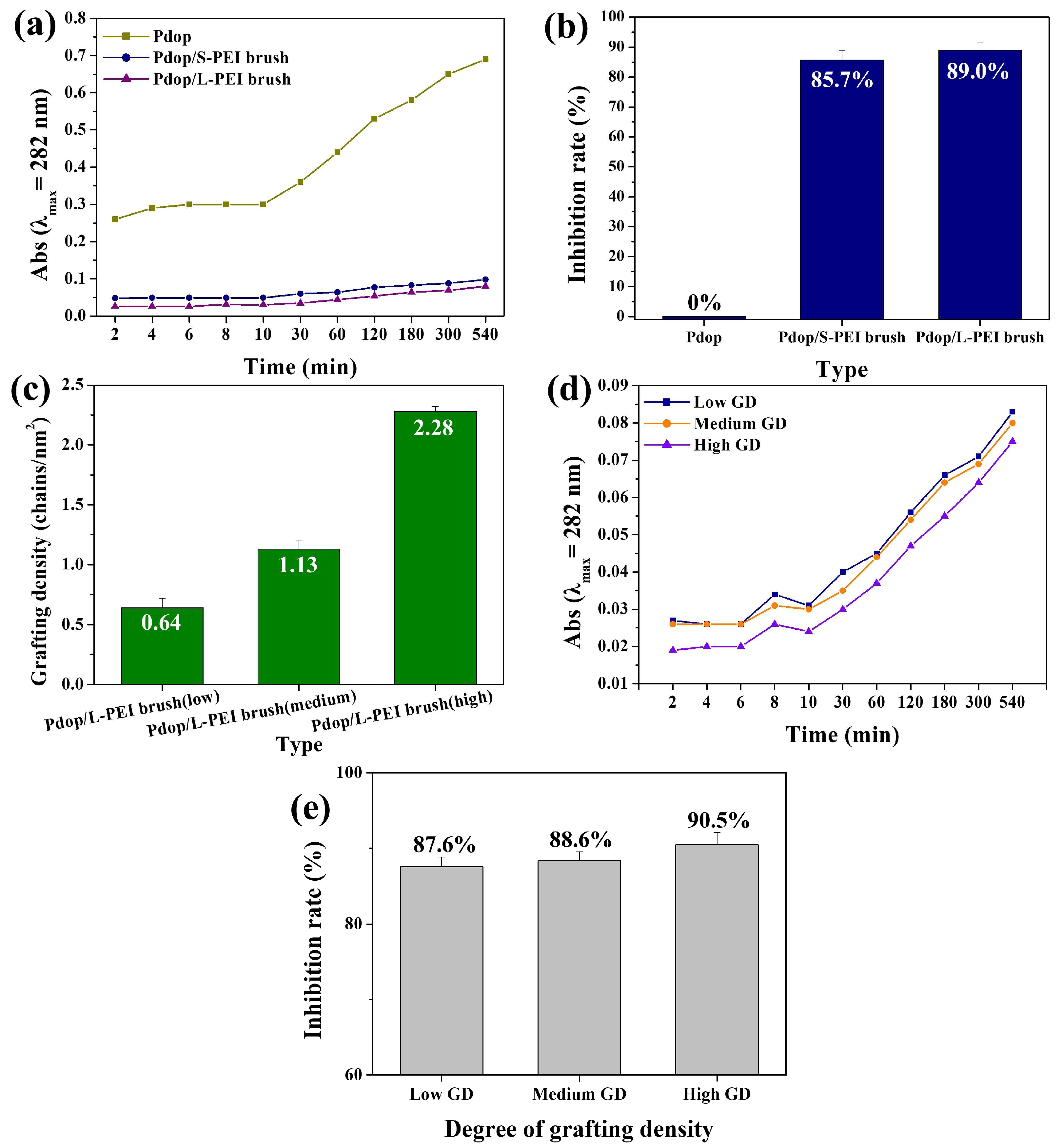
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, W.; Zeng, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zeng, W.; Mei, L.; Zhao, Y. Versatile polydopamine platforms: Synthesis and promising applications for surface modification and advanced nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8537–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, V. Polydopamine nanomaterials: Recent advances in synthesis methods and applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaang, B.K.; Han, N.; Jang, W.; Koo, H.Y.; Lee, Y.B.; Choi, W.S. Crossover magnetic amphiprotic catalysts for oil/water separation, the purification of aqueous and non-aqueous pollutants, and organic synthesis. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wan, J.; Zhou, W.; Shao, J.; Chen, S.; Hou, H.; Lei, Z. A durable efficient oil–water separation material: Polydopamine coating on modified stainless steel mesh. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 686, 162168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Tu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gui, X. An environmentally friendly and superhydrophobic melamine sponge self-roughened by in-situ controllably grown polydopamine nanoparticle for efficient oil-water separation. Colloids Surf. A 2025, 705, 135567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kaang, B.K.; Han, N.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, W.S. An anti-overturn Janus sponge with excellent floating stability for simultaneous pollutant remediation and oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16371–16381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, W.S. Cube sugar-like sponge/polymer brush composites for portable and user-friendly heavy metal ion adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Liu, D.; Liu, W.; Song, Z.; Shang, S.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Cui, S. Graphene oxide/polydopamine modified montmorillonite/carboxymethyl chitosan composite aerogel for efficient removal of Pb2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+: Adsorption behavior, mechanism and DFT study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 339, 126585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Hou, M.; Gao, Z. Polydopamine-modified sodium alginate hydrogel for microplastics removal: Adsorption performance, characteristics, and kinetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 297, 139947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaang, B.K.; Han, N.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, W.S. Polyelectrolyte Brush-Grafted Polydopamine-Based Catalysts with Enhanced Catalytic Activity and Stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Ji, Y.; Wang, H.; Yao, W. Polydopamine-assisted integration of BaTiO3 nanoparticles into PVDF membranes for high-performance piezocatalytic water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 509, 161211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Xie, Q.; Jing, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Sun, X.; Duan, B.; Qi, C.; Su, H. A Comprehensive study on the reduction of 4-NP using Au/Polydopamine catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 680, 161376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ni, J.; Xie, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yao, J. Tubular ZIF@mesoporous polydopamine composite with enhanced catalytic activity for photo-driven CO2 fixation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 366, 132816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yin, B.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, H.; Hou, D. Graphene oxide regulated by polydopamine towards improved cooperative protection of polysiloxane coatings for cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; An, C.; Ma, Z.; Wu, B. Tunable polydopamine coating: Surface modification of polymer bonded explosives to enhance thermal stability and combustion performance. Colloids Surf. A 2025, 709, 136118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Bae, J.Y.; Koo, H.Y.; Lee, Y.B.; Choi, W.S. A Remote-Controlled Generation of Gold@ Polydopamine (core@ shell) Nanoparticles via Physical-Chemical Stimuli of Polydopamine/Gold Composites. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Song, X.; Song, K.; Geng, Z.; Pan, Y.T.; Song, P.; Yang, R. Synchronous preparation and modification of LDH hollow polyhedra by polydopamine: Synthesis and application. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 654, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, Z.; Duan, G.; Han, X.; Yang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, J.; Jian, S.; et al. Large-scale hierarchically porous polydopamine loaded rattan-based solar evaporator with high stability to salinity changes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 213, 118457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Pan, L.; He, Z.; Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Jun, S.C.; Lu, B.; Liang, S.; et al. Stabling zinc metal anode with polydopamine regulation through dual effects of fast desolvation and ion confinement. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 13, 2203523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhlifi, S.E.; Ball, V. Polydopamine as a stable and functional nanomaterial. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 186, 110719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.H.; Jung, Y.J.; Koo, H.Y.; Choi, W.S. Amphiphilic magnetic particles dispersed in water and oil for the removal of hydrophilic and hydrophobic microplastics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 26849–26861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, I.S.; Bettinger, C.J. Polydopamine nanostructures as biomaterials for medical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6895–6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.; Jiang, X. Polydopamine coated selenide molybdenum: A new photothermal nanocarrier for highly effective chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, X. Polydopamine-coated carbon nanotube catalytic membrane with enhanced water decontamination and antifouling capability under photothermal assistance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 358, 130304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; Jia, J.; Tuo, X.; Gong, Y.; Quan, F. Preparation of photothermal alginate/chitosan derivative/CuS@polydopamine composite fibers and application in desalination. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xia, J.; Li, L.; Lv, Q.; Zhao, K.; Ahmad, M.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, S.; Ye, F.; Zhang, Q. Comprehensive enhancement of photocatalytic H2O2 generation and antibacterial efficacy on carbon nitride through a straightforward polydopamine coating strategy. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 56, 105566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Cui, W. Ultrathin polydopamine coated TiO2 to anchor Pt nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 115, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ye, F.; Lv, Q.; Xia, J.; Chen, N.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Zhao, K.; Zeng, Z.; Ahmad, M.; et al. Polydopamine-coated hollow carbon nitride as a full-spectral response photocatalyst for efficient H2O2 production via redox dual pathways. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 363, 124802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, J.; Tjardts, T.; Symalla, F.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Faupel, F.; Aktas, C.; Coy, E.; Veziroglu, S. Boric acid modified polydopamine and nanocolumnar hydrogenated TiO2 nanocomposite with improved photocatalytic performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 686, 162118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environ mental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Yuan, F.; Chen, C.; Wu, J.; Gong, R.; Yuan, G.; Zeng, H.; Pei, J.; Chen, T. Degradation products of polydopamine restrained inflammatory response of LPS-stimulated macrophages through mediation TLR-4-MYD88 dependent signaling pathways by antioxidant. Inflammation 2019, 42, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Tang, F.; Jin, Z. Free-standing polydopamine films generated in the presence of different metallic ions: The comparison of reaction process and film properties. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 18347–18354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Ma, Z. Ultrasensitive amperometric immunoassay for carcinoembryonic antigens by using a glassy carbon electrode coated with a polydopamine-Pb(II) redox system and a chitosan-gold nanocomposite. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.K.; Kumar, J.; Nalwa, H.S. Handbook of Polyelectrolytes and Their Applications; American Scientific Publishers: Valencia, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lone, M.S.; Merino-Chavez, O.D.; Ricks, N.J.; Hammond, M.C.; Noriega, R. Electron transfer drives the photosensitized polymerization of contrast agents by flavoprotein tags for correlative microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 23797–23805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Lee, N.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, S.; Shin, D.-S.; Lee, S.-M. Ultra-selective detection of Fe2+ ion by redox mechanism based on fluorescent polymerized dopamine derivatives. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 30582–30587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.M.; Mohan, T.R.; Branton, A.; Trivedi, D.; Nayak, G.; Mishra, R.K.; Jana, S. Biofield treatment: A potential strategy for modification of physical and thermal properties of indole. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 2, 1000152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, S.H.; Kim, E.J.; Koo, H.Y.; Choi, W.S. Surface Modification of Polydopamine Particles with Polyethyleneimine Brushes for Enhanced Stability and Reduced Fragmentation. Polymers 2025, 17, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091209
Son SH, Kim EJ, Koo HY, Choi WS. Surface Modification of Polydopamine Particles with Polyethyleneimine Brushes for Enhanced Stability and Reduced Fragmentation. Polymers. 2025; 17(9):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091209
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Su Hyeon, Eun Jin Kim, Hye Young Koo, and Won San Choi. 2025. "Surface Modification of Polydopamine Particles with Polyethyleneimine Brushes for Enhanced Stability and Reduced Fragmentation" Polymers 17, no. 9: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091209
APA StyleSon, S. H., Kim, E. J., Koo, H. Y., & Choi, W. S. (2025). Surface Modification of Polydopamine Particles with Polyethyleneimine Brushes for Enhanced Stability and Reduced Fragmentation. Polymers, 17(9), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091209





