Facile Cellulose Dissolution and Characterization in the Newly Synthesized 1,3-Diallyl-2-ethylimidazolium Acetate Ionic Liquid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the IL
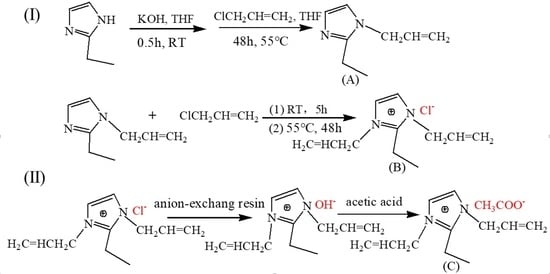
2.2.1. Quaternization Reaction
2.2.2. Anion Exchange
2.3. Measurements of Impurity Content of the ILs
2.4. Dissolution of Bamboo Dissolving Pulp Cellulose in the Synthesized [AAeim][OAc] and [AAeim][OAc]/DMSO Co-Solvent System
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Determination of Physical Properties of the Synthesized IL
2.6.1. Solubility Measurement
2.6.2. Viscosity Measurement
2.6.3. Conductivity Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure of the Synthesized IL
3.2. Physical Properties of the Synthesized IL
3.3. Solubilities of Bamboo Dissolving Pulp Cellulose in a [AAeim][OAc] and [AAeim][OAc]//DMSO Co-Solvent System
3.4. Structure and Thermal Stability of the Regenerated Cellulose
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, D.; Yang, J.; Jiao, C. Dicationic Ionic Liquids as Environmentally Benign Catalysts for Biodiesel Synthesis. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Li, M.; Yuan, T.; Xu, F.; Sun, R. Effect of ionic liquid/organic solvent pretreatment on the enzymatic hydrolysis of corncob for bioethanol production. Part 1: Structural characterization of the lignins. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L. Conversion of carbohydrates into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural catalyzed by acidic ionic liquids in dimethyl sulfoxide. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Y.; Zheng, D.; Wang, S. Rapid and solvent-saving liquefaction of woody biomass using microwave-ultrasonic assisted technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Fan, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Y.; Zheng, D.; Wang, S. Efficient liquefaction of woody biomass in polyhydric alcohol with acidic ionic liquid as a green catalyst. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 81, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wu, M.; Shi, R.; Chen, L. Highly efficient synthesis of biodiesel catalyzed by CF3SO3H-functionalized ionic liquids: Experimental design and study with response surface methodology. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2017, 121, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xing, H.; Su, B.; Yu, K.; Bao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Q. Improved separation efficiency using ionic liquid–cosolvent mixtures as the extractant in liquid–liquid extraction: A multiple adjustment and synergistic effect. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181–182, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogerstraete, T.V.; Onghena, B.; Binnemans, K. Homogeneous Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Metal Ions with a Functionalized Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.; Fontaine, O.; Roche, J.; Bouffier, L.; Kuhn, A.; Zigah, D. Electropolymerization of polypyrrole by bipolar electrochemistry in an ionic liquid. Langmuir 2014, 30, 2973–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Tu, J.; Xiong, H.; Wang, S. Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of heme proteins immobilised in carbon-coated nickel magnetic nanoparticle-chitosan-dimethylformamide composite films in room-temperature ionic liquids. Bioelectrochemistry 2013, 94, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Fan, M. Versatile fabrication of a superhydrophobic and ultralight cellulose-based aerogel for oil spillage clean-up. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 28297–28306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.H.; Zhang, P.; Ma, J.Z.; Ji, P.T.; Li, Y.R.; Jia, S.T. Long-lived superhydrophobic colorful surfaces. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3588–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. Effect of Alkyl Chain Length in Anions on Thermodynamic and Surface Properties of 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Carboxylate Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3458–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; He, J. 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium Chloride Room Temperature Ionic Liquid: A New and Powerful Nonderivatizing Solvent for Cellulose. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 8272–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, R. Instantaneous dissolution of cellulose in organic electrolyte solutions. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, M.W. Electrospinning Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; He, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Han, C.C. Electrospinning of native cellulose from nonvolatile solvent system. Polymer 2008, 49, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungprapa, S.; Puangparn, T.; Weerasombut, M.; Jangchud, I.; Fakum, P.; Semongkhol, S.; Meechaisue, C.; Supaphol, P. Electrospun cellulose acetate fibers: Effect of solvent system on morphology and fiber diameter. Cellulose 2007, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, B.; Xiang, R.; Wu, Y.; Wu, D. Electrospinning of polyacrylonitrile fibers from ionic liquid solution. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 98, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, Y.; Sugimoto, A.; Ohno, H. Superior solubility of polysaccharides in low viscosity, polar, and halogen-free 1,3-dialkylimidazolium formates. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3295–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Effects of anionic structure and lithium salts addition on the dissolution of cellulose in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquid solvent systems. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, G.; Schiehser, S.; Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T. Side reaction of cellulose with common 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 7322–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.; Yen, Y.; Chu, Y. Baylis-Hillman reaction in [bdmim][PF6] ionic liquid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 4673–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Wada, M.; Ohno, H. Cellulose dissolution with polar ionic liquids under mild conditions: Required factors for anions. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Janssen, M.H.A.; van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R.A. Room-temperature ionic liquids that dissolve carbohydrates in high concentrations. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Greiner, L.; Leitner, W. Cellulose solubilities in carboxylate-based ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 2476–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Cao, L.; Wang, B. Facile cellulose dissolution without heating in [C 4 mim][CH 3 COO]/DMF solvent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Jin, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, G. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids and its application: A mini-review. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindman, B.; Karlström, G.; Stigsson, L. On the mechanism of dissolution of cellulose. J. Mol. Liq. 2010, 156, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Chen, J. Densities and viscosities for ionic liquids mixtures containing [eOHmim][BF4], [bmim][BF4] and [bpy][BF4]. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 77, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.S.M.C.; Almeida, H.F.D.; Freire, M.G.; Lopes-da-Silva, J.A.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Santos, L.M.N.B. The effect of n vs. iso isomerization on the thermophysical properties of aromatic and non-aromatic ionic liquids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2016, 423, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Wang, Q.; Guo, S.; Zhao, D.; Chen, C. The role and potential of morpholinium-based ionic liquids in dissolution of cellulose. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 92, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Hydrogen-Bonding and the Dissolution Mechanism of Uracil in an Acetate Ionic Liquid: New Insights from NMR Spectroscopy and Quantum Chemical Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 4109–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Viscosities and Conductivities of 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Carboxylates Ionic Liquids at Different Temperatures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 3102–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S. Insight into the cosolvent effect of cellulose dissolution in imidazolium-based ionic liquid systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 9042–9049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.; Liu, C.; Yue, F.; Sun, R.; Kennedy, J.F. Ultrasound-assisted dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Tashiro, K.; Hongo, T.; Shirataki, H.; Yamane, C.; Ii, T. Influence of Water on Structure and Mechanical Properties of Regenerated Cellulose Studied by an Organized Combination of Infrared Spectra, X-ray Diffraction, and Dynamic Viscoelastic Data Measured as Functions of Temperature and Humidity. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X.; Sun, R. Comparison of physical properties of regenerated cellulose films fabricated with different cellulose feedstocks in ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.O.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Rajulu, A.V. Preparation and properties of self-reinforced cellulose composite films from Agave microfibrils using an ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.Y.; Yoo, D.I.; Shin, Y.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Park, W.H.; Youk, J.H. Crystalline structure analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide by means of X-ray diffraction and FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2376–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, J. Room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs): A new and versatile platform for cellulose processing and derivatization. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 147, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cao, S.; Fan, M.; Huang, L.; Chen, L. Facile Cellulose Dissolution and Characterization in the Newly Synthesized 1,3-Diallyl-2-ethylimidazolium Acetate Ionic Liquid. Polymers 2017, 9, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100526
Zhang H, Xu Y, Li Y, Lu Z, Cao S, Fan M, Huang L, Chen L. Facile Cellulose Dissolution and Characterization in the Newly Synthesized 1,3-Diallyl-2-ethylimidazolium Acetate Ionic Liquid. Polymers. 2017; 9(10):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100526
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hui, Yaoguang Xu, Yuqi Li, Zexiang Lu, Shilin Cao, Mizi Fan, Liulian Huang, and Lihui Chen. 2017. "Facile Cellulose Dissolution and Characterization in the Newly Synthesized 1,3-Diallyl-2-ethylimidazolium Acetate Ionic Liquid" Polymers 9, no. 10: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100526
APA StyleZhang, H., Xu, Y., Li, Y., Lu, Z., Cao, S., Fan, M., Huang, L., & Chen, L. (2017). Facile Cellulose Dissolution and Characterization in the Newly Synthesized 1,3-Diallyl-2-ethylimidazolium Acetate Ionic Liquid. Polymers, 9(10), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100526