The Effect of Fluid Shear Stress on the In Vitro Release Kinetics of Sirolimus from PLGA Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Sirolimus-Carrying PLGA Films
2.3. Release of Sirolimus
2.4. Analysis of Sirolimus
2.5. Sirolimus-Carrying PLGA Film Degradation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
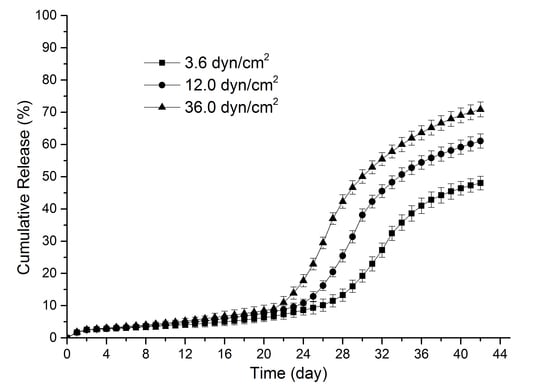
3.1. Sirolimus Release Kinetics
3.2. Degradation of PLGA Films with Sirolimus
3.3. Discussion of Release Profiles
3.4. Research Limitations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gummert, J.F.; Ikonen, T.; Morris, R.E. Newer immunosuppressive drugs: A review. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 1366–1380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morice, M.C.; Serruys, P.W.; Sousa, J.E.; Fajadet, J.; Ban Hayashi, E.; Perin, M.; Colombo, A.; Schuler, G.; Barragan, P.; et al. A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisz, G.; Leon, M.B.; Holmes, D.R.; Kereiakes, D.J.; Popma, J.J.; Teirstein, P.S.; Cohen, S.A.; Wang, H.; Cutlip, D.E.; Moses, J.W. Five-year follow-up after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: Results of the SIRIUS (Sirolimus-Eluting Stent in De-Novo Native Coronary Lesions) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisari, A.; Pistritto, A.M.; Piccolo, R.; La Manna, A.; Danzi, G.B. The Ultimaster Biodegradable-Polymer Sirolimus-Eluting Stent: An Updated Review of Clinical Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.M.; Boyle, F.J. Drug-eluting stents for coronary artery disease: A review. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausleiter, J.; Kastrati, A.; Wessely, R.; Dibra, A.; Mehilli, J.; Schratzenstaller, T.; Graf, I.; Renke-Gluszko, M.; Behnisch, B.; Dirschinger, J.; et al. Prevention of restenosis by a novel drug-eluting stent system with a dose-adjustable, polymer-free, on-site stent coating. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, J.E.; Costa, M.A.; Abizaid, A.; Feres, F.; Seixas, A.C.; Tanajura, L.F.; Mattos, L.A.; Falotico, R.; Jaeger, J.; Popma, J.J. Four-year angiographic and intravascular ultrasound follow-up of patients treated with sirolimus-eluting stents. Circulation 2005, 111, 2326–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virmani, R.; Guagliumi, G.; Farb, A.; Musumeci, G.; Grieco, N.; Motta, T.; Mihalcsik, L.; Tespili, M.; Valsecchi, O.; Kolodgie, F.D. Localized hypersensitivity and late coronary thrombosis secondary to a sirolimus-eluting stent should we be cautious? Circulation 2004, 109, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeewandara, T.M.; Wise, S.G.; Ng, M.K.C. Biocompatibility of coronary stents. Materials 2014, 7, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, C.M.; Muramatsu, T.; Iqbal, J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Onuma, Y.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Haude, M.; Lemos, P.A.; Warnack, B.; Serruys, P.W. Bioresorbable drug-eluting magnesium-alloy scaffold for treatment of coronary artery disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24492–24500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexis, F.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Rath, S.K.; Boey, F. In vitro study of release mechanisms of paclitaxel and rapamycin from drug-incorporated biodegradable stent matrices. J. Control. Release 2004, 98, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotts, G.; Park, T.G. Protein delivery from poly (lactic–co–glycolic acid) biodegradable microspheres: Release kinetics and stability issues. J. Microencapsul. 1998, 15, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benicewicz, B.C.; Hopper, P.K. Review: Polymers for Absorbable Surgical Sutures—Part II. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 1991, 6, 64–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdhanie, L.I.; Aubuchon, S.R.; Boland, E.D.; Knapp, D.C.; Barnes, C.P.; Simpson, D.G.; Wnek, G.E.; Bowlin, G.L. Thermal and mechanical characterization of electrospun blends of poly (lactic acid) and poly (glycolic acid). Polym. J. 2006, 38, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.S.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, H.Y.; Jin, S.; Shim, J.H.; Yun, W.S.; Jeong, C.M.; Huh, J.B. Comparative Efficacies of Collagen-Based 3D Printed PCL/PLGA/β-TCP Composite Block Bone Grafts and Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Bone Substitute for Bone Regeneration. Materials 2017, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, J.C.; Tipton, A.J. Synthetic biodegradable polymers as orthopedic devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.P.; Feitosa, A.; Oliveira, F.C.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; da Silva, E.N.; Dias, G.G.; Sales, F.A.; Sousa, B.L.; Barroso-Neto, I.L.; Pessoa, C.; et al. Controlled Release of Nor-β-lapachone by PLGA Microparticles: A Strategy for Improving Cytotoxicity against Prostate Cancer Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanao, F.; Rosa, P.; Bosco, R.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.; Kersten-Niessen, M.J.; Wolke, J.G.; den Beucken, J.J.; Jansen, J.A. RANKL delivery from calcium phosphate containing PLGA microspheres. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 3123–3130. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Valenzuela, C.A.; Guerrero-Germán, P.; Tejeda-Mansir, A.; Esquivel, R.; Guzmán-Z, R.; Lucero-Acuña, A. Folate Functionalized PLGA Nanoparticles Loaded with Plasmid pVAX1-NH36: Mathematical Analysis of Release. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijns, W.; Vrolix, M.; Verheye, S.; Schoors, D.; Slagboom, T.; Gosselink, M.; Benit, E.; Donohoe, D.; Knape, C.; Attizzani, G.F.; et al. Randomised study of a bioabsorbable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting stent: Results of the DESSOLVE II trial. EuroIntervention 2015, 10, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusinaru, D.; Vrolix, M.; Verheye, S.; Chowdhary, S.; Schoors, D.; Di Mario, C.; Desmet, W.; Donohoe, D.J.; Ormiston, J.A.; Knape, C.; et al. Bioabsorbable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting stent implantation preserves coronary vasomotion: A DESSOLVE II trial sub-study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 86, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansky, A.J.; Kastrati, A.; Edelman, E.R.; Parise, H.; Ng, V.G.; Ormiston, J.; Wijns, W.; Byrne, R.A. Comparison of the Absorbable Polymer Sirolimus-Eluting Stent (MiStent) to the Durable Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stent (Xience) (from the DESSOLVE I/II and ISAR-TEST-4 Studies). Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.G. Degradation of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres: Effect of copolymer composition. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrell, S.; Cameron, R.E. The effect of initial polymer morphology on the degradation and drug release from polyglycolide. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Garcia, C.A.; Mikos, A.G. In vitro degradation of thin poly (dl-lactic-co-glycolic acid) films. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 46, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolnik, B.S.; Burgess, D.J. Effect of acidic pH on PLGA microsphere degradation and release. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Fan, Y. Effect of cyclic loading on in vitro degradation of poly (l-lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2010, 21, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Feng, X.; Jia, X.; Fan, Y. Influences of tensile load on in vitro degradation of an electrospun poly (l-lactide-co-glycolide) scaffold. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2991–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Chu, Z.; Yao, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y. The effects of tensile stress on degradation of biodegradable PLGA membranes: A quantitative study. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 124, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, A.M.; Alper, S.L.; Izumo, S. Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. JAMA 1999, 282, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, P.; Fan, Z.; Sun, A.; Zhan, F.; Fan, Y.; Deng, X. Nitric oxide transport in normal human thoracic aorta: Effects of hemodynamics and nitric oxide scavengers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, P.; Fan, Z.; Sun, A.; Zhan, F.; Fan, Y.; Deng, X. Enhanced accumulation of LDLs within the venous graft wall induced by elevated filtration rate may account for its accelerated atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 2014, 236, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Cancel, L.M.; Tarbell, J.M. Effect of shear stress on water and LDL transport through cultured endothelial cell monolayers. Atherosclerosis 2014, 233, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofili, E.O.; Labovitz, A.J.; Kern, M.J. Coronary flow velocity dynamics in normal and diseased arteries. Am. J. Cardiol. 1993, 71, D3–D9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentzel, J.J.; Krams, R.; Schuurbiers, J.C.; Oomen, J.A.; Kloet, J.; van der Giessen, W.J.; Serruys, P.W.; Slager, C.J. Relationship between neointimal thickness and shear stress after Wallstent implantation in human coronary arteries. Circulation 2001, 103, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofili, E.O.; Kern, M.J.; Vrain, J.A.S.; Donohue, T.J.; Bach, R.; Al-Joundi, B.; Aguirre, F.V.; Castello, R.; Labovitz, A.J. Differential characterization of blood flow, velocity, and vascular resistance between proximal and distal normal epicardial human coronary arteries: Analysis by intracoronary Doppler spectral flow velocity. Am. Heart J. 1995, 130, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.; Tseng, D.Y.; Squire, J.C.; Edelman, E.R. Balloon-Artery Interactions During Stent Placement A Finite Element Analysis Approach to Pressure, Compliance, and Stent Design as Contributors to Vascular Injury. Circ. Res. 1999, 84, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.K.; Devarakonda, S.B.; Rajamohan, D.; Back, L.H. Developed pulsatile flow in a deployed coronary stent. Biorheology 2007, 44, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Guo, M.; Yao, J.; Xu, P.; Feng, W.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, G.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Fan, Y. The effect of fluid shear stress on the in vitro degradation of poly (lactide–co–glycolide) acid membranes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2016, 104, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Feng, C.; Guo, M.; Ding, X.; Feng, W.; Gao, Y.; Yao, J.; et al. Effects of different fluid shear stress patterns on the in vitro degradation of poly (lactide–co–glycolide) acid membranes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nukala, R.K.; Boyapally, H.; Slipper, I.J.; Mendham, A.P.; Douroumis, D. The application of electrostatic dry powder deposition technology to coat drug-eluting stents. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merciadez, M.; Alquier, L.; Metha, R.; Patel, A.; Wang, A. A novel method for the elution of sirolimus (rapamycin) in drug-elution stents. Dissolut. Technol. 2011, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamberi, M.; Nayak, S.; Myo-Min, K.; Carter, T.P.; Hancock, L.; Feder, D. A novel accelerated in vitro release method for biodegradable coating of drug eluting stents: Insight to the drug release mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 37, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehlaghi, V.; Shadpoor, M.T.; Najarian, S. Analysis of wall shear stress in stented coronary artery using 3D computational fluid dynamics modeling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 197, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Boey, F.Y.; Loo, J.S.; Tan, L.P. Controlled release of sirolimus from a multilayered PLGA stent matrix. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5588–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidlitz, A.; Nagel, S.; Semmling, B.; Sternberg, K.; Kroemer, H.K.; Weitschies, W. In vitro dissolution testing of drug-eluting stents. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2013, 14, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krueger, J.W.; Young, D.F.; Cholvin, N.R. An in vitro study of flow response by cells. J. Biomech. 1971, 4, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Fan, Y.; Deng, X. Vascular smooth muscle cell glycocalyx modulates shear-induced proliferation, migration, and NO production responses. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H76–H83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, E. Flow injection analysis of polymeric excipients used in pharmaceutical formulations. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2006, 11, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.X.; Shi, Y.P. A novel zein-based dry coating tablet design for zero-order release. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 370, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, N.A.; Buchanan, F.J.; Orr, J.F.; Dickson, G.R. Degradation of poly-l-lactide. Part 1: In vitro and in vivo physiological temperature degradation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2004, 218, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, J.G.; Kim, J.H.; Heo, J.S.; Choi, J.W.; Jang, Y.S.; Yoon, J.; Lee, S.J.; Kwon, I.K. Development of a biodegradable sirolimus-eluting stent coated by ultrasonic atomizing spray. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 5689–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Challa, P.; Epstein, D.L.; Yuan, F. Controlled release of ethacrynic acid from poly (lactide-co-glycolide) films for glaucoma treatment. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4279–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Venkatraman, S.S. Effect of polymer type on the dynamics of phase inversion and drug release in injectable in situ gelling systems. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, S.C.J.; Ooi, C.P.; Boey, Y.C.F. Influence of electron-beam radiation on the hydrolytic degradation behaviour of poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA). Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3809–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, S.; Bressloff, N.W.; Forrester, A.I.; Curzen, N. The influence of strut-connectors in stented vessels: A comparison of pulsatile flow through five coronary stents. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengier, F.; Delles, M.; Weber, T.F.; Böckler, D.; Ley, S.; Kauczor, H.U.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H. In vitro validation of flow measurements in an aortic nitinol stent graft by velocity-encoded MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 80, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Il’ichev, Y.V.; Alquier, L.; Maryanoff, C.A. Degradation of rapamycin and its ring-opened isomer: Role of base catalysis. Arkivoc 2007, 12, 110–131. [Google Scholar]
- Rouf, M.A.; Bilensoy, E.; Vural, İ.; Hıncal, A.A. Determination of stability of rapamycin following exposure to different conditions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, S46. [Google Scholar]
- Simamora, P.; Alvarez, J.M.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Solubilization of rapamycin. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 213, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, I.; Bai, C.Z.; Hwang, J.; Park, J.; Park, J.S.; Kim, D.J. Suppression of neointimal hyperplasia by sirolimus-eluting expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) haemodialysis grafts in comparison with paclitaxel-coated grafts. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Chu, Z.; Li, X.; Kang, H.; Yang, X.; Fan, Y. Effects of aqueous medium, Tween-20 and flow on the stability of sirolimus. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2017, 17, 1750039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Shear Stress | Phase | Period (Day) | kd (% Day−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.6 dyn/cm2 | Phase I | 1–2 | ND | - |
| Phase II | 3–23 | 0.24 | 0.953 | |
| Phase III | 24–36 | 2.97 | 0.960 | |
| Phase IV | 37–42 | 1.03 | 0.987 | |
| 12.0 dyn/cm2 | Phase I | 1–2 | ND | - |
| Phase II | 3–22 | 0.30 | 0.976 | |
| Phase III | 23–32 | 4.37 | 0.973 | |
| Phase IV | 33–42 | 1.37 | 0.972 | |
| 36.0 dyn/cm2 | Phase I | 1–2 | ND | - |
| Phase II | 3–21 | 0.34 | 0.986 | |
| Phase III | 22–29 | 5.43 | 0.987 | |
| Phase IV | 30–42 | 1.71 | 0.971 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Q.; Chu, Z.; Li, X.; Kang, H.; Yang, X.; Fan, Y. The Effect of Fluid Shear Stress on the In Vitro Release Kinetics of Sirolimus from PLGA Films. Polymers 2017, 9, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9110618
Zheng Q, Chu Z, Li X, Kang H, Yang X, Fan Y. The Effect of Fluid Shear Stress on the In Vitro Release Kinetics of Sirolimus from PLGA Films. Polymers. 2017; 9(11):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9110618
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Quan, Zhaowei Chu, Xiaoming Li, Hongyan Kang, Xiao Yang, and Yubo Fan. 2017. "The Effect of Fluid Shear Stress on the In Vitro Release Kinetics of Sirolimus from PLGA Films" Polymers 9, no. 11: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9110618
APA StyleZheng, Q., Chu, Z., Li, X., Kang, H., Yang, X., & Fan, Y. (2017). The Effect of Fluid Shear Stress on the In Vitro Release Kinetics of Sirolimus from PLGA Films. Polymers, 9(11), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9110618