Abstract
As and Cd in soil can be assimilated and accumulated by vegetables and can be subsequently ingested by humans. Contradictory effects of organic fertilizer application on As and Cd accumulation in soil have been reported in previous studies. An eight-year greenhouse study was conducted on a sandy loam soil in Beijing, China to investigate the effects of organic fertilizer application rate on soil properties, and As and Cd accumulation in soil. The contamination risk of pak choi grown after eight years’ application of organic fertilizer was also evaluated. Soil organic carbon increased 3.0–3.8 times with low, medium and high rates of fertilizer application in 2018 compared to the initial soil. Organic fertilizer application significantly increased soil nutrients and microbial biomass while it mildly affected soil pH. The bioavailability of As/Cd has decreased after eight years’ application of organic fertilizer. Pak choi crop harvested from all three treatments in 2018 did not pose a threat to human health, even for life-time consumption. Soil total As content significantly decreased with organic fertilizer application, mainly due to the lower As content in the applied fertilizer than that in soil. Continuous application of clean organic fertilizer can be adopted to reduce the contamination risk of highly contaminated soil in the soil–plant system.
1. Introduction
Trace element contamination in soil poses a threat to food safety and public health. According to the first Chinese national soil pollution survey conducted from 2005 to 2013, approximately 26 million ha of arable land in China was contaminated with trace elements, with Arsenic (As) and Cadmium (Cd) being the principal contaminants in 2.7% and 7.0% of arable land, respectively [1,2]. Based on the data from 548 soil samples, the average As and Cd contents were 6.48 and 0.13 mg kg−1 in facility vegetable production nation-wide, with 1.6 and 5.3% of the area being contaminated with As and Cd, respectively [3].
Manure from intensive livestock and poultry production is one of the main sources of trace elements in agricultural soils. Excessively high As and Cd contents were reported in 162 commercial organic fertilizers where total As contents ranged from 0 to 14.1 mg kg−1 and total Cd contents ranged from 2.0 to 256.0 mg kg−1 [4]. However, a substantial improvement had been made after issuing of the industry standards on toxic and harmful substances in commercial organic fertilizer in 2012 [5]. Huang et al. [6] analyzed 126 commercial organic fertilizers and reported average As and Cd contents of 5.6 mg kg−1 (range, 0–23.3 mg kg−1) and 1.2 mg kg−1 (range, 0.1–5.3 mg kg−1), respectively.
Long-term organic fertilizer application has positive effects on soil organic matter content increases, soil enzyme activity, microbial abundance, carbon sequestration and soil productivity. Therefore, it contributes to the establishment of sustainable production with additional economic and environmental benefits [7,8,9]. However, continuous organic fertilization can increase the risk of trace element contamination risk of soil and crops. Trace element accumulation in soil and the consequent health risk from different crops (e.g., rice, peanut and vegetables) grown in these soils, following continuous fertilization with manure-derived organic fertilizer, have often been reported [4,10,11,12,13]. Nevertheless, several studies have indicated that continuous organic fertilizer application did not necessarily cause As and Cd accumulation in soil and crops. Gul et al. [14] reported that organic fertilizer, derived from cattle manure or sheep manure, reduced trace elements (including As and Cd) and bioavailability, and retarded the transfer of As and Cd from contaminated soil to crops. Chaney [15] reported increased soil As contents in some studies, but the opposite in other studies after organic fertilizer application. Organic fertilizer has been promoted as an alternative to chemical fertilizer to improve soil quality, increase crop production and alleviate contamination from manure discharges, and it is essential to minimize trace element pollution from organic fertilizer application to ensure food safety [16].
Given that organic fertilizer is frequently used in vegetable production, and the increasing demands for food safety and clean production, there is a pressing requirement for more information on As and Cd behavior in the soil–crop system following continuous organic fertilizer application. The objectives of this study were to (1) clarify the effects of long-term organic fertilizer application on soil properties, such pH, organic carbon (C), soil nutrient supply and microbial biomass, As and Cd bioavailability and accumulation in soil; (2) evaluate the health risk of pak choi grown on these soils; and (3) determine the key factor on whether As and Cd contents increase or decrease with organic fertilizer application in the soil–crop system.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted on a sandy loam soil in a plastic solar greenhouse in Yanqing District, Beijing, China from March 2011 to December 2018. Before 2011, the greenhouse was used for organic vegetable production. Soil properties (0–30 cm) before planting in 2011 were: electrical conductivity (soil:water = 1:5, w/w) of 0.33 mS cm−1, pH (soil:water = 1:2.5, w/w) of 8.1, soil organic carbon content of 6.7 g kg−1, total nitrogen (N) content of 1.4 g kg−1, Olsen phosphorus (P) content of 106.4 mg kg−1 and exchangeable potassium (K) content of 192.3 mg kg−1. Total soil As and Cd contents were 7.73 and 0.15 mg kg−1 in March 2011, respectively.
The total cropped area of the greenhouse was 336.0 m2 (56.0 m × 6.0 m). A randomized complete block design was used with three treatments of different organic fertilizer rates. Each treatment had three replications. Each block (6.0 m × 4.2 m) consisted of three plots with the middle one as the sampling plot. There were additional border zones along the eastern and western sides of the greenhouse.
2.1. Fertilizer Treatments
There were three fertilizer rate treatments: low, medium and high application rates. From March 2011 to February 2014, 52.5, 105 and 210 t DW ha−1 of organic fertilizer (mixture of chicken and cattle manure, prepared locally) were applied twice a year before planting in March and August (incorporated with a plough to 10–15 cm) to the soil. Properties of the organic fertilizer were determined before each application with an average pH of 7.7, organic C content of 177.9 g kg−1, total N content of 8.8 g kg−1, total P content of 8.6 mg kg−1 total K content of 16.5 mg kg−1, total As content of 3.03 mg kg−1 and total Cd content of 0.14 mg kg−1 over applications from March 2011 to February 2014 [17].
To ensure a more consistent nutrient supply, the locally prepared fertilizer was replaced by a commercially produced organic fertilizer (Beijing Dongxiang Environmental Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China) made from sheep manure. The application rates were adjusted to 30, 60 and 90 t DW ha−1 for each application from March 2014 to August 2018 (incorporated with a plough to 10–15 cm). Organic fertilizer properties: pH of 7.6, organic C content of 224.7 g kg−1, total N content of 12.9 g kg−1, total P content of 12.6 mg kg−1, and total K content of 18.7 mg kg−1, total As content of 1.65 mg kg−1 and total Cd content of 0.42 mg kg−1 averaged over applications from March 2014 to August 2018.
Two or three different vegetable crops were grown in the greenhouse each year: tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) from March to August, and then one or two leafy vegetables such as celery (Apium graveliens L.), lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.), cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitate) or pak choi (Brassica rapa ssp. Chinensis) were grown from August to March. Irrigation, pest control and regular management of the crops were conducted as required, following local practices. The pak choi crop used for plant analyses was planted on November 2018 and harvested on December 2018.
2.2. Soil Sample Collection and Analysis
Soil samples (0–30 cm) were taken during August to October each year from 2011 to 2017 (excluding 2015), air-dried and then stored at room temperature. Soil samples (0–30 cm) taken on 11 December 2018 were similarly processed. All soil samples from 2011 to 2018 were analyzed for soil pH, soil organic C content, total As and Cd contents, HCl extractable As content (HCl-As) and diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) and extractable Cd content (DTPA-Cd). In addition, soil microbial biomass C (MBC), soil microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN), soil total N, Olsen P and exchangeable K were determined in soil samples taken in 2018.
Soil pH (soil:water, 1:2.5, w/w) was determined with air-dried soil. Soil organic C was determined following digestion with 0.8 M K2Cr2O7 and 18.4 M H2SO4, by titration with 0.2 M FeSO4 after the addition of 2–3 drops of phenanthroline complex as an indicator [18]. Soil MBC and MBN were determined according to Vance et al. [19] with a total organic C and total N analyzer (Multi N/C 3100, Analytic Jena, Jena, Germany). Air-dried soil samples were microwave digested with HNO3 (68%, GR) and HF (40%, GR) (HNO3:HF, 7:3, v/v) and then the total As and Cd contents in soil were determined with an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, Agilent 7700X, Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) [20].
For the determination of total N, air-dried soil samples were digested with 18.4 M H2SO4 using a mixed K2SO4-CuSO4-Se (ratios 100:10:1) catalyst; analysis was conducted with a continuous flow analyzer (Auto Analyzer 3 System, SEAL Analytical GmbH, Germany) after filtration. Olsen P content was determined according to Olsen et al. [21] Soil-exchangeable K was extracted with 1 M ammonium acetate, and analyzed with an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (ZEEnit700P, Analytic Jena, Jena, Germany).
DTPA-Cd was extracted with 5 mM DTPA solution, following the method issued by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China [22]. HCl-As was extracted with 0.1 M HCl following Zhang et al. [23] Sequential extractions of As (exchangeable, surface absorption, bound to iron and aluminum, bound to calcium and residual fractions) and Cd (exchangeable, bound to carbonates, bound to iron and manganese oxides, bound to organic matter and residual fractions) were conducted according to Shiowatana et al. [24] and Tessier et al. [25], respectively. As and Cd contents of different fractions were determined with ICP-MS.
2.3. Plant Sample Collection and Analysis
Leaf samples were taken from six pak choi plants from the sampling plot of each treatment on 4 December 2018. Theleaves were washed by distilled water, dried and ground. After digestion with HNO3 (68%, GR: guaranteed reagent) and H2O2 (30%, GR) (HNO3:H2O2, 5:3, v/v) in a teflon digestion vessel [26], leaf As and Cd contents were determined using an ICP-MS.
2.4. Data Analysis
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for soil pH, soil organic C and trace elements accumulation (total soil As and Cd, HCl-As and DTPA-Cd) as a function of fertilizer application rate and year were conducted using the PROC MIXED procedure in the SAS statistical software package (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Repeated measures were used for year effect. Soil properties (MBN, MBC, total N, Olsen P and available K), crop yield, and plant As and Cd contents in 2018 were analyzed with PROC ANOVA as a function of fertilizer application rate. Means were compared using the Least Significant Difference (LSD) test at the 5% probability level. Means of soil pH, organic C, HCl-As, DTPA-Cd, total As and Cd were compared within treatments for year effect.
The health risk assessment criteria and equations used are listed below:
where is the As/Cd content in pak choi leaf, and is the total As/Cd content in soil [27].
is the exposure frequency (365 days per year); is the exposure duration (70 years); is daily vegetable consumption (0.35 kg vegetable consumption per day per capita in China) [28]; is the As/Cd content of pak choi leaf in fresh weight (mg kg−1); is the reference dose (0.3 × 10−3 mg kg−1 body weight per day and 1 × 10−3 mg kg−1 body weight per day for As and Cd, respectively) [29]; is the average body weight (60 kg). is the averaged exposure time (365 days per year) [30,31].
Estimated soil total As and Cd contents were calculated under the assumptions of consistent organic fertilizer supply, zero plant uptake and zero soil leaching.
where is the average content of trace element in the applied organic fertilizer from 2011 to 2018 (2.36 and 0.28 mg kg−1 for As and Cd, respectively); is the average annual input of organic fertilizer from 2011 to 2018 (80, 159 and 285 t ha−1 for low, medium and high application rates, respectively); is the trace element content in the initial soil (7.73 and 0.15 mg kg−1 for As and Cd, respectively); is the soil bulk density (1.4 g cm−3) in the initial soil; is the sampling soil depth (0.3 m). All figures were plotted with Originpro 2016 (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Properties
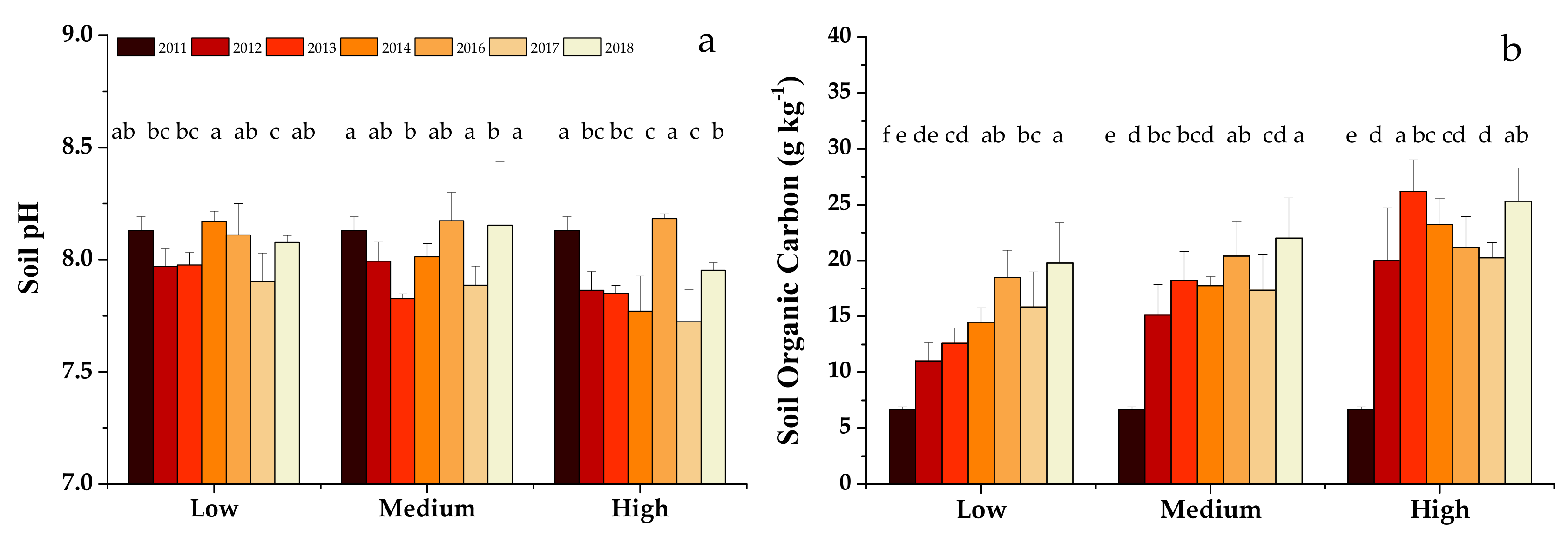
Soil pH was mildly affected by organic fertilizer application rate and year (within a range from 7.7 to 8.2 for all treatments from 2011 to 2018, Figure 1a). Soil organic C was significantly increased with increasing organic fertilizer application rate and year (Figure 1b). By 2018, soil organic C contents had increased by 2.0, 2.3 and 2.8 times for low, medium and high application rates, respectively, in comparison to its content in the initial soil. Soil organic C content gradually increased when the low rate organic fertilizer was continuously applied. For medium and high rate organic fertilizer treatments, it increased appreciably after one year and then changed slightly thereafter.
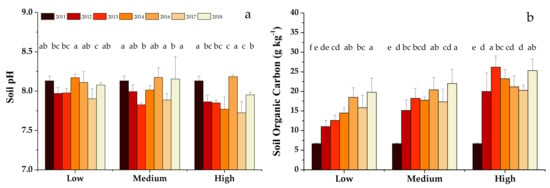
Figure 1.
Soil pH (a) and organic carbon (b) of three treatments from 2011 to 2018. Different letters above the vertical bars indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
At the end of the study in 2018, soil nutrient contents (total N, Olsen P and exchangeable K) and microbial biomass (MBC and MBN) significantly increased with organic fertilizer application rates (Table 1). MBC and MBN contents in soil of the high fertilizer treatment were 50% and 48% higher than in soil that received the low fertilizer treatment, respectively. Total N, Olsen P and exchangeable K greatly increased from 1.4 g kg−1, 106.4 mg kg−1 and 192.3 mg kg−1 in the initial soil in 2011 to 2.6 g kg−1, 312.7 mg kg−1 and 229.2 mg kg−1 in high rate fertilizer treatment in 2018, respectively.

Table 1.
Soil nutrients and microbial biomass in the initial soil in 2011 and in three treatments in 2018.
The significant increases in soil organic C, soil microbial biomass and Olsen P from continuous manure application observed in the present study are consistent with the results of a meta-analysis of data from 132 long-term studies (≥10 years) of organic fertilizer application on soil properties [32]. Large additions of organic material from organic fertilizer application were responsible for observed increases in these soil characteristics [33,34].
Soil pH was little affected in the three organic fertilizer treatments after eight years of application, the similar pH values of the initial soil (8.1) and organic fertilizer (7.6 and 7.7) being the likely explanation. Results from previous studies suggest that organic fertilizer application can either increase the pH of acidic soil or decrease the pH of alkaline soil [35,36,37]. Differences between pH of the initial soil and of the applied organic fertilizer partially explain the changes in soil pH [32,38], organic acids from increased microbial activity associated with the decomposition of applied organic fertilizer being an additional factor [39].
According to the Beijing soil nutrient index scoring system [40], total N (1.87–2.58 g kg−1), Olsen P (227.40–312.70 mg kg−1), and exchangeable K (145.36–229.20 mg kg−1) contents of all treatments in 2018 were rated as being high or extremely high. Thus, non-point source pollution should also be considered when applying organic fertilizer in a large amount or for long-term use.
3.2. As and Cd Bioavailability and Plant Uptake
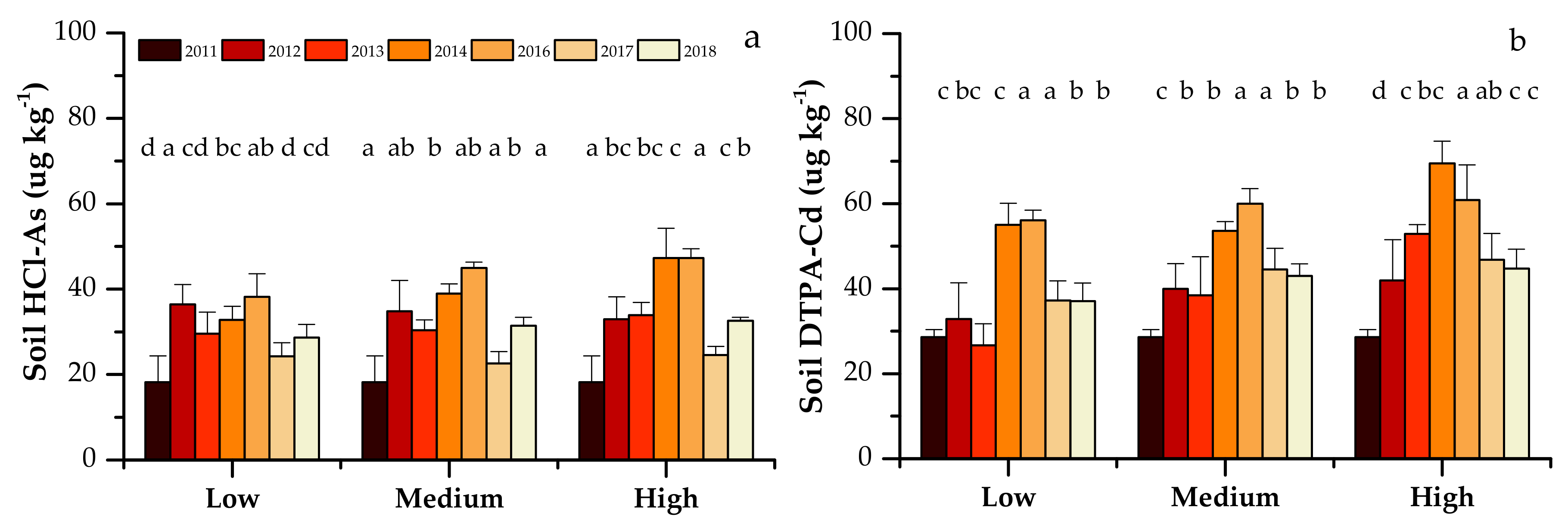
The bioavailability of As/Cd was evaluated by single extraction (HCl and DTPA extraction) and sequential extraction (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Continuous organic fertilizer application generally increased soil HCl-As and soil DTPA-Cd contents during this study (Figure 2). Soil HCl-As significantly increased from an initial value of 18.2 μg kg−1 in 2011 to 28.7, 31.4 and 32.6 μg kg−1 in 2018 in the low, medium and high fertilizer rate treatments, respectively (Figure 2a). Soil DTPA-Cd significantly increased from an initial value of 28.6 μg kg−1 in 2011 to 37.1, 43.0 and 44.7 μg kg−1 in 2018 in the low, medium and high fertilizer rate treatments, respectively (Figure 2b).
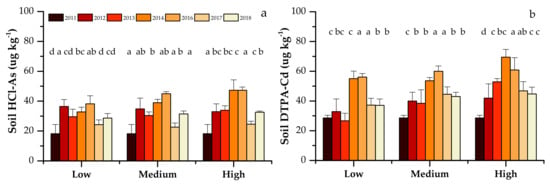
Figure 2.
Soil HCl-As (a) and DTPA-Cd (b) of three treatments from 2011 to 2018. Different letters above the vertical bars indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
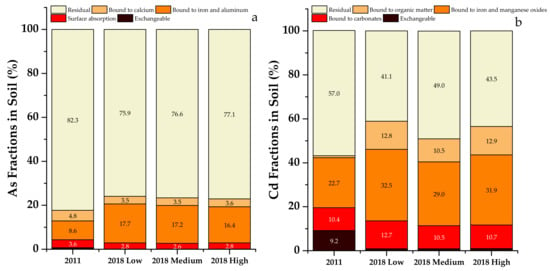
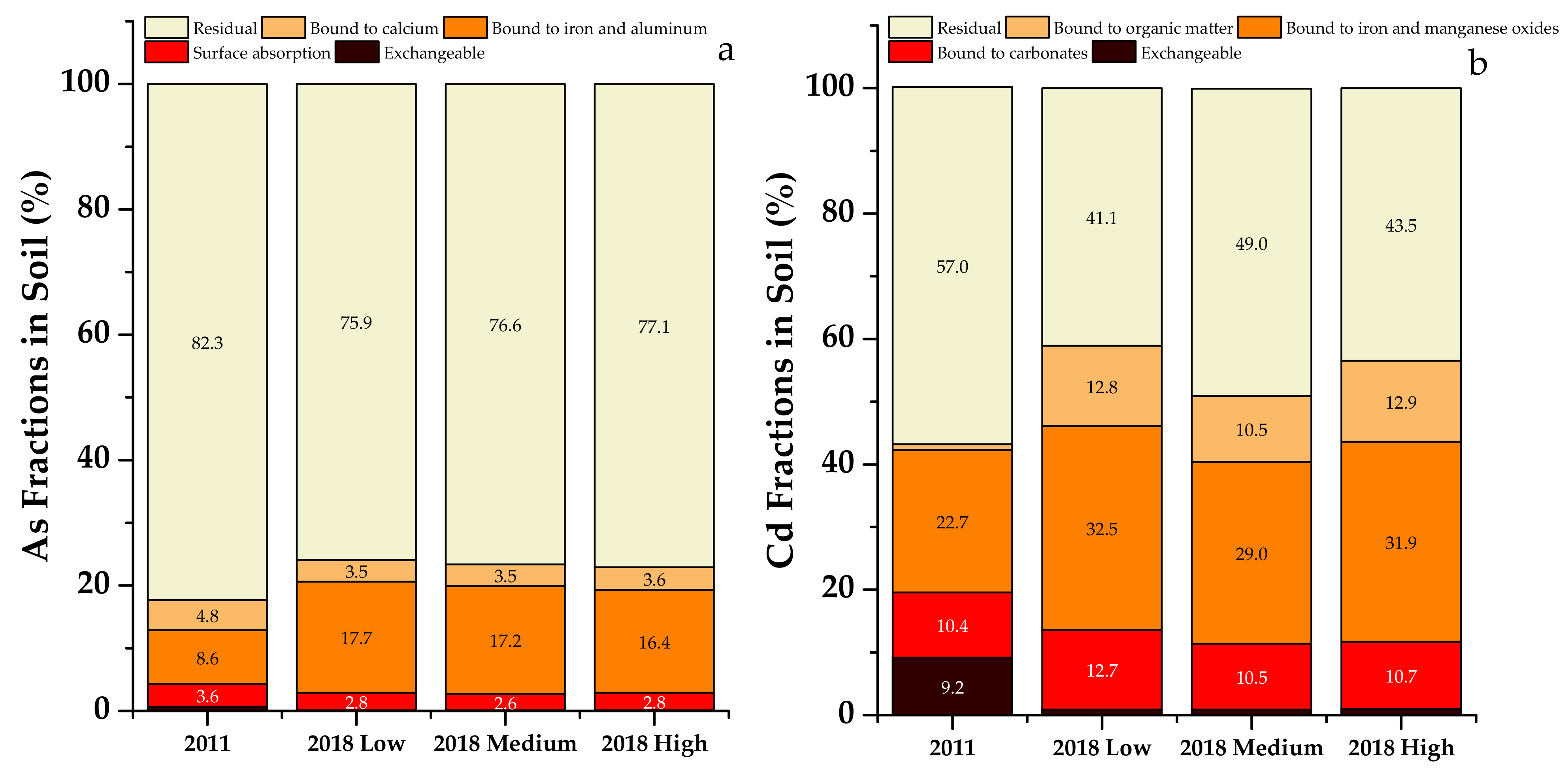
Figure 3.
Forms of soil As (a) and Cd (b) in 2011 and in all three treatments in 2018. Percentage of As and Cd forms less than 2% are not labeled.
The residual fraction was the main form of both As and Cd, which decreased after eight years of application of organic fertilizer, in comparison to that in 2011 (Figure 3). However, the most susceptible fraction of As and Cd for plant uptake was the exchangeable fraction, which substantially decreased compared to that in 2011. During the same period, the fractions less susceptible to plant uptake, such as As-bound to iron and aluminum (increased by about 9%), Cd-bound to iron and manganese (increased by about 10%) and Cd-bound to organic matter (increased by about 11%), all increased. These results suggest that organic fertilizer application to this alkaline soil contributed to the conversion of As and Cd to fractions less susceptible for plant uptake. Compared to single extraction, sequential extraction of trace elements is more helpful in elucidating their transformation between inert and labile fractions.
In 2018, pak choi yield (ranging between 21.5 to 26.1 t ha−1) increased with increasing organic fertilizer application rates (Table 2). The As content in pak choi leaves is significantly decreased, with increasing organic fertilizer application rates, while leaf Cd contents did not significantly change (Table 2). The highest leaf As and Cd contents were 0.008 and 0.003 mg kg−1 FW respectively, which are within the maximum permitted contents for leafy vegetables (0.5 mg kg−1 for As and 0.2 mg kg−1 FW for Cd) in China [41]. The BCF and THQ values of As and Cd in all three treatments were much less than 1, indicating that pak choi in this study did not act as an accumulator and did not constitute a risk to human health for life-time exposure (Table 2). Based on yield and plant uptake, pak choi leaves in this study absorbed 0.17 g ha−1 As and 0.07 g ha−1 Cd at a maximum in 2018.

Table 2.
Pak-choi yield, trace elements uptake and health risk assessment in 2018.
The bioavailability of trace elements has often been determined by single or sequential extractions [42]. Variable effects of organic fertilizer applications on As and Cd availability determined by single extractions have been reported, as increases [43,44] or decreases [45,46]. Sequential extraction provides detailed information on the changes in trace element fractions. Previous studies reported reduced content of exchangeable Cd fraction [45,46], and the transformation of the exchangeable Cd fraction into fractions bound to iron and manganese oxides or organic matter with organic fertilizer application [47,48]. Additionally, these studies reported that residual As fraction transformed to the Fe and Mn oxide bound fraction [46]. The results from this study were consistent with these observations of soil Cd and As transformation to less labile fractions.
Organic fertilizer changes the bioavailability of As and Cd by altering soil properties, such as organic matter content and soil pH [46,48,49,50]. Increased microbial degradation of organic matter provides increased amounts of functional groups such as carbonyl and phenolic-OH that can increase trace elements binding [51,52]. Another important reason may be that manure application adds trace element sorbents such as Fe, Mn and Al oxides to soil, which could bind with trace elements, thereby decreasing the exchangeable fractions [53]. These various mechanisms may explain the transformation of As and Cd to less susceptible fractions for plant uptake in this study. Plant As and Cd in 2018 decreased (significant or not) with increasing organic fertilizer application rates in this study. Reduced As and Cd solubility in soil after organic fertilizer application were responsible for reduced As/Cd content in plants in previous studies [46,54]. While the exchangeable contents of As and Cd in soil were not significantly different between treatments, higher yields with higher organic fertilizer application rates resulted in lower As and Cd contents in the plant. THQ values less than 1 from contaminated soil have been reported in previous studies. Bui et al. [55] reported THQ values of As (range of 0.50–0.90) and Cd (range of 0.10–0.25) in vegetables (including leafy, stem and roots vegetables) grown on trace elements contaminated soil (Cd: 1.9–3.8 mg kg−1, As: 28.9–39.3 mg kg−1). Similar results were reported by Garg et al. [56], of a THQ value of 0.013 for Cd in Brassica campestris leaves with a 240 g per day consumption rate on a Cd contaminated soil (average Cd content of 6.05 mg kg−1). The results from previous studies and this study indicated that life-time consumption of vegetables may not necessarily cause damage to human health, even when they are harvested from contaminated soil. Differences in trace elements uptake and transfer to the edible parts between species can influence such risk assessments.
3.3. As and Cd Accumulation in Soil
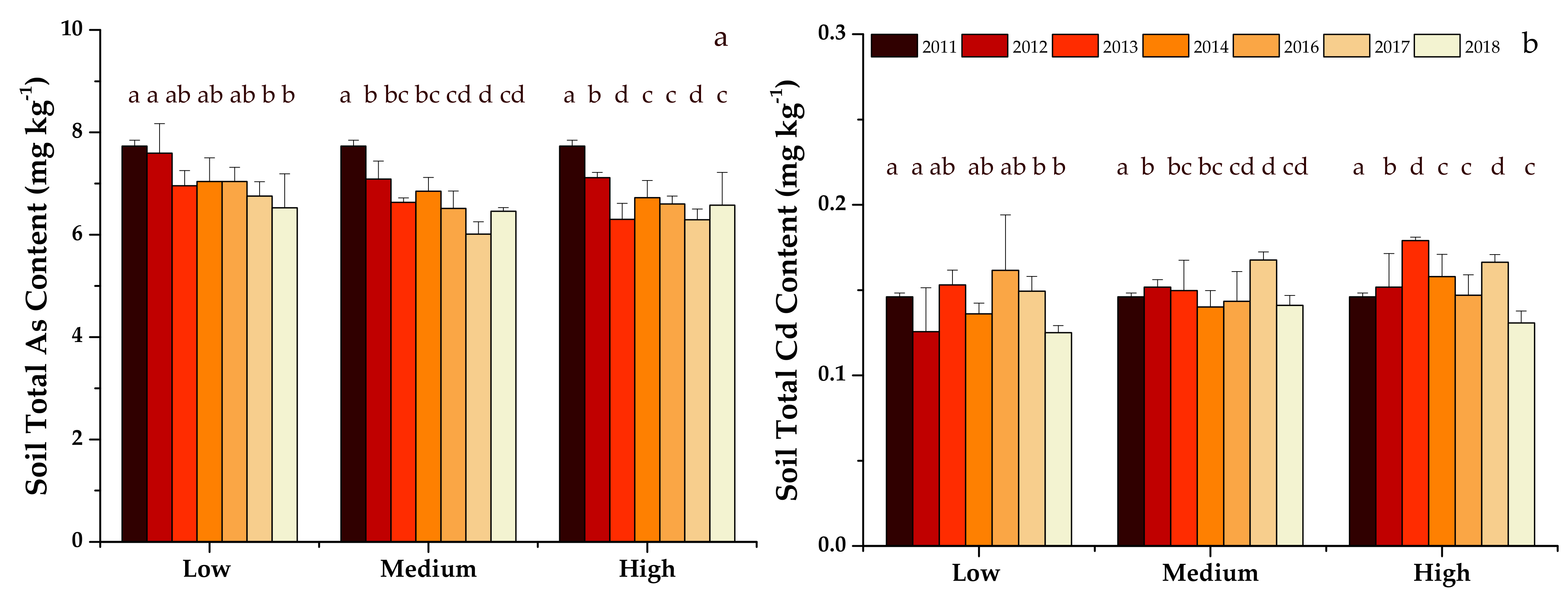
The total As content in soil significantly decreased with continuous organic fertilizer application for all three treatments during this study (Figure 4a). By the end of study in 2018, soil total As contents decreased from 7.73 mg kg−1 in the initial soil to 6.53, 6.46 and 6.58 mg kg−1 with low, medium and high fertilizer application rate treatments, respectively. Soil total Cd contents of the three treatments fluctuated within a narrow range (0.13–0.16 mg kg−1) throughout the study (Figure 4b). By the end of the study in 2018, soil total Cd contents were 0.12, 0.14 and 0.13 mg kg−1 for low, medium and high fertilizer application rates treatments, respectively, which were not significantly different to the initial content of 0.15 mg kg−1 in 2011.
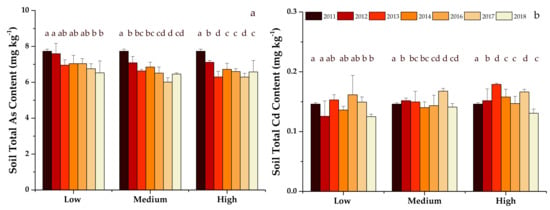
Figure 4.
Soil total As (a) and Cd (b) contents in three fertilizer rate treatments from 2011 to 2018. Different letters above the vertical bars indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
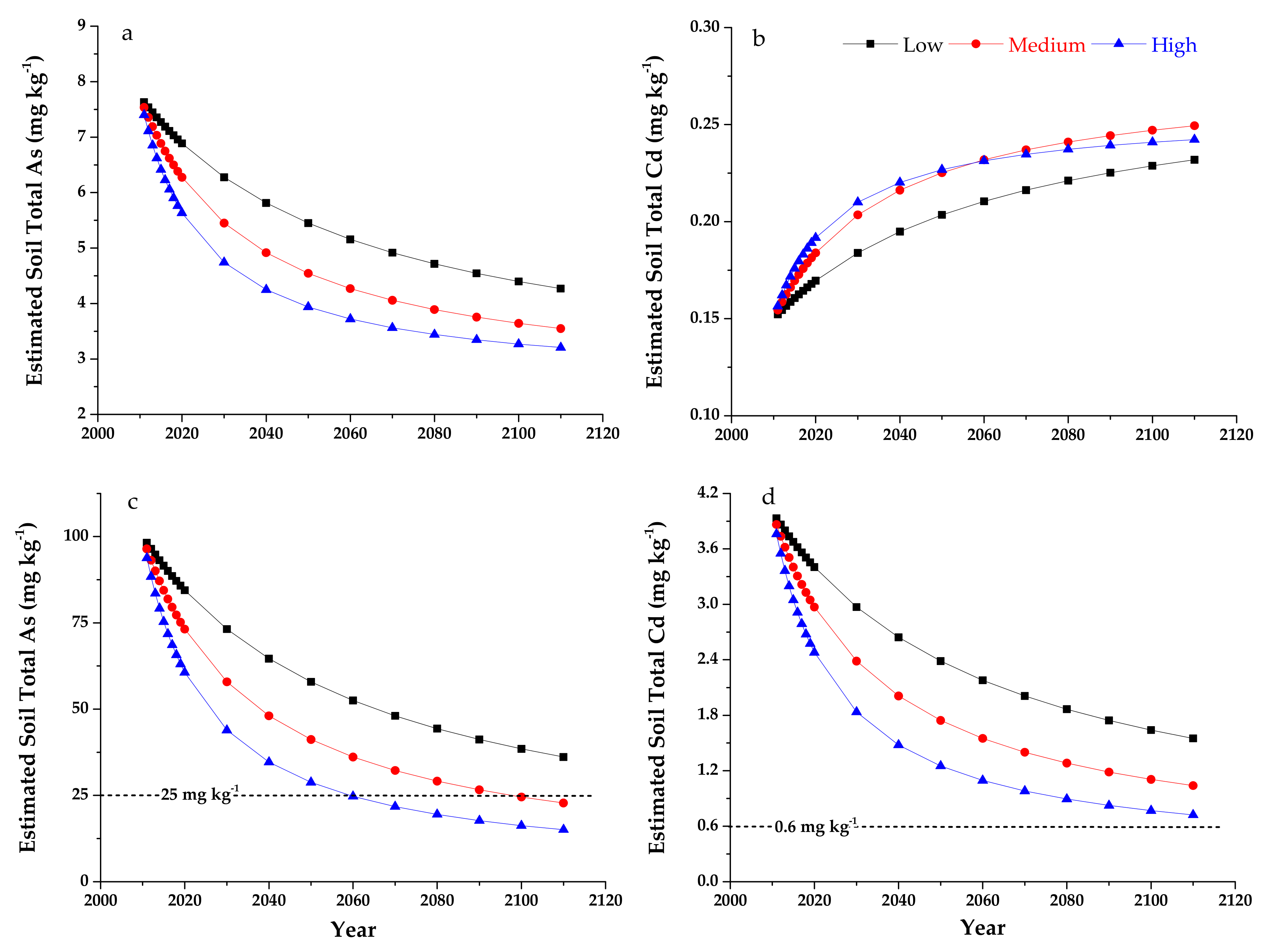
Lower As content (an average of 2.36 mg kg−1) in applied organic fertilizer than the initial soil (7.73 mg kg−1) was considered the reason for the decreased soil As contents in this study. To further examine this hypothesis, we estimated soil total As content in the following 100 years under the same condition as those in this study. Organic fertilizer with average As and Cd contents of 2.36 and 0.28 mg kg−1, respectively applied at low, medium and high rates of 80, 159 and 285 t ha−1 respectively were averaged over eight years of this study. Plant uptake of As and Cd were relatively small (2.5 g ha−1 As and 0.7 g ha−1 Cd as estimated leaf uptake of ten growing seasons for pak choi each year, respectively) in relation to the annual input from organic fertilizer (194.88 and 20.60 g ha−1 for As and Cd in the low rate treatment) and therefore were neglected in the calculation. The top soil (0–30 cm) was considered as a sink (containing total As content of 32,466 g ha−1 in 2011 with a soil bulk density of 1.4 g cm−3) with continuous As addition (average As input of 194.88, 389.76 and 723.83 g ha−1 in low, medium and high organic fertilizer treatments each year, respectively) under the assumptions of zero plant uptake and soil leaching (Figure 5a).
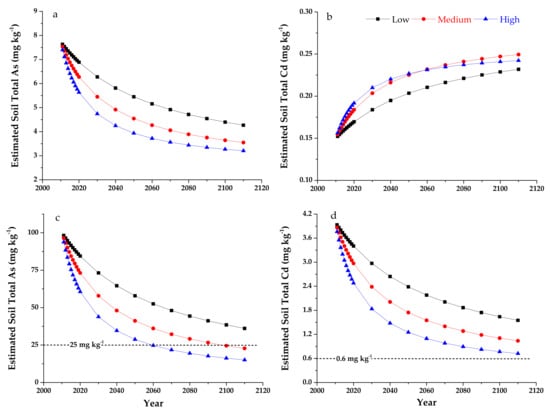
Figure 5.
Estimated soil total As (a,c) and Cd (b,d) contents with continuous organic fertilizer application. Dotted line in a and c indicates a soil As risk screening value of 25 mg kg−1, while it indicates a soil Cd risk screening value of 0.6 mg kg−1 at soil pH > 7.5.
Estimated soil As content decreased with increasing organic fertilizer application year and rate, gradually to the As level in the organic fertilizer (2.36 mg kg−1) over the next 100 years (Figure 5a). A strong diluting effect of the relatively clean organic fertilizer on soil total As contents occurred at a relatively high rate in the first 30 years and then reached a plateau. Extrapolating this calculation to 2110, the estimated total As contents would be 4.27, 3.55 and 3.21 mg kg−1 in the top 30 cm soil for the low, medium and high organic fertilizer treatments, respectively. In contrast, organic fertilizer contained higher Cd content (an average of 0.28 mg kg−1) than in the initial soil (0.15 mg kg−1). Total Cd content in the top 30 cm soil was 630 g ha−1 in 2011, while the average Cd inputs were of 20.60, 41.21 and 68.25 g ha−1 in low, medium and high fertilizer application rates each year, respectively. Therefore, the estimated total soil Cd contents with on-going organic fertilizer application increased gradually towards the value of the Cd content of organic fertilizer (Figure 5b). After 100 years, in 2110, the estimated soil total Cd contents would be 0.22, 0.23 and 0.23 mg kg−1 in the top 30 cm soil for the low, medium and high organic fertilizer treatments, respectively.
Agricultural products are considered to be a negligible safety risk when they are grown in soils with trace element contents lower than the risk screening values for agricultural land (25 mg kg−1 for As and 0.6 mg kg−1 for Cd at soil pH > 7.5, respectively) in China. However, cultivation of edible agriculture products is not allowed once the soil trace element contents reach the risk intervention values (100 mg kg−1 for As and 4 mg kg−1 for Cd at soil pH > 7.5, respectively) [57]. Based on the conclusion from this study that soil trace element contents can be decreased by continuous application of clean organic fertilizer with low trace elements contents, we propose the application of clean organic fertilizer to lower the contamination risk of soil with high As and Cd levels. Therefore, we estimated the change of soil As and Cd contents under the consumption of continuous organic fertilizer application (as in this study) on a soil with the risk intervention values (100 mg kg−1 for As and 4 mg kg−1 for Cd at soil pH > 7.5, respectively, Figure 5c,d). The results showed that it would take 50 and 88 years of application of organic fertilizer at high and medium rates to reduce the soil As content below 25 mg kg−1, respectively. In 2110, after 100 years of application, soil As content (36.12 mg kg−1) would still be higher than the risk screening value with the low application rate. For an initial soil with Cd of 4 mg kg−1, continuous organic fertilizer application like this study also would decrease soil Cd content. However, soil total Cd content would still be higher than 0.6 mg kg−1 (range of 0.72–1.55 mg kg−1) after 100 years application for all three treatments (Figure 5d). It would take 139, 263 and 525 years to decrease soil Cd content from 4 mg kg−1 to less than 0.6 mg kg−1 if the organic fertilizer was applied at the high, medium and low application rates as used in this study, respectively.
In a relatively closed environment, such as a greenhouse, soil trace element contents depend on the organic fertilizer input, the rate and frequency of its application and the crops grown [58]. The result in this study demonstrated that differences of trace element contents between soil and organic fertilizer determines whether they will accumulate in soil or not. Similar results were reported in a vegetable production field by Zhen et al. [44], where total soil As content significantly decreased from 8.63 to 7.14 mg kg−1, and total soil Cd significantly increased from 0.11 to 0.54 mg kg−1 after 15 years application of organic fertilizer that contained lower As content and higher Cd content that the initial soil, respectively. Previous studies also reported soil Cd accumulation following continuous application of organic fertilizer with higher Cd content than that of the initial soil [45,46,59,60,61].
Decreased trace elements in soil after long-term organic fertilizer application was explained as the equilibrium state of trace elements in soil–plant systems in the relatively closed environment [44,62]. However, crop removal and soil leaching were almost negligible compared to their high addition from organic fertilizer. Xu et al. [61] reported that crop removal (soybean and maize) and soil leaching amount of the trace element was less than 8.49% and 1.29% (4.36 and 0.73 g ha−1, respectively) of the input quantity from organic fertilizer application. Zhou et al. [63] reported maize and wheat uptake (straw and grain) of Cd were 2.03 and 1.92 g ha−1 when applied with 42 t ha−1 manure fertilizer each season, and most of the trace elements applied from organic fertilizer remained in the top 30 cm soil layer.
Xu et al. [61] had the similar level of Cd annual input from organic fertilizer with this study (26.3 and 65.7 g ha−1 in their study, and 20.60 and 68.25 g ha−1 in this study for low and high application rates, respectively) on uncontaminated soils (0.2 mg kg−1 in their study and 0.15 mg kg−1 in this study). However, the organic fertilizer they applied contained about a 10 times higher Cd content (2.87 mg kg−1) than it is in this study (0.28 mg kg−1). Consequently, soil total Cd content increased by 84.34–362.66% after ten years in their study, while it did not significantly change after eight years in this study. These results prove our theory that long-term application of clean organic fertilizer with low trace element contents can decrease their content in soil.
To ensure food safety and clean production, measurements such as controlling trace elements in fertilizers, decreasing its availability in soil by amendments (manure, zeolites, lime and biochar etc.), and adopting low trace elements accumulating cultivars are recommended [2,14,44]. Continuous organic fertilizer application in this study has controlled trace element input, decreased trace elements bioavailability for plant uptake and reduced trace element contents in soil, while providing vegetables with no health risk, which is a good choice for clean production.
4. Conclusions
In this study, eight years’ application of organic fertilizer significantly affected soil properties by increasing soil nutrients, soil organic C and microbial biomass (MBC and MBN). Soil pH was less affected because of the similar pH of the soil and the organic fertilizer used.
Compared to single extraction, sequential extraction was more precise to evaluate the bioavailability of trace elements. Long-term application of organic fertilizer with low trace element contents to alkaline soil in northern China transformed the susceptible fraction of As and Cd into less soluble fractions compared to those in the initial soil. Pak choi grown in this study did not constitute a risk for human health after eight years’ application of organic fertilizer.
Differences in trace element contents between the applied organic fertilizer and the initial soil are important determinants of whether trace elements will accumulate in soil during long-term application. The application of clean organic fertilizer with lower trace element contents compared with that in soil can decrease the contamination risk of soil. Trace element contents in soil and organic fertilizer, soil properties, soil nutrients, fertilizer composition, fertilizer application rate and frequency should be considered when certain organic fertilizer is applied, especially when organic fertilizer contains higher contents of trace elements than soil or on highly contaminated soils which creates the potential risk of trace element accumulation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: G.Z. and Y.S., J.X.; Funding acquisition, G.Z., Y.S., N.S., J.X.; Methodology, N.S., S.L.; Data curation and formal analysis, N.S., Y.P., Q.C.; Original draft preparation, N.S.; Writing, review and editing, N.S., R.B.T., G.Z., S.L., L.S., J.Y., Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key Research and Development Projects (2017YFD0801400), Innovation Program of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences (KJCX20180705), Projects of Joint Task on Prevention and Control of Heavy metal Pollution in Arable Land of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Beijing Innovation Team of Technology System in Dairy Industry (BAIC06-2022), and China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-23-B15).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- MEP (Ministry of Environment Protection of China). National Soil Pollution Survey Bulletin. 2014. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/foot/site1/20140417/782bcb88840814ba158d01.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2021).
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, F. Phytoexclusion of heavy metals using low heavy metal accumulating cultivars: A green technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.; Shao, X.; Ma, H. Characteristics and affecting factors of heavy metals content in greenhouse vegetable soils in China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 263–274. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Contents of heavy metal in commercial organic fertilizer and organic wastes. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2005, 24, 392–397. [Google Scholar]
- MARA (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China). Standards on Organic Fertilizer in Agriculture of People’s Republic of China (NY525-2012); The Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Huang, S.; Tang, J.; Li, C. Status of heavy metals, nutrients, and total salts in commercial organic fertilizers and organic wastes in China. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci. 2017, 23, 162–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, T. Responses of soil labile organic carbon and carbon management index to different long-term fertilization treatments in a typical yellow soil region. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 54, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, B.; Das, S.; Nielsen, R.; Hergert, G.W. Maize yields from manure and mineral fertilizers in the 100-year-old Knorr-Holden Plot. Agron. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, X.; Ghimire, R.; Sainju, U.M.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, F. Responses of soil bacterial community and enzyme activity to organic matter components under long-term fertilization on the loess plateau of china. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 103992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Teng, Y.; Christie, P.; Luo, Y. Effects of long-term fertilizer applications on peanut yield and quality and on plant and soil heavy metal accumulation. Pedosphere 2017, 30, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Huang, D.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Xu, C.; Xiong, J.; Wang, H.; Duan, M. Distribution and availability of cadmium in profile and aggregates of a paddy soil with 30-year fertilization and its impact on Cd accumulation in rice plant. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Ullah, A.; Tahir, N. A field evidence of Cd, Zn and Cu accumulation in soil and rice grains after long-term (27 years) application of swine and green manures in a paddy soil. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J.; Islam, M.S.; Weng, L.; Li, Y. Cd, Cu, and Zn accumulations caused by long-term fertilization in greenhouse soils and their potential risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gul, S.; Naz, A.; Fareed, I.; Irshad, M. Reducing heavy metals extraction from contaminated soils using organic and inorganic amendments—A review. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1423–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Chaney, R.L. Food safety issues for mineral and organic fertilizers. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 51–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Study on bottlenecks and counter measures of promoting organic fertilizers in Shanghai suburbs. China Environ. Prot. Ind. 2008, 3, 28–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Junxiang, X.U.; Guoyuan ZO, U.; Qinping SU, N.; Yufei, L.I.; Jijin, L.I. Effects of application manure on Olsen-P accumulation and distribution in soil profile and the yield of vegetable. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2016, 30, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Sumner, M.E., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measure soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Hu, S.; Gao, S. Reassessment of HF/HNO3 decomposition capability in the high-pressure digestion of felsic rocks for multi-element determination by ICP-MS. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2012, 36, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Cole, C.V.; Watanabe, F.S.; Dean, L.A. Estimation of Available Phosphorous in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; United States Department of Agriculture, USDA Circ.939: Washington DC, USA, 1954.
- MEE (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China). Soil-Determination of Bioavailable Form of Eight Elements-Extraction with Buffered DTPA Solution/Inductively Couple Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (HJ 804-2016); MEE (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China): Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhang, C.; Cheng, L.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J. Study on determination of available arsenic in soil by ICP-MS. Chin. J. Anal. Lab. 2011, 30, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiowatana, J.; Mclaren, R.G.; Chanmekha, N.; Samphao, A. Heavy metals in the environment-fractionation of arsenic in soil by a continuous-flow sequential extraction method. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bission, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, A.A.; Khoshgoftarmanesha, A.H.; Malakoutib, M.J.; Bahramib, H.A.; Chaneyc, R.L. Root uptake and shoot accumulation of cadmium by lettuce at various Cd:Zn ratios in nutrient solution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Atashpaz, B.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Damalas, C.A. Heavy metal bioavailability and accumulation in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) irrigated with treated wastewater in calcareous soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Deng, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Vegetable and fruit consumption among chinese adults and associated factors: A nationally representative study of 170,847 adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). EPA Region 3 Risk-Based Concentration Table. 2014. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/search/index.cfm (accessed on 27 August 2021).
- Song, B.; Lei, M.; Chen, T.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, D. Assessing the health risk of heavy metals in vegetables to the general population in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayame, R.; Pigai, Y.; Mallongi, A. Assessing the target hazard quotients of lead via drinking water and seafood consumption from Paniai Lake, Paniai Regency Papua, Indonesia 2013. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2013, 2, 2137–2147. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Shen, Q.; Singh, B.; Cayuela, M.L. The long-term role of organic amendments in building soil nutrient fertility: A meta-analysis and review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 111, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, L.; Langer, U.; Böhme, F. Microbial biomass, enzyme activities and microbial community structure in two European long-term field experiments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 109, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.H.; Haynes, R.J. Organic matter accumulation and fertilizer-induced acidification interact to affect soil microbial and enzyme activity on a long-term sugarcane management experiment. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 41, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Sommerfeldt, T.G.; Entz, T. Soil chemistry after eleven annual applications of cattle feedlot manure. J. Environ. Qual. 1991, 20, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, S.; Raupp, J.; Joergensen, R.G. Effects of fertilizer and spatial heterogeneity in soil pH on microbial biomass indices in a long-term field trial of organic agriculture. Plant Soil 2010, 328, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlustoš, P.; Hejcman, M.; Hůlka, M.; Patáková, M.; Kunzová, E.; Száková, J. Mobility and plant availability of risk elements in soil after long-term application of farmyard manure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 23561–23572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikinya, O.; Mufwanzala, N. Chicken manure-enhanced soil fertility and productivity: Effects of application rates. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2010, 1, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Majewska, M.; Kurek, E.; Rogalski, J. Microbially mediated cadmium sorption/desorption processes in soil amended with sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Dou, G.; Zhu, K.; Yuan, X.; Liu, G.; Pan, C. Effect of returning potato starch processing wastewater on nutrients and heavy metals in soils. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2020, 37, 666–671. [Google Scholar]
- CFDA (China Food and Drug Administration). National Food Safety Standards-Limits on Contaminants in Food (National Standards for the People’s Republic of China, GB 2762-2017); CFDA (China Food and Drug Administration): Beijing, China, 2017.
- Han, H.; Lee, J.; Ko, M.; Kim, K. Comparison of five extraction methods for evaluating cadmium and zinc immobilization in soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 4203–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Pi, J. Effects of long-term fertilization practices on heavy metal cadmium accumulation in the surface soil and rice plants of double-cropping rice system in southern china. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 19836–19844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, H.; Jia, L.; Huang, C.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Wan, Y. Long-term effects of intensive application of manure on heavy metal pollution risk in protected-field vegetable production. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yao, Y.; Wan, Y.; Qi, W.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, Y.; Su, D.; Li, H. Effects of continuous fertilization on bioavailability and fractionation of cadmium in soil and its uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 215, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Li, H. Accumulation and bioavailability of heavy metals in an acid soil and their uptake by paddy rice under continuous application of chicken and swine manure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Chaney, R.L.; Hallfrisch, J.G.; Xue, Q. Effect of biosolids processing on lead bioavailability in an urban soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Xu, M.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Shen, P. Effects of organic matter on the stabilization process of added cadmium and lead in red soil and black soil. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2011, 30, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.I. Influence of soil characteristics and arsenic, cadmium, and lead contamination on their accumulation levels in rice and human health risk through intake of rice grown nearby abandoned mines. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2012, 54, 575–582. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X.; Li, Y. Effect of soil pH and organic matter content on heavy metals availability in maize (Zea mays, L.) rhizospheric soil of non-ferrous metals smelting area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hietala, K.A.; Roane, T.M. Microbial remediation of metals. In Advances in Applied Bioremediation; Kuhad, R.C., Ward, O.P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 17, pp. 201–220. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.N.; Camara, A.Y.; Li, H.F. Effects of the addition and aging of humic acid-based amendments on the solubility of cd in soil solution and its accumulation in rice. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basta, N.T.; Ryan, J.A.; Chaney, R.L. Trace element chemistry in residual-treated soil: Key concepts and metal bioavailability. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Ma, L. Effects of compost and phosphate on arsenic accumulation from soils near pressure-treated wood. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, A.T.K.; Nguyen, H.T.H.; Nguyen, M.N.; Tran, T.H.T.; Vu, T.V.; Nguyen, C.H.; Reynolds, H.L. Accumulation and potential health risks of cadmium, lead and arsenic in vegetables grown near mining sites in northern Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.K.; Yadav, P.; Mor, S.; Singh, B.; Pulhani, V. Heavy metals bioconcentration from soil to vegetables and assessment of health risk caused by their ingestion. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 157, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEE (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China). National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Soil Environmental Quality-Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB15618-2018); MEE (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China): Beijing, China, 2018.
- Mazur, Z.; Mazur, T. The influence of long-term fertilization with slurry, manure and NPK on the soil content of trace elements. J. Elementol. 2016, 21, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.P.; Li, J.J.; Liu, B.S.; Gao, L.J.; Xu, J.X.; Zou, G.Y.; Liu, B.C. Cadmium accumulation in soil and celery from a long-term manure applied field experiment. Adv. Mater. Res 2013, 726–731, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Xin, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H. The influence of long-term fertilization on cadmium (cd) accumulation in soil and its uptake by crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, W.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, H. Potential risk of cadmium in a soil-plant system as a result of long-term (10 years) pig manure application. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wei, D.; Zhu, Y. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Lv, J.; Nan, S. Accumulation, availability, and uptake of heavy metals in a red soil after 22-year fertilization and cropping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15154–15163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).