Strategic Tillage Effects on Crop Yields, Soil Properties, and Weeds in Dryland No-Tillage Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Set-Up
2.2. Weed Density Evaluation
2.3. Soil Physical Properties
2.4. Soil Chemical Properties
2.5. Evaluation of Crop Yields
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Precipitation
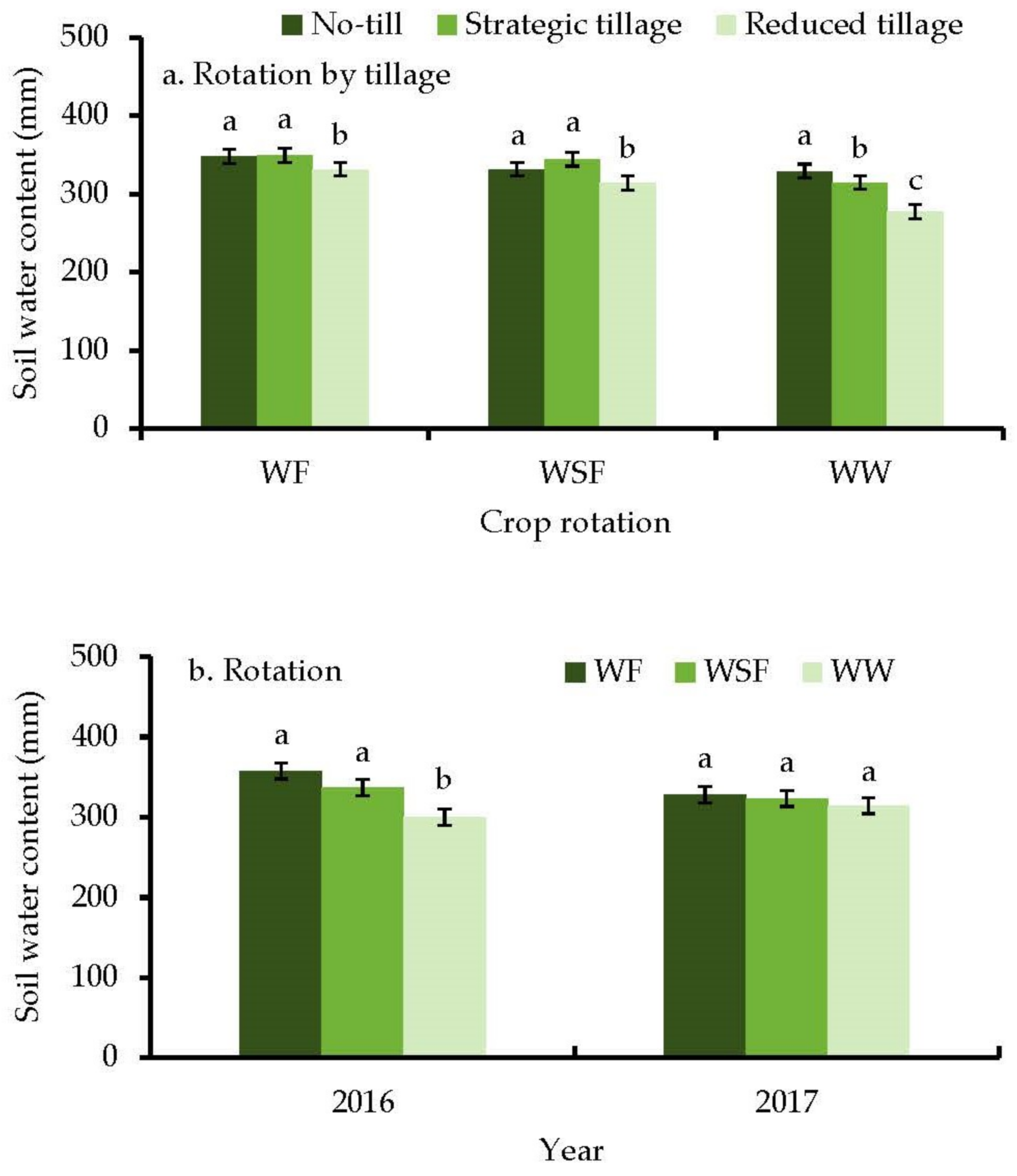
3.2. Weed Counts, and Soil Water Content
3.3. Bulk Density and Aggregate Size Fractions
3.4. Soil pH and Soil Organic Carbon
3.5. Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium
3.6. Micronutrients: Fe, Cu, Mn, Zn
3.7. Grain Yields
4. Discussion
4.1. Strategic Tillage Effects
4.2. Crop Rotation Effect
5. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Triplett, G.B.; Dick, W.A. No-tillage crop production: A revolution in agriculture! Agron. J. 2008, 100, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N.C.; Allen, B.L.; Baumhardt, R.L.; Lyon, D.J. Research achievements and adoption of no-till, dryland cropping in the semi-arid U.S. Great Plains. Field Crops Res. 2012, 132, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumhardt, R.L.; Schwartz, R.C.; Jones, O.R.; Scanlon, B.R.; Reedy, R.C.; Marek, G.W. Long-term conventional and no-tillage effects on field hydrology and yields of a dryland crop rotation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Ruis, S.J. No-tillage and soil physical environment. Geoderma 2018, 326, 164–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.P.; Moody, P.W.; Bell, M.J.; Seymour, N.P.; Dalal, R.C.; Freebairn, D.M.; Walker, S.R. Strategic tillage in no-till farming systems in Australia’s northern grains-growing regions: II. Implications for agronomy, soil and environment. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 152, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obour, A.K.; Mikha, M.M.; Holman, J.D.; Stahlman, P.W. Changes in soil surface chemistry after fifty years of tillage and nitrogen fertilization. Geoderma 2017, 308, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettler, T.A.; Lyon, D.J.; Doran, J.W.; Powers, W.L.; Stroup, W.W. Soil quality assessment after weed-control tillage in a wheat-fallow cropping system. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, Y.P.; Seymour, N.P.; Walker, S.R.; Bell, M.J.; Freebairn, D.M. Strategic tillage in no-till farming systems in Australia’s northern grains-growing regions: I. Drivers and implementation. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 152, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Crawford, M.; Carvalhais, L.C.; Dang, Y.P.; Dennis, P.G.; Schenk, P.M. Strategic tillage on a Grey Vertosol after fifteen years of no-till management had no short-term impact on soil properties and agronomic productivity. Geoderma 2016, 267, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baan, C.D.; Grevers, M.C.J.; Schoenau, J.J. Effects of a single cycle of tillage on long-term no-till prairie soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 89, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M.; Rincon-Florez, V.; Balzer, A.; Dang, Y.P.; Carvalhais, L.C.; Liu, H.; Schenk, P.M. Changes in the soil quality attributes of continuous no-till farming systems following a strategic tillage. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, I.; Günal, H.; Acar, M.; Acir, N.; Barut, Z.B.; Budak, M. Strategic tillage may sustain the benefits of long-term no-till in a Vertisol under Mediterranean climate. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 185, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quincke, J.A.; Wortmann, C.S.; Mamo, M.; Franti, T.; Drijber, R.A.; Garcia, J.P. One-time tillage of no-till systems: Soil physical properties, phosphorus runoff, and crop yield. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, C.S.; Drijber, R.A.; Franti, T.G. One-time tillage of no-till cropland five years post-tillage. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandy, A.S.; Robertson, G.P.; Thelen, K.D. Do productivity and environmental trade-offs justify periodically cultivating no-till cropping systems? Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.P.; Wortmann, C.S.; Mamo, M.; Drijber, R.; Tarkalson, D. One-time tillage of no-till: Effects on nutrients, mycorrhizae, and phosphorus uptake. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Obour, A.; Jha, P.; Liu, R.; Manuchehri, M.R.; Dille, J.A.; Holman, J.; Stahlman, P.W. Integrating cover crops for weed management in the semi-arid U.S. Great Plains: Opportunities and challenges. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.A. Winter wheat and grain sorghum production as influenced by depth of soil water, tillage and cropping system. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2001, 56, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Obour, A.K.; Holman, J.D.; Dille, J.A.; Kumar, V.V. Effects of spring-planted cover crops on weed suppression and winter wheat grain yield in western Kansas. Kans. Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossman, R.B.; Reinsch, T.G. Bulk density and linear extensibility. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Part 4. SSSA Book Series 5; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 201–225. [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo, J.R.; Perkins, K.S. Aggregate stability and size distribution. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Part 4. SSSA Book Series 5; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Leikam, D.F.; Lamond, R.E.; Mengel, D.B. Soil Test Interpretations and Fertilizer Recommendations. MF-2586. MF-2586. Kansas State University, Agric. Expt. Station and Coop. Ext. Serv. Manhattan, KS. 2003. Available online: http://www.ksre.k-state.edu/bookstore/pubs/mf2586.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Thomas, G.W. Soil pH and soil acidity. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3: Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of the Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, D.; Peterson GAPratt, P.F. Lithium, sodium, and potassium. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, 2nd ed.; Page, A.L., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 225–246. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, W.L.; Norvell, W.A. Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3: Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute Inc. Statistical Analysis System; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Conyers, M.; van der Rijt, V.; Oates, A.; Poile, G.; Kirkegaard, J.; Kirkby, C. The strategic use of minimum tillage within conservation agriculture in southern New South Wales, Australia. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 193, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikha, M.M.; Vigil, M.F.; Benjamin, J.G. Long-term tillage impacts on soil aggregation and carbon dynamics under wheat-fallow in the central Great Plains. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, L.R.; Schlegel, A.J. Yield-water supply relationships of grain sorghum and winter wheat. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, A.J.; Assefa, Y.; Haag, L.A.; Thompson, C.R.; Holman, J.D.; Stone, L.R. Yield and soil water in three dryland wheat and grain sorghum rotations. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vyn, T.J.; Sutton, J.C.; Raimbault, B.A. Crop sequence and tillage effects on winter wheat development and yield. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1991, 71, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlegel, A.J.; Assefa, Y.; Haag, L.A.; Thompson, C.R.; Stone, L.R. Long-term tillage on yield and water use of grain sorghum and winter wheat. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlegel, A.J.; Dhuyvetter, K.C.; Thompson, C.R.; Havlin, J.L. Agronomic and economic impacts of tillage and rotation on wheat and sorghum. J. Prod. Agric. 1999, 12, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, P.W. Tillage effects on dryland wheat and sorghum production in the southern Great Plains. Agron. J. 1994, 86, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, J.; Arnet, K.; Dille, A.; Maxwell, S.; Obour, A.; Roberts, T.; Roozeboom, K.; Schlegel, A. Can cover (or forage) crops replace fallow in the semiarid Central Great Plains? Crop Sci. 2017, 58, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, D.C.; Vigil, M.F. Wheat yield and yield stability of eight dryland crop rotations. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obour, A.K.; Chen, C.; Sintim, H.Y.; McVay, K.; Lamb, P.; Obeng, E.; Mohammed, Y.A.; Khan, Q.; Afshar, R.K.; Zheljazkov, V.D. Camelina sativa as a fallow replacement crop in wheat based crop production systems in the US Great Plains. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.D.; Perris, R.; Munn, M.; Dunsford, K.; Robertson, F.; Hollaway, G.J.; O’Leary, G.J. Effects of long-term rotation and tillage practice on grain yield and protein of wheat and soil fertility on a Vertosol in a medium-rainfall temperate environment. Crop Pasture Sci. 2019, 70, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, A.J.; Assefa, Y.; Haag, L.A.; Thompson, C.R.; Stone, L.R. Soil water and water use in long-term dryland crop rotations. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowman, R.A.; Vigil, M.F.; Nielsen, D.C.; Anderson, R.L. Soil organic matter changes in intensively cropped dryland systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Holman, J.D.; Schlegel, A.J.; Tatarko, J.; Shaver, T.M. Replacing fallow with cover crops in a semiarid soil: Effects on soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherrod, L.A.; McMaster, G.S.; Delgado, J.A.; Schipanski, M.E.; Fonte, S.J.; Montenieri, R.L.; Larson, K. Soil carbon pools in dryland agroecosystems as affected by several years of drought. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherrod, L.A.; Peterson, G.A.; Westfall, D.G.; Ahuja, L.R. Soil organic carbon pools after 12 years in no-till dryland agroecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barak, P.; Jobe, B.O.; Kreuger, A.R.; Peterson, L.A.; Laird, D.A. Effects of long-term soil acidification due to nitrogen fertilizer inputs in Wisconsin. Plant Soil 1997, 197, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.; Mahmood, T.; Islam, K.R. Effect of long-term no-till and conventional tillage practices on soil quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 131, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, S.G.; Prochnow, L.I.; Kiehl, J.C.; Pauletti, V.; Martin-Neto, L. Chemical forms in soil and availability of manganese and zinc to soybean in soil under different tillage systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Month | Precipitation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 30-Year Average | |
| mm | ||||
| January | 17 | 32 | 11 | 11 |
| February | 18 | 3 | 4 | 19 |
| March | 14 | 38 | 20 | 32 |
| April | 190 | 199 | 19 | 54 |
| May | 77 | 116 | 123 | 82 |
| June | 87 | 97 | 100 | 88 |
| July | 88 | 39 | 195 | 85 |
| August | 96 | 78 | 135 | 75 |
| September | 53 | 55 | 98 | 57 |
| October | 17 | 50 | 171 | 37 |
| November | 30 | 6 | 21 | 22 |
| December | 15 | 1 | 58 | 18 |
| Total | 702 | 714 | 955 | 580 |
| 0 to 15 cm | 15 to 30 cm | MWD | Soil Water Storage (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tillage System | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | mm | 2016 | 2017 | 2-Year Avg. | |
| NT § | 1.26 ± 0.10 a ‡ | 1.19 ± 0.09 a | 1.05 ± 0.4 a | 340 ± 27 a | 332 ± 18 a | 336 ± 23 a |
| ST | 1.19 ± 0.09 b | 1.19 ± 0.09 a | 1.06 ± 0.6 a | 345 ± 25 a | 328 ± 16 a | 336 ± 22 a |
| RT | 1.19 ± 0.11 b | 1.18 ± 0.06 a | 0.69 ± 0.2 b | 310 ± 38 b | 306 ± 19 a | 308 ± 29 b |
| Crop Rotation | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | MWD | Soil Water Storage (mm) | |||
| WF | 1.22 ± 0.12 ab | 1.21 ± 0.07 a | 0.93 ± 0.5 b | 358 ± 15 a | 328 ± 10 a | 343 ± 20 a |
| WSF | 1.25 ± 0.08 a | 1.17 ± 0.11 a | 0.72 ± 0.3 b | 337 ± 22 a | 323 ± 18 ab | 330 ± 21 a |
| WW | 1.17 ± 0.09 b | 1.18 ± 0.05 a | 1.17 ± 0.4 a | 300 ± 32 b | 315 ± 29 b | 307 ± 30 b |
| Rotation | 0–5 cm | 5–15 cm | 15–30 cm | 0–5 cm | 5–15 cm | 15-30 cm | 0–5 cm | 5–15 cm | 15–30 cm |
| Soil pH | Soil organic carbon | Potassium | |||||||
| g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ||||||||
| WF § | 5.71 ± 0.20 a ‡ | 6.17 ± 0.12 ab | 6.89 ± 0.10 a | 13.6 ± 0.8 b | 11.4 ± 0.6 a | 8.9 ± 0.8 a | 558 ± 40 a | 559 ± 28 a | 544 ± 36 a |
| WSF | 5.87 ± 0.22 a | 6.29 ± 0.18 a | 6.86 ± 0.10 a | 13.7 ± 1.6 b | 11.2 ± 0.5 a | 9.2 ± 0.5 a | 539 ± 43 ab | 511 ± 28 b | 523 ± 21 a |
| WW | 5.27 ± 0.22 b | 6.06 ± 0.44 b | 6.99 ± 0.21 a | 17.4 ± 5.1 a | 12.2 ± 1.9 a | 10.0 ± 1.2 a | 516 ± 46 b | 528 ± 26 b | 544 ± 30 a |
| Iron | Manganese | Copper | |||||||
| mg kg−1 | |||||||||
| WF | 53.3 ± 7.1 b | 39.1 ± 7.5 b | 22.3 ± 1.5 a | 27.2 ± 4.1 b | 20.9 ± 2.6 ab | 11.7 ± 1.9 a | 1.5 ± 0.06 b | 1.4 ± 0.13 a | 1.2 ± 0.06 a |
| WSF | 46.8 ± 6.9 b | 34.6 ± 5.3 b | 22.2 ± 3.0 a | 25.8 ± 4.4 b | 20.1 ± 2.8 b | 12.0 ± 1.6 a | 1.5 ± 0.11 b | 1.4 ± 0.13 a | 1.3 ± 0.07 a |
| WW | 77.3 ± 11.3 a | 45.7 ± 14.6 a | 22.2 ± 3.4 a | 42.6 ± 6.8 a | 24.6 ± 9.7 a | 11.5 ± 3.1 a | 1.6 ± 0.11 a | 1.4 ± 0.18 a | 1.2 ± 0.07 a |
| Tillage | 0–5 | 5–15 | 15–30 | 0–5 | 5–15 | 15–30 | 0–5 | 5–15 | 15–30 | 0–5 | 5–15 | 15–30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | ||||||||||||
| Soil Organic Carbon | Nitrate-N | Ammonium-N | Potassium | |||||||||
| g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |||||||||||
| NT § | 16.7 ± 4.9 a ‡ | 11.8 ± 0.9 a | 9.2 ± 0.8 a | 33.2 ± 9.4 ab | 16.3 ± 6.8 a | 7.6 ± 2.2 a | 13.2 ± 6.9 a | 3.3 ± 1.6 a | 2.6 ± 0.7 a | 516 ± 29 b | 538 ± 40 a | 543 ± 34 a |
| ST | 15.1 ± 2.8 a | 12.0 ± 1.7 a | 9.9 ± 0.9 a | 37.4 ± 9.4 a | 16.9 ± 6.4 a | 9.9 ± 2.9 a | 8.3 ± 4.3 b | 3.2 ± 1.9 a | 2.6 ± 0.6 a | 515 ± 27 b | 517 ± 27 a | 535 ± 31 a |
| RT | 13.2 ± 1.1 b | 11.0 ± 0.6 a | 9.1 ± 1.1 a | 30.7 ± 6.9 b | 15.8 ± 3.1 a | 11.2 ± 1.1 a | 4.4 ± 1.6 c | 2.7 ± 0.7 a | 2.5 ± 0.8 a | 582 ± 39 a | 543 ± 28 a | 535 ± 25 a |
| Parameter | SOC | pH | NO3-N | P | K | Zn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | −0.71 *** | ||||||
| NO3 | 0.62 *** | −0.69 *** | |||||
| P | 0.73 *** | −0.76 *** | 0.83 *** | ||||
| K | −0.17 | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.09 | |||
| Zn | 0.53 *** | −0.54 *** | 0.53 *** | 0.63 *** | 0.11 | ||
| Fe | 0.79 *** | −0.89 *** | 0.61 *** | 0.76 *** | −0.08 | 0.55 *** | |
| Mn | 0.76 *** | −0.92 *** | 0.53 *** | 0.66 *** | −0.07 | 0.46 *** | 0.90 *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obour, A.K.; Holman, J.D.; Simon, L.M.; Schlegel, A.J. Strategic Tillage Effects on Crop Yields, Soil Properties, and Weeds in Dryland No-Tillage Systems. Agronomy 2021, 11, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040662
Obour AK, Holman JD, Simon LM, Schlegel AJ. Strategic Tillage Effects on Crop Yields, Soil Properties, and Weeds in Dryland No-Tillage Systems. Agronomy. 2021; 11(4):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040662
Chicago/Turabian StyleObour, Augustine K., Johnathon D. Holman, Logan M. Simon, and Alan J. Schlegel. 2021. "Strategic Tillage Effects on Crop Yields, Soil Properties, and Weeds in Dryland No-Tillage Systems" Agronomy 11, no. 4: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040662
APA StyleObour, A. K., Holman, J. D., Simon, L. M., & Schlegel, A. J. (2021). Strategic Tillage Effects on Crop Yields, Soil Properties, and Weeds in Dryland No-Tillage Systems. Agronomy, 11(4), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040662





