Yield of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L. var. napus) in a Short-Term Monoculture and the Macronutrient Accumulation in Relation to the Dose and Method of Sulphur Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Experimental Design
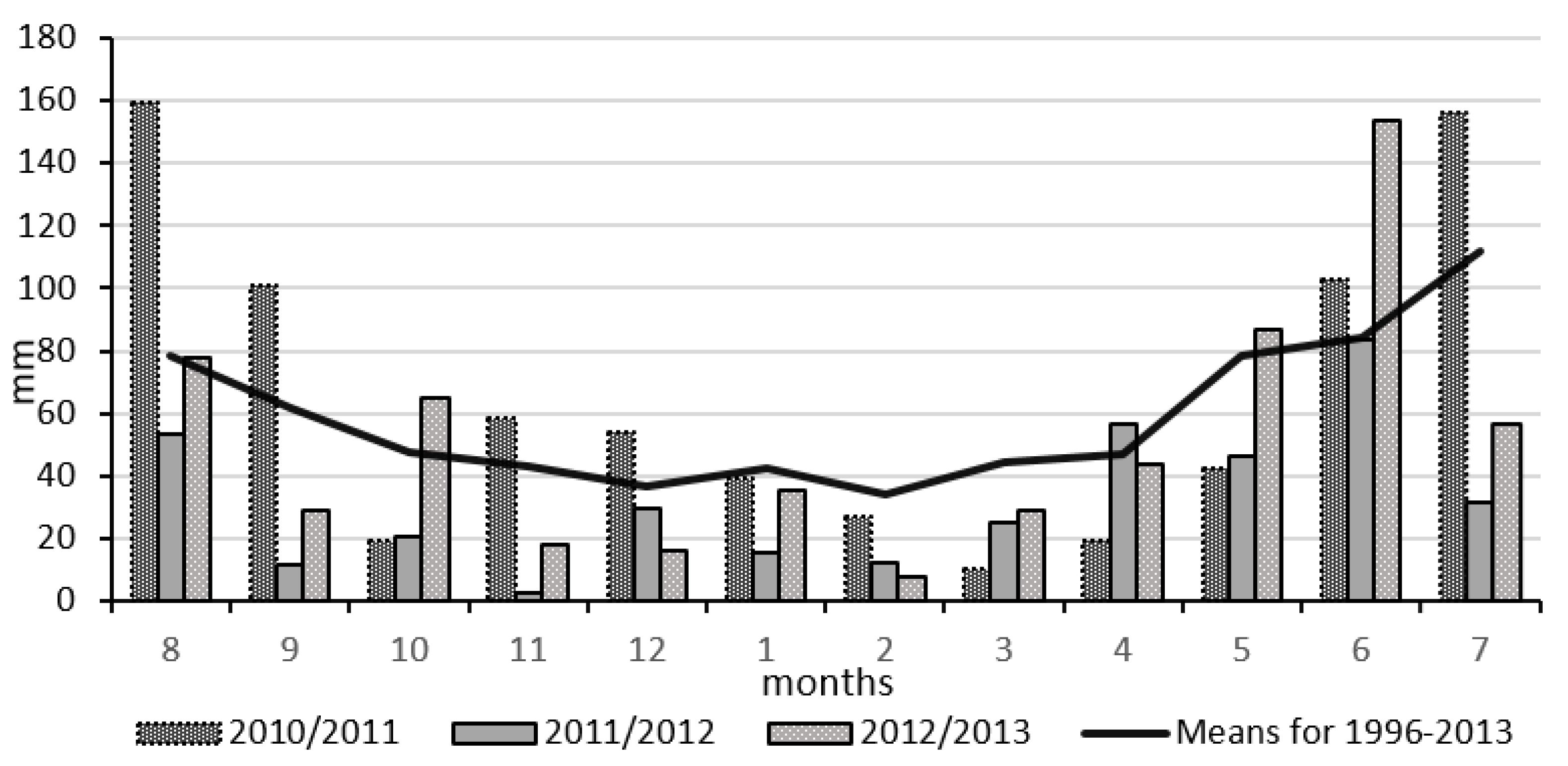
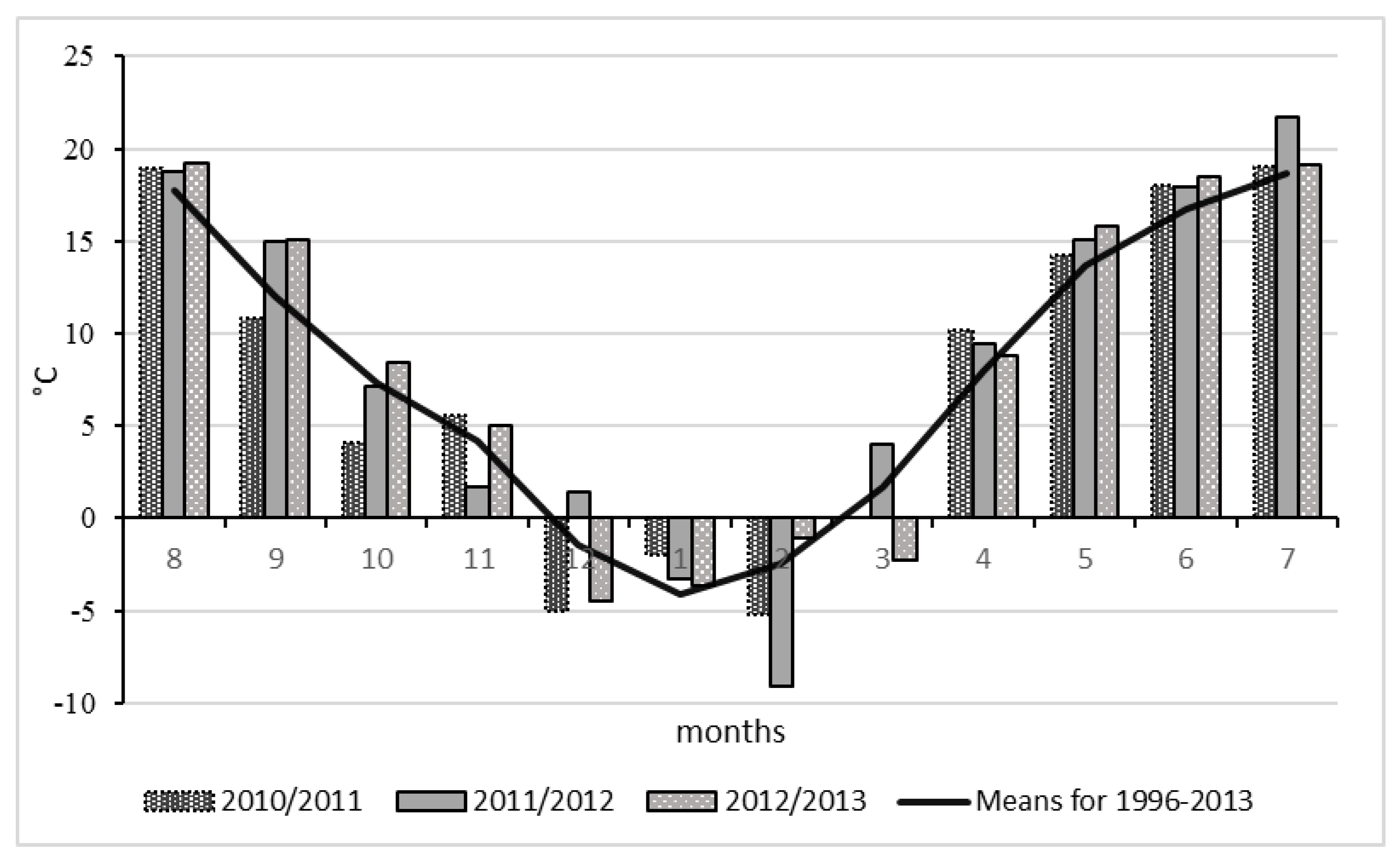
2.2. Meteorological Conditions
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
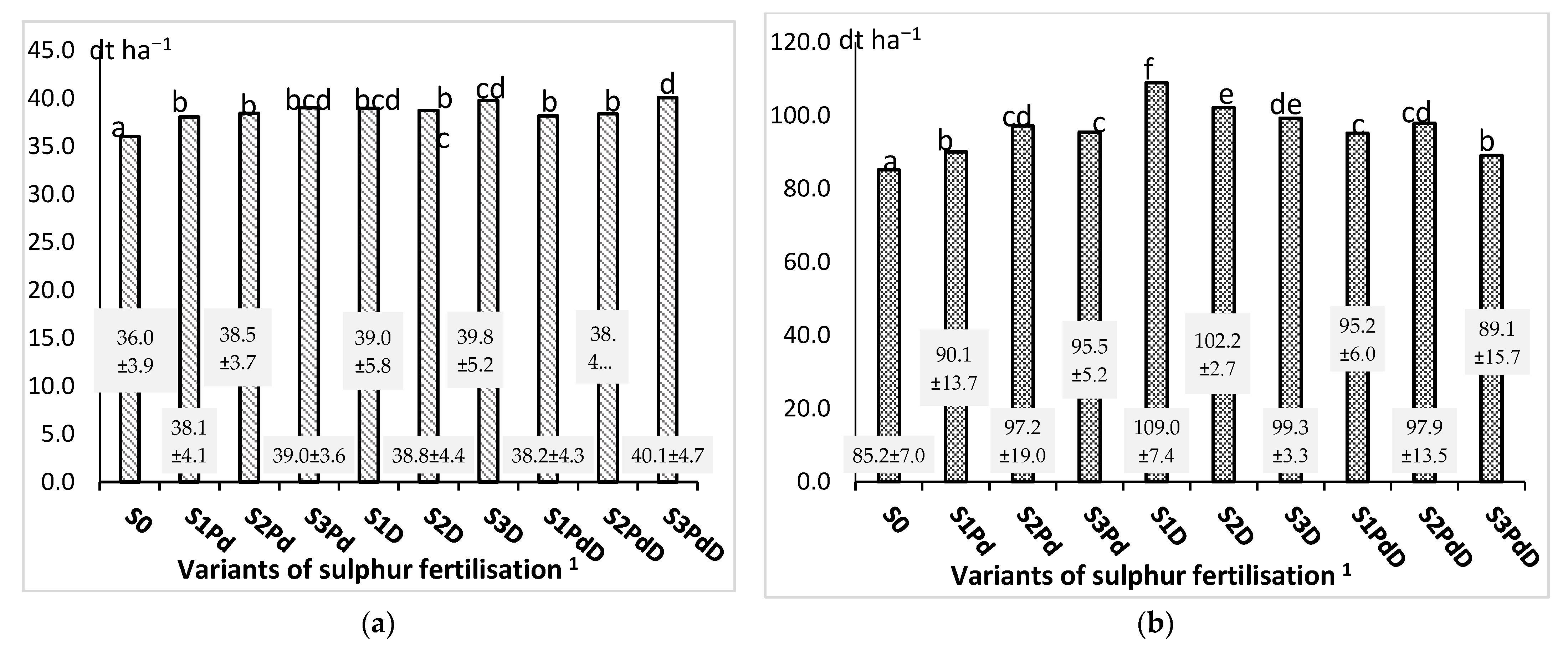
3.1. Yield of Seeds and Straw
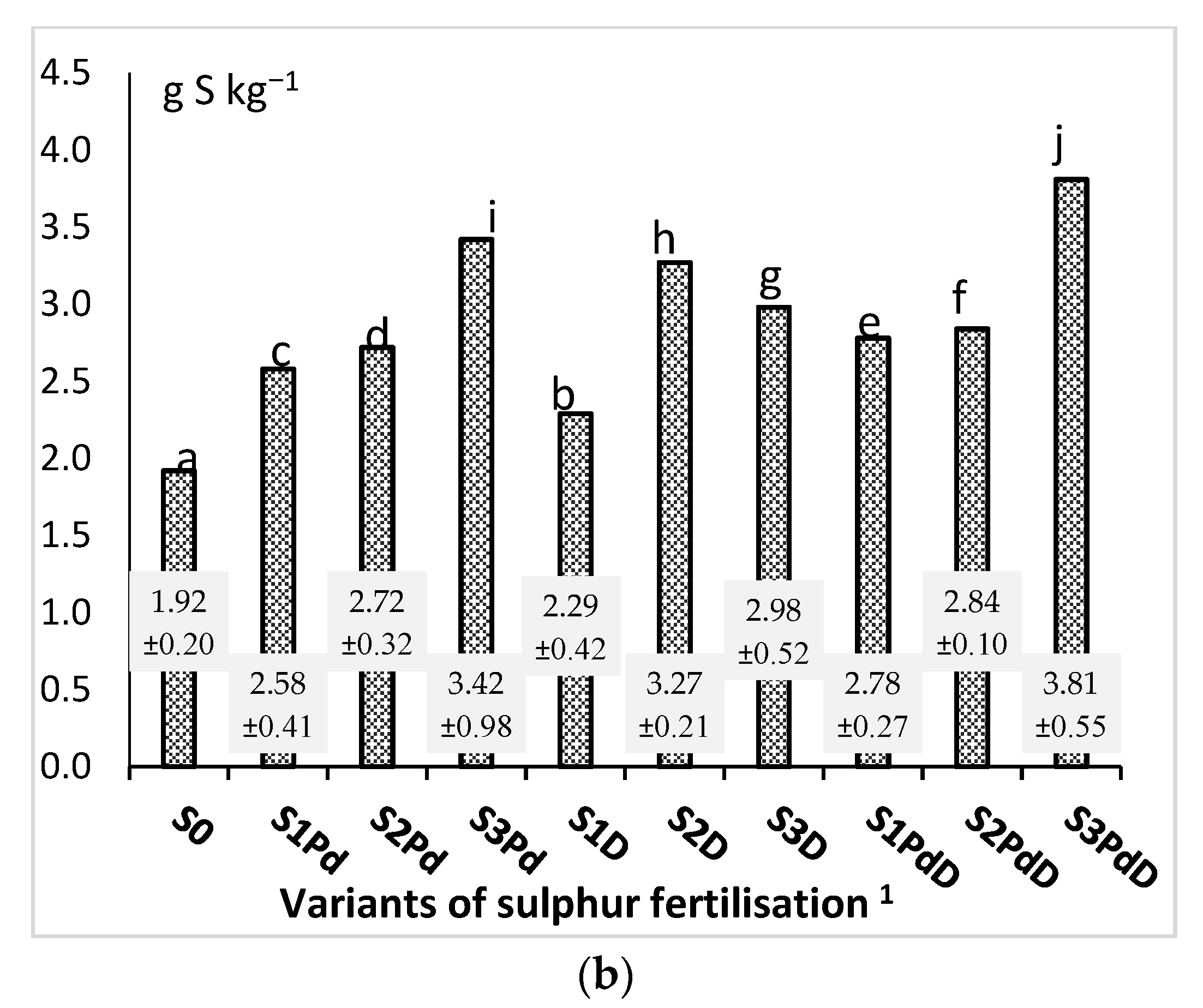
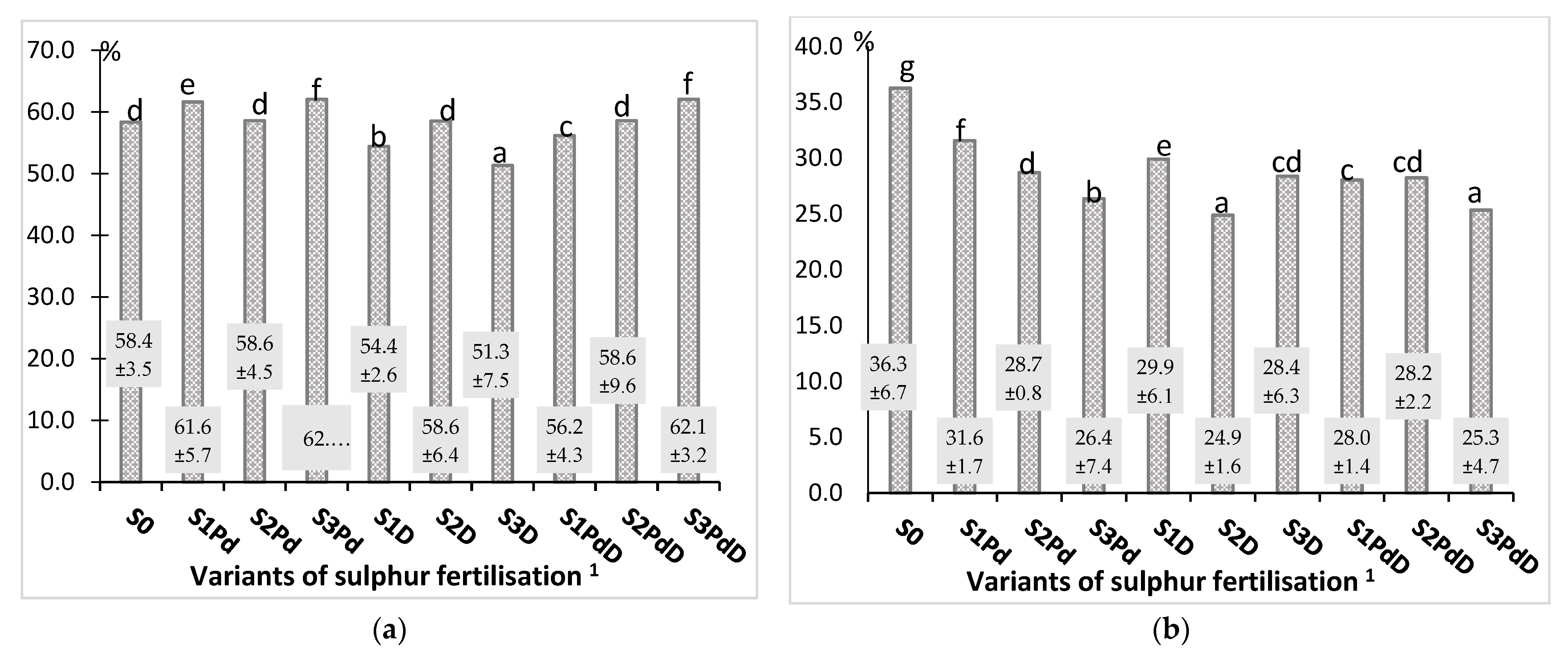
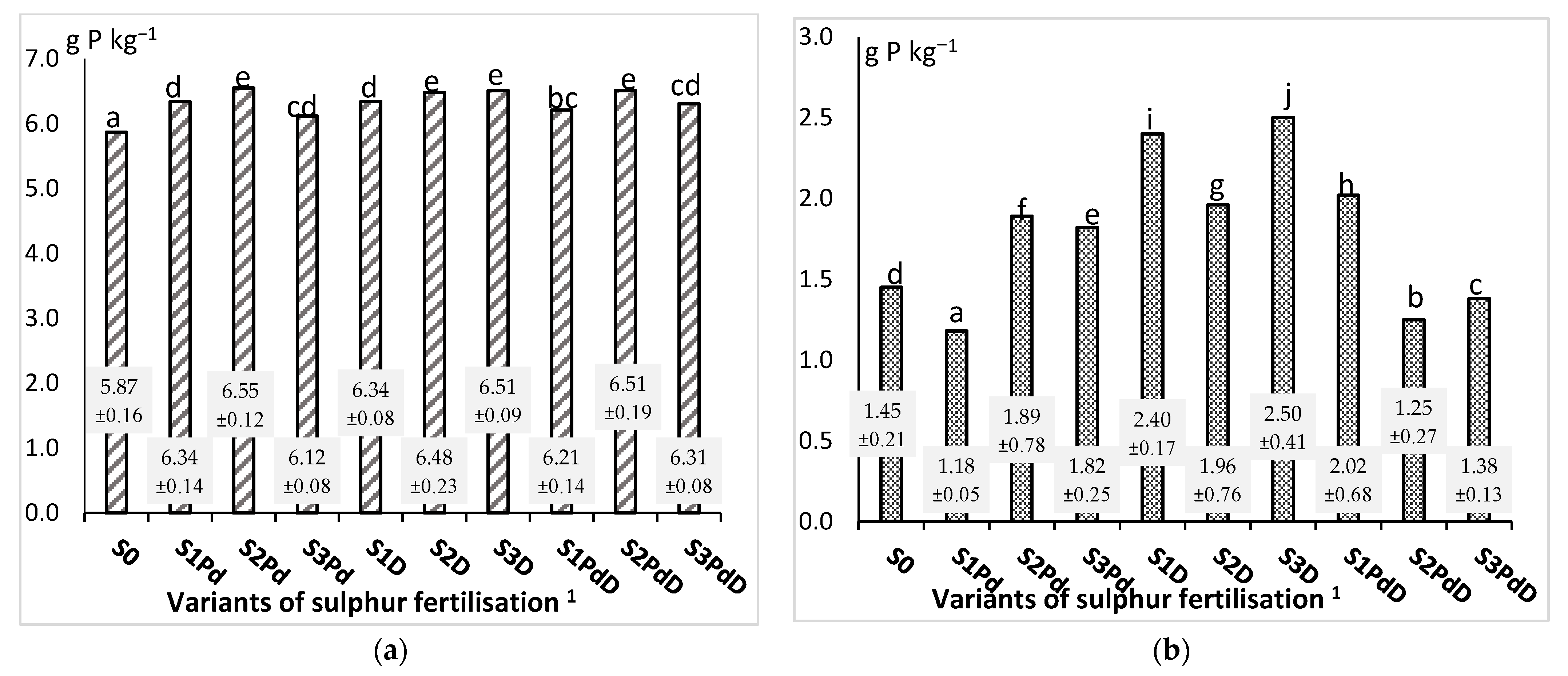
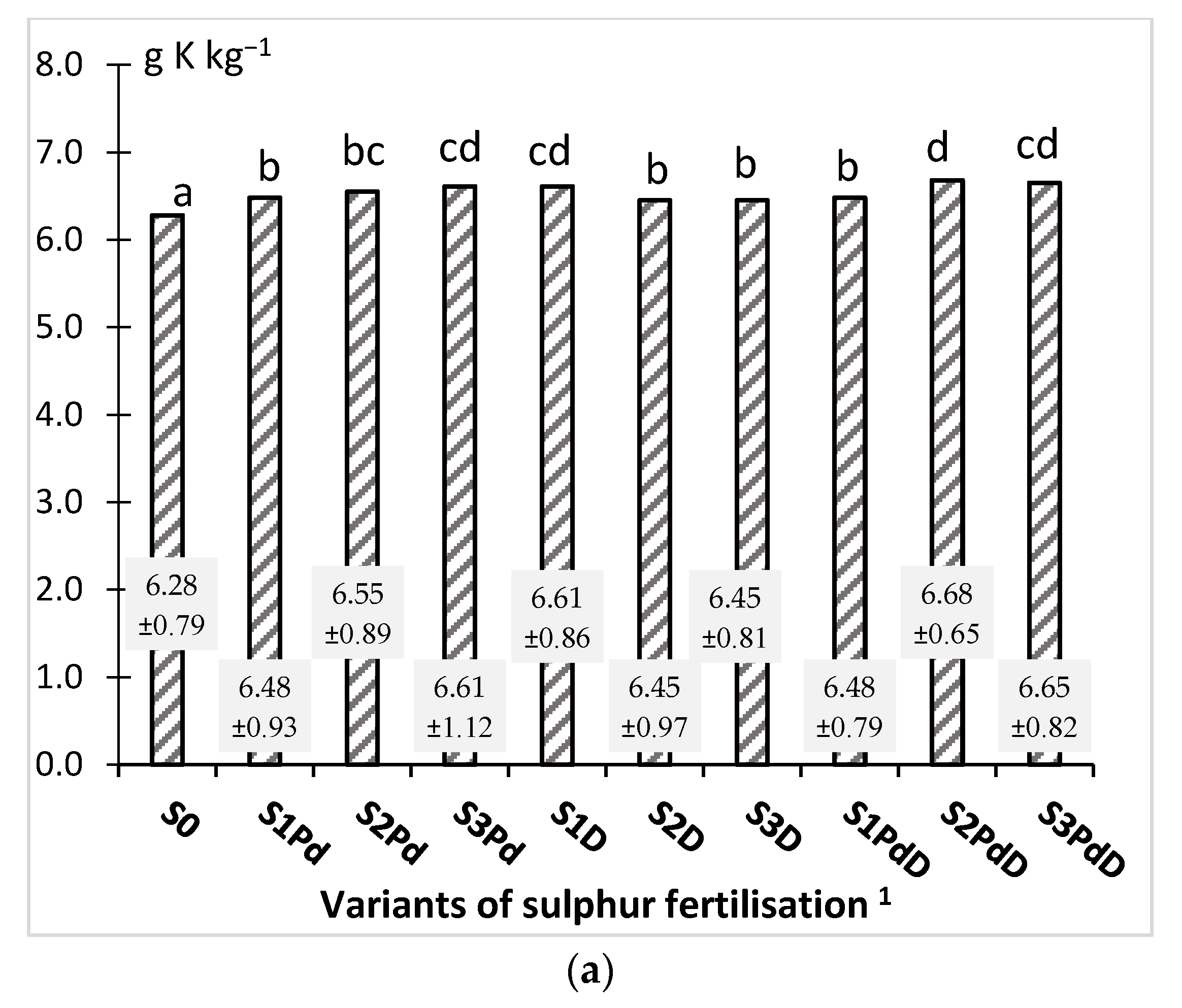
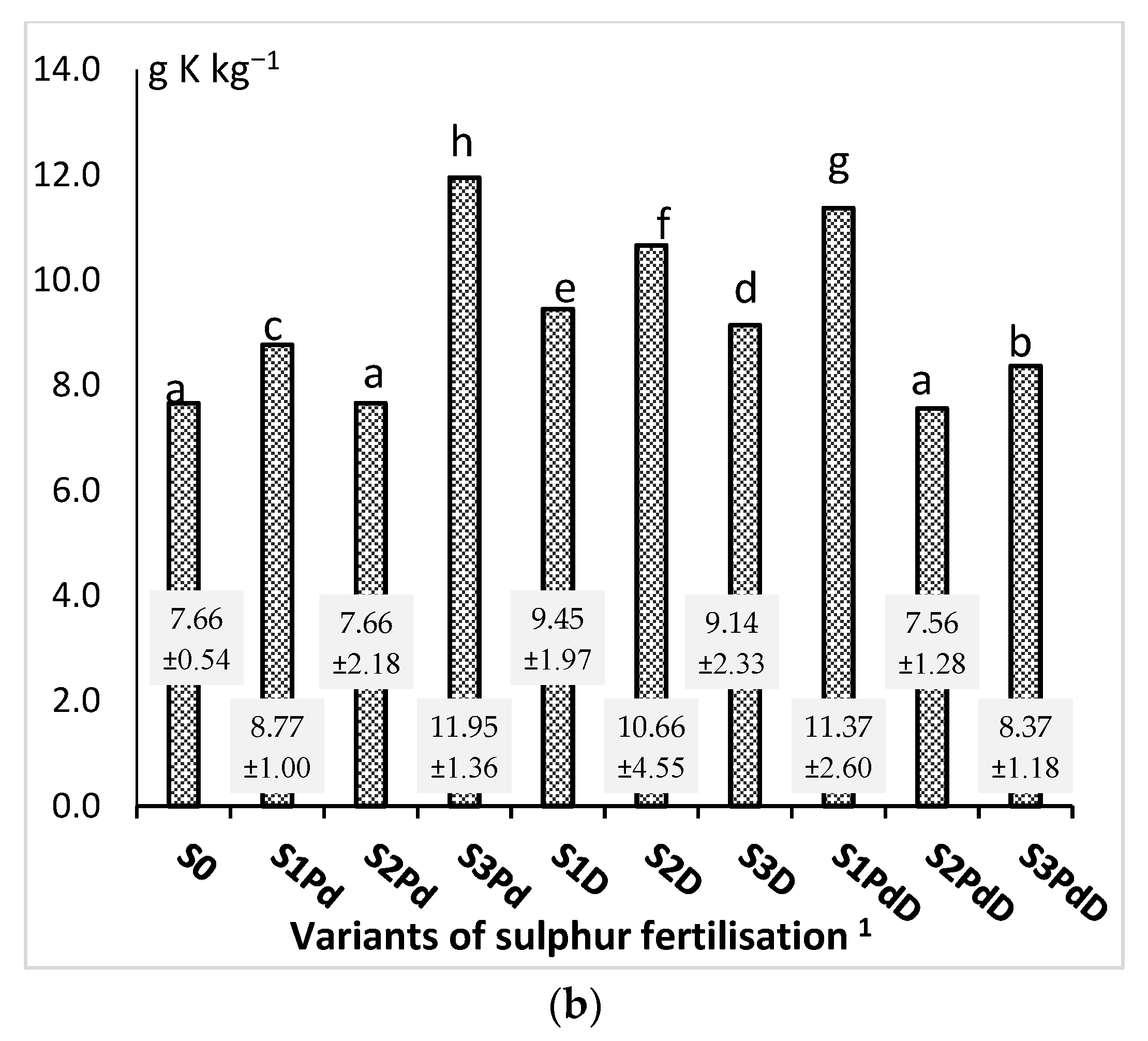
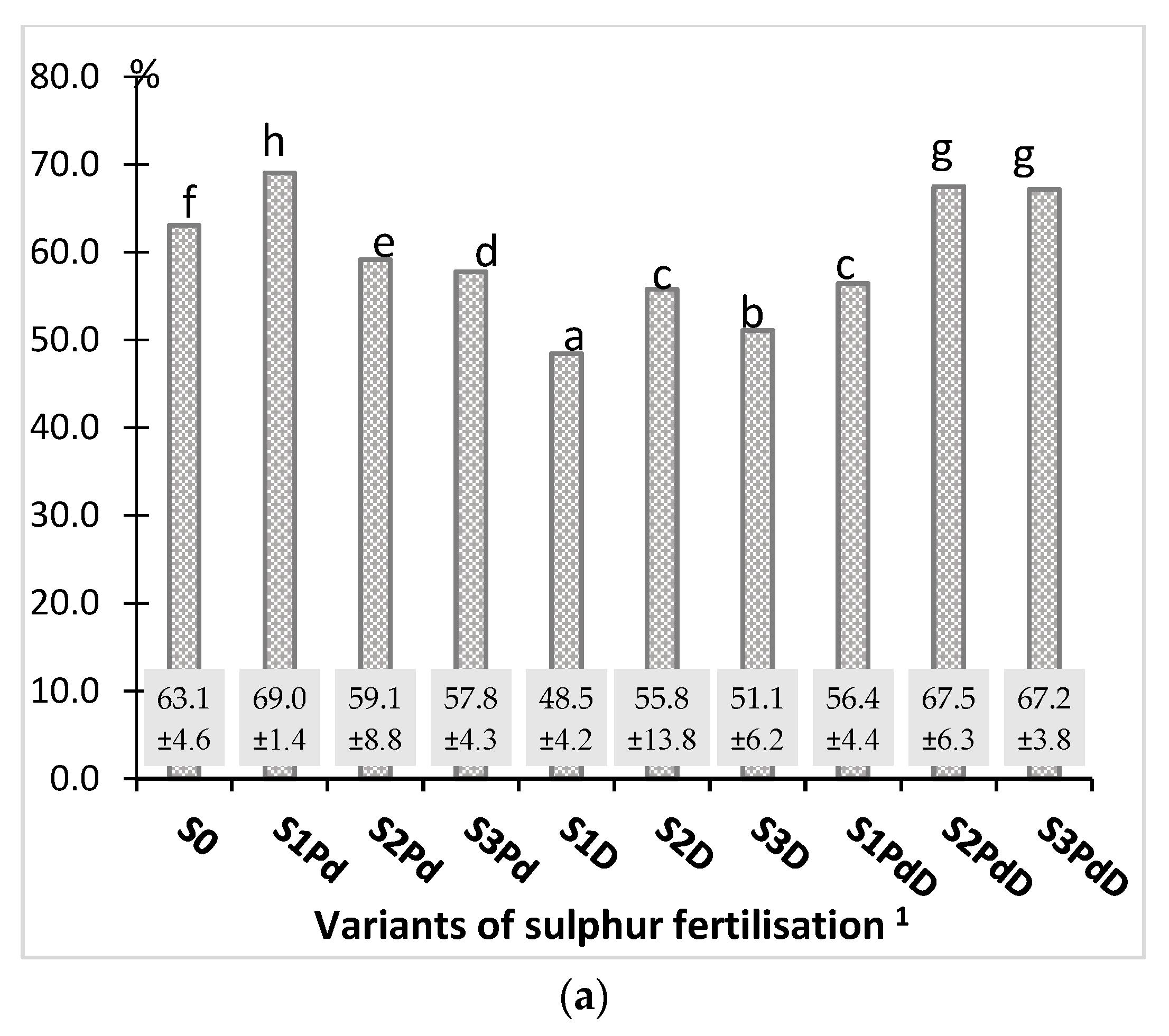
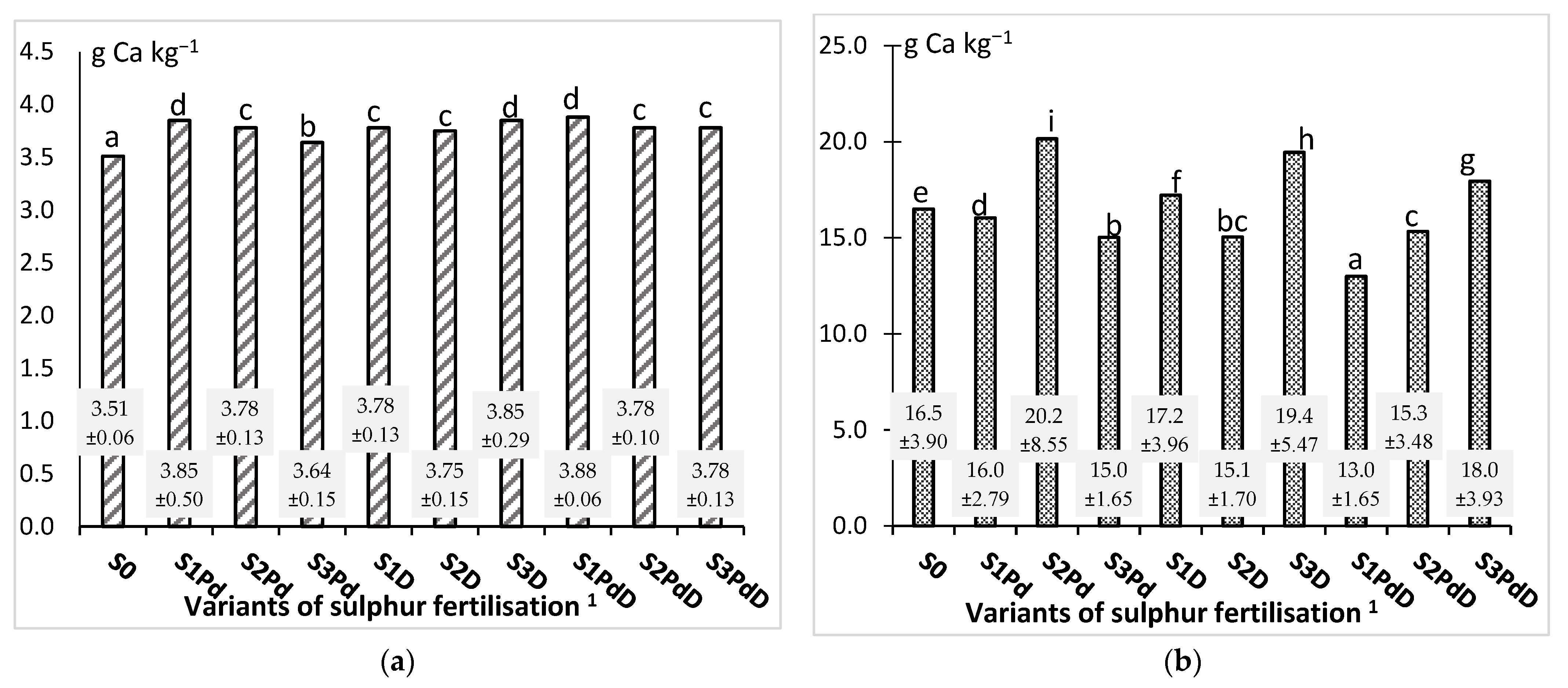
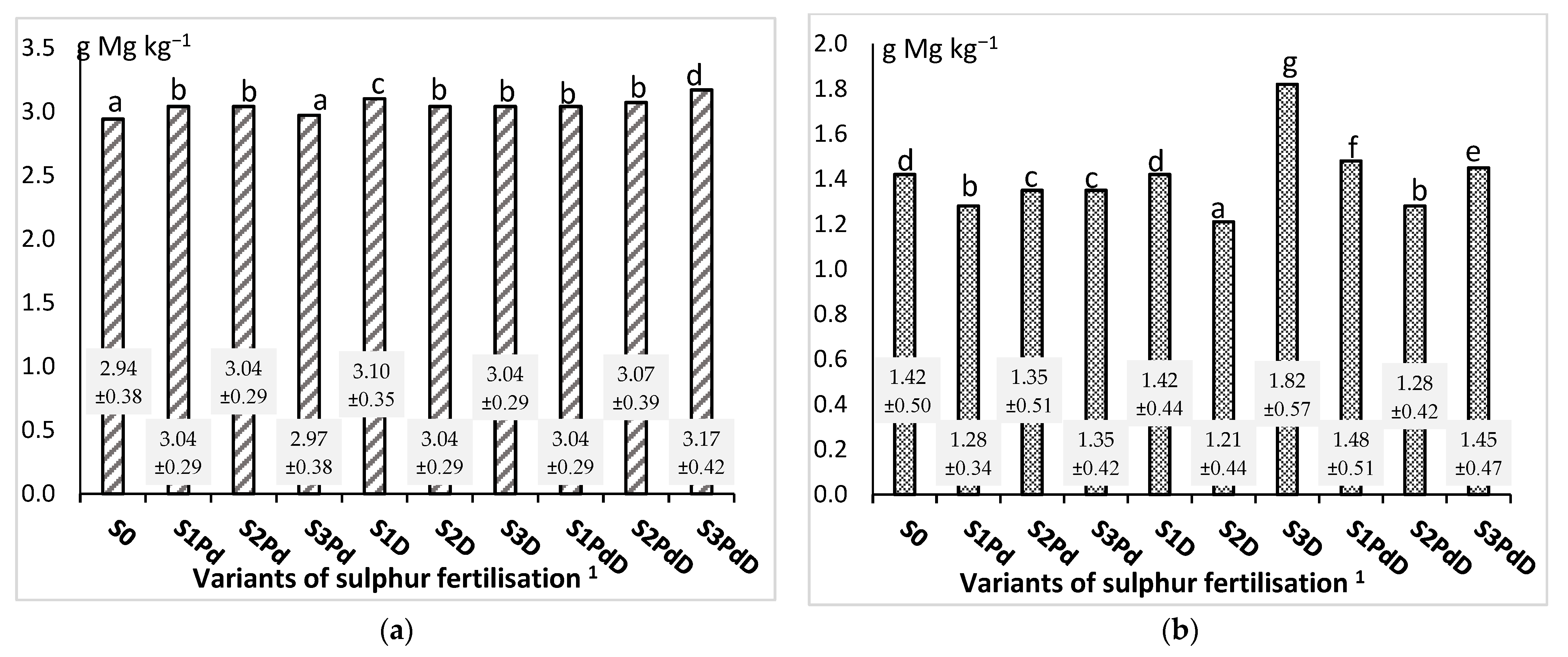
3.2. The Macronutrient Content and the Harvest Index of the Accumulation of Elements
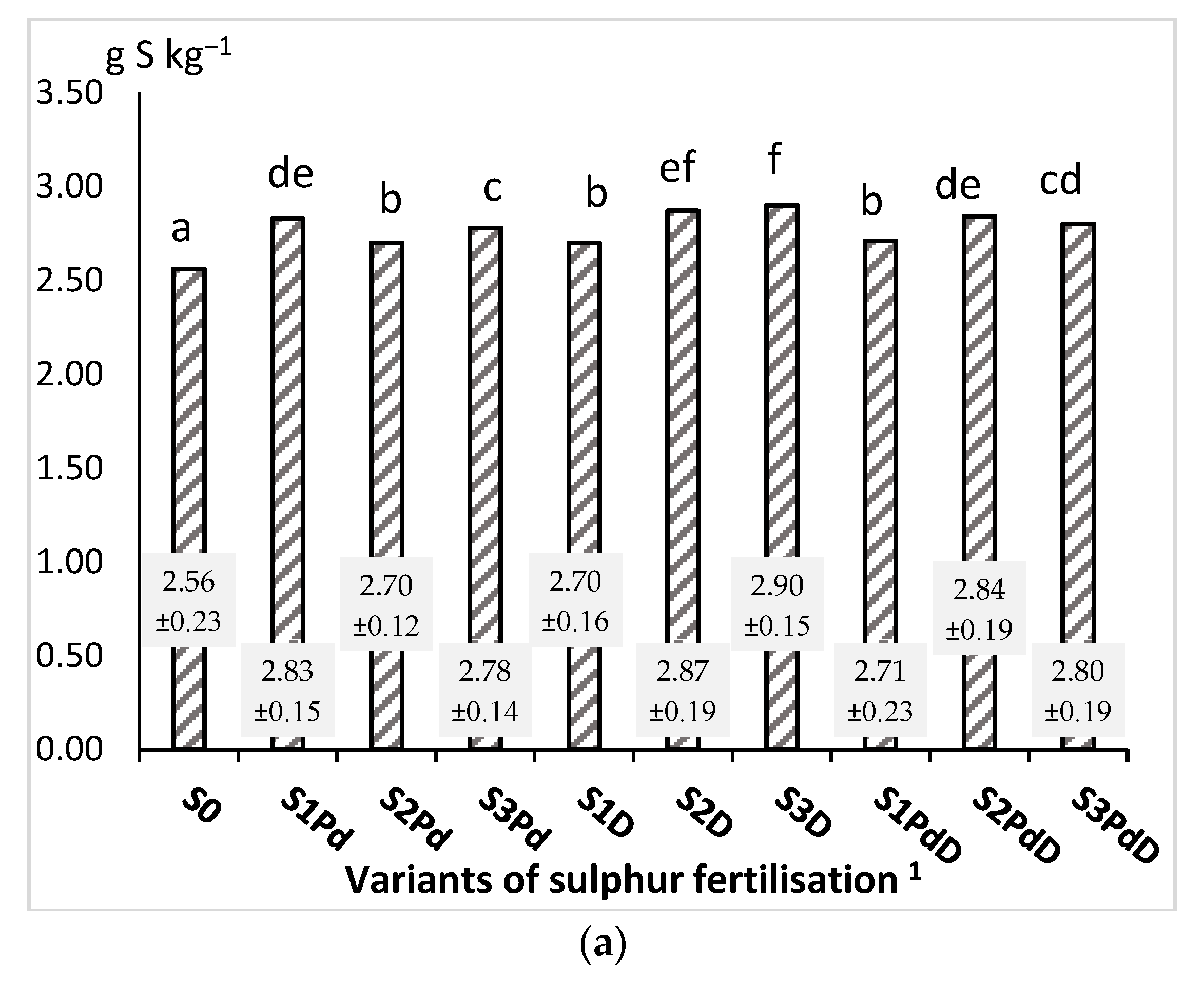
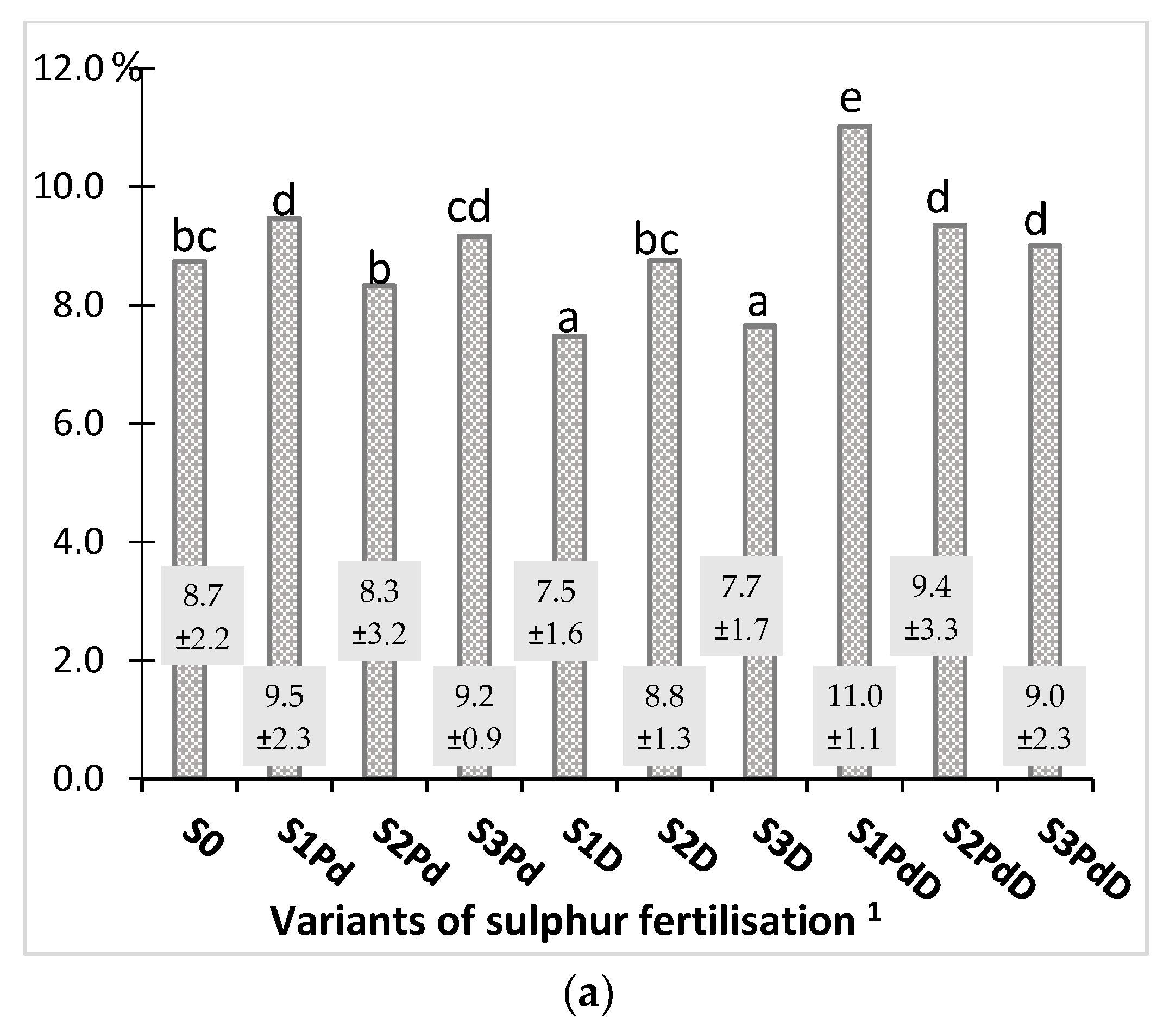
3.2.1. Nitrogen and Sulphur
3.2.2. Phosphorus and Potassium
3.2.3. Calcium and Magnesium
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kozłowska-Strawska, J.; Badora, A. Selected problems of sulfur management in crops. Pol. J. Nat. Sci. 2013, 28, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Barczak, B.; Skinder, Z.; Piotrowski, R. Sulphur as a factor that affects nitrogen effectiveness in spring rapeseed agrotechnics. Part III. Agronomic use efficiency of nitrogen. Acta Sci. Pol. Agric. 2017, 16, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, D.A.; Sokólski, M.; Jankowski, K.J. A Multi-criteria evaluation of the effectiveness of nitrogen and sulfur fertilization in different cultivars of winter rapeseed-productivity, economic and energy balance. Energies 2020, 13, 4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazzi, C.; Städler, E. Influence of plant sulphur nutrition on oviposition and larval performance of the diamondback moth. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2004, 111, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, I.; Anjum, N.A.M.; Diva, I.; Abdin, M.Z.; Iqbal, M. Effect of timing of sulfur fertilizer application on growth and yield of rapeseed. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 28, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barłóg, P.; Grzebisz, W.; Diatta, J. Effect of timing and nitrogen fertilizers on nutrients content and uptake by winter oilseed rape. Part II. Dynamics of nutrients uptake. In Chemistry for Agriculture; Górecki, H., Dobrzański, Z., Kafarski, P., Eds.; Czech-Pol Trade: Prague, Czech Republic; Brussels, Belgium, 2005; Volume 6, pp. 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski, K.J.; Kijewski, Ł.; Groth, D.; Skwierawska, M.; Budzyński, W.S. The effect of sulfur fertilization on macronutrient concentrations in the post-harvest biomass of rapeseed (Brassica napus L. ssp. oleifera Metzg). J. Elem. 2015, 20, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.; Abdin, M.Z. Interactive effect of sulphur and nitrogen on the oil and protein contents and on the fatty acid profiles of oil in the seeds of rapeseed (Brassica campestris L.) and mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern. and Coss.). J Agron. Crop Sci. 2000, 185, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, T.; Wachter, A. Sulfur metabolism: A versatile platform for launching defense operations. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahbakhsh, H.; Pakgohar, N.; Karimi, A. Effects of nitrogen and sulphur fertilizers on yield, yield components and oil content of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Asian J. Plant Sci. 2006, 5, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski, K.J.; Budzyński, W.; Szymanowski, A. Influence of the rate and timing of sulphur fertilization on winter oilseed rape yield. Rośliny Oleiste Oilseed Crops 2008, XXIX, 76–90. [Google Scholar]
- Egesel, C.Ö.; Gül, M.K.; Kahrıman, F. Changes in yield and seed quality traits in rapeseed genotypes by sulphur fertilization. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, R.F.; Bell, R.W.; Raphael, C.; Eslick, H. Sources of sulfur for dry matter, seed yield, and oil concentration of canola grown in sulfur deficient soils of south-western Australia. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 1180–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, F.; Hossain, F.; Mondal, M.d.R.I. Influence of sulphur on morpho-physiological and yield parameters of rapeseed (Brassica campestris L.). Bangladesh J. Agric. Res. 2012, 37, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dash, N.R.; Ghosh, G.K. Efficacy of gypsum and magnesium sulfate as sources of sulfur to rapeseed in lateritic soils. J. Plant Nutr. 2012, 35, 2156–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz-Cholewa, U.; Kieloch, R. Effect of sulphur and micronutrients fertilization on yield and fat content in winter rape seeds (Brassica napus L.). Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwil., S. The effect of foliar feeding under different soil fertilization conditions on the yield structure and quality of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Electron. J. Pol. Agric. Univ. 2016, 19, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Tuncturk, R.; Tuncturk, M. The effect of different sulphur doses on the yield and quality of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 6952–6957. [Google Scholar]
- Podleśna, A. The effect of sulfur fertilization on concentration and uptake of nutrients by winter oilseed rape. (Wpływ nawożenia siarką na zawartość i pobieranie składników pokarmowych przez rzepak ozimy). Rośliny Oleiste Oilseed Crops 2004, XXV, 627–636. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczor, A.; Brodowska, M. Effect of liming and sulphur fertilization on the growth and yielding of spring forms of wheat and rape. Part II. Rape. (Wpływ wapnowania i nawożenia siarką na wzrost, rozwój i plonowanie form jarych pszenicy i rzepaku. Cz. II. Rzepak). Acta Agrophys. 2003, 1, 661–666. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Christie, P. Enhanced uptake of soil Pb and Zn by Indian mustard and winter wheat following combined soil application of elemental sulphur and EDTA. Plant Soil 2004, 261, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jankowski, K.; Kijewski, Ł.; Skwierawska, M.; Krzebietke, S.; Mackiewicz-Walec, E. Effect of sulfur fertilization on the concentrations of copper, zinc and manganese in the roots, straw and oil cake of rapeseed (Brassica napus L. ssp oleifera Metzg). J. Elem. 2014, 19, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lošák, T.; Hrivna, L.; Richter, R. Effect of increasing doses of nitrogen and sulphur on yields, quality and chemical composition of winter rape. Zesz. Probl. Post. Nauk. Rol. 2000, 472, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.J. Sulphur uptake, yield responses and the interactions between nitrogen and sulphur in winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus). J. Agric. Sci. 1996, 126, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRB. IUSS Working Group. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, update 2015 International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. In World Soil Resources Reports; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; No. 106. 201. [Google Scholar]
- The Polish Committee for Standarization. PKN Polish Standard PN-ISO 10390. In Soil Quality-Determination of pH. PKN; The Polish Committee for Standarization: Warszawa, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Catalog of Research Methods at Chemical and Agricultural Stations; Regional Chemical and Agricultural Station in Lublin: Lublin, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- The Polish Committee for Standarization. PKN Polish Standard PN-R-04023. In Chemical and Agricultural Analysis of Soil–Determination of Available Phosphorus in Mineral Soils; PKN: Warszawa, Poland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- The Polish Committee for Standarization. PKN Polish Standard PN-R-04022. In Chemical and Agricultural Analysis of Soil–Determination of Available Potassium in Mineral Soils; PKN: Warszawa, Poland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- The Polish Committee for Standarization. PKN Polish Standard PN-R-04020:1994/Az1. In Chemical and Agricultural Analysis of soil–Determination of Available Magnesium Content; PKN: Warszawa, Poland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lancashire, P.D.; Bleiholder, H.; Van den Boom, T.; Langelüddeke, P.; Strauss, R.; Weber, E.; Witzenberger, A. A uniform decimal code for growth stages of crops and weeds. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1991, 119, 561–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: Database of plant protection products. www.ior.poznan.pl (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Kapuściński, J.; Nowak, R. The frequency of the occurrence of droughts and post-droughts periods in mid-west Poland on the example of Poznań, Wałcz and Wieluń. In Kształtowanie i ochrona środowiska leśnego; Miler, A., Ed.; Klimat a las. Wyd. AR: Poznań, Poland, 2003; pp. 76–88. [Google Scholar]
- Skowera, B.; Jędrszczyk, E.; Kopcińska, J.; Ambroszczyk, A.M.; Kołtun, A. The effects of hydrothermal conditions during vegetation period on fruit quality of processing tomatoes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kamińska, W.; Kardasz, T.; Strahl, A. Metody badań laboratoryjnych w stacjach chemiczno-rolniczych. Część 2. Badanie materiału roślinnego. In Laboratory Test Methods in Chemical and Agricultural Stations. Part 2. Examination of Plant Material. Wyd.; IUNG: Puławy, Poland, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zając, T.; Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Oleksy, A.; Lorenc-Kozik, A.; Ratajczak, K. Analysis of yield and plant traits of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) cultivated in temperate region in light of the possibilities of sowing in arid areas. Acta Agrobot. 2016, 69, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brachaczek, A.; Kaczmarek, J.; Jędryczka, M. Warm and wet autumns favour yield losses of oilseed rape caused by phoma stem canker. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanović-Jeromela, A.; Terzić, S.; Jankulovska, M.; Zorić, M.; Kondić-Špika, A.; Jocković, M.; Hristov, N.; Crnobarac, J.; Nagl, N. Dissection of year related climatic variables and their effect on winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) development and yield. Agronomy 2019, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarecki, W. The size and quality of winter rape seed yield depending on the cultivar type. Agron. Sci. 2021, LXXVI, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielebski, F. Share of yield components in the creation of yield of winter oilseed rape hybrids. (Udział elementów struktury plonu w kształtowaniu plonu nasion mieszańcowych odmian rzepaku ozimego). Rośliny Oleiste Oilseed Crops 2005, XXVI, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Stępień, A.; Wojtkowiak, K.; Pietrzak-Fiećko, R. Nutrient content, fat yield and fatty acid profile of winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) grown under different agricultural production systems. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 77, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cwalina-Ambroziak, B.; Stępień, A.; Kurowski, T.P.; Głosek-Sobieraj, M.; Wiktorski, A. The health status and yield of winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) grown in monoculture and in crop rotation under different agricultural production systems. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegewald, H.; Koblenz, B.; Wensch-Dorendorf, M.; Christen, O. Impacts of high intensity crop rotation and N management on oilseed rape productivity in Germany. Crop Pasture Sci. 2016, 67, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różyło, K.; Pałys, E. Influence of crop rotation and row spacing on weed infestation of winter rape grown on rendzina soil. Acta Sci. Pol. Agric. 2011, 10, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Sieling, K.; Christen, O.; Nemati, B.; Hanus, H. Effects of previous cropping on seed yield and yield components of oil-seed rape (Brassica napus L.). Eur. J. Agron. 1997, 6, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskulska, I.; Jaskulski, D.; Kotwica, K.; Piekarczyk, M.; Wasilewski, P. Yielding of winter rapeseed depending on the forecrops and soil tillage methods. (Plonowanie rzepaku ozimego w zależności od przedplonów i sposobów uprawy roli). Ann. UMSC Sec. Agric. 2014, 69, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski, K.J.; Budzyński, W.; Szymanowski, A. Effect of sulfur on the quality of winter rape seeds. J. Elem. 2008, 13, 521–534. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubus, M.; Toboła, P. Content of total and sulphate sulphur in winter oilseed rape depending on fertilization. (Zawartość siarki ogólnej i siarczanowej w rzepaku ozimym w zależności od nawożenia). Rośliny Oleiste Oilseed Crops 2005, XXIV, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wielebski, F.; Wójtowicz, M. Effect of spring sulphur fertilization on yield and glucosinolate content in seeds of winter oilseed rape composite hybrids. (Wpływ wiosennego nawożenia siarką na plon i zawartość glukozynolanów w nasionach odmian mieszańcowych złożonych rzepaku ozimego). Rośliny Oleiste Oilseed Crops 2003, XXIV, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Gallejones, P.; Castellón, A.; del Prado, A.; Unamunzaga, O.; Aizpurua, A. Nitrogen and sulphur fertilization effect on leaching losses, nutrient balance and plant quality in a wheat-rapeseed rotation under a humid Mediterranean climate. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 93, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielebski, F. The effect of sulphur fertilization on the yield of different breeding forms of winter oilseed rape in the conditions of diverse nitrogen rates. (Wpływ nawożenia siarką w warunkach stosowania zróżnicowanych dawek azotu na plonowanie różnych typów odmian rzepaku ozimego). Rośliny Oleiste–Oilseed Crops 2011, XXXII, 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.J.; Evans, E.J.; Bilsborrow, P.E. Varietal differences in sulphur uptake and utilization in relation to glucosinolate accumulation in oilseed rape. In Proceedings of the 9th International Rapeseed Congress, Cambridge, UK, 4–7 July 1995; Volume 1, pp. 271–273. [Google Scholar]
- Withers, P.J.A.; Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Evans, E.J.; Sinclair, A.H. Sulphur inputs for optimum yields of cereals. Asp. Appl. Biol. 1997, 50, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Janzen, H.H.; Bettany, J.R. Sulfur nutrition of rapeseed. II. Effect of time of sulfur application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.A.; Mahli, S.S.; Karamanos, R.E. Sulfur management for rapeseed. Field Crops Res. 2012, 128, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podleśna, A. The effect of soil and foliar application of sulfur on the yield and mineral composition of winter oilseed rape plants. (Wpływ doglebowego i dolistnego stosowania siarki na plon i skład mineralny roślin rzepaku ozimego). Ann. UMCS Sec. E 2009, LXIV, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, S.B.; Mullins, G.L. Foliar burn and wheat grain yield responses following topdress-applied nitrogen and sulphur fertilizers. J. Plant Nutr. 2004, 27, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Blake-Kalff, M.M.A.; Link, A.; Tucker, M. Crop response to sulphur fertilization in Europe. Nawozy I Nawożenie–Fertil. Fertil. 2003, 3, 26–51. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, E.J.; Batchelor, S.E.; Walker, K.C. The effect of foliar applied sulphur on individual glukosinolates in oilseed rape seed. J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 1995, 158, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneklaus, S.; Bloem, E.; Schnug, E. Sulphur in agroecosystems. Folia Univ. Agric. Stetin. 2000, 204, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Fismes, J.; Vong, P.C.; Guckert, A.; Frossard, E. Influence of sulfur on apparent N-use efficiency, yield and quality of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) grown on a calcareous soil. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 12, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dłużniewska, J.; Nadolnik, M.; Kulig, B. Fungal diseases of winter oilseed rape under the different level of nitrogen and sulphur fertilization. (Choroby rzepaku ozimego w zależności od poziomu zaopatrzenia roślin w azot i siarkę). Prog. Plant Protect. Post. Ochr. Roś. 2011, 51, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Kurowski, T.; Majchrzak, B.; Jankowski, K. Effect of sulfur fertilization on the sanitary state of plants of the family Brassicaceae. Acta Agrobot. 2010, 63, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Kok, L.J.; Castro, A.; Durenkamp, M.; Stuiver, C.E.; Westerman, S.; Yang, L.; Stulen, I. Sulphur in plant phisiology. Nawozy I Nawożenie–Fertil. Fertil. 2003, 2, 55–80. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, N.A.; Gill, S.S.; Umar, S.; Ahmad, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, E. Improving growth and productivity of oleiferous Brassicas under changing environment: Significance of nitrogen and sulphur nutrition, and underlying mechanisms. Sci. World J. 2012, 657808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriksen, J.; Nielsen, M.; Mortensen, J.V.; Schjorring, J.K. Redistribution of sulphur during generative growth of barley plants with different sulphur and nitrogen status. Plant Soil 2001, 230, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Ahmad, G.; Arif, M.; Jan, M.T.; Marwat, K.B. Quality parameters of canola as affected by nitrogen and sulfur fertilization. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczak, B.; Barczak, T.; Skinder, Z.; Piotrowski, R. Proportions of nitrogen and sulphur in spring rapeseeds depending on fertilization with these elements. J. Elem. 2020, 25, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, A.; Wojtkowiak, K.; Pietrzak-Fiećko, R. Influence of a crop rotation system and agrotechnology level on the yielding and seed quality of winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) varieties Castille and Nelson. J. Elem. 2018, 23, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwierawska, M.; Benedycka, Z.; Jankowski, K.; Skwierawski, A. Sulphur as a fertiliser component determining crop yield and quality. J. Elem. 2016, 21, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grzebisz, W. Technologie nawożenia roślin uprawnych–fizjologia plonowania. In Tom 1. Oleiste, Okopowe i Strączkowe; PWRiL: Poznań, Poland, 2011; p. 413. [Google Scholar]
- Barczak, B.; Knapowski, T.; Kozera, W.; Ralcewicz, M. Effects of sulphur fertilisation on the content and uptake of macroelements in narrow-leaf lupin. Rom. Agric. Res. 2014, 31, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Skwierawska, M.; Zawartka, L.; Zawadzki, B. The effect of different rates and forms of applied sulphur on nutrient composition of planted crops. Plant Soil Environ. 2008, 54, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majumder, S.; Halder, T.K.; Saha, D. Integrated nutrient management of rapeseed (Brassica campestris L. var. yellow sarson) grown in a typic haplaquept soil. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2017, 9, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szczepanek, M.; Siwik-Ziomek, A. P and K accumulation by rapeseed as affected by biostimulant under different NPK and S fertilization doses. Agronomy 2019, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brodowska, M.; Kaczor, A. The effect of various forms of sulphur and nitrogen on calcium and magnesium content and uptake in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and cocksfoot (Dactylis glomerata L.). J. Elem. 2009, 14, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarecki, W. The reaction of winter oilseed rape to different foliar fertilization with macro- and micronutrients. Agriculture 2021, 11, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, C.z.; Baturo, A.; Lenc, L.; Trzciński, J. Downy mildew (P. parasitica) and powdery mildew (E. cruciferarum) occurrence on spring oilseed rape cv. Star depending on differentiated fertilisation with nitrogen and sulphur. (Występowanie mączniaka rzekomego (Perono-spora parasitica/Pers.ex Fr./Fr.) i mączniaka prawdziwego (Erysiphe crucifererum Opiz ex L. Junell) na rzepaku jarym odmiany Star przy zróżnicowanym nawożeniu azotem i siarką). Rośliny Oleiste Oilseed Crops 2002, XXIII, 391–408. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Granulometric composition | Clayey silt | |
| Sand (2.0–0.05 mm) | % | 12.0 |
| Dust (0.05–0.02 mm) | 39.0 | |
| (0.02–0.002 mm) | 35.0 | |
| Loam (<0.002 mm) | 14.0 | |
| pHKCl | 6.2 | |
| Corg | g kg−1 | 18.1 |
| Ntot. | 1.6 | |
| Content of available nutrients | ||
| P | mg kg−1 | 34.9 |
| K | 93.8 | |
| Mg | 64.5 | |
| S-SO4 | 8.23 | |
| (I) Sulphur Dose | (II) Method of Sulphur Application | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pd Soil Application Sowing | D | PdD | |
| Foliar | Mixed = ½ Pd+ ½ D | ||
| S0 | S0 | ||
| S1 | S1Pd | S1D | S1PdD |
| 20 kg S ha−1 | One-time application—before budding (BBCH 35) | Foliar application: I. before budding (BBCH 35)—10 kg S ha−1. | |
| S2 | S2Pd | S2D (1/2 DI + 1/2 DII) | S2PdD (½Pd + ½D) |
| 40 kg S ha−1 | I. before budding (BBCH 35), II. beginning of flowering (BBCH 57) | Foliar application: I. before budding (BBCH 35)—20 kg S ha−1 | |
| S3 | S3Pd | S3D (1/3 DI + 1/3 DII + 1/3 DIII) | S3PdD (½Pd + ½D) |
| 60 kg S ha−1 | I. before budding (BBCH 35), II. beginning of flowering (BBCH 57), III. full flowering (BBCH 65) | Foliar application: I. before budding (BBCH 35)—15 kg S ha−1, II. beginning of flowering (BBCH 57)—15 kg S ha−1 | |
| The Growing Season | Temperature (°C) | Rainfall | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deviation from the Long-term Average | Long-Term Average | % of the Long-Term Average | Long-Term Average (mm) | |||||
| 2010/2011 | 2011/2012 | 2012/2013 | 2010/2011 | 2011/2012 | 2012/2013 | |||
| Autumn August–November | −0.4 | +0.4 | +1.7 | 10.3 | 146.7 | 38.2 | 82.2 | 230.8 |
| Winter dormancy December–March | −1.5 | −0.2 | −1.3 | −1.6 | 83.6 | 52.7 | 55.8 | 157.4 |
| Spring April–July | +1.1 | +1.7 | +1.3 | 14.3 | 100 | 67.9 | 106.3 | 321.5 |
| Year | Months | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| April | May | June | July | August | September | |
| 2010 | – | – | – | – | 2.72 | 3.12 |
| 2011 | 0.64 | 0.92 | 1.90 | 2.66 | 0.91 | 0.25 |
| 2012 | 2.01 | 0.99 | 1.55 | 0.47 | 1.30 | 0.64 |
| 2013 | 1.77 | 1.78 | 2.78 | 0.96 | – | – |
| The long-term average for 1996–2013 | 1.97 | 1.84 | 1.68 | 1.93 | 1.43 | 1.71 |
| Variants of Sulphur Fertilisation 1 | Seeds Yield (dt ha−1) | Straw Yield (dt ha−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | |
| S0 | 39.16 de ± 0.75 | 30.60 a ± 0.47 | 38.36 d ± 1.30 | 83.10 cd ± 2.91 | 78.40 bc ± 1.21 | 94.00 fgh ± 3.18 |
| S1Pd | 39.79 def ± 0.42 | 32.88 ab ± 0.40 | 41.55 fg ± 1.20 | 94.78 ghi ± 0.90 | 74.20 ab ± 0.89 | 107.40 no ± 3.10 |
| S2Pd | 40.95 efg ± 0.73 | 33.12 bc ± 0.54 | 41.33 efg ± 0.77 | 106.5 lłm ± 2.54 | 69.50 a ± 1.13 | 115.60 pq ± 2.16 |
| S3Pd | 41.84 fgh ± 0.75 | 33.72 c ± 0.71 | 41.54 fg ± 0.95 | 90.2 efg ± 1.95 | 94.70 ghi ± 1.99 | 101.70 j–n ± 2.34 |
| S1D | 41.76 fg ± 0.74 | 30.96 abc ± 0.99 | 44.19 hij ± 0.79 | 117.8 n ± 2.07 | 100.70 i–l ± 3.22 | 108.60 o ± 1.94 |
| S2D | 40.76 efg ± 0.80 | 32.76 abc ± 0.71 | 42.74 g–j ± 0.88 | 104.6k lłm ± 2.06 | 102.10 klł ± 2.21 | 100.10 h–l ± 2.06 |
| S3D | 42.28 g–j ± 0.75 | 32.64 abc ± 1.03 | 44.42 j ± 0.53 | 100.2 h–l ± 1.78 | 96.00 g–j ± 3.02 | 101.80 j–n ± 1.21 |
| S1PdD | 40.76 efg ± 0.56 | 32.52 abc ± 0.71 | 41.29 efg ± 0.86 | 87.9 def ± 1.43 | 104.40 l–o ± 2.28 | 93.40 fg ± 1.94 |
| S2PdD | 41.64 fg ± 0.92 | 32.28 abc ± 0.86 | 41.20 efg ± 0.59 | 106.3 k–m ± 1.98 | 77.70 bc ± 2.06 | 109.70 op ± 1.58 |
| S3PdD | 42.10 f–i ± 0.80 | 33.60 c ± 0.59 | 44.50 j ± 0.89 | 86.80 de ± 1.66 | 71.30 a ± 1.25 | 109.40 op ± 2.20 |
| Mean | 41.10 B ± 1.21 | 32.51 A ± 1.21 | 42.11 C ± 1.97 | 97.91 B ± 10.69 | 86.88 A ± 13.34 | 104.17 C ± 7.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stepaniuk, M.; Głowacka, A. Yield of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L. var. napus) in a Short-Term Monoculture and the Macronutrient Accumulation in Relation to the Dose and Method of Sulphur Application. Agronomy 2022, 12, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010068
Stepaniuk M, Głowacka A. Yield of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L. var. napus) in a Short-Term Monoculture and the Macronutrient Accumulation in Relation to the Dose and Method of Sulphur Application. Agronomy. 2022; 12(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleStepaniuk, Mariusz, and Aleksandra Głowacka. 2022. "Yield of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L. var. napus) in a Short-Term Monoculture and the Macronutrient Accumulation in Relation to the Dose and Method of Sulphur Application" Agronomy 12, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010068
APA StyleStepaniuk, M., & Głowacka, A. (2022). Yield of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L. var. napus) in a Short-Term Monoculture and the Macronutrient Accumulation in Relation to the Dose and Method of Sulphur Application. Agronomy, 12(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010068







