Discovery of Novel N-Pyridylpyrazole Thiazole Derivatives as Insecticide Leads
Abstract
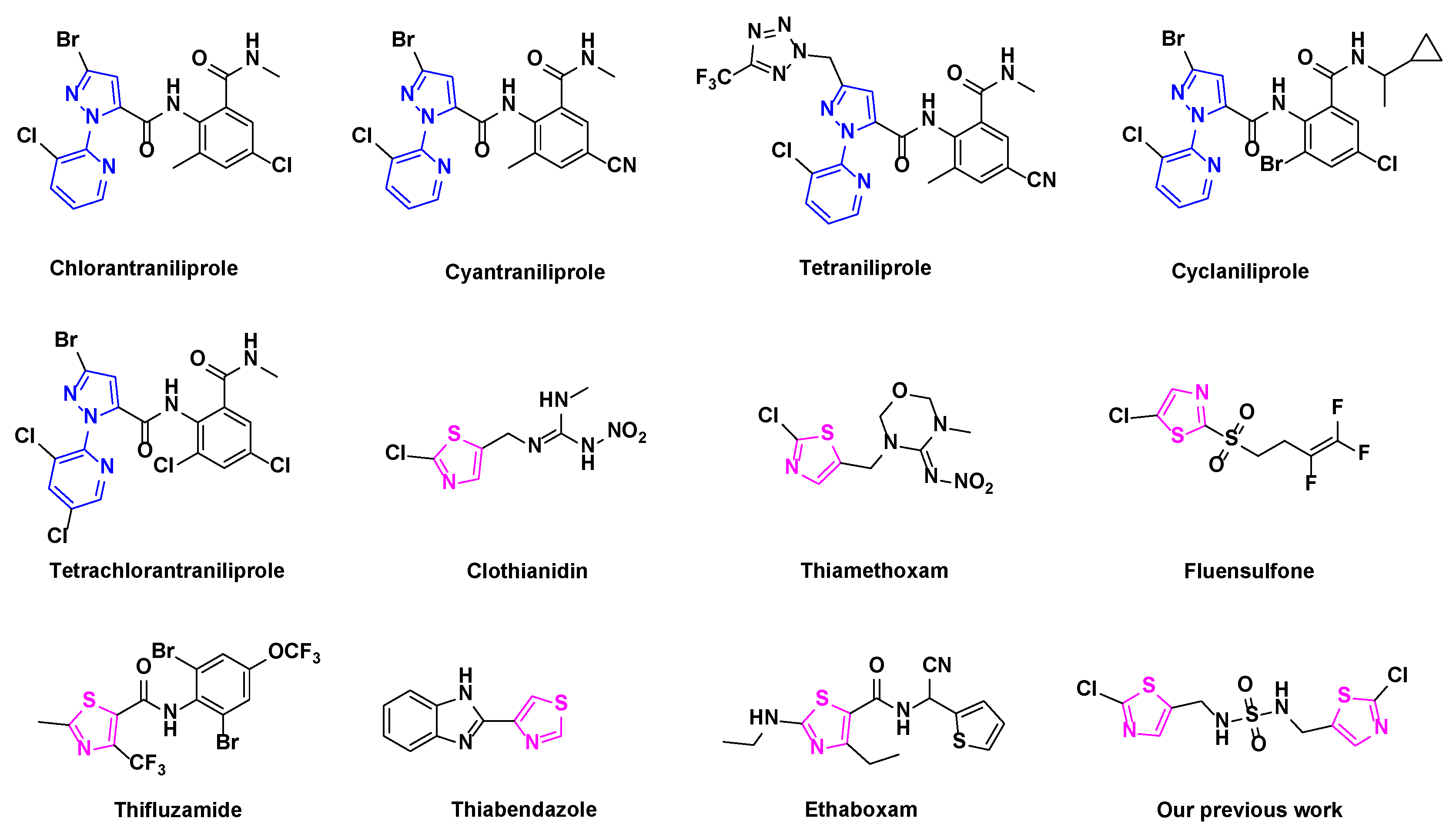
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation and Chemicals
2.2. General Synthetic Procedures
2.3. Biological Materials and Methods
2.3.1. Bioassays with P. xylostella and S. exigua
2.3.2. Bioassays with S. frugiperda
3. Results and Discussion
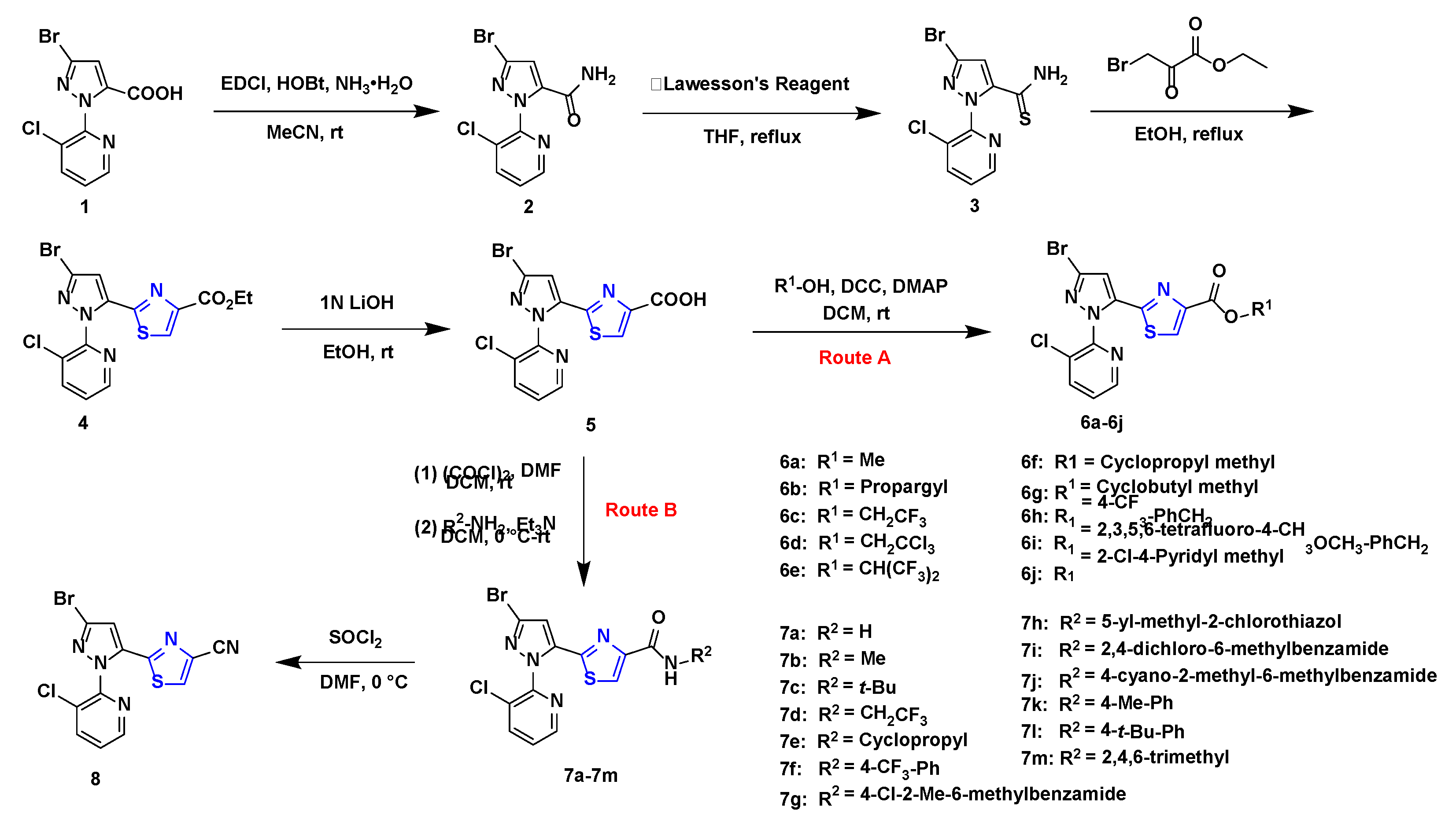
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Insecticidal Activities
3.3. Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savary, S.; Ficke, A.; Aubertot, J.-N.; Hollier, C. Crop losses due to diseases and their implications for global food production losses and food security. Food Secur. 2012, 4, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, M.; Tufenkji, N.; White, J.C. Nano-enabled strategies to enhance crop nutrition and protection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Feng, X.; Liu, S.-S.; You, M.; Furlong, M.J. Biology, ecology, and management of the diamondback moth in China. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.D.; Thierfelder, C.; Baudron, F.; Chinwada, P.; Midega, C.; Schaffner, U.; Johnnie, V. Agro-ecological options for fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda JE Smith) management: Providing low-cost, smallholder friendly solutions to an invasive pest. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevik, K.; Schoville, S.D.; Mota-Sanchez, D.; Chen, Y.H. Pesticide durability and the evolution of resistance: A novel application of survival analysis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.-Q.; Liu, D.; Sheng, C.-W.; Casida, J.E.; Wang, C.; Song, P.-P.; Chen, Y.-M.; Han, Z.-J.; Zhao, C.-Q. Acute toxicity, bioconcentration, elimination and antioxidant effects of fluralaner in zebrafish, danio rerio. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Q.X.; Song, B. Recent research progress in and perspectives of mesoionic insecticides: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11039–11053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, S.; Yan, Y.; Lin, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C.; Xu, H. Design, synthesis, and insecticidal activity of 5,5-disubstituted 4,5-dihydropyrazolo [1,5-a]quinazolines as novel antagonists of gaba receptors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15005–15014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberth, C.; Jeanmart, S.; Luksch, T.; Plant, A. Current challenges and trends in the discovery of agrochemicals. Science 2013, 341, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, T.C.; Bryant, R.J. Impact of natural products on discovery of, and innovation in, crop protection compounds. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberth, C. Agrochemical lead optimization by scaffold hopping. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanguenat, A. The story of a new insecticidal chemistry class: The diamides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, A.; Liu, C.; Yang, X.; Dekeyser, M. Application of the intermediate derivatization approach in agrochemical discovery. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7079–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Guan, A.; Yang, J.; Chai, B.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y. Efficient approach to discover novel agrochemical candidates: Intermediate derivatization method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Lai, Q.; Lai, F.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, C.; Xu, H. Design, synthesis, and insecticidal activities of novel 5-substituted 4,5-dihydropyrazolo [1,5-a]quinazoline derivatives. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, I.; di Liberto, M.G.; Kaufman, T.S.; Derita, M.G.; Bracca, A.B.J. Synthesis and evaluation of aromatic methoxime derivatives against five postharvest phytopathogenic fungi of fruits. Main structure-activity relationships. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahm, G.P.; Stevenson, T.M.; Selby, T.P.; Freudenberger, J.H.; Cordova, D.; Flexner, L.; Bellin, C.A.; Dubas, C.M.; Smith, B.K.; Hughes, K.A.; et al. Rynaxypyr™: A new insecticidal anthranilic diamide that acts as a potent and selective ryanodine receptor activator. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6274–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, T.P.; Lahm, G.P.; Stevenson, T.M.; Hughes, K.A.; Cordova, D.; Annan, I.B.; Barry, J.D.; Benner, E.A.; Currie, M.J.; Pahutski, T.F. Discovery of cyantraniliprole, a potent and selective anthranilic diamide ryanodine receptor activator with cross-spectrum insecticidal activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 6341–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazenok, S.; Lindner, W.; Scheffel, H. Method for Producing Tetrazole-Substituted Anthranilic Acid Diamide Derivarives by Reacting Benzoxazinones with Amines. U.S. Patent No. 8,916,710, 7 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi, T.; Morita, M.; Nakamoto, K.; Hisamatsu, A. Anthranilamides, Process for the Production Thereof, Pest Controllers Containing the Same. U.S. Patent No. 7,612,100, 25 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Song, Y. 1-Substituted Pyridyl-Pyrazolyl Amide Compounds and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent 8,492,409, 23 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Yu, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Meng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, L.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Synthesis, insecticidal evaluation, and 3d-qasr of novel anthranilic diamide derivatives containing n-arylpyrrole as potential ryanodine receptor activators. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9319–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Xiong, L.; Luo, M.; Wang, J.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, D. Synthesis, larvicidal activities and antifungal activities of novel chlorantraniliprole derivatives and their target in the ryanodine receptor. Molecules 2015, 20, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, R.; Gao, S.; Ma, S.-H.; Tang, H.-J.; Yang, J.-J.; Diao, Y.-M.; Wang, H.-L.; Zhu, H.-J. Structure-based bioisosterism design, synthesis, insecticidal activity and structure-activity relationship (SAR) of anthranilic diamide analogues containing 1,2,4-oxadiazole rings. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Xu, H. Novel amino acid ester-chlorantraniliprole conjugates: Design, synthesis, phloem accumulation and bioactivity. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zheng, S.; Zou, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Xu, H. Synthesis of novel pesticidal n,n′-disubstituted sulfamide derivatives using sulfur(vi) fluorine exchange click reaction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 5798–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Beck, M.E. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists: A milestone for modern crop protection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9464–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearn, J.; Ludlow, E.; Dillon, J.; O’Connor, V.; Holden-Dye, L. Fluensulfone is a nematicide with a mode of action distinct from anticholinesterases and macrocyclic lactones. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2014, 109, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeschke, P. The unique role of halogen substituents in the design of modern agrochemicals. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Q.X.; Song, B. Chemical nematicides: Recent research progress and outlook. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12175–12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckelbarger, J.D.; Parker, M.H.; Yap, M.C.H.; Buysse, A.M.; Babcock, J.M.; Hunter, R.; Adelfinskaya, Y.; Samaritoni, J.G.; Garizi, N.; Trullinger, T.K. Synthesis and biological activity of a new class of insecticides: The n-(5-aryl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)amides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Ning, Y. Comprehensive overview of carboxamide derivatives as succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 957–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Xu, K.; Lai, Q.; Zhao, C.; Xu, H. Design, synthesis and insecticidal-activity evaluation of n-pyridylpyrazolo-5-methyl amines and its derivatives. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2020, 57, 4304–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Fan, Z.-J.; Guo, X.-F.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Xu, J.-H.; Song, Y.-Q.; Yurievich, M.Y.; Belskaya, N.P.; Bakulev, V.A. Synthesis of 1,2,3-thiadiazole and thiazole-based strobilurins as potent fungicide candidates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Yu, L.; Hsiang, T.; Huang, D.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Du, X.; Li, J. The influence of steric configuration of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid-amino acid conjugates on fungicidal activity and systemicity. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 3323–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, H.; Sun, P.; Meng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhou, S.; Ma, Y.; et al. Synthesis, insecticidal activities, and structure-activity relationship of phenylpyrazole derivatives containing a fluoro-substituted benzene moiety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11282–11289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-B.; Li, Y.-X.; Zhang, X.-L.; Hua, X.-W.; Wu, C.-C.; Wei, W.; Wan, Y.-Y.; Cheng, D.-D.; Xiong, L.-X.; Yang, N.; et al. Novel anthranilic diamide scaffolds containing n-substituted phenylpyrazole as potential ryanodine receptor activators. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3697–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q. Biomimetic synthesis of iridoid alkaloids as novel leads for fungicidal and insecticidal agents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12577–12584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compd. | Mortality Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| P. xylostella | S. exigua | S. frugiperda | |
| 4 | 24.24 ± 3.03 de | 21.58 ± 2.52 d | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 6a | 43.33 ± 3.33 f | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 6b | 80.61 ± 0.61 j | 29.09 ± 0.91 e | 60.66 ± 1.57 g |
| 6c | 51.52 ± 3.03 g | 28.54 ± 2.49 e | 19.95 ± 2.56 c |
| 6d | 17.50 ± 2.50 bc | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 48.48 ± 1.52 f |
| 6e | 69.80 ± 1.75 i | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 6f | 21.82 ± 2.78 cde | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 6g | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 28.18 ± 0.91 d |
| 6h | 68.48 ± 4.24 i | 46.97 ± 1.52 g | 61.87 ± 1.77 g |
| 6i | 21.21 ± 3.03 cde | 62.94 ± 0.70 i | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 6j | 25.76 ± 2.98 e | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 6.36 ± 3.19 b |
| 7a | 18.79 ± 0.61 bcd | 18.18 ± 0.00 c | 22.22 ± 2.78 c |
| 7b | 6.06 ± 3.03 a | 10.00 ± 0.00 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 7c | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 28.18 ± 0.91 e | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 7d | 39.39 ± 3.03 f | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 9.09 ± 0.00 a |
| 7e | 62.42 ± 1.21 h | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 28.18 ± 0.91 d |
| 7f | 12.73 ± 2.73 b | 58.52 ± 1.48 h | 90.30 ± 0.30 h |
| 7g | 100.00 ± 0.00 l | 100.00 ± 0.00 k | 100.00 ± 0.00 j |
| 7h | 88.14 ± 1.86 k | 38.13 ± 1.77 f | 38.13 ± 1.77 e |
| 7i | 100.00 ± 0.00 l | 94.44 ± 2.78 j | 97.22 ± 2.78 ij |
| 7j | 100.00 ± 0.00 l | 100.00 ± 0.00 k | 100.00 ± 0.00 j |
| 7k | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 7l | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 7m | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 8 | 60.66 ± 1.57 h | 16.43 ± 2.71 c | 20.13 ± 1.17 c |
| IDC b | 100.00 ± 0.00 l | 100.00 ± 0.00 k | 93.64 ± 3.19 hi |
| CHL c | 100.00 ± 0.00 l | 100.00 ± 0.00 k | 100.00 ± 0.00 j |
| Pests | Compd. | LC50 (mg/L) | 95% CI (mg/L) * | Slope ± SE | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. xylostella | 7g | 5.32 | 3.95–7.18 | 2.10 ± 0.32 | 1.83 |
| 7h | 16.45 | 12.04–22.47 | 1.85 ± 0.30 | 2.66 | |
| 7i | 8.96 | 6.55–12.26 | 1.94 ± 0.30 | 1.83 | |
| 7j | 10.11 | 6.06–16.87 | 1.76 ± 0.34 | 2.65 | |
| IDC | 5.01 | 3.94–6.35 | 2.32 ± 0.33 | 2.40 | |
| S. exigua | 7g | 6.75 | 5.33–8.56 | 2.52 ± 0.34 | 4.82 |
| 7i | 14.42 | 10.61–19.61 | 2.07 ± 0.32 | 1.35 | |
| 7j | 12.15 | 6.06–16.87 | 1.51 ± 0.29 | 2.94 | |
| IDC | 4.31 | 3.28–5.66 | 2.08 ± 0.28 | 0.87 | |
| S. frugiperda | 7f | 12.66 | 9.31–17.22 | 1.67 ± 0.28 | 0.93 |
| 7g | 7.64 | 4.84–12.05 | 1.97 ± 0.37 | 2.05 | |
| 7i | 9.41 | 7.24–12.23 | 2.12 ± 0.30 | 2.62 | |
| 7j | 8.22 | 6.19–10.91 | 1.86 ± 0.29 | 1.41 | |
| IDC | 11.15 | 9.00–13.82 | 2.60 ± 0.34 | 2.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Peng, H.; Tang, J.; Fan, S.; Zhao, C.; Xu, H.; Yao, G. Discovery of Novel N-Pyridylpyrazole Thiazole Derivatives as Insecticide Leads. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102472
Yang S, Peng H, Tang J, Fan S, Zhao C, Xu H, Yao G. Discovery of Novel N-Pyridylpyrazole Thiazole Derivatives as Insecticide Leads. Agronomy. 2022; 12(10):2472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102472
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shuai, Hongxiang Peng, Jiahong Tang, Shuting Fan, Chen Zhao, Hanhong Xu, and Guangkai Yao. 2022. "Discovery of Novel N-Pyridylpyrazole Thiazole Derivatives as Insecticide Leads" Agronomy 12, no. 10: 2472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102472
APA StyleYang, S., Peng, H., Tang, J., Fan, S., Zhao, C., Xu, H., & Yao, G. (2022). Discovery of Novel N-Pyridylpyrazole Thiazole Derivatives as Insecticide Leads. Agronomy, 12(10), 2472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102472







