Brevibacillus laterosporus as a Natural Biological Control Agent of Soil-Dwelling Nematodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Preparations and Analyses
2.2. In Vitro Bioassays with Panagrellus redivivus
2.3. Experiments with M. incognita
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
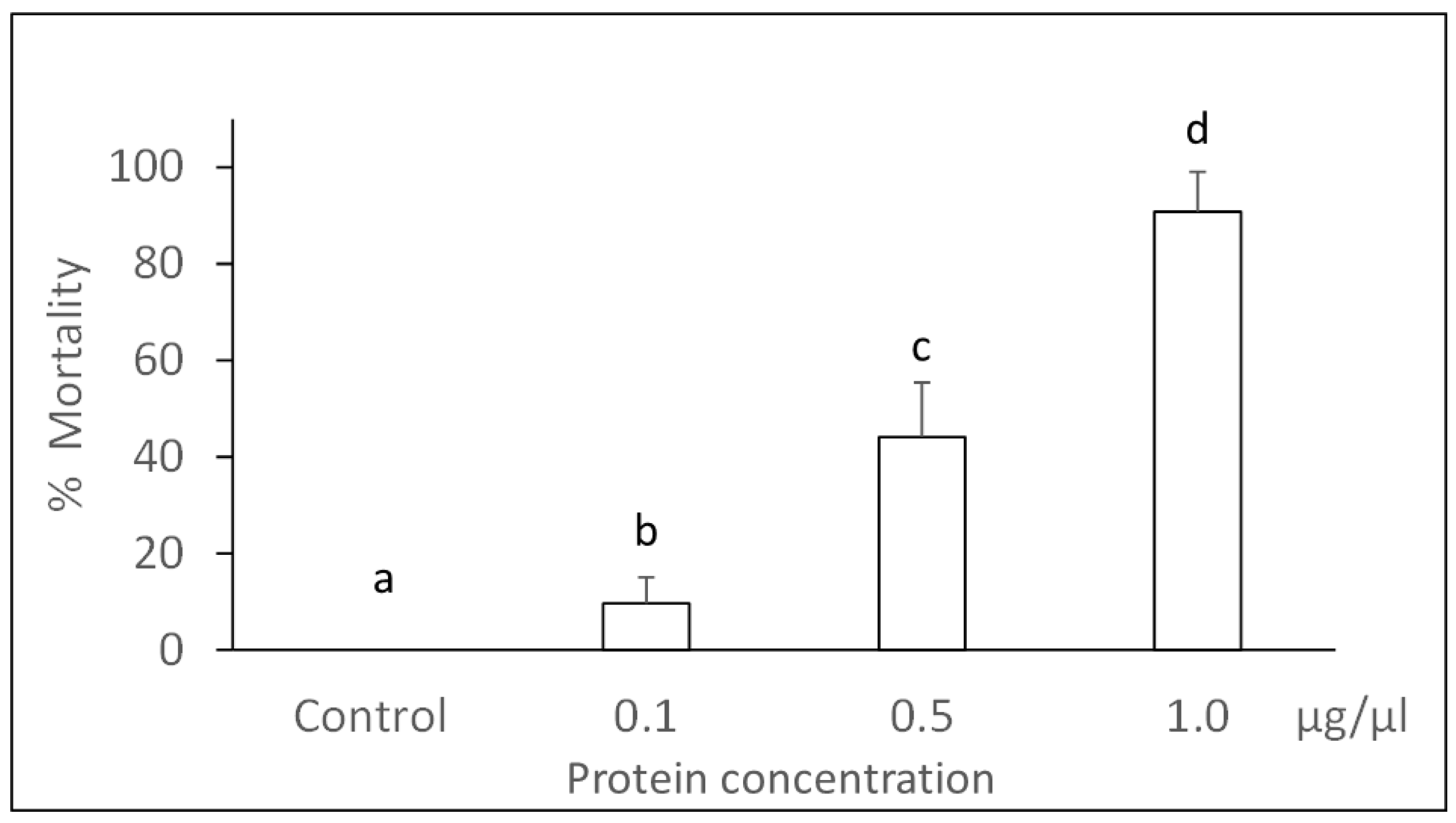
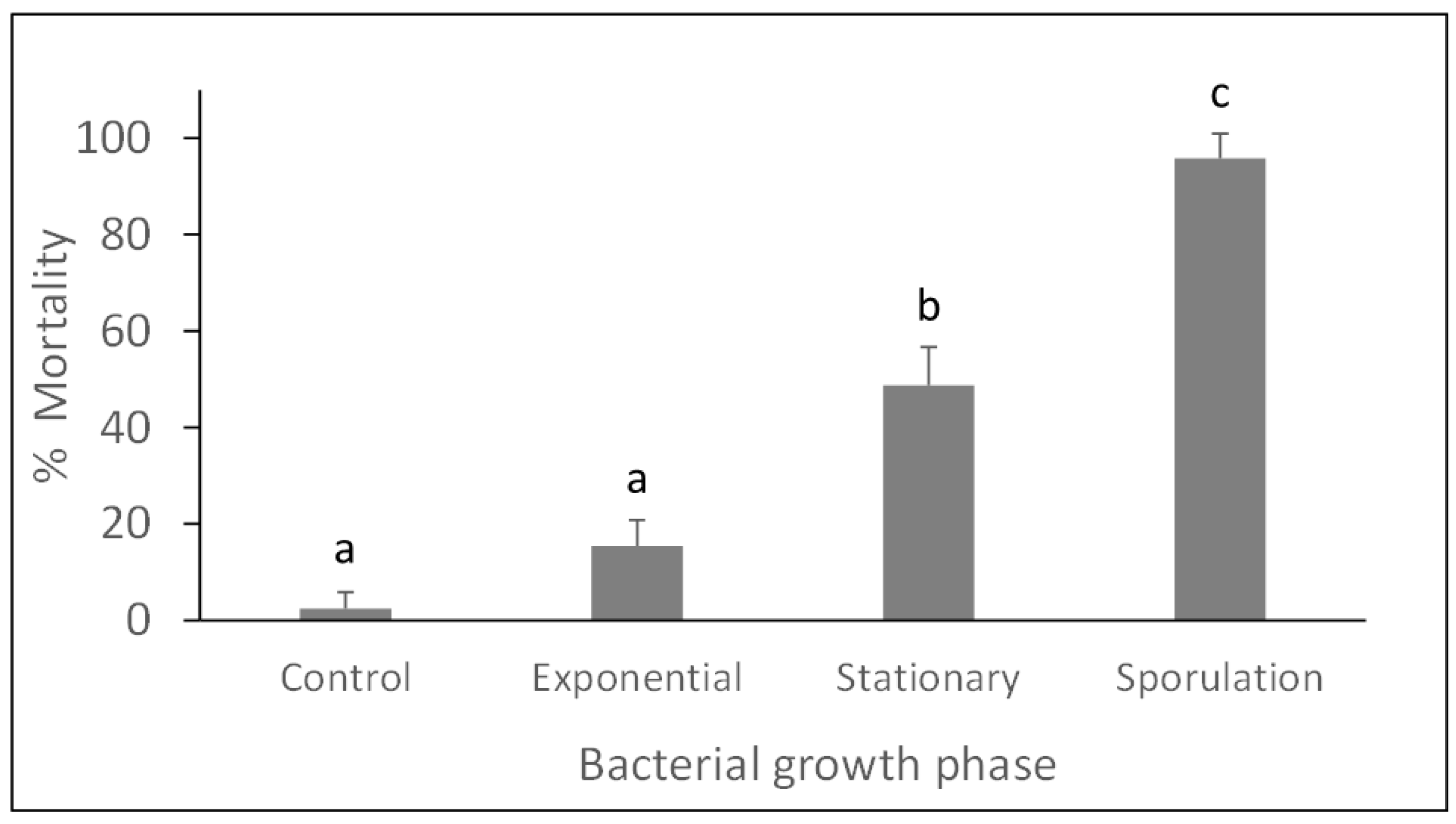
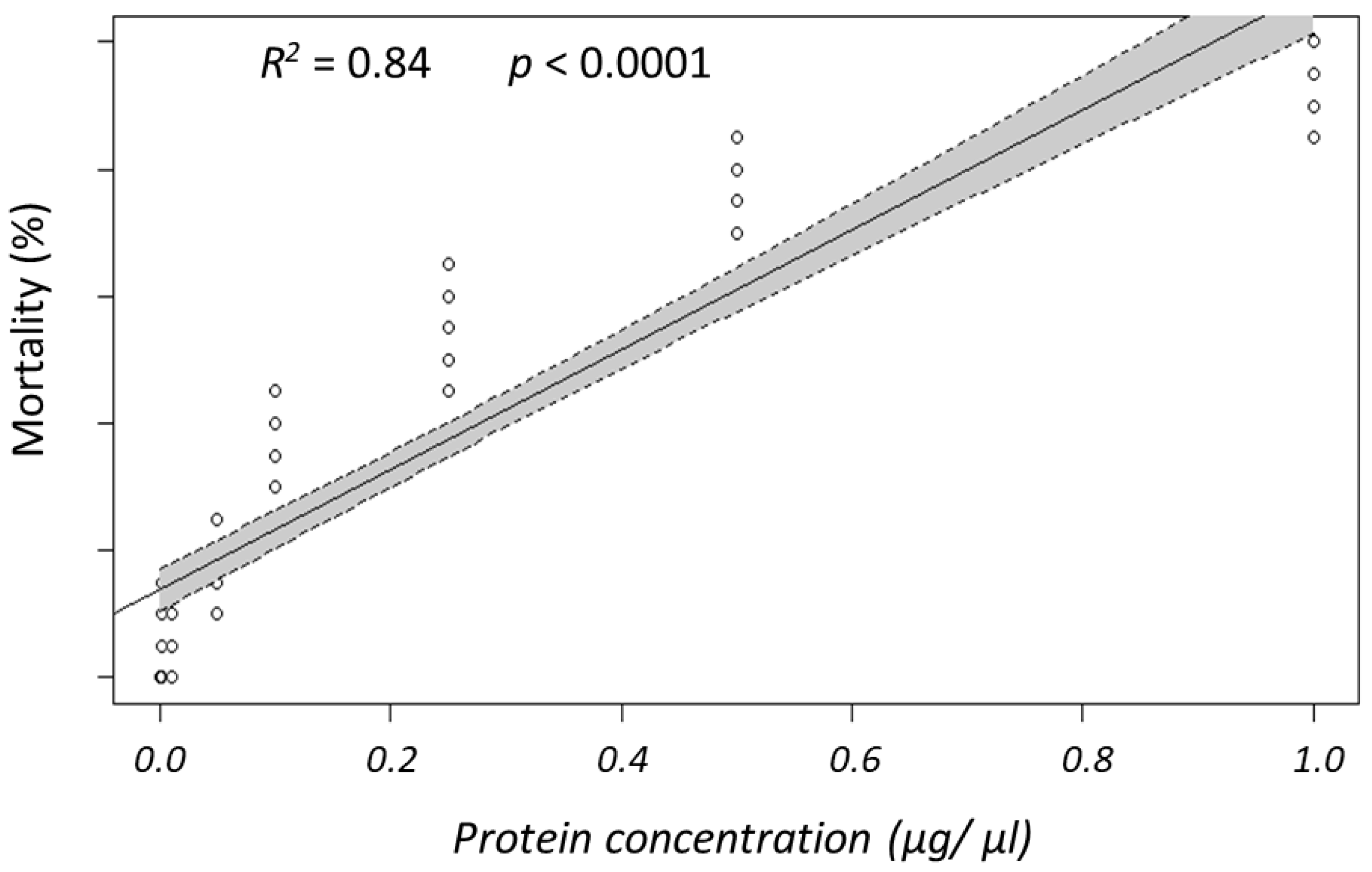
3.1. Bioassays with Panagrellus redivivus
3.2. Experiments with Meloidogyne incognita
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruiu, L. Brevibacillus laterosporus, a pathogen of invertebrates and a broad-spectrum antimicrobial species. Insects 2013, 4, 476–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Lv, D.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, B. Biocontrol effects of Brevibacillus laterosporus AMCC100017 on potato common scab and its impact on rhizosphere bacterial communities. Biol. Control 2017, 106, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Xiao, C.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Sui, J.; Sa, R.; Guo, T.L.; Liu, X. Antifungal activity of Brevibacillus laterosporus JX-5 and characterization of its antifungal components. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 1605–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, L.; Zeng, H.; Yang, X.; Yuan, J.; Shi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, M.; Han, L.; Qiu, D. Purification and characterization of a novel antimicrobial peptide from Brevibacillus laterosporus strain A60. Peptides 2012, 33, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiu, L.; Satta, A.; Floris, I. Emerging entomopathogenic bacteria for insect pest management. Bull. Insectol. 2013, 66, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Djukic, M.; Poehlein, A.; Thürmer, A.; Daniel, R. Genome sequence of Brevibacillus laterosporus LMG 15441, a pathogen of invertebrates. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, L.H.; Tian, B.Y.; Xiong, R.; Zhu, M.Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, K.Q. Proteases from Bacillus: A new insight into the mechanism of action for rhizobacterial suppression of nematode populations. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.Z.; Hale, K.; Carta, L.; Platzer, E.; Wong, C.; Fang, S.C.; Aroian, R.V. Bacillus thuringiensis crystal proteins that target nematodes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2760–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L.; Crickmore, N.; Peng, D.; Sun, M. Are nematodes a missing link in the confounded ecology of the entomopathogen Bacillus thuringiensis? Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.Q. Bacteria used in the biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes: Populations, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 61, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tian, B.; Niu, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K. An extracellular protease from Brevibacillus laterosporus G4 without parasporal crystals can serve as a pathogenic factor in infection of nematodes. Res. Microbiol. 2005, 156, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, G.M.; Ameen, H.H.; Abdel-Aziz, S.M.; El-Sayed, G.M. In vitro evaluation of some isolated bacteria against the plant parasite nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Bull. Natl Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elgawad, M.M.M. Plant-parasitic nematode threats to global food security. J. Nematol. 2014, 46, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Marche, M.G.; Mura, M.E.; Ruiu, L. Brevibacillus laterosporus inside the insect body: Beneficial resident or pathogenic outsider? J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 137, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marche, M.G.; Mura, M.E.; Falchi, G.; Ruiu, L. Spore surface proteins of Brevibacillus laterosporus are involved in insect pathogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marche, M.G.; Satta, A.; Floris, I.; Lazzeri, A.M.; Ruiu, L. Inhibition of Paenibacillus larvae by an extracellular protein fraction from a honeybee-borne Brevibacillus laterosporus strain. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 227, 126303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglierchio, D.R.; Schmitt, R.V. On the methodology of nematode extraction from field samples: Comparison of methods for soil extraction. J. Nematol. 1983, 15, 450. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. In R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Javed, K.; Javed, H.; Qiu, D. Biocontrol Potential of Purified Elicitor Protein PeBL1 Extracted from Brevibacillus laterosporus Strain A60 and Its Capacity in the Induction of Defense Process against Cucumber Aphid (Myzus persicae) in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Biology 2020, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; An, J.; You, C.; Zhou, B.; Hao, Y. The growth-promoting mechanism of Brevibacillus laterosporus AMCC100017 on apple rootstock Malus robusta. Hortic. Plant J. 2022, 8, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiu, L. Plant-growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) against insects and other agricultural pests. Agronomy 2020, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, S.; Muniz, E.R.; Tani, C.; Conti, B.; Ruiu, L. Insecticidal potential of Brevibacillus laterosporus against dipteran pest species in a wide ecological range. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 177, 107493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, D.; Sun, M. Nematicidal spore-forming Bacilli share similar virulence factors and mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glare, T.R.; Durrant, A.; Berry, C.; Palma, L.; Ormskirk, M.M.; Cox, M.P. Phylogenetic determinants of toxin gene distribution in genomes of Brevibacillus laterosporus. Genomics 2020, 112, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Yang, J.; Lian, L.; Wang, C.; Li, N.; Zhang, K.Q. Role of an extracellular neutral protease in infection against nematodes by Brevibacillus laterosporus strain G4. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, Y.C. Screening for nematicidal activities of Bacillus species against root knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita). Am. J. Exp. Agric. 2013, 3, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Sharma, V.; Patil, P.B.; Korpole, S. Identification, purification and characterization of laterosporulin, a novel bacteriocin produced by Brevibacillus sp. strain GI-9. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marche, M.G.; Camiolo, S.; Porceddu, A.; Ruiu, L. Survey of Brevibacillus laterosporus insecticidal protein genes and virulence factors. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 155, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, M.E.; Ruiu, L. Brevibacillus laterosporus pathogenesis and local immune response regulation in the house fly midgut. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 145, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Bacterial Growth Phase | Mortality 1 (%) |
|---|---|
| Control | 2.1 ± 3.3 a |
| Exponential | 28.3 ± 15.7 b |
| Stationary | 58.3 ± 7.5 c |
| Sporulation | 94.6 ± 5.8 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamze, R.; Ruiu, L. Brevibacillus laterosporus as a Natural Biological Control Agent of Soil-Dwelling Nematodes. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112686
Hamze R, Ruiu L. Brevibacillus laterosporus as a Natural Biological Control Agent of Soil-Dwelling Nematodes. Agronomy. 2022; 12(11):2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112686
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamze, Rim, and Luca Ruiu. 2022. "Brevibacillus laterosporus as a Natural Biological Control Agent of Soil-Dwelling Nematodes" Agronomy 12, no. 11: 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112686
APA StyleHamze, R., & Ruiu, L. (2022). Brevibacillus laterosporus as a Natural Biological Control Agent of Soil-Dwelling Nematodes. Agronomy, 12(11), 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112686







