Metabolic Resistance to Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase-Inhibiting Herbicide Cyhalofop-Butyl in a Chinese Echinochloa crus-galli Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
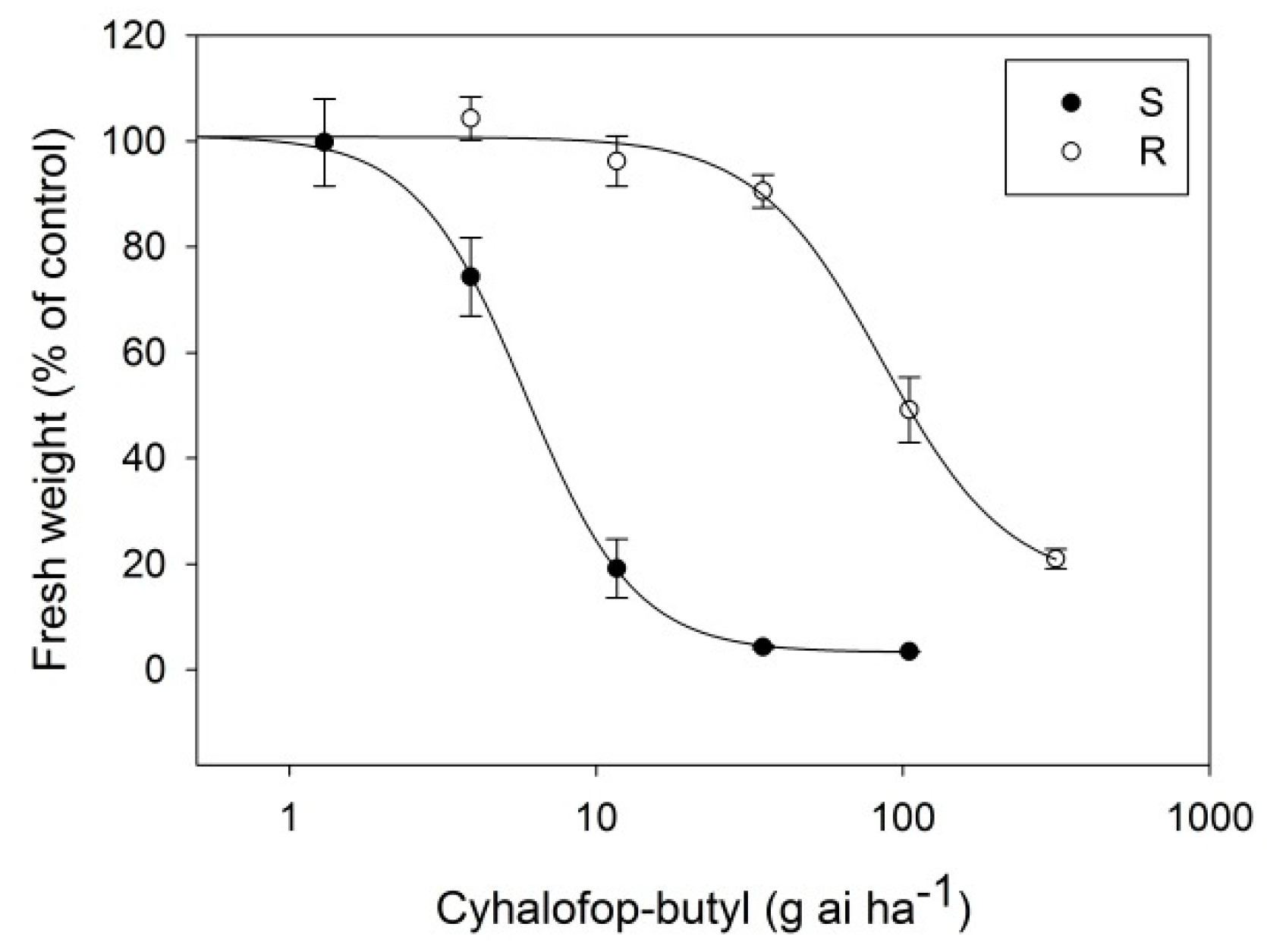
2.2. Dose-Response to Cyhalofop-Butyl
2.3. Response to ACCase Inhibitors
2.4. Response to Other Herbicides Used in Direct-Seeding Rice Fields
2.5. ACCase Genes Isolation and Sequencing
2.6. Cyhalofop-Butyl Metabolism in S and R Plants of E. crus-galli
2.7. Metabolic Inhibitors Effect on Resistance to Cyhalofop-Butyl
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Resistance level to Cyhalofop-Butyl
3.2. Resistance Pattern to Different Herbicides
3.3. ACCase Gene Sequencing
3.4. Enhanced Cyhalofop-Butyl Metabolism in R Plants
3.5. Metabolic Inhibitors Eeffect on Cyhalofop-Butyl Resistance
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, L.Y.; Gao, Y.; Fang, J.P.; Chen, G.Q. Research progress on the herbicide-resistance of weeds in rice fields in China. Plant Prot. 2018, 44, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Gu, T.; Zhao, B.; Yang, X.; Peng, Q.; Li, Y.; Bai, L. Effects of common Echinochloa varieties on grain yield and grain quality of rice. Field Crops Res. 2017, 203, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Konishi, T.; Nagano, Y. The compartmentation of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase in plants. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottis, B.V.; Mattice, J.D.; Talbert, R.E. Determination of antagonism between cyhalofop-butyl and other rice (Oryza sativa) herbicides in barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4064–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.A.; Collavo, A.; Ovejero, R.; Shivrain, V.; Walsh, M.J. The challenge of herbicide resistance around the world: A current summary. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2246–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Gao, H.; Pan, L.; Yao, Z.; Dong, L. Mechanism of resistance to cyhalofop-butyl in Chinese sprangletop (Leptochloa chinensis (L.) Nees). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 143, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Cai, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Di, Y.; Yuan, S. Molecular basis of resistance to ACCase-inhibiting herbicide cyhalofop-butyl in Chinese sprangletop (Leptochloa chinensis (L.) Nees) from China. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 158, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Di, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Deng, W. Target-site resistance to cyhalofop-butyl in bearded sprangletop (Diplachne fusca) from China. Weed Sci. 2019, 67, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Xia, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Yuan, S. Cyhalofop-butyl and glyphosate multiple-herbicide resistance evolved in an Eleusine indica population collected in Chinese direct-seeding rice. J. Agric Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2623–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Pan, L.; Liu, D.; Cheng, X.; Ma, G.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Bai, L. Confirmation and characterization of cyhalofop-butyl–resistant Chinese sprangletop (Leptochloa chinensis) populations from China. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Mao, D.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, L.; Wang, L. Whole transcriptome analysis resulted in the identification of Chinese sprangletop (Leptochloa chinensis) genes involved in cyhalofop-butyl tolerance. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liao, M.; Zhao, N.; Cao, H. Investigating resistance levels to cyhalofop-butyl and mechanisms involved in Chinese sprangletop (Leptochloa chinensis L.) from Anhui Province, China. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 186, 105165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; He, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Dong, L. A novel mutation Asp-2078-Glu in ACCase confers resistance to ACCase herbicides in barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 168, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Fu, W.; Li, Y. Investigating the resistance levels and mechanisms to penoxsulam and cyhalofop-butyl in barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) from Ningxia Province, China. Weed Sci. 2021, 69, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, S.B.; Yu, Q. Evolution in action: Plants resistant to herbicides. Ann. Rev. Plant. Physiol. 2010, 61, 317–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaundun, S.S. Resistance to acetyl-CoA carboxylase-inhibiting herbicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Z.B.; Jin, T.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, J.X. Cloning and sequence analysis of plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase cDNA from two Echinochloa crusgalli biotypes. J. Pestic. Sci. 2011, 36, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwakami, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Matsushima, K.; Watanabe, H.; Hamamura, K.; Uchino, A. Multiple-herbicide resistance in Echinochloa crus-galli var. formosensis, an allohexaploid weed species, in dry-seeded rice. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 119, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.I.; Norsworthy, J.K.; González-Torralva, F.; Piveta, L.B.; Priess, G.L.; Barber, L.T.; Butts, T.R. Absorption, translocation, and metabolism of florpyrauxifen-benzyl and cyhalofop-butyl in cyhalofop-butyl-resistant barnyardgrass [Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P. Beauv.]. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 180, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanizadeh, H.; Harrington, K.C. Non-target Site Mechanisms of Resistance to Herbicides. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2017, 36, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakami, S.; Endo, M.; Saika, H.; Okuno, J.; Nakamura, N.; Yokoyama, M.; Watanabe, H.; Toki, S.; Uchino, A.; Inamura, T. Cytochrome P450 CYP81A12 and CYP81A21 are associated with resistance to two acetolactate synthase inhibitors in Echinochloa phyllopogon. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakami, S.; Kamidate, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ishizaka, M.; Endo, M.; Suda, H.; Nagai, K.; Sunohara, Y.; Toki, S.; Uchino, A.; et al. CYP81A P450s are involved in concomitant cross-resistance to acetolactate synthase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase herbicides in Echinochloa phyllopogon. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimaano, N.G.; Yamaguchi, T.; Fukunishi, K.; Tominaga, T.; Iwakami, S. Functional characterization of cytochrome P450 CYP81A subfamily to disclose the pattern of cross-resistance in Echinochloa phyllopogon. Plant Mol. Biol. 2020, 102, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Shi, L.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Q.; Bai, L. CYP81A68 confers metabolic resistance to ALS and ACCase-inhibiting herbicides and its epigenetic regulation in Echinochloa Crus-Gall. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, S.; Yang, Q. Enhanced metabolism confers a high level of cyhalofop-butyl resistance in a Chinese sprangletop (Leptochloa chinensis (L.) Nees) population. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.A.; Nandula, V.K.; Grier, L.; Showmaker, K.C.; Bond, J.A.; Peterson, D.G.; Ray, J.D.; Shaw, D.R. Characterization of fenoxaprop-p-ethyl-resistant junglerice (Echinochloa colona) from Mississippi. Weed Sci. 2016, 64, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seefeldt, S.S.; Jensen, J.E.; Fuerst, E.P. Log-logistic analysis of herbicide dose-response relationships. Weed Technol. 1995, 9, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro-Blanco, I.; Romano, Y.; Palmerin, J.A.; Gordo, R.; Palma-Bautista, C.; Prado, R.D.; Osuna, M.D. Different mutations providing target site resistance to ALS-and ACCase-inhibiting herbicides in Echinochloa spp. from rice fields. Agriculture 2021, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Norsworthy, J.K.; González-Torralva, F.; Piveta, L.B.; Barber, L.T.; Butts, T.R. Cross-resistance of barnyardgrass [Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P. beauv.] to aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 184, 105089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torra, J.; Montull, J.M.; Taberner, A.; Onkokesung, N.; Boonham, N.; Edwards, R. Target-site and non-target-site resistance mechanisms confer multiple and cross-resistance to ALS and ACCase inhibiting herbicides in Lolium rigidum from spain. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 625138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Ahmad-Hamdani, M.S.; Han, H.; Christoffers, M.J.; Powles, S.B. Herbicide resistance-endowing ACCase gene mutations in hexaploidy wild oat (Avena fatua): Insights into resistance evolution in a hexaploidy species. Heredity 2013, 110, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Yu, Q.; Owen, M.; Cawttray, G.R.; Powles, S.B. widespread occurrence of both metabolic and target-site herbicide resistance mechanisms in Lolium rigidum populations. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Bai, C.; Dong, L. Fenoxaprop-p-ethyl resistance conferred by cytochrome P450s and target site mutation in Alopecurus japonicas. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, L. Identification and expression of main genes involved in non-target site resistance mechanisms to fenoxaprop-p-ethyl in Beckmannia syzigachne. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2619–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanniccari, M.; Gigón, R.; Larsen, A. Cytochrome P450 herbicide metabolism as the main mechanism of cross-resistance to ACCase- and ALS-inhibitors in Lolium spp. populations from Argentina: A molecular approach in characterization and detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 600301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Garcia, J.G.; Torra, J.; Palma-Bautista, C.; Cruz, R.A.; Prado, R.D. Point mutations and cytochrome P450 can contribute to resistance to ACCase-inhibiting herbicides in three Phalaris species. Plants 2021, 10, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Bai, L.; Pan, L. Enhanced metabolism evolved high-level resistance to fenoxaprop-p-ethyl in Alopecurus japonicas. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Norsworthy, J.K.; González-Torralva, F.; Priess, G.L.; Barber, L.T.; Butts, T.R. Non-target-site resistance mechanism of barnyardgrass [Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P. Beauv.] to florpyrauxifen-benzyl. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.J.; Goggin, D.E.; Powles, S.B. Non-target-site-based resistance to ALS-inhibiting herbicides in six Bromus rigidus populations from Western Australian cropping fields. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Han, H.; Cawthray, G.R.; Wang, S.F. Powles, S.B. Enhanced rates of herbicide metabolism in low herbicide-dose selected resistant Lolium rigidum. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Powles, S.B. Metabolism-based herbicide resistance and cross-resistance in crop weeds: A threat to herbicide sustainability and global crop production. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Yang, J.; Jiang, M.; Liao, M.; Cao, H. Identification of essential genes involved in metabolism-based resistance mechanism to fenoxaprop-p-ethyl in Polypogon fugax. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tao Gu, T.; Dong, M.; Peng, Q.; Bai, L.; Li, Y. Quantitative proteomics reveals ecological fitness cost ofmulti-herbicide resistant barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli L.). J. Proteom. 2017, 150, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type | Herbicides | Formulation 1 and Company | Treatment Doses (g ai ha−1) | Field Recommended Dose (g ai ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACCase inhibitors | Cyhalofop-butyl | 100 g L−1 EC, Dow AgroSciences | S: 0, 1.30 3.89, 11.67, 35, 105 R: 0, 3.89, 11.67, 35, 105, 315 | 105 |
| Metamifop | 10% EC, FMC | S: 0, 1.48, 4.4, 13.33, 40, 120 R: 0, 4.44, 13.33, 40, 120, 360 | 120 | |
| Fenoxaprop-p-ethyl | 69 g L−1 EW, Bayer CropScience | S: 0, 0.26, 0.77, 2.3, 6.9, 20.7 R: 0, 0.77, 2.3, 6.9, 20.7, 62.1 | 62.1 | |
| Clethodim | 120 g L−1 EC, Qingdao Modern Agrochemical | S: 0, 0.3, 0.89, 2.67, 8, 24 R: 0, 0.89, 2.67, 8, 24, 72 | 72 | |
| Pinoxaden | 5% EC, Syngenta | S: 0, 0.56, 1.67, 5, 15, 45 R: 0, 1.67, 5, 15, 45, 135 | 45 | |
| ALS inhibitors | Penoxsulam | 25 g L−1 OD, Dow AgroSciences | S: 0, 0.37, 1.11, 3.33, 10, 30 R: 0, 1.11, 3.33, 10, 30, 90 | 30 |
| Bispyribac-sodium | 10% SC, Jiangsu Hormone Research Institute | S: 0, 0.56, 1.67, 5, 15, 45 R: 0, 1.67, 5, 15, 45, 135 | 45 | |
| Auxin mimic herbicides | Quinclorac | 75% WG, Jiangsu Hormone Research Institute | S: 0, 5.56, 16.67, 50, 150, 450 R: 0, 50, 150, 450, 1350, 4050 | 450 |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 3% EC, Dow AgroSciences | S: 0, 0.23, 0.67, 2, 6, 18 R: 0, 0.67, 2, 6, 18, 54 | 18 |
| Herbicides | S | R | RI 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR50 ± SE 1 | p | GR50 ± SE | p | ||
| Cyhalofop-butyl | 5.6 ± 0.6 | <0.01 | 75.8 ± 8.7 | <0.01 | 13.5 |
| Metamifop | 8.1 ± 0.5 | <0.01 | 23.7 ± 1.3 | <0.01 | 2.9 |
| Fenoxaprop-p-ethyl | 1.2 ± 0.1 | <0.01 | 4.9 ± 0.9 | <0.01 | 4.1 |
| Clethodim | 2.1 ± 0.2 | <0.01 | 9.8 ± 0.8 | <0.01 | 4.7 |
| Pinoxaden | 3.7 ± 0.5 | <0.01 | 23.7 ± 3.2 | <0.01 | 6.4 |
| Penoxsulam | 3.2 ± 1.1 | 0.02 | 28.6 ± 2.19 | <0.01 | 8.9 |
| Bispyribac-sodium | 11.64 ± 2.67 | 0.02 | 14.18 ± 0.94 | <0.01 | 1.2 |
| Quinclorac | 116.63 ± 17.17 | 0.01 | >4050.00 | 0.03 | >34.7 |
| Florpyrauxifen-benzyl | 3.4 ± 0.2 | <0.01 | 10.1 ± 0.6 | <0.01 | 3.0 |
| Time (h) | Cyhalofop-Butyl (μg kg−1) | Cyhalofop Acid (μg kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | R | S | R | |
| 2 | 0.85 ± 0.10 | 0.94 ± 0.12 | 0.71 ± 0.08 | 0.67 ± 0.07 |
| 24 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 0.57 ± 0.09 | 0.21 ± 0.05 * |
| 48 | 0.027 ± 0.008 | 0.024 ± 0.004 | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 0.08 ± 0.02 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wei, T.; Lv, M.; Li, Y. Metabolic Resistance to Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase-Inhibiting Herbicide Cyhalofop-Butyl in a Chinese Echinochloa crus-galli Population. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112724
Yang Q, Yang X, Zhu J, Wei T, Lv M, Li Y. Metabolic Resistance to Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase-Inhibiting Herbicide Cyhalofop-Butyl in a Chinese Echinochloa crus-galli Population. Agronomy. 2022; 12(11):2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112724
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qian, Xia Yang, Jinlei Zhu, Tian Wei, Min Lv, and Yongfeng Li. 2022. "Metabolic Resistance to Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase-Inhibiting Herbicide Cyhalofop-Butyl in a Chinese Echinochloa crus-galli Population" Agronomy 12, no. 11: 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112724
APA StyleYang, Q., Yang, X., Zhu, J., Wei, T., Lv, M., & Li, Y. (2022). Metabolic Resistance to Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase-Inhibiting Herbicide Cyhalofop-Butyl in a Chinese Echinochloa crus-galli Population. Agronomy, 12(11), 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112724






