Vermicomposting of Lavender Waste: A Biological Laboratory Investigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Design and Vermicomposting
2.3. Biological Analysis
2.4. Seed Germination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Earthworm Development
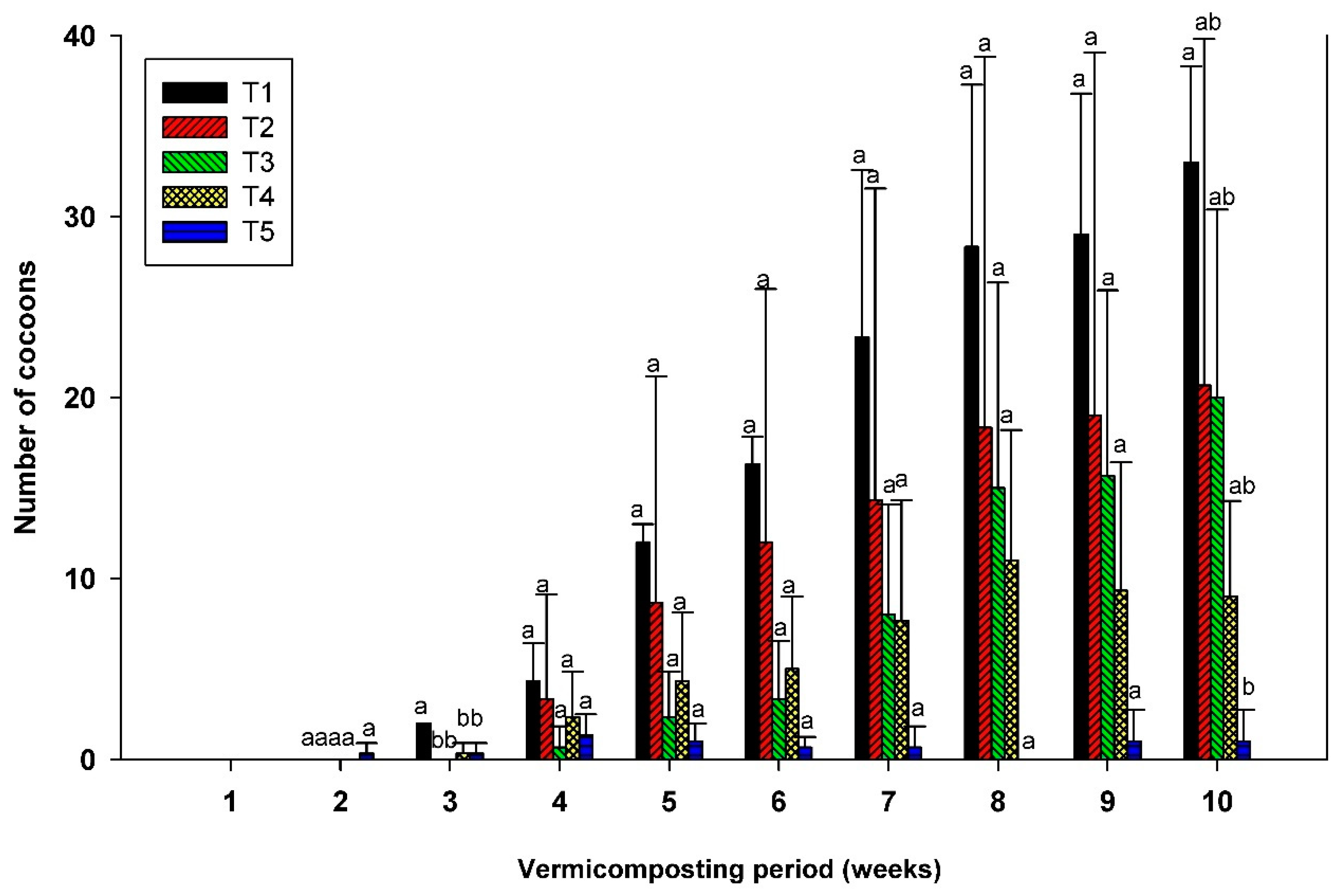
3.2. Cocoon Production
3.3. Hatchling Formation and Number of Clitellated Earthworms
3.4. Mortality
3.5. Germination Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GI | germination index |
| GP | germination percentage |
| HM | horse manure |
| NC | number of cocoons |
| PR | cocoon production ratio |
| RRG | relative root growth |
| RSG | relative seed germination |
| RShG | relative shoot growth |
| SD | standard deviation |
References
- Kochhar, S.L. Essential Oil Yielding Plants. In Economic Botany: A Comprehensive Study; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2016; pp. 576–614. ISBN 9781316675397. [Google Scholar]
- Kale, R.D. Earthworms: Nature’s Gift for Utilization of Organic Wastes in Asia. In Earthworm Ecology; Edwards, C.A., Ed.; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 381–399. ISBN 978-1884015748. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Sinha, R.K. 7-Vermicomposting of Organic Wastes by Earthworms: Making Wealth from Waste by Converting ‘Garbage into Gold’ for Farmers. In Advanced Organic Waste Management; Hussain, C., Hait, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 93–120. ISBN 978-0-323-85792-5. [Google Scholar]
- González-Moreno, M.Á.; García Gracianteparaluceta, B.; Prieto Cobo, E. Agroindustrial Organic Waste Management as a Proposal for Climate Change Mitigation. In Proceedings of the CCCC 2022, III International Conference on Climate Change Communication, Seville, Spain, 27–28 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Bakar, M.S.; Ahmed, A.; Jeffery, D.M.; Hidayat, S.; Sukri, R.S.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Jamil, F.; Khurrum, M.S.; Inayat, A.; Moogi, S.; et al. Pyrolysis of Solid Waste Residues from Lemon Myrtle Essential Oils Extraction for Bio-Oil Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 123913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco, A.; Espuelas, S.; Marcelino, S.; Echeverría, Á.M.; Prieto, E. Characterization of Biomass Briquettes from Spent Coffee Grounds and Xanthan Gum Using Low Pressure and Temperature. Bioenergy Res. 2019, 13, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Solórzano, S.B.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Cuevas-González, R.; Guillén-Navarro, K. Optimal Conditions to Produce Extracts of Compost and Vermicompost from Oil Palm and Coffee Pulp Wastes. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.; Mataraarachchi, S. A Review of Landfills, Waste and the Nearly Forgotten Nexus with Climate Change. Environments 2021, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. In Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E.S., Mintenbeck, K., Alegría, A., Craig, M., Langsdorf, S., Löschke, S., Möller, V., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Waste Framework Directive. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/waste-and-recycling/waste-framework-directive_en (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Edwards, C.A.; Arancon, N.Q. The Use of Earthworms in the Breakdown of Organic Wastes to Produce Vermicom-posts and Animal Feed Protein. In Earthworm Ecology; Edwards, C.A., Ed.; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 345–379. ISBN 978-1884015748. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, V.K.; Gupta, R. Vermicomposting of Agro-Industrial Processing Waste. In Biotechnology for Agro-Industrial Residues Utilisation: Utilisation of Agro-Residues; Singh nee’ Nigam, P.P.A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 431–456. ISBN 978-1-4020-9941-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Garg, V.K. Industrial Wastes and Sludges Management by Vermicomposting. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 243–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Sajid, N.; Khalid, A.; Riaz, L.; Rabbani, M.M.; Syed, J.H.; Malik, R.N. A Review on Vermicomposting of Organic Wastes. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Lee, L.H.; Wu, T.Y. Sustainability of Using Composting and Vermicomposting Technologies for Organic Solid Waste Biotransformation: Recent Overview, Greenhouse Gases Emissions and Economic Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 111, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soobhany, N. Insight into the Recovery of Nutrients from Organic Solid Waste through Biochemical Conversion Processes for Fertilizer Production: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, H.; Deka, S.; Baruah, C.K.; Das, J.; Hoque, S.; Sarma, H.; Sarma, N.S. Vermicomposting Potentiality of Perionyx Excavatus for Recycling of Waste Biomass of Java Citronella-An Aromatic Oil Yielding Plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 11212–11217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, H.; Deka, S.; Baruah, C.K.; Das, J.; Hoque, S.; Sarma, N.S. Vermicomposting of Distillation Waste of Citronella Plant (Cymbopogon Winterianus Jowitt.) Employing Eudrilus Eugeniae. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6944–6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, T.; Barman, A.; Kalita, P.; Lahkar, J.; Deka, H. Vermicomposting of Citronella Bagasse and Paper Mill Sludge Mixture Employing Eisenia Fetida. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouché, M.B. Lombriciens de France: Écologie et Systématique; Annales de Zoologie-Ecologie Animale; Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique: Paris, France, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Elvira, C.; Sampedro, L.; Benítez, E.; Nogales, R. Vermicomposting of Sludges from Paper Mill and Dairy Industries with Eisenia Andrei: A Pilot-Scale Study. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 63, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Suthar, S. Vermicomposting of Herbal Pharmaceutical Industry Waste: Earthworm Growth, Plant-Available Nutrient and Microbial Quality of End Materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Garg, V.K. Vermicomposting-An Effective Tool for the Management of Invasive Weed Parthenium Hysterophorus. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5891–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Khoram, M.R.; Gholami, M.; Eslami, H. Pistachio Waste Management Using Combined Composting-Vermicomposting Technique: Physico-Chemical Changes and Worm Growth Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Singh, J.; Vig, A.P. Potential Utilization of Bagasse as Feed Material for Earthworm Eisenia Fetida and Production of Vermicompost. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Moreno, M.A.; García Gracianteparaluceta, B.; Marcelino Sádaba, S.; Zaratiegui Urdin, J.; Robles Domínguez, E.; Pérez Ezcurdia, M.A.; Seco Meneses, A. Feasibility of Vermicomposting of Spent Coffee Grounds and Silverskin from Coffee Industries: A Laboratory Study. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatua, C.; Sengupta, S.; Krishna Balla, V.; Kundu, B.; Chakraborti, A.; Tripathi, S. Dynamics of Organic Matter Decomposition during Vermicomposting of Banana Stem Waste Using Eisenia Fetida. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucconi, F.; Monaco, A.; Forte, M.; Bertoldi, M.D. Phytotoxins during the Stabilization of Organic Matter. In Compost. Agric. Wastes; Gasser, J.K.R., Ed.; Elsevier Applied Science Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zucconi, F.; Forte, M.; Monaco, A.; De Bertoldi, M. Biological Evaluation of Compost Maturity. BioCycle 1981, 22, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Tiquia, S.M.; Tam, N.F.Y. Elimination of Phytotoxicity during Co-Composting of Spent Pig-Manure Sawdust Litter and Pig Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 65, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiquia, S.M. Evaluating Phytotoxicity of Pig Manure from the Pig-on-Litter System. In Proceedings of the International Composting Symposium; Warman, P.R., Taylor, Y.B.R., Eds.; CBA Press Inc.: Truro, NS, Canada, 2000; pp. 625–647. [Google Scholar]
- Tiquia, S.M. Reduction of Compost Phytotoxicity during the Process of Decomposition. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, N.J.; Bosker, T.; Lantinga, E.A. Effects of Cattle Dung from Farms with Different Feeding Strategies on Germination and Initial Root Growth of Cress (Lepidium Sativum L.). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 93, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Das, S.; Goswami, L.; Das, P.; Sahariah, B.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Intensification of Vermitechnology for Kitchen Vegetable Waste and Paddy Straw Employing Earthworm Consortium: Assessment of Maturity Time, Microbial Community Structure, and Economic Benefit. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, T.; Paul, R.K.; Sonar, I.; Sanyal, S.; Ahmed, K.Z.; Boruah, R.K.; Das, D.K.; Dutta, A.K. Chromium in Soil and Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Infusion: Does Soil Amendment with Municipal Solid Waste Compost Make Sense? Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, C.; Singh, J.; Parkash, C. Vermicompost and Vermiwash as Supplement to Improve Seedling, Plant Growth and Yield in Linum Usitassimum L. for Organic Agriculture. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2017, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Deka, P.; Goswami, L.; Sahariah, B.; Hussain, N.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Vermiremediation of Toxic Jute Mill Waste Employing Metaphire Posthuma. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15418–15431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency)Seed Germination/Root Elongation Toxicity Test. EG-12. In Environmental Effects Test Guidelines: Part Two; Office of Pesticides & Toxic Substances: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, N.F.Y.; Tiquia, S. Assessing Toxicity of Spent Pig Litter Using a Seed Germination Technique. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1994, 11, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmegam, N.; Vijayan, P.; Prakash, M.; John Paul, J.A. Vermicomposting of Paper Industry Sludge with Cowdung and Green Manure Plants Using Eisenia Fetida: A Viable Option for Cleaner and Enriched Vermicompost Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moreno, M.A.; García Gracianteparaluceta, B.; Espuelas Zuazu, S.; Prieto Cobo, E.; Seco Meneses, A. A Small-Scale Study of Optimization of Vermicomposting of Coffee Industry Wastes Focused on Growth Rate. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Reuse and Recycling of Materials (ICRM-2020), Kottayam, Kerala, India, 11–13 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Negi, R.; Suthar, S. Degradation of Paper Mill Wastewater Sludge and Cow Dung by Brown-Rot Fungi Oligoporus Placenta and Earthworm (Eisenia Fetida) during Vermicomposting. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, V.S.; Kalamdhad, A.S.; Khwairkpam, M. Feasibility of Eudrilus Eugeniae and Perionyx Excavatus in Vermicomposting of Water Hyacinth. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Li, S.; Carson, M.A.; Chang, S.X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; An, Z.; Sun, X. Spent Mushroom Substrate and Cattle Manure Amendments Enhance the Transformation of Garden Waste into Vermicomposts Using the Earthworm Eisenia Fetida. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, S.; Pandey, B.; Gusain, R.; Gaur, R.Z.; Kumar, K. Nutrient Changes and Biodynamics of Eisenia Fetida during Vermicomposting of Water Lettuce (Pistia Sp.) Biomass: A Noxious Weed of Aquatic System. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.A.; Dominguez, J.; Neuhauser, E.F. Growth and Reproduction of Perionyx Excavatus (Perr.) (Megascolecidae) as Factors in Organic Waste Management. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1998, 27, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.; Edwards, C.A.; Webster, M. Vermicomposting of Sewage Sludge: Effect of Bulking Materials on the Growth and Reproduction of the Earthworm Eisenia Andrei. Pedobiologia 2000, 44, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frederickson, J.; Butt, K.R.; Morris, R.M.; Catherine, D. Combining Vermicultura with Traditional Green Waste Composting Systems. Soil BiolBiochem 1997, 29, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluzeau, D.; Fayolle, L.; Hubert, M. The Adaptation Value of Reproductive Strategy and Mode in Three Epigeous Earthworm Species. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvira, C.; Dominguez, J.; Briones, M.J.I. Growth and Reproduction of Eisenia Andrei and E. Fetida (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae) in Different Organic Residues. Pedobiologia 1996, 40, 377–384. [Google Scholar]
- Haimi, J. Growth and Reproduction of the Compost-Living Earthworms Eisenia Andrei and E. Fetida. Rev. DÉcologie Biol. Sol. 1990, 27, 415–421. [Google Scholar]
- Nogales, R.; Thompson, R.; Calmet, A.; Benítez, E.; Gómez, M.; Elvira, C. Feasibility of Vermicomposting Residues from Olive Oil Production Obtained Using Two Stage Centrifugation. J. Environ. Sci. Health-Part ToxicHazardous Subst. Environ. Eng. 1998, 33, 1491–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, S.; Singh, S. Feasibility of Vermicomposting in Biostabilization of Sludge from a Distillery Industry. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, R.; Suthar, S. Vermistabilization of Paper Mill Wastewater Sludge Using Eisenia Fetida. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X. Using Cow Dung and Spent Coffee Grounds to Enhance the Two-Stage Co-Composting of Green Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.; Lin, W.; Ye, J.; Liao, H.; Yu, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhou, S. Insights into Compositional Changes of Dissolved Organic Matter during a Full-Scale Vermicomposting of Cow Dung by Combined Spectroscopic and Electrochemical Techniques. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unuofin, F.O.; Mnkeni, P.N.S. Optimization of Eisenia Fetida Stocking Density for the Bioconversion of Rock Phosphate Enriched Cow Dung-Waste Paper Mixtures. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| No. of Treatment | HM (%) | Lavender (%) |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0 | 100 |
| T2 | 25 | 75 |
| T3 | 50 | 50 |
| T4 | 75 | 25 |
| T5 | 100 | 0 |
| A | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Values (and Standard Deviations) of Bread Wheat Seed Assay Germination Parameters | |||||
| Treatment | GP (%) | RSG (%) | RRG (%) | RShG (%) | GI (%) |
| T1 | 36.7 ± 11.5 a | 130.6 ± 48.8 a | 218.4 ± 129.7 a | 584.0 ± 500.2 a | 245.5 ± 91.4 a |
| T2 | 26.7 ± 5.8 a | 100.0 ± 50.0 a | 266.2 ± 149.2 a | 775.3 ± 644.6 a | 223.9 ± 116.1 a |
| T3 | 30.0 ± 10.0 a | 105.6 ± 41.9 a | 74.7 ± 31.0 a | 52.8 ± 37.5 a | 70.4 ± 2.3 a |
| T4 | 46.7 ± 20.8 a | 186.1 ± 144.9 a | 101.1 ± 51.0 a | 156.8 ± 118.7 a | 205.7 ± 225.1 a |
| T5 | 33.3 ± 30.6 a | 100.0 ± 100.0 a | 112.6 ± 139.4 a | 326.4 ± 423.9 a | 202.2 ± 292.2 a |
| B | |||||
| Mean Values (and Standard Deviations) of Pardina Lentil Seed Assay Germination Parameters | |||||
| Treatment | GP (%) | RSG (%) | RRG (%) | RShG (%) | GI (%) |
| T1 | 83.3 ± 5.8 a | 89.6 ± 10.0 a | 114.0 ± 29.8 a | 145.2 ± 45.7 a | 101.8 ± 26.6 ab |
| T2 | 96.7 ± 5.8 a | 103.7 ± 6.4 a | 208.1 ± 101.3 a | 325.6 ± 193.3 a | 215.3 ± 100.4 a |
| T3 | 90.0 ± 0.0 a | 96.7 ± 5.8 a | 108.7 ± 44.5 a | 156.8 ± 112.0 a | 106.7 ± 47.8 ab |
| T4 | 83.3 ± 11.5 a | 90.0 ± 17.3 a | 134.3 ± 22.1 a | 164.8 ± 79.4 a | 123.4 ± 40.8 ab |
| T5 | 63.3 ± 25.2 a | 67.0 ± 22.8 a | 91.6 ± 85.7 a | 98.4 ± 115.7 a | 56.7 ± 50.1 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Moreno, M.Á.; García Gracianteparaluceta, B.; Marcelino Sádaba, S.; Prieto Cobo, E.; Seco Meneses, A. Vermicomposting of Lavender Waste: A Biological Laboratory Investigation. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122957
González-Moreno MÁ, García Gracianteparaluceta B, Marcelino Sádaba S, Prieto Cobo E, Seco Meneses A. Vermicomposting of Lavender Waste: A Biological Laboratory Investigation. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122957
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Moreno, Miguel Ángel, Beñat García Gracianteparaluceta, Sara Marcelino Sádaba, Eduardo Prieto Cobo, and Andrés Seco Meneses. 2022. "Vermicomposting of Lavender Waste: A Biological Laboratory Investigation" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122957
APA StyleGonzález-Moreno, M. Á., García Gracianteparaluceta, B., Marcelino Sádaba, S., Prieto Cobo, E., & Seco Meneses, A. (2022). Vermicomposting of Lavender Waste: A Biological Laboratory Investigation. Agronomy, 12(12), 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122957








