Prediction of the Effect of Nutrients on Plant Parameters of Rice by Artificial Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Details
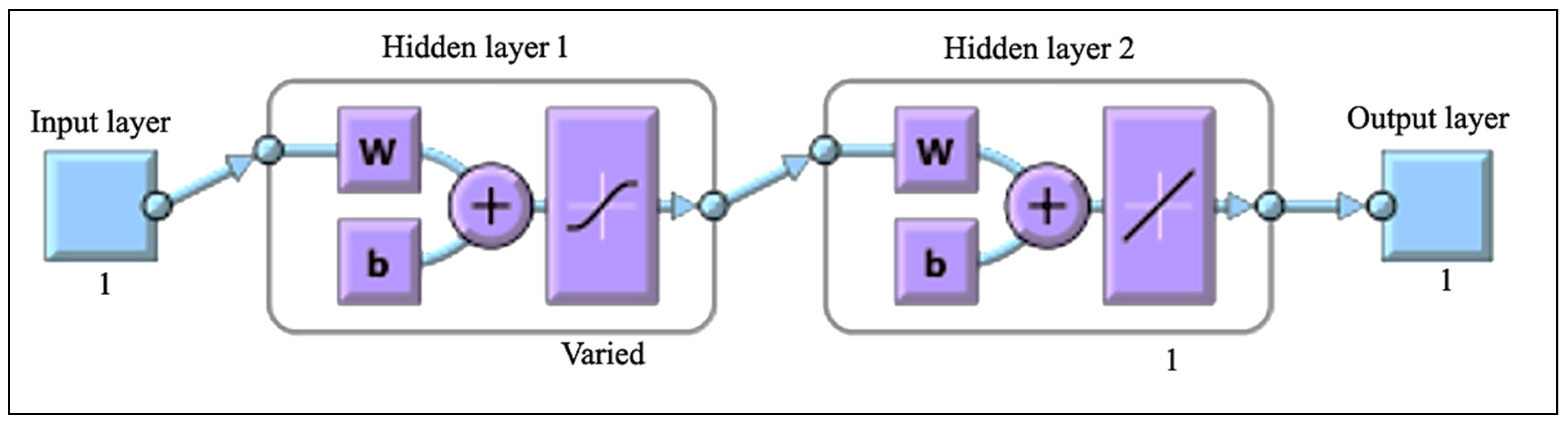
2.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Model
3. Results and Discussion
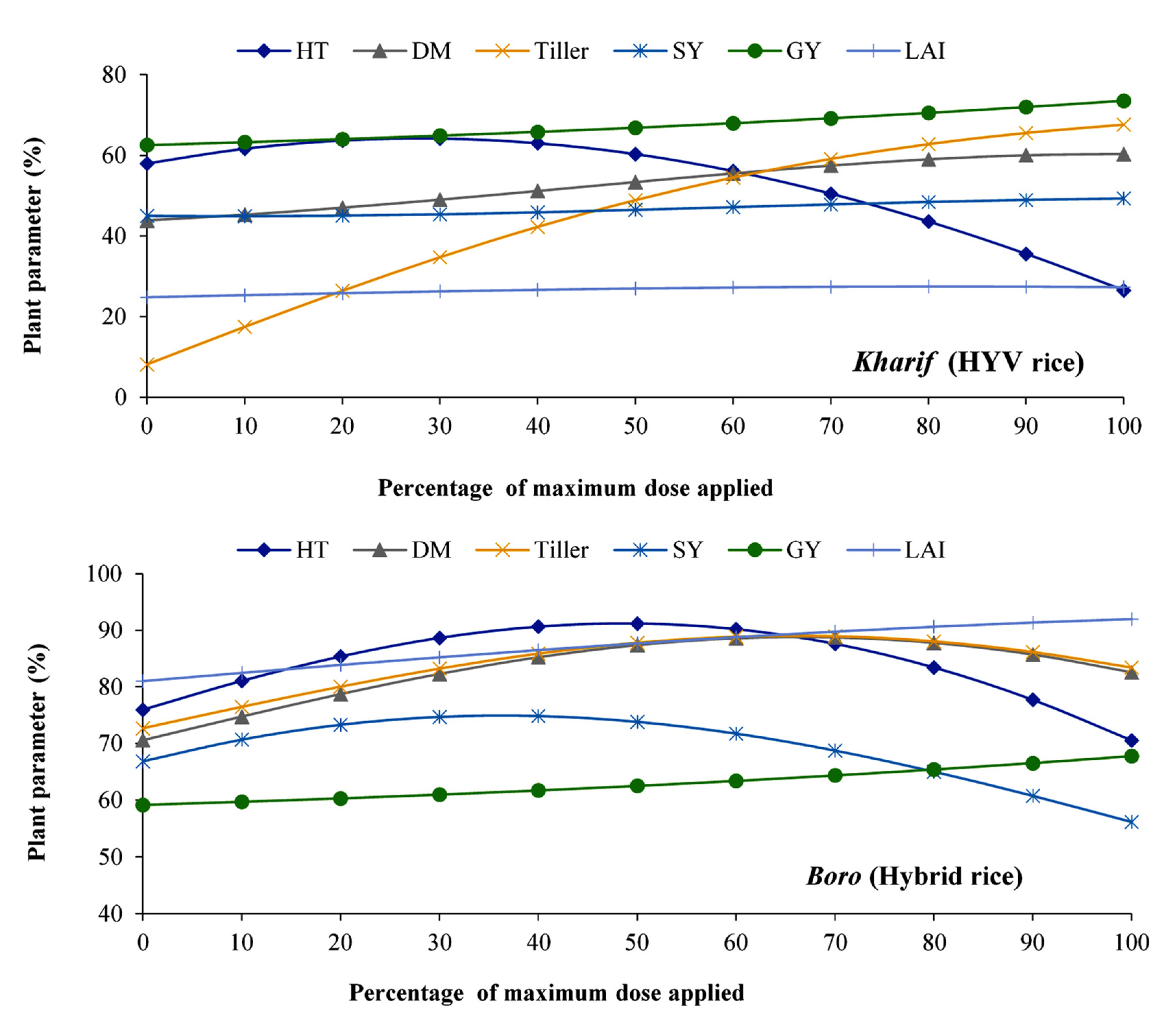
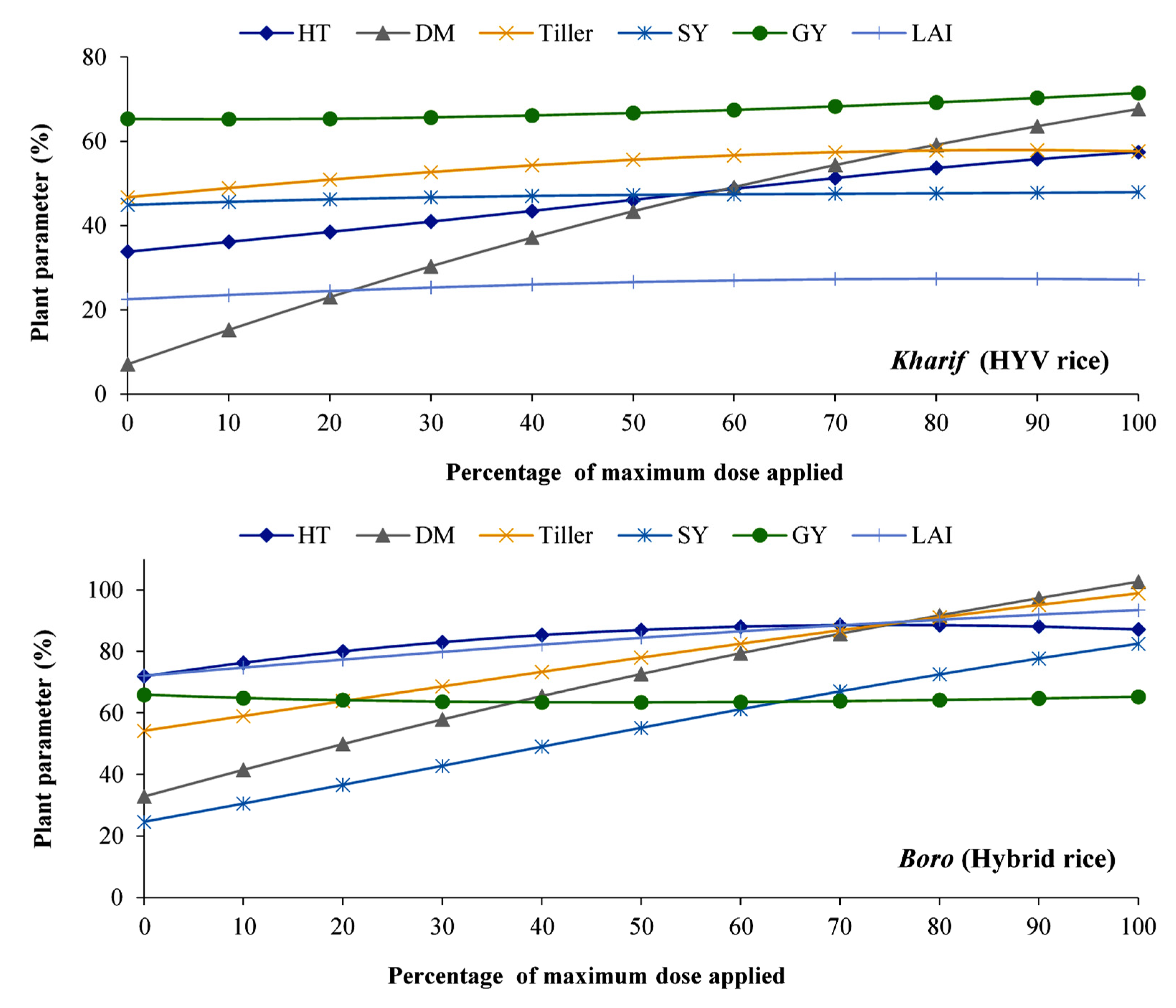
3.1. Effect of Nitrogen on Different Plant Parameters of Kharif and Boro Rice
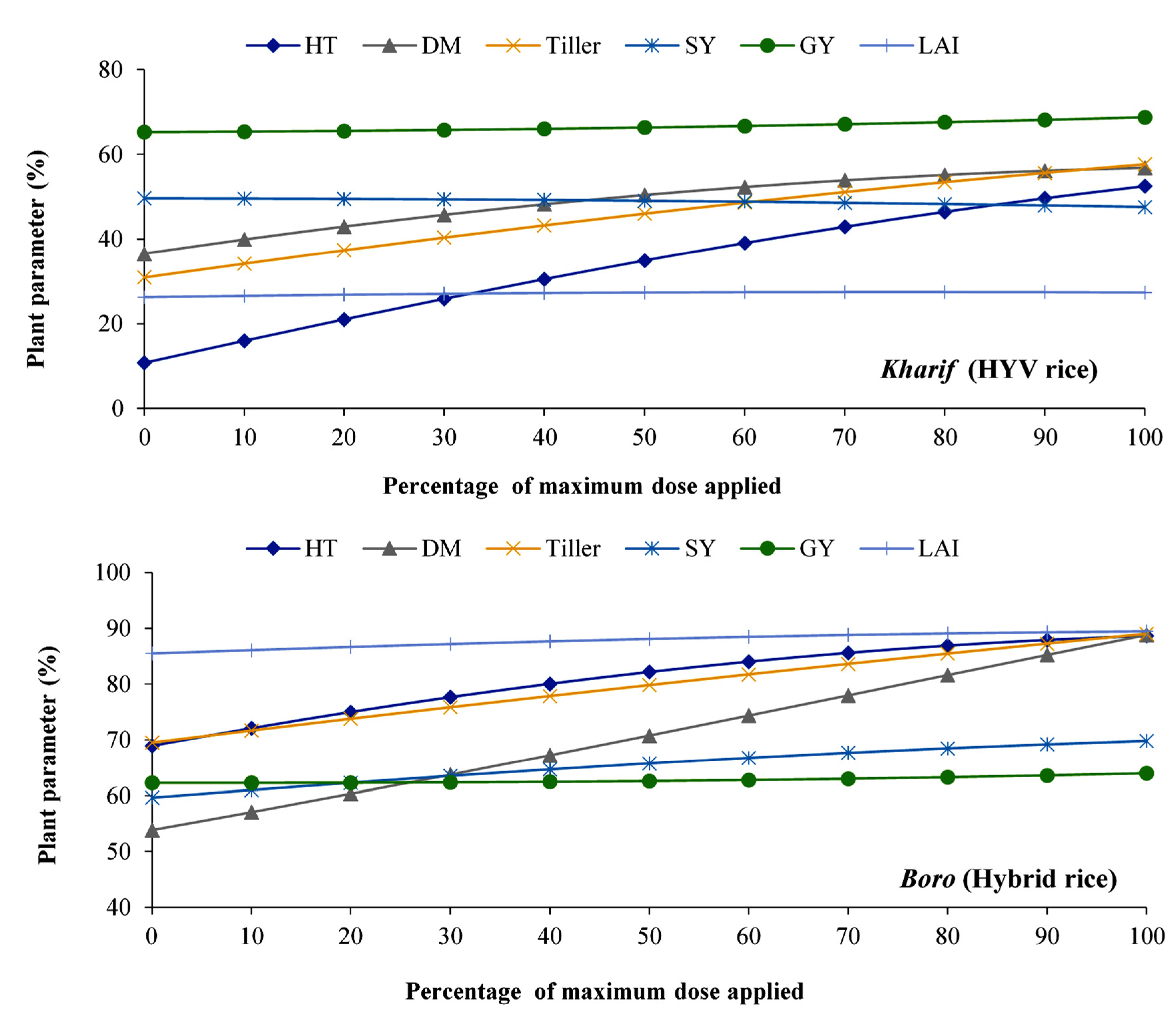
3.2. Effect of Phosphorous on Different Plant Parameters of Kharif and Boro Rice
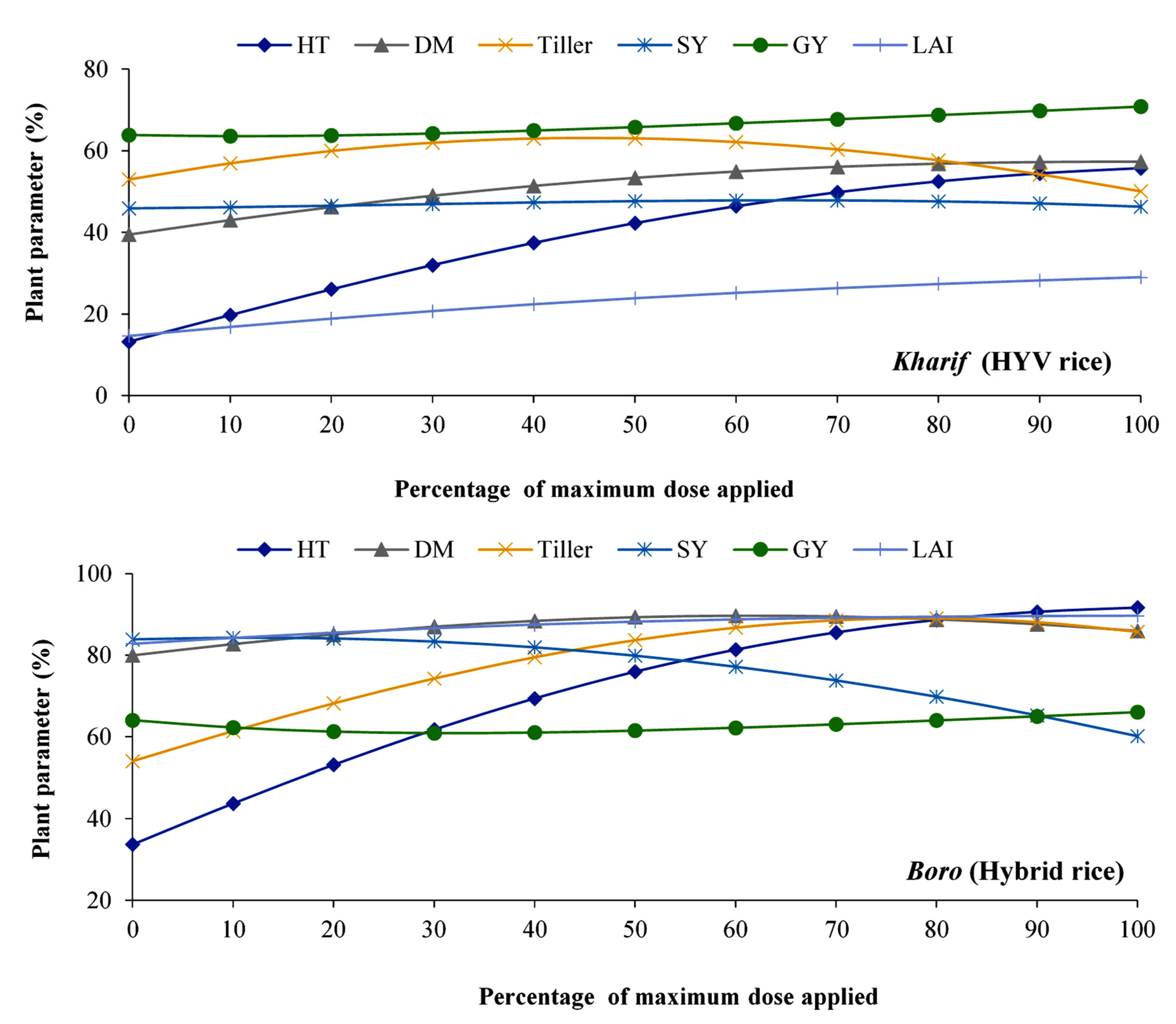
3.3. Effect of Potassium on Different Plant Parameters of Kharif and Boro Season Rice
3.4. Effect of Zinc on Different Plant Parameters of Kharif and Boro Season Rice
3.5. Effect of Sulfur on Different Plant Parameters of Kharif and Boro Season Rice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pattanayak, S.; Jena, S.; Das, P.; Maitra, S.; Shankar, T.; Praharaj, S.; Mishra, P.; Mohanty, S.; Pradhan, M.; Swain, D.K.; et al. Weed management and crop establishment methods in rice (Oryza sativa L.) influence the soil microbial and enzymatic activity in sub-tropical environment. Plants 2022, 14, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangaraj, S.; Paikaray, R.K.; Maitra, S.; Pradhan, S.R.; Garnayak, L.M.; Satapathy, M.; Swain, B.; Jena, S.; Nayak, B.; Shankar, T.; et al. Integrated nutrient management improves the growth and yield of rice and greengram in a rice—greengram cropping system under the coastal plain agro-climatic condition. Plants 2022, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.H.; Fu, L.D.; Song, Y.T.; Chen, W.F. Effects of nitrogen application on nitrogen metabolism and related physiological characteristics of leaves of rice of different plant types. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2017, 45, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tong, T.; Potcho, P.M.; Huang, S.; Ma, L.; Tang, X. Nitrogen effects on yield, quality and physiological characteristics of giant rice. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.T.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, T.H.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.J. Effects of nitrogen reduction at different growth stages on rice population production characteristics and preliminary analysis of nitrogen reduction strategies. J. Yangzhou Univ. 2020, 65, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Tayefe, M.; Gerayzade, A.; Amiri, E.; Zade, A.N. Effect of nitrogen on rice yield, yield components and quality parameters. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.Z.; Ji, W.W. Effects of nitrogen application on osmotic regulators in leaves of different plant types of rice. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, A.; Aminul, I.A.; Sarkar, M.I.U.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmed, M.N.; Islam, M.R. Nitrogen response of two high yielding rice varieties as influenced by nitrogen levels and growing seasons. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2020, 6, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, H.A.S.; Barzan, R.R.; Contreras, M.S.; Brito, O.R. Growth, yield and agronomic efficiency of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cv. IAPAR 117 affected by nitrogen rates and sources. Acta Agron. 2017, 66, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, A.M.; Gewaily, E.E.; Osman, M.M.A. Effects of nitrogen levels on growth, yield and nitrogen use efficiency of some newly released Egyptian rice genotypes. Open Agric. 2018, 3, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairunniza-Bejo, S.; Zulkifli, Z.; Muharam, F.M. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer to growth, biomass and grain yield of paddy. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1152, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, B.M.; Nuhu, I.R.; Ato, E.; Naathanial, B. Effect of nitrogen rates on the growth and yield of three rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties in rain-fed lowland in the forest agro-ecological zone of Ghana. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 5, 878–885. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Zhao, R.; Liu, Y.T.; Yao, F.W.; Tang, W.B. Effect of different amount of nitrogen on the yield and the quality of high quality rice and its nitrogen utilization efficiency. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2019, 45, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Horie, T.; Shiraiwa, T. A model explaining genotypic and environmental variation of rice spikelet number per unit area measured by cross-locational experiments in Asia. Field Crop. Res. 2006, 97, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hou, W.; Zhou, W.; Lu, J.; Xing, Y.; Li, X. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilization affects the flowering time of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 20, e00753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Blaser, S.R.; Schlüter, S.; Shen, J.; Vetterlein, D. Effect of localised phosphorus application on root growth and soil nutrient dynamics in situ–comparison of maize (Zea mays) and faba bean (Vicia faba) at the seedling stage. Plant Soil 2019, 441, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Jin, Y.; Turner, N.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Siddique, K.; Li, F.-M. Phosphorus application increases root growth, improves daily water use during the reproductive stage, and increases grain yield in soybean subjected to water shortage. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 166, 103816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.L.; Bindraban, P.S.; Schröder, J.J.; Conijn, J.G.; Van der Meer, H.G. Phosphorus in Agriculture: Global Resources, Trends and Developments. Report to the Steering Committee Technology Assessment of the Ministry of Agriculture; Plant Research International: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, A.; Fukuda, T.; Vejchasarn, P.; Nestler, J.; Pariasca-Tanaka, J.; Wissuwa, M. The role of root size versus root efficiency in phosphorus acquisition in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.X.; Weng, X.Y.; Yang, Y. Effect of phosphorus deficiency on the photosynthetic characteristics of rice plants. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 54, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosef, T.S. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer on growth and yield rice (Oryza sativa L). Int. J. Agron. Plant Prod. 2012, 3, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Amtmann, A.; Troufflard, S.; Armengaud, P. The effect of potassium nutrition on pest and disease resistance in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zheng, Q.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. The critical role of potassium in plant stress response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7370–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmaca, G. Antioxidant effects of sulfur-containing amino acids. Yonsei Med. J. 2004, 45, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawahar, S.; Vaiyapuri, V. Effect of sulphur and silicon fertilization on growth and yield of rice. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2010, 9, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Meena, M.K.; Upadhyaya, A. Effect of sulphur and zinc on rice performance and nutrient dynamics in plants and soil of Indo Gangetic plains. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.U.; Aziz, T.; Farooq, M.; Wakeel, A.; Rengel, Z. Zinc nutrition in rice production systems: A review. Plant. Soil 2012, 361, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadi, R.; Dastan, S.; Yasari, E. Role of zinc fertilizer on grain yield and some qualities parameters in Iranian rice genotypes. Ann. Biol. Res. 2012, 3, 4519–4527. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, P.; Piekutowska, M.; Niedbała, G. Selection of independent variables for crop yield prediction using artificial neural network models with remote sensing data. Land 2021, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H. Artificial Neural Networks: Approximation and Learning Theory; Blackwell: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.K.; Chandwani, V. Artificial Neural Networks as Universal Function Approximators. Int. J. Emerg. Trend Engin. Devel. 2012, 4, 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyay, D.; Kocaefe, D.; Kocaefe, Y.; Morais, B. An artificial neural network model for predicting the CO2 reactivity of carbon anodes used in the primary aluminum production. Neural Comp. Appl. 2015, 28, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Mulla, D.J.; Robert, P.C. Identifying important factors influencing corn yield and grain quality variability using artificial neural networks. Precis. Agric. 2006, 7, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalbert, R.A.; Amado, T.; Corassa, G.; Pott, L.P.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Ciampitti, I.A. Satellite-based soybean yield forecast: Integrating machine learning and weather data for improving crop yield prediction in southern Brazil. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 284, 107886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analysis of soils. J. Agron. 1951, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1973; pp. 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Subbiah, B.V.; Asija, G.L. A rapid procedure for the determination of available nitrogen in soils. Curr. Sci. 1956, 25, 259–260. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, R.H.; Kurtz, L.T. Determinations of total, organic and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanway, J.J.; Heidel, H. Soil analyses methods as used in Iowa State College Soil Testing Laboratory. Iowa Agric. 1952, 57, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, W.L.; Norvell, W.A. Development of DTPA soil test for Zn, Fe, Mn and Cu. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnin, L.; Yien, C.H. Turbid metric Determination of Available Sulphates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1950, 15, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, T.; Malik, G.C.; Banerjee, M.; Dutta, S.; Maitra, S.; Praharaj, S.; Sairam, M.; Kumar, D.S.; Dessoky, E.S.; Hassan, M.M.; et al. Productivity and Nutrient Balance of an Intensive Rice–Rice Cropping System Are Influenced by Different Nutrient Management in the Red and Lateritic Belt of West Bengal, India. Plant 2021, 10, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anas, M.; Liao, F.; Verma, K.K.; Muhammad, A.S.; Mahmood, A.; Chen, Z.-L.; Li, Q.; Zeng, X.-P.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.-R. Fate of nitrogen in agriculture and environment: Agronomic, eco-physiological and molecular approaches to improve nitrogen use efficiency. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Buresh, R.J.; Huang, J.; Zhong, X.; Zou, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Hu, R.; Tang, Q.; et al. Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by site-specific N management. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, M.S.; Shankar, T.; Maitra, S.; Adhikary, R.; Swamy, G.V.V.S.N. Productivity, nutrient uptake and nutrient use efficiency of summer rice (Oryza sativa) as influenced by integrated nutrient management practices. Crop Res. 2020, 55, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, R.K.; Neupane, M.P.; Singh, S.P. Effect of phosphorus levels and bio-organic sources on growth and yield of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 11, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.; Nahar, K.; Hossain, M.; Mahmud, J.A.; Hossen, M.; Masud, A.A.C.; Fujita, M. Potassium: A vital regulator of plant responses and tolerance to abiotic stresses. Agron. 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, T.; Maitra, S.; Ram, M.S.; Mahapatra, R. Influence of integrated nutrient management on growth and yield attributes of summer rice (Oryza sativa L.). Crop Res. 2020, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shabala, S.; Pottosin, I. Regulation of potassium transport in plants under hostile conditions: Implications for abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. Physiol. Plant 2014, 151, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T. The role of zinc in auxin synthesis in the tomato plan. Am. J. Bot. 1948, 35, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukumararaja, T.M.; Sriramachandrasekharan, M.V. Effect of zinc on yield, zinc nutrition and zinc use efficiency of lowland rice. J. Agric. Technol. 2012, 8, 551–561. [Google Scholar]
- Hemesh, K.; Brar, B.S. Role of sulphur in cereal crops: A review. J. Pharm. Phytochem. 2020, 9, 1864–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.A.; Manaf, A.; Hussain, M.; Farooq, S.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M. Sulphur fertilization improves the sesame productivity and economic returns under rainfed conditions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2013, 15, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Chandel, R.S.; Singh, K.; Singh, A.K.; Sudhakar, P.C.; Singh, K. Effect of sulphur nutrition in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern and Coss.) grown in sequence. Ind. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 8, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.; Choudhary, M.R.; Sengupta, S.; Mishra, S.; Rani, V. Economic aspect of vermicompost and sulphur application in the garlic cultivation. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 2546–2548. [Google Scholar]
- Savin, I.Y.; Stathakis, D.; Negre, T.; Isaev, V.A. Prediction of crop yields with the use of neural networks. Russ. Agric. Sci. 2007, 33, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, K.A.; Sanjay, H.A.; Deshmukh, A. A parameter based customized artificial neural network model for crop yield prediction. J. Artif. Intel. 2016, 9, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khairunniza-Bejo, S.; Samihah Mustaffha, S.; Ismail, W.I.W. Application of Artificial Neural Network in Predicting Crop Yield: A Review. J. Food Sci. Eng. 2014, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]

| Particulars | Character/Value | Methodology | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Texture | Sandy loam | Hydrometer method | Bouyoucos [35] |
| pH | 5.65 | Determined by pH meter in 1:2.5 ratio of soil water suspension | Jackson [36] |
| Electrical conductivity (EC) (dS m−1) | 0.26 | Solubridge method | Jackson [36] |
| Available nitrogen (kg ha−1) | 230.0 | Alkaline permanganate method | Subbiah and Asija [37] |
| Available phosphorous (kg ha−1) | 11.2 | Bray’s method | Bray and Kurtz [38] |
| Available potassium (kg ha−1) | 125.2 | Flame photometer method | Hanway and Heidel [39] |
| Available zinc (mg kg−1) | 0.22 | Diethylenetriaminepentaacetate (DTPA) extractable Zn estimation by Atomic Absorption spectroscopy (AAS) | Shaw and Dean [40] |
| Available sulphur (kg ha−1) | 10.5 | Turbid-metric Method | Chesnin and Yien [41] |
| Season | Variety/Hybrid | Characteristics | Duration | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kharif | HYV | Drought and submergence tolerant and resistant to Bacterial Leaf Blight (BLB) Yield potential: 5.5–6.0 t/ha | 150 days | High yielding variety (HYV): MTU 7029 Developed byAPRRI & RARS, Maruteru, India |
| Boro | Hybrid | Resistant to Bacterial Leaf Blight (BLB). Yield potential: 5.5 t/ha | 150 days | Arize 6444 GOLD Developed by Bayer’s Crop Science |
| Kharif Season | Boro Season | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatments | N | P | K | Zn | S | Treatments | N | P | K | Zn | S |
| K1 | 80 | 40 | 40 | 25 | 20 | B1 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 25 | 20 |
| K2 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 25 | 20 | B2 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 25 | 20 |
| K3 | 0 | 40 | 40 | 25 | 20 | B3 | 0 | 60 | 60 | 25 | 20 |
| K4 | 80 | 20 | 40 | 25 | 20 | B4 | 120 | 30 | 60 | 25 | 20 |
| K5 | 80 | 0 | 40 | 25 | 20 | B5 | 120 | 0 | 60 | 25 | 20 |
| K6 | 80 | 40 | 20 | 25 | 20 | B6 | 120 | 60 | 30 | 25 | 20 |
| K7 | 80 | 40 | 0 | 25 | 20 | B7 | 120 | 60 | 0 | 25 | 20 |
| K8 | 80 | 40 | 40 | 12.5 | 20 | B8 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 12.5 | 20 |
| K9 | 80 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 20 | B9 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 0 | 20 |
| K10 | 80 | 40 | 40 | 25 | 10 | B10 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 25 | 10 |
| K11 | 80 | 40 | 40 | 25 | 0 | B11 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 25 | 0 |
| K12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | B12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Treatments | Plant Height (cm) | Dry Matter Accumulation (g) | Leaf Area Index | Number of Tillers | Grain Yield (t ha−1) | Straw Yield (t ha−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015–2016 | 2014 | 2015–2016 | 2014 | 2015–2016 | 2014 | 2015–2016 | 2014 | 2015–2016 | 2014 | 2015–2016 | |
| K1 | 119.7 | 119.5 | 1301.1 | 1315.5 | 4.87 | 4.88 | 317.3 | 306.8 | 5.5 | 5.7 | 7.6 | 7.6 |
| K2 | 110.2 | 112.0 | 1247.6 | 1257.8 | 4.86 | 4.85 | 298.6 | 295.2 | 4.6 | 5 | 7 | 7.2 |
| K3 | 96.8 | 94.0 | 660.6 | 662.8 | 3.85 | 3.82 | 257.8 | 259.1 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 5.1 | 5.3 |
| K4 | 116.8 | 117.2 | 1235.9 | 1249.2 | 4.85 | 4.86 | 300.2 | 291.6 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 7.4 | 7.5 |
| K5 | 98.5 | 98.9 | 1009.9 | 1016.4 | 4.83 | 4.84 | 280.3 | 274.0 | 5 | 5.1 | 7.3 | 7.4 |
| K6 | 114.7 | 115.4 | 1230.8 | 1235.6 | 4.86 | 4.87 | 310.2 | 296.4 | 5.1 | 5.2 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| K7 | 96.6 | 92.5b | 1006.4 | 1012.4 | 4.82 | 4.84 | 271.5 | 277.4 | 5 | 5.1 | 7.1 | 7.4 |
| K8 | 111.7 | 116.6 | 1229.8 | 1245.6 | 4.87 | 4.88 | 309.3 | 296.0 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| K9 | 98.9 | 96.7 | 1003.1 | 1009.7 | 3.97 | 3.98 | 274.7 | 274.1 | 4.9 | 5.1 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| K10 | 116.3 | 112.1 | 1220.1 | 1225.5 | 4.87 | 4.88 | 305.3 | 293.1 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 7.5 | 7.6 |
| K11 | 98.1 | 93.8 | 1042.3 | 1045.7 | 4.85 | 4.87 | 275.2 | 271.3 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| K12 | 88.6 | 87.6 | 518.0 | 514.5 | 3.52 | 3.56 | 201.7 | 195.9 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 4.1 | 4.1 |
| B1 | 122.0 | 124.8 | 1519.3 | 1515.1 | 5.54 | 5.53 | 361.3 | 360.3 | 6.6 | 6.6 | 8.5 | 8.6 |
| B2 | 117.0 | 119.0 | 1424.7 | 1410.6 | 5.51 | 5.50 | 360.0 | 361.8 | 5.8 | 6.0 | 7.9 | 8.2 |
| B3 | 98.4 | 94.4 | 759.2 | 766.7 | 4.48 | 4.41 | 300.8 | 320.3 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 6.0 | 5.9 |
| B4 | 118.0 | 116.8 | 1454.0 | 1451.8 | 5.51 | 5.45 | 357.2 | 353.0 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 8.3 | 8.5 |
| B5 | 95.2 | 94.5 | 1325.0 | 1313.9 | 5.51 | 5.43 | 320.3 | 320.3 | 6.0 | 6.1 | 7.9 | 8.0 |
| B6 | 120.0 | 118.9 | 1453.7 | 1452.8 | 5.52 | 5.48 | 347.2 | 362.5 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 8.4 | 8.5 |
| B7 | 99.3 | 98.1 | 1320.9 | 1320.3 | 5.43 | 5.48 | 321.5 | 323.3 | 6.1 | 6.2 | 8.3 | 8.3 |
| B8 | 118.0 | 124.7 | 1451.2 | 1450.8 | 5.44 | 5.48 | 350.3 | 352.7 | 6.3 | 6.4 | 8.4 | 8.5 |
| B9 | 101.2 | 98.9 | 1306.9 | 1310.1 | 4.64 | 4.63 | 321.7 | 323.5 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 8.5 | 8.5 |
| B10 | 115.0 | 119.2 | 1457.8 | 1452.1 | 5.50 | 5.49 | 345.3 | 356.9 | 6.2 | 6.3 | 8.5 | 8.5 |
| B11 | 100.1 | 98.2 | 1325.0 | 1315.3 | 5.45 | 5.47 | 315.2 | 320.3 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 8.4 | 8.2 |
| B12 | 87.0 | 81.7 | 582.1 | 591.8 | 4.14 | 4.04 | 271.1 | 275.2 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 5.9 | 5.8 |
| Nutrient | The Minimum Dose Applied (kg ha−1) | The Maximum Dose Applied (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | 0 | 120 |
| Phosphorous | 0 | 60 |
| Potassium | 0 | 60 |
| Zinc | 0 | 25 |
| Sulphur | 0 | 20 |
| Plant Parameter | Number of Neurons for Hidden Layer 1 | R2 for All Data | R2 for Validation Data | Data within a Defined Range (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height (HT) (cm) at 120 DAT | 40 | 0.948 | 0.857 | 85.410% for ±1.3 |
| Leaf area index (LAI) at 60 DAT | 11 | 0.990 | 0.962 | 91.667% for ±0.05 |
| Dry matter accumulation (DM) (g) 120 DAT | 32 | 0.989 | 0.950 | 91.667% for ±5 |
| Number of tillers at 120 DAT | 40 | 0.988 | 0.923 | 93.750% for ±8 |
| Grain yield (GY) (t ha−1) | 4 | 0.997 | 0.975 | 85.416% for ±0.1 |
| Straw yield (SY) (t ha−1) | 49 | 0.996 | 0.989 | 91.667% for ±0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shankar, T.; Malik, G.C.; Banerjee, M.; Dutta, S.; Praharaj, S.; Lalichetti, S.; Mohanty, S.; Bhattacharyay, D.; Maitra, S.; Gaber, A.; et al. Prediction of the Effect of Nutrients on Plant Parameters of Rice by Artificial Neural Network. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092123
Shankar T, Malik GC, Banerjee M, Dutta S, Praharaj S, Lalichetti S, Mohanty S, Bhattacharyay D, Maitra S, Gaber A, et al. Prediction of the Effect of Nutrients on Plant Parameters of Rice by Artificial Neural Network. Agronomy. 2022; 12(9):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092123
Chicago/Turabian StyleShankar, Tanmoy, Ganesh Chandra Malik, Mahua Banerjee, Sudarshan Dutta, Subhashisa Praharaj, Sagar Lalichetti, Sahasransu Mohanty, Dipankar Bhattacharyay, Sagar Maitra, Ahmed Gaber, and et al. 2022. "Prediction of the Effect of Nutrients on Plant Parameters of Rice by Artificial Neural Network" Agronomy 12, no. 9: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092123
APA StyleShankar, T., Malik, G. C., Banerjee, M., Dutta, S., Praharaj, S., Lalichetti, S., Mohanty, S., Bhattacharyay, D., Maitra, S., Gaber, A., Das, A. K., Sharma, A., & Hossain, A. (2022). Prediction of the Effect of Nutrients on Plant Parameters of Rice by Artificial Neural Network. Agronomy, 12(9), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092123











