Optimized Nitrogen Fertilizer Rate Can Increase Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency for Open-Field Chinese Cabbage in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Treatments
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Yield and Commodity Yield
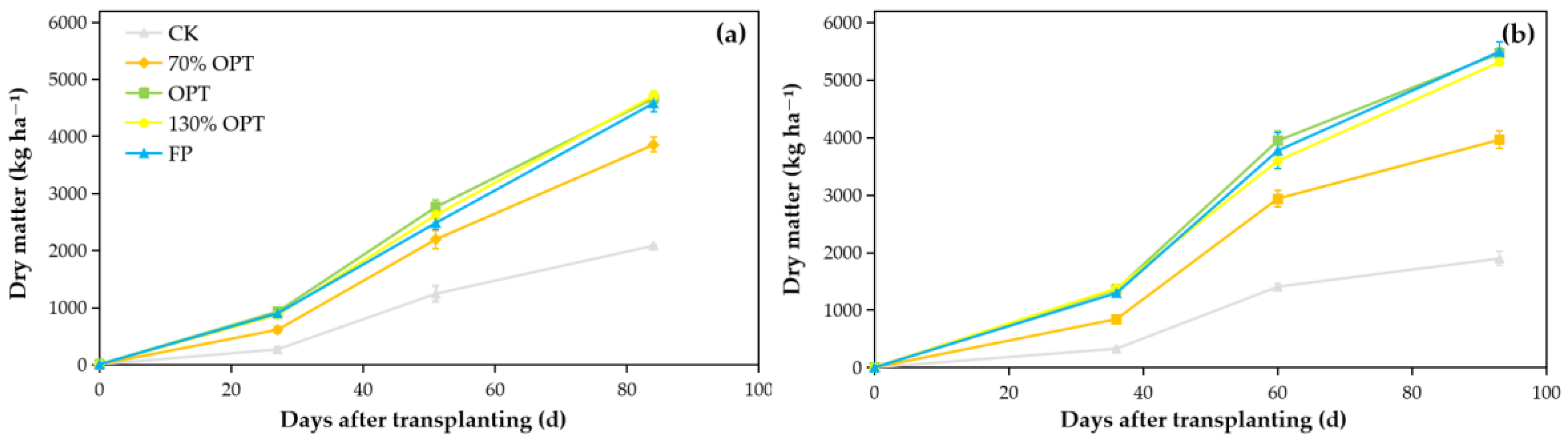
3.2. Aboveground DMB
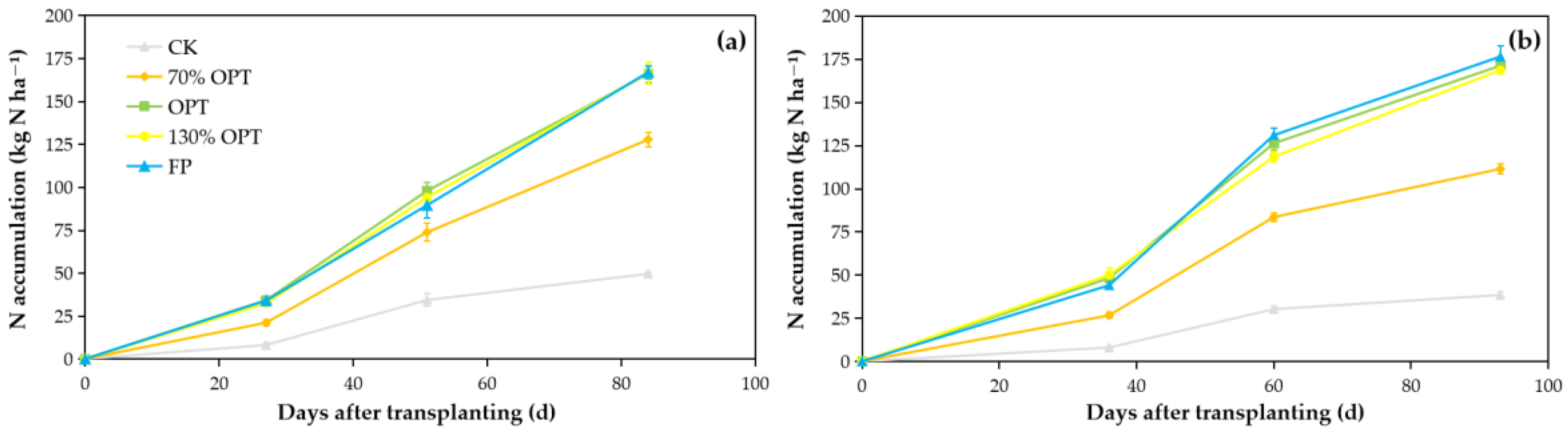
3.3. Plant N Absorption and Accumulation
3.4. SPAD Values
3.5. NUE
3.6. Residual Soil Nmin
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Chinese Cabbage Yield to N Application Rates
4.2. NUE
4.3. Root-Zone Soil Nmin
4.4. The Critical Plant N Concentration and Root-Zone Soil Nmin Were Determined
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruda, N. Impact of environmental factors on product quality of greenhouse vegetables for fresh consumption. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2005, 24, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Gruda, N.; Li, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Duan, Z. Global vegetable supply towards sustainable food production and a healthy diet. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dou, Z.; Shi, X.; Zou, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Guan, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, B.; et al. Innovative management programme reduces environmental impacts in Chinese vegetable production. Nat. Food 2020, 2, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NBSC. China Statistical Yearbook; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Tang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, S. Reducing potential of chemical fertilizers and scientific fertilization countermeasure in vegetable production in China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2017, 23, 1480–1493, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, F.; Guo, G.; Cheng, T.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Liang, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. An Integrated Nitrogen Management Strategy Promotes Open-Field Pepper Yield, Crop Nitrogen Uptake, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Southwest China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.B.; Incrocci, L.; Van Ruijven, J.; Massa, D. Reducing contamination of water bodies from European vegetable production systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 240, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.M.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Bai, J.; Meng, Q.; Hou, P.; Yue, S.; Roemheld, V.; et al. Integrated soil-crop system management for food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6399–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Li, X.; Christie, P.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, F. Influence of root zone nitrogen management and a summer catch crop on cucumber yield and soil mineral nitrogen dynamics in intensive production systems. Plant Soil 2008, 313, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Song, Z.; Chen, X. Accumulation and distribution characteristics of biomass and nitrogen in bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) under different fertilization strategies. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2018, 98, 2681–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, K.; Fan, Z.; Wei, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, J. Simulating the fate of nitrogen and optimizing water and nitrogen management of greenhouse tomato in North China using the EU-Rotate_N model. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 128, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Lv, H.; Batchelor, W.; Lian, X.; Wang, Z.; Lin, S.; Hu, K. Simulating nitrate and don leaching to optimize water and n management practices for greenhouse vegetable production systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, P.; Ding, W.; Ullah, S.; Abbas, T.; Li, M.; Ai, C.; Zhou, W. Identifying the critical nitrogen fertilizer rate for optimum yield and minimum nitrate leaching in a typical field radish cropping system in china. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Miao, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Liu, C. On-farm evaluation of winter wheat yield response to residual soil nitrate–N in North China Plain. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. Tiller development affected by nitrogen fertilization in a high-yielding wheat production system. Crop Sci. 2020, 60, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Lu, F.; Yan, P.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X. Elucidating population establishment associated with N management and cultivars for wheat production in China. Field Crop. Res 2014, 163, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumm, I.; Schenk, M. Influence of nitrogen supply on the occurrence of calcium deficiency in field grown lettuce. Acta Hortic. 1992, 339, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zou, C.; Gao, X.; Guan, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, X. Nitrous oxide emissions in Chinese vegetable systems: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, T.; You, X.; Gao, M.-R. Nutrient release from weathering of purplish rocks in the Sichuan Basin, China. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Han, Z.; Duo, J.; Ci, E.; Ni, J.; Xie, D.; Wei, C. Relationships between the lithology of purple rocks and the pedogenesis of purple soils in the Sichuan Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Li, S.; Jin, J.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Cui, R. Performance of an optimized nutrient management in north-central China. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körschens, M.; Albert, E.; Armbruster, M.; Barkusky, D.; Baumecker, M.; Behle-Schalk, L.; Bischoff, R. Effect of mineral and organic fertilization on crop yield, nitrogen uptake, carbon and nitrogen balances, as well as soil organic carbon content and dynamics: Results from 20 European long-term field experiments of the twenty-first century. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2013, 59, 1017–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, M.A.; Abou-Hussein, S.D.; El-Tohamy, W.A. Tomato yield, nitrogen uptake and water use efficiency as affected by planting geometry and level of nitrogen in an arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 169, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yin, X.; Raza, S.; Tong, Y. Optimising nitrogen fertilisation: A key to improving nitrogen-use efficiency and minimising nitrate leaching losses in an intensive wheat/maize rotation (2008–2014). Field Crop. Res. 2017, 206, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Mao, L.L.; Li, Y.Z.; Ding, J.J.; Lin, W.; Ahmed, S.; Abbas, A. Effect of Different Fertilizations on the Plant-Available Nitrogen in Soil Profile (0–100 cm): A Study on Chinese Cabbage. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 863760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, H.; Pandey, A.; Lam, S.K.; Davies, R.; Hassan, R.; Riches, D.; Chen, D. Opportunities to improve nitrogen use efficiency in an intensive vegetable system without compromising yield. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 50, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Christie, P.; Li, J. Environmental implications of low nitrogen use efficiency in excessively fertilized hot pepper (Capsicum frutescens L.) cropping systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 111, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmelikova, L.; Schmid, H.; Anke, S.; Hülsbergen, K.-J. Nitrogen-use efficiency of organic and conventional arable and dairy farming systems in Germany. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2021, 119, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, C.; Sørensen, P.; Frossard, E.; Dubois, D.; Mäder, P.; Nanzer, S.; Oberson, A. Nitrogen use efficiency of 15n-labelled sheep manure and mineral fertilizer applied to microplots in long-term organic and conventional cropping systems. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2008, 83, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.K.; Tahir, M.M.; Rahim, N. Effect of N Fertilizer Source and Timing on Yield and N Use Efficiency of Rainfed Maize (Zea mays L.) in Kashmir–Pakistan. Geoderma 2013, 195, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Fan, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, L.; Xiong, Z. Combined effects of nitrogen fertilization and biochar on the net global warming potential, greenhouse gas intensity and net ecosystem economic budget in intensive vegetable agriculture in southeastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 100, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ma, X.; Gao, X.; Cao, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Guo, G.; Liang, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Innovative nitrogen management strategy reduced N2O emission while maintaining high pepper yield in subtropical condition. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 354, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Hao, M.; Malhi, S. Accumulation of nitrate N in the soil profile and its implications for the environment under dryland agriculture in northern China: A review. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 90, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, W. Optimizing nitrogen input to reduce nitrate leaching loss in greenhouse vegetable production. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 111, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meter, K.J.; Basu, N.B.; Veenstra, J.J.; Burras, C.L. The nitrogen legacy, emerging evidence of nitrogen accumulation in anthropogenic landscapes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 35014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ye, Y.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z. Determining the optimal nitrogen rate for summer maize in China by integrating agronomic, economic, and environmental aspects. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 3031–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Xing, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; He, G.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Cao, H.; Luo, L.; Zan, Y.; Meng, X.; et al. Optimizing nitrogen input by balancing winter wheat yield and residual nitrate-N in soil in a long-term dryland field experiment in the Loess Plateau of China. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 181, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Christie, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, F. Root zone soil nitrogen management to maintain high tomato yields and minimum nitrogen losses to the environment. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 125, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | Fertilizer Application Rates (N-P2O5-K2O, kg ha−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling Period | Rosette Period | Heading Period | Total | |
| CK | 0–60–145 | 0–30–72.5 | 0–30–72.5 | 0–120–290 |
| 70% OPT | 52.5–60–145 | 70–30–72.5 | 52.5–30–72.5 | 175–120–290 |
| OPT | 75–60–145 | 100–30–72.5 | 75–30–72.5 | 250–120–290 |
| 130% OPT | 97.5–60–145 | 130–30–72.5 | 97.5–30–72.5 | 325–120–290 |
| FP | 270–115–125 | 90–57.5–62.5 | 90–57.5–62.5 | 450–230–250 |
| Year | Treatment ¹ | Aboveground Plant N Concentration (g kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rosette Period | Heading Period | Harvest Period | ||
| 2019–2020 | CK | 30.9 ± 0.3 c | 21.8 ± 1.2 b | 23.8 ± 0.1 c |
| 70% OPT | 34.9 ± 0.8 b | 33.7 ± 0.2 a | 33.2 ± 0.5 b | |
| OPT | 37.0 ± 1.0 ab | 35.5 ± 0.3 a | 35.6 ± 0.5 a | |
| 130% OPT | 37.3 ± 1.4 ab | 35.8 ± 0.7 a | 35.3 ± 0.8 a | |
| FP | 38.0 ± 0.6 a | 35.9 ± 1.3 a | 36.5 ± 0.5 a | |
| 2020–2021 | CK | 24.8 ± 0.7 d | 21.6 ± 1.1 c | 20.4 ± 0.4 c |
| 70% OPT | 31.6 ± 0.3 c | 28.5 ± 0.6 b | 28.2 ± 0.5 b | |
| OPT | 35.4 ± 0.3 ab | 32.1 ± 0.4 a | 31.3 ± 0.2 a | |
| 130% OPT | 36.2 ± 1.0 a | 33.0 ± 0.6 a | 31.7 ± 0.4 a | |
| FP | 34.1 ± 0.7 b | 33.1 ± 0.5 a | 32.1 ± 0.5 a | |
| Source of varieties | ||||
| Treatment(T) | *** | *** | *** | |
| Year(Y) | *** | *** | *** | |
| T × Y | ns 2 | ns | ns | |
| Year | Treatment ¹ | SPAD Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rosette Period | Heading Period | Harvest Period | ||
| 2019–2020 | CK | 26.3 ± 0.3 c | 25.2 ± 0.6 c | 26.8 ± 0.3 c |
| 70% OPT | 28.6 ± 0.6 b | 30.1 ± 0.3 b | 30.8 ± 0.4 b | |
| OPT | 30.9 ± 0.2 a | 33.0 ± 0.3 a | 32.6 ± 0.2 a | |
| 130% OPT | 30.7 ± 0.4 a | 32.1 ± 0.5 a | 32.4 ± 0.2 a | |
| FP | 31.4 ± 0.4 a | 33.1 ± 0.3 a | 32.8 ± 0.4 a | |
| 2020–2021 | CK | 27.0 ± 1.2 c | 27.9 ± 1.1 c | 25.2 ± 0.7 c |
| 70% OPT | 37.0 ± 0.4 b | 38.7 ± 0.5 b | 31.2 ± 0.5 b | |
| OPT | 39.1 ± 0.3 a | 41.3 ± 0.5 a | 33.9 ± 0.3 a | |
| 130% OPT | 39.9 ± 0.5 a | 41.0 ± 0.5 a | 33.7 ± 0.4 a | |
| FP | 40.1 ± 0.5 a | 42.4 ± 0.5 a | 33.6 ± 0.5 a | |
| Source of varieties | ||||
| Treatment(T) | *** | *** | ns 2 | |
| Year(Y) | *** | *** | *** | |
| T × Y | *** | *** | * | |
| Year | Treatment ¹ | REN (%) | NAE (kg kg−1) | PFPN (kg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019–2020 | 70% OPT | 44.5 ± 2.4 a | 493 ± 15 a | 853 ± 15 a |
| OPT | 46.4 ± 2.0 a | 441 ± 11 b | 693 ± 11 b | |
| 130% OPT | 35.9 ± 1.9 b | 332 ± 15 c | 526 ± 15 c | |
| FP | 26.0 ± 0.8 c | 238 ± 10 d | 378 ± 10 d | |
| 2020–2021 | 70% OPT | 41.4 ± 1.6 b | 641 ± 25a | 801 ± 25 a |
| OPT | 52.9 ± 1.6 a | 629 ± 20 a | 741 ± 20 b | |
| 130% OPT | 39.8 ± 0.5 b | 471 ± 14 b | 557 ± 14 c | |
| FP | 30.5 ± 1.4 c | 349 ± 13 c | 412 ± 13 d | |
| Source of varieties | ||||
| Treatment(T) | *** | *** | *** | |
| Year(Y) | *** | *** | *** | |
| T × Y | ns 2 | ns | ns | |
| Year | Treatment ¹ | Soil Mineral Nmin (kg ha−1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rosette Period | Heading Period | Harvest Period | ||||||||
| 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 40–60 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 40–60 cm | 0–20 cm | 20–40 cm | 40–60 cm | ||
| 2019–2020 | CK | 10.4 ± 2.6 d | 14.1 ± 0.8 c | 13.0 ± 0.8 e | 19.5 ± 2.5 c | 27.8 ± 0.3 e | 18.8 ± 1.4 c | 12.1 ± 1.4 b | 18.0 ± 0.7 c | 15.7 ± 1.7 d |
| 70% OPT | 24.7 ± 3.2 c | 37.2 ± 7.4 b | 26.0 ± 2.7 d | 31.1 ± 5.9 b | 39.1 ± 9.3 d | 30.5 ± 3.5 b | 31.0 ± 2.2 a | 43.0 ± 6.1 c | 31.4 ± 3.6 c | |
| OPT | 43.9 ± 2.8 b | 36.7 ± 4.0 b | 29.1 ± 2.8 c | 35.6 ± 3.4 b | 51.1 ± 5.6 c | 34.5 ± 8.2 b | 29.3 ± 1.7 a | 53.8 ± 1.4 b | 57.1 ± 7.2 b | |
| 130% OPT | 49.2 ± 11 b | 82.9 ± 19 a | 88.1 ± 18.3 b | 36.6 ± 4.0 b | 58.2 ± 10 b | 67.3 ± 5.1 a | 31.4 ± 4.7 a | 43.5 ± 3.6 c | 80.2 ± 14 a | |
| FP | 64.6 ± 16 a | 82.3 ± 17 a | 91 ± 13.3 a | 53.0 ± 3.5 a | 70.8 ± 3.3 a | 64.3 ± 4.3 a | 33.8 ± 2.3 a | 63.1 ± 7.6 a | 78.6 ± 19 a | |
| 2020–2021 | CK | 8.9 ± 0.4 d | 9.8 ± 0.7 d | 9.7 ± 1.1 d | 7.3 ± 0.1 c | 8.9 ± 0.3 d | 8.1 ± 0.1 d | 6.0 ± 0.6 e | 5.8 ± 0.5 c | 5.5 ± 0.1 d |
| 70% OPT | 13.0 ± 1.0 c | 20.7 ± 1.9 c | 16.9 ± 0.4 c | 12.7 ± 4.4 b | 13.7 ± 3.6 c | 13.3 ± 3.2 c | 16.6 ± 4.6 d | 4.6 ± 0.2 c | 4.7 ± 0.3 d | |
| OPT | 17.6 ± 3.4 b | 30.6 ± 7.6 b | 28.5 ± 4.6 b | 12.8 ± 1.7 b | 18.5 ± 3.2 c | 19.5 ± 5.5 c | 34.0 ± 6.8 c | 8.0 ± 1.5 c | 12.3 ± 2.9 c | |
| 130% OPT | 22.0 ± 1.1 a | 52.6 ± 2.3 a | 35.5 ± 3.5 b | 25.4 ± 5.7 a | 38.8 ± 6.3 b | 49.6 ± 11 b | 46.0 ± 11 b | 35.8 ± 6.6 b | 36.4 ± 2.5 b | |
| FP | 24.4 ± 4.4 a | 55.2 ± 3.8 a | 58.3 ± 9.1 a | 25.9 ± 3.2 a | 59.9 ± 7.5 a | 78.0 ± 7.5 a | 58.4 ± 14 a | 67.0 ± 12 a | 53.3 ± 6.7 a | |
| Source of varieties | ||||||||||
| Treatment(T) | *** | * | ns 2 | * | *** | ns | ns | *** | *** | |
| Year(Y) | *** | *** | *** | ns | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| T × Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, H.; Zhang, F.; Fu, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Guo, G.; Tian, Y.; Liang, T.; Zhou, N.; et al. Optimized Nitrogen Fertilizer Rate Can Increase Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency for Open-Field Chinese Cabbage in Southwest China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13061578
Cao H, Zhang F, Fu J, Ma X, Wang J, Liu F, Guo G, Tian Y, Liang T, Zhou N, et al. Optimized Nitrogen Fertilizer Rate Can Increase Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency for Open-Field Chinese Cabbage in Southwest China. Agronomy. 2023; 13(6):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13061578
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Hailin, Fen Zhang, Jian Fu, Xiao Ma, Junjie Wang, Fabo Liu, Guangzheng Guo, Yiming Tian, Tao Liang, Na Zhou, and et al. 2023. "Optimized Nitrogen Fertilizer Rate Can Increase Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency for Open-Field Chinese Cabbage in Southwest China" Agronomy 13, no. 6: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13061578
APA StyleCao, H., Zhang, F., Fu, J., Ma, X., Wang, J., Liu, F., Guo, G., Tian, Y., Liang, T., Zhou, N., Wang, Y., Chen, X., & Wang, X. (2023). Optimized Nitrogen Fertilizer Rate Can Increase Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency for Open-Field Chinese Cabbage in Southwest China. Agronomy, 13(6), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13061578





