Remote Sensing Monitoring of Rice Diseases and Pests from Different Data Sources: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Remote Sensing Monitoring Mechanism of Rice Pests and Diseases
- (1)
- Destruction of plant pigment systems (chlorophylls, carotenoids, anthocyanins, etc.). This can be caused by rice blight and stripe blight.
- (2)
- Changes in biomass and leaf area index. This can be caused by rice leaf blight, rice leaf roller, and rice planthopper.
- (3)
- Water loss. This can be caused by diseases like rice bacterial leaf blight.
3. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Rice Diseases and Pest from Different Data Sources
3.1. Hyperspectral Technology
3.2. Multispectral Technology
3.3. Image Information
3.4. Fluorescence Technology
3.5. Thermal Infrared Imaging Technology
3.6. Multi-Source Data Fusion
4. Methods for Monitoring Rice Diseases and Pests Using Remote Sensing
4.1. Feature Selection and Extraction
4.2. The Methods for Rice Diseases and Pests Monitoring
4.3. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Rice Pests and Diseases at Different Scales
4.4. General Framework for Monitoring Rice Pests and Diseases
5. Challenges and Prospects in the Monitoring of Rice Diseases and Pests
- (1)
- The mechanism of remote sensing for monitoring pests and diseases in rice is unclear. Converse to other crops, such as wheat and corn, the spectral acquisition in rice is susceptible to the influence of underlying water bodies during the planting process, making it difficult to obtain weak information related to pests and diseases. Therefore, the mechanism of remote sensing monitoring in rice is unclear. One of the challenges in rice remote sensing monitoring is to eliminate the impact of water bodies on disease information, especially before the jointing stage. Furthermore, it is necessary to elucidate the mechanism of rice remote sensing monitoring by considering the underlying physiological and biochemical changes in rice under stress.
- (2)
- Insufficient research on different stages of rice pest and disease infestation. Rice has different pest and disease patterns and damage symptoms at different growth stages. For example, rice blast is divided into seedling blast, leaf blast, spike, and neck blast at different growth stages of rice. Considering pathogenesis as a whole or focusing on a certain stage of pest and disease infestation is not sufficient for comprehensively and objectively monitoring rice under pest and disease stress. Therefore, precise monitoring needs to be conducted at different infestation stages of major rice pests and diseases. Early monitoring, in particular, needs to be strengthened, as it is an important period for precise pest and disease control.
- (3)
- Insufficient research on the differentiation of various pests and diseases in rice. There are many kinds of rice pests and diseases, and different pests, diseases, and non-pest (e.g., water and fertilizer) stresses may all show similar symptoms; therefore, their spectral representations will be similar. It is impossible to establish a library of exclusive features for specific diseases, as the differences in the characteristics of different pests and diseases are not sufficiently recognized. There is a need to establish exclusive features of different rice pests and diseases and to construct an accurate remote sensing monitoring model for rice pests and diseases in complex environments.
- (4)
- Insufficient integration of multi-source data. At present, remote sensing monitoring of rice pests and diseases is mainly based on optical remote sensing information. In southern China, however, cloudy and rainy weather makes data acquisition difficult. The incorporation of thermal imaging, fluorescence, satellite data, and habitat information related to the occurrence of pests and diseases is also limited. The fusion of different platforms and data sources is necessary to enrich data information and to improve the monitoring and early detection of rice pests and diseases.
- (5)
- Lack of data and information sharing. Adequate survey data are key to rice pest and disease modeling. The occurrence and prevalence of rice pests and diseases are diffuse in nature, and the sharing of crop pest and disease information from different provinces, cities, and countries will help data mining and model training and promote the research and application of crop pest and disease monitoring. For example, the smartphone-based mobilization of farmers and frontline workers in the field can provide timely information such as the occurrence level of diseases and pests in agricultural fields. This mobilization has the potential to establish corresponding observation networks for sharing field survey data, experimental data, and modeling methods on a continental or global scale.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variables | Definition and Algorithm | References |
|---|---|---|
| RBI (ratio blast index) | R1148/R1301 | [36] |
| NDBI (normalized difference blast index) | (R1148 − R1301)/(R1148 + R1301) | [36] |
| RVI14 (modest vegetation index) | Rgreen/Rmid-infrared | [34] |
| SDI14 (standard difference index) | (Rgreen − Rmid-infrared)/(Rgreen + Rmid-infrared) | [34] |
| green peak amplitude (Rg) | Maximum reflectance in the 510–560 nm green band | [42] |
| red valley amplitude (Ro) | Minimum reflectance in the 640–680 nm red band | [42] |
| SDy | Sum of the first order derivative values within the yellow edge | [106] |
| SDb | Sum of the first order derivative values within the blue edge | [106] |
References
- Tian, L.; Xue, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Cheng, T. Spectroscopic detection of rice leaf blast infection from asymptomatic to mild stages with integrated machine learning and feature selection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 257, 112350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker-Ritt, A.B.; Carlini, C.R. Fungitoxic and insecticidal plant polypeptides. Pept. Sci. 2012, 98, 367–384. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, K.; Mani, V. Emergence of bacterial panicle blight caused by Burkholderia glumae in North India. Plant Dis. 2015, 15, 150311115126000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, I. A review of remote sensing applications in agriculture for food security: Crop growth and yield, irrigation, and crop losses. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cai, D.; Li, G. Image recognition of four rice leaf diseases based on deep learning and support vector machine. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 179, 105824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ge, S.L.; Zhao, K.H.; Huang, S.W. First Report of Fusarium incarnatum Causing Spikelet Rot on Rice in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Fu, Q.; Zhu, D. Nonchemical pest control in China rice: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Guan, Q.; Luo, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Liang, D.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D. New optimized spectral indices for identifying and monitoring winter wheat diseases. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2516–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Roh, J.-H.; Kim, H.Y. Early Forecasting of Rice Blast Disease Using Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Networks. Sustainability 2018, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvajal-Yepes, M.; Cardwell, K.; Nelson, A.; Garrett, K.A.; Giovani, B.; Saunders, D.G.O.; Kamoun, S.; Legg, J.P.; Verdier, V.; Lessel, J.; et al. A global surveillance system for crop diseases. Science 2019, 364, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, C.F.; Stephens, E.C.; Kopainsky, B.; Jones, A.D.; Parsons, D.; Garrett, J. Food security outcomes in agricultural systems models: Current status and recommended improvements. Agric. Syst. 2021, 188, 103028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, W.; Kc, S. Global Human Capital: Integrating Education and Population. Science 2011, 333, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez Escamilla, R. Food Security and the 2015–2030 Sustainable Development Goals: From Human to Planetary Health: Perspectives and Opinions. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2017, 1, e000513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suryono, H.; Kuswanto, H.; Iriawan, N. Two-Phase Stratified Random Forest for Paddy Growth Phase Classification: A Case of Imbalanced Data. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kanda, E.; Kitada, K.; Ishiguro, K.; Torigoe, Y. Detection of rice panicle blast with multispectral radiometer and the potential of using airborne multispectral scanners. Phytopathology 2001, 91, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Wang, F.; Yi, Q.; Xie, L.; Yao, X. A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Research Progress and Trends in Rice Remote Sensing over the Past 42 Years (1980–2021). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.G. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) in Precision Agriculture: Applications and Challenges. Energies 2021, 15, 217. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Pu, R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Hao, Y. Using high spatial resolution satellite imagery for mapping powdery mildew at a regional scale. Precis. Agric. 2016, 17, 332–348. [Google Scholar]
- Delalieux, S.; Somers, B.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Aardt, J.A.N.V.; Keulemans, W.; Coppin, P. Hyperspectral indices to diagnose leaf biotic stress of apple plants, considering leaf phenology. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 1887–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, W.; González-Moreno, P.; Luke, B.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, H.; Liu, L. Wavelet-Based Rust Spectral Feature Set (WRSFs): A Novel Spectral Feature Set Based on Continuous Wavelet Transformation for Tracking Progressive Host–Pathogen Interaction of Yellow Rust on Wheat. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Q.; Huang, W.; Cui, X.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L. New spectral index for detecting wheat yellow rust using Sentinel-2 multispectral imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.F.; Xu, H.; Song, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wiyao, K.T.; Zhai, Z. Applying spectral fractal dimension index to predict the SPAD value of rice leaves under bacterial blight disease stress. Plant Methods 2022, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wang, Z.; Xue, B.; Li, D.; Zheng, H.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Cheng, T. A disease-specific spectral index tracks Magnaporthe oryzae infection in paddy rice from ground to space. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 285, 113384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Huang, Y.B.; Pu, R.L.; Gonzalez-Moreno, P.; Yuan, L.; Wu, K.H.; Huang, W.J. Monitoring plant diseases and pests through remote sensing technology: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 165, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Shi, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C. Detection of Rise Damage by Leaf Folder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis) Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Based Hyperspectral Data. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashourloo, D.; Mobasheri, M.; Huete, A. Developing two spectral disease indices for detection of wheat leaf rust (Pucciniatriticina). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4723–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chemura, A.; Mutanga, O.; Dube, T. Separability of coffee leaf rust infection levels with machine learning methods at Sentinel-2 MSI spectral resolutions. Precis. Agric. 2017, 18, 859–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, Q.; Liu, X. Hyperspectral detection of rice damaged by rice leaf folder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis). Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 82, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, R.K. Changes in spectral characteristics of rice canopy infested with brown planthopper and leaffolder. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Laxman, B.; Rao, S.V.C.K.; Seshasai, M.V.R.; Dadhwal, V.K. Monitoring of bacterial leaf blight in rice using ground-based hyperspectral and LISS IV satellite data in Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India. Pans Pest Artic. News Summ. 2015, 61, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.H. Early assessment of the yield loss in rice due to the brown planthopper using a hyperspectral remote sensing method. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2016, 62, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, L.X.; Dong, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.; Huang, W.J.; Han, L.H.; Gonzalez-Moreno, P.; Ma, H.Q.; Ye, H.C.; Sobeih, T. A Deep Learning-Based Approach for Automated Yellow Rust Disease Detection from High-Resolution Hyperspectral UAV Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, M. Detection of rice sheath blight for in-season disease management using multispectral remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2005, 7, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadifar, F.; Wayayok, A.; Mansor, S.; Shafri, H.Z. Detection of BPH (brown planthopper) sheath blight in rice farming using multispectral remote sensing. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Biswas, A.; VimalKumar, C.; Sinha, P. Deep Learning Analysis of Rice Blast Disease Using Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, N.; Adak, S.; Das, D.K.; Sahoo, R.N.; Mukherjee, J.; Kumar, A.; Chinnusamy, V.; Das, B.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Rajashekara, H.; et al. Spectral characterization and severity assessment of rice blast disease using univariate and multivariate models. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1067189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, M.; Christensen, T.; Li, W.; Tang, H. Remote sensing analysis of rice disease stresses for farm pest management using wide-band airborne data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Yan, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Wu, K. Diagnosing the symptoms of sheath blight disease on rice stalk with an in-situ hyperspectral imaging technique. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 209, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chai, R.; He, Y. Early detection of rice blast (Pyricularia) at seedling stage in Nipponbare rice variety using near-infrared hyper-spectral image. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 6809–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Qi, J.G.; Wang, N.N.; Zhu, Z.R.; Luo, J.; Liu, L.J.; Tang, J.; Cheng, J.A. Hyperspectral discrimination of foliar biotic damages in rice using principal component analysis and probabilistic neural network. Precis. Agric. 2018, 19, 973–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Cheng, C.H. Spectral characteristics of rice plants infested by brown planthopper. Proc. Natl. Sci. Counc. Repub. China Part B Life Sci. 2001, 25, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Guo, S.; Tan, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D. Identification of Rice Sheath Blight through Spectral Responses Using Hyperspectral Images. Sensors 2020, 20, 6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, N.; Adak, S.; Das, D.; Sahoo, R.; Kumar, A.; Viswanathan, C.; Mukherjee, J.; Gakhar, S. Characterization of Rice Blast Disease Using Greenness Index, Canopy Temperature and Vegetation Indices. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmi, Y.; Gangwar, S.; Agrawal, D.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, H.S. Leaf image analysis-based crop diseases classification. Signal Image Video Process. 2021, 15, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, M.; Kumar, D. A comprehensive survey on leaf disease identification & classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 33897–33925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trkolu, M.; Hanbay, D. Plant disease and pest detection using deep learning-based features. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2019, 27, 1636–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonys, G.; Wickramarachchi, N. An image recognition system for crop disease id. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2009 International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 28–31 December 2009; pp. 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, H.B.; Shah, J.P.; Dabhi, V.K. Detection and classification of rice plant diseases. Intell. Decis. Technol. 2017, 11, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, K.; Srinivasan, S. Feature Extraction and Classification of Plant Leaf Diseases Using Deep Learning Techniques. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 73, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Sreenivasu, S.V.N.; Mahalaxmi, U.S.B.K.; Sharma, H.; Patil, D.D.; Asenso, E. Hybrid Feature-Based Disease Detection in Plant Leaf Using Convolutional Neural Network, Bayesian Optimized SVM, and Random Forest Classifier. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 2845320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethy, P.K.; Barpanda, N.K.; Rath, A.K.; Behera, S.K. Deep feature based rice leaf disease identification using support vector machine. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Chen, G.; Li, C.; Fu, J.; Liang, H. Convolutional Rebalancing Network for the Classification of Large Imbalanced Rice Pest and Disease Datasets in the Field. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 671134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Du, K.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, F.; Chu, J.; Sun, Z. A segmentation method for greenhouse vegetable foliar disease spots images using color information and region growing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 142, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Xu, M.; Xu, Z.; Ye, H.; Zhou, C. Multi-feature decision fusion algorithm for disease detection on crop surface based on machine vision. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 9471–9484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwi Pupitasari, T.; Basori, A.; Yufit Riskiawan, H.; Sarwo Setyohadia, D.P.S.; Agus Kurniasari, A.; Firgiyanto, R.; Firdausiah Mansur, A.B.; Yunianta, A. Intelligent Detection of Rice Leaf Diseases Based on Histogram Color and Closing Morphological. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2022, 34, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimm, H.; Guan, K.; Burroughs, C.H.; Peng, B.; Wu, G. Quantifying high-temperature stress on soybean canopy photosynthesis: The unique role of sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2403–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Miller, J.R.; Mohammed, G.H.; Noland, T.L.; Sampson, P.H. Chlorophyll Fluorescence Effects on Vegetation Apparent Reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischler, Y.K.; Thiessen, E.; Hartung, E. Early optical detection of infection with brown rust in winter wheat by chlorophyll fluorescence excitation spectra. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 146, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, J.; Guan, L. Tracking photosynthetic injury of Paraquat-treated crop using chlorophyll fluorescence from hyperspectral data. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 46, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Han, X.; Wu, J. Evaluating the utility of solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence for drought monitoring by comparison with NDVI derived from wheat canopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Zou, Q.; Yan, J.; Dong, Y.; Li, B. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Winter Wheat Stripe Rust Based on mRMR-XGBoost Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, S.N.; Subhash, N.; Ravi, V.; Saravanan, R.; Mohanan, C.N.; Nita, S.; Kumar, T.M. Detection of mosaic virus disease in cassava plants by sunlight-induced fluorescence imaging: A pilot study for proximal sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 2880–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Catalina, A.; González, M.R.; Martín, P. Relationships between net photosynthesis and steady-state chlorophyll fluorescence retrieved from airborne hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porcar-Castell, A.; Tyystjärvi, E.; Atherton, J.; Van der Tol, C.; Flexas, J.; Pfündel, E.E.; Moreno, J.; Frankenberg, C.; Berry, J.A. Linking chlorophyll a fluorescence to photosynthesis for remote sensing applications: Mechanisms and challenges. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4065–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neinavaz, E.; Schlerf, M.; Darvishzadeh, R.; Gerhards, M.; Skidmore, A.K. Thermal infrared remote sensing of vegetation: Current status and perspectives. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.G.; Serraj, R.; Loveys, B.R.; Xiong, L.; Wheaton, A.; Price, A.H. Thermal infrared imaging of crop canopies for the remote diagnosis and quantification of plant responses to water stress in the field. Funct. Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ludovisi, R.; Tauro, F.; Salvati, R.; Khoury, S.; Harfouche, A. UAV-Based Thermal Imaging for High-Throughput Field Phenotyping of Black Poplar Response to Drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoglou-Grammatikis, P.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Lagkas, T.; Moscholios, I. A Compilation of UAV Applications for Precision Agriculture. Comput. Netw. 2020, 172, 107148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, R.; Navas-Cortés, J.A.; Lucena, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J. High-resolution airborne hyperspectral and thermal imagery for early detection of Verticillium wilt of olive using fluorescence, temperature and narrow-band spectral indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Yuan, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, R.; Sun, J.; Mao, H. Tea diseases detection based on fast infrared thermal image processing technology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3459–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, G.; Modica, G. Applications of UAV Thermal Imagery in Precision Agriculture: State of the Art and Future Research Outlook. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Huang, J.F.; Shi, J.J.; Tao, R.X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.L. Characterizing and estimating rice brown spot disease severity using stepwise regression, principal component regression and partial least-square regression. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2007, 8, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanal, S.; Fulton, J.; Shearer, S. An overview of current and potential applications of thermal remote sensing in precision agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 139, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Oerke, E.-C.; Steiner, U.; Dehne, H.-W. Recent advances in sensing plant diseases for precision crop protection. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cai, F.; Tian, J.; Williams, T. Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multisource Remote Sensing Data: Literature Survey, Taxonomy, Principles, Applications, and Future Directions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Z.; Song, L.; Duan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Feng, W. Monitoring wheat powdery mildew based on hyperspectra, thermal infrared, and RGB image data fusion. Sensors 2021, 22, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Wu, B.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C. Investigation on Data Fusion of Multisource Spectral Data for Rice Leaf Diseases Identification Using Machine Learning Methods. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 577063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, X. Habitat monitoring to evaluate crop disease and pest distributions based on multi-source satellite remote sensing imagery. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2017, 145, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Ye, H.; Huang, W.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Chen, S. Integrating Spectral Information and Meteorological Data to Monitor Wheat Yellow Rust at a Regional Scale: A Case Study. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques da Silva, J.R.; Damásio, C.V.; Sousa, A.M.O.; Bugalho, L.; Pessanha, L.; Quaresma, P. Agriculture pest and disease risk maps considering MSG satellite data and land surface temperature. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yones, M.S.; Arafat, S.; Abou, H.A.F.; Abd Elrahman, H.A.; Dah, H.F. Determination of the best timing for control application against cotton leaf worm using remote sensing and geographical information techniques. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2012, 15, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Pu, R.; Yuan, L.; Huang, W.; Nie, C.; Yang, G. Integrating Remotely Sensed and Meteorological Observations to Forecast Wheat Powdery Mildew at a Regional Scale. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 7, 4328–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ruzouq, R.; Gibril, M.B.A.; Shanableh, A.; Kais, A.; Hamed, O.; Al-Mansoori, S.; Khalil, M.A. Sensors, Features, and Machine Learning for Oil Spill Detection and Monitoring: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhao, D.; Guan, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Z.; Li, G.; Xu, T. A deep convolutional neural network-based wavelength selection method for spectral characteristics of rice blast disease. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M. Assessment of the severity of bacterial leaf blight in rice using canopy hyperspectral reflectance. Precis. Agric. 2010, 11, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.H.; Jiang, P.; Xie, K.; Wang, F.J. Research on optimal predicting model for the grading detection of rice blast. Opt. Rev. 2019, 26, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Potgieter, J.; Arif, K.M. Plant Disease Detection and Classification by Deep Learning. Plants 2019, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thaiyalnayaki, K.; Joseph, C. Classification of plant disease using SVM and deep learning. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharim, M.N.A.; Wayayok, A.; Abdullah, A.F.; Shariff, A.R.M.; Husin, E.M.; Mahadi, M.R. Predictive zoning of pest and disease infestations in rice field based on UAV aerial imagery. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2022, 25, 831–840. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Rubiya, A.; Raja, B.S. Classification of rice disease using digital image processing and svm classifier. Int. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2015, 7, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kahar, M.; Mutalib, S.; Abdul-Rahman, S. Early Detection and Classification of Paddy Diseases with Neural Networks and Fuzzy Logic. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Mathematical and Computational Methods in Science and Engineering, MACMESE, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–25 April 2015; pp. 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Wu, H.F.; Huang, J.F. Application of neural networks to discriminate fungal infection levels in rice panicles using hyperspectral reflectance and principal components analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 72, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, P.; Muharam, F.M.; Ahmad, K.; Mansor, S.; Seman, I.A. Early detection of ganoderma basal stem rot of oil palms using artificial neural network spectral analysis. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, B.; Cao, G.; Hu, C.; Chen, C. Monitoring the Rice Panicle Blast Control Period Based on UAV Multispectral Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Land 2023, 12, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J. Discrimination of rice panicles by hyperspectral reflectance data based on principal component analysis and support vector classification. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2010, 11, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saleem, M.H.; Potgieter, J.; Arif, K.M. Automation in Agriculture by Machine and Deep Learning Techniques: A Review of Recent Developments. Precis. Agric. 2021, 22, 2053–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Hao, H.; Zhang, X.B.; Zhu, L.F.; Zheng, K.F.; Jin, Q.Y.; Zeng, F.P. Estimation of rice neck blasts severity using spectral reflectance based on BP-neural network. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 2461–2466. [Google Scholar]
- Narmadha, R.-P.; Sengottaiyan, N.; Kavitha, R.-J. Deep Transfer Learning Based Rice Plant Disease Detection Model. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2022, 31, 1257–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, V.; Trivedi, N.K.; Singh, A.; Mohamed, H.G.; Noya, I.D.; Kaur, P.; Goyal, N. A Transfer Learning-Based Artificial Intelligence Model for Leaf Disease Assessment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, G.; Chinnappan, J. Hybridization of ResNet with YOLO classifier for automated paddy leaf disease recognition: An optimized model. J. Field Robot. 2022, 39, 1087–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xingen, Z.; Jian, Z.; Yubin, L.; Chao, X.; Dong, L.; Zonghua, W. Detection of rice sheath blight using an unmanned aerial system with high-resolution color and multispectral imaging. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0187470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Davidw, L.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J. Identification of yellow rust in wheat using in-situ spectral reflectance measurements and airborne hyperspectral imaging. Precis. Agric. 2007, 8, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, J.P.; Watt, M.S.; Pearse, G.D.; Heaphy, M.; Dungey, H.S. Assessing very high resolution UAV imagery for monitoring forest health during a simulated disease outbreak. Int. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 131, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachik, N.A.; Hashim, N.; Wayayok, A.; Man, H.C.; Ali, M.M. Optical imaging techniques for rice diseases detection: A review. J. Agric. Food Eng. 2020, 1, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Taberner, M.; García-Haro, F.J.; Camps-Valls, G.; Grau-Muedra, G.; Nutini, F.; Crema, A.; Boschetti, M. Multitemporal and multiresolution leaf area index retrieval for operational local rice crop monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. Interdiscip. J. 2016, 187, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Pu, R.; Heald, R.C. Analysis of in situ hyperspectral data for nutrient estimation of giant sequoia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1827–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

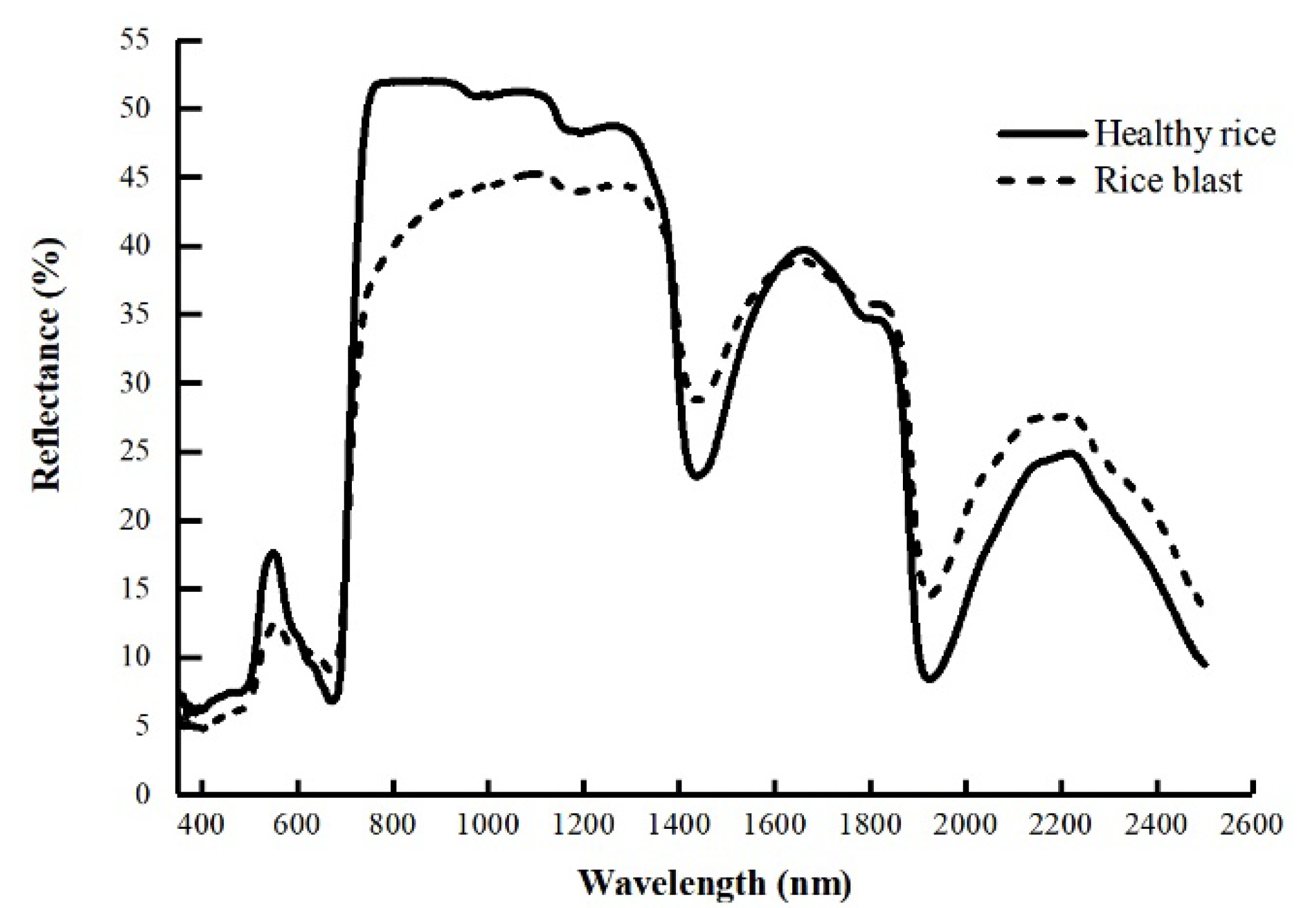
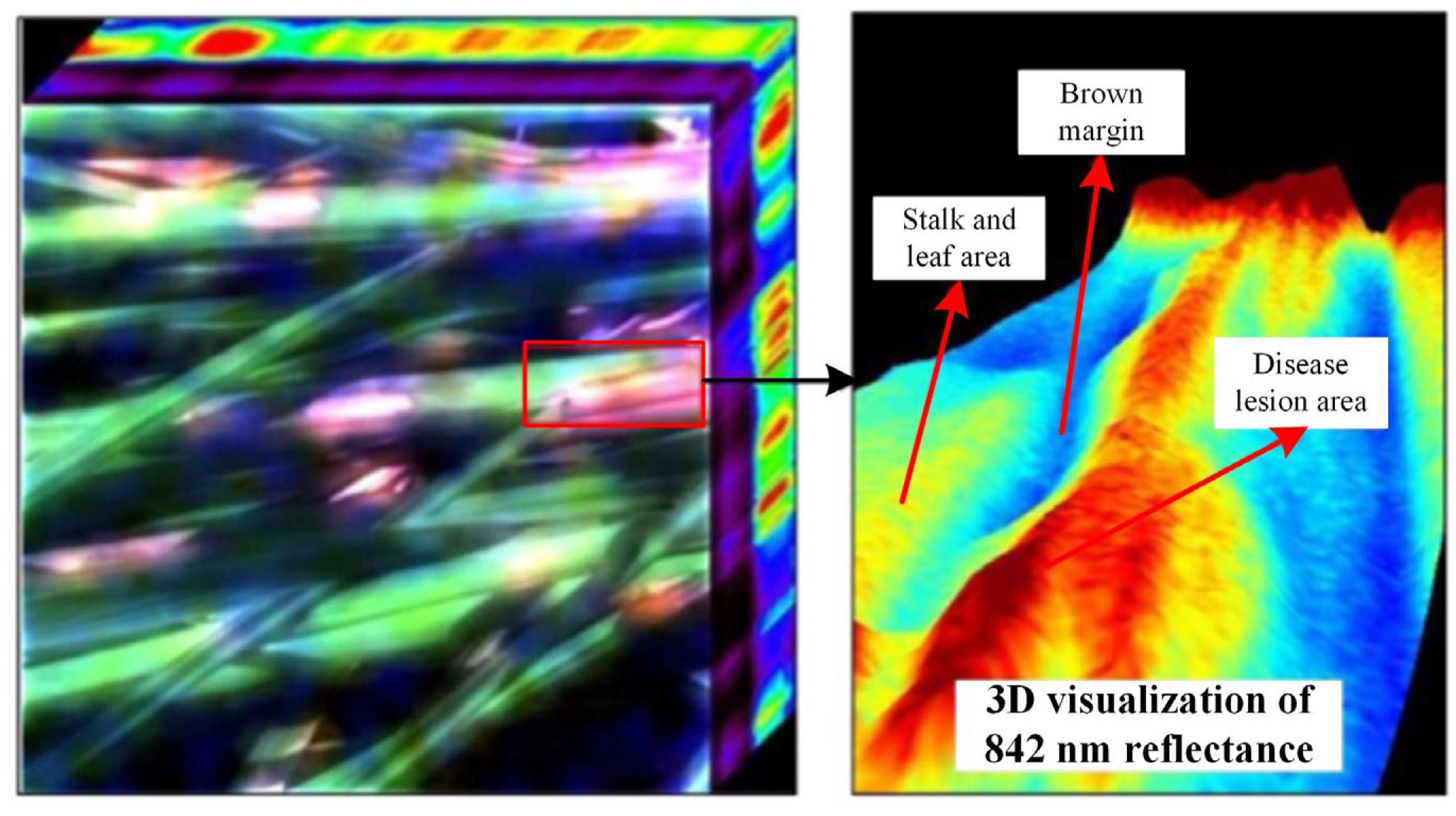
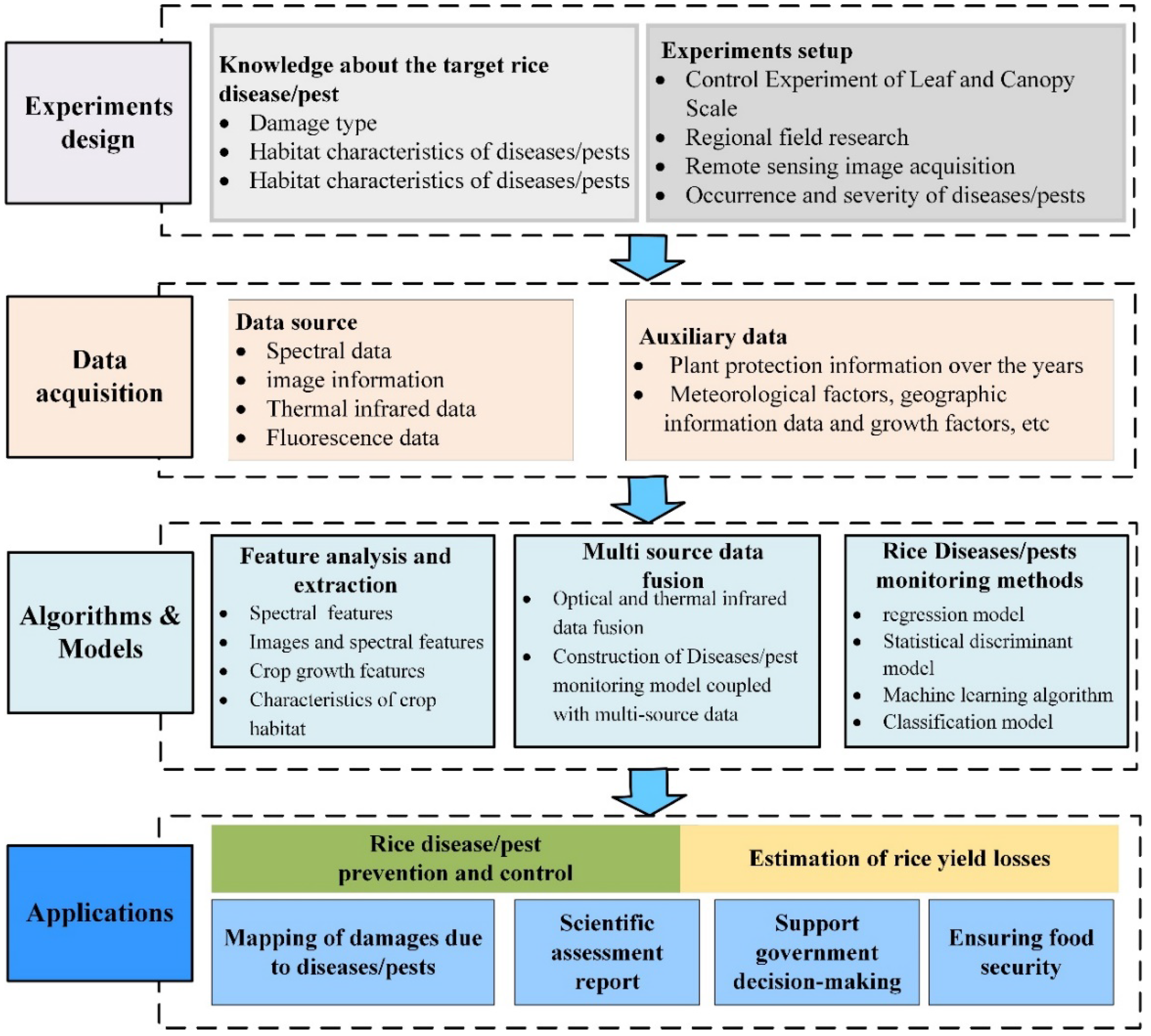
| Data Source | Data Characteristics | Data Acquisition Equipment | Monitoring Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-imaging hyperspectral | High spectral resolution and rich bands | ASD (Analytical Spectral Devices) FieldSpec spectrometer | Leaf scale, canopy scale, field scale |
| Image hyperspectral | High spectral resolution, rich bands and image information | Scanning imaging spectrometer Airborne hyperspectral imager | Leaf scale, canopy scale, field scale, regional scale |
| Multispectral | Large monitoring range, low cost | Multispectral imaging camera (MS-4100) Satellite imagery (Landsat, TM, Sentinel-2A/B, Quickbird, WorldView-2, HJ-CCD, IKONOS) UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) multispectral image | Field scale, regional scale, global scale |
| Imaging | Rich disease and pest symptom information | Camera Imaging spectrometer (Headwall) UAV hyperspectral/multispectral sensor | Leaf scale, canopy scale, field scale |
| Fluorescence | Sensitive pointers for photosynthetic functions | Fluorescence spectrum (PAM-2100) IMAGING-PAM | Leaf scale, canopy scale |
| Thermal infrared | Quick collection, non-destructive | Thermal infrared imager (FLIR) Thermal infrared satellite image (TM, ASTER, HJ-IRS) | Field scale, regional scale |
| Bands/Indices | Rice Diseases or Pests | Sensitive Features | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral band | Sheath blight | R494, R666 | [38] |
| Rice blast | R1188, R1339, R1377, R1432, R1614 | [39] | |
| Rice panicle blast | 430–530, 580–680, 1480–2000 nm, R459, R546, R569, R590, R775, R981 | [1,15] | |
| Rice glume blight | R450–R850 | [40] | |
| Brown planthopper | R737–R925, R426 | [29,41] | |
| R750–R1000, R400–R531, R567–R705 | [31] | ||
| Leaf folder | R757 | [29] | |
| R410, R470, R490, R570, R625, R665, and R720 | [25] | ||
| Spectral indices | Rice planthopper | SAVI | [29] |
| Sheath blight | (Rg − Ro)/(Rg + Ro), (SDy − SDb)/(SDy + SDb), nitrogen reflectance index (NRI) | [42] | |
| Rice blast disease | GNDVI, EVI, NDMI, SAVI | [35,43] | |
| RBI and NDBI | [36] | ||
| BPH (brown planthopper) sheath blight | RVI14, SDI14 and SDI24 | [33,34] | |
| Rice leaf folder | GNDVI | [29] | |
| (R490–R470), (R400–R470)/(R400–R490) | [25] |
| Category | Methods | Categories of Rice Diseases and Pests | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical discriminant analysis | Discriminant analysis | rice blast | [15] |
| Linear regression analysis | rice panicle blast | [97] | |
| Bacterial leaf blight (BLB), bacterial panicle blight (BPB), and stem borer(SB) | [89] | ||
| Partial least squares regression | brown planthopper, rice blast | [29,41] | |
| Machine learning algorithms | Support vector machines | rice panicle blast, leaffolder, sheath blight | [90] |
| Random forest (RF) | rice blast | [84] | |
| Artificial neural networks (ANN) | leaf blight, leaf blast, and sheath blight | [91] | |
| BP Neural Artificial Network | rice panicle blast | [97] | |
| Probabilistic neural network | Pyricularia grisea Sacc, Bipolaris oryzae Shoem, Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie and Cnaphalocrocis medinalis Guen | [40] | |
| Learning Vector Quantization (LVQ) Neural Network | rice panicle blast | [92] | |
| Deep learning algorithom | A neural network-based deep learning model | Rice Blast Disease | [35,84] |
| DenseNet169-MLP | Leaf blight, Brown spot, Leaf smut | [98] | |
| Convolutional Neural Networks- based Deep Learning (CNN-based DL) | Blight, blast, brown spot | [99] | |
| ResNet with YOLO classifier | paddy leaf disease | [100] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Q.; Huang, W.; Xia, Q.; Dong, Y.; Ye, H.; Jiang, H.; Chen, S.; Huang, S. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Rice Diseases and Pests from Different Data Sources: A Review. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071851
Zheng Q, Huang W, Xia Q, Dong Y, Ye H, Jiang H, Chen S, Huang S. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Rice Diseases and Pests from Different Data Sources: A Review. Agronomy. 2023; 13(7):1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071851
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Qiong, Wenjiang Huang, Qing Xia, Yingying Dong, Huichun Ye, Hao Jiang, Shuisen Chen, and Shanyu Huang. 2023. "Remote Sensing Monitoring of Rice Diseases and Pests from Different Data Sources: A Review" Agronomy 13, no. 7: 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071851
APA StyleZheng, Q., Huang, W., Xia, Q., Dong, Y., Ye, H., Jiang, H., Chen, S., & Huang, S. (2023). Remote Sensing Monitoring of Rice Diseases and Pests from Different Data Sources: A Review. Agronomy, 13(7), 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071851









