Growth and Photosynthetic Responses to Increased LED Light Intensity in Korean Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) Sprouts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
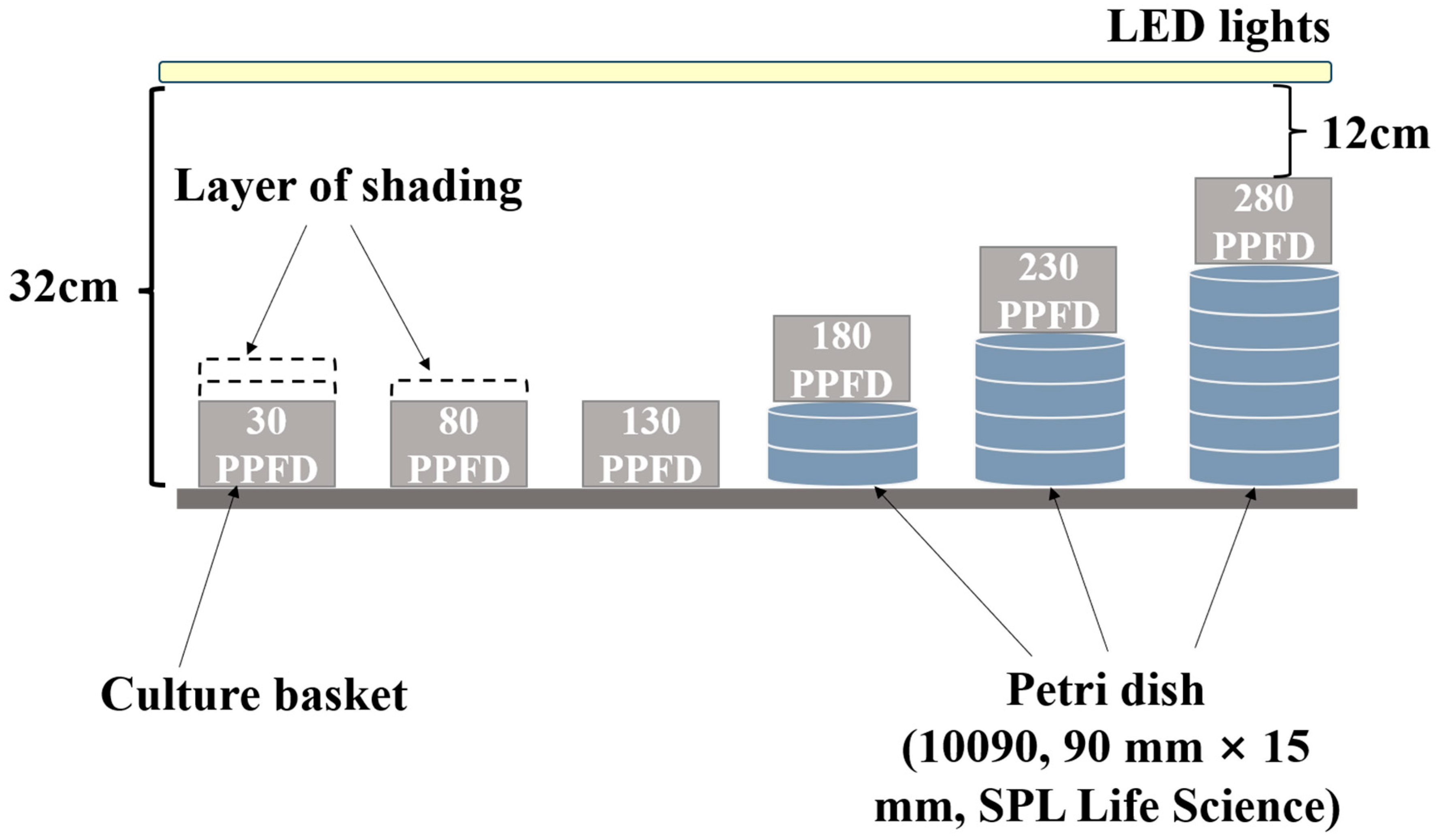
2.2. Experimental Design and Treatments
2.3. Destructive Sampling and Growth Parameter Measurements
2.4. Analysis of the Photosynthetic Parameters
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Plant Growth and Morphylogy as Affected by Light Intensity
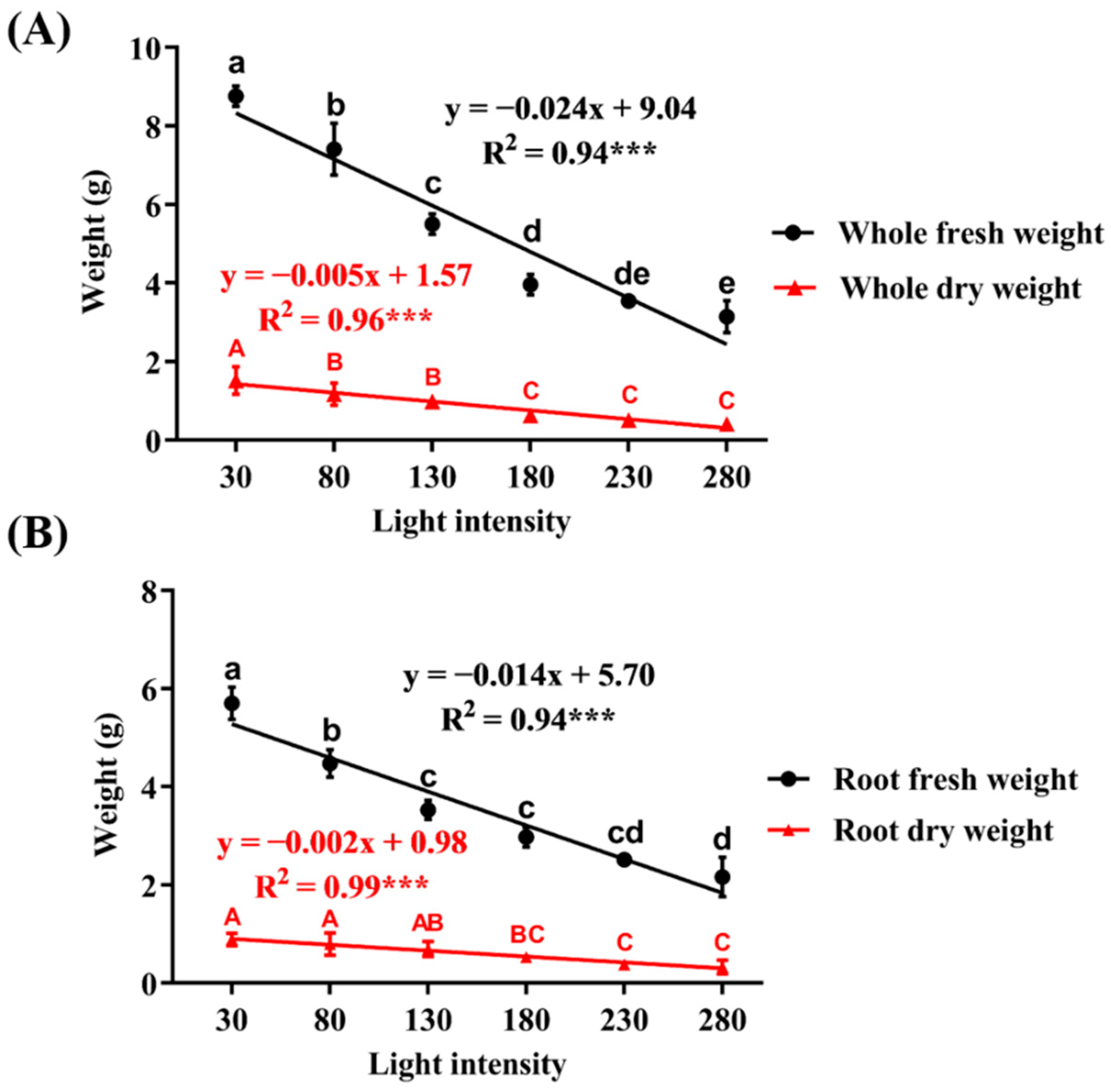
3.2. Fresh Weight and Dry Weight as Affected by Light Intensity
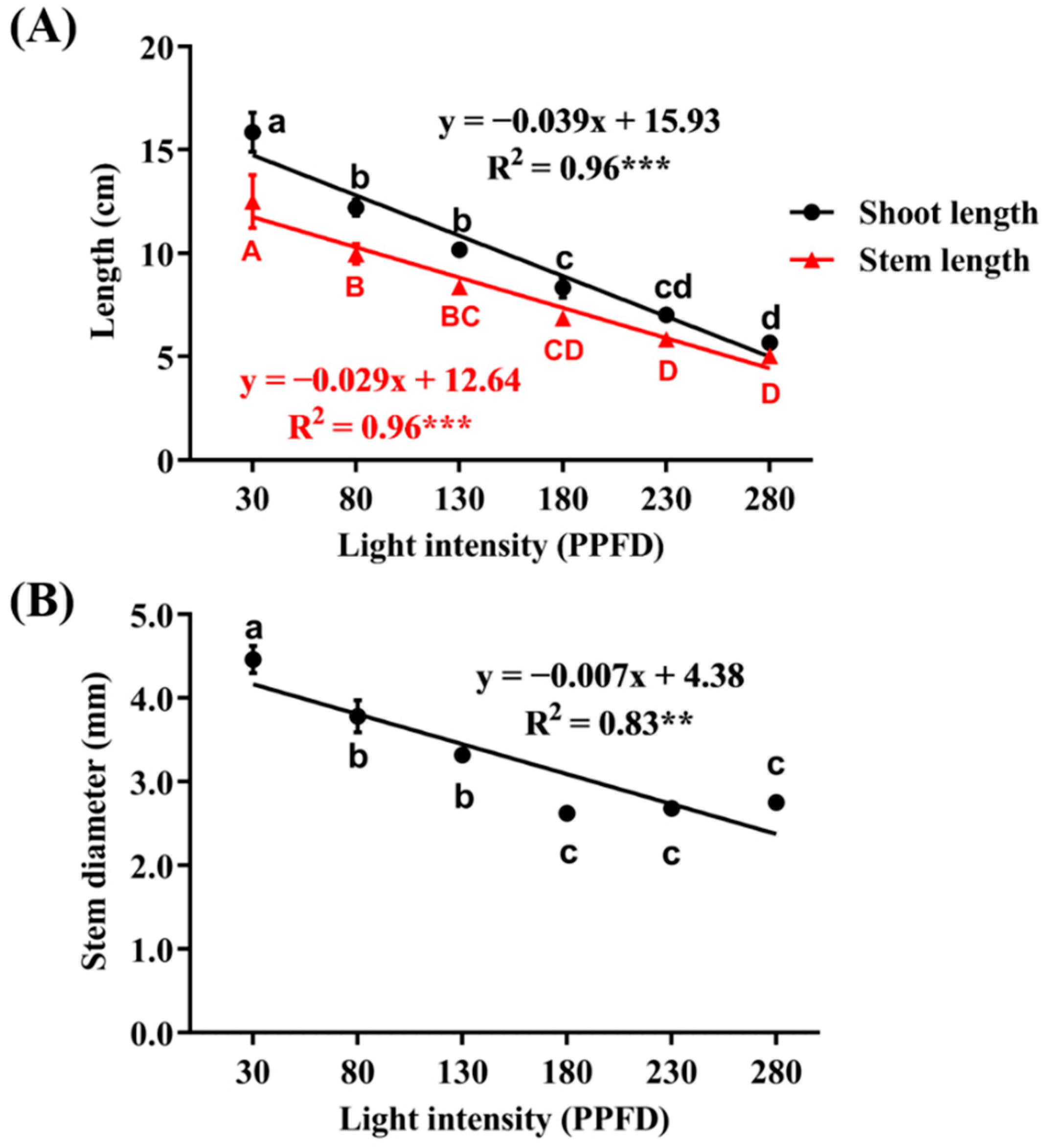
3.3. Shoot Length, Stem Length, and Stem Diameter as Affected by Light Intensity
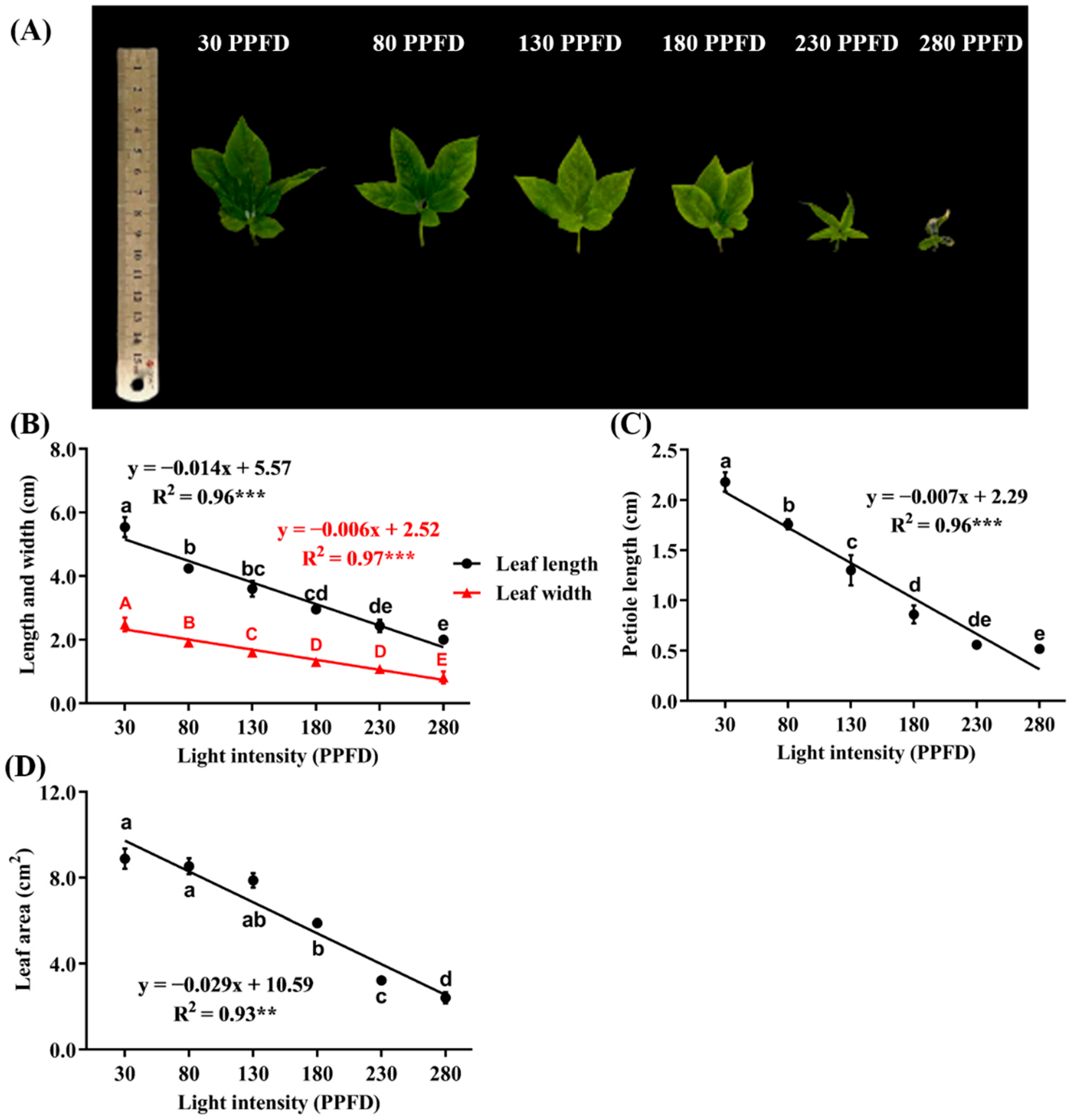
3.4. Leaf-Related Parameters as Affected by Light Intensity
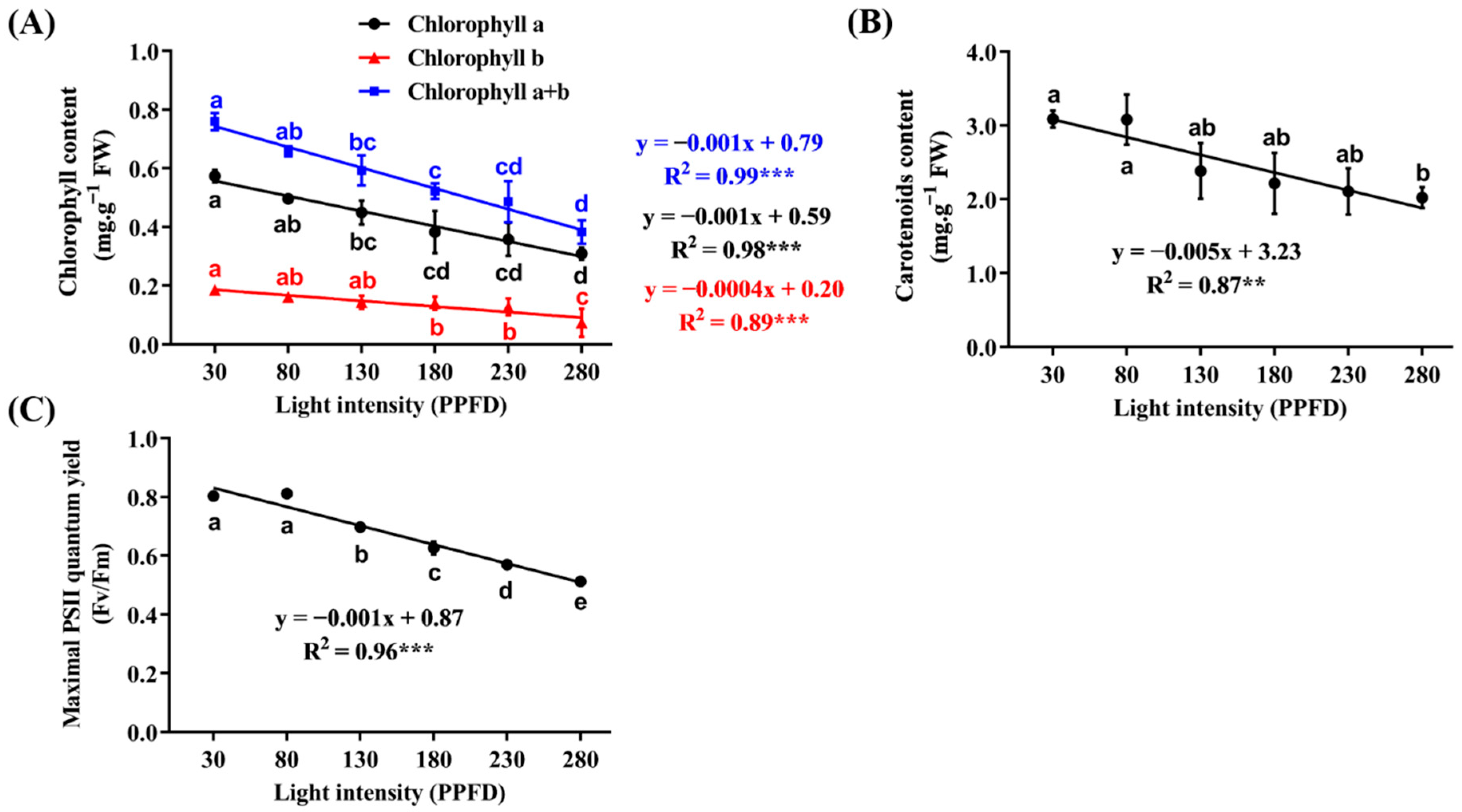
3.5. Photosynthetic Activity as Affected by Light Intensity
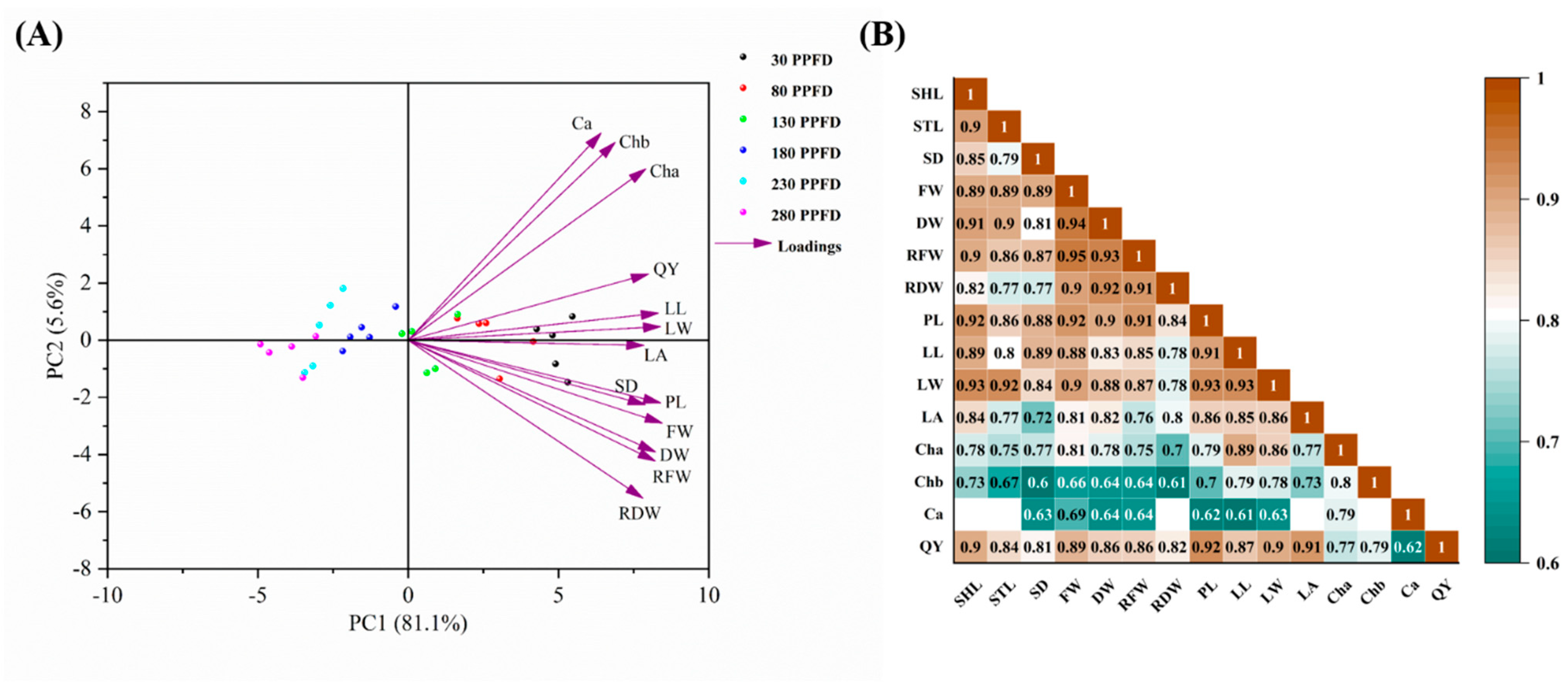
3.6. Multivariate Data Analysis (PCA and Pearson Correlation Analysis) among the Investigated Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth and Morphological Characteristics
4.2. Photosynthetic Characteristics
4.3. Correlations among the Studied Paremeters and Treatments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, M.Y.; Jeon, B.S.; Bock, J.Y. Free, esterified, and insoluble-bound phenolic acids in white and red Korean ginsengs (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer). Food Chem. 2002, 79, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Hwang, I.; Song, J.-Y.; Jee, Y. Acidic polysaccharide of Panax ginseng as a defense against small intestinal damage by whole-body gamma irradiation of mice. Acta Histochem. 2011, 113, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buettner, C.; Yeh, G.Y.; Phillips, R.S.; Mittleman, M.A.; Kaptchuk, T.J. Systematic review of the effects of ginseng on cardiovascular risk factors. Ann. Pharmacother. 2006, 40, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.-S.; Song, J.H.; Choi, P.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Shin, K.-S.; Ham, J.; Kang, K.S. Stimulation of innate immune function by Panax ginseng after heat processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4652–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.-C. Biosynthesis and biotechnological production of ginsenosides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 717–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeg, I.-H.; So, S.-H. The world ginseng market and the ginseng (Korea). J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.-M.; Lim, J.-J.; Ahn, M.-S.; Jeong, H.-N.; An, T.-J.; Kim, S.-H. Comparative phenolic compound profiles and antioxidative activity of the fruit, leaves, and roots of Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) according to cultivation years. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuronuma, T.; Wang, Q.; Ando, M.; Watanabe, H. Effects of Different Light Intensities on the Growth and Accumulation of Photosynthetic Products in Panax ginseng C. A. Meyers. Environ. Control Biol. 2020, 58, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Nguyen, T.K.L.; Oh, M.-M. Growth and ginsenosides content of ginseng sprouts according to LED-based light quality changes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zuo, T.-T.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.-Y.; Yang, W.-Z.; Guo, D.-A. Advances and challenges in ginseng research from 2011 to 2020: The phytochemistry, quality control, metabolism, and biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 875–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Ryu, B.R.; Azad, M.O.K.; Rahman, M.H.; Rana, M.S.; Lim, J.-D.; Lim, Y.-S. Exogenous putrescine enhances salt tolerance and ginsenosides content in Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) sprouts. Plants 2021, 10, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.M.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, D.Y.; Jung, J.G.; Kim, M.J.; Jeong, J.B.; Jang, S.-N.; Lee, G.O.; Sim, H.-S.; Kang, M.J. Comprehensive Comparison of Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Panax ginseng Sprouts by Different Cultivation Systems in a Plant Factory. Plants 2022, 11, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.B.; Yu, J.; Suh, S.J.; Jang, I.B.; Kwon, K.B. Growth and ginsenoside content in different parts of ginseng sprouts depending on harvest time. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 2018, 26, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Kim, S.C.; Seong, J.A.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, D.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, J.G.; Jeong, E.H.; Son, K.-H.; Cho, K.M. Comparison of ginsenoside contents and antioxidant activity according to the size of ginseng sprout has produced in a plant factory. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, N.; Chung, J.-P. High-brightness LEDs—Energy efficient lighting sources and their potential in indoor plant cultivation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, I.-C.; Moon, K.H.; Song, E.Y.; Wi, S.H.; Seo, H.-H.; Moon, Y.E.; Reddy, V.; Yang, J.; Sicher, R.; Oh, S. Growth and physiological responses of Chinese cabbage to different light intensity until leafy head formation. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, I.; Do, G.; Hwang, H.; Suh, S.; Yu, J.; Jang, I.; Moon, J.; Chun, C. Morphological development and photosynthetic acclimation of Panax ginseng seedlings to irradiation by light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2021, 62, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, I.; Olivier, A. The biology and forest cultivation of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) in Canada. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2003, 83, 877–891. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-C.; Li, G.; Jiang, C.; Yang, B.; Yang, H.-J.; Xu, H.-Y.; Huang, L.-Q. Tissue-specific distribution of ginsenosides in different aged ginseng and antioxidant activity of ginseng leaf. Molecules 2014, 19, 17381–17399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskell, J.-A.; Parmenter, G.; Eaton-Rye, J.J. Decreased Hill reaction rates and slow turnover of transitory starch in the obligate shade plant Panax quinquefolius L. (American ginseng). Planta 2002, 215, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rural Development Administration (RDA). Good Agricultural Practice of Ginseng; Revised Ed.; Rural Development Administration: Suwon, Republic of Korea, 2012; pp. 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R. Growth, quality, and nitrogen assimilation in response to high ammonium or nitrate supply in cabbage (Brassica campestris L.) and lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.M.; Johnson, G.; Kiirats, O.; Edwards, G.E. New Fluorescence Parameters for the Determination of QA Redox State and Excitation Energy Fluxes. Photosynth. Res. 2004, 79, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadiq, N.B.; Kwon, H.; Park, N.I.; Hamayun, M.; Jung, J.-H.; Yang, S.-H.; Jang, S.-W.; Kabadayı, S.N.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J. The Impact of Light Wavelength and Darkness on Metabolite Profiling of Korean Ginseng: Evaluating Its Anti-Cancer Potential against MCF-7 and BV-2 Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakodi, M.; Lee, S.-C.; Yang, T.-J. Comparative transcriptome analysis of heat stress responsiveness between two contrasting ginseng cultivars. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-R.; Shi, F.-X.; Zhou, Y.-X.; Li, Y.-L.; Wang, X.-F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.-T.; Liu, B.; Xiao, H.-X.; Li, L.-F. Genetic and epigenetic diversities shed light on domestication of cultivated ginseng (Panax ginseng). Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1612–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, P.; Sun, Z.; Cheng, L.; Han, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, L. LED Light Irradiations Differentially Affect the Physiological Characteristics, Ginsenoside Content, and Expressions of Ginsenoside Biosynthetic Pathway Genes in Panax ginseng. Agriculture 2023, 13, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Pham, M.D.; Cui, M.; Lee, H.; Hwang, H.; Jang, I.; Chun, C. Growth and physiological responses of Panax ginseng seedlings as affected by light intensity and photoperiod. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2022, 63, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-C.; Chae, Q.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kang, Y.-H. Effects of Light and Photosynthetic Electron Transport System on the Generation of Singlet Oxygen (1O2) in Ginseng Thylakoid Membrane. J. Ginseng Res. 1990, 14, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.S. Characteristics of photosynthesis among new cultivars of ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer). J. Ginseng Res. 2002, 26, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, M.H.; Kim, S.I.; Liu, J.R.; Yang, D.C.; Lim, Y.P.; Kwon, K.-H.; Yoo, J.S.; Park, Y.M. Proteomic analysis of Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer). J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 815, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, M.H.; Heo, E.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.I.; Kwon, K.H.; Seo, J.B.; Kwon, O.; Yoo, J.S.; Park, Y.M. Proteome analysis of the responses of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer leaves to high light: Use of electrospray ionization quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry and expressed sequence tag data. Proteomics 2003, 3, 2351–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.H. Transcriptome analysis of Panax ginseng response to high light stress. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 312–320. [Google Scholar]
- Parmenter, G.; Littlejohn, R. Effect of shade on growth and photosynthesis of Panax ginseng. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2000, 28, 255–269. [Google Scholar]
- Proctor, J.; Dorais, M.; Bleiholder, H.; Willis, A.; Hack, H.; Meier, V. Phenological growth stages of North American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius). Ann. Appl. Biol. 2003, 143, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Joo, S.C.; Shi, J.; Hu, C.; Quan, S.; Hu, J.; Sukweenadhi, J.; Mohanan, P.; Yang, D.-C.; Zhang, D. Metabolic dynamics and physiological adaptation of Panax ginseng during development. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Proctor, J.T.; Louttit, D.; Jiao, J. Seasonal growth and root respiration of North American ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 1998, 22, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.-X.; Xu, Z.-G.; Liu, X.-Y.; Tang, C.-M.; Wang, L.-W.; Han, X.-L. Effects of light intensity on the growth and leaf development of young tomato plants grown under a combination of red and blue light. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 153, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Proctor, J.T.; Palmer, J.W.; Follett, J.M. Growth, dry matter partitioning and photosynthesis in North American ginseng seedlings. J. Ginseng Res. 2010, 34, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialet-Chabrand, S.; Matthews, J.S.; Simkin, A.J.; Raines, C.A.; Lawson, T. Importance of fluctuations in light on plant photosynthetic acclimation. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 2163–2179. [Google Scholar]
- Terashima, I.; Hanba, Y.T.; Tazoe, Y.; Vyas, P.; Yano, S. Irradiance and phenotype: Comparative eco-development of sun and shade leaves in relation to photosynthetic CO2 diffusion. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 343–354. [Google Scholar]
- Athanasiou, K.; Dyson, B.C.; Webster, R.E.; Johnson, G.N. Dynamic acclimation of photosynthesis increases plant fitness in changing environments. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kono, M.; Terashima, I. Long-term and short-term responses of the photosynthetic electron transport to fluctuating light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 137, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, W.E. The relation between chlorophyll content and rate of photosynthesis. J. Gen. Physiol. 1935, 18, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttery, B.; Buzzell, R. The relationship between chlorophyll content and rate of photosynthesis in soybeans. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1977, 57, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R. Root GS and NADH-GDH play important roles in enhancing the ammonium tolerance in three bedding plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1061. [Google Scholar]
- Sathasivam, R.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. An update on biosynthesis and regulation of carotenoids in plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 140, 290–302. [Google Scholar]
- Demmig-Adams, B.; Gilmore, A.M.; Iii, W.W.A. In vivo functions of carotenoids in higher plants. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Maltsev, Y.; Maltseva, K.; Kulikovskiy, M.; Maltseva, S. Influence of light conditions on microalgae growth and content of lipids, carotenoids, and fatty acid composition. Biology 2021, 10, 1060. [Google Scholar]
- Demmig-Adams, B.; ADAMS III, W. Carotenoid composition in sun and shade leaves of plants with different life forms. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Öquist, G.; Chow, W. On the relationship between the quantum yield of Photosystem II electron transport, as determined by chlorophyll fluorescence and the quantum yield of CO2-dependent O2 evolution. Photosynth. Res. 1992, 33, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janka, E.; Körner, O.; Rosenqvist, E.; Ottosen, C.-O. Using the quantum yields of photosystem II and the rate of net photosynthesis to monitor high irradiance and temperature stress in chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflora). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, A.I.; Rafudeen, M.S.; Gomaa, A.M.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Exogenous melatonin enhances the reactive oxygen species metabolism, antioxidant defense-related gene expression, and photosynthetic capacity of Phaseolus vulgaris L. to confer salt stress tolerance. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 173, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R. Difference between Day and Night Temperature (DIF) and Light Intensity Affect Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Panax ginseng Meyer Sprouts. Plants 2023, 12, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, J.Y.; Xiao, X.Y.; Lin, R.C.; Cheng, Y.Y. Simultaneous determination of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng with different growth ages using high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. PCA 2006, 17, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R. Growth and Photosynthetic Responses to Increased LED Light Intensity in Korean Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) Sprouts. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092375
Song J, Yang J, Jeong BR. Growth and Photosynthetic Responses to Increased LED Light Intensity in Korean Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) Sprouts. Agronomy. 2023; 13(9):2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092375
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jinnan, Jingli Yang, and Byoung Ryong Jeong. 2023. "Growth and Photosynthetic Responses to Increased LED Light Intensity in Korean Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) Sprouts" Agronomy 13, no. 9: 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092375
APA StyleSong, J., Yang, J., & Jeong, B. R. (2023). Growth and Photosynthetic Responses to Increased LED Light Intensity in Korean Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) Sprouts. Agronomy, 13(9), 2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092375








