Abstract
Screening the edible parts of low-cadmium (Cd) and high-nutrient crop cultivars is an effective method for reducing Cd intake and enhancing the absorption of beneficial elements for humans. In a hydroponic experiment with Cd toxicity treatment (5 μmol/L CdCl2), we analyzed the differences in the absorption and transport characteristics of Cd and mineral nutrients in 30 rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) cultivars during the seedling stage, as well as the correlations between various elements. Firstly, Pearson correlation analysis indicated that Cd content in the shoot parts of 30 rapeseed cultivars was not correlated with the Cd uptake ability of the roots and was obviously positively correlated with the Cd translocation coefficient from root to shoot (r = 0.452 *, p < 0.05). Hierarchical clustering selected 26 cultivars with lower Cd content in the shoots, and correlation analysis of Cd and other nutrient element contents in the shoots of the 26 cultivars revealed significant negative correlations (r = −0.40 *, p < 0.05; r = −0.45 *, p < 0.05) between iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg) content and Cd content, while potassium (K), calcium (Ca), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn) content had no correlation with Cd content. Then, hierarchical clustering screened 19 cultivars with higher dry weight, 4 cultivars with higher K content, 1 cultivar with higher Ca content, 8 cultivars with higher Mn content, and 3 cultivars with higher Zn content. Finally, a Venn diagram identified four superior rapeseed cultivars with lower Cd and higher nutrients in the shoots, namely, OJ114 (lower Cd, higher Mn and K content), BN365 (lower Cd, higher Mn, Fe, and Zn content), BN275 (lower Cd, higher Ca, Zn, Mn, and Fe content), and BN112 (lower Cd, higher K, Mg, Fe, and Mn content).
1. Introduction
Cadmium (Cd) is one of the important heavy metal elements widely distributed in the natural environment with strong biological toxicity [1]. With the advancement of society and the continuous development of industry and agriculture, the problem of Cd pollution is becoming increasingly prominent. The area of Cd-contaminated soil and the yield of Cd-exceeded agricultural product are showing an increasing trend year by year. As the primary pollutant affecting the quality of agricultural land soil, Cd is readily absorbed by crops with high water solubility. It can cause leaf chlorosis and withering in plants, obstructs photosynthesis, and causes oxidative stress within cells and internal tissue structural damage, thereby inhibiting crop growth and development, and impacting the safety and quality of agricultural products [2,3,4,5,6]. Simultaneously, the issue of soil Cd pollution poses a significant threat to the “safety of every bite of food” that humans take and has become a global focus of attention. The accumulation of Cd in the human body irreversibly damages the kidneys, liver, bones, reproductive system, blood system, and nervous system [7], leading to bone pain, diabetes, emphysema, hypertension, and even cancer in severe cases [8]. The United Nations Environment Programme also lists Cd as the foremost hazardous substance among the 12 globally hazardous substances [9]. The human body can ingest Cd through respiration, diet, skin contact, daily necessities, etc., and ingestion of crops is the main way for Cd to accumulate in the human body. Therefore, reducing the Cd content in the edible parts of crops not only directly promotes crop growth and increases crop yield but also indirectly reduces human Cd intake and maintains food safety and human health. Selecting and cultivating advantageous crop cultivars with high Cd tolerance or low Cd content in the edible parts has become an effective approach to safeguarding crop yield and quality, and reducing Cd intake risk [10,11].
Inadequate ingestion of mineral nutrients, especially trace elements, is also a widespread issue harming human health. According to surveys, approximately 60% and 30% of the world’s population suffer from iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn) deficiencies, respectively, and insufficient calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and manganese (Mn) for humans is also very common in developing countries [12]. Crops, including grains, fruits, and vegetables, contain a cultivar of mineral nutrients and are a good source of the mineral elements needed by the human body. Crop cultivars with high nutritional value should possess greater capability to absorb mineral elements and transport them to the edible parts. Currently, many studies are dedicated to selecting crop cultivars rich in mineral nutrients such as Fe, Zn, Mg, and selenium (Se) [13,14]. Moreover, it has been proved that mineral nutrients can effective alleviate the damage of Cd to crops and minimize the entry of Cd into the food chain [15,16], while the internal interaction between Cd and mineral nutrients remains unknown.
As one of the extensively cultivated crops in China, rapeseed has the characteristics of short growth cycle and strong adaptability to environmental stress [17]. Rapeseed not only is an important oilseed crop in China but also is widely consumed as a popular vegetable due to its delicious taste and ability to balance the intake of various trace elements [18]. Furthermore, rapeseed also can be used as green storage feed, contributing to the development of animal husbandry. Thus, higher yield, lower pollutants, and higher mineral nutrients in the edible parts of rapeseed are very important for human health and the development of the rapeseed industry. Currently, studies on the selection of high-quality rapeseed cultivars have made certain progress, but the emphasis has been more on selecting cultivars with high yield, high nutrient utilization efficiency, strong stress resistance, or low heavy metal accumulation [19,20,21]. Although there are reports on the differences in the absorption and transportation characteristics of Cd and mineral elements of different crop cultivars [14,22], few studies have aimed to screen rapeseed cultivars with lower Cd and higher nutrient elements in edible organs. Screening the rapeseed cultivars with low Cd and high mineral nutrient content in the edible parts and revealing the influencing mechanism of Cd and crop cultivars and mineral elements are of great significance for ensuring the yield and quality of oil crops, food safety, and human health.
Therefore, a hydroponic experiment was conducted to explore the difference in Cd absorption and translocation between 30 rapeseed cultivars, as well as the interaction between Cd and other elements. Furthermore, advantageous rapeseed cultivars with low Cd and high nutrient elements were screened basing on the Cd content in the edible shoot parts, dry biomass weight, and nutrient element content. This study provides a theoretical basis and technical support for the high-quality and efficient production of rapeseed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
This experiment was conducted in a completely randomized design in the artificial climate chamber at Qingdao Agricultural University. Fully matured rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) seeds of 30 cultivars provided by Hunan Agricultural University (Table 1) were selected and soaked in 75% ethanol for 15 min in a 10 mL centrifuge tube. They were then washed 3 times with deionized water to remove the ethanol. After adding an appropriate amount of deionized water, the seeds were incubated and shaken at 37 °C at 200 rpm for 6 h to break dormancy and then were evenly sown in gauze. The gauze with seeds was fixed to the upper part of the seedling tray and distilled water was added to the tray to ensure the seeds were soaked. The trays were kept in a dark environment at 25–28 °C for 7 d until two true leaves fully expanded. Seedlings with consistent growth in the shoot and root parts were selected and transferred to 10 L black polyethylene boxes. The purpose was to screen rapeseed cultivars with lower Cd content and higher nutrient element content in the aboveground parts, so only Cd stress treatment (5 μmol/L CdCl2) was set up in this experiment. Each rapeseed cultivar included 10 seedlings as 10 biological replicates. The nutrient solution, consisting of macroelements and trace elements, was provided using the formulas of Hoagland and Arnon nutrient solutions [23]: Ca(NO3)2·4H2O (5.0 mmol/L), KNO3 (5.0 mmol/L), KH2PO4 (1.0 mmol/L), MgSO4 (2.0 mmol/L), EDTA-Fe (0.05 mmol/L), H3BO3 (46 × 10−3 μmol/L), MnCl2 (9 × 10−3 μmol/L), ZnSO4 (0.8 × 10−3 μmol/L), CuSO4 (3.2 × 10−3 μmol/L), Na2MoO4 (0.37 × 10−3 μmol/L). The nutrient solution was changed every 5 d, starting from 1/4 concentration and increasing to 1/2 concentration until the full-strength nutrient solution was used. After culturing at Cd-free solution of 1/4 concentration and 1/2 concentration for 10 d, all seedlings were transferred to solution of Cd treatment (5 μmol/L CdCl2).

Table 1.
Labels of corresponding rapeseed cultivar.
After being treated with 5 μmol/L CdCl2 for 5 d, the leaf chlorosis with different degrees was observed in different rapeseed cultivars. The plants were grown for a total of 22 d in a greenhouse with a light intensity of 300–320 μmol m−2 s−1, a daytime/nighttime temperature of 25 °C/22 °C, and a light/dark photoperiod of 16 h/8 h [24].
2.2. Measurement Items and Methods
2.2.1. Determination of Dry Matter Accumulation in Rapeseed
After 5 d of Cd treatment, the rapeseed seedlings were separated into roots and shoot parts. After washing with deionized water, they were fully dried in an oven at 75 °C. The dried root and shoot samples were then weighed using a precision balance to determine the dry weight of different plant parts of different cultivars.
2.2.2. Determination of Nutrient Element Content in Different Parts of Rapeseed
The dried samples were ground into fine powder and 0.10 g of the powdered sample was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid (HNO3). After digesting in a water bath for 2 h at 100 °C, the samples were diluted and filtered. Then, the content of Cd, Fe, Mn, K, Zn, Ca, etc. was measured using an Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer (ICP-MS; PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.2.3. Absorption and Translocation Capacity to Cd of Rapeseed
The absorption of Cd per unit root (μg·g−1) = [Cd content in shoot (μg·g−1) × dry weight of shoot (g) + Cd content in root (μg·g−1) × dry weight of root (g)]/dry weight of root (g).
The Cd translocation coefficient = Cd content in shoot (μg·g−1)/Cd content in root (μg·g−1) [14].
2.3. Data Analysis
The experimental data were processed and analyzed using Excel 2016, SPSS 18.0, and visualizations were created using Origin 2021. The relationship between variables was determined through Pearson correlation analysis. Clustering analysis was performed using the Euclidean distance and Ward’s linkage method, and the vertical axis and horizontal axis of the tree chart represented the content level of different elements and the name of different rapeseed cultivars, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Plant Biomass among Different Rapeseed Cultivars
At the 5 μM Cd treatment level, significant differences in the dry biomass of shoot and root systems were observed between different rapeseed cultivars (Figure 1). The dry biomass of the shoot parts of rapeseed ranged from 0.052 g·plant−1 in S2 (BN170) to 0.124 g·plant−1 in S3 (BN275), with an average of 0.086 g·plant−1 (Figure 1a). The dry biomass of roots ranged from 0.003 g·plant−1 in S9 (BN017) to 0.010 g·plant−1 in S3 (LV35), with an average of 0.006 g·plant−1 (Figure 1b). Comprehensive analysis of shoot and root dry weight revealed that S18, S26, S30, S5, and S3 (QW343, OJ114, LV35, BN269, and BN275) were more tolerant to Cd toxicity, while S11, S12, S24, and S7 (BN085, BN129, ZQ484, BN219) were more sensitive to Cd toxicity. The differences in biomass among different cultivars of rapeseed may be due to variations in genetic characteristics or Cd absorption and transport characteristics between cultivars.
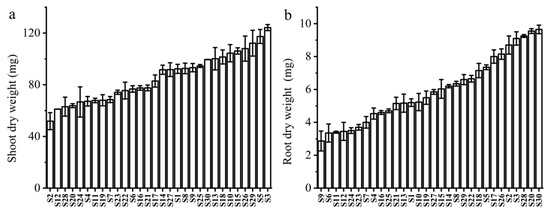
Figure 1.
Dry weights of different cultivars of rapeseed shoots (a) and roots (b) measured after 5 days with 5 μmol/L Cd concentration.
3.2. Variations in Cd Uptake and Transportation among Different Rapeseed Cultivars
The Cd content in the shoots and roots (on a dry weight basis) both showed obvious difference between the 30 different cultivars. The variation in Cd content in the shoots ranged from 49.36 μg·g−1 for S15 (BN067) to 146.44 μg·g−1 for S30 (LV35), with an average level of 93.63 μg·g−1. And the Cd content in the shoots of high-Cd cultivar was 2.97 times that of the low-Cd cultivar (Figure 2a). The range of Cd content in the roots of different rapeseed cultivars varies from 734.74 μg·g−1 (S15: BN067) to 3306.87 μg·g−1 (S24: ZQ484), and the Cd content in the roots of high-Cd cultivar was 4.51 times that of the low-Cd cultivar (Figure 2b).
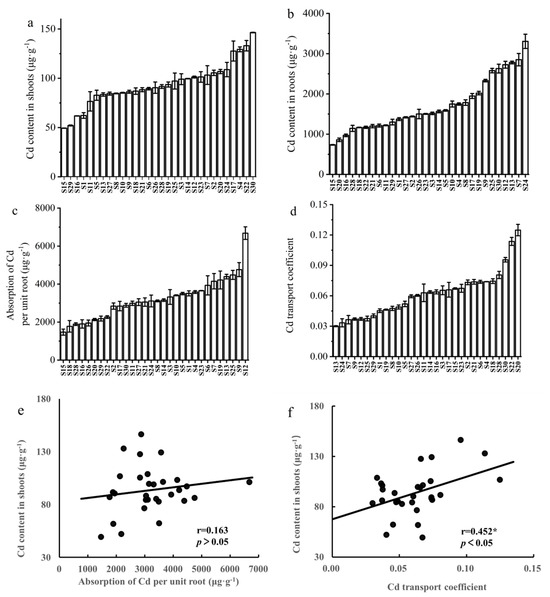
Figure 2.
Cadmium content in shoots (a) and roots (b), the absorption of Cd per unit root (c), and transport coefficient (d) of different rapeseed cultivars; the correlation between Cd content in shoots and the absorption of Cd per unit root (e) and transport coefficient (f) of 15-day rapeseed seedlings. * indicates significant difference at p < 0.05.
The differences in Cd content in the shoots are mainly due to the plant’s ability to absorb Cd by the roots and Cd transport from the roots to the shoots. The Cd absorption capacity of the plant’s roots was reflected by the Cd absorption amount per unit root. The Cd transport coefficient, the ratio of shoot Cd content to root Cd content, was used to evaluate the plant’s ability to transport Cd from the roots to the shoots. The results indicated significant differences in the Cd absorption capacity and the Cd transport capacity among the 30 rapeseed cultivars (Figure 2c,d). Further analysis of the correlation between shoot Cd content and Cd absorption per unit root, as well as the correlation between shoot Cd content and Cd transport coefficient, of the 30 rapeseed cultivars (Figure 2e,f) clarified the relationship between the shoot Cd content and Cd absorption and transport capacity among different rapeseed cultivars. The results showed no remarkable correlation between shoot Cd content and the root’s ability to absorb Cd (r = 0.163, p > 0.05), and a significant positive correlation between shoot Cd content and the Cd transport coefficient (r = 0.452 *, p < 0.05), suggesting that the difference in shoot Cd content among different rapeseed cultivars primarily depended on the varying Cd translocation ability.
3.3. Selection of Rapeseed Cultivars with Low Cd and High Nutritional Element Content
To select the advantageous rapeseed cultivars with low Cd content in the shoots, hierarchical cluster analysis was conducted and the Euclidean distance and Ward’s method were used to quantitatively classify the Cd content in the shoots of 30 different rapeseed cultivars into two major clusters: 4 high-Cd and 26 low-Cd rapeseed cultivars (Figure 3a). The shoot Cd content range of the 4 rapeseed cultivars was 127.62–146.44 μg·g−1 and the shoot Cd content of the 26 cultivars with low shoot Cd content ranged from 49.36 to 112.52 μg·g−1. Cluster analysis of the dry weight of the shoots divided the 26 low-Cd cultivars into two clusters: 19 cultivars with higher dry matter and 7 cultivars with lower dry matter (Figure 3b). The correlation analysis of dry matter accumulation and Cd content in the shoots of 26 rapeseed cultivars indicated a significant negative correlation between shoot dry weight and Cd content in the shoots (Figure 3c), indicating that Cd toxicity inhibited dry mass accumulation in the shoots.
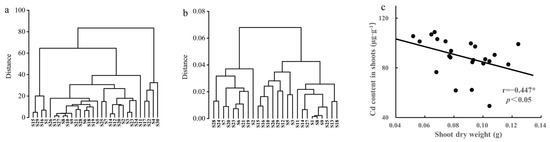
Figure 3.
Cluster of Cd content in shoots of 30 rapeseed cultivars (a), dry weight of 26 cultivars (b), and correlation between aboveground cadmium content and biomass dry weight of 26 rapeseed cultivars (c). * indicates significant difference at p < 0.05.
The rapeseed cultivars with low Cd and high nutritional elements in the edible shoot parts are more advantageous for agricultural production and human health. This study explored the relationship between shoot Cd content and other nutritional elements by conducting a correlation analysis of Cd, Mg, K, Ca, Fe, Mn, and Zn content in 26 low-Cd rapeseed cultivars (Figure 4a). The results suggested that Fe and Mg content had a significant negative correlation with Cd content (r = −0.40 *, p < 0.05; r = −0.45 *, p < 0.05). However, the correlation between K, Ca, Mn, Zn, and Cd content in the shoots was not significant. Therefore, among the selected 26 low-Cd cultivars, it was possible to identify cultivars with both low Cd content and high nutritional elements in edible shoots.
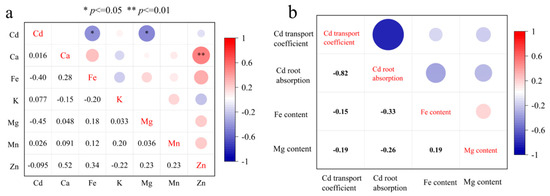
Figure 4.
Correlation of various nutritional elements in shoots of 26 different cultivars of rapeseed (a); the correlation between transport coefficient, root cadmium absorption, and iron and magnesium content (b).
Further correlation analysis of the shoot Fe and Mg content with the root’s ability to absorb and translocate Cd revealed that the difference in Fe and Mg content among cultivars had no obvious relationship with Cd absorbed by roots and the transport coefficient of Cd (Figure 4b), suggesting that the difference in Cd absorption and transport capacity was not the primary cause of the differences in Fe and Mg content among cultivars.
According to the hierarchical clustering analysis of K, Ca, Mn, and Zn content in the shoots, 4 cultivars with higher K content S11, S12, S13, and S26 (BN085, BN129, BN112, and OJ114), 1 cultivar with higher Ca content (S3: BN275), 8 cultivars with higher Mn content (S26: OJ114, S13: BN112, S3: BN275, S5: BN269, S18: QW343, S6: BN141, S19: QW303, and S1: BN365), and 3 cultivars (S3: BN275, S1: BN365, and S28: OJ117) with higher Zn content were further selected from 26 low-Cd rapeseed cultivars (Figure 5).
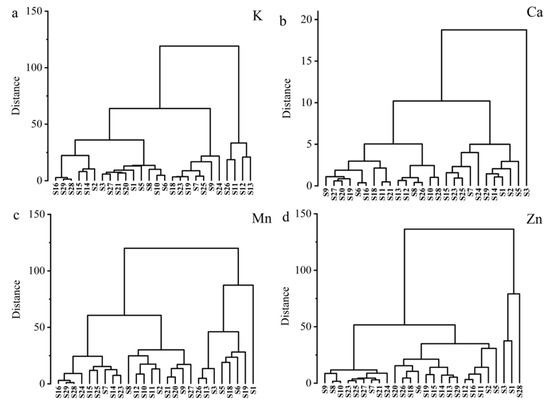
Figure 5.
Cluster analyses of K (a), Ca (b), Mn (c), and Zn (d) in shoots of 26 rapeseed cultivars.
A Venn diagram was further utilized to analyze the 19 cultivars with higher dry matter accumulation, 4 cultivars with higher K content, 1 cultivar with higher Ca content, 8 cultivars with higher Mn content, and 3 cultivars with higher Zn content in the shoots (Figure 6). As a result, S26 (OJ114) and S13 (BN112) were identified as cultivars with higher dry biomass, K and Mn. S1 (BN365) was identified as a cultivar with higher dry biomass, Mn and Zn, and S3 (BN275) was identified as a cultivar with higher dry biomass, Ca, Mn, and Zn.
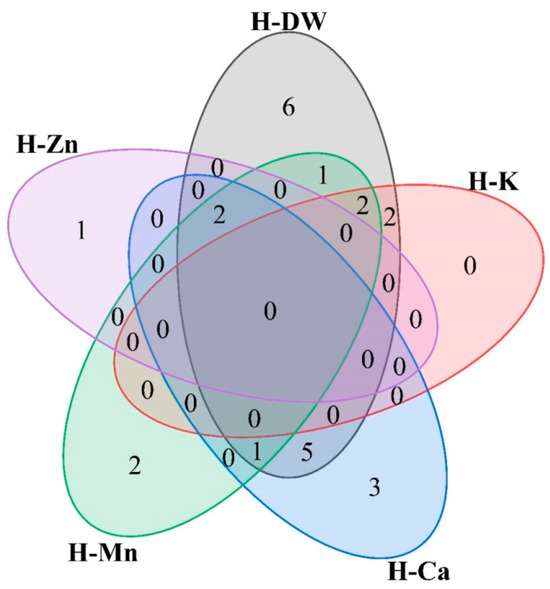
Figure 6.
Venn diagram of different advantageous cultivar groups from 26 rapeseed cultivars with lower Cd content in shoots. The five ellipses represent rapeseed cultivars with five characteristics. H-K represents high K content cultivars, H-DW represents high dry weight cultivars, H-Ca represents high Ca content cultivars, H-Mn represents high Mn content cultivars, H-Zn represents high Zn content cultivars.
The correlation analysis of shoot Cd and different nutrient element content showed a significant negative correlation between Cd and Fe, as well as Mg. Hierarchical cluster analysis of the Fe and Mg content in the 26 lower Cd rapeseed cultivars revealed that BN365 and BN275 were cultivars with higher Fe, while BN112 was a cultivar with higher Fe and Mg content (Figure 7).
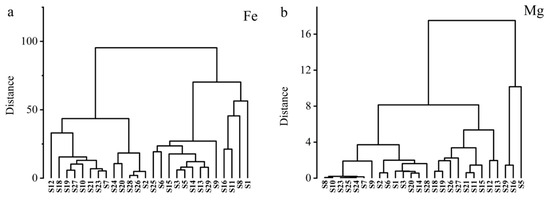
Figure 7.
Cluster analyses of aboveground Fe (a) and Mg (b) content in 26 low-Cd rapeseed cultivars.
Taking into account the analysis results of Figure 6 and Figure 7, four superior rapeseed cultivars were selected: OJ114—a cultivar with lower Cd, higher Mn and K content; BN112—a cultivar with lower Cd, higher K, Mg, Fe, and Mn content; BN365—a cultivar with lower Cd, higher Mg, Fe, and Zn content; and BN275—a cultivar with lower Cd, higher Ca, Mg, Fe, and Zn content.
4. Discussion
Rapeseed is not only a main oilseed crop but also a vegetable crop and green storage forage [18]. Screening and breeding healthy and nutritious rapeseed cultivars are very important to ensure the healthy development of the rapeseed industry and the culinary safety of humans. Cadmium is considered the primary pollutant affecting the quality of agricultural soil. Reducing the unit Cd content in the edible parts of rapeseed is an effective measure to reduce human and livestock Cd intake, thereby ensuring food safety [25]. For crops, the Cd content in the shoots is related to multiple factors, and the ability of roots to absorb Cd and the transport coefficient of Cd into the shoot parts is generally considered to be the main factor affecting the shoot Cd content [26,27]. Research on different maize cultivars has shown that the shoot Cd content is significantly correlated with both root Cd absorption and Cd translocation coefficient [14]. In the present study, although the 30 different rapeseed cultivars showed significant differences in absorption and transport Cd capacity, the shoot Cd content was only significantly positively correlated with the Cd translocation coefficient (r = 0.452 *, p < 0.05) (Figure 2f). The results indicated that the difference in shoot Cd content among the 30 rapeseed cultivars mainly depended on the varying ability to transport Cd from roots to shoots.
Based on the accumulation of Cd in crop leaves or seeds, numerous studies have screened out multiple low-Cd cultivars [11,24,28] and have revealed the intrinsic mechanisms underlying low Cd absorption and translocation [11,24,29]. However, there is limited research on the differences in mineral element content among different rapeseed cultivars [30], especially screening cultivars with low Cd and high mineral nutrients in the edible parts due to the complexity of the relationship between Cd and mineral nutrients. Mineral elements are essential nutrients for plant growth and development, and are also crucial for human health. The human body mainly supplements the necessary nutrients through food intake, and a monotonous diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies [31]. Therefore, a rapeseed cultivar with lower Cd and higher mineral element content has greater significance for promoting cultivation. Firstly, 26 low-Cd rapeseed cultivars were selected from 30 cultivars based on the Cd content in the shoots. And then, the analysis of the shoot mineral element content of the 26 low-Cd rapeseed cultivars revealed significant inter-cultivar differences in K, Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, and Zn content in the shoots (Figure 4a), which may be due to the influence of Cd on the absorption and transport of mineral elements, or may be determined by the genetic characteristics of different rapeseed cultivars. The absorption of Cd2+ by roots utilizes ion carriers or channels such as Fe2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, and Ca2+ [32,33], while the upward translocation of Cd2+ relies on transport proteins for Ca2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+ [34,35,36]. Thus, there is a competitive relationship between Cd2+ and Fe2+, Zn2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, and Ca2+, that is, Cd inhibits the absorption and transport of these nutrients [37,38]; in turn, Fe2+, Mn2+, and Ca2+ significantly reduce Cd accumulation in plant tissues [39,40] due to heavy metal P1B-ATPases (HMAs) elucidating competitive interaction in metal transport between Cd and mineral elements in plants [17]. The correlation analysis of the shoot Cd, K, Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, and Zn content revealed a significant negative correlation between Cd and Fe and Mg content but a weak correlation with other elements (Figure 4a). While further analysis showed that the differences in shoot Fe and Mg content in different rapeseed cultivars were not related to the absorption and translocation of Cd (Figure 4b). Therefore, it was speculated that the differences in the content of various nutritional elements in different rapeseed cultivar shoots were determined by the genetic characteristics of the cultivars instead of being greatly influenced by Cd’s absorption and translocation.
The ability of plants to absorb and transport nutrients is jointly determined by the growth stage, nutrient level, and genetic characteristics, etc. [41,42,43]. Although the ability to absorb Cd for different crops varies during different growth stages, the research on 12 wheat cultivars has reported that the distribution of Cd and arsenic in roots at the seedling stage was consistent with the pattern at the mature stage [44]. Deng et al. (2019) also studied the Cd enrichment and translocation characteristics of six maize cultivars with different Cd accumulation and found consistent inter-cultivar differences in Cd in roots, stems, and grains at the tasseling and mature stages [45]. Simplified selection based on simple indicators during the seedling stage can improve crop cultivar selection efficiency. Further hierarchical cluster analysis and a Venn diagram were used to identify four advantageous cultivars (OJ114: lower Cd, higher Mn and K in shoots; BN112: lower Cd, higher K, Mg, Fe, and Mn in shoots; BN365: lower Cd, higher Mg, Fe, and Zn in shoots; BN275: lower Cd, higher Ca, Mg, Fe, and Zn in shoots) from 30 rapeseed cultivars (Figure 5 and Figure 6). Rapeseed is highly sensitive to different soil Cd levels, and maybe the physiological response, and the absorption and transportation of different elements in rapeseed varied under different soil Cd conditions. Therefore, although the results of the seedling stage screening provide a certain reference value, they may not completely predict the absorption and translocation of Cd and other elements throughout the entire growth period. The screened rapeseed cultivars with lower Cd and higher nutrients in the shoots need to be further validated in field experiments under different Cd conditions.
5. Conclusions
In this study, significant differences in the absorption and transportation abilities of Cd were observed among 30 rapeseed cultivars. And among the 30 cultivars, the difference in the Cd content in the shoots was mainly determined by Cd root–shoot transportation (r = 0.452 *, p < 0.05), while it was not highly correlated with the root’s ability to absorb Cd. Moreover, Fe and Mg content had a significant negative correlation with Cd content (r = −0.40 *, p < 0.05; r = −0.45 *, p < 0.05), while no correlation between K, Ca, Mn, Zn, and Cd content in the shoots was detected. Through comprehensive analysis of the content of Cd and other nutrient elements in the shoots, four low-Cd and high-nutrient element rapeseed cultivars were selected from 30 rapeseed cultivars. Among the four cultivars, OJ114 has lower Cd but higher Mn and K content in the shoots; BN112 has lower Cd but higher K, Mg, Fe, and Mn content in the shoots; BN365 has lower Cd but higher Mg, Fe, and Zn content in the shoots; and BN275 has lower Cd but higher Ca, Mg, Fe, and Zn content in the shoots. Although the absorption and transport characteristics of various elements during the seedling stage are beneficial to quickly screen low-Cd and high-nutrient element rapeseed cultivars to a certain extent, it is essential to study the field performance of the advantageous cultivars in different soil with varying Cd level. The results provide technical support for screening rapeseed cultivars with high-quality and efficient production.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to this study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by X.T. and H.Z. The first draft of the manuscript was written by X.W. and H.T. The manuscript was revised and polished by G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR202102190565), and the Start-up Fund for Introduced Talent of Qingdao Agricultural University (1121013).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest financial or otherwise.
References
- Peralta-Videa, J.; Zhao, L.; Lopez-Moreno, M.; de la Rosa, G.; Hong, J.; Gardea-Torresdey, J. Nanomaterials and the environment: A review for the biennium 2008–2010. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Niazi, N.; Antunes, M. Cadmium bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. Vol. 2017, 241, 73–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ronzan, M.; Piacentini, D.; Fattorini, L.; Della Rovere, F.; Eiche, E.; Riemann, M.; Falasca, G. Cadmium and arsenic affect root development in Oryza sativa L. negatively interacting with auxin. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 151, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, H.; Guan, C.; Zhang, Z. Boron alleviates cadmium toxicity in Brassica napus by promoting the chelation of cadmium onto the root cell wall components. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, H.; Guan, C.; Zhang, Z. Boron mitigates cadmium toxicity to rapeseed (Brassica napus) shoots by relieving oxidative stress and enhancing cadmium chelation onto cell walls. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Tian, H.; Tang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, G.; Wu, X. NPs-Ca promotes Cd accumulation and enhances Cd tolerance of rapeseed shoots by affecting Cd transfer and Cd fixation in pectin. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 140001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Cai, L.; Li, S. Advances in soil cadmium pollution remediation methods and bioremediation research. Environ. Dev. 2014, 3, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, D.; Yamaji, N.; Kono, I.; Huang, C.F.; Ando, T.; Yano, M.; Ma, J. Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16500–16505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fan, C.; Li, X.; Huang, J. Breeding strategies for improving the yield and quality of oilseed crops: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4482. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Tang, T.; Song, H.; Guan, C.; Huang, J.; Hua, Y. A multiomics approach reveals the pivotal role of subcellular reallocation in determining rapeseed resistance to cadmium toxicity. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5437–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.; Broadley, M. Biofortification of crops with seven mineral elements often lacking in human diets–iron, zinc, copper, calcium, magnesium, selenium and iodine. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 49–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; An, D. Screening and identification of wild diploid wheat and its progeny with enriched micronutrient germplasm resources. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2011, 19, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Wan, Y. Uptake and transport characteristics of cadmium and nutrients in different cultivars of maize (Zea mays) at seedling stage. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 744–753. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Li, R.; Lu, Y.; Bai, Z. Sustainable management of cadmium-contaminated soils as affected by exogenous application of nutrients: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113081–113095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Yu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Ping, Z.; Xiao, Z. Transcriptional analysis of heavy metal P1B-ATPases (HMAs) elucidates competitive interaction in metal transport between cadmium and mineral elements in rice plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 287–297. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R. China’s grain and oil production, sales, and import and export situation. China Oils Fats 2022, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, P.; Cheng, Y.; Feng, L.; Fu, G.; Zhang, X. Relationship among yield components and selection criteria for yield improvement in early rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Dar, Z.; Dar, S. Breeding strategies for improving rice yield—A review. Agric. Sci. 2015, 6, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schiessl, S.; Quezada-Martinez, D.; Orantes-Bonilla, M.; Snowdon, R. Transcriptomics reveal high regulatory diversity of drought tolerance strategies in a biennial oil crop. Plant Sci. 2020, 297, 110515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, Z.; Pogoda, C.; Reinert, S.; Kane, N.; Hulke, B. Breeding for sustainable oilseed crop yield and quality in a changing climate. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, X. Differences in plant growth, Cd and nutrient uptake, Cd translocation between two tobacco cultivars under Cd stress. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland, D.; Arnon, D. The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. Circ. 1950, 347, 357–359. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Tian, H.; Li, L.; Guan, C.; Zhang, Z. Higher Cd-accumulating oilseed rape has stronger Cd tolerance due to stronger Cd fixation in pectin and hemicellulose and higher Cd chelation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, H.; Guo, Z.; Shi, L.; Feng, W.; Xiao, X.; Peng, C. Effects of mixed amendments on the phytoavailability of cd in contaminated paddy soil under a rice-rape rotation system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14128–14136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, D.; Xue, R.; Long, J.; Lin, X.; Lin, Y.; Jia, L.; Zeng, R.; Song, Y. Effects of boron, silicon and their interactions on cadmium accumulation and toxicity in rice plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 267, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Liu, H.; Rengel, Z.; Gao, W.; Nie, Z.; Li, C.; Hou, M.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, P. Boron inhibits cadmium uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by regulating gene expression. Plant Sci. 2020, 297, 110522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Zhou, X.; Fan, L.; Qu, L. Screening and evaluation of rapeseed cultivars suitable for planting in cadmium-contaminated farmland. Mol. Plant Breed. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Wu, C.; Long, H. Effects of cadmium stress on growth and cadmium accumulation characteristics of Brassica napus L. seedings. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 2023, 2, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Lu, J.W.; Chen, F.; Li, Y. Application of ICP-MS to detection of mineral elements in double-low and double-high rapeseed. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2009, 9, 2571–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Caldelas, C.; Weiss, D. Zinc homeostasis and isotopic fractionation in plants: A review. Plant Soil 2017, 411, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadana, U.; Samal, D.; Claassen, N. Differences in manganese efficiency of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and raya (Brassica juncea L.) as related to root-shoot relations and manganese influx. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2003, 166, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, F.; Pan, X.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, D. Characterization of cadmium uptake and translocation in a cadmium-sensitive mutant of rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 57, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaney, R. How Does Contamination of Rice Soils with Cd and Zn Cause High Incidence of Human Cd Disease in Subsistence Rice Farmers. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Q.; Liu, Z. Effects of manganese concentrations and transporters on uptake and translocation of cadmium in rice seedlings. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, R.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.C.; Tong, Z.; Huo, W.; Chi, K.; Fan, H. Cadmium absorption and translocation of amaranth (Amaranthus mangostanus L.) affected by iron deficiency. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, G.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lv, C.; Bai, L.; Dai, J. Cultivar-specific response of rhizosphere bacterial community to uptake of cadmium and mineral elements in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Bai, B.; Xie, Y.; Yao, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wu, J. Spatial ionomics provides new insights into the accumulation and transport of mineral ions in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Cadmium stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 208, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Prasad, M. Iron-and manganese-assisted cadmium tolerance in Oryza sativa L.: Lowering of rhizotoxicity next to functional photosynthesis. Planta 2015, 241, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Juang, K. Alleviation effects of calcium and potassium on cadmium rhizotoxicity and absorption by soybean and wheat roots. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qi, Y.; Yin, C.; Liu, X. Effects of nitrogen reduction at different growth stages on maize water and nitrogen utilization under shallow buried drip fertigated irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Riaz, M.; Yan, L.; Jiang, C. Distribution and mobility of foliar-applied boron (10B) in citrange rootstock under different boron conditions. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cui, K.; Qi, X.; Wu, Y.; Huang, J.; Peng, S. Varietal responses of root characteristics to low nitrogen application explain the differing nitrogen uptake and grain yield in two rice varieties. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1244281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Zhu, S.; Bai, S.; Xia, Y.; Luo, L.; Cai, Q. The transportation and accumulation of arsenic, cadmium, and phosphorus in 12 wheat cultivars and their relationships with each other. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Wu, J.; Lu, W.; Guan, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Z. Differences in cadmium accumulation and translocation in different Zea mays cultivars. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).