Characterization and Evaluation of an Electrostatic Knapsack Sprayer Prototype for Agricultural Crops
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Knapsack Sprayer
2.2. Spray Droplet Size, Flow Rate, and Charge Quantification
2.3. Spray Distribution Profile
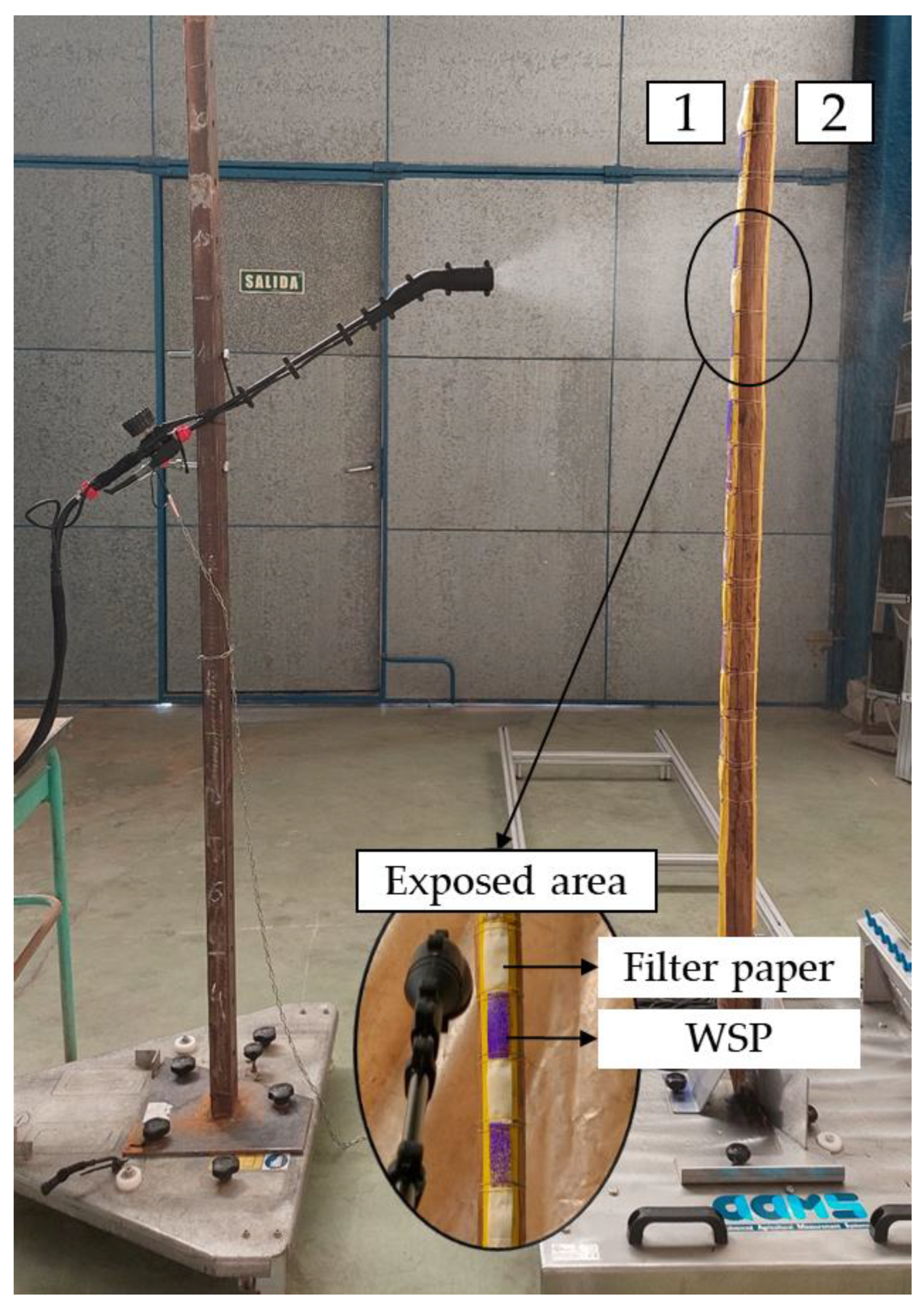
2.4. Coverage and Deposition Evaluation in Laboratory Conditions
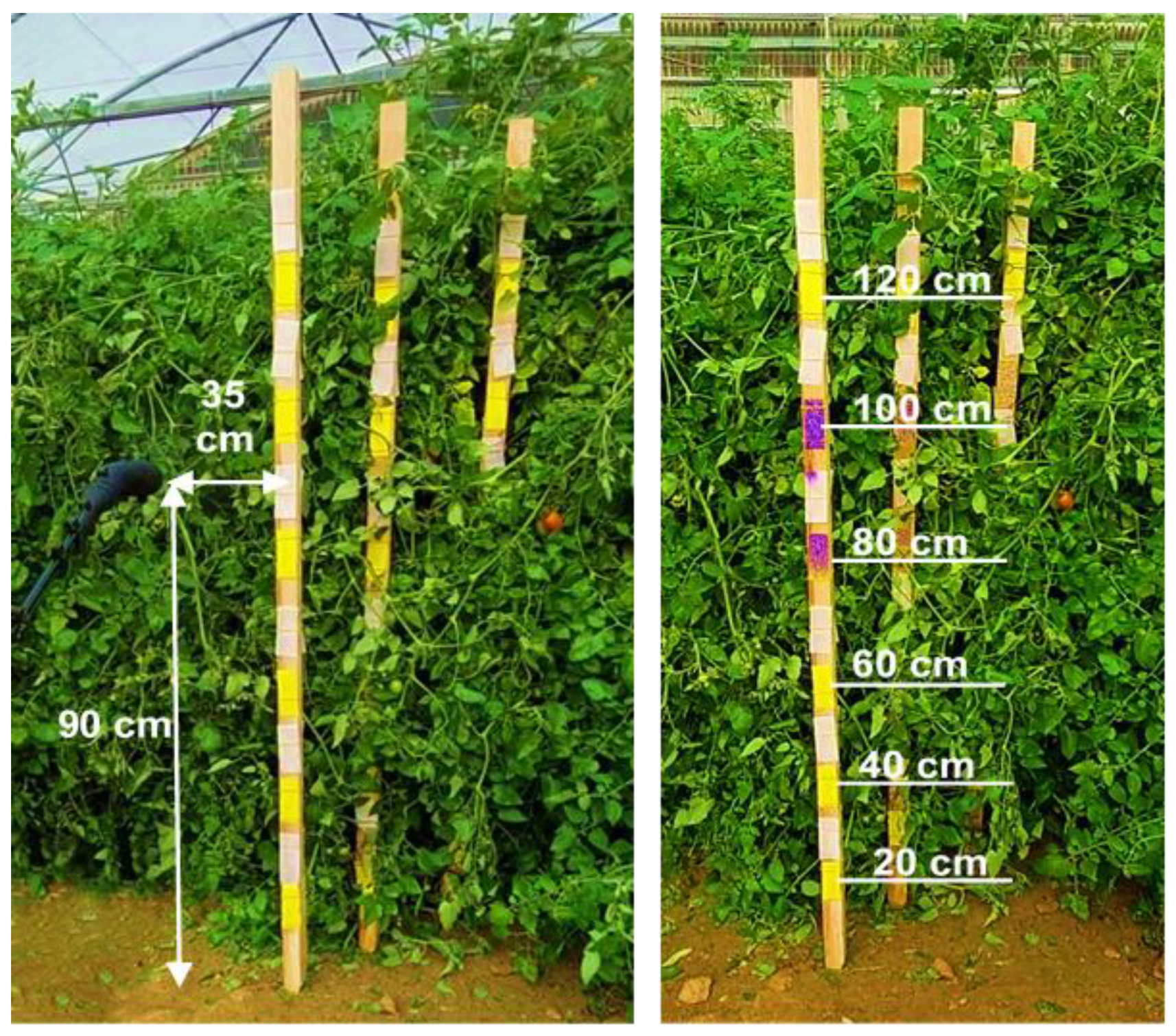
2.5. Coverage and Deposition Evaluation in Crop Conditions
2.6. Statistical Analysis of Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spray Droplet Size, Flow Rate, and Charge-to-Mass Ratio
3.2. Spray Distribution Profile
3.3. Laboratory Coverage/Deposition Tests
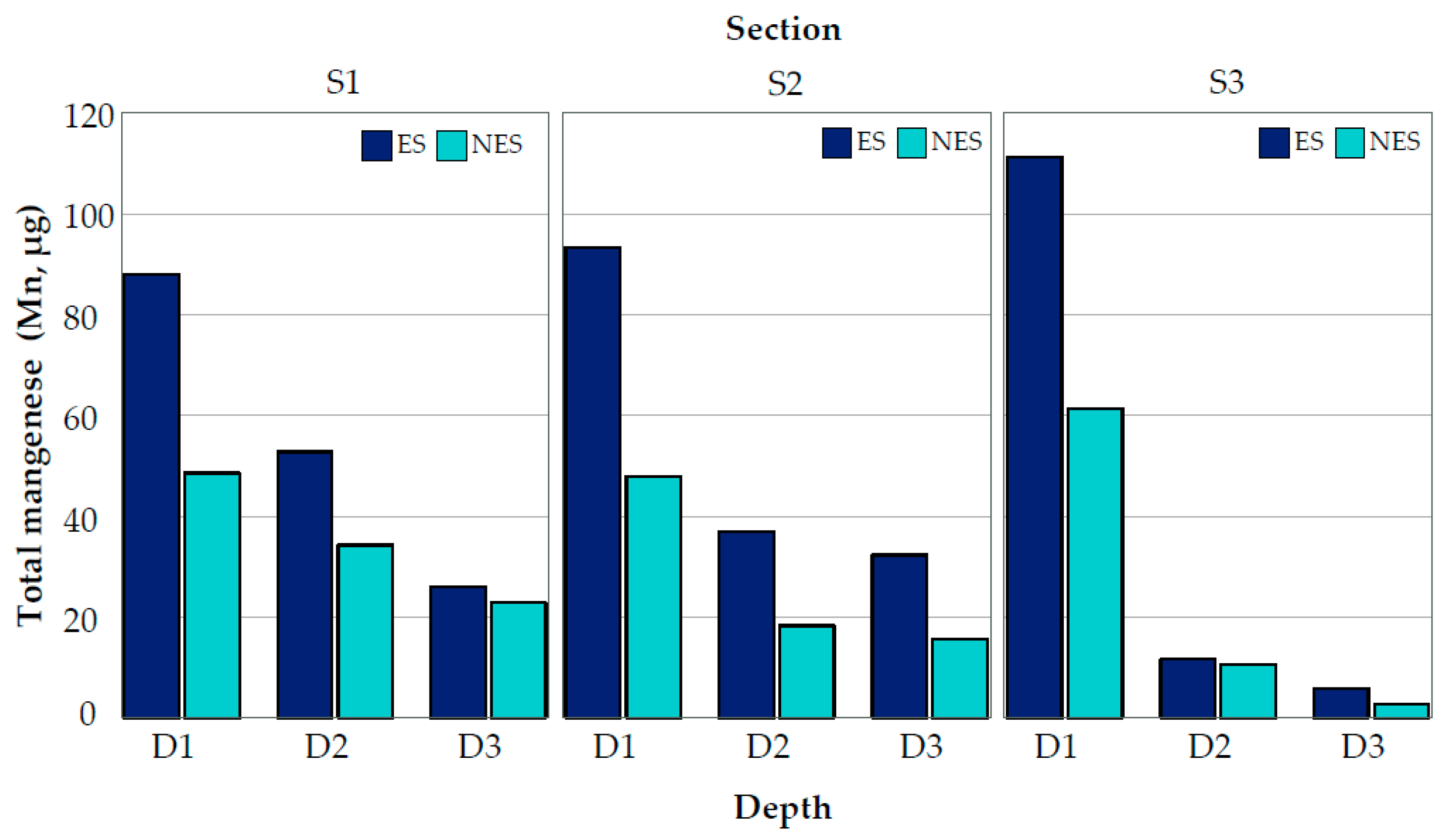
3.4. Coverage and Deposition in Crop Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doruchowski, G.; Balsari, P.; Van de Zande, J. Development of a crop adapted spray application system for sustainable plant protection in fruit growing. Int. Symp. Appl. Precis. Agric. Fruits Veg. 2009, 824, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.; Escolà, A.; Rosell, J.; Planas, S.; Val, L. Variable rate application of plant protection products in vineyard using ultrasonic sensors. Crop. Prot. 2007, 26, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, J.; Gil, E.; Llop, J.; Escolà, A. Variable rate dosing in precision viticulture: Use of electronic devices to improve application efficiency. Crop. Prot. 2010, 29, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Chen, L.; Ozkan, E.; Falchieri, D. Foliar deposition and coverage on young apple trees with PWM-controlled spray systems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.; Thompson, S.; Balachandran, W. Electroclamping forces for controlling bulk particulate flow: Charge relaxation effects. J. Electrost. 1996, 37, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.K.; Khanchi, A.; Chauhan, A.; Kumar, A.; Akkireddi, S.R.K.; Jangra, A.; Kanawade, R.; Manivannan, N.; Mitchell, G.R. Real-time measurement of droplet size and its distribution of an air-induced air-assisted electrostatic nozzle. J. Electrost. 2022, 115, 103665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dante, E.T.; Gupta, C. Deposition studies of an electrostatic spinning disc sprayer. Trans. ASAE 1991, 34, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.P.; Duc, T.X. Deposition studies of a hand-held air-assisted electrostatic sprayer. Trans. ASAE 1996, 39, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.P.; Singh, G.; Muhaemin, M.; Dante, E.T. Field performance of a hand-held electrostatic spinning-disc sprayer. Trans. ASAE 1992, 35, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.E. Electrostatically charged sprays. In Pesticide Application Methods; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 275–298. [Google Scholar]
- Pascuzzi, S.; Cerruto, E. Spray deposition in “tendone” vineyards when using a pneumatic electrostatic sprayer. Crop. Prot. 2015, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.K.; Praveen, B.; Sahoo, H.K.; Patel, B.; Kumar, A.; Singh, M.; Nayak, M.K.; Rajan, P. An advance air-induced air-assisted electrostatic nozzle with enhanced performance. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 135, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Castle, G.; Adamiak, K. Factors affecting deposition in electrostatic pesticide spraying. J. Electrost. 2008, 66, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, V.R.; Ghanshyam, C.; Kumar, P.M.; Kapur, P. Electrostatic hand pressure knapsack spray system with enhanced performance for small scale farms. J. Electrost. 2013, 71, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.K.; Kundu, M.; Sahoo, H.K.; Nayak, M.K. Enhanced performance of an air-assisted electrostatic nozzle: Role of electrode material and its dimensional considerations in spray charging. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2016, 9, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.K.; Ghanshyam, C.; Kapur, P. Characterization of electrode material for electrostatic spray charging: Theoretical and engineering practices. J. Electrost. 2013, 71, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatawkar, D.S.; Dhalin, D.; James, P.S.; Subhagan, S.R. Electrostatic induction spray-charging system (embedded electrode) for knapsack mist-blower. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 39, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laryea, G.N.; No, S.-Y. Development of electrostatic pressure-swirl nozzle for agricultural applications. J. Electrost. 2003, 57, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maski, D.; Durairaj, D. Effects of charging voltage, application speed, target height, and orientation upon charged spray deposition on leaf abaxial and adaxial surfaces. Crop. Prot. 2010, 29, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S.M.; A Harrison, M.; Law, S.E. Electrostatic application of antimicrobial sprays to sanitize food handling and processing surfaces for enhanced food safety. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2011, 301, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, M.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, K.; Singh, B. Studies on effect of electrostatic spraying in orchards. Agric. Eng. Int. 2014, 16, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Salcedo, R.; Llop, J.; Campos, J.; Costas, M.; Gallart, M.; Ortega, P.; Gil, E. Evaluation of leaf deposit quality between electrostatic and conventional multi-row sprayers in a trellised vineyard. Crop. Prot. 2020, 127, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llop, J. Improvement of spray application process in greenhouse tomato crop: Assessment of adapted spraying technologies and methods for canopy characterization. In Departament d’Enginyeria Agroalimentària i Biotecnologia; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Hermosilla, J.; Pérez-Alonso, J.; Martínez-Carricondo, P.; Carvajal-Ramírez, F.; Agüera-Vega, F. Evaluation of Electrostatic Spraying Equipment in a Greenhouse Pepper Crop. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan-Mor, S.; Ronen, B.; Ohaliav, K. The effect of air velocity and proximity on the charging of sprays from conventional hydraulic nozzles. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 121, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ramos, F.J.; Serreta, A.; Boné, A.; Vidal, M. Applicability of a 3D laser scanner for characterizing the spray distribution pattern of an air-assisted sprayer. J. Sensors 2018, 2018, 5231810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya, K.; Bayat, A. Determining effects of induction electrode geometry on charging efficiency of droplets in pesticide electrostatic spraying applications. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 4, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5682-2:1997; Equipment for Crop Protection—Spraying Equipment—Part 2: Test Methods for Hydraulic Sprayers. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- Law, S.E.; Cooper, S.C. Induction charging characteristics of conductivity enhanced vegetable-oil sprays. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 0075–0079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, J.; Green, R. An electrostatic charging system for hydraulic spray nozzles. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1982, 27, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ramos, F.J.; Vidal, M.; Bone, A. Field evaluation of an air-assisted sprayer equipped with two reversed rotation fans. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2009, 25, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.; Walklate, P.; Murray, R.; Richardson, G. Spray deposits and losses in different sized apple trees from an axial fan orchard sprayer: 1. Effects of spray liquid flow rate. Crop. Prot. 2001, 20, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.; Salcedo, R.; Soler, A.; Ortega, P.; Llop, J.; Campos, J.; Oliva, J. Relative efficiencies of experimental and conventional foliar sprayers and assessment of optimal LWA spray volumes in trellised wine grapes. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2462–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentjes, A.; Jansen, B.; Pozarlik, A.K. Spray characteristics of an air-assisted electrostatic atomiser. J. Electrost. 2022, 115, 103654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihm, K.D.; Kim, B.H.; McFarland, A.R. Atomization, charge, and deposition characteristics of bipolarly charged aircraft sprays. At. Sprays 1992, 2, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latheef, M.A.; Carlton, J.B.; Kirk, I.W.; Hoffmann, W.C. Aerial electrostatic-charged sprays for deposition and efficacy against sweet potato whitefly (Bemisia tabaci) on cotton. Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.E.; Latheef, M.A.; López, J.D. Electrostatically charged aerial application improved spinosad deposition on early season cotton. J. Electrost. 2019, 97, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, R.; Sánchez, E.; Zhu, H.; Fàbregas, X.; García-Ruiz, F.; Gil, E. Evaluation of an electrostatic spray charge system implemented in three conventional orchard sprayers used on a commercial apple trees plantation. Crop. Prot. 2023, 167, 106212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Dong, X.; Qiu, B. Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Deposition Coverage of Air-Assisted Electrostatic Spray on Tomato Leaves. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ou, M.; Dong, X.; Zhou, W.; Dai, S.; Jia, W. Spraying performance and deposition characteristics of an improved air-assisted nozzle with induction charging. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1309088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


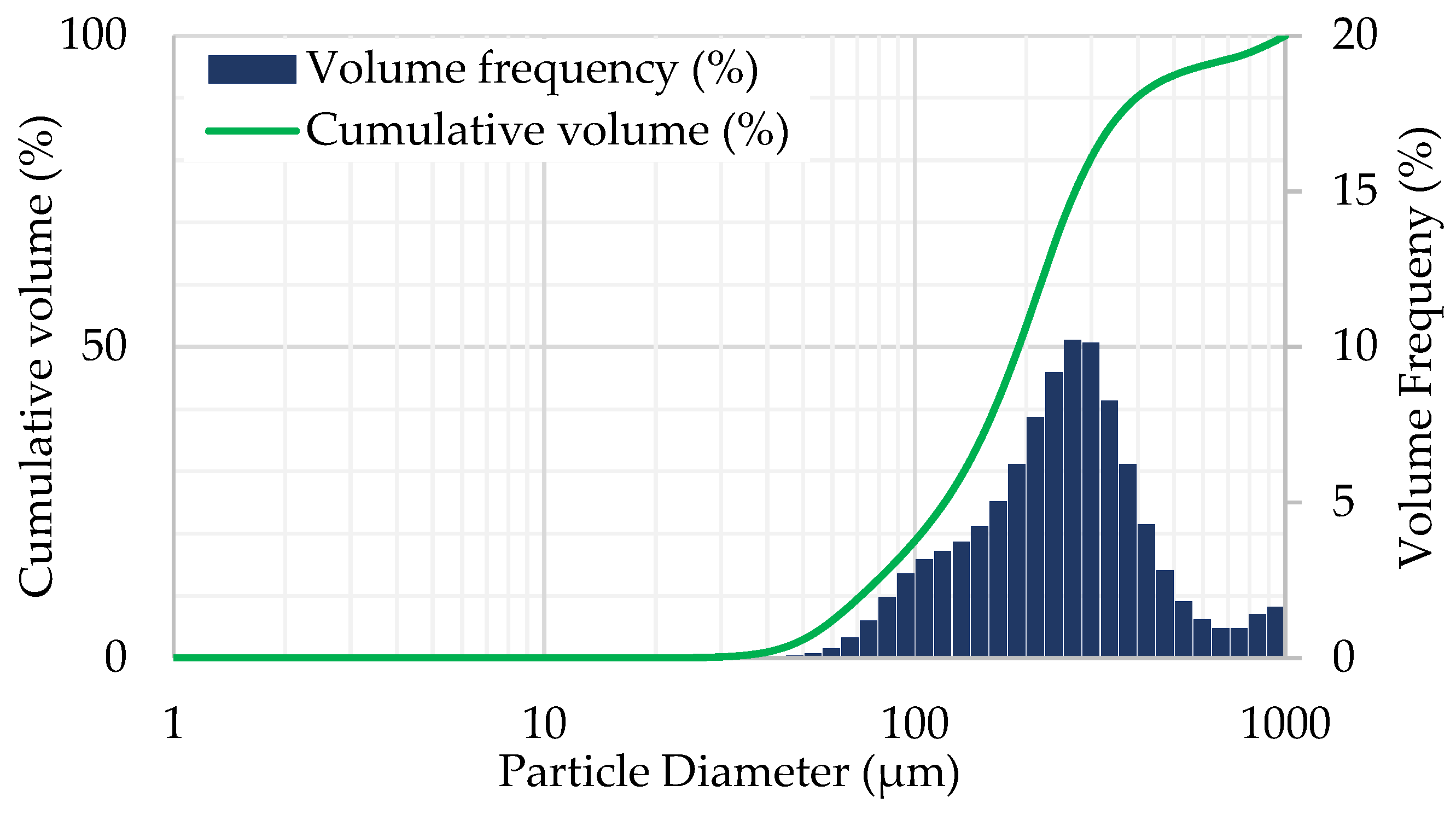



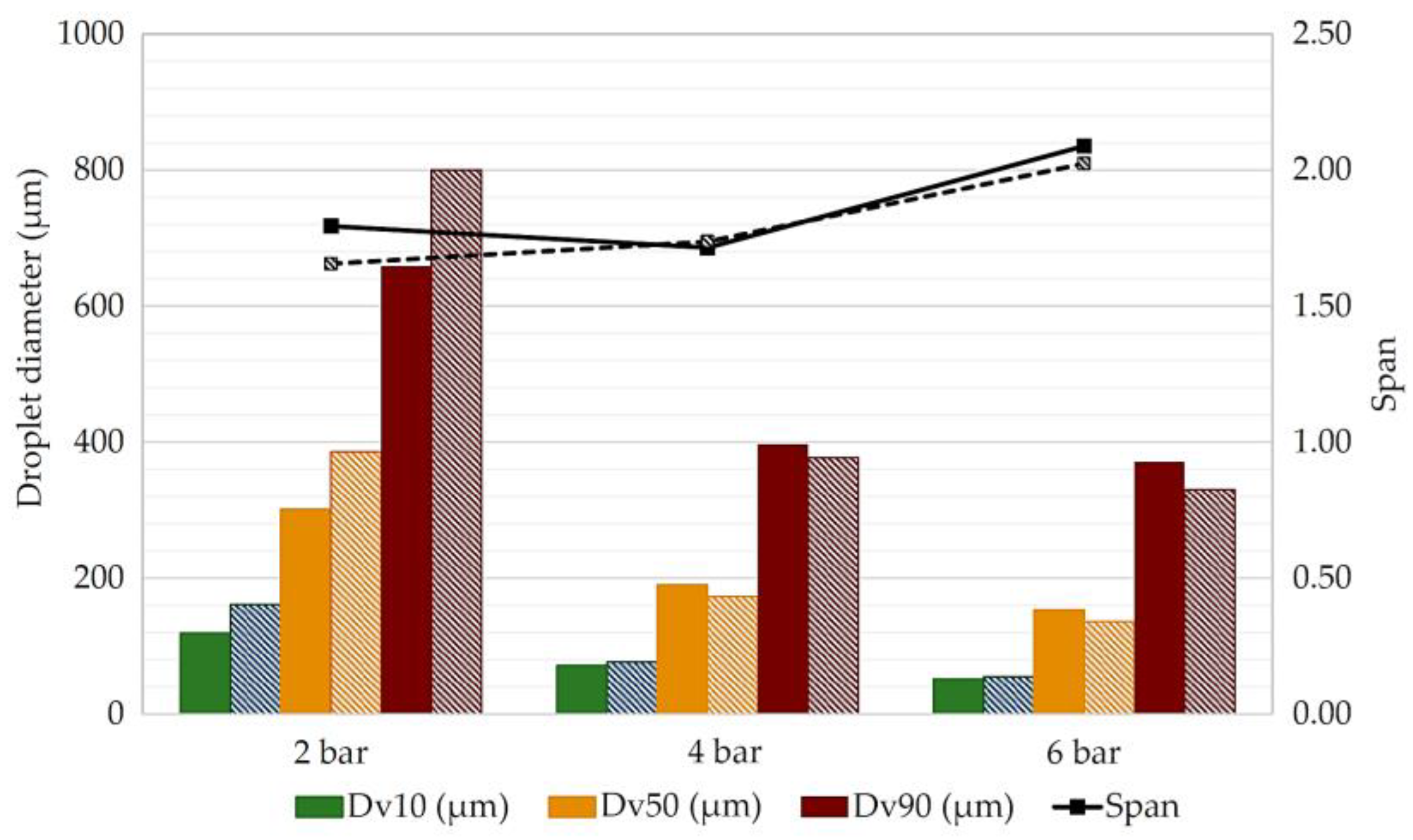



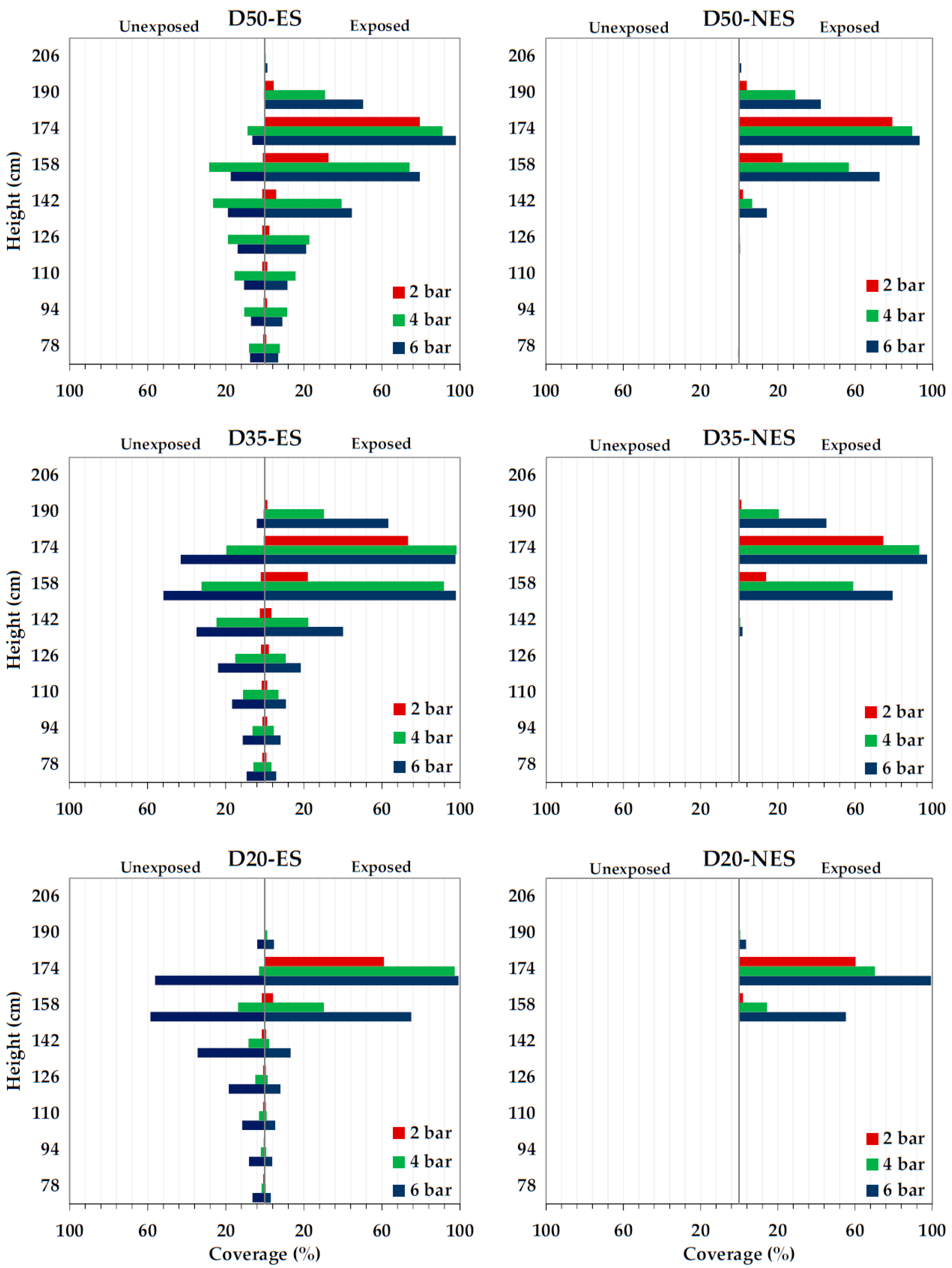
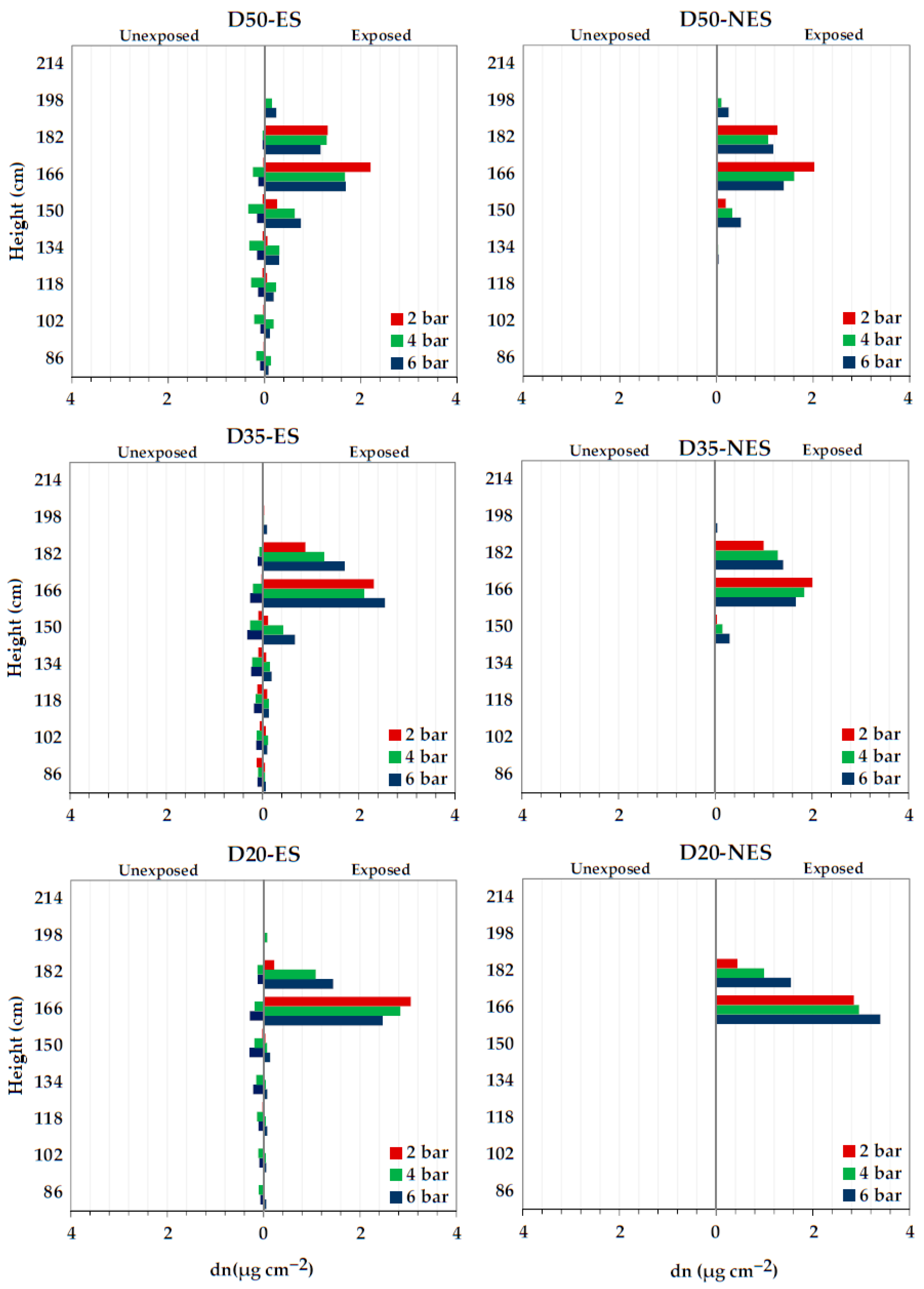
| Sprayer Configuration * | Fluid Pressures (Bar) | Application Distances (cm) | Collector Heights (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ES; NES | 2; 3; 4; 5 and 6 | 35; 50 and 65 | 120; 140; 160 and 180 |
| Water-Sensitive Paper (cm) | Filter Paper (cm) |
|---|---|
| 78 | 86 |
| 94 | 102 |
| 110 | 118 |
| 126 | 134 |
| 142 | 150 |
| 158 | 166 |
| 174 | 182 |
| 190 | 198 |
| 206 | 214 |
| Distance (cm) | Pressure (bar) | ES | NES | Increase (%) on Exposed Side Compared to NES * | Total Increase (%) Compared to NES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposed Side | Unexposed Side | Exposed Side | Unexposed Side | ||||
| 20 | 2 | 16.55 | 0.82 | 15.57 | 0.00 | 0.98 | 0.90 |
| 4 | 32.73 | 6.28 | 21.30 | 0.00 | 11.43 | 8.86 | |
| 6 | 48.01 | 38.33 | 39.54 | 0.00 | 8.47 | 23.40 | |
| 35 | 2 | 25.03 | 1.15 | 22.48 | 0.00 | 2.55 | 1.85 |
| 4 | 60.60 | 19.18 | 43.33 | 0.00 | 17.27 | 18.23 | |
| 6 | 74.73 | 33.29 | 55.89 | 0.00 | 18.84 | 26.07 | |
| 50 | 2 | 30.55 | 0.55 | 26.83 | 0.00 | 3.72 | 2.14 |
| 4 | 58.90 | 15.93 | 45.48 | 0.00 | 13.42 | 14.68 | |
| 6 | 68.07 | 10.67 | 55.58 | 0.20 | 12.49 | 11.48 | |
| Distance (cm) | Pressure (bar) | ES | NES | Increase (%) on Exposed Side Compared to NES * | Total Increase (%) Compared to NES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposed Side | Unexposed Side | Exposed Side | Unexposed Side | ||||
| 20 | 2 | 1.10 | 0.02 | 1.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.82 |
| 4 | 1.33 | 0.17 | 1.32 | 0.00 | 0.76 | 13.64 | |
| 6 | 1.35 | 0.23 | 1.34 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.00 | |
| 35 | 2 | 1.11 | 0.04 | 1.01 | 0.00 | 9.90 | 13.86 |
| 4 | 1.27 | 0.18 | 1.09 | 0.00 | 16.51 | 33.03 | |
| 6 | 1.64 | 0.22 | 1.12 | 0.00 | 46.43 | 66.07 | |
| 50 | 2 | 1.26 | 0.02 | 1.16 | 0.00 | 8.62 | 10.34 |
| 4 | 1.20 | 0.21 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 20.00 | 41.00 | |
| 6 | 1.20 | 0.11 | 1.02 | 0.00 | 17.65 | 28.43 | |
| Section | Depth | Coverage (%) | Deposition (μg cm−2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES | NES | ES | NES | ||||||
| Exposed Side | Unexposed Side | Exposed Side | Unexposed Side | Exposed Side | Unexposed Side | Exposed Side | Unexposed Side | ||
| S1 | D1 | 57.59 | 18.60 | 47.66 | 0.00 | 1.08 | 0.11 | 0.67 | 0.00 |
| D2 | 56.69 | 0.00 | 42.28 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 0.00 | |
| D3 | 42.18 | 0.00 | 19.99 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.00 | |
| S2 | D1 | 56.71 | 4.58 | 42.69 | 0.00 | 1.26 | 0.03 | 0.65 | 0.00 |
| D2 | 48.03 | 0.06 | 35.27 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.00 | |
| D3 | 31.37 | 0.00 | 20.93 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.00 | |
| S3 | D1 | 59.89 | 4.93 | 31.66 | 0.00 | 1.16 | 0.37 | 0.86 | 0.00 |
| D2 | 20.34 | 0.00 | 13.66 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.00 | |
| D3 | 3.54 | 0.00 | 6.92 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vigo-Morancho, A.; Videgain, M.; Boné, A.; Vidal, M.; García-Ramos, F.J. Characterization and Evaluation of an Electrostatic Knapsack Sprayer Prototype for Agricultural Crops. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2343. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102343
Vigo-Morancho A, Videgain M, Boné A, Vidal M, García-Ramos FJ. Characterization and Evaluation of an Electrostatic Knapsack Sprayer Prototype for Agricultural Crops. Agronomy. 2024; 14(10):2343. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102343
Chicago/Turabian StyleVigo-Morancho, Alba, María Videgain, Antonio Boné, Mariano Vidal, and Francisco Javier García-Ramos. 2024. "Characterization and Evaluation of an Electrostatic Knapsack Sprayer Prototype for Agricultural Crops" Agronomy 14, no. 10: 2343. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102343
APA StyleVigo-Morancho, A., Videgain, M., Boné, A., Vidal, M., & García-Ramos, F. J. (2024). Characterization and Evaluation of an Electrostatic Knapsack Sprayer Prototype for Agricultural Crops. Agronomy, 14(10), 2343. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102343






