Key Soil Abiotic Factors Driving Soil Sickness in Lycium barbarum L. Under Long-Term Monocropping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
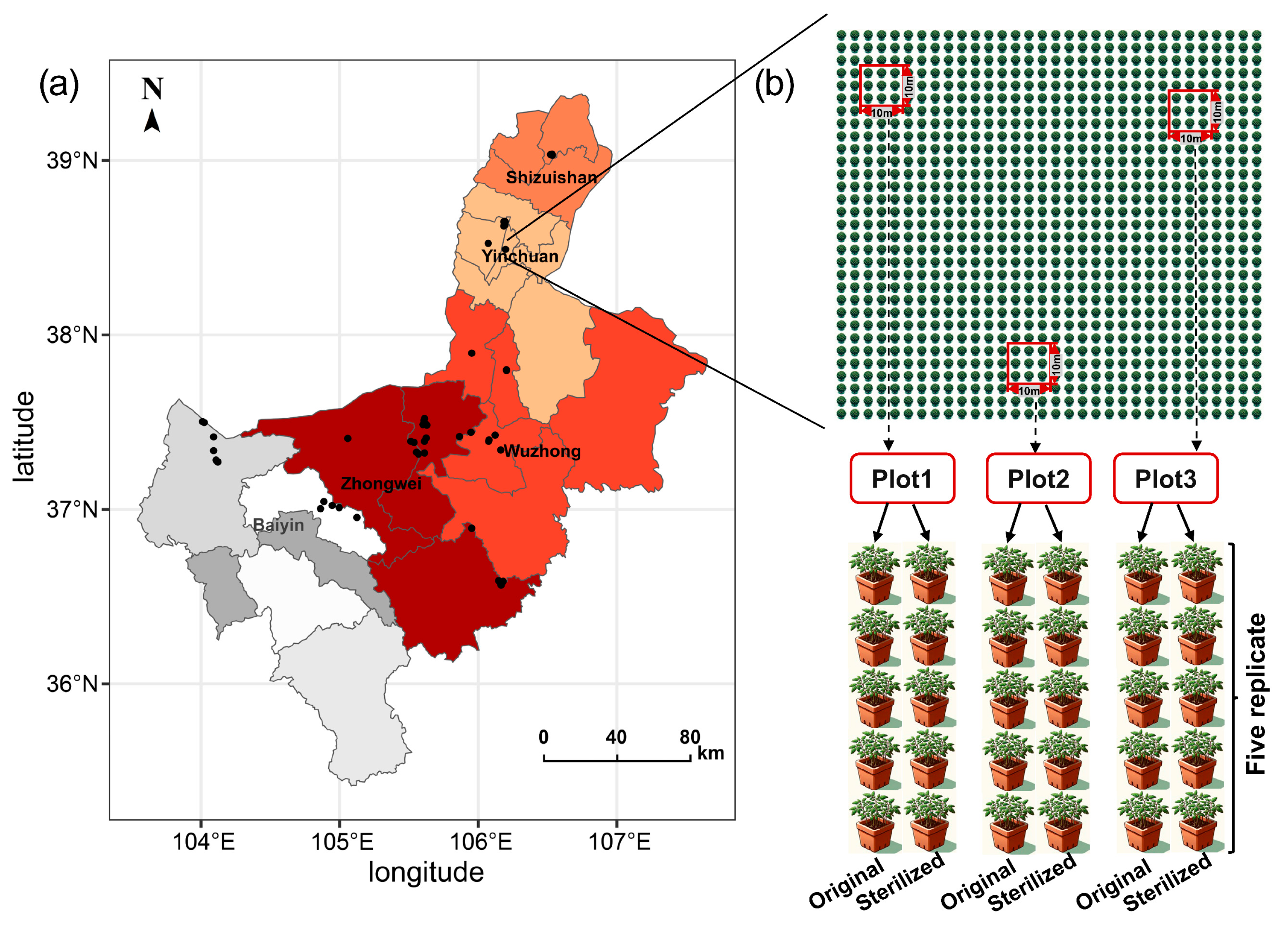
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Pot Experiment
2.3. Soil Abiotic Property Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
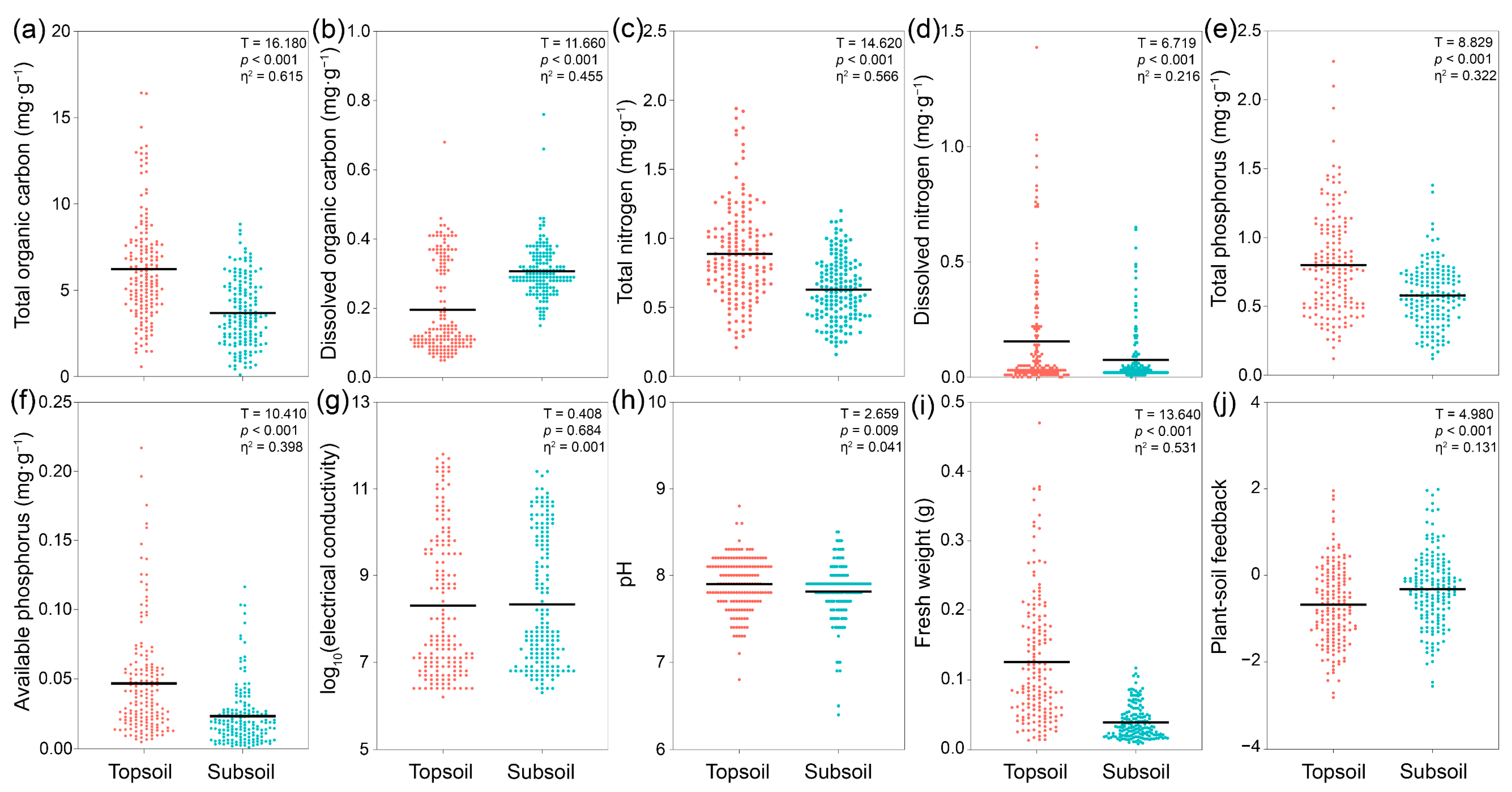
3.1. Differences in Soil Abiotic Properties, Shoot Fresh Weight, and PSF Between Topsoil and Subsoil
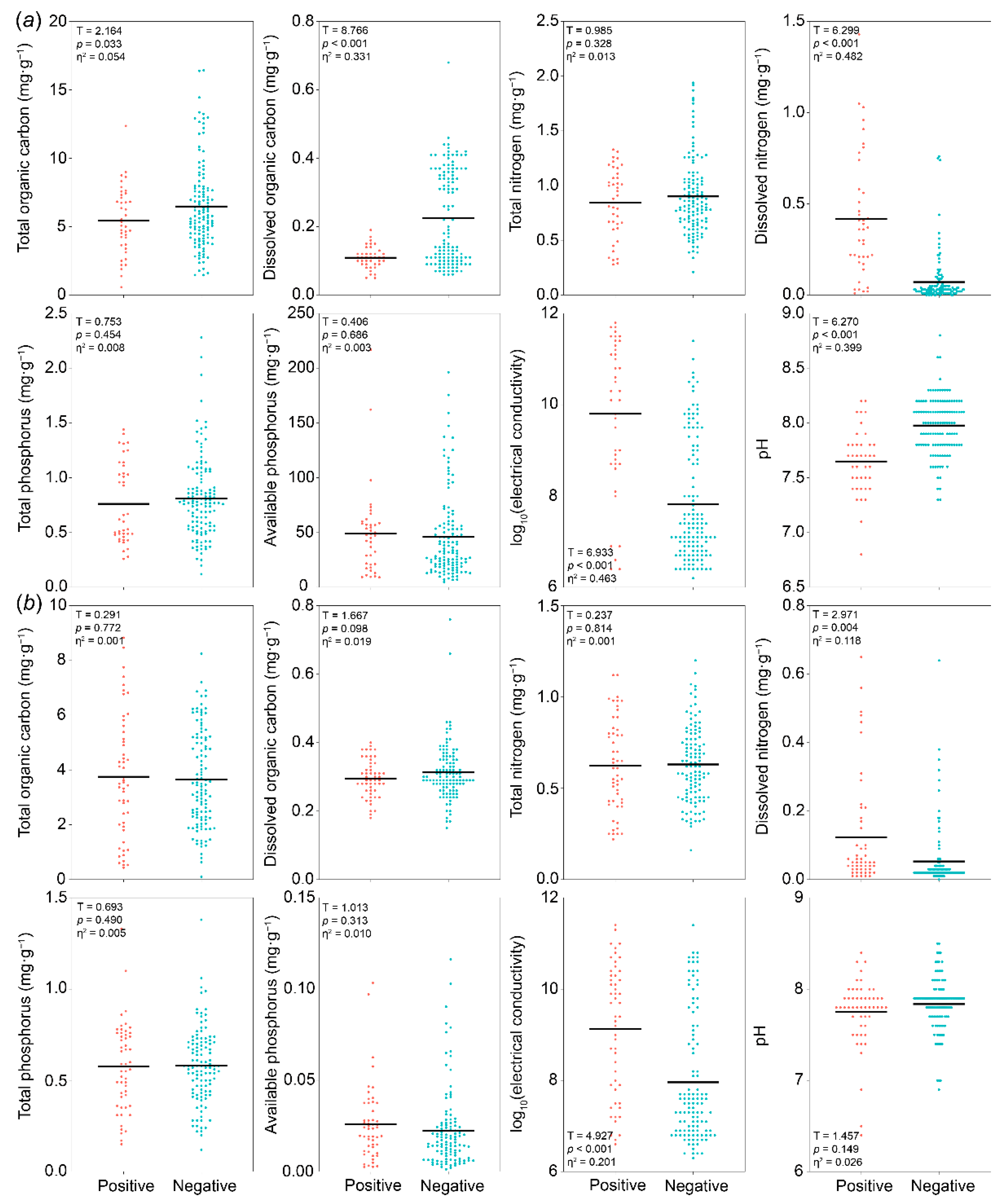
3.2. Differences in Soil Properties Between Positive and Negative PSF Samples
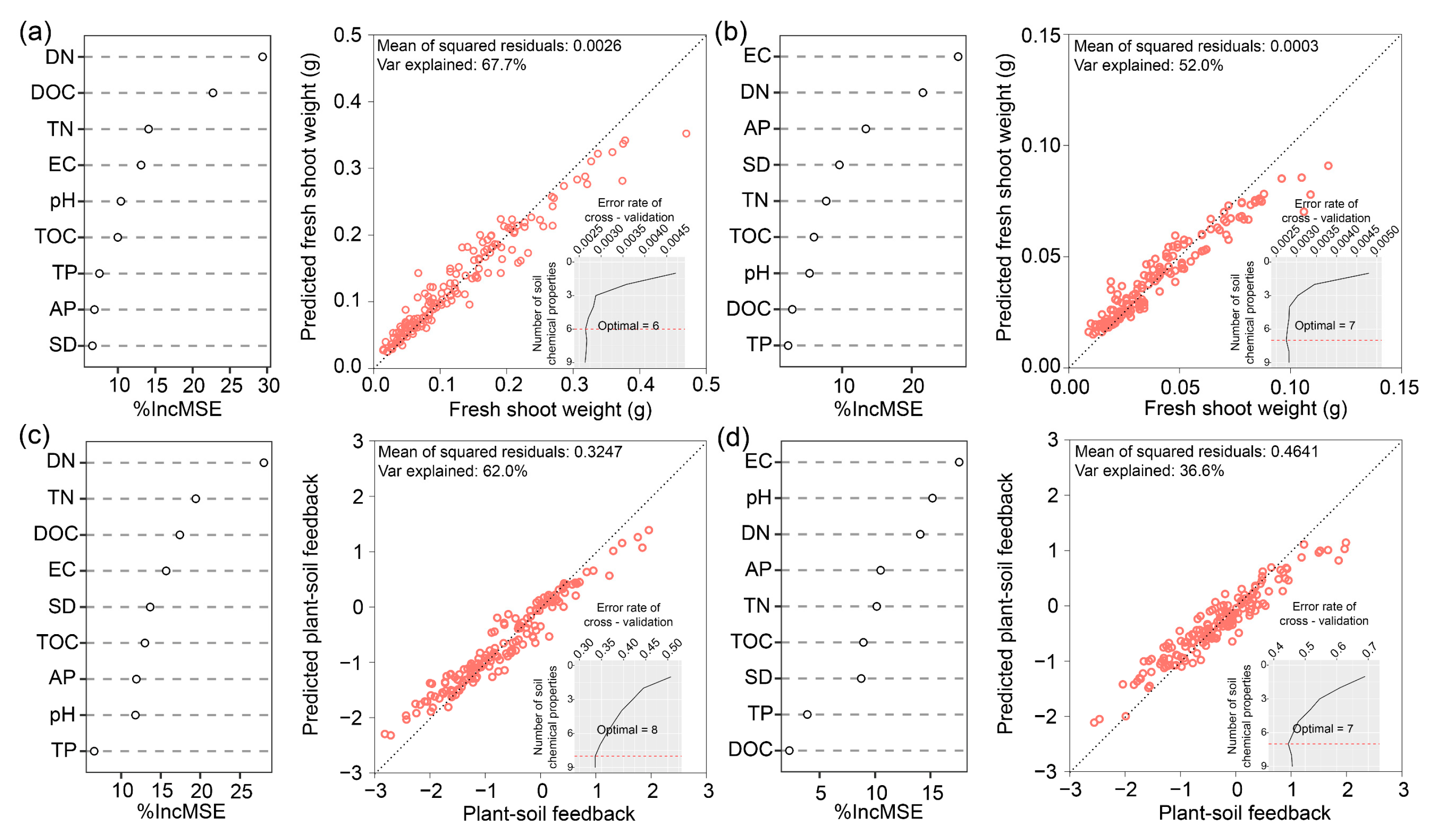
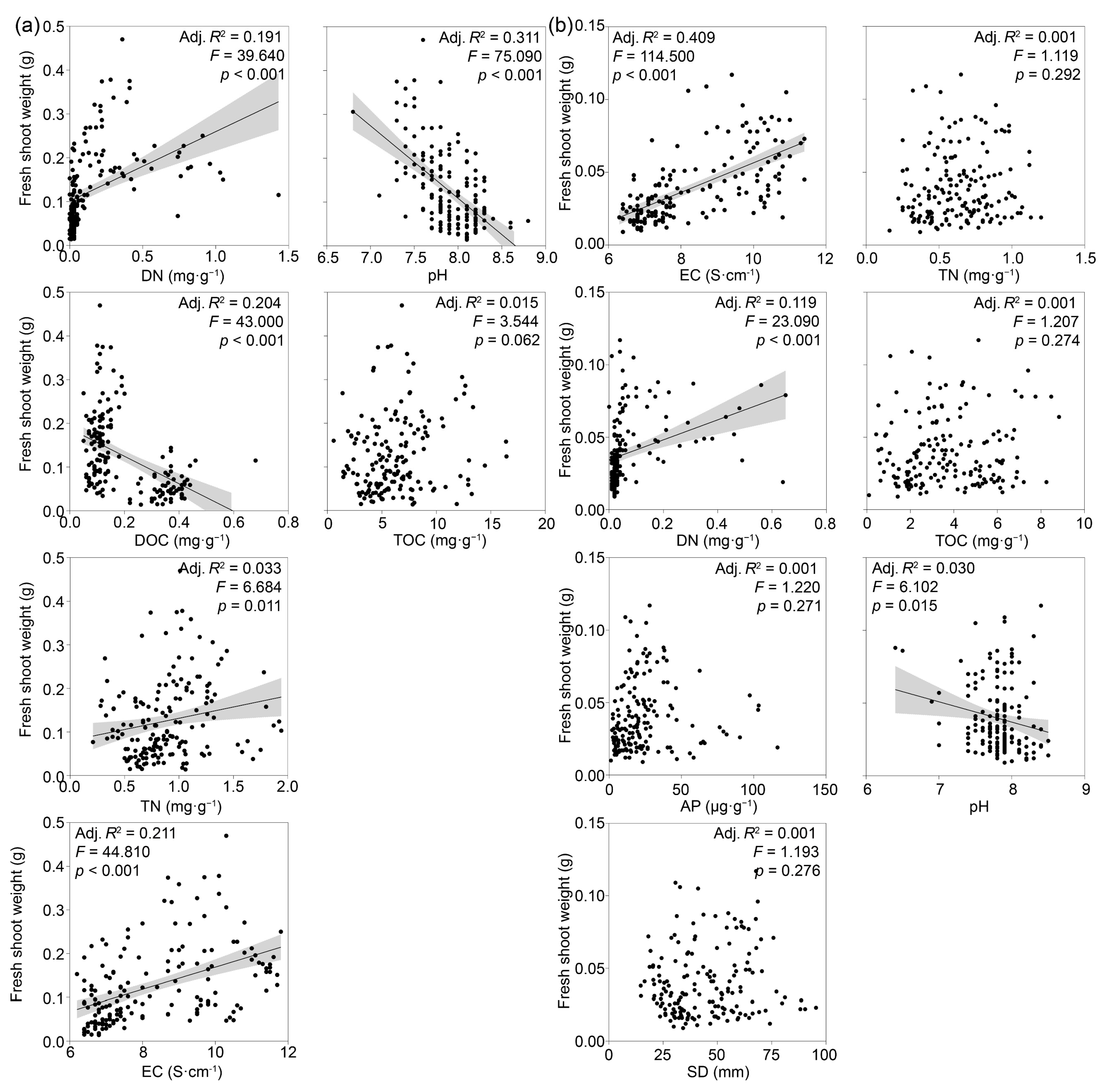
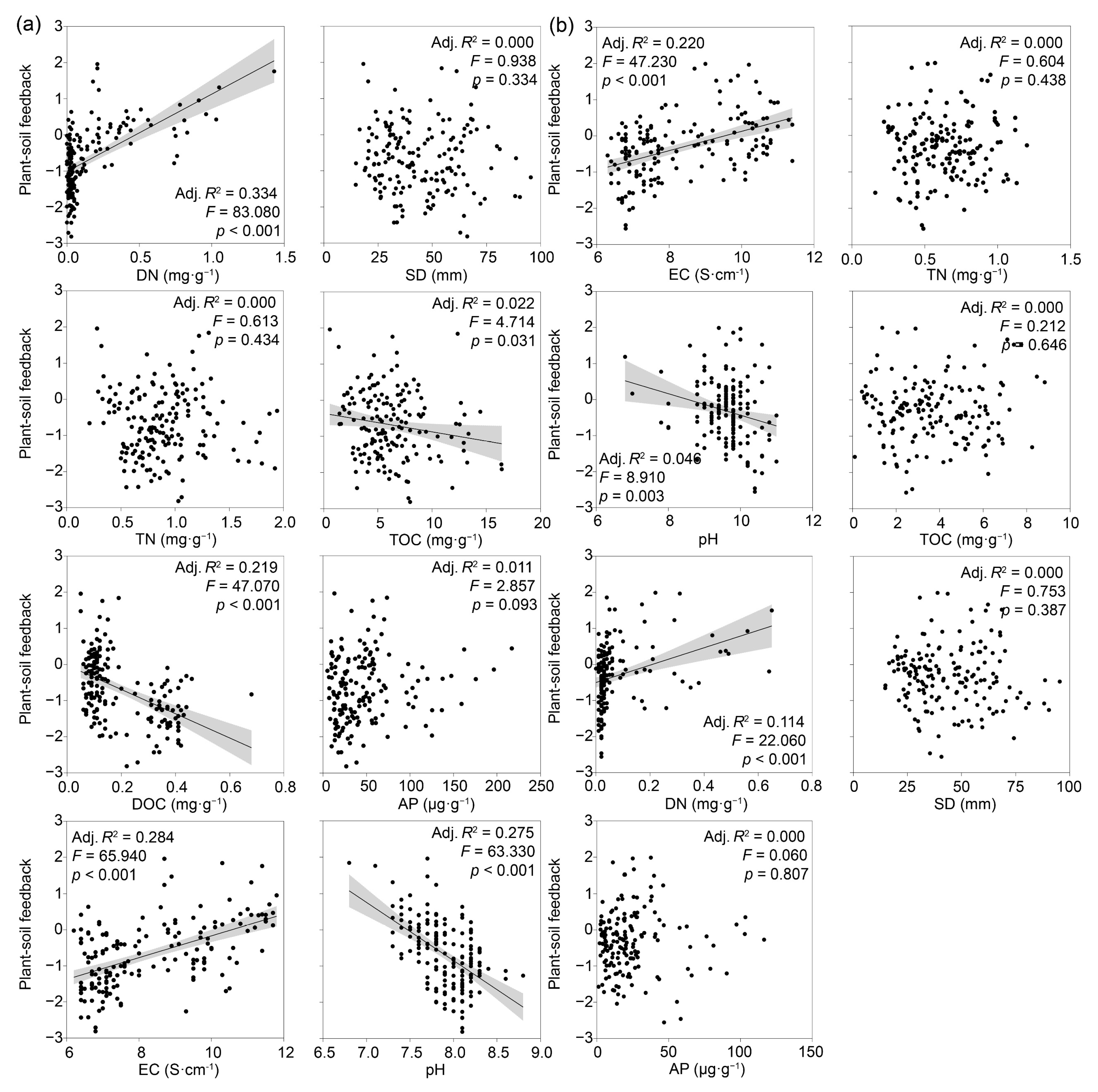
3.3. Factors Driving Shifts in Shoot Fresh Weight and PSF Rates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, J.A.; Klironomos, J. Mechanisms of plant-soil feedback: Interactions among biotic and abiotic drivers. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.F.; Song, L.X.; Xia, X.J.; Mao, W.H.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q. Plant-soil feedbacks and soil sickness: From mechanisms to application in agriculture. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarano, G.; Zotti, M.; Antignani, V.; Marra, R.; Scala, F.; Bonanomi, G. Soil sickness and negative plant-soil feedback: A reappraisal of hypotheses. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 99, 545–570. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, T.C.S.P.; Dias, M.I.; Calhelha, R.C.; Alves, M.J.; Celestino, S.B.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phenolic compounds profile, nutritional compounds and bioactive properties of Lycium barbarum L.: A comparative study with stems and fruits. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 122, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Heinrich, M.; Zou, Y.; Reich, E.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Weckerle, C.S. Quality variation of goji (fruits of Lycium spp.) in China: A comparative morphological and metabolomic analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Robinson, B.H.; Zhao, X. Water-use patterns of Chinese wolfberry (Lycium barbarum L.) on the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, X.; Ma, C.; Ma, S.; Ma, X.; Zhu, X.; Xu, P.; Zhu, H.; Cao, X.; Liang, W. Monocropping decouples plant-bacteria interaction and strengthens phytopathogenic fungi colonization in the rhizosphere of a perennial plant species. Plant Soil 2019, 445, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, X.; Ma, S.; Ma, C.; Liu, Z.; Xu, P.; Zhu, H.; Liang, W.; Kardol, P. Lycium barbarum L. (goji berry) monocropping causes microbial diversity loss and induces Fusarium spp. enrichment at distinct soil layers. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 168, 104107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Weil, R.R.; Zhu, L.; Nan, X. Forage radish cover crops improve soil quality and fruit yield of Lycium barbarum L. in an arid area of northwest China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Ma, S.; Ma, C.; Song, Y.; Gao, N.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Na, X.; Wang, L. Effects of long-term monocropping on soil microbial metabolic activity and diversity in topsoil and subsoil horizons of Lycium barbarum fields. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2023, 32, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Zheng, G. Effect of stand age on soil microbial community structure in wolfberry (Lycium barbarum L.) fields. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Jia, K.; Zheng, G.; Long, X. Seasonal variation rather than stand age determines bacterial diversity in the rhizosphere of wolfberry (Lycium barbarum L.) associated with soil degradation. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1518–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, X.; Zheng, G.; Xing, Z.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Lu, J.; Ma, F. Effects of monocropping on diversity and structure of the bacterial community in rhizosphere of replanted Lycium barbarum L. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 1280–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Ma, C.; Xu, P.; Zheng, G.; Na, X. Effects of long-term monocropping of Lycium barbarum L. on function and composition of fungal community in rhizosphere of replanted Lycium barbarum L. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2019, 56, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zou, N.; Liang, X.; Zhou, X.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Tian, Y.; Lin, J. Effects of nitrogen input on soil bacterial community structure and soil nitrogen cycling in the rhizosphere soil of Lycium barbarum L. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1070817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Ma, P.; Xu, X. Comprehensive assessment of fertilization spatial variability of soil chemical properties and relationships among nutrients, apple yield and orchard age: A case study in Luochuan County, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, P.A.; Ahamed, S.; Carré, F.; Hartemink, A.E.; Hempel, J.; Huising, J.; Lagacherie, P.; McBratney, A.B.; Mckenzie, N.J.; Mendonça-Santos, M.D.; et al. Digital soil map of the world. Science 2009, 325, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, N.; Gao, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Xing, R. Effects of root rot on microbial communities associated with goji berry (Lycium barbarum) in the Qaidam Basin, China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2023, 167, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Song, L.; Gao, H.; Cao, B. Fruit morphological and nutritional quality features of goji berry (Lycium barbarum L.) during fruit development. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 308, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Bradford, M.A. Microbial formation of stable soil carbon is more efficient from belowground than aboveground input. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 12, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilschut, R.A.; Van der Putten, W.H.; Garbeva, P.; Harkes, P.; Harkes, K.; Kulkarni, P.; Martens, H.; Geisen, S. Root traits and belowground herbivores relate to plant-soil feedback variation among congeners. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Tian, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Christie, P.; Chen, H.; Lee, J.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Six, J. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in intensively managed arable soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 150, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Hu, J.; Chen, K.; Yao, J.; Yu, Z.; Lin, X. Soil microbial activity measured by microcalorimetry in response to long-term fertilization regimes and available phosphorous on heat evolution. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Yue, P.; Li, K.; Liu, X.; Tripathi, B.M.; Chu, H. Salinity is a key determinant for soil microbial communities in a desert ecosystem. mSystems 2019, 4, e00225-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, G.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, B.; Zhou, H.; et al. Experimental warming has not affected the changes in soil organic carbon during the growing season in an alpine meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 847680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, F.; Tscharntke, T.; Bischoff, G.; Grass, I. Floral resource diversification promotes solitary bee reproduction and may offset insecticide effects: Evidence from a semi-field experiment. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, N.; Hu, B.; Jin, T.; Xu, H.; Qin, Y.; Yan, P.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; et al. NRT1.1B is associated with root microbiota composition and nitrogen use in field-grown rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doetterl, S.; Stevens, A.; Six, J.; Merckx, R.; Oost, K.V.; Pinto, M.C.; Casanova-Katny, A.; Muñoz, C.; Boudin, M.; Venegas, E.Z.; et al. Soil carbon storage controlled by interactions between geochemistry and climate. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 780–783. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Shao, M.; Wang, Y. Spatial patterns of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus across the entire Loess Plateau region of China. Geoderma 2013, 197, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, W.; Lin, Y.; Nan, X.; Yuan, J. Soil organic carbon pool and the production of goji berry (Lycium barbarum L.) as affected by different fertilizer combinations under drip fertigation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 933124. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, P.; Qin, S. Responses of soil microbial communities to a short-term application of seaweed fertilizer revealed by deep amplicon sequencing. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 125, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Ramesh, L.M.; Reynolds, H.L. The next frontier of plant-soil feedback research: Unraveling context dependence across biotic and abiotic gradients. J. Veg. Sci. 2017, 28, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, D.; Wu, J.; Ma, M.; Li, G.; Wang, M.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Shi, W. PIN5 is involved in regulating NH4+ efflux and primary root growth under high-ammonium stress via mediating intracellular auxin transport. Plant Soil 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeckman, F.; Motte, H.; Beeckman, T. Nitrification in agricultural soils: Impact factors and mitigation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 50, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Shi, J.; Zeng, L.; Xu, J.; Wu, L. Impacts of continuous excessive fertilization on soil potential nitrification activity and nitrifying microbial community dynamics in greenhouse system. J. Soils Sediments. 2017, 17, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, W.; Ren, W. Characterization of soil salinization and its driving factors in a typical irrigation area of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, L.; Fan, G.; Xie, S.; Li, F. Effects of aerated brackish water irrigation on growth of Lycium barbarum seedlings. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 310, 111721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Kong, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Banerjee, S.; Ishii, S.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Gao, J.; Feng, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Halophytes increase rhizosphere microbial diversity, network complexity, and function in inland saline ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, X.; Huang, L.; Shao, M. Vertical distribution of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus in the critical zone on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena. 2018, 166, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Putten, W.H.; Bardgett, R.D.; Bever, J.D.; Bezemer, T.M.; Casper, B.B.; Fukami, T.; Kardol, P.; Klironomos, J.N.; Kulmatiski, A.; Schweitzer, J.A.; et al. Plant-soil feedbacks: The past, the present and future challenges. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, S.; Bonanomi, G.; Incerti, G.; Chiusano, M.L.; Termolino, P.; Mingo, A.; Senatore, M.; Giannino, F.; Cartenì, F.; Rietkerk, M.; et al. Inhibitory and toxic effects of extracellular self-DNA in litter: A mechanism for negative plant-soil feedbacks? New Phytol. 2015, 205, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Peng, T.; Ma, S.; Ma, C.; Gao, N.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.; Pu, M.; Na, X. Analyzing the autotoxicity of phenolic acids from Lycium barbarum L. leaves. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 2, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. Effect of benzoic acid on soil microbial communities associated with soilborne peanut diseases. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 110, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Depth | Controlling Factor | Fresh Shoot Weight | Plant–Soil Feedback Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topsoil | Soil abiotic property | −0.156 NS | −0.241 ** |
| Subsoil | 0.117 NS | −0.080 NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Qi, C.; Song, Y.; Peng, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, K.; Pu, M.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; He, X.; et al. Key Soil Abiotic Factors Driving Soil Sickness in Lycium barbarum L. Under Long-Term Monocropping. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112525
Liu Z, Qi C, Song Y, Peng T, Zhang C, Li K, Pu M, Sun H, Li J, He X, et al. Key Soil Abiotic Factors Driving Soil Sickness in Lycium barbarum L. Under Long-Term Monocropping. Agronomy. 2024; 14(11):2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112525
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ziyu, Chang Qi, Yanfang Song, Tong Peng, Chuanji Zhang, Kaile Li, Meiyun Pu, Hao Sun, Junjie Li, Xiaoqi He, and et al. 2024. "Key Soil Abiotic Factors Driving Soil Sickness in Lycium barbarum L. Under Long-Term Monocropping" Agronomy 14, no. 11: 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112525
APA StyleLiu, Z., Qi, C., Song, Y., Peng, T., Zhang, C., Li, K., Pu, M., Sun, H., Li, J., He, X., Cheng, Z., Fei, P., Wang, X., Bi, Y., & Na, X. (2024). Key Soil Abiotic Factors Driving Soil Sickness in Lycium barbarum L. Under Long-Term Monocropping. Agronomy, 14(11), 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112525






