Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals a Tissue-Specific Pathway Involved in Nitrogen Utilization Between Genotypes with Different Nitrogen Use Efficiencies in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Samples Collected
2.2. Determination of Biomass, 15N Abundance, and Total N Content
2.3. RNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Annotation
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
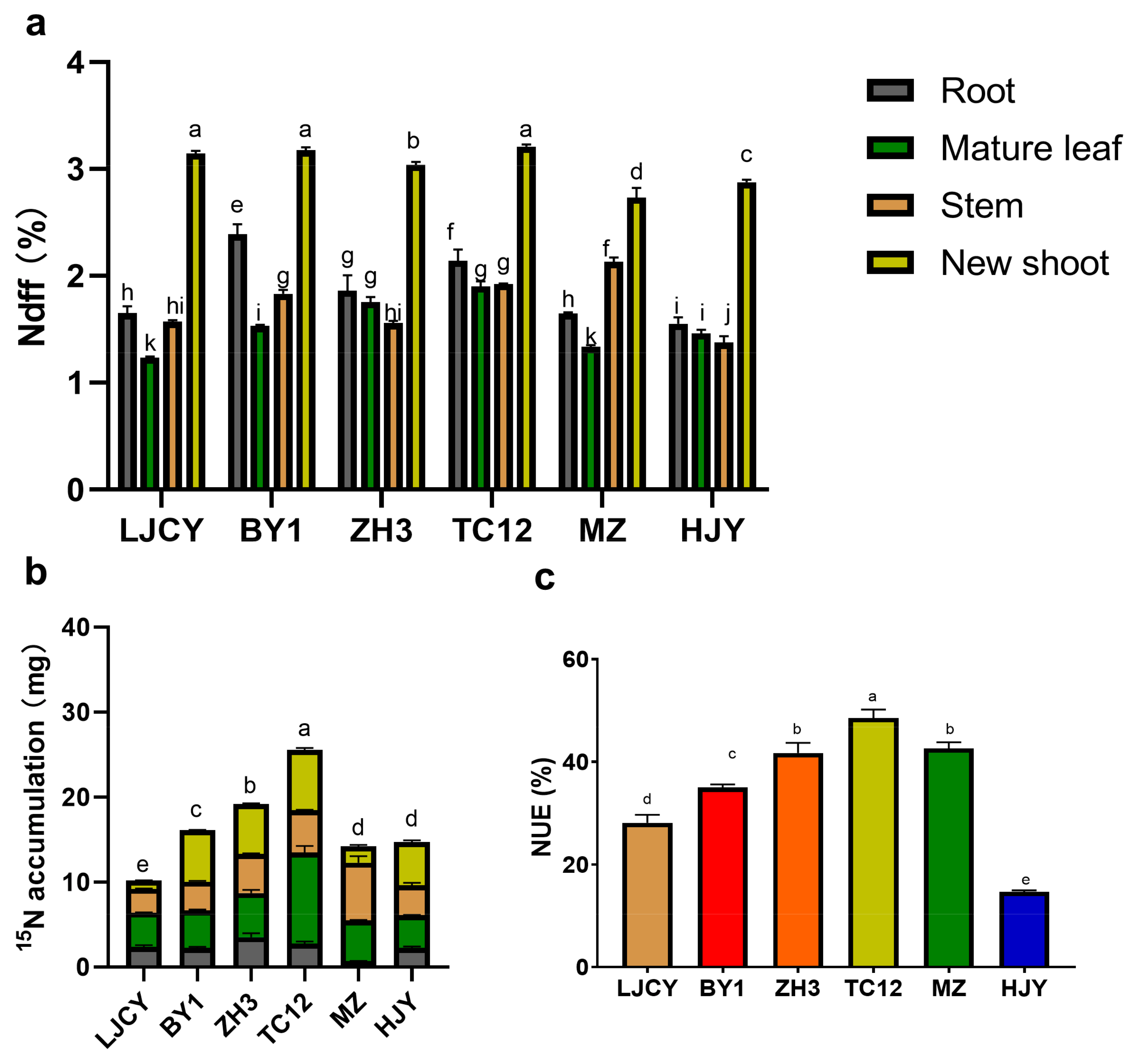
3.1. Comparison of NUEs Among Different Tea Cultivars
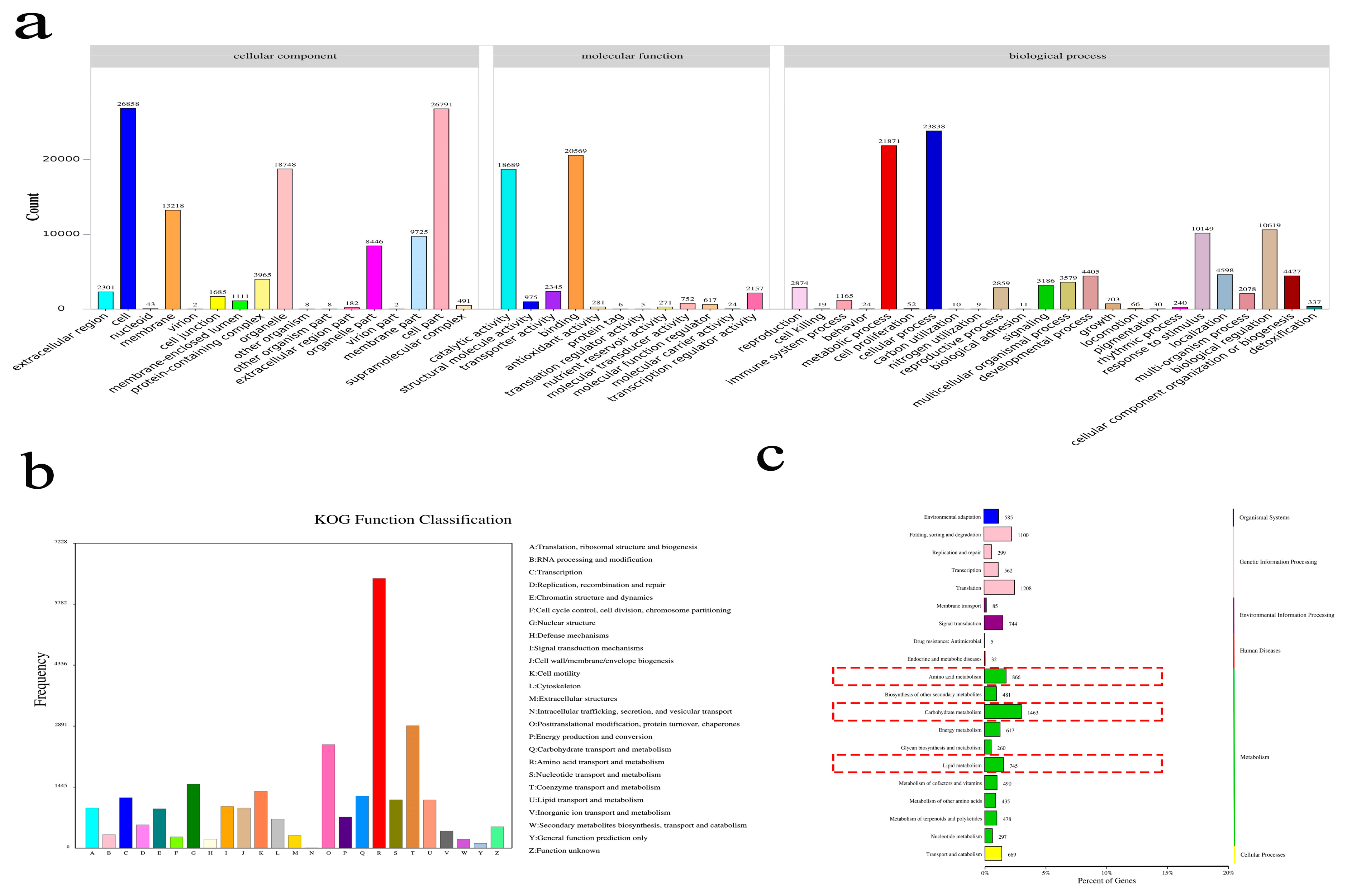
3.2. Global Expression Analysis of the Two Cultivars
3.3. Analysis of DEGs Involved in Nitrogen Uptake and Transport Between the Two Cultivars in Different Tissues
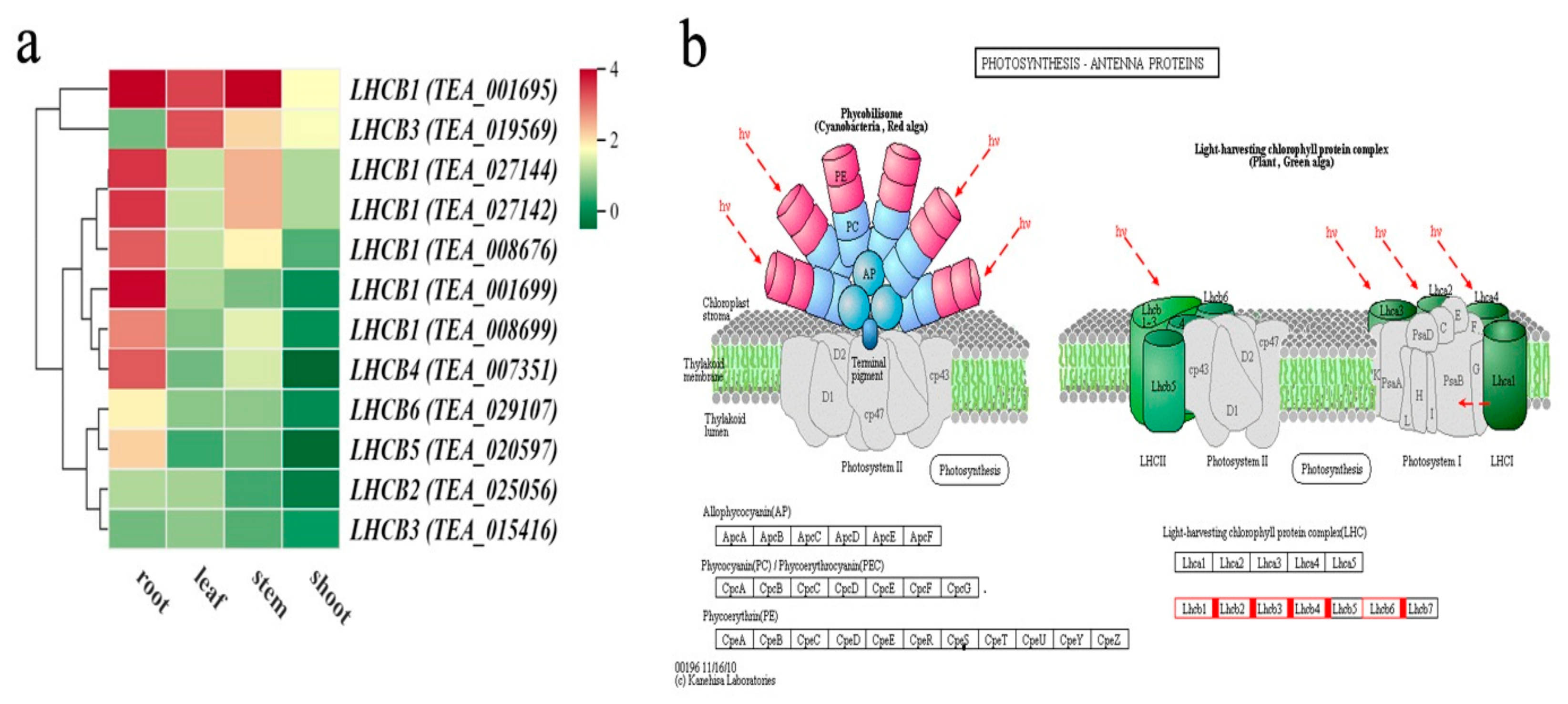
3.4. Analysis of DEGs Involved in Photosynthesis in Different Tissues Between the Two Cultivars
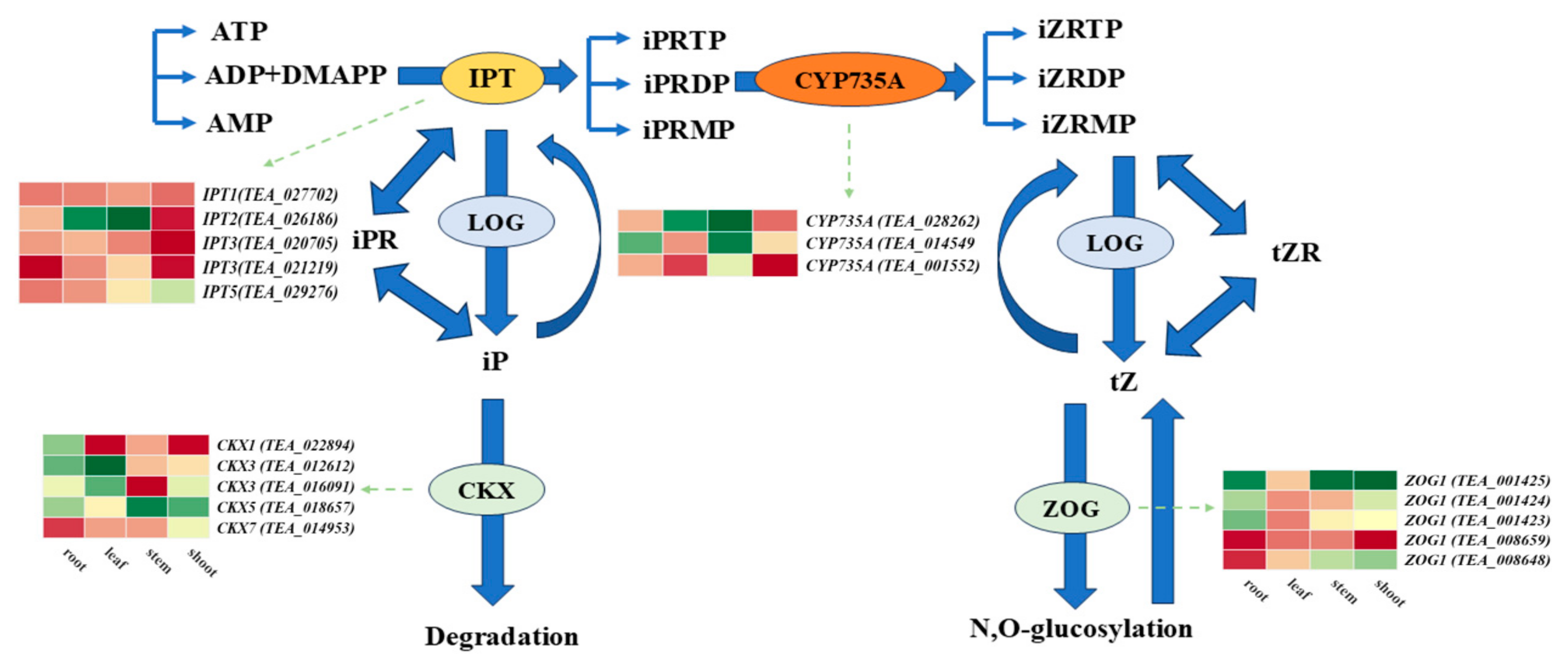
3.5. Analysis of DEGs Involved in Cytokinin Metabolism in Different Tissues Between the Two Cultivars
3.6. Validation of RNA-Seq Results by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, J.; Gerendás, J.; Härdter, R.; Sattelmacher, B. Effect of root zone pH and form and concentration of nitrogen on accumulation of quality-related components in green tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 87, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.H.; Liao, J.M.; Chen, J.H.; Li, A.S.; Lin, M.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Huang, W.; Sun, B.M.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.Q.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of fresh tea cv. Lingtou Dancong) leaf quality under different nitrogen fertilization regimes. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, C.L.; Xu, B.; Han, Y.T.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.L.; Liu, W.X.; Wan, S.Q.; Tan, H.; Liu, Y.Z.; et al. Synthetic nitrogen fertilizers alter the soil chemistry, production and quality of tea. A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Ni, K.; Long, L.Z.; Ruan, J.Y. Nitrogen transport and assimilation in tea plant (Camellia sinensis): A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1249202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Ni, K.; Shi, Y.Z.; Yi, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Fang, L.; Ma, L.F.; Ruan, J.Y. Effects of long-term nitrogen application on soil acidification and solution chemistry of a tea plantation in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.B.; Muller, C.; Wang, S.Q. Mechanistic insights into the effects of N fertilizer application on NO-emission pathways in acidic soil of a tea plantation. Plant Soil 2015, 389, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.C.; Lakshmanan, P.; Zhang, W.S.; Wang, X.Z.; Liu, B.; Ni, K.; Ruan, J.Y.; Shi, X.J.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S. Large loss of reactive nitrogen and the associated environmental damages from tea production in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 377, 109252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.Y.; Sun, Z.L.; Zhang, X.J.; Han, X.Y. Novel Aspects of Regulation of Nitrogen Responses in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis (L.)). Agronomy 2023, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Wei, K.; Ruan, L.; Bai, P.X.; Wu, L.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Cheng, H. Systematic Investigation and Expression Profiles of the Nitrate Transporter 1/Peptide Transporter Family (NPF) in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis (L.)). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xuan, Y.M.; Wang, S.M.; Fan, D.M.; Wang, X.C.; Zheng, X.Q. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of the ammonium transporter gene family in tea plants (Camellia sinensis (L.)). Physiol. Plant. 2022, 174, e13646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.D.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Fan, K.; Ruan, J.Y. Isolation and characterization of chloroplastic glutamine synthetase gene (CsGS2) in tea plant. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.W.; Li, H.; Wang, W.L.; Wu, Z.J.; Cui, X.; Zhuang, J. CsGOGAT Is Important in Dynamic Changes of Theanine Content in Postharvest Tea Plant Leaves under Different Temperature and Shading Spreadings. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9693–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, K.W.; Wang, Y.; Qian, W.J.; Sun, L.T.; Shen, J.Z.; Ding, Z.T.; Fan, K. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal the molecular mechanism of amino acid transport between source and sink during tea shoot development. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.T.; Gai, Z.S.; Wang, Y.; Fan, K.; Sun, L.T.; Wang, H.; Ding, Z.T. Comprehensive proteome analyses of lysine acetylation in tea leaves by sensing nitrogen nutrition. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.H.; Chen, C.S.; Zhao, S.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, Q.S.; Ruan, Q.C.; Chen, Z.H.; You, X.M.; Shan, R.Y.; Li, X.L.; et al. Molecular and physiological mechanisms of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) leaf and root in response to nitrogen deficiency. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, H.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y.Q.; Ni, D.J.; et al. Metabolome and RNA-seq Analysis of Responses to Nitrogen Deprivation and Resupply in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) Roots. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 932720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yao, Q.Y.; Xia, E.H.; Gao, L.Z. Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Analyses Reveal Nitrogen Influences on the Accumulation of Flavonoids and Amino Acids in Young Shoots of Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis L.) Associated with Tea Flavor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9828–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Burgos, A.; Zhang, Q.F.; Tang, D.D.; Shi, Y.Z.; Ma, L.F.; Yi, X.Y.; Ruan, J.Y. Analyses of transcriptome profiles and selected metabolites unravel the metabolic response to NH4+ and NO3− as signaling molecules in tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.). Sci. Hortic. 2017, 218, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.Y.; Li, H.P.; Tai, Y.L.; Dong, C.X.; Cheng, X.M.; Xia, E.H.; Chen, Z.P.; Li, F.; Wan, X.C.; Zhang, Z.L. Transcriptional regulation of amino acid metabolism in response to nitrogen deficiency and nitrogen forms in tea plant root (Camellia sinensis L.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, F.; Wan, Q.; Ruan, J.Y. Transcriptome analysis using RNA-Seq revealed the effects of nitrogen form on major secondary metabolite biosynthesis in tea (Camellia sinensis) plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018, 40, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Wei, K.; Li, J.W.; He, M.D.; Wu, L.Y.; Aktar, S.; Wang, L.Y.; Cheng, H. Responses of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) with different low nitrogen tolerances during recovery from nitrogen deficiency. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.S.; Zhong, Q.S.; Lin, Z.H.; Yu, W.Q.; Wang, M.K.; Chen, Z.H.; You, X.M. Screening tea varieties for nitrogen efficiency. J. Plant Nutr. 2017, 40, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.F.; Shi, Y.Z.; Ruan, J.Y. Nitrogen absorption by field-grown tea plants (Camellia sinensis) in winter dormancy and utilization in spring shoots. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.D.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Ma, L.F.; Shi, Y.Z.; Ruan, J.Y. Preferential assimilation of NH4+ over NO3− in tea plant associated with genes involved in nitrogen transportation, utilization and catechins biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2020, 291, 110369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, L.; Wu, W. Using 15N labeling to study the differences in nitrogen fertilizer utilization efficiency among different varieties of tea trees. Fujian Tea 2005, 1, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Bai, P.X.; Ruan, L.; Zhang, C.C.; Wei, K.; Cheng, H. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of ammonium transporters in tea plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) under different nitrogen treatments. Gene 2018, 658, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; He, W.; Yuan, Q.Y.; Wei, K.; Ruan, L.; Wang, L.Y.; Cheng, H. Transcriptome analysis identifies CsNRT genes involved in nitrogen uptake in tea plants, with a major role of CsNRT2.4. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegeder, M.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Source and sink mechanisms of nitrogen transport and use. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezhneva, L.; Kiba, T.; Feria-Bourrellier, A.B.; Lafouge, F.; Boutet-Mercey, S.; Zoufan, P.; Sakakibara, H.; Daniel-Vedele, F.; Krapp, A. The Arabidopsis nitrate transporter NRT2.5 plays a role in nitrate acquisition and remobilization in nitrogen-starved plants. Plant J. 2014, 80, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, X.C.; Yan, Y.; He, C.X.; Wang, J.; Sun, M.T.; Li, Y.S. Amino Acid Transporters on Amino Acid Absorption, Transport and Distribution in Crops. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lv, C.J.; Zou, Z.W.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, J.J.; Zhu, X.J.; Ma, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.L.; Fang, W.P. CsAAP7.2 is involved in the uptake of amino acids from soil and the long-distance transport of theanine in tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Tree Physiol. 2022, 42, 2369–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Zhang, Q.F.; Tang, D.D.; Shi, Y.Z.; Ma, L.; Liu, M.Y.; Ruan, J.Y. Dynamics of nitrogen translocation from mature leaves to new shoots and related gene expression during spring shoots development in tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2020, 183, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Ma, D.N.; Zaman, F.; Hao, X.L.; Xia, L.; Zhang, E.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.L.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; et al. Identification of the lysine and histidine transporter family in Camellia sinensis and the characterizations in nitrogen utilization. Hortic. Plant J. 2024, 10, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Dong, C.X.; Yang, T.Y.; Bao, S.L.; Fang, W.P.; Lucas, W.J.; Zhang, Z.L. The tea plant CsLHT1 and CsLHT6 transporters take up amino acids, as a nitrogen source, from the soil of organic tea plantations. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ding, G.D.; Yang, N.M.; White, P.J.; Ye, X.S.; Cai, H.M.; Lu, J.W.; Shi, L.; Xu, F.S. Comparative genome and transcriptome analysis unravels key factors of nitrogen use efficiency in Brassica napus L. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 712–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, W.; Sarwar, N.; Hafeez, O.B.; Arif, M.A.R.; Akhtar, M.; Yang, G.Z. Exploring genotypic variations in cotton associated with growth and nitrogen use efficiency. J. Plant Nutr. 2024, 47, 3231–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Z.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, S. Function of hormone signaling in regulating nitrogen-use efficiency in plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 294, 154191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Vankova, R.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Tran, L.S.P. Cytokinins: Metabolism and function in plant adaptation to environmental stresses. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smehilová, M.; Dobrusková, J.; Novák, O.; Takác, T.; Galuszka, P. Cytokinin-Specific Glycosyltransferases Possess Different Roles in Cytokinin Homeostasis Maintenance. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.L.; Xie, R.R.; Tian, H.; Wang, Q.L.; Guo, F.Q. Putative zeatin O-glucosyltransferase OscZOG1 regulates root and shoot development and formation of agronomic traits in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.W.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, C.C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H.Q.; Ding, C.Q.; Li, N.A.; Wang, L.; Zeng, J.M.; et al. Uncovering the complex regulatory network of spring bud sprouting in tea plants: Insights from metabolic, hormonal, and oxidative stress pathways. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1263606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Sun, K.; Qin, X.; Gong, S.; Li, Z.; Fan, K. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals a Tissue-Specific Pathway Involved in Nitrogen Utilization Between Genotypes with Different Nitrogen Use Efficiencies in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis). Agronomy 2024, 14, 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122824
Wang M, Sun K, Qin X, Gong S, Li Z, Fan K. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals a Tissue-Specific Pathway Involved in Nitrogen Utilization Between Genotypes with Different Nitrogen Use Efficiencies in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis). Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122824
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Min, Kangwei Sun, Xujun Qin, Shuting Gong, Zhipeng Li, and Kai Fan. 2024. "Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals a Tissue-Specific Pathway Involved in Nitrogen Utilization Between Genotypes with Different Nitrogen Use Efficiencies in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis)" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122824
APA StyleWang, M., Sun, K., Qin, X., Gong, S., Li, Z., & Fan, K. (2024). Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals a Tissue-Specific Pathway Involved in Nitrogen Utilization Between Genotypes with Different Nitrogen Use Efficiencies in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis). Agronomy, 14(12), 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122824




