First Report of Leaf Spot Disease (“Negrilla”) on Agave salmiana Otto Ex Salm-Dyck (ssp. salmiana) Plants Caused by Bipolaris zeae Zivan in Mexico
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains Isolation
2.2. Morphological Characterization
2.3. Molecular Characterization
2.4. Pathogenicity Tests
3. Results and Discussion
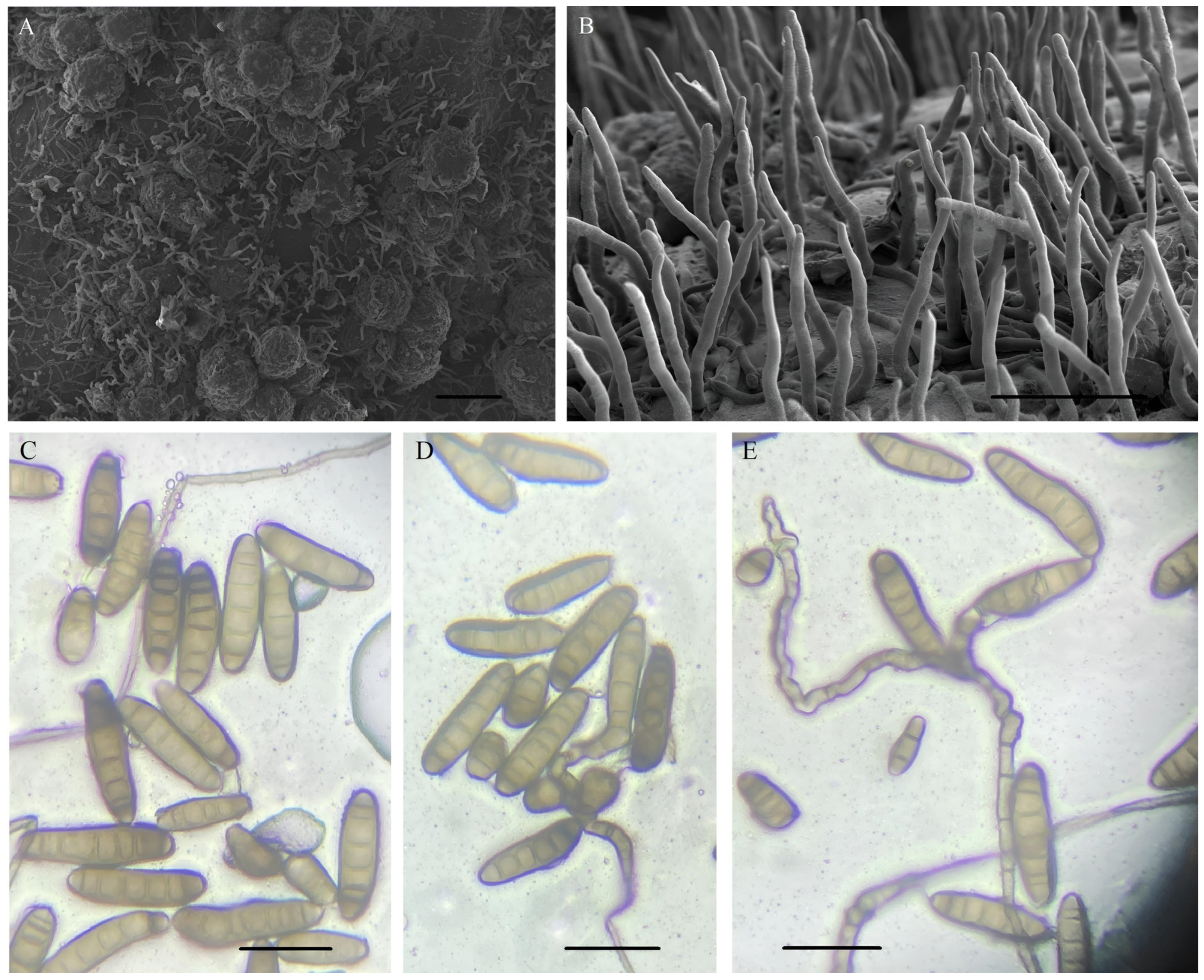
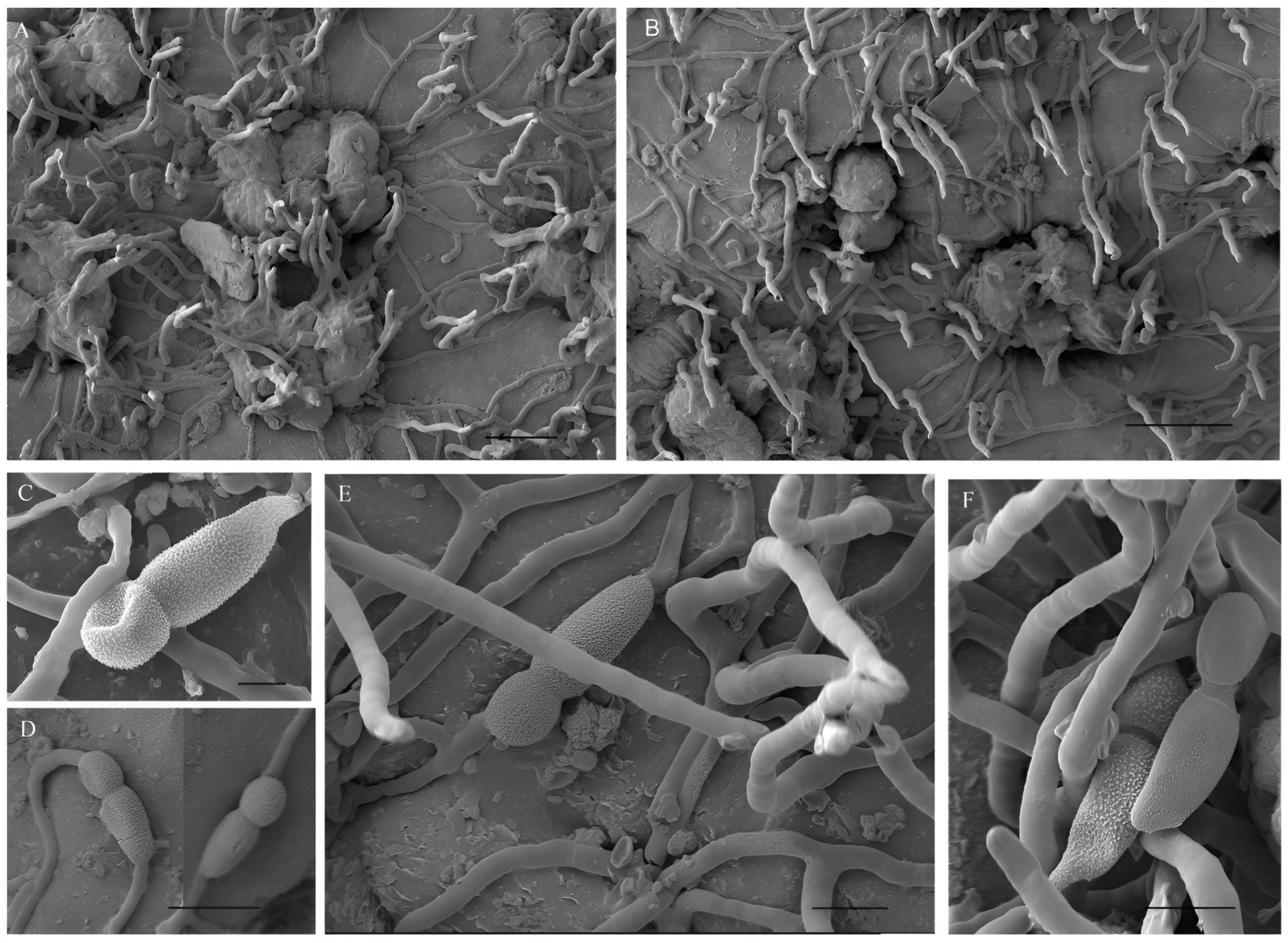
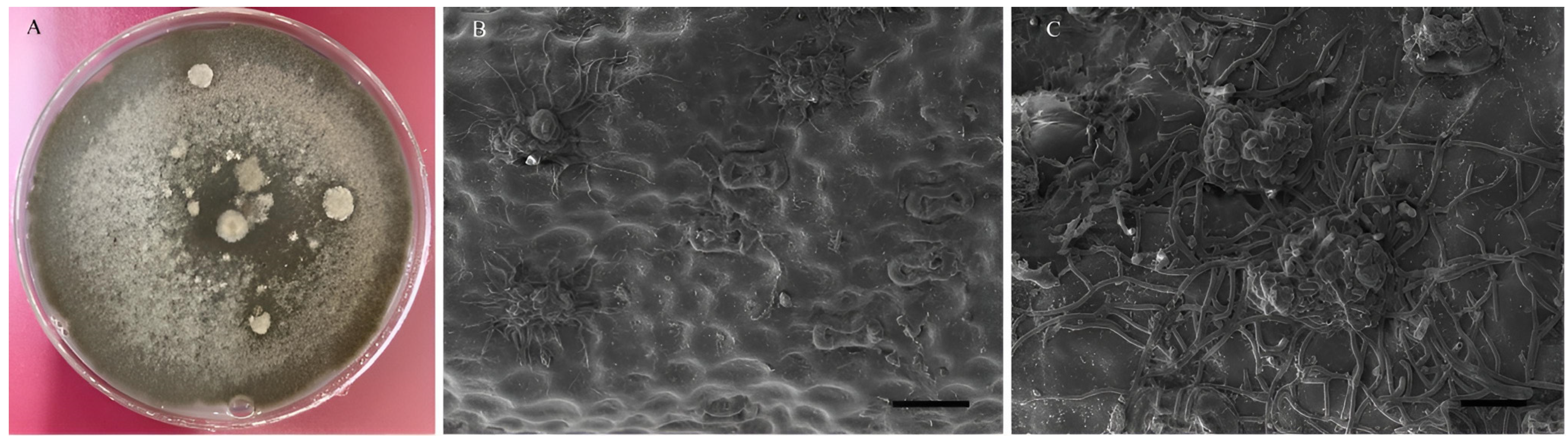
3.1. Morphological Characterization
3.2. Molecular Characterization
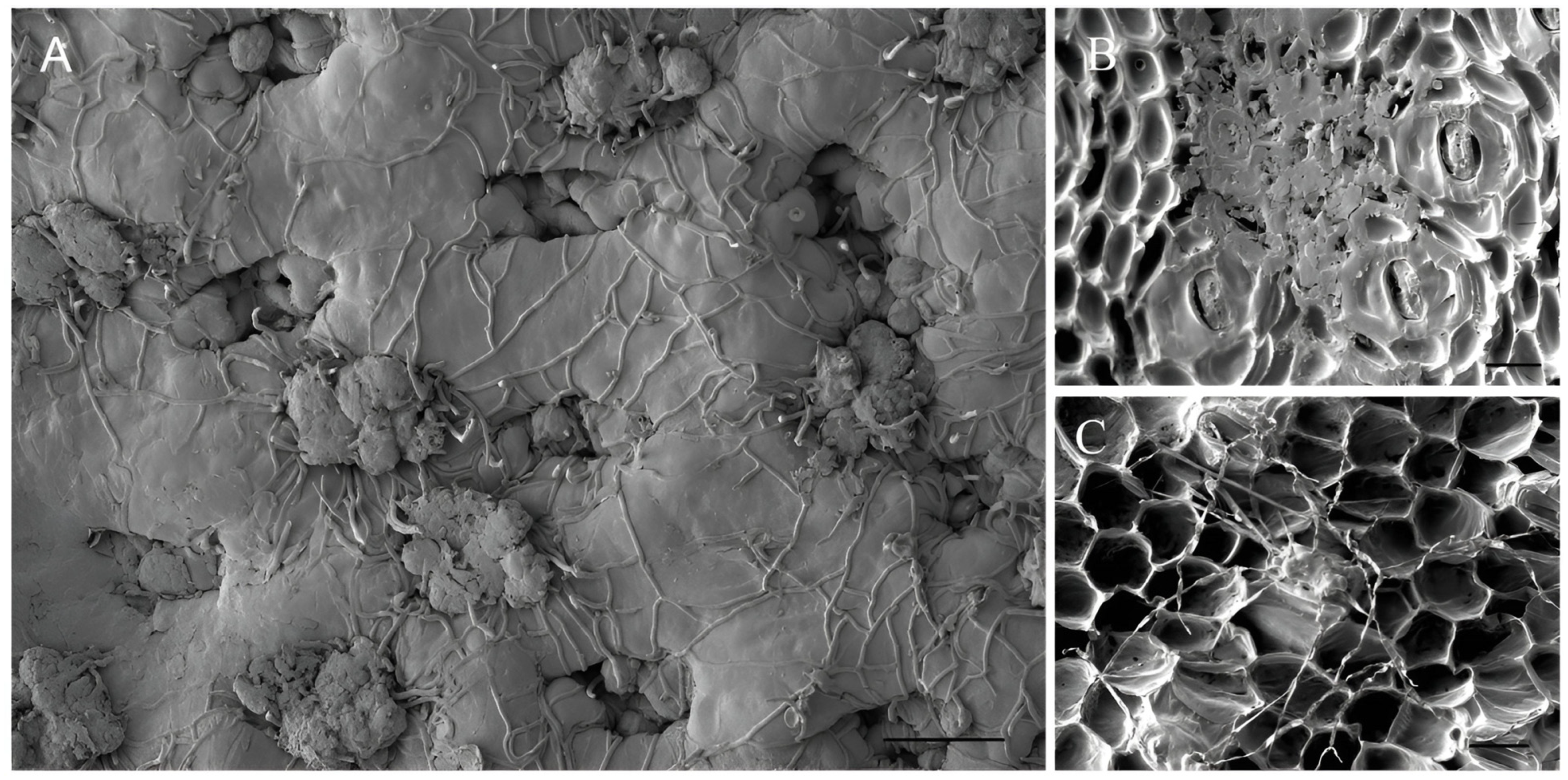
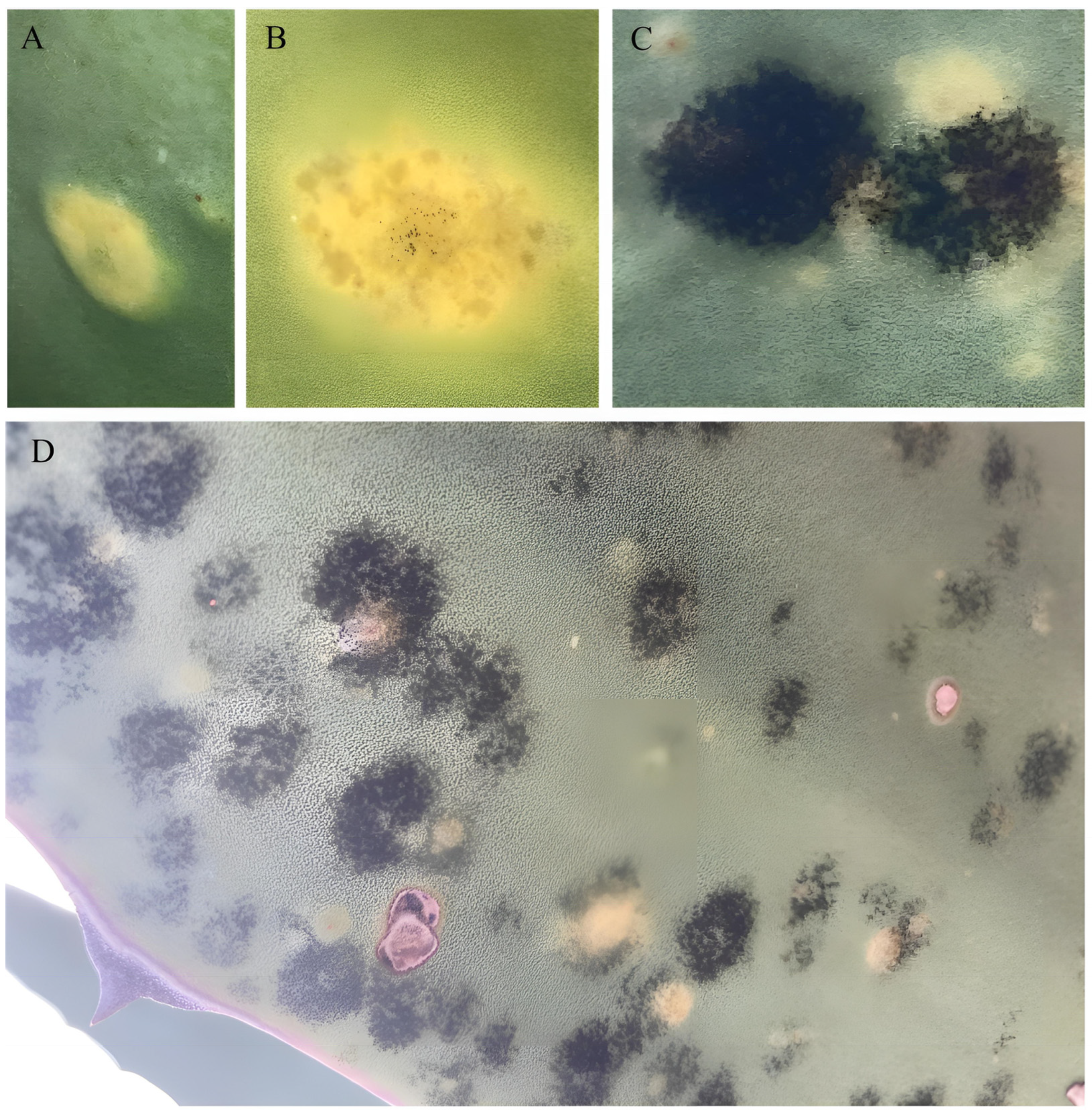
3.3. Bipolaris zeae Pathogenicity Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sivanesan, A. Graminicolous Species of Bipolaris, Curvularia, Drechslera, Exserohilum and Their Teleomorphs, 10th ed.; No. 158; CAB International Mycological Institute: Wallingford, UK, 1987; pp. 10–267. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, R.; González, M.S. Caracterización y patogenicidad de hongos del complejo Helminthosporium asociados al cultivo del arroz en Venezuela. Bioagro 2008, 20, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker, R.A. Nomenclature of Drechslera and Bipolaris, grass parasites segregated from ‘Helminthosporium’. Canad. J. Bot. 1959, 37, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsler, C. Phytopathological and taxonomical aspects of Ophilobolus, Pyrenophora, Helminthosporium and a new genus Cochliobolus. Phytopathological 1934, 24, 973. [Google Scholar]
- Manamgoda, D.S.; Cai, L.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Crous, P.W.; Madrid, H.; Chukeatirote, E.; Shivas, R.G.; Tan, Y.P.; Hyde, K.D. A phylogenetic and taxonomic re-evaluation of the Bipolaris–Cochliobolus—Curvularia Complex. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manamgoda, D.S.; Rossman, A.Y.; Castlebury, L.A.; Crous, P.W.; Madrid, H.; Chukeatirote, E.; Hyde, K.D. The genus Bipolaris. Stud. Micol. 2014, 79, 221–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Crous, P.W.; Schoch, C.L.; Hyde, K.D. Pleosporales. Fungal Divers. 2012, 53, 1–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbee, M.L.; Pirseyedi, M.; Hubbard, S. Cochliobolus phylogenetics and the origin of known, highly virulent pathogens, inferred from ITS and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene sequences. Mycologia 1999, 91, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-González, L.; De Mello-Prado, R.; Silva-Campos, C.N.; Barbosada-Silva, J.G. Desarrollo de la mancha foliar por Bipolaris maydis (teleomorfo: Cochliobolus heterostrophus) en maíz dulce en función de nitrógeno, potasio y silicio en invernadero. Cienc. Tecnol. Agropecuaria 2020, 21, e1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Cortes, T.; Zavala-González, E.A.; Pérez, E.V.H.; Aparicio-Burgos, J.E.; Cuervo-Parra, J.A. Characterization of Cochliobolus sativus and Pyrenophora teres fungi belonging to the leaf spot complex of barley (Hordeum vulgare) isolated from barley seeds in Mexico. Chilean J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 37, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.X.; Qi, Y.J.; Wang, L.H.; Li, C.J. First report of leaf spot disease on Fagopyrum esculentum caused by Bipolaris zeae in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 10, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-España, V.H.; Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Aparicio, B.J.E.; Morales-Ovando, M.A.; Peralta, G.M.; Romero-Cortes, T. Importancia de la capa cuticular durante la colonización del hongo causante de la negrilla en Agave salmiana Otto ex Salm-Dyck ssp. salmiana. Rev. Mex. Cienc. For. 2022, 13, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Santoyo, C.I.; Leyva-Mir, S.G.; Camacho-Tapia, M.; Tovar-Pedraza, J.M.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Villaseñor-Mir, H.E.; García-León, E. Aggressiveness of Bipolaris sorokiniana and Alternaria alternata isolates on wheat cultivars in Mexico. Rev. Mex. Fitopatol. 2018, 36, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Cortes, T.; Tamayo-Rivera, L.; Morales-Ovando, M.A.; Aparicio-Burgos, J.E.; Pérez-España, V.H.; Peralta-Gil, M.; Cuervo-Parra, J.A. Growth and yield of purple Kculli corn plants under different fertilization schemes. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockus, W.W.; Bowden, R.L.; Hunger, R.M.; Morrill, W.L.; Murray, T.D.; Smiley, R.W. Diseases caused by fungi and fungus-like organisms. In Compendium of Wheat Diseases and Pests, 3rd ed.; The American Phytopatological Society: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2010; pp. 15–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manamgoda, D.S.; Cai, L.; Bahkali, A.H.; Chukeatirote, E.; Hyde, K.D. Cochliobolus: An overview and current status of species. Fungal Divers. 2011, 51, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Sano, A.; Aragane, N.; Fukuoka, M.; Tanaka, M.; Kawaura, F.; Fukuno, Y.; Matsuishi, E.; Hayashi, S. Disseminated infection by Bipolaris spicifera in an immunocompetent subject. Med. Mycol. 2008, 46, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khizzi, N.; Bakheshwain, S.; Parvez, S. Bipolaris: A plant pathogen causing human infections: An emerging problem in Saudi Arabia. Res. J. Microbiol. 2010, 5, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piontelli, L.E. Opportunistic species of clinical relevance in the Bipolaris Shoemaker & Curvularia Boedijn genera: Its characterization under newest taxonomic criteria. Taxonomía 2015, 30, 40–63. [Google Scholar]
- Carballo, C.M.; Matthews, S.; Spesso, M.F.; Consigli, C. Primer aislamiento en la Argentina de Bipolaris cynodontis en la uña. Dermatol. Argen. 2018, 24, 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Guarner, J.; Brandt, E.M. Histopathologic diagnosis of fungal infections in the 21st century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 247–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.P.; Crous, P.W.; Shivas, R.G. Eight novel Bipolaris species identified from John L. Alcorn’s collections at the Queensland Plant Pathology Herbarium (BRIP). Mycol. Prog. 2016, 15, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, K.C.; Sutton, D.A.; Fothergill, A.W.; Cano, J.; Gené, J.; Madrid, H.; De Hoog, S.; Crous, P.W.; Guarro, J. Diversity of Bipolaris species in clinical samples in the United States and their antifungal susceptibility profiles. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 4061–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, H.; da Cunha, K.C.; Gené, J.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Cano, J.; Sutton, D.A.; Guarro, J.; Crous, P.W. Novel Curvularia species from clinical specimens. Persoonia 2014, 33, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, A.S.; Manzar, N.; Maurya, A.; Mishra, D.D.; Singh, R.P.; Sharma, P.K. Development of Diagnostic Markers and Applied for Genetic Diversity Study and Population Structure of Bipolaris sorokiniana Associated with Leaf Blight Complex of Wheat. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzar, N.; Kashyap, A.S.; Maurya, A.; Rajawat, M.V.S.; Sharma, P.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Roy, M.; Saxena, A.K.; Singh, H.V. Multi-Gene Phylogenetic Approach for Identification and Diversity Analysis of Bipolaris maydis and Curvularia lunata Isolates Causing Foliar Blight of Zea mays. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mereles, G.L. Calidad Fisiológica, Identificación de Hongos y su Incidencia en la Pudrición de la Mazorca de Maíz Zea mays L. en el Municipio de Tepalcing., Morelos. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Autónoma Agraria Antonio Narro, Coahuila, México, December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Leyva-Mir, S.G.; Villaseñor-Mir, H.E.; Tovar-Pedraza, J.M.; García-León, E. Respuesta de genotipos de avena a la infección por Bipolaris victoriae y Bipolaris sorokiniana. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agric. 2019, 10, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pedroso, A.T.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Bautista-Baños, S.; Ventura-Zapata, E.; Cortez-Rocha, M.O.; Ramírez-Arrebato, M.A. Efecto in vitro de un quitosano de masa molecular media sobre dos cepas de Bipolaris oryzae aisladas en México y Cuba. Biotecnol. Apl. 2021, 38, 2201–2205. [Google Scholar]
- Sivanesan, A. New Bipolaris, Curvularia, and Exserohilum species. Mycol. Res. 1992, 6, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.J.; Hernández, D.E.M.; López, V.E.; Álvarez, C.J. Aislamiento e identificación del fitopatógeno causal de viruela o “negrilla” en Agave salmiana de municipios del estado de Hidalgo, México. Sci. Fungorum 2022, 53, e1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Cariño, H.F.; Guadarrama-Mendoza, P.C.; Sánchez-López, V.; Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Ramírez-Reyes, T.I.; Valadez-Blanco, R. Biocontrol of Alternaria alternata and Fusarium oxysporum by Trichoderma asperelloides and Bacillus licheniformis in tomato plants. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J G. 2020, 113, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Felix, Y.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Cai, L.; Chen, Q.; Marincowitz, S.; Barnes, I.; Bensch, K.; Braun, U.; Camporesi, E.; Damm, U.; et al. Genera of phytopathogenic fungi: GOPHY 1. Stud. Mycol. 2017, 86, 99–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Sánchez-López, V.; Romero-Cortes, T.; Ramírez-Lepe, M. Hypocrea/Trichoderma viridescens ITV43 with potential for biocontrol of Moniliophthora roreri Cif & Par, Phytophthora megasperma and Phytophthora capsici. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Cortes, T.; López-Pérez, P.A.; Pérez, E.V.H.; Medina-Toledo, A.K.; Aparicio-Burgos, J.E.; Cuervo-Parra, J.A. Confrontation of Trichoderma asperellum VSL80 against Aspergillus niger via the effect of enzymatic production. Chil. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 35, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, J.M.; Rygiewicz, P.T. Fungal-specific PCR primers developed for analysis of the ITS region of environmental DNA extracts. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Schwartz, S.; Wagner, L.; Miller, W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reveles, H.R.G.; Maldonado, T.C.; Chávez, R.I.; Muñoz, E.J.J.; Moreno, G.A. Vigencia de los Postulados de Koch en la reproducción de Trichinella spiralis en modelo experimental. Rev. Electrón. Vet. 2014, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, D.E.; García, N.J.R.; Peña, V.C.B.; Ramírez, T.H.M.; Morales, R.V. Tamaño de la semilla, emergencia y Desarrollo de la plántula de maguey (Agave salmiana Otto ex Salm-Dyck). Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2011, 34, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelló, A.; Sisterna, M.N.; Cortese, P. Scale for appraising the leaf blight of wheat caused by Alternaria triticimaculans. Cereal Res. Commun. 1998, 26, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analytical Software, Statistix 10, 1st ed.; Analytical Software: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 7–445.
- Sisterna, M.; Wolcan, S. Bipolaris zeae on Pennisetum clandestinum in Argentina. Summa Phytopathol. 1990, 16, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Nazareno, d.A.J.R.; d’Avila, C.M.J.; Michalski, M.V.; Rodrigues, R.A.; Santos, S.M.; Saraiva, N.A.S. Transmissao e Patogenicidade de duas Espécies de Bipolaris Associadas as Sementes de Panicum Maximum Jacq, 1st ed.; Embrapa Cerrados: Brasilia, Brazil, 2009; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.X.; Liang, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, X.Q.; Zhou, X.Q.; Johnson, R.D.; Li, C.J.; Wang, J.J.; et al. First Report of Leaf Spot of Hemarthria altissima Caused by Bipolaris zeae in China. Plant Dis. 2016, 101, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnis, M.A.; Rossman, Y.A.; Kleczewski, M.N.; Flory, L.S. Bipolaris microstegii Minnis, Rossman, Kleczewski & S.L. Flory, sp. nov. Persoonia 2012, 29, 150–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Qi, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Wu, C.; Chang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Guoshu, G. Etiology and Symptoms of Maize Leaf Spot Caused by Bipolaris spp. in Sichuan, China. Pathogens 2020, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Rivero, G.; Sánchez-Teyes, L.F.; De la Cruz-Arguijo, E.; Ramírez-González, M.S.; Larralde-Corona, C.P.; Narvaez-Zapata, J.A. Bioprospecting for Fungi with Potential Pathogenic Activity on Leaves of Agave tequilana Weber var. Azul. GenBank Direct Submission, 11 October 2018. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/MK041914.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Valencia, Y.T.; Martin, M.R.; Cruz, L.J.R.; Pérez, B.D.; Magaña, A.A.; Cortés, V.A.; Nexticapan, G.A. Identification and Molecular Characterization Phytopathogenic Fungi in Agave tequilana in Mexico. GenBank Direct Submission, 2 August 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/OR388091.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Mora-Aguilera, J.A.; Cabrera-Huerta, E.; Nava-Díaz, C.; Hernández-Castro, E. First report of Epicoccum sorghinum on Agave Mezcal (Agave angustifolia). GenBank Direct Submission, 19 June 2018. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/MH497563.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Romero-Cortes, T.; Aparicio-Burgos, J.E. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Phytopathogenic Fungi, Associated with Agave salmiana and Agave lechuguilla Plants with Disease Symptoms “Negrilla”, in the State of Hidalgo, Mexico. GenBank Direct Submission, 25 May 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/OR047544.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Campos-Rivero, G.; Sánchez-Teyes, L.F.; De la Cruz-Arguijo, E.; Ramírez-González, M.S.; Larralde-Corona, C.P.; Narvaez-Zapata, J.A. Bioprospecting for Fungi with Potential Pathogenic Activity on Leaves of Agave tequilana Weber var. Azul. GenBank Direct Submission, 11 October 2018. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/MK041894.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Romero-Cortes, T.; Aparicio-Burgos, J.E. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Phytopathogenic Fungi, Associated with Agave salmiana and Agave lechuguilla Plants with Disease Symptoms “Negrilla”, in the State of Hidalgo, Mexico. GenBank Direct Submission, 25 May 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/OR047545.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Flores-Nuñez, N.M.; Camarena-Pozos, D.A.; Partida-Martínez, L.P. Volatiles Emitted by Fungi Associated with the Phyllosphere of Agaves and Cacti are Diverse and Able to Promote Plant Growth. GenBank Direct Submission, 3 April 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/MT279265.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Romero-Cortes, T.; Aparicio-Burgos, J.E. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Phytopathogenic Fungi, Associated with Agave salmiana and Agave lechuguilla Plants with Disease Symptoms “Negrilla”, in the State of Hidalgo, Mexico. GenBank Direct Submission, 25 May 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/OR047542.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Tapia-Tussell, R.; Solis, S.; Pérez-Brito, D. Identification and Molecular Characterization of Ligninolytic Fungi from Yucatan, Mexico. GenBank Direct Submission, 17 June 2009. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/GQ280375.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Romero-Cortes, T.; Aparicio-Burgos, J.E. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Phytopathogenic Fungi, Associated with Agave salmiana and Agave lechuguilla Plants with Disease Symptoms “Negrilla”, in the State of Hidalgo, Mexico. GenBank Direct Submission, 25 May 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/OR047532.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Mohammadi, A.; Amini, Y. Molecular characterization and identification of Acrostalagmus luteoalbus from Saffron in Iran. Agric. Sci. Dev. 2015, 4, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Toju, H.; Tanabe, A.S.; Yamamoto, S.; Sato, H. High-coverage ITS primers for the DNA-based identification of ascomycetes and basidiomycetes in environmental samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgulis, A.; Coulouris, G.; Raytselis, Y.; Madden, T.L.; Agarwala, R.; Schäffer, A.A. Database indexing for production MegaBLAST searches. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visagie, C.M.; Bhiya, T.; Kgatle, G. Alternaria Diversity from South Africa. GenBank Direct Submission. 22 May 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/MT505870.1 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Vu, D.; Groenewald, M.; de Vries, M.; Gehrmann, T.; Stielow, B.; Eberhardt, U.; Al-Hatmi, A.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Cardinali, G.; Houbraken, J.; et al. Large-scale generation and analysis of filamentous fungal DNA barcodes boosts coverage for kingdom fungi and reveals thresholds for fungal species and higher taxon delimitation. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 92, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbee, M.L. Molecular Phylogenetics of Cochliobolus. GenBank Direct Submission, 30 July 1998. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/af081452 (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Bohl, S.K.; Harmon, P.F.; Clay, K.; Goss, E.M.; Flory, S.L. Widespread Independent Emergence and Accumulation of Fungal pathogens Reduce Fecundity of an Invasive Grass. GenBank Direct Submission, Submitted 10 August 2014. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/km507725 (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Adetunji, M.C.; Mwanza, M. Fungal Profile of Groundnut sold in Mafikeng, North West, South Africa. GenBank Direct Submission, 26 April 2019. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/mk841439 (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Berbee, M.; Pirseyedi, M.; Hubbard, S. GenBank Direct Submission. 10 June 1998. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/af071325 (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Berbee, M.; Pirseyedi, M.; Hubbard, S. GenBank Direct Submission. 10 June 1998. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/af071329 (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Ahmadpour, A.; Donyadoost-Chelan, M.; Heidarian, Z.; Javan-Nikkhah, M. New species of Bipolaris and Curvularia on grass species in Iran. Rostaniha 2011, 12, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Staiger, S.; Seufert, P.; Arand, K.; Burghardt, M.; Popp, C.; Riederer, M. The permeation barrier of plant cuticles: Uptake of active ingredients is limited by very long-chain aliphatic rather than cyclic wax compounds. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 3405–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-España, V.H.; Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Paz-Camacho, C.; Morales-Ovando, M.A.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, G.C.; Robles-Olvera, V.J.; López-Pérez, P.A.; Romero-Cortes, T. General characterization of cuticular membrane isolated from Agave salmiana. Int. J. Bio-resour. Stress Manag. 2019, 10, 046–052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centro Internacional de Mejoramiento de Maíz y Trigo (CIMMYT). Enfermedades del Maíz: Una Guía Para su Identificación en el Campo, 4th ed.; CIMMYT: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2004; pp. 18–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Romero-Cortes, T.; Aparicio-Burgos, J.E. Isolation and Molecular Identification of phytopathogenic Fungi, Associated with Agave salmiana and Agave lechuguilla Plants with Disease Symptoms “Negrilla”, in the State of Hidalgo, Mexico. GenBank Direct Submission, 25 May 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/OR047538.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Romero-Cortes, T.; Aparicio-Burgos, J.E. Isolation and Molecular Identification of Phytopathogenic Fungi, Associated with Agave salmiana and Agave lechuguilla Plants with Disease Symptoms “Negrilla”, in the State of Hidalgo, Mexico. GenBank Direct Submission, 25 May 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide/OR047536.1 (accessed on 1 March 2024).



| Strain | Strain Accession | Species | Total Score | Query Cover (%) | Identity (%) | Accesion Closest Hit | Accession Length (pb) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JCP-N01 | ON630338 | B. zeae | 1003 | 100 | 99.64 | MT505870 | 863 | Visagie et al. [61] |
| JCP-N02 | ON630339 | B. zeae | 985 | 100 | 99.63 | MT505870 | 863 | Visagie et al. [61] |
| JCP-N03 | ON630340 | B. zeae | 976 | 100 | 99.63 | MT505870 | 863 | Visagie et al. [61] |
| JCP-N04 | ON630341 | B. zeae | 976 | 100 | 99.44 | MT505870 | 863 | Visagie et al. [61] |
| JCP-N05 | ON630342 | B. zeae | 959 | 100 | 99.62 | MT505870 | 863 | Visagie et al. [61] |
| JCP-N06 | ON630343 | B. zeae | 985 | 100 | 99.63 | MT505870 | 863 | Visagie et al. [61] |
| JCP-N07 | ON630344 | B. zeae | 1011 | 100 | 99.64 | MT505870 | 863 | Visagie et al. [61] |
| JCP-N08 | ON630345 | B. zeae | 968 | 100 | 99.62 | KJ909787 | 568 | Manamgoda et al. [6] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero-Cortes, T.; Pérez España, V.H.; Pescador-Rojas, J.A.; Rangel-Cortés, E.; Armendaríz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Cuervo-Parra, J.A. First Report of Leaf Spot Disease (“Negrilla”) on Agave salmiana Otto Ex Salm-Dyck (ssp. salmiana) Plants Caused by Bipolaris zeae Zivan in Mexico. Agronomy 2024, 14, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030623
Romero-Cortes T, Pérez España VH, Pescador-Rojas JA, Rangel-Cortés E, Armendaríz-Ontiveros MM, Cuervo-Parra JA. First Report of Leaf Spot Disease (“Negrilla”) on Agave salmiana Otto Ex Salm-Dyck (ssp. salmiana) Plants Caused by Bipolaris zeae Zivan in Mexico. Agronomy. 2024; 14(3):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030623
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero-Cortes, Teresa, Victor H. Pérez España, José A. Pescador-Rojas, Eduardo Rangel-Cortés, María M. Armendaríz-Ontiveros, and Jaime A. Cuervo-Parra. 2024. "First Report of Leaf Spot Disease (“Negrilla”) on Agave salmiana Otto Ex Salm-Dyck (ssp. salmiana) Plants Caused by Bipolaris zeae Zivan in Mexico" Agronomy 14, no. 3: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030623
APA StyleRomero-Cortes, T., Pérez España, V. H., Pescador-Rojas, J. A., Rangel-Cortés, E., Armendaríz-Ontiveros, M. M., & Cuervo-Parra, J. A. (2024). First Report of Leaf Spot Disease (“Negrilla”) on Agave salmiana Otto Ex Salm-Dyck (ssp. salmiana) Plants Caused by Bipolaris zeae Zivan in Mexico. Agronomy, 14(3), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030623







