Abstract
Traditional deep learning models for fruit and vegetable classification are usually implemented via training on an unchanged dataset. However, changing fruit and vegetable categories is a very common occurrence in the context of real agricultural sales. When dealing with changes related to variety, deep learning models need to be retrained on the entire updated dataset. The retraining process is time-consuming and inefficient, and it may even cause the ‘catastrophic forgetting’ problem. In response to this challenge, the Adversarial Domain Adaptation Class Incremental Learning (ADA-CIL) method is introduced. This approach employs adversarial domain adaptation techniques combined with core-set selection strategies to effectively extract and integrate cross-domain features. We utilize the ResNet34 architecture as the backbone for feature extraction due to its deep residual learning framework, which is robust in handling the complexities of large and varied image datasets. It achieves a dynamic balance in learning between new and existing categories, significantly enhancing the model’s generalization capabilities and information retention efficiency. The FruVeg dataset, composed of three sub-datasets, includes over 120,000 color images, covering more than 100 different categories of fruits and vegetables collected from various domains and backgrounds. The experimental results on the FruVeg dataset show that the ADA-CIL method achieves an average accuracy of 96.30%, a forgetting rate of 2.96%, a cumulative accuracy of 96.26%, and a current accuracy of 98.60%. The ADA-CIL method improves the average accuracy by 1.65% and 1.82% compared to iCaRL and BiC, respectively, and it reduces the forgetting rate by 2.69% and 2.76%. These performance metrics demonstrate the ADA-CIL method’s impressive ability to handle incremental category and domain changes, highlighting its capability to effectively maintain the intra-class stability and exhibit exceptional adaptability in dynamic learning environments.
1. Introduction
The classification of fruits and vegetables by their variety is an important part of the agricultural marketing process [1,2,3,4]. This classification contributes to improving the efficiency of the economic transformation of agricultural products, optimizing the use of resources, reducing waste, providing a more efficient shopping experience for consumers, and improving human health [4,5]. Automated classification techniques [6,7,8] are necessary because such tasks are traditionally performed manually, with no guarantee of efficiency or accuracy [9].
Computer vision technology [10,11,12,13,14,15,16] provides an efficient solution to this problem. Bolle et al. [17] achieved, for the first time, the classification and recognition of multiple types of randomly placed fruit and vegetable produce by extracting the color and texture features of the image, and they developed the Veggie Vision intelligent fruit and vegetable recognition system. In recent years, reports [18,19] have illustrated that deep learning techniques can play an important role in the classification of fruits and vegetables at supermarket self-checkout counters. In the context of our research, especially within retail environments, such as those in China, fruits and vegetables are typically weighed and priced together during the checkout process. As a result, we have adopted a unified classification approach for both fruits and vegetables in our study. This classification strategy not only simplifies the checkout procedure but also enhances the efficiency and applicability of self-checkout systems. Rojas et al. [20] utilized lightweight convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to automate the image classification of fruits and vegetables, thereby speeding up the checkout process in retail stores. Each fruit has a unique RGB code, which is considered as a feature vector along with the RGB histogram and K-means center point. Accuracy can reach up to 95%. Zhenbo Li et al. [21] proposed an improved VGG network model that achieved a 96.5% classification and recognition accuracy in their vegetable image dataset. Bazame et al. [22] introduced a practical fruit recognition expert system built using the EfficientNet and MixNet deep neural network series, enhancing the accuracy and speed of fruit identification. Hameed et al. [23] proposed a class distribution-aware adaptive margin method with clustering embedding, which achieved significant improvements in clustering and classification. Gulzar [24] developed TL-MobileNetV2, an enhanced MobileNetV2 model with customized headers and transfer learning, achieving 99% precision, recall, and F1 scores for fruit classification. Gao et al. [25] addressed the challenge of classifying fruits and vegetables with similar shapes but differing nutritional values by employing data augmentation and feature enhancement in conjunction with Vision Transformer (ViT) technology [26]. Alkanan et al. [27] successfully implemented an efficient classification system for corn diseases using an enhanced MobileNetV2 model, demonstrating excellent performance in terms of precision, recall, and F1 scores.
These classification methods have contributed significantly to the automation of fruit and vegetable classification. However, in an actual shopping center, supermarket, or retail shop, it is commonplace to add, delete, or change fruit or vegetable categories. This ongoing need to accommodate these new varieties necessitates the retraining of deep learning models on entire datasets, which is not only time-consuming but also fraught with inefficiencies. More importantly, this retraining often leads to “catastrophic forgetting [28]”, where previous knowledge is lost when new information is added. Consequently, there is a pressing need to develop advanced classification methods that can quickly adapt to new and existing varieties without the need for extensive retraining. This study focuses on overcoming these challenges through incremental learning techniques [29,30,31,32], which update the model using only new data, thus preserving existing knowledge and ensuring stable and accurate classification across variable conditions, such as changes in season, climate, and geographic location.
To address the challenges of dynamic real-world scenarios, this study focuses on exploring the generalized class incremental learning problem. Within this problem framework, we introduce and reinforce the concept of domain labels, expanding to “class + domain” incrementality. This implies that, in a continuous data stream, both the categories and domain distribution of fruits and vegetables change over time and across locations. This study proposes the Adversarial Domain Adaptation Class Incremental Learning (ADA-CIL) method, aimed at optimizing the classification process of fruits and vegetables. This method employs a domain adaptive adversarial neural network structure, effectively reducing domain drift issues [33]. By combining knowledge distillation strategies and core-set selection, this method not only mitigates the “catastrophic forgetting” problem but also facilitates effective retrospective learning by preserving high-quality samples. Furthermore, an online sample generation strategy based on mix-up is introduced, which not only increases the diversity of the sample set but also avoids the limitations of the memory pool size, effectively alleviating data imbalance issues. Our main contributions can be summarized as follows.
- The ADA-CIL method is developed, combining adversarial domain adaptation and core-set selection to address dynamic changes in fruit and vegetable classification.
- The ResNet34 architecture is employed for robust feature extraction, optimizing the performance on diverse image datasets within the incremental learning framework.
- A dynamic balance between learning new categories and retaining existing ones enhances the model’s generalization and reduces catastrophic forgetting.
- The ADA-CIL method demonstrates proven adaptability and stability across various domains, being effective in real-world agricultural settings with frequent category and domain changes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
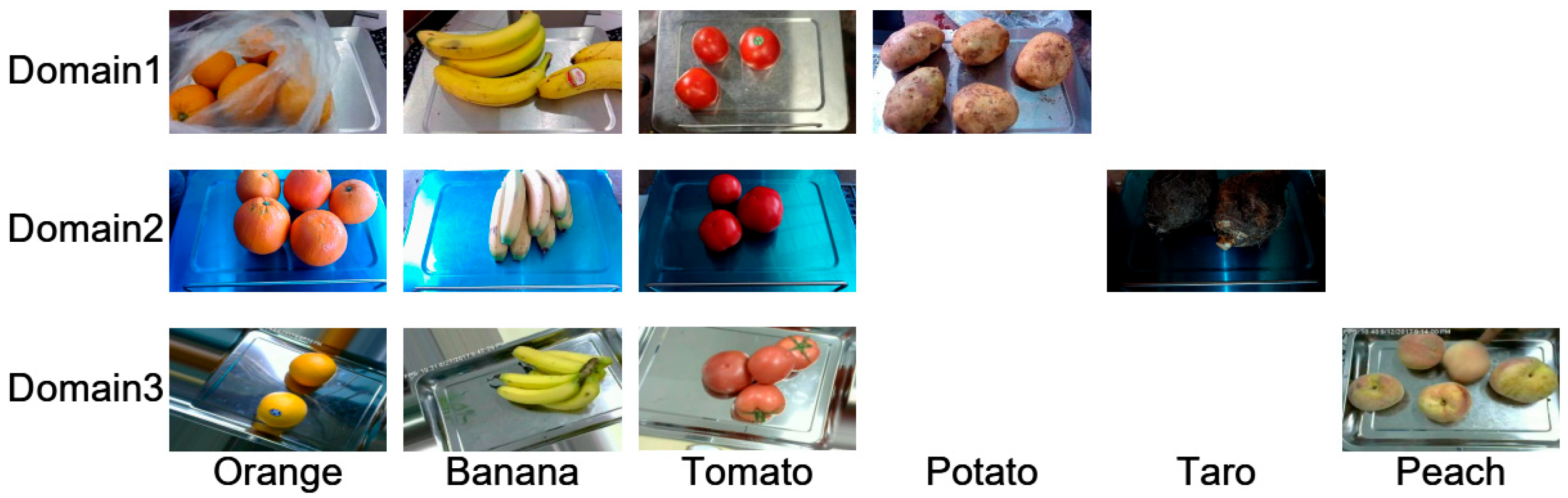
This study utilizes a comprehensive dataset named FruVeg, which consists of three sub-datasets from different domains, comprising over 120,000 color images that cover more than 100 types of fruits and vegetables. Example images from this dataset are displayed in Figure 1. Each sub-dataset was collected in unique backgrounds and locations, covering a wide range of external conditions, such as lighting, shooting angles, and obstructions, to ensure the comprehensiveness and practical applicability of the dataset. Notably, the images from domains 1 and 2 were captured with the same high-dynamic-range infrared-enhanced wide-angle camera, while those from domain 3 were collected with a different camera. The images were captured at the fruit and vegetable weighing stations in supermarkets across China, at a rate of one frame per second. The data underwent rigorous manual selection to ensure image quality (Table 1).
Figure 1.
Example images from FruVeg dataset.

Table 1.
Camera specifications. Camera 1 and camera 2 were source from Xi’an, China.
In terms of category composition, the FruVeg dataset shows significant intersections and differences across the three domains. Domain 1 contains 90 categories, each with 500 to 1500 images; domain 2 comprises 45 categories, each with 300 to 500 images; and domain 3 includes 15 categories, each with 50 to 100 images. Notably, there are 35 overlapping categories between these domains, such as 35 shared between domains 1 and 2; 9 shared between domains 1 and 3; and 4 overlapping categories between domains 2 and 3. Additionally, 3 categories are present across all domains.
To ensure accuracy and convenience in data processing, the FruVeg dataset employs a unique labeling strategy. The same category, when present in different domains, is assigned different labels to reflect its unique attributes in different environments. For example, tomatoes are labeled as 131, 132, and 133 in domains 1, 2, and 3, respectively, to distinguish the features of different domains. However, for simplification in experimental processing and analysis, these labels are uniformly mapped back to the original labels of domain 1, i.e., 131, during category mapping calculations. This approach maintains the distinctiveness between the different domains while facilitating consistent analyses.
2.2. Problem Definition
Our study defines a generalized class incremental learning problem. Let us assume a series of potential data streams , where each data stream contains a set of data samples , representing the data samples, corresponding class labels, and domain labels of the i-th category in data stream , respectively. This study assumes that each category has multiple domains, representing different variations, such as changes in the background or style. Furthermore, each data stream is defined as the union of two sets . represents the data of entirely new categories, while represents the data of existing categories.
The model is defined as a feature extraction network , where represents the parameters. The category classifier is denoted as , and the domain classifier is represented by . After learning from data , the model is updated from to . The sample set is defined as , where . Before the start of incremental learning, the initial model is defined as M0M_0M0. Additionally, the incremental learning process is defined as a series of operations :
where represents the maximum storage space used to retain old samples or other useful data. Each phase describes the process of updating the model from the previous round’s state to the current round’s state .
2.3. Architecture of ADA-CIL
In response to the complex task of incremental learning for fruit and vegetable classification, the ADA-CIL method proposed in this study aims to address the combined challenge of class and domain incrementation.
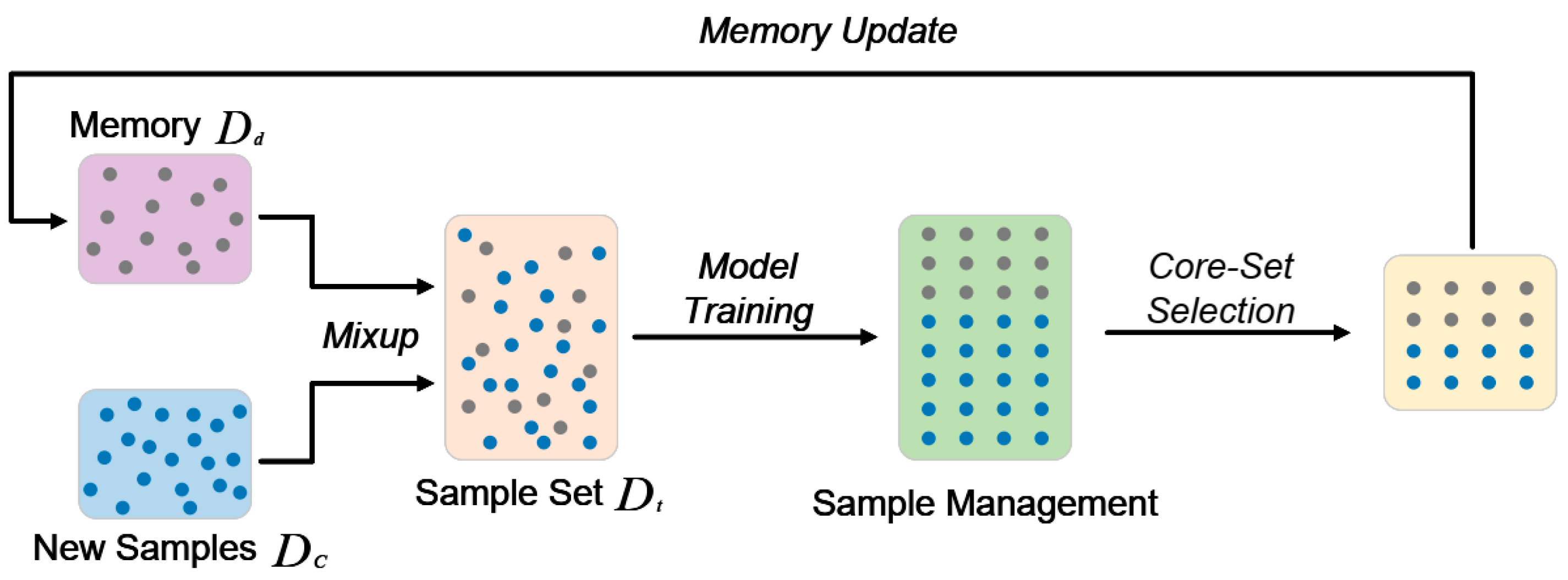
The ADA-CIL method employs an end-to-end training framework, as illustrated in Figure 2. This framework consists of four key components: the construction of the sample set, model training, sample management, and memory updating. This comprehensive framework offers a holistic and efficient solution for handling incremental learning tasks.
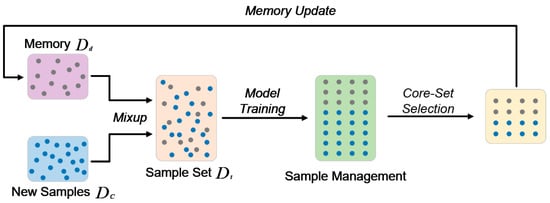
Figure 2.
End-to-end training framework of ADA-CIL. The blue dots represent new samples, while the grey dots represent old samples.
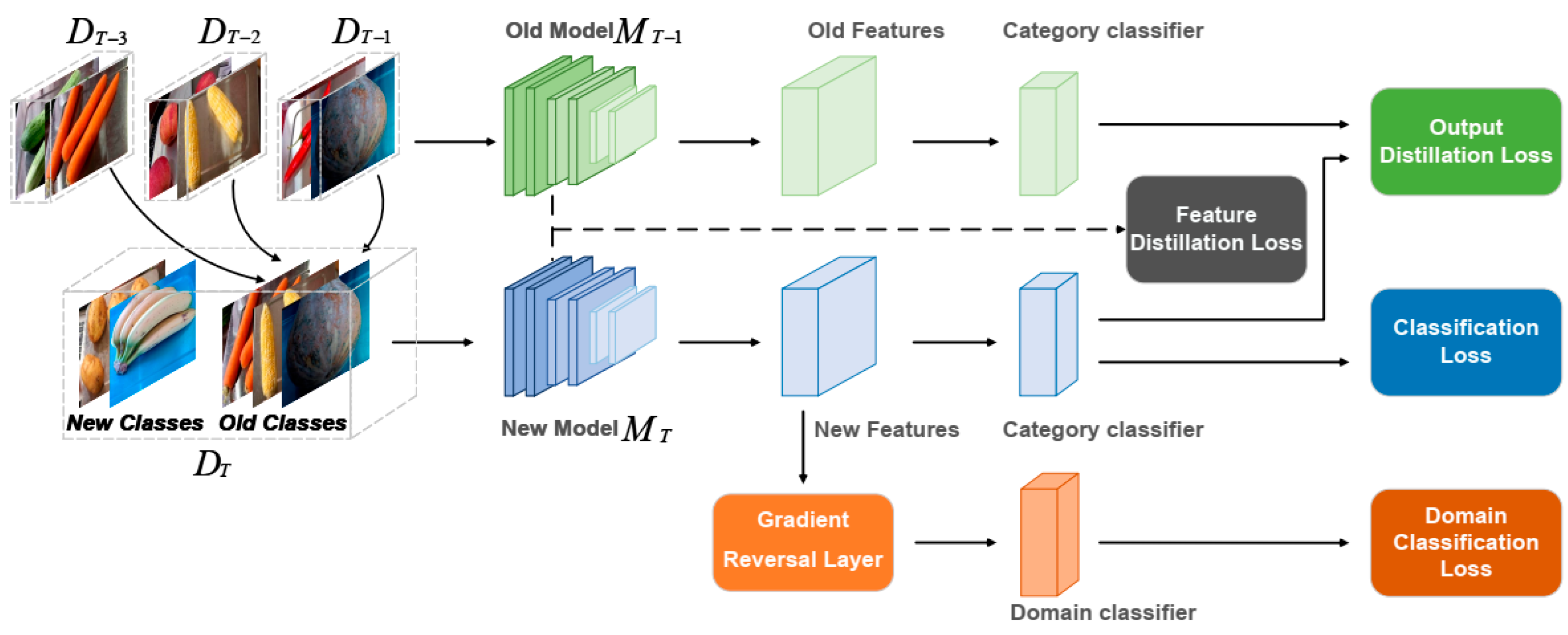
The network architecture used during the ADA-CIL training process is shown in Figure 3. In this framework, the old model’s main role is to maintain the existing knowledge, while the new model focuses on learning the newly introduced categories. To ensure the continuity and consistency of the knowledge, knowledge distillation techniques are utilized. This involves comparing the intermediate and output features of the new model with the corresponding features of the old model, ensuring that the original learning achievements are not lost while integrating new information. Additionally, to facilitate the model’s generalization across different domains, the output features of the new model establish an adversarial relationship with the domain classifier via a gradient reversal layer.
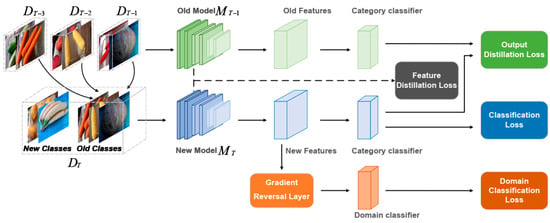
Figure 3.
Network architecture of ADA-CIL.
2.4. Adversarial Domain Adaptation
In addressing the “class + domain” incremental learning task, particularly in the complex context of fruit and vegetable classification, this study draws on the core concept of domain adaptation [34] and adopts an adversarial learning strategy [35] to address the challenge. In designing the ADA-CIL network structure, we skillfully integrated the objectives of category recognition and domain adaptation. The aim is to enhance the model’s generalization ability in classifying fruits and vegetables across different domains through adversarial training.
During the model learning process, the feature extractor is responsible for extracting data features and passing them to the domain classifier. The domain classifier is tasked with identifying the source domain of the information and calculating the domain classification loss. Through the gradient reversal layer, this loss causes a reversal in the direction of the gradients for the feature extractor during backpropagation. This design strategy creates an adversarial relationship between the feature extractor and the domain classifier: the domain classifier tries to categorize information into the correct domain, while the feature extractor strives to extract common features across domains, making it difficult for the domain classifier to accurately determine the source of information. When the domain classifier fails to correctly identify the domain labels, it indicates that the feature extractor has successfully mapped samples from different domains to the same feature space. Meanwhile, the role of the category classifier is to ensure that the network effectively completes the final classification task.
Summarizing the above, we define the loss function for our adversarial domain adaptation network component as follows:
where and represent the category classification loss and domain classification loss, respectively. The category classification loss is defined as
The domain classification loss is defined as
, as a dynamic parameter, is defined as
where is a constant of 10, and represents the relative iteration process, i.e., the ratio of the current iteration number to the total number of iterations.
2.5. Distillation and Core-Set Selection
To effectively preserve the knowledge of previously learned samples, this study concurrently applies knowledge distillation and core-set selection strategies in the ADA-CIL model. Through knowledge distillation, the model can capture and retain the important features and decision boundaries of the old model, which is crucial in maintaining the accurate recognition of previously learned categories. In the stages of feature extraction and classification, we use multi-level information constraints to distill old knowledge.
Specifically, we treat the model from the previous round (t − 1) as the teacher network and the model initialized in the current round (t) as the student model. In this framework, the teacher network generates soft labels to provide indirect guidance for the student model, thereby helping it to learn and adapt to new data while retaining knowledge of the old data.
The classification distillation loss is defined as
where represents the soft labels generated by the teacher network, and represents the predictive output of the student model. These concepts are further defined as
This approach allows the student model to more effectively capture and retain existing knowledge by imitating the output of the teacher network, rather than learning directly from hard labels.
Additionally, we incorporate constraints on the output feature maps of the intermediate layers in both the new and old models during the distillation process to further ensure stability when processing old samples. Specifically, we use the feature map outputs of the intermediate layer of the old model as a guiding layer to guide the learning of the intermediate layer feature maps and logit outputs of the new model. The distillation loss is defined as follows:
where and represent the feature map outputs of the intermediate layer in the teacher and student networks, respectively, and and are the corresponding transformation functions. is a metric function that calculates the similarity between the feature maps of the teacher and student networks, namely the cosine similarity.
Parallel to knowledge distillation, another key strategy is core-set selection, which plays an indispensable role in our ADA-CIL model. To maximize the preservation of old sample knowledge, we adopt a core-set selection strategy combining sample representativeness and uncertainty to build data storage after each round of training.
For the selection of representative samples, we employ the K-medoids clustering algorithm [36] to cluster the samples of each category in the feature space, identifying the most representative samples. These samples are selected by minimizing the total sum of the distances from all samples in this category to their nearest representative sample point.
Then, for the selection of uncertain samples, we consider the boundaries of the categories and domains. As our study’s task scenario involves both category incrementation and domain adaptation, we use the margin sample method [37] to select uncertain samples near the category boundaries. The category uncertainty score and domain uncertainty score are defined as the difference between the posterior probabilities of the most likely and second most likely categories predicted by the model. We assess all samples based on these scores and select those with the highest uncertainty to join the memory pool. To balance the impact of representativeness and uncertainty on sample selection, we determine the number of representative and uncertain samples based on the number of incremental training rounds and the number of samples retained per category, ensuring the effective use of the limited storage resources.
2.6. Online Sample Generation
In this study, to address the issue of the limited data sample volume and to increase the sample diversity, we adopt an online sample generation strategy based on the mix-up technique. Mix-up is a data augmentation technique that blends two randomly chosen samples through linear interpolation, thereby generating new samples. Specifically, this process is achieved via the following Formula (9):
where and are the selected original samples, and are their corresponding labels, and is a random mixing coefficient within the range [0, 1].
2.7. Experimental Setup
All experiments in this study were conducted on a Xubuntu 16.04 LTS 64-bit operating system equipped with dual Titan XP GPUs, manufactured by NVIDIA Corporation in Santa Clara, CA, USA. The experimental setup was configured with Python 3.7 in conjunction with the torch 1.7.0 framework.
In the FruVeg dataset, we randomly divided the data into training, testing, and validation sets at a ratio of 7:2:1. For all images in the FruVeg dataset, we performed standardization processes, including resizing the images to a uniform resolution of 224 × 224 pixels and carrying out normalization. To enhance the model’s generalization, we implemented data augmentation strategies such as random flipping and rotation of the images during the training phase. It is noted that these preprocessing steps were not applied during the testing phase.
The ADA-CIL experiments began with 50 categories, with 10 new categories added in each round of incremental training, amounting to 10 rounds of incremental learning in total. Prior to initiating incremental learning training, we conducted a series of preliminary experiments on the domain 1 dataset. These experiments encompassed classic image classification networks such as the VGG [38] and ResNet [39] series, as well as lightweight networks including MobileNet [40] and ShuffleNet [41]. After carefully considering factors such as training time, model size, average accuracy, and portability, we ultimately selected ResNet34 as the backbone network for our incremental learning framework. The model was trained using the SGD optimizer for 200 epochs, with an initial learning rate of 0.1, momentum of 0.9, and a weight decay parameter of 0.0002. The learning rate was reduced to 10% of its original value at the 80th, 120th, and 170th epochs. The batch size of the model was set to 128, and the size of the memory pool was set to 1000 samples to ensure the uniform distribution of old samples in the memory.
For comparison, this study selected joint training, iCaRL [42], and BiC [43] as baseline methods. Joint training encompasses all current and previous data, serving as the theoretical upper limit for incremental learning performance. The iCaRL method employs a novel exemplar-based strategy to manage the retention of old classes alongside new ones, aiming to maintain the model’s accuracy over sequential learning tasks. Meanwhile, BiC focuses on mitigating the bias towards newly added classes by adjusting the final classifier layers during the training of incremental batches, addressing the common challenge of catastrophic forgetting in incremental learning setups.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation Methods
In this study, to comprehensively evaluate the model’s performance in an incremental learning environment, we adopted four key metrics: the average accuracy, forgetting, cumulative accuracy, and current accuracy. These metrics were used to collectively assess the model’s ability to avoid forgetting old knowledge and its capacity to learn new knowledge.
The average accuracy reflects the model’s overall performance across all incremental learning tasks. It is calculated as follows:
where represents the average accuracy of all tasks after the i-th incremental learning task completed. This metric is an important standard in measuring the model’s overall performance.
Forgetting measures the extent to which the model forgets old tasks after learning new ones. It is defined as
where . This metric focuses on the model’s ability to retain previously learned content throughout the continuous learning process.
The cumulative accuracy measures the model’s overall recognition ability for all data that it has learned so far, while the current accuracy focuses on the model’s performance on the most recent learning task, i.e., the recognition accuracy of newly added categories after the latest round of incremental learning.
3.2. Results Based on the FruVeg Dataset
A series of incremental learning experiments were conducted on the fruit and vegetable categories within the FruVeg dataset in this study, aiming to evaluate the performance of various methods in handling such complex classification tasks. In Table 2, the experimental results based on the FruVeg dataset are displayed.

Table 2.
Experimental results based on the FruVeg dataset (%).
The results reveal that joint training, as a reference under ideal conditions, achieved an average accuracy of 97.0%. However, given its limitations in real-world application scenarios, developing incremental learning methods more suited to practical situations is particularly important. For instance, the BiC method, despite its excellent performance in terms of current accuracy (99.28%), exhibited poorer performance in terms of average accuracy and average forgetting, highlighting its inadequacy in handling both new and old knowledge.
Among the incremental learning methods compared, iCaRL and BiC both demonstrated relatively balanced performance but still had room for improvement. The ADA-CIL method proposed in this study excelled in multiple metrics, with an average accuracy of 96.30%, significantly surpassing the compared methods. More importantly, ADA-CIL achieved a remarkably low average forgetting rate of only 2.96%, effectively proving its significant advantage in retaining old knowledge. Additionally, it demonstrated efficiency and robustness in terms of its cumulative accuracy and current accuracy, achieving 96.26% and 98.60%, respectively.
The comparative analysis clearly showed that ADA-CIL consistently outperformed iCaRL and BiC across various metrics. While iCaRL manages the retention of old knowledge effectively through exemplar storage, ADA-CIL reduces the reliance on large memory footprints, maintaining high accuracy with fewer stored examples. Unlike BiC, which primarily targets the correction of biases towards newly introduced classes, ADA-CIL adopts a more balanced strategy, ensuring fair performance across all classes without the need for extensive bias adjustments. This finding not only highlights ADA-CIL’s robustness but also illustrates its adaptability to real-world scenarios, where data variability is a significant challenge.
These results not only validate the effectiveness of ADA-CIL in balancing the learning and retention of new and old knowledge but also showcase its potential in handling the challenging task of classifying fruits and vegetables in the FruVeg dataset.
3.3. Ablation Experiment
In this study, we conducted two sets of ablation experiments to extensively analyze the specific impact of key components of the ADA-CIL model on performance. The first set of experiments (Table 3) focused on the impact of the adversarial domain adaptation () and knowledge distillation strategies (), while the second set (Table 4) focused on the role of core-set selection and the mix-up strategy.

Table 3.
Ablation experiment results for adversarial domain adaptation and knowledge distillation strategies (%).

Table 4.
Ablation experiment results for core-set selection and mix-up (%).
In the ablation experiments focusing on adversarial domain adaptation and knowledge distillation, we found that the baseline model relying only on the category loss function () performed poorly in terms of average accuracy and forgetting. The results showed that adding the adversarial domain adaptation strategy () slightly improved the model’s average classification accuracy from 90.32% to 90.85%, and the forgetting rate decreased from 9.53% to 8.79%. Further integrating the knowledge distillation strategy () significantly enhanced the model’s performance, raising the accuracy to 93.48%, emphasizing the crucial role of knowledge distillation in enhancing stability. Notably, when both the adversarial domain adaptation and knowledge distillation strategies were applied simultaneously, the model achieved a significant improvement in average classification accuracy to 95.33% and a substantial reduction in forgetting to 4.94%, further confirming the significant optimization effect of these two strategies in synergy on the model performance.
In the second set of ablation experiments, we focused on core-set selection and the mix-up strategy, exploring their explicit impacts on the model’s overall performance. The core-set selection strategy effectively improved the model’s accuracy, raising it from the baseline of 95.33% to 95.53%, and reduced the forgetting rate to 4.87%. The mix-up strategy showed excellent performance in reducing forgetting to 3.37%, but it had a slightly negative impact on the accuracy, reducing it to 94.74%. Notably, when these two strategies were combined, the model’s accuracy was further improved to 96.30% and its forgetting was reduced to 2.96%, achieving the best performance in terms of both accuracy and forgetting.
In summary, these two sets of ablation experiments revealed that in incremental learning tasks, especially in the complex classification scenario of fruits and vegetables, the integration of knowledge distillation, adversarial domain adaptation, core-set selection, and the mix-up strategy is key to optimizing model performance. These strategies not only improve model performance when applied individually but also produce synergistic effects when used in combination, further optimizing the model’s accuracy and forgetting rate. This has important implications for the design of efficient incremental learning models.
3.4. Effects of Number of Incremental Categories
To gain a deeper understanding of how class increments of different scales affect the algorithm’s performance, this study established two experimental scenarios, introducing 10 and 20 new categories in each round of incremental learning, respectively.
From Table 5, it can be observed that when the number of incremental categories is set to 10, ADA-CIL shows an improvement of 1.65% and 1.82% in the average classification accuracy compared to iCaRL and BiC, respectively. When the number of incremental categories is increased to 20, the improvement in the average classification accuracy of ADA-CIL compared to the other algorithms is 1.61% and 3.42%, respectively. Notably, ADA-CIL even surpasses the theoretical maximum value of joint training in terms of the classification accuracy for old samples. This finding indicates that ADA-CIL has a significant advantage in the replay memory of old data, especially in scenarios involving a larger influx of new data.

Table 5.
Impact of incremental category numbers on experimental results (%).
However, it is worth noting that both ADA-CIL and the other algorithms show a decline in the cumulative accuracy when the number of incremental categories increases from 10 to 20. This trend reveals a critical challenge: the algorithms’ ability to retain their memory of old data is impacted when faced with a large amount of new data. This highlights the importance of developing strategies within incremental learning algorithms that can effectively manage larger increments of new categories while maintaining a high accuracy on previously learned categories.
3.5. Memory Size Variability
To systematically assess the impact of the memory replay pool size on the model performance, we used two different memory sizes, 800 and 1000, in our experiments.
From the results in Table 6, it can be observed that when the memory size is 800, ADA-CIL’s average classification accuracy is lower than that of the iCaRL algorithm. This phenomenon might be due to the reduced proportion of representative samples and increased proportion of uncertain samples in the core set during incremental training, which impacts the model’s ability to remember old samples. In the later stages of training, there could be situations in which there are very few or even no representative samples. However, when the memory size is increased to 1000, ADA-CIL outperforms iCaRL and BiC by 1.65% and 1.82% in terms of the average classification accuracy, respectively. This suggests that with a larger memory space, the combination of strategies of sample uncertainty and representativeness serves to more effectively maintain the memory of old samples, thereby enhancing the overall model performance.

Table 6.
Impact of memory size on experimental results (%).
3.6. Influence of Sample Generation Proportion
From the results in Table 7, it can be seen that as the proportion of online sample generation increases, the overall performance of the model improves, especially in terms of its resistance to forgetting. When the sample generation proportion is 1, meaning that all old samples are involved in online generation, the model exhibits the strongest resistance to forgetting and the highest cumulative accuracy. This finding indicates that using a higher proportion of old samples for online generation is an effective strategy that can significantly enhance the model’s performance in incremental learning scenarios.

Table 7.
Impact of sample generation proportion on experimental results (%).
Although mix-up is a relatively simple method for sample generation, its time cost in incremental learning problems still needs to be considered. Particularly in scenarios requiring frequent training, mix-up may lead to additional computational costs. However, the experimental results suggest a good balance between this additional cost and the improvement in model performance.
4. Conclusions
This study introduces a method utilizing Adversarial Domain Adaptation Class Incremental Learning (ADA-CIL) as a classification engine for fruits and vegetables. ADA-CIL is well suited to the dynamic domain of fruit and vegetable varieties. The main contribution of this research lies in its employment of incremental learning combined with adversarial domain adaptation and core-set selection strategies, enabling the model to extract cross-domain general features and effectively retain key information with limited storage resources. The experimental results in the dynamic data environment of the FruVeg dataset demonstrate significant improvements in the average classification accuracy and memory retention capabilities compared to traditional benchmark models.
Regarding fruit and vegetable classification, considering that existing incremental learning methods mostly focus on fully supervised problem settings, while the data encountered in real scenarios are more likely to be unlabeled and may include common categories between new and old data, there is a gap between existing incremental learning methods and practical application scenarios. This challenge necessitates the exploration of incremental learning in semi-supervised or unsupervised settings to bridge this gap and enhance the model’s applicability to real-world data. Therefore, our future research will focus on incremental learning problems under semi-supervised or unsupervised settings. Moreover, the experiments revealed that the limit on the number of samples determines the upper limit of the memory settings. In practical applications, due to factors such as labeling, the number of samples for new categories may be small, leading to the small-sample problem and the resulting data imbalance issue, which requires further research. Addressing these challenges will require the development of strategies that improve data efficiency and sample diversity. At the same time, given the potential application of incremental learning on lightweight devices, exploring lightweight incremental learning methods suitable for food classification has become a valuable research direction. This approach is crucial for practical deployments, where computational resources and energy consumption are limited. This research direction is significant not only in terms of improving the efficiency and accuracy of fruit and vegetable classification systems; it could also have a profound impact in terms of advancing precision agriculture technology, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices and enhanced food production systems (Supplementary Materials).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy14061275/s1, Figure S1. Experimental results for each training phase of ADA-CIL on the FruVeg dataset; Table S1. Detailed Information of FruVeg Dataset, Including the Number of Images per Category.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and K.G.; methodology, H.C.; software, Q.L.; validation, K.G., H.C. and Q.L.; formal analysis, Y.Z.; investigation, Q.L.; resources, J.L.; data curation, Q.L.; writing—original draft preparation, K.G.; writing—review and editing, H.C.; visualization, H.H.; supervision, S.R.; project administration, J.L.; funding acquisition, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62301405 and Grant 61976167; the Science and Technology Projects of Xi’an, China, under Grant 201809170CX11JC12; the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province (2022JQ-708); and the National Natural Science Foundation Youth Fund under Grant XJS220208.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in the GitHub repository at https://github.com/Hl-Chen9/FruVeg-dataset (accessed on 14 May 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sivaranjani, A.; Senthilrani, S.; Ashok Kumar, B.; Senthil Murugan, A. An overview of various computer vision-based grading system for various agricultural products. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K. Globalization’s effects on world agricultural trade, 1960–2050. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3007–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.S.; Hill, J.D.; Chase, C.A.; Johanns, A.M.; Liebman, M. Increasing cropping system diversity balances productivity, profitability and environmental health. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, A.; Bansal, A. Fruits and vegetables quality evaluation using computer vision: A review. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2021, 33, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q. Review of smart robots for fruit and vegetable picking in agriculture. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, A.; Hauagge, D.C.; Wainer, J.; Goldenstein, S. Automatic fruit and vegetable classification from images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 70, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrener, J.; Posch, K.; Leitner, R. Hyperspectral fruit and vegetable classification using convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, P.M.; Brummell, D.A. Biochemical bases of appearance and texture changes in fresh-cut fruit and vegetables. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.Y.; Feng, Y.Z.; Sun, D.W. Recent progress of hyperspectral imaging on quality and safety inspection of fruits and vegetables: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.W.; Aditya, S.; Sivakumar, N.; Dcunha, S.; Qu, C.; Taylor, C.J.; Das, J.; Kumar, V. Robust fruit counting: Combining deep learning, tracking, and structure from motion. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1045–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Rahnemoonfar, M.; Sheppard, C. Deep count: Fruit counting based on deep simulated learning. Sensors 2017, 17, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulzar, Y. Enhancing soybean classification with modified inception model: A transfer learning approach. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2024, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, K.; Chai, D.; Rassau, A. A comprehensive review of fruit and vegetable classification techniques. Image Vis. Comput. 2018, 80, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.W. Efficient extraction of deep image features using convolutional neural network (CNN) for applications in detecting and analysing complex food matrices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, E.; Gulzar, Y.; Yeafi, A.; Jendoubi, S.; Dhawi, F.; Mir, M.S. Advancing automatic plant classification system in Saudi Arabia: Introducing a novel dataset and ensemble deep learning approach. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 2693–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, Y.; Ünal, Z.; Ayoub, S.; Reegu, F.A.; Altulihan, A. Adaptability of deep learning: Datasets and strategies in fruit classification. BIO Web Conf. EDP Sci. 2024, 85, 01020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolle, R.M.; Connell, J.H.; Haas, N.; Mohan, R.; Taubin, G. Veggievision: A produce recognition system. In Proceedings of the Third IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV’96), Sarasota, FL, USA, 2–4 December 1996; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- Femling, F.; Olsson, A.; Alonso-Fernandez, F. Fruit and vegetable identification using machine learning for retail applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 14th International Conference on Signal-Image Technology & Internet-Based Systems (SITIS), Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, 26–29 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Al-Hammadi, M.; Muhammad, G. Automatic fruit classification using deep learning for industrial applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Aranda, J.L.; Nunez-Varela, J.I.; Cuevas-Tello, J.C.; Rangel-Ramirez, G. Fruit classification for retail stores using deep learning. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition: 12th Mexican Conference, MCPR 2020, Morelia, Mexico, 24–27 June 2020; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, F.; Zhu, L.; Yue, J. Vegetable recognition and classification based on improved VGG deep learning network model. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2020, 13, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazame, H.C.; Molin, J.P.; Althoff, D.; Martello, M. Detection, classification, and mapping of coffee fruits during harvest with computer vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 183, 106066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, K.; Chai, D.; Rassau, A. Class distribution-aware adaptive margins and cluster embedding for classification of fruit and vegetables at supermarket self-checkouts. Neurocomputing 2021, 461, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, Y. Fruit image classification model based on MobileNetV2 with deep transfer learning technique. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xiao, Z.; Deng, Z. High accuracy food image classification via vision transformer with data augmentation and feature augmentation. J. Food Eng. 2024, 365, 111833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Alkanan, M.; Gulzar, Y. Enhanced corn seed disease classification: Leveraging MobileNetV2 with feature augmentation and transfer learning. Front. Appl. Math. Stat. 2024, 9, 1320177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Mirza, M.; Xiao, D.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. An empirical investigation of catastrophic forgetting in gradient-based neural networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6211. [Google Scholar]
- Rannen, A.; Aljundi, R.; Blaschko, M.B.; Tuytelaars, T. Encoder based lifelong learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1320–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.; Pan, X.; Loy, C.C.; Wang, Z.; Lin, D. Learning a unified classifier incrementally via rebalancing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 831–839. [Google Scholar]
- Dhar, P.; Singh, R.V.; Peng, K.C.; Wu, Z.; Chellappa, R. Learning without memorizing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5138–5146. [Google Scholar]
- van de Ven, G.M.; Tuytelaars, T.; Tolias, A.S. Three types of incremental learning. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, L.; Guan, T.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y. Taking a closer look at domain shift: Category-level adversaries for semantics consistent domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2507–2516. [Google Scholar]
- Ganin, Y.; Lempitsky, V. Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 1180–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.S.; Jun, C.H. A simple and fast algorithm for K-medoids clustering. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 3336–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Luo, H.; Zhang, C. Margin sample mining loss: A deep learning based method for person re-identification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.00478. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–20 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Rebuffi, S.A.; Kolesnikov, A.; Sperl, G.; Lampert, C.H. icarl: Incremental classifier and representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2001–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Fu, Y. Large scale incremental learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 374–382. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).