Effects of Cultivar Type and Node Position on Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics of Ratoon Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Details
2.2. Sampling and Measurements
2.3. Operation Formula
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
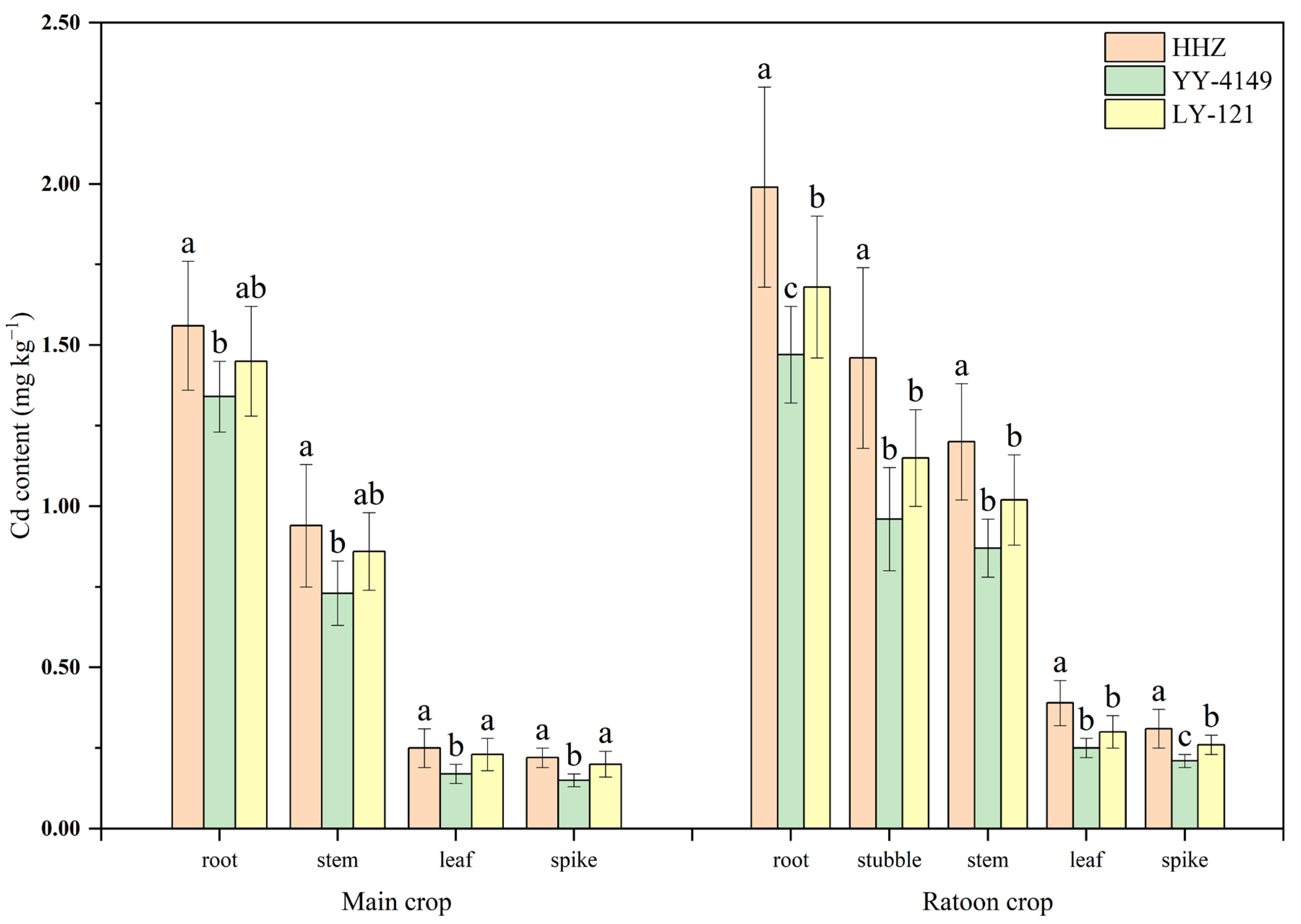
3.1. Differences in Cd Uptake and Transport among Ratoon Rice Cultivars
3.1.1. Cd Content
3.1.2. Cd Bioaccumulation (BAF) and Translocation (TF) Factors
3.1.3. Cd Accumulation
| Season | Stage | Cultivar | Stem | Leaf | Spike | Stubble | Total Accumulation in Aboveground Parts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main crop | Transplanting stage to Heading stage | HHZ | 1458.13 a | 273.66 a | 228.37 a | 1960.16 a | |
| YY-4149 | 1074.74 b | 227.80 b | 153.65 b | 1456.19 c | |||
| LY-121 | 1244.26 ab | 235.76 b | 171.15 ab | 1651.17 b | |||
| Heading stage to Mid-filling stage | HHZ | 250.71 a | 163.19 a | 494.59 a | 908.49 a | ||
| YY-4149 | 186.93 b | 121.17 b | 347.79 b | 655.89 b | |||
| LY-121 | 187.47 b | 98.18 b | 389.38 b | 675.03 b | |||
| Mid-filling stage to Maturity stage | HHZ | 803.56 b | −139.35 b | 956.64 a | 1620.85 b | ||
| YY-4149 | 909.33 ab | −119.47 b | 788.56 b | 1578.42 b | |||
| LY-121 | 969.87 a | −30.34 a | 933.47 a | 1873.00 a | |||
| Ratoon crop | Before the Heading stage | HHZ | 1577.92 a | 378.97 a | 885.01 a | 1759.44 a | 4601.34 a |
| YY-4149 | 1026.03 b | 223.47 b | 856.49 a | 982.28 b | 3088.27 b | ||
| LY-121 | 1177.31 b | 360.71 a | 800.65 a | 1319.67 ab | 3658.34 b | ||
| Heading stage to Mid-filling stage | HHZ | 210.24 a | 219.27 a | 591.64 a | 315.45 b | 1336.60 a | |
| YY-4149 | 169.11 b | 140.04 b | 188.31 c | 426.03 a | 923.49 b | ||
| LY-121 | 236.14 a | 169.85 b | 359.65 b | 371.19 ab | 1136.83 ab | ||
| Mid-filling stage to Maturity stage | HHZ | 935.84 a | −114.64 a | 92.75 b | −454.29 b | 459.66 b | |
| YY-4149 | 640.56 b | −76.01 a | 316.00 a | −246.71 a | 633.84 a | ||
| LY-121 | 708.15 b | −125.56 a | 215.10 a | −425.86 b | 371.83 b |
3.2. Differences in the Cd Contents of the Ratoon Crop and Different Nodes of the Main Crop
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in Cd Uptake and Accumulation among Cultivars
4.2. Differences in the Cd Contents of Ratoon Rice and Different Nodes of the Main Crop
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Q.; Ni, Y.; Huang, S.; Zuo, T.; Wang, J.; Ni, W. Effects of substituting chemical fertilizers with manure on rice yield and soil labile nitrogen in paddy fields of China: A meta-analysis. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruq, G.; Taha, R.M.; Prodhan, Z.H. Rice Ratoon Crop: A Sustainable Rice Production System for Tropical Hill Agriculture. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5785–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, A.; Jiang, G.; Sun, H.; Jiang, M.; Man, J.; Ling, X.; Cui, K.; Huang, J.; Peng, S.; et al. Ratoon rice technology: A green and resource-efficient way for rice production. Adv. Agron. 2020, 159, 135–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Chen, Q.; Wang, W.; Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L. The growth and yield of a wet-seeded rice-ratoon rice system in central China. Field Crops Res. 2017, 208, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, D.L.; Bond, J.A.; Blanche, S. Evaluation of main-crop stubble height on ratoon rice growth and development. Field Crops Res. 2009, 114, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiong, H.; Jiang, P. The ratoon rice system with high yield and high efficiency in China: Progress, trend of theory and technology. Field Crops Res. 2021, 272, 108282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Cassman, K.G.; Huang, J.; Peng, S.; Grassini, P. Can ratoon cropping improve resource use efficiencies and profitability of rice in central China? Field Crops Res. 2019, 234, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Yang, C.; Yu, X.; Zheng, C.; Xiao, S.; Xu, L.; Cui, K.; Huang, J.; Peng, S. On-farm comparison in grain quality between main and ratoon crops of ratoon rice in Hubei Province, Central China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 7259–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.L.; Cai, L. Implications for prenatal cadmium exposure and adverse health outcomes in adulthood. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 403, 115161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Tang, Z.; McGrath, S.P. Soil Contamination in China: Current Status and Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 750–759. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/soil-contamination-china-current-status/docview/1677894783/se-2 (accessed on 3 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Persson, D.P.; Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, T. Exposure of cerium oxide nanoparticles to the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii decreases the uptake of cadmium via the apoplastic pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 125955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borggaard, O.K.; Holm, P.E.; Strobel, B.W. Potential of dissolved organic matter (DOM) to extract As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from polluted soils: A review. Geoderma 2019, 343, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawab, J.; Khan, S.; Aamir, M.; Shamshad, I.; Qamar, Z.; Din, I.; Huang, Q. Organic amendments impact the availability of heavy metal(loid)s in mine-impacted soil and their phytoremediation by Penisitum americanum and Sorghum bicolor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.S.; Du, X.; Weng, L.P.; Zhu, Y.G. Effects of rice straw on the speciation of cadmium (Cd) and copper (Cu) in soils. Geoderma 2008, 146, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Shao, G.; Tang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Tang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, F.J. Genotypic and Environmental Variations in Grain Cadmium and Arsenic Concentrations Among a Panel of High Yielding Rice Cultivars. Rice 2017, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Xu, W.; Xie, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, L.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Dai, C.; et al. Variation of a major facilitator superfamily gene contributes to differential cadmium accumulation between rice subspecies. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lei, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Qian, H.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yao, W. Study on the Removal of Cadmium in Rice Using Microbial Fermentation Method. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, D.; Yamaji, N.; Kono, I.; Huang, C.F.; Ando, T.; Yano, M.; Ma, J.F. Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16500–16505. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/gene-limiting-cadmium-accumulation-rice/docview/807286634/se-2 (accessed on 3 April 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, A.; Chen, L.; et al. Genetic Diversity, Rather than Cultivar Type, Determines Relative Grain Cd Accumulation in Hybrid Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1407. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/genetic-diversity-rather-than-cultivar-type/docview/1835375105/se-2 (accessed on 10 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Ji, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Abdeen, M.A. Research Progress and Prospect of Mechanized Harvesting Technology in the First Season of Ratoon Rice. Agriculture 2022, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Peng, S.; Qi, M.; Xiong, Z.; Deng, S.; Wang, F. Comparison of grain cadmium and arsenic concentration between main and ratoon crop in rice ratooning system. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 134017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; Tu, N.; Yi, Z. Cadmium accumulation and distribution in ratooning rice from different nodes and its differences with main crop. J. South. Agric. 2020, 51, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhou, W.; Tu, N. Effects of Stubble Height of the Main Crop on Source-Sink Characteristics and Assimilates T ransportation in Ratooning Rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2009, 23, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Meng, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Cao, T.; Cheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X. Effects of Biochar on Cadmium Accumulation in Rice and Cadmium Fractions of Soil: A Three-Year Pot Experiment. Bioresources 2017, 12, 622–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Feng, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Gielen, G.; Wu, W. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) plantation affects the stability of biochar in paddy soil. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Cui, C.; Han, Y.; Chen, P.; Tu, N.; Yi, Z. Silicon calcium fertilizer application and foliar spraying with silicon fertilizer decreases cadmium uptake and translocation in rice grown in polluted soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Z.; Zhang, L.-H.; Ma, J.; Li, X.-Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.-P.; Wang, R.-Q. Effects of Water Stress on Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Protection System in Rice during Grain-Filling Stage. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Sun, L.; Zhou, H.; Yang, F.; Mao, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Dai, J.; Xiao, G.; et al. Additive, dominant parental effects control the inheritance of grain cadmium accumulation in hybrid rice. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ma, H.; Li, S.; Deng, H.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Robust identification of low-Cd rice varieties by boosting the genotypic effect of grain Cd accumulation in combination with marker-assisted selection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Li, F.; Tam, N.F.; Liu, C.; Ouyang, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z. Variations in grain cadmium and arsenic concentrations and screening for stable low-accumulating rice cultivars from multi-environment trials. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Q.; Jiang, Y.R.; Ming, X.Q.; Wang, J.R.; Tang, W.B.; Sun, L. Introgressing the allelic variation of a major locus in reducing the grain cadmium accumulation in indica rice hybrids. Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.F.; Lestari, P.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, B.W. Identification of quantitative trait loci for cadmium accumulation and distribution in rice (Oryza sativa). Genome 2013, 56, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.Y.; Zhu, C.; Ren, Y.F.; Jiang, D.A.; Sun, Z.X. Root morphology and cadmium uptake kinetics of the cadmium-sensitive rice mutant. Biol. Plant. 2007, 51, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Ishimaru, Y.; Shimo, H.; Ogo, Y.; Senoura, T.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Nakanishi, H. The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocito, F.F.; Lancilli, C.; Dendena, B.; Lucchini, G.; Sacchi, G.A. Cadmium retention in rice roots is influenced by cadmium availability, chelation and translocation. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 994–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, T.-Q.; Han, X.; Ding, Z.-L.; Yang, X.-E.; Jin, Y.-F. Cadmium accumulation in different pakchoi cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B 2012, 13, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Mao, Y.; Cheng, W.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G. Genotypic and environmental variation in chromium, cadmium and lead concentrations in rice. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 153, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zhou, Z.; Yi, Y.; Chen, G. Transcriptome analysis reveals the roles of stem nodes in cadmium transport to rice grain. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naimi, M.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Effects of soaking, acidity and temperature on cadmium and lead removal from rice. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; He, A.; Wang, W.; Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L. Comparisons of regeneration rate and yields performance between inbred and hybrid rice cultivars in a direct seeding rice-ratoon rice system in central China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 223, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Season | Cultivars | Branch | Empty Grain | Grain Husk | Brown Rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main crop | HHZ | 0.30 a | 0.22 a | 0.19 a | 0.17 a |
| YY-4149 | 0.19 b | 0.15 b | 0.13 b | 0.12 b | |
| LY-121 | 0.27 a | 0.19 b | 0.18 a | 0.15 a | |
| Ratoon crop | HHZ | 0.39 a | 0.33 a | 0.25 a | 0.22 a |
| YY-4149 | 0.28 c | 0.23 b | 0.17 b | 0.15 b | |
| LY-121 | 0.33 b | 0.25 b | 0.22 a | 0.19 a |
| Treatments | Root | Stem | Leaf | Brown Rice | Stubble |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main crop | |||||
| HHZ | 3.467 a | 2.089 a | 0.556 a | 0.379 a | |
| YY-4149 | 2.978 b | 1.622 b | 0.378 b | 0.265 b | |
| LY-121 | 3.222 ab | 1.911 ab | 0.511 a | 0.334 a | |
| Ratoon crop | |||||
| HHZ | 4.422 a | 2.667 a | 0.867 a | 0.484 a | 3.244 a |
| YY-4149 | 3.267 c | 1.933 b | 0.556 b | 0.330 b | 2.133 c |
| LY-121 | 3.622 b | 2.267 b | 0.667 b | 0.431 a | 2.556 b |
| Treatments | Root-to- Stem | Root-to- Leaf | Root-to- Brown Rice | Stem-to- Brown Rice | Leaf-to- Brown Rice | Root-to- Stubble | Stubble-to- Brown Rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main crop | |||||||
| HHZ | 0.603 a | 0.160 a | 0.109 a | 0.181 a | 0.680 a | ||
| YY-4149 | 0.545 b | 0.127 b | 0.090 a | 0.164 a | 0.657 a | ||
| LY-121 | 0.593 a | 0.159 a | 0.103 a | 0.174 a | 0.662 a | ||
| Ratoon crop | |||||||
| HHZ | 0.623 a | 0.196 a | 0.111 a | 0.183 a | 0.584 a | 0.734 a | 0.151 a |
| YY-4149 | 0.592 a | 0.170 a | 0.102 a | 0.172 a | 0.560 a | 0.653 b | 0.156 a |
| LY-121 | 0.626 a | 0.184 a | 0.110 a | 0.176 a | 0.600 a | 0.706 ab | 0.157 a |
| Cultivar | Stem | Leaf | Branch | Empty Grain | Grain Husk | Brown Rice | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The 2nd node from the top | HHZ | 0.95 a | 0.32 a | 0.33 a | 0.26 a | 0.23 a | 0.19 a |
| YY-4149 | 0.78 b | 0.21 c | 0.22 b | 0.18 b | 0.15 b | 0.13 b | |
| LY-121 | 0.88 ab | 0.26 b | 0.30 a | 0.20 b | 0.19 ab | 0.17 a | |
| The 3rd node from the top | HHZ | 1.24 a | 0.34 a | 0.34 a | 0.30 a | 0.24 a | 0.21 a |
| YY-4149 | 0.80 b | 0.24 b | 0.29 b | 0.25 b | 0.19 b | 0.14 b | |
| LY-121 | 1.14 a | 0.31 a | 0.32 a | 0.29 a | 0.20 b | 0.17 ab | |
| The 4th and 5th node from the top | HHZ | 1.76 a | 0.44 a | 0.49 a | 0.38 a | 0.30 a | 0.28 a |
| YY-4149 | 1.25 b | 0.29 b | 0.33 b | 0.29 b | 0.21 c | 0.18 b | |
| LY-121 | 1.37 b | 0.39 a | 0.38 b | 0.31 b | 0.26 b | 0.25 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, S.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, P.; Tu, N.; Zhou, W.; Yi, Z. Effects of Cultivar Type and Node Position on Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics of Ratoon Rice. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071401
Yuan S, Jiang Y, Chen P, Tu N, Zhou W, Yi Z. Effects of Cultivar Type and Node Position on Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics of Ratoon Rice. Agronomy. 2024; 14(7):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071401
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Shuai, Yanfang Jiang, Pingping Chen, Naimei Tu, Wenxin Zhou, and Zhenxie Yi. 2024. "Effects of Cultivar Type and Node Position on Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics of Ratoon Rice" Agronomy 14, no. 7: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071401
APA StyleYuan, S., Jiang, Y., Chen, P., Tu, N., Zhou, W., & Yi, Z. (2024). Effects of Cultivar Type and Node Position on Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics of Ratoon Rice. Agronomy, 14(7), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071401





