Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis of Major Compound Variation in Essential Oil among Some Red Oregano Genotypes in Albania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
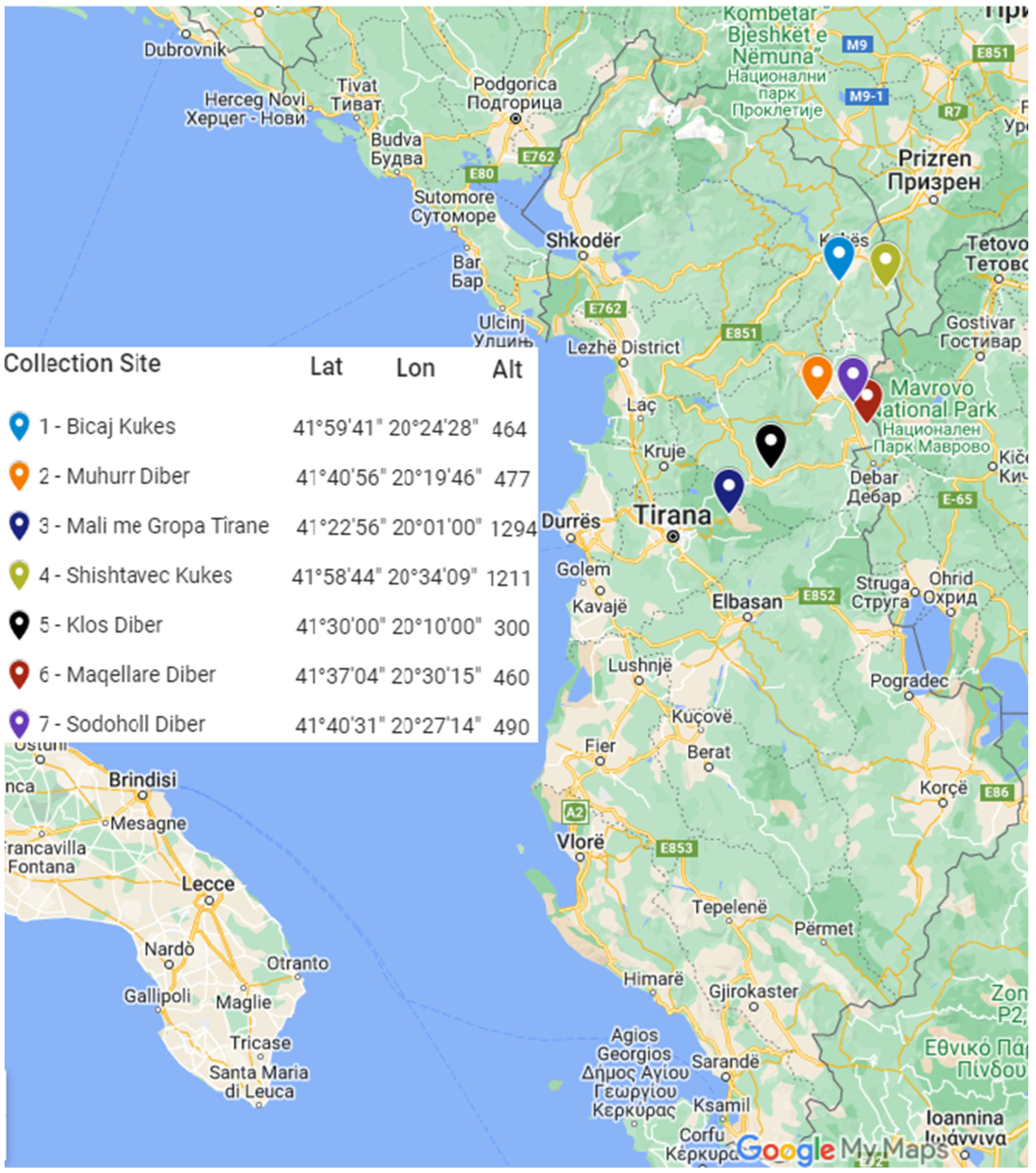
2.1. Experimental Design and Plant Characterization
2.2. Harvesting and Sample Preparation
2.3. Essential Oil Extraction
2.4. Gas Chromatography Analysis (GC/FID)
2.5. Gas Chromatography−–Mass Spectrometry Analysis (GC/MS)
2.6. Identification of Compounds
2.7. Principal Component and Cluster Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biodiversity, Microclimates, Ecological Importance, and Conservation Implications
3.2. Correlations between the 15 Major Compounds of Red Oregano Collected in Seven Different Locations in Albania
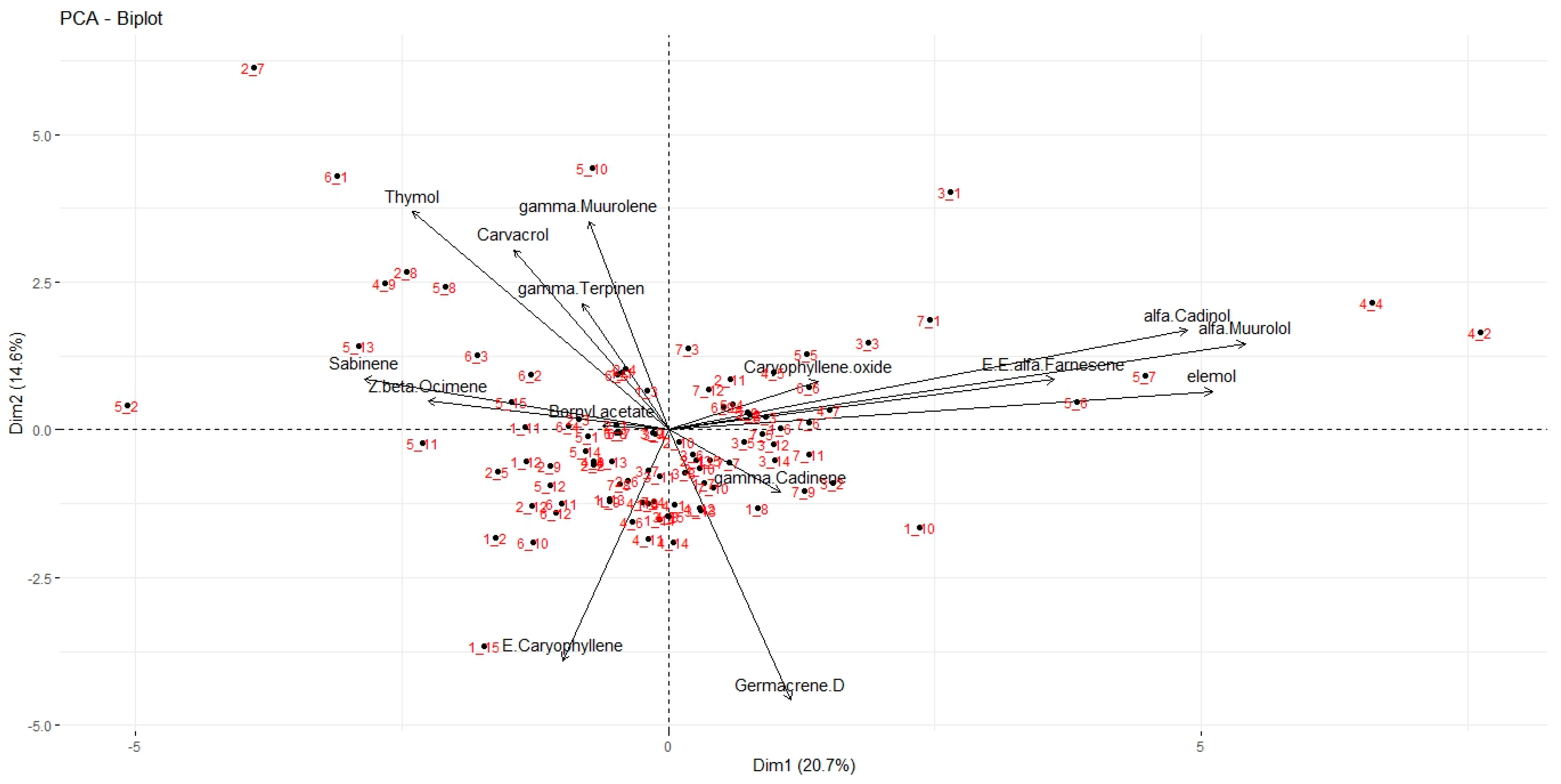
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
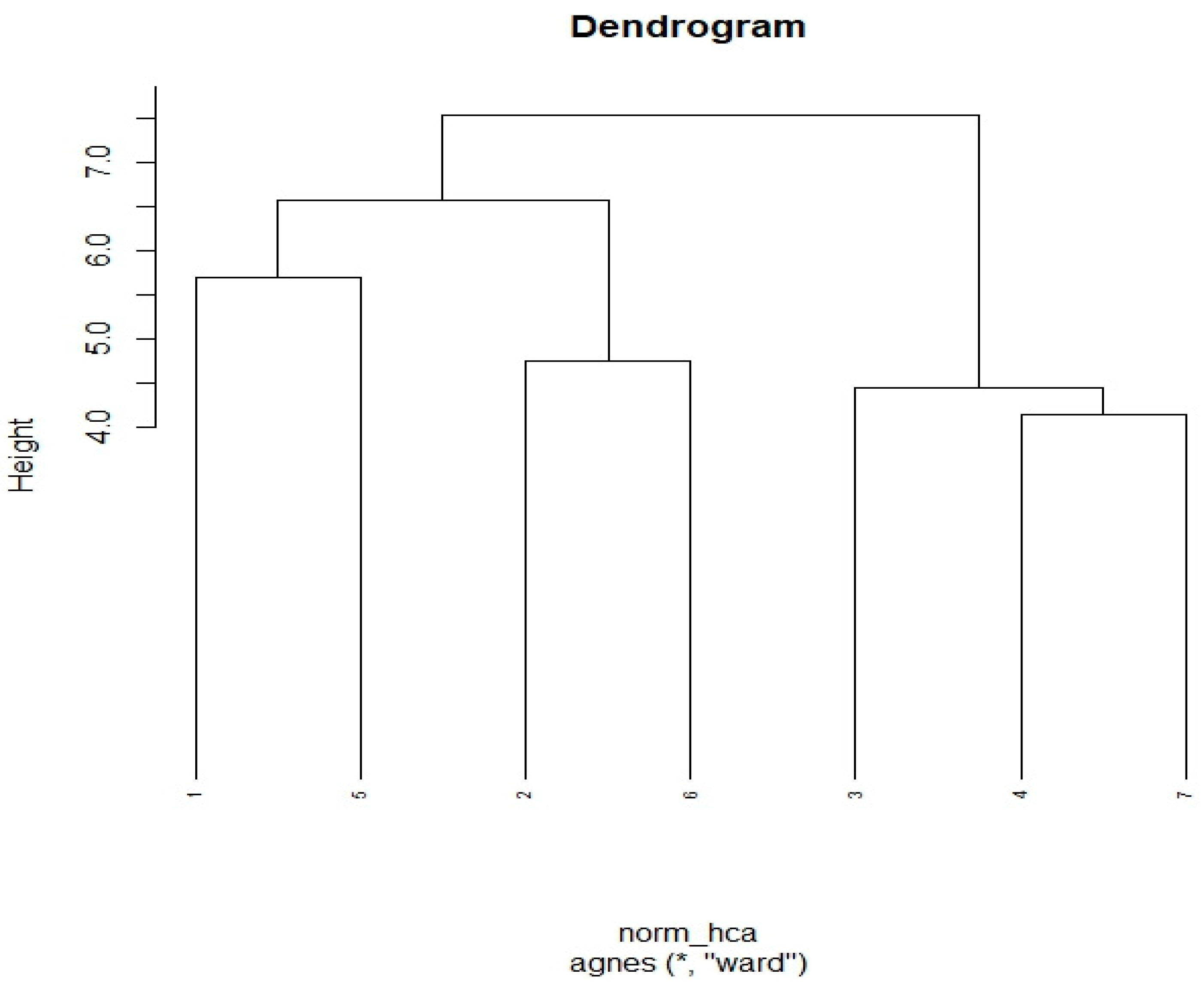
3.4. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ietswaart, J.H. A Taxonomic Revision of the Genus Origanum (Labiatae); Leiden Botanical Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1980; Volume 4, ISBN 9789060214633. [Google Scholar]
- Demiri, M. Flora Ekskursioniste e Shqipërisë; Shtëpia Botuese e Librit Shkollor: Tirana, Albania, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkini, S. Taxonomy, diversity and distribution of Origanum species. In Oregano: Proceedings of the IPGRI International Workshop on Oregano, 8–12 May 1996, CIHEAM, Valenzano (Bari), Italy; Padulosi, S., Ed.; Bioversity International: Rome, Italy, 1997; pp. 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Oliwier, G.W. The world market of oregano. In Oregano: Proceedings of the IPGRI International Workshop on Oregano, 8–12 May 1996, CIHEAM, Valenzano (Bari), Italy; Padulosi, S., Ed.; Bioversity International: Rome, Italy, 1997; pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Lukas, B.; Schmiderer, C.; Novak, J. Phytochemical diversity of Origanum vulgare L. subsp. vulgare (Lamiaceae) from Austria. Bioch. Syst. Ecol. 2013, 50, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’antuono, L.; Galletti, G.; Bocchini, P. Variability of essential oil content and composition of Origanum vulgare L. populations from a north Mediterranean area (Liguria region, Northern Italy). Ann. Bot. 2000, 86, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mockute, D.; Bernotiene, G.; Judzentiene, A. The essential oil of Origanum vulgare L. ssp. vulgare growing wild in Vilnius district (Lithuania). Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pieroni, A. Local plant resources in the ethnobotany of Theth, a village in the Northern Albanian Alps. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2008, 55, 1197–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ličina, B.Z.; Stefanović, O.D.; Vasić, S.M.; Radojević, I.D.; Dekić, M.S.; Čomić, L.R. Biological activities of the extracts from wild growing Origanum vulgare L. Food Control 2013, 33, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaki, M.R.A.; Pahlavan, Y.; Sepehri, G.; Sheibani, V.; Pahlavan, B. Antinociceptive effect of aqueous extract of Origanum vulgare L. in male rats: Possible involvement of the GABAergic system. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gonceariuc, M.; Balmuș, Z.; Benea, A.; Barsan, V.; Sandu, T. Biochemical diversity of the Origanum vulgare ssp. vulgare L. and Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum (link) Ietswaart genotypes from Moldova. J. ASM Life Sci. 2015, 2, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ibraliu, A.; Kadiasi, N.; Gjoni, Z.; Gruda, N.S. Biodiversity of vegetable wild relatives and medicinal and aromatic plants in a nature park located in eastern Albania. Acta Hortic. 2024, 1391, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonceariuc, M.; Balmu¸s, Z.; Sandu, T.; Romanciuc, G.; Gonceariuc, N. Essential oil of Origanum vulgare ssp. vulgare L. and Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum (Link) Ietswaart from Moldova: Content and chemical composition. Int. J. Agric. Innov. Res. 2014, 3, 659–663. [Google Scholar]
- Ciocârlan, V. Illustrated Flora of Romania. Pteridophyta et Spermatophyta; Ceres Publishing House: Bucharest, Romania, 2009; p. 662. ISBN 9789734008179. [Google Scholar]
- Dragoeva, A.P.; Koleva, V.P.; Nanova, Z.D.; Kaschieva, M.Z. Allelopathy of cold water extracts from Origanum vulgare ssp. vulgare L. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2014, 3, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weglarz, Z.; Kosakowska, O.; Przybył, J.L.; Pióro−Jabrucka, E.; Baczek, K. The Quality of Greek Oregano (O. vulgare L. ssp. hirtum (Link) Ietsw.) and Common Oregano (O. vulgare L. ssp. vulgare) cultivated in the temperate climate of central Europe. Foods 2020, 9, 1671. [Google Scholar]
- Sarikurkcu, C.; Aktumsek, A.; Zengin, G.; Oskay, M.; Ceylan, R.; Uysal, S. Composition, antioxidant, antimicrobial and enzyme inhibition activities of two O. vulgare subspecies (subsp. vulgare and subsp. hirtum) essential oils. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 70, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oniga, I.; Puscas, C.; Silaghi−Dumitrescu, R.; Olah, N.K.; Sevastre, B.; Marica, R.; Marcus, I.; Sevastre−Berghian, A.C.; Benedec, D.; Pop, C.E. Origanum vulgare ssp. vulgare: Chemical composition and biological studies. Molecules 2018, 23, 2077. [Google Scholar]
- Kosakowska, O.; Weglarz, Z.; Pióro−Jabrucka, E.; Jaroslaw, L.; Przybyl, J.L.; Krasniewska, K.; Gniewosz, M.; Baczek, K. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of essential oils and hydroethanolic extracts of Greek Oregano (O. vulgare L. subsp. hirtum (Link) Ietswaart) and Common Oregano (O. vulgare L. subsp. vulgare). Molecules 2021, 26, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, E.; Mancini, E.; Roscigno, G.; Mignola, E.; Scafati, O.T.; Senatore, F. Chemical composition and biological activity of essential oils of Origanum vulgare L. subsp. vulgare L. under different growth conditions. Molecules 2013, 18, 14948–14960. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stešević, D.; Jaćimović, Ž.; Šatović, Z.; Šapčanin, A.; Jančan, G.; Kosović, M.; Damjanović−Vratnica, B. Chemical characterization of wild growing Origanum vulgare populations in Montenegro. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padulosi, S. Oregano: Proceedings of the IPGRI International Workshop on Oregano, 8–12 May 1996, CIHEAM, Valenzano (Bari), Italy; Bioversity International: Rome, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Skoula, M.; Harborne, J.B. The taxonomy and chemistry of Origanum. In Oregan: The Genera Origanum and Lipia; Kintzios, S., Ed.; Medicinal and Aromatic Plants–Industrial Profiles; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2002; pp. 67–108. ISBN 9780429218972. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi, A.; Yan, F.; Honermeier, B. Herbage yield, essential oil content and composition of three oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) populations as affected by soil moisture regimes and nitrogen supply. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2009, 29, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, B.; Schmiderer, C.; Novak, J. Essential oil diversity of European Origanum vulgare L. (Lamiaceae). Phytochemistry 2015, 119, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadiasi, N.; Hajdari, A.; Christian, I.; Tako, R.; Ibraliu, I. Variability of the Essential Oil Composition in Origanum vulgare subsp. vulgare Collected in Albania. Albanian J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/IPGRI. Genebank Standards; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy; International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy; Allured Publication: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal Component Analysis, 2nd ed.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bro, R.; Smilde, A.K. Principal Component analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K. Principal Component analysis: Most favourite tool in chemometrics. Resonance 2017, 22, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.D.; Nguyen, L.T.T.; Nguyen, A.; Yun, U.; Vo, B. A method for efficient clustering of spatial data in network space. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 11653–11670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, R.; Ballabio, D.; Consonni, V.; Grisoni, F. A new concept of higher−order similarity and the role of distance/similarity measures in local classification methods. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 157, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, M. Chemical composition and insecticidal potential of different Origanum spp. (Lamiaceae) essential oils against four stored product pests. Turk. J. Entomol. 2020, 44, 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hajiabad, S.M.; Novak, J.; Honermeier, B. Content and composition of essential oil of four Origanum vulgare L. accessions under reduced and normal light intensity conditions. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2016, 89, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, B.; Marques, A.; Ramos, C.; Serrano, C.; Matos, O.; Neng, N.R.; Nogueira, J.M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Nunes, M.L. Chemical composition and bioactivity of different oregano (Origanum vulgare) extracts and essential oil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2707–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonceariuc, M.; Muntean, M.V.; Butnara, V.; Duda, M.M.; Benea, A.; Jelezneac, T.; Vornicu, Z.; Cotelea, L.; Botnarenco, P. Quality Variation of the Moldovan Origanum vulgare L. ssp. vulgare L. and Origanum vulgare L. ssp. hirtum (Link) Ietsw. Varieties in Drought Conditions. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkini, S.; Karousou, R.; Lanaras, T. Essential oils of Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum, their stability and development in the Mediterranean climate of Greece. J. Essent. Oil Res. 1995, 7, 557–564. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, M.; Galletti, G.C.; Bocchini, P.; Carnacini, A. Essential oil chemical composition of wild populations of Italian oregano spice (Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum (Link) Ietswaart). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3741–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mastro, G.; Mincione, A. Essential oil yield and quality of Origanum vulgare L. ssp. hirtum (Link) Ietswaart, in relation to harvesting time. J. Essent. Oil Res. 1997, 9, 389–397. [Google Scholar]
- Novák, J.; Penzes, B.; Deans, S.G. Comparative study on essential oil composition of Origanum species from Hungary. Plant Growth Regul. 2001, 34, 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Napoli, E.; Giovino, A.; Carrubba, A.; How Yuen Siong, V.; Rinoldo, C.; Nina, O.; Ruberto, G. Variations of Essential Oil Constituents in Oregano (Origanum vulgare subsp. viridulum (=O. heracleoticum) over Cultivation Cycles. Plants 2020, 9, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Crocoll, C.; Asbach, J.; Novak, J.; Gershenzon, J.; Degenhardt, J. Terpene synthases of oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) and their roles in the pathway and regulation of terpene biosynthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 73, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radusiene, J.; Judzentiene, A.; Peèiulytë, D.; Janulis, V. Chemical composition of essential oil and antimicrobial activity of Origanum vulgare. Biologija 2005, 4, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatta, S.; Tewaria, G.; Pandea, C.; Punethaa, D.; Prakashb, O. Antioxidative potential and compositional variation among Origanum vulgare L. collected from different districts of Kumaun Himalayas, Uttarakhand. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2020, 32, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurzynska−Wierdak, R. Herb Yield and Chemical Composition of Common Oregano [Origanum vulgare L.] Essential Oil According to the Plant’s Developmental Stage. Herba Pol. 2009, 55, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi, A.; Hadian, J.; Gholami, M.; Friedt, W.; Honermeier, B. Correlations between Genetic, Morphological, and Chemical Diversities in a Germplasm Collection of the Medicinal Plant Origanum vulgare L. Chem. Biodivers. 2012, 9, 2784–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annemer, S.; Farah, A.; Stambouli, H.; Assouguem, A.; Almutairi, M.H.; Sayed, A.A.; Peluso, I.; Bouayoun, T.; Talaat Nouh, N.A.; El Ouali Lalami, A.; et al. Chemometric Investigation and Antimicrobial Activity of Salvia rosmarinus Spenn Essential Oils. Molecules 2022, 27, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gong, M.; Cai, Q.; Chen, X.; Lijia, M. Complex Network Clustering by Multi−objective Discrete Particle Swarm Optimization Based on Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2014, 18, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Major Compounds | KIcal | KIlit | Individuals/Plants | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P8 | P9 | P10 | P11 | P12 | P13 | P14 | P15 | Means | |||
| Sabinene | 977 | 975 | 2.48 | 0.01 | 0.82 | 1.49 | 1.40 | 1.79 | 2.15 | 0.98 | 3.94 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 10.96 | 2.40 | 3.33 | 0.01 | 2.12 |
| Z−β−Ocimene | 1041 | 1037 | 1.71 | 0.55 | 1.42 | 0.84 | 0.01 | 1.37 | 1.33 | 0.45 | 2.78 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 5.09 | 1.15 | 1.44 | 0.01 | 1.21 |
| γ−Terpinen | 1063 | 1059 | 1.28 | 1.22 | 1.67 | 0.54 | 2.15 | 0.01 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 2.41 | 0.01 | 12.69 | 1.77 | 2.27 | 0.56 | 0.01 | 1.88 |
| Bornyl acetate | 1286 | 1285 | 1.30 | 0.01 | 2.82 | 1.16 | 3.80 | 0.84 | 2.15 | 2.29 | 5.30 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 2.98 | 0.47 | 2.09 | 0.01 | 1.68 |
| Thymol | 1293 | 1290 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.47 | 0.72 | 0.01 | 0.41 |
| Carvacrol | 1303 | 1299 | 22.27 | 0.01 | 17.38 | 4.93 | 2.51 | 2.90 | 2.91 | 1.99 | 2.86 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.19 | 0.72 | 0.01 | 3.98 |
| E−Caryophyllene | 1423 | 1419 | 15.89 | 27.68 | 5.87 | 23.61 | 17.60 | 21.57 | 13.41 | 19.12 | 14.55 | 16.95 | 21.17 | 19.89 | 23.62 | 23.89 | 57.70 | 21.50 |
| γ−Muurolene | 1482 | 1479 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0.19 |
| Germacrene D | 1484 | 1481 | 25.14 | 27.07 | 35.95 | 39.51 | 36.84 | 31.21 | 45.21 | 37.78 | 41.7 | 38.95 | 27.04 | 25.71 | 39.30 | 34.99 | 42.30 | 35.25 |
| E,E−α−Farnesene | 1509 | 1505 | 2.85 | 0.01 | 2.87 | 2.33 | 3.22 | 4.66 | 2.99 | 3.91 | 1.13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.95 | 2.19 | 2.87 | 0.01 | 2.07 |
| γ−Cadinene | 1518 | 1513 | 3.79 | 0.01 | 2.53 | 4.02 | 1.08 | 0.74 | 2.72 | 6.48 | 3.98 | 8.35 | 0.01 | 1.92 | 2.23 | 7.86 | 0.01 | 3.05 |
| Elemol | 1550 | 1548 | 2.99 | 0.01 | 2.67 | 2.37 | 3.43 | 4.32 | 3.46 | 3.48 | 2.53 | 13.68 | 4.67 | 1.75 | 1.74 | 2.21 | 0.01 | 3.29 |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 1588 | 1583 | 2.92 | 0.01 | 2.36 | 1.91 | 4.63 | 5.38 | 3.62 | 3.12 | 2.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.95 | 2.27 | 2.68 | 0.01 | 2.19 |
| α−Muurolol | 1648 | 1646 | 1.72 | 0.01 | 1.47 | 1.45 | 2.00 | 3.27 | 1.74 | 2.14 | 1.39 | 6.79 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 1.22 | 1.40 | 0.01 | 1.71 |
| α−Cadinol | 1661 | 1655 | 3.61 | 0.01 | 4.24 | 2.88 | 3.77 | 5.43 | 3.41 | 4.16 | 2.23 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.95 | 2.06 | 2.13 | 0.01 | 2.39 |
| Sabinene | Z−β−Ocimene | γ−Terpinen | Bornylacetate | Thymol | Carvacrol | E−Caryoph | γ−Muurolene | Germacr.D | E−E−α−Farne | γ−Cadinene | Elemol | Cary.oxide | α−Muurolol | α−Cadinol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sabinene | 1 | 0.9 ** | 0.4 | −0.4 | 0.2 | 0.9 ** | 0.2 | 0.4 | −0.5 | −0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | −0.5 | 0.1 | 0 |
| Z−β−Ocimene | 1 | 0.7 * | −0.1 | −0.2 | 0.7 * | 0.1 | 0 | −0.3 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | −0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | |
| γ−Terpinen | 0.2 | −0.6 * | 0.4 | 0.3 | −0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.8 ** | 0.7 * | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.3 | |||
| Bornylacetate | 0.1 | −0.4 | −0.6 * | −0.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | ||||
| Thymol | 0.3 | −0.4 | 0.5 | −0.6 * | −0.7 * | −0.7 * | −0.7 * | −0.7 * | −0.6 * | −0.5 | |||||
| Carvacrol | 0.4 | 0.3 | −0.4 | −0.7 * | 0.2 | 0 | −0.7 * | −0.2 | −0.4 | ||||||
| E−Caryophyllene | −0.2 | −0.1 | −0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | −0.3 | 0.3 | −0.2 | |||||||
| γ−Muurolene | −0.5 | −0.4 | −0.2 | −0.3 | −0.4 | −0.4 | −0.2 | ||||||||
| Germacrene.D | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.7 * | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||||||||
| E−E−α−Farnesene | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.9 ** | 0.5 | 0.7 | ||||||||||
| γ−Cadinene | 0.8 ** | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |||||||||||
| Elemol | 0.2 | 0.9 ** | 0.7 * | ||||||||||||
| Caryophylleneoxide | 0.1 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||
| α−Muurolol | 0.9 ** | ||||||||||||||
| α−Cadinol | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadiasi, N.; Tako, R.; Ibraliu, A.; Stanys, V.; Gruda, N.S. Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis of Major Compound Variation in Essential Oil among Some Red Oregano Genotypes in Albania. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071419
Kadiasi N, Tako R, Ibraliu A, Stanys V, Gruda NS. Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis of Major Compound Variation in Essential Oil among Some Red Oregano Genotypes in Albania. Agronomy. 2024; 14(7):1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071419
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadiasi, Najada, Rea Tako, Alban Ibraliu, Vidmantas Stanys, and Nazim S. Gruda. 2024. "Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis of Major Compound Variation in Essential Oil among Some Red Oregano Genotypes in Albania" Agronomy 14, no. 7: 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071419
APA StyleKadiasi, N., Tako, R., Ibraliu, A., Stanys, V., & Gruda, N. S. (2024). Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis of Major Compound Variation in Essential Oil among Some Red Oregano Genotypes in Albania. Agronomy, 14(7), 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071419








