Coupled Efficacy of Magneto-Electric Water Irrigation with Foliar Iron Fertilization for Spinach Growth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Area Overview
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement of Indicators
- Soil moisture content
- 2.
- Plant height, aboveground fresh weight, and yield
- 3.
- Total accumulation of carbon, nitrogen, and iron in the aboveground part of spinach
- 4.
- Soluble protein and soluble sugar content
- 5.
- Water use efficiency
- 6.
- Spinach water consumption
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Magneto-Electric Irrigation with Iron Fertilizer Concentration Effects on Various Spinach Indexes
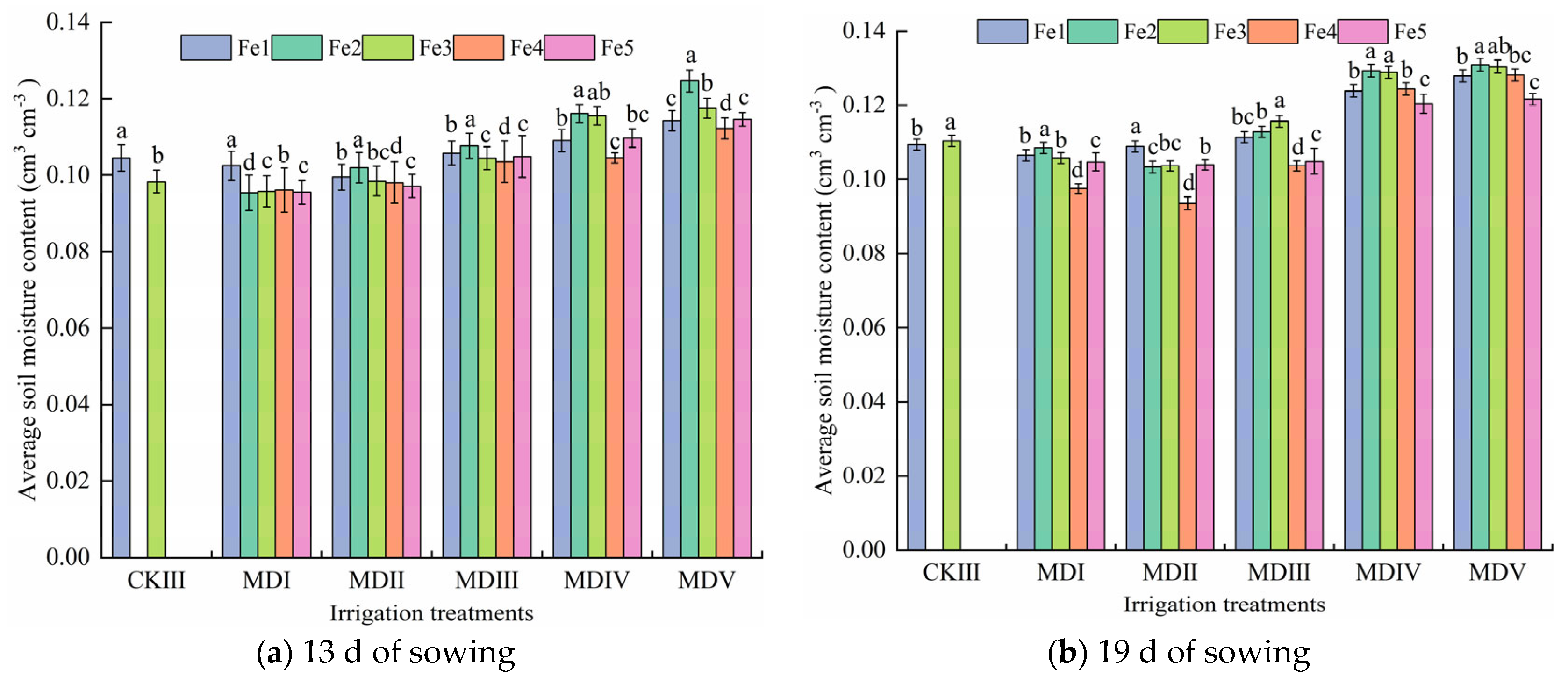
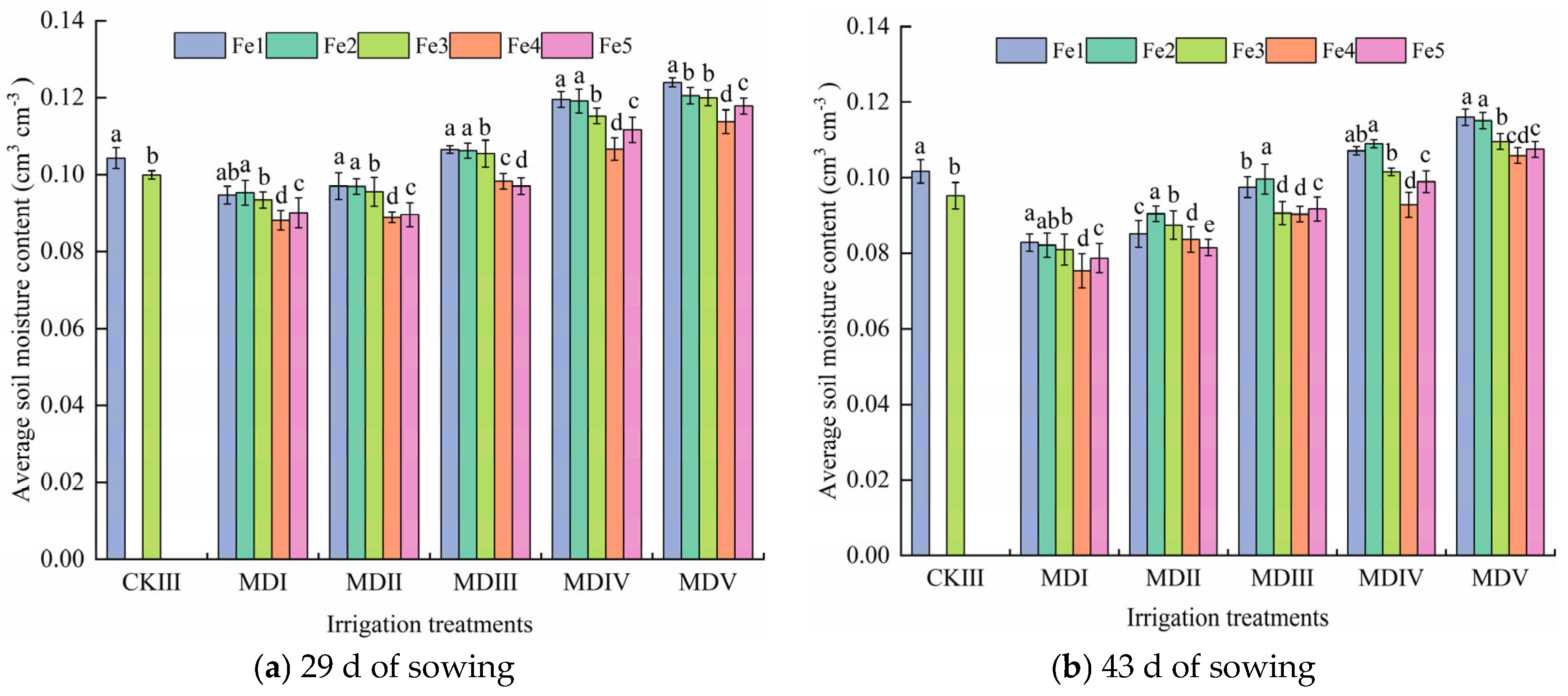
3.2. Effect of Magneto-Electric Irrigation with Iron Fertilizer Concentration on Soil Moisture Content
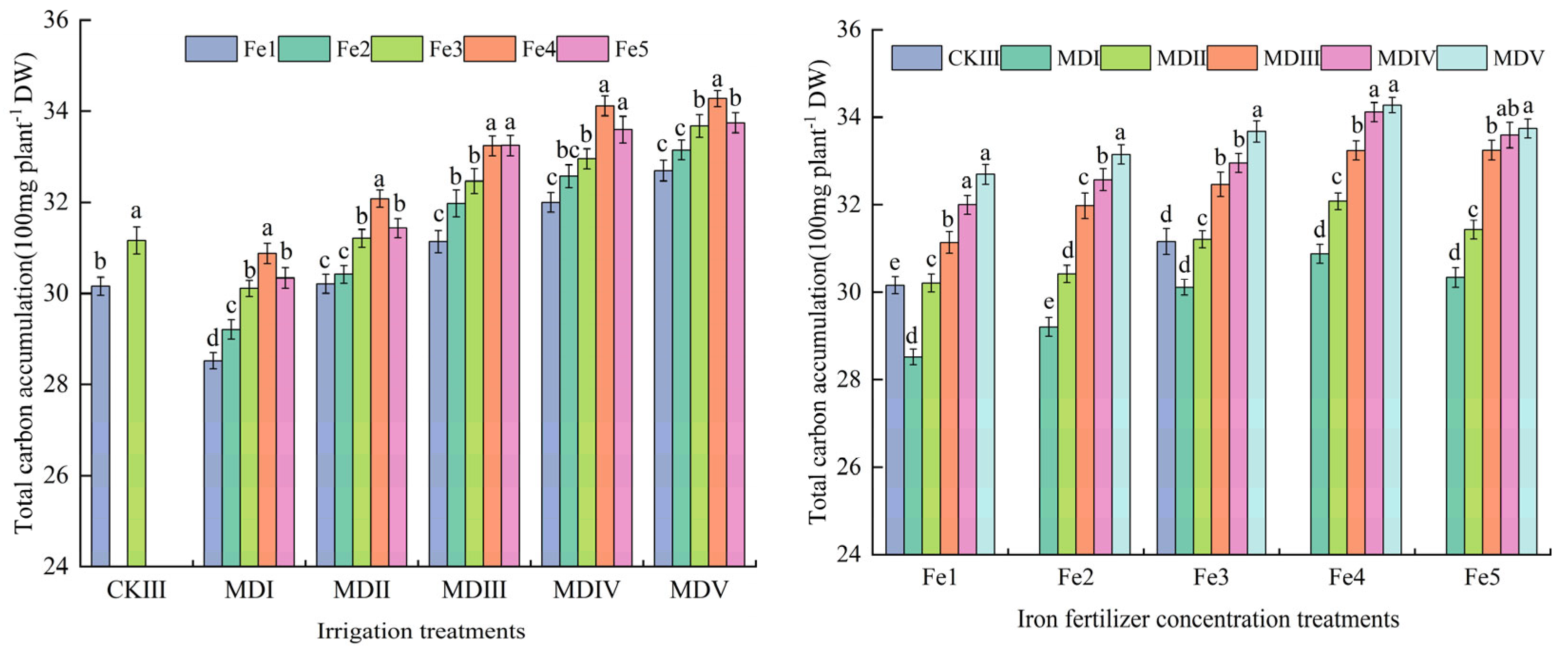
3.3. Effect of Magneto-Electric Irrigation with Iron Fertilizer Concentration on Total Accumulation of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Iron in the Aboveground Part of Spinach
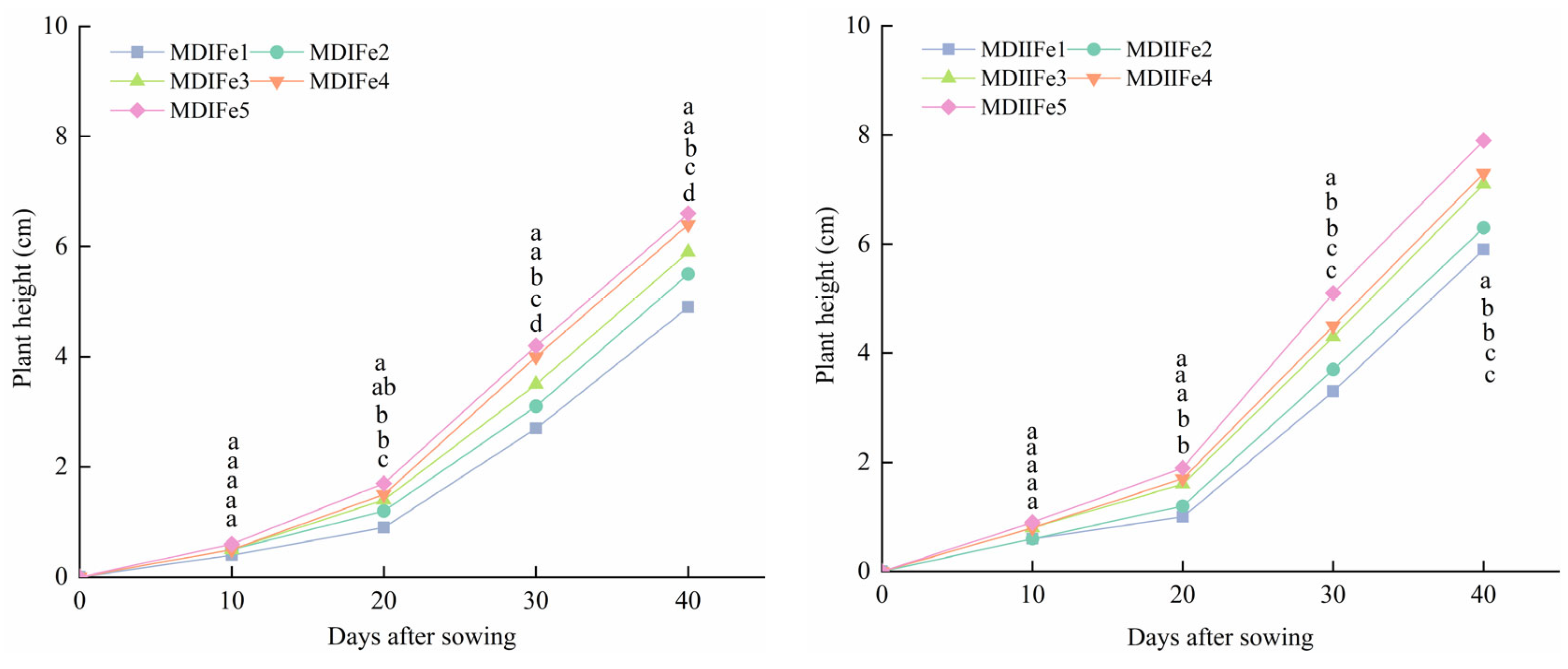
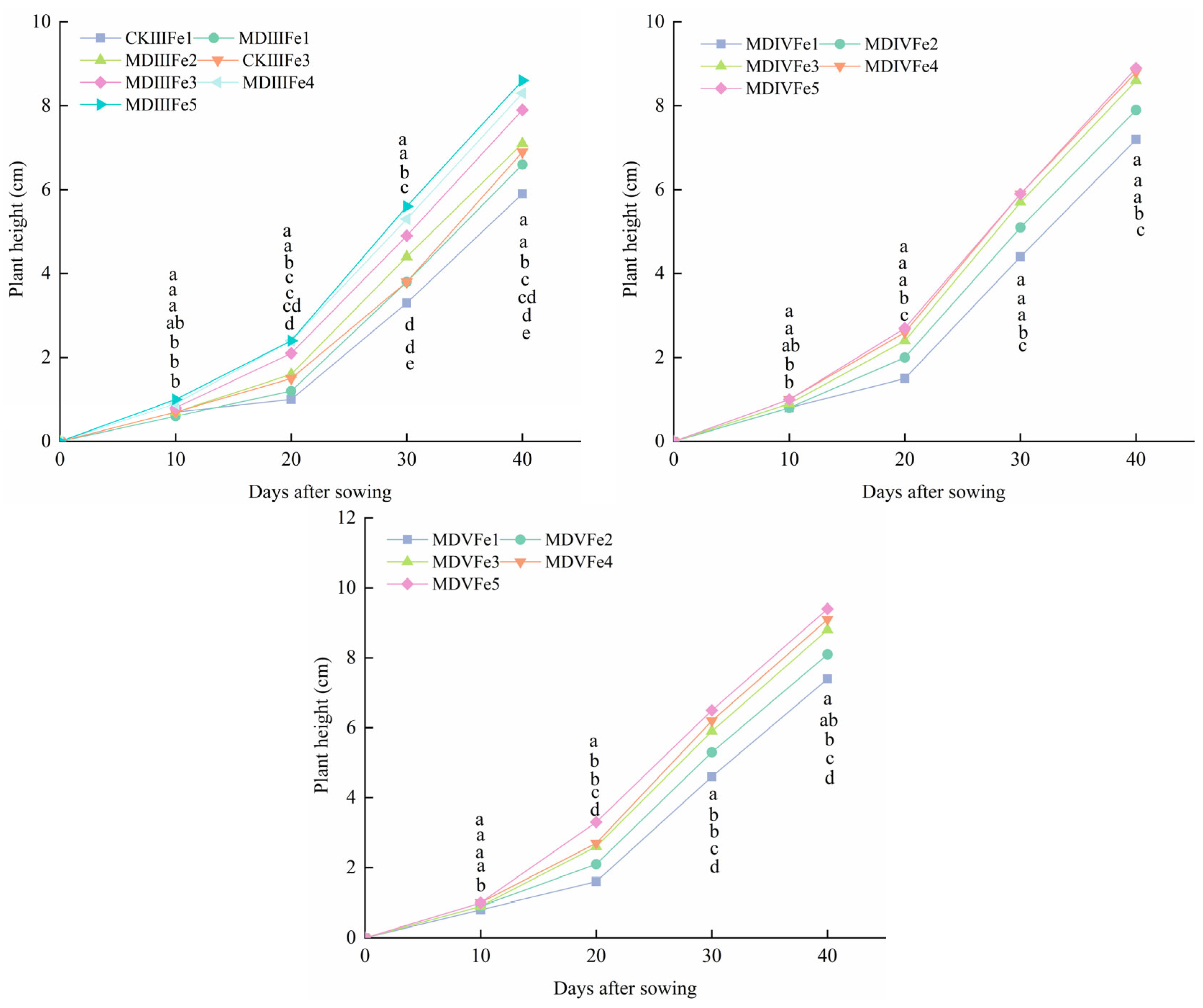
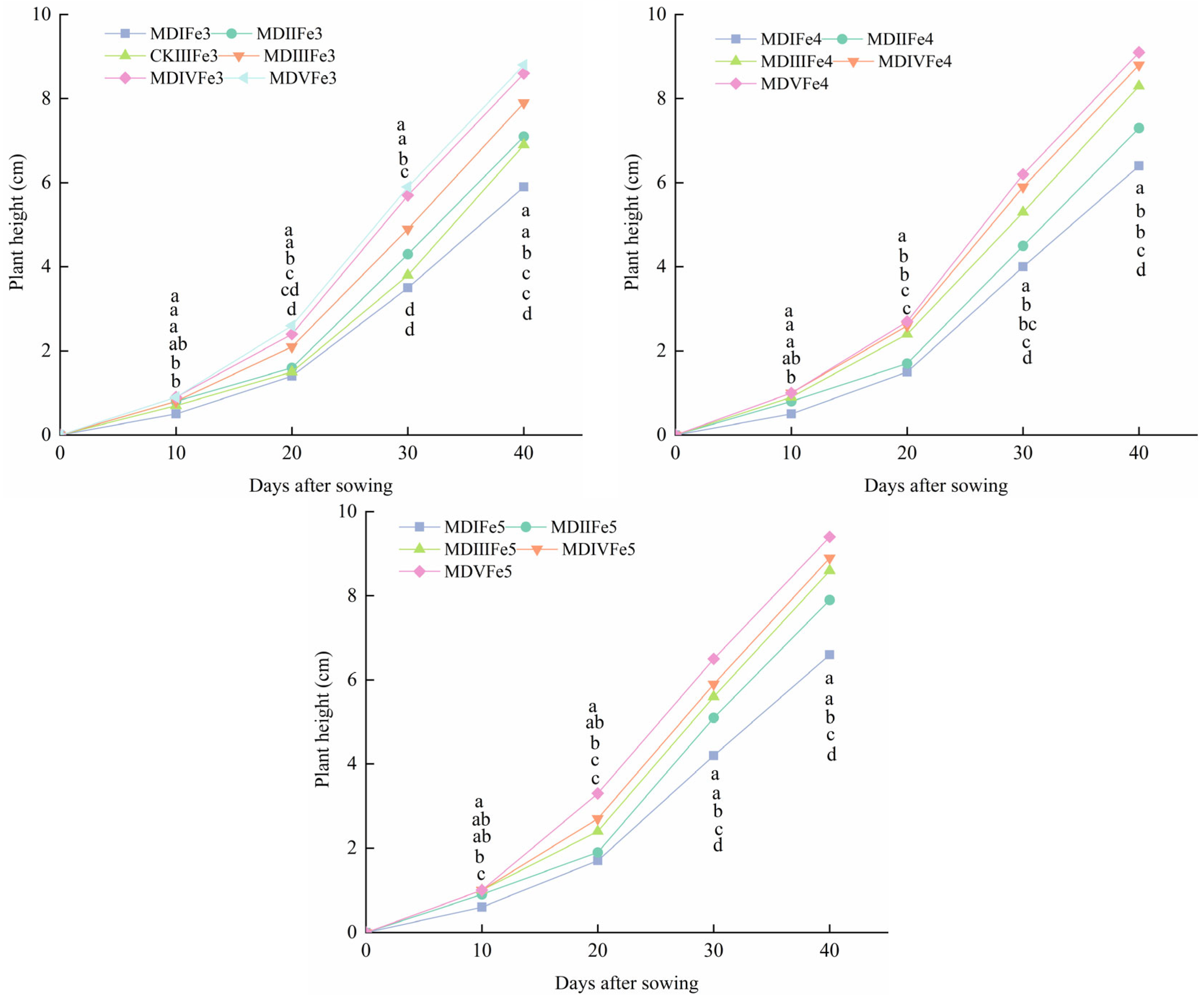
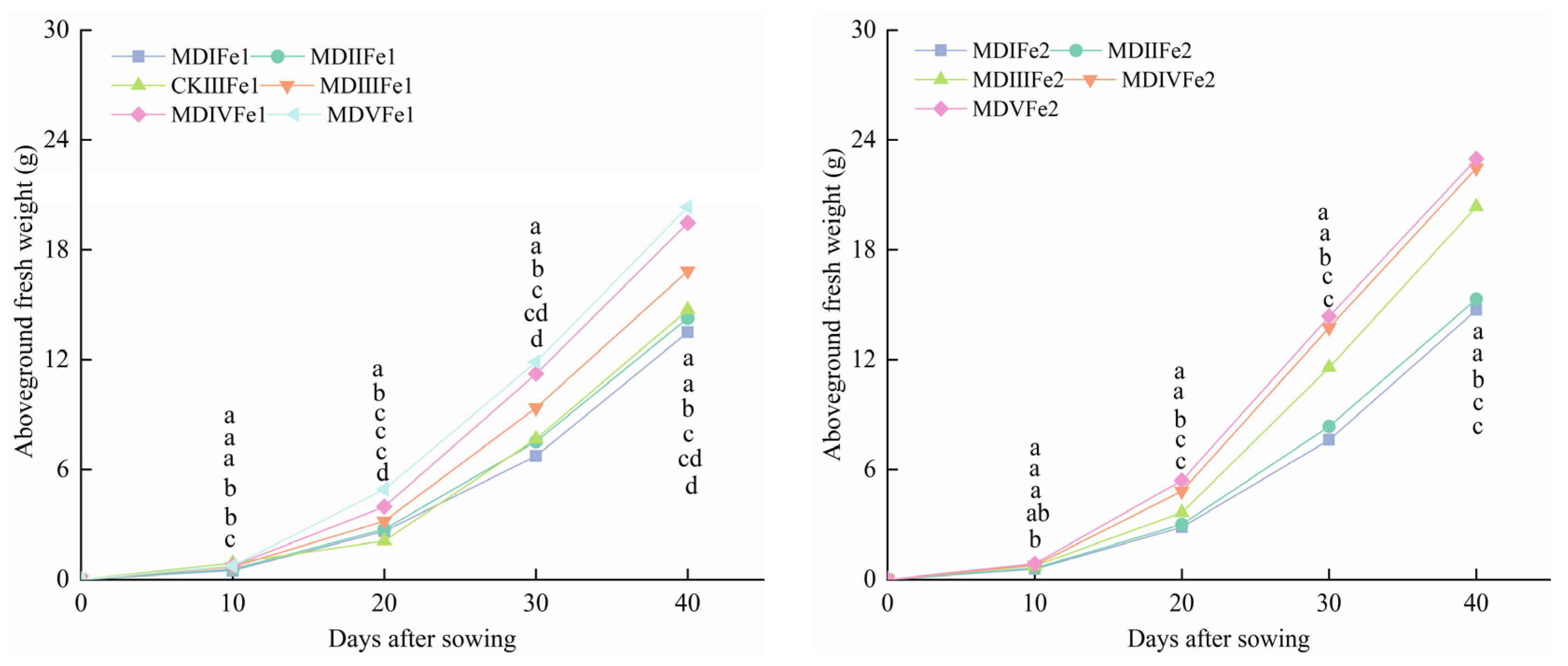
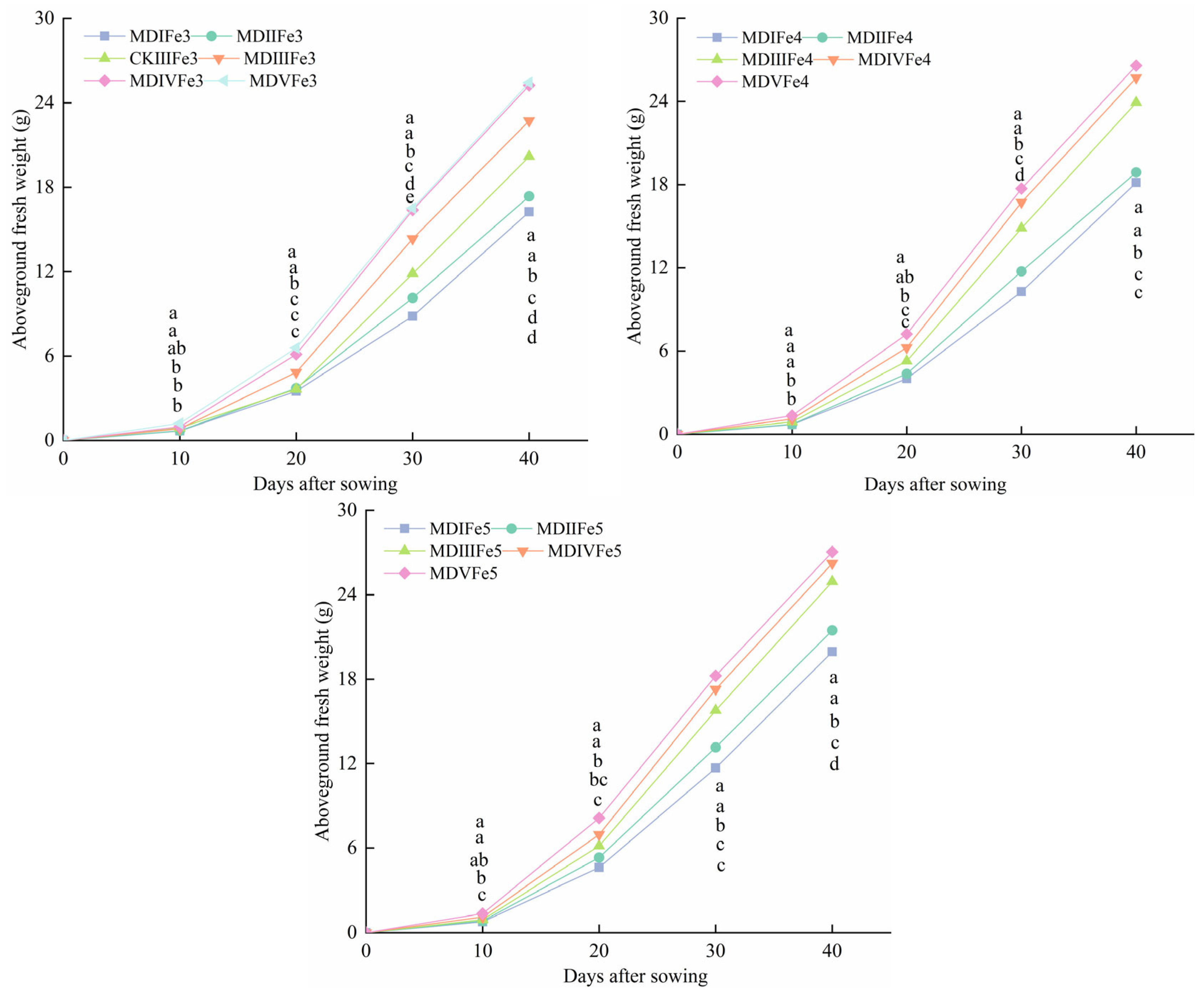
3.4. Effect of Magneto-Electric Irrigation with Iron Fertilizer Concentration on Spinach Growth Characteristics
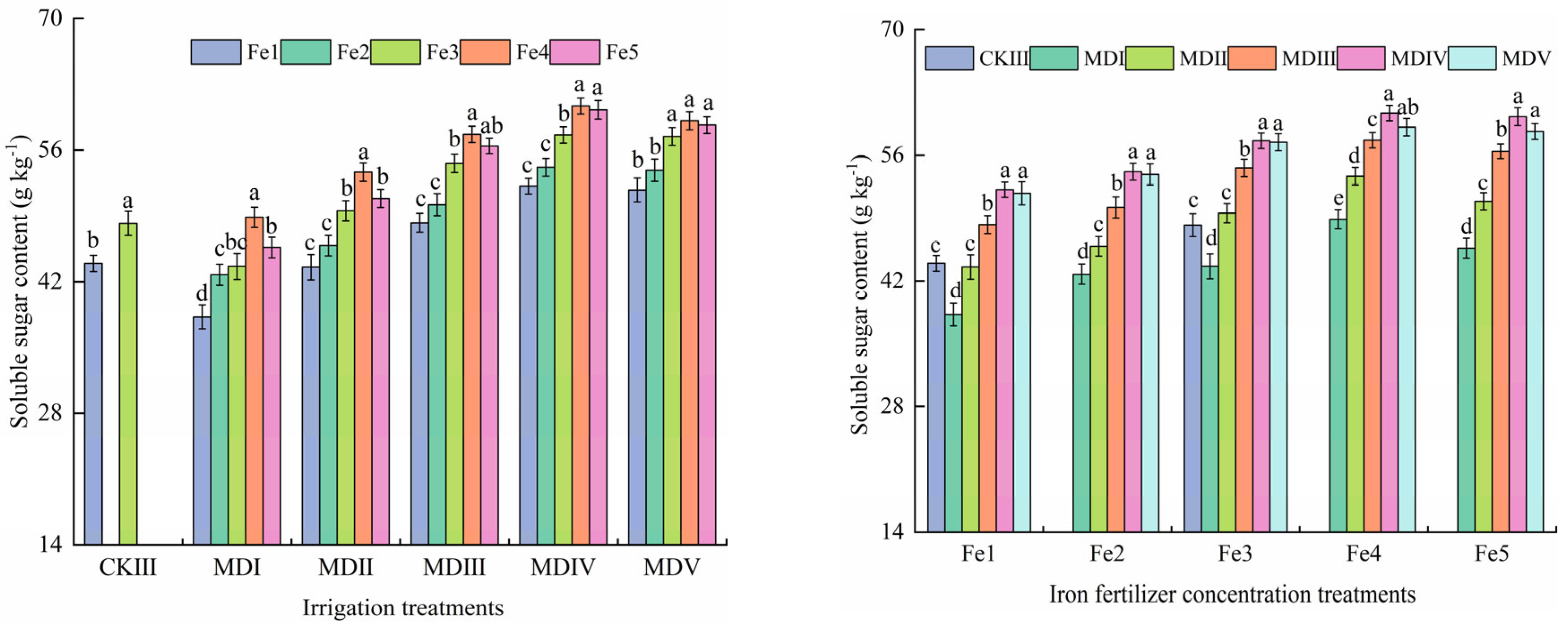
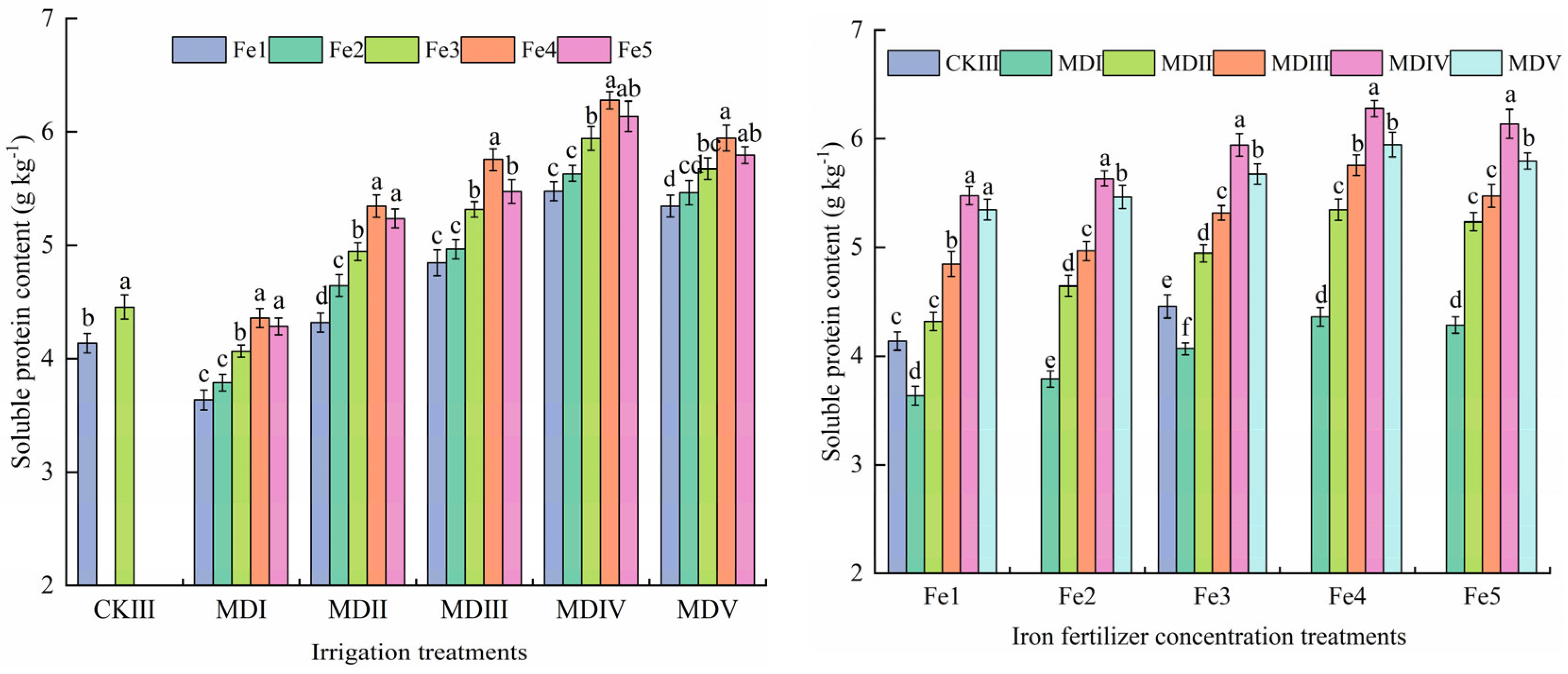
3.5. Effect of Magneto-Electric Irrigation with Iron Fertilizer Concentration on Spinach Quality
3.6. Spinach Water Consumption and Water Use Efficiency under Magneto-Electric Irrigation with Foliar Iron Fertilizer Application
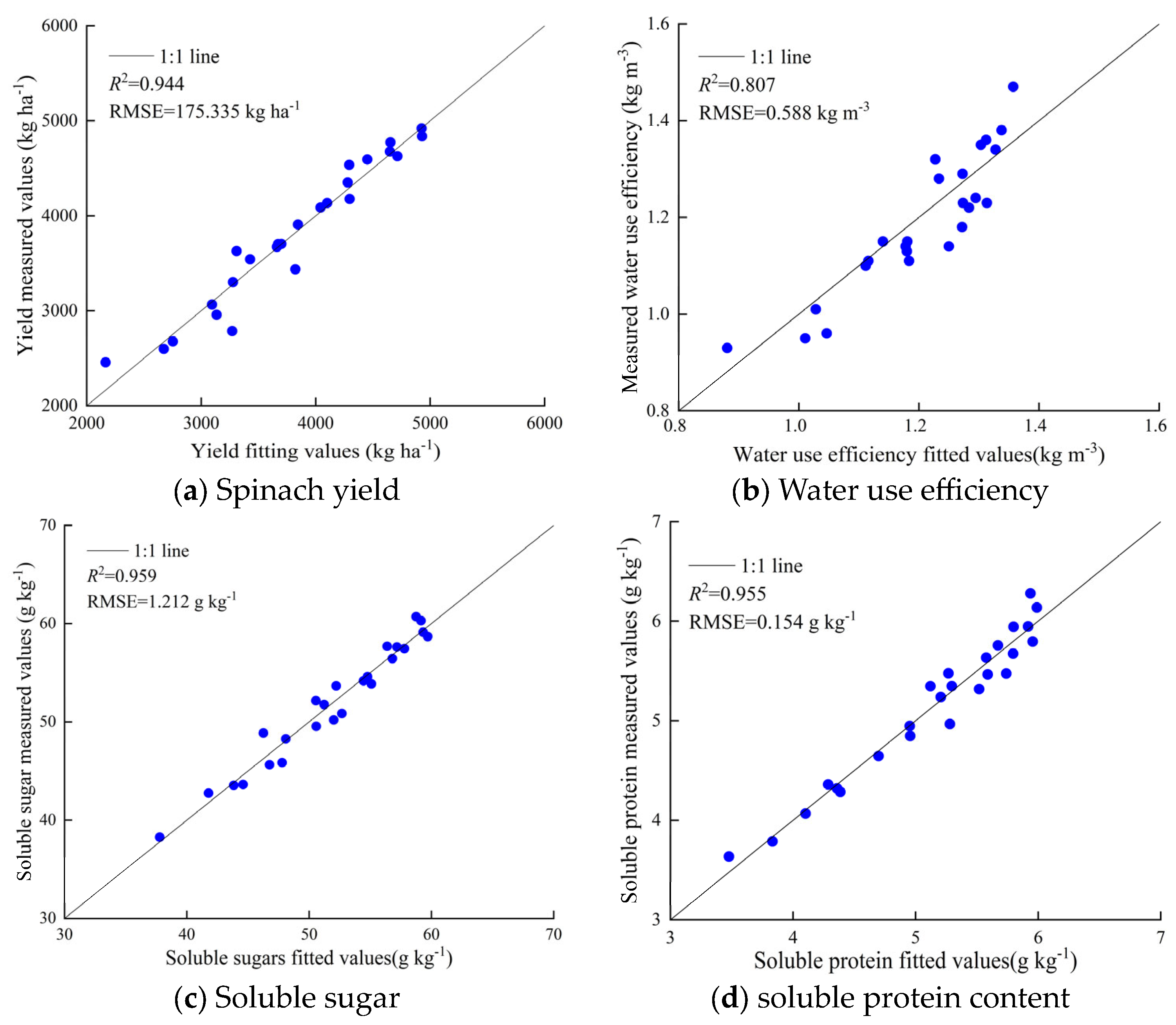
3.7. Water–Fertilizer Production Function and Comprehensive Evaluation of Appropriate Water–Fertilizer Dosage for Spinach Based on Grey Correlation Method
4. Discussion
- Effect of magneto-electric irrigation with foliar iron fertilizer on spinach nutrient accumulation
- 2.
- Effect of magneto-electric irrigation with foliar iron fertilizer on spinach growth characteristics
- 3.
- Effect of magnetization to remove electrons through drip irrigation with foliar iron fertilizer on spinach quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.D.; Shi, X.Y.; Zhang, H. Current situation, problems and recommendations for vegetable seed industry in China. China Cucurbits Veg. 2021, 34, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.L. Spinach Cultivation Technology. Agric. Henan 2022, 28, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, W.L. Research about Development and Prospect of Agricultural—Water—Use Stakeholders in China. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2018, 39, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.J.; Sun, Y.; Ning, S.R.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhou, B.B.; Su, L.J.; Shan, Y.Y. Effects of Activated Irrigation Water on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Crop Growth and Analysis of the Probable Pathway. Adv. Earth Sci. 2019, 34, 660–670. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Y.; Zhao, G.Q.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.J. Advances in the application of activated water irrigation. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2019, 36, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Dobránszki, J. From mystery to reality: Magnetized water to tackle the challenges of climate change and for cleaner agricultural production. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 139077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, D.B.; Nesic, S.; Bosnic, D.; Kostic, L.; Nikolic, M.; Samardzic, J.T. Silicon Alleviates Iron Deficiency in Barley by Enhancing Expression of Strategy II Genes and Metal Redistribution. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 444132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.L.; Jin, J.Y.; Yang, L.P. Study on the content and distribution of soil available magnesium and foreground of magnesium fertilizer in China. Soil Fertil. 2004, 2, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Verbruggen, N.; Hermans, C. Physiological and molecular responses to magnesium nutritional imbalance in plants. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, M.; Feng, M.S.; Ao, Y.; Wu, W. Effect of foliar spraying of iron fertilizer on growth and development, yield and mineral elements of taro. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Tayade, P.R.; Sapkal, V.S.; Sapkal, R.S.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Rode, C.V.; Shinde, V.M.; Kanade, G.S. A method to minimize the global warming and environmental pollution. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shao, G.S.; Chen, M.X.; Wang, D.Y.; Xu, C.M.; Mou, R.; Cao, Z.Y.; Zhang, F. Using iron fertilizer to control Cd accumulation in rice plants: A new promising technology. Sci. China Ser. C Life Sci. 2008, 51, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Apaolaza, L.; García-Marco, S.; Nadal, P.; Lucena, J.J.; Sierra, M.A.; Gómez-Gallego, M.; Ramírez-López, P.; Rosa, E. Structure and fertilizer properties of byproducts formed in the synthesis of EDDHA. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4355–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição Gomes, M.A.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Souza, A.N.; Vitória, A.P. Metal phytoremediation: General strategies, genetically modified plants and applications in metal nanoparticle contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 134, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.G. Mechanism of Leaf Vegetables Enriched with Fe and Its Affecting Factors. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Borowski, E. Uptake and transport of iron ions (Fe+2, Fe+3) supplied to roots or leaves in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) plants growing under different light conditions. Acta Agrobot. 2013, 66, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Xie, J.B.; Wei, K. Effect of Magnetization-De-Electronic Integrated Activation Water on Water-Salt Transport Characteristics of Salinized Soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.L.; Zhao, L.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Fan, J. Effects of Magnetized Water Irrigation on the Growth and Physiologica Characteristies of Cucumber Seedlings Under Salt Stress. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 358–366. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.B.; Yan, L.S.; Cao, Z.X.; We, L.F.; Chen, Z.Z. Physical and Chemical Properties of Magnetized Water. J. Hunan Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 1999, 1, 22–26+33. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, E.J.L.; Ramalho, T.C.; Magriotis, Z.M. Influence of magnetic field on physical-chemical properties of the liquid water: Insights from experimental and theoretical models. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 888, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.B.; Zhang, F.C.; Duan, C.Y.; Abdelghany, A.E.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.J. Characteristics of Soil Infiltration and Water and Nitrogen Transport under Irrigation with Magnetized Nitrogen Fertilizer Solution. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 316–324. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ogaidi, A.A.M.; Wayayok, A.; Rowshon, M.K.; Abdullah, A.F. The influence of magnetized water on soil water dynamics under drip irrigation systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 180 Pt A, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Peng, S.Z.; Wei, Z.; Hou, H.J. Characteristics of rice leaf photosynthetic light response curve with different water and nitrogen regulation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Akita, R.; Kamiyama, C.; Hikosaka, K. Polygonum sachalinense alters the balance between capacities of regeneration and carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate in response to growth CO2 increment but not the nitrogen allocation within the photosynthetic apparatus. Physiol. Plant. 2012, 146, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabi, B.; Freseneau, C.; Ghaderi, N.; Bolandnazar, S.; Streb, P.; Badeck, F.W.; Citerne, S.; Tangama, M.; David, A.; Ghashghaie, J. Stomatal and non-stomatal limitations are responsible in down-regulation of photosynthesis in melon plants grown under the saline condition: Application of carbon isotope discrimination as a reliable proxy. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ma, F.Y. Irrigation with magnetically treated saline water influences the growth and photosynthetic capability of vitis vinifera L. seedlings. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 262, 109056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.M.; Bo, X.; Kidron, G.J.; Hu, K. Respiration rate of moss-dominated biocrusts and their relationships with temperature and moisture in a semiarid ecosystem. Catena 2019, 183, 104195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bityutskii, N.P.; Yakkonen, K.L.; Lukina, K.A.; Semenov, K.N. Fullerenol increases effectiveness of foliar iron fertilization in iron-deficient cucumber. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cao, H.; Fu, Y.Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.D. The Effects of Irrigation Amount and Method on Soil CO2 Emission and Yield of Summer Maize. J. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 42, 31–39+73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, R.X.; Chu, G.X.; Wang, W.B. Effects of Magnetized Water in Agriculture. Agric. Eng. 2012, 2, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Abadía, J.; Vázquez, S.; Rellán-Álvarez, R.; El-Jendoubi, H.; Abadía, A.; Álvarez-Fernández, A.; López-Millán, A.F. Towards a knowledge-based correction of iron chlorosis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 49, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.B.; Shi, L.Y.; He, J.B.; He, J.J. Effect of Foliar Application of Iron Fertilizer on Agronomic, Yield and Quality Characters of Potato. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2023, 29, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.F.; Zhang, J.H.; Yu, S.M.; Hu, Z.H.; Jin, Q.Y. Magnetized water irrigation enhanced rice growth and development, improved yield and quality. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.L.; Tian, C.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Zhu, L.F.; Zhang, J.H.; Cao, X.C.; Jin, Q.Y. Research advance in the roles of water-nitrogen-oxygen factors in mediating rice growth, photosynthesis and nitrogen utilization in paddy soils. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1498–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Xu, F.P.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, K.Y.; Wang, X.R.; Li, Y.K. Treating Ammonia Nitrogen Wastewater Using a Biological Aerated Filter. J. Irrig. Drain. 2016, 35, 98–100+104. [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker, N.W.R. The relationships among iron-stress response, iron efficiency and iron uptake of plants. J. Plant Nutr. 1986, 9, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, K.; Raiendran, C.; Kulandaivelu, G. Differential responses of iron, magnesium, and zinc deficiency on Pigment composition, nutrient content, and Photosynthetic activity in tropical fruit crops. Photosynthetica 2001, 38, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.L. Effect of Foliar Iron and Zinc Fertilizer on Yield and Quality of Sweet Potato. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Sun, J.S.; Wang, C.C. Research on the Effects of Irrigation on the Quality of Vegetables. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2011, 4, 81–84+87. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, Q.J.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y. Effects of magnetoelectric water irrigation combined with foliar iron fertilizer on the growth characteristics and iron absorption of spinach. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 327, 112824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavallali, V.; Kiani, M.; Hojati, S. Iron nano-complexes and iron chelate improve biological activities of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, C.F.; Wang, R. Effects of foliar iron supplement on physiological regulation and quality improvement of wine grapes in eastern Helan Mountains. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2021, 6, 233–238. [Google Scholar]






| Irrigation Water Type | Treatments | Irrigation Volume (m3 ha−1) | Iron Fertilizer Concentration (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional water | CK III Fe1 | 2400 | 0 |
| CK III Fe3 | 0.1 | ||
| Magneto-electric water | MD I Fe1 | 1500 | 0 |
| MD I Fe2 | 0.05 | ||
| MD I Fe3 | 0.1 | ||
| MD I Fe4 | 0.15 | ||
| MD I Fe5 | 0.2 | ||
| MD II Fe1 | 1950 | 0 | |
| MD II Fe2 | 0.05 | ||
| MD II Fe3 | 0.1 | ||
| MD II Fe4 | 0.15 | ||
| MD II Fe5 | 0.2 | ||
| MD III Fe1 | 2400 | 0 | |
| MD III Fe2 | 0.05 | ||
| MD III Fe3 | 0.1 | ||
| MD III Fe4 | 0.15 | ||
| MD III Fe5 | 0.2 | ||
| MD IV Fe1 | 2850 | 0 | |
| MD IV Fe2 | 0.05 | ||
| MD IV Fe3 | 0.1 | ||
| MD IV Fe4 | 0.15 | ||
| MD IV Fe5 | 0.2 | ||
| MD V Fe1 | 3300 | 0 | |
| MD V Fe2 | 0.05 | ||
| MD V Fe3 | 0.1 | ||
| MD V Fe4 | 0.15 | ||
| MD V Fe5 | 0.2 |
| Irrigation Water Type | Dissolved Oxygen in Water (mg L−1) | Surface Tension (mN m−1) | pH | Mineralization (g L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional water | 8.77 ± 0.02 | 73.95 ± 0.52 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 1.21 ± 0.12 |
| Magneto-electric water | 10.01 ± 0.16 | 70.11 ± 0.07 | 7.6 ± 0.2 | 1.21 ± 0.09 |
| Norm | Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation Water Type × Iron Fertilizer Concentration | Irrigation Volume × Iron Fertilizer Concentration | Irrigation Volume | Irrigation Water Type | Iron Fertilizer Concentration | |
| F | ns | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| PH | ns | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| TCC | ns | ns | ** | * | ** |
| TNC | ns | ns | ** | * | ** |
| TIC | ns | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| SS | ns | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| SP | ns | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| Iron Fertilizer Concentration | Irrigation Volume | Water Consumption of Spinach at Different Sowing Days (mm) | Total Water Consumption (mm) | Water Use Efficiency (kg m−3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–13 d | 14–19 d | 20–29 d | 30–43 d | ||||
| Fe1 | MD I | 40.1 | 32.4 | 36.8 | 49 | 158.3 | 0.93 |
| MD II | 32.4 | 52.8 | 55.2 | 53.5 | 193.9 | 0.96 | |
| CK III | 50.3 | 57.1 | 62.8 | 61.4 | 231.6 | 1.05 | |
| MD III | 46.2 | 61.7 | 78.1 | 77.1 | 263.1 | 1.28 | |
| MD IV | 51.7 | 67.9 | 83 | 94.8 | 297.4 | 1.10 | |
| MD V | 65 | 72.7 | 89.3 | 102.4 | 329.4 | 0.95 | |
| Fe2 | MD I | 30.9 | 40.4 | 46.8 | 49 | 167.1 | 1.01 |
| MD II | 33.8 | 51.5 | 56 | 65.7 | 207 | 1.11 | |
| MD III | 53.4 | 60.4 | 76.7 | 77.2 | 267.7 | 1.14 | |
| MD IV | 57.6 | 67.2 | 82 | 95.4 | 302.2 | 1.32 | |
| MD V | 62.1 | 83.1 | 90.1 | 104.2 | 339.5 | 1.11 | |
| Fe3 | MD I | 33.9 | 46.4 | 53.2 | 60.2 | 193.7 | 1.23 |
| MD II | 35.5 | 37.7 | 55.1 | 65.9 | 194.2 | 1.18 | |
| CK III | 55.1 | 62.2 | 65.5 | 64.2 | 247 | 1.16 | |
| MD III | 51.6 | 75.7 | 81.4 | 79.9 | 288.6 | 1.34 | |
| MD IV | 60.4 | 73.4 | 88.5 | 83.2 | 305.5 | 1.24 | |
| MD V | 65.7 | 88.2 | 88.7 | 88.8 | 331.4 | 1.29 | |
| Fe4 | MD I | 33.6 | 59.2 | 55.2 | 55.2 | 203.2 | 1.14 |
| MD II | 36.2 | 70.3 | 68.5 | 61.2 | 236.2 | 1.36 | |
| MD III | 54.7 | 73.6 | 78.1 | 82.8 | 289.2 | 1.47 | |
| MD IV | 60.9 | 80.4 | 87 | 91.8 | 320.1 | 1.23 | |
| MD V | 72.3 | 88.8 | 92.2 | 103.4 | 356.7 | 1.15 | |
| Fe5 | MD I | 31.2 | 55.4 | 52 | 58.2 | 196.8 | 1.13 |
| MD II | 36.4 | 64.9 | 56.1 | 58 | 215.4 | 1.35 | |
| MD III | 48.9 | 64.7 | 75.3 | 77.4 | 266.3 | 1.38 | |
| MD IV | 63.4 | 71.9 | 87.6 | 92 | 314.9 | 1.22 | |
| MD V | 66.1 | 95.7 | 89.6 | 100.2 | 351.6 | 1.15 | |
| Implicit Variable | Regression Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Spinach yield | Y = −413.496F2 − 0.022W2 + 132.294F + 1.881W + 0.403FW − 1.671 | 0.944 |
| Water use efficiency | WUE = −9.714F2 − 0.002W2 + 4.146F + 0.113W − 0.047FW − 0.314 | 0.807 |
| Soluble sugar | SS = −232.991F2 − 0.044W2 + 93.598F + 2.872W − 0.141FW + 4.66 | 0.959 |
| Soluble protein content | SP = −17.023F2 − 0.007W2 + 8.985F + 0.438W − 0.069FW − 1.518 | 0.955 |
| Treatments | TNC | TCC | TIC | F | WUE | SS | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK III Fe1 | 0.626 | 0.731 | 0.366 | 0.477 | 0.964 | 0.401 | 0.84 |
| CK III Fe3 | 0.713 | 0.782 | 0.47 | 0.621 | 0.973 | 0.473 | 0.86 |
| MD I Fe1 | 0.558 | 0.661 | 0.366 | 0.453 | 0.954 | 0.333 | 0.809 |
| MD I Fe2 | 0.586 | 0.689 | 0.414 | 0.476 | 0.961 | 0.385 | 0.818 |
| MD I Fe3 | 0.618 | 0.729 | 0.46 | 0.51 | 0.979 | 0.397 | 0.835 |
| MD I Fe4 | 0.697 | 0.767 | 0.498 | 0.612 | 0.971 | 0.487 | 0.854 |
| MD I Fe5 | 0.689 | 0.74 | 0.467 | 0.558 | 0.971 | 0.427 | 0.849 |
| MD II Fe1 | 0.629 | 0.734 | 0.366 | 0.468 | 0.956 | 0.395 | 0.851 |
| MD II Fe2 | 0.651 | 0.744 | 0.439 | 0.489 | 0.969 | 0.43 | 0.873 |
| MD II Fe3 | 0.715 | 0.785 | 0.486 | 0.537 | 0.975 | 0.501 | 0.894 |
| MD II Fe4 | 0.823 | 0.836 | 0.68 | 0.668 | 0.99 | 0.615 | 0.923 |
| MD II Fe5 | 0.75 | 0.798 | 0.632 | 0.579 | 0.989 | 0.533 | 0.915 |
| MD III Fe1 | 0.673 | 0.781 | 0.394 | 0.524 | 0.983 | 0.474 | 0.887 |
| MD III Fe2 | 0.722 | 0.83 | 0.472 | 0.626 | 0.971 | 0.516 | 0.895 |
| MD III Fe3 | 0.79 | 0.861 | 0.567 | 0.722 | 0.988 | 0.648 | 0.921 |
| MD III Fe4 | 0.913 | 0.915 | 0.745 | 0.842 | 1 | 0.788 | 0.956 |
| MD III Fe5 | 0.857 | 0.916 | 0.614 | 0.782 | 0.992 | 0.725 | 0.933 |
| MD IV Fe1 | 0.763 | 0.831 | 0.401 | 0.597 | 0.968 | 0.568 | 0.933 |
| MD IV Fe2 | 0.778 | 0.868 | 0.51 | 0.71 | 0.987 | 0.632 | 0.946 |
| MD IV Fe3 | 0.86 | 0.895 | 0.614 | 0.862 | 0.98 | 0.785 | 0.971 |
| MD IV Fe4 | 0.976 | 0.986 | 0.873 | 0.933 | 0.979 | 1 | 1 |
| MD IV Fe5 | 0.936 | 0.943 | 0.722 | 0.893 | 0.978 | 0.965 | 0.988 |
| MD V Fe1 | 0.832 | 0.876 | 0.423 | 0.626 | 0.956 | 0.556 | 0.923 |
| MD V Fe2 | 0.85 | 0.909 | 0.492 | 0.733 | 0.969 | 0.621 | 0.932 |
| MD V Fe3 | 0.889 | 0.949 | 0.723 | 0.874 | 0.984 | 0.776 | 0.949 |
| MD V Fe4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.972 | 0.877 | 0.971 |
| MD V Fe5 | 0.982 | 0.955 | 0.872 | 0.961 | 0.972 | 0.847 | 0.959 |
| Indicators | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation | Weights (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 20.561 | 4.236 | 0.206 | 21.109 |
| TNC | 15.474 | 2.326 | 0.150 | 15.403 |
| TCC | 31.873 | 1.504 | 0.047 | 4.836 |
| TIC | 27.228 | 4.201 | 0.154 | 15.809 |
| WUE | 1.185 | 0.134 | 0.113 | 11.562 |
| SS | 51.4 | 7.909 | 0.154 | 15.766 |
| SP | 5.085 | 0.770 | 0.151 | 15.515 |
| Evaluation Item | Relatedness | Rankings |
|---|---|---|
| CK III Fe1 | 0.0850 | 24 |
| CK III Fe3 | 0.0962 | 17 |
| MD I Fe1 | 0.0800 | 27 |
| MD I Fe2 | 0.0840 | 26 |
| MD I Fe3 | 0.0880 | 23 |
| MD I Fe4 | 0.0963 | 19 |
| MD I Fe5 | 0.0921 | 21 |
| MD II Fe1 | 0.0848 | 25 |
| MD II Fe2 | 0.0892 | 22 |
| MD II Fe3 | 0.0955 | 18 |
| MD II Fe4 | 0.1100 | 9 |
| MD II Fe5 | 0.1024 | 13 |
| MD III Fe1 | 0.0915 | 20 |
| MD III Fe2 | 0.0987 | 16 |
| MD III Fe3 | 0.1092 | 11 |
| MD III Fe4 | 0.1241 | 5 |
| MD III Fe5 | 0.1160 | 8 |
| MD IV Fe1 | 0.0991 | 15 |
| MD IV Fe2 | 0.1075 | 12 |
| MD IV Fe3 | 0.1204 | 7 |
| MD IV Fe4 | 0.1370 | 2 |
| MD IV Fe5 | 0.1301 | 4 |
| MD V Fe1 | 0.1016 | 14 |
| MD V Fe2 | 0.1088 | 10 |
| MD V Fe3 | 0.1236 | 6 |
| MD V Fe4 | 0.1390 | 1 |
| MD V Fe5 | 0.1333 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Mu, W.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J. Coupled Efficacy of Magneto-Electric Water Irrigation with Foliar Iron Fertilization for Spinach Growth. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071482
Zheng M, Sun Y, Wang Q, Bai Y, Mu W, Zhang J, Lu Z, Wang J. Coupled Efficacy of Magneto-Electric Water Irrigation with Foliar Iron Fertilization for Spinach Growth. Agronomy. 2024; 14(7):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071482
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Ming, Yan Sun, Quanjiu Wang, Yungang Bai, Weiyi Mu, Jianghui Zhang, Zhenlin Lu, and Jian Wang. 2024. "Coupled Efficacy of Magneto-Electric Water Irrigation with Foliar Iron Fertilization for Spinach Growth" Agronomy 14, no. 7: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071482
APA StyleZheng, M., Sun, Y., Wang, Q., Bai, Y., Mu, W., Zhang, J., Lu, Z., & Wang, J. (2024). Coupled Efficacy of Magneto-Electric Water Irrigation with Foliar Iron Fertilization for Spinach Growth. Agronomy, 14(7), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071482





