Abstract
With the continuous expansion of petroleum exploitation, a large amount of petroleum hydrocarbons has leaked into the Earth’s soil, which seriously threatens ecological health. Hence, a series of experiments were conducted to evaluate the performance of natural attenuation (NA), rice husk (RH), and biochar derived from rice husk (RHBC) in enhancing the bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. When the biodegradation time reached 100 d, the total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPHs) biodegradation amounts of NA, RH, and RHBC were 3688.2, 4557.9, and 5913.3 mg/kg, which was equal to the biodegradation efficiency of 32.8, 40.6, and 52.6%, respectively. Compared with NA and RH, the biodegradation efficiency of n-alkanes C11–C15 (C11 represents n-alkanes with 11 carbons, namely n-Hendecane) C16–C29, and C30–C40 in RHBC increased to 69.7~82.5%, 42.4~81.5%, and 30.2~48.1%, equivalent to 12.2~34.5%, 6.9~31.2%, and 13.5~37.1% more than NA and RH, respectively. Moreover, the half-life of biodegradation in RHBC was shorted to 83.3 d, equal to 49.7 and 67.9% of NA and RH, respectively. Furthermore, the application of RHBC could improve the dehydrogenase activity in soil and promote the growth and reproduction of petroleum-degrading bacteria (PDB), which enhances the biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. This study exhibited that biochar formed from biomass pyrolysis is a potential biostimulator in enhancing the remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil by indigenous bacteria.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, petroleum has been widely exploited as one of the most important energy sources in the world, and has inevitably leaked into the Earth’s soil [1,2]. After entering the soil, petroleum pollutants will gradually accumulate on the soil surface, resulting in an increase in the viscosity of the soil, thereby clogging the soil pores and reducing the soil permeability [3,4]. At the same time, petroleum pollutants will form a surface mucosa in the roots of plants, which will affect the respiration of plant roots and the absorption of nutrients and water [5]. In severe cases, it will cause plant roots to rot, thus affecting the growth and yield of crops. In addition, petroleum is a kind of complex mixture, including alkanes, cycloalkanes, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons [6]. As reported, some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are considered to have the potential to cause distortion, cancer, and change the genetic material of cells [7,8,9]. Based on the above reasons, the remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil is an urgent problem to be solved.
Common remediation technologies for petroleum-contaminated soil include physical remediation, chemical oxidation, and phytoremediation [5,10,11]. As an alternative, biodegradation showed low costs, simple operation, and good environmental friendliness in the remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil [7,12]. Therefore, biodegradation using the natural ability of microorganisms to metabolize petroleum hydrocarbons is one of the most promising methods and has to date been successfully applied to remediate petroleum-contaminated soil [13,14]. Nevertheless, the natural attenuation (NA) of organic pollutants in soil by indigenous microorganisms is generally limited by various factors, such as nutrient level, moisture content, pH value, pollutant concentration, and electron transfer efficiency, especially in semi-arid areas. Previous studies have shown that the application of biostimulation in petroleum-related environments can be used as a feasible method for the remediation of contaminated sites [15,16]. Therefore, many researchers have found that various biostimulation methods, such as adding nutrients and waste biomass, improve the metabolic activity of indigenous microorganisms, thus accelerating the biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons [17,18]. Among biostimulation methods, the application of biochar is considered to be one of the most multifunctional and cost-effective ways [19,20]. Biochar is a highly aromatic and carbon-rich porous solid particulate matter produced via the high-temperature pyrolysis of biomass under anaerobic or anoxic conditions [19,21,22]. In addition, biochar is usually described as containing a large amount of carbon and nutrients, having a rich pore structure and a large specific surface area, and possessing lots of oxygen-containing groups. Accordingly, it is generally considered a multifunctional material and has been widely used to enhance the biological treatment of wastewater [23].
In this study, we will use a waste biomass-rice husk (RH), which is widely produced in the agricultural field, as a raw material for the preparation of biochar and compare the enhanced effect of RH itself and its derived rice husk-biochar (RHBC) on the bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil in semi-arid areas. Our objectives are as follows: (1) determining the performance of RH and RHBC in enhanced biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons, (2) exploring the kinetics of biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons under different system conditions, (3) investigating the biodegradation characteristics of n-alkanes, and (4) evaluating the effects of adding RH and RHBC on enzyme activity and microbial growth.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Contaminated Soil and Chemicals
A petroleum-contaminated soil sample was collected from Yan’an, Shaanxi Province. Before the experiment, the soil sample was crushed and sifted through a 2 mm sieve. The physicochemical properties of the soil sample are shown in Table 1. 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC, analytically pure), hydrochloric acid (HCl, 37%), sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 98%), n-hexane (C6H14, chromatographically pure), and acetone (C3H6O, chromatographically pure) were obtained from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Toluene (C7H8, 98%), triphenylformazan nitrogen (C19H16N4, 92%), glucose (C6H12O6, ≥99.5%), ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3, analytically pure), potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4, analytically pure), dipotassium hydrogenphosphate (K2HPO4, analytically pure), magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4·7H2O, analytically pure), calcium dichloride (CaCl2, analytically pure), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium (C10H18N2Na2O10, 98%), and 1,3,5-triphenyl formazan (TPF, analytically pure) were brought from Zhengzhou Paini chemical reagent factory (Zhengzhou, China). All chemical reagents were not further purified.

Table 1.
The physicochemical properties of soil sample.
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of RHBC
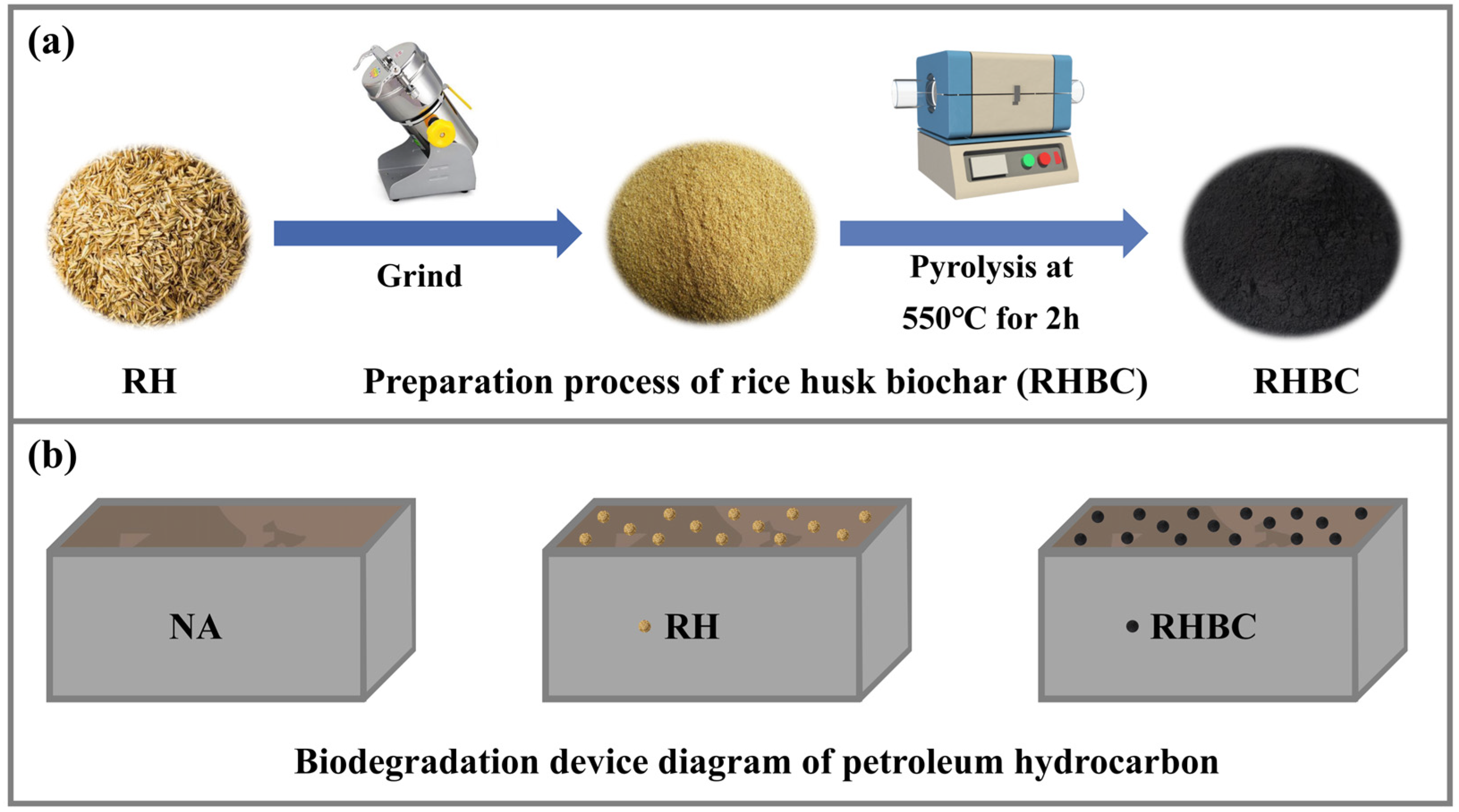
The RH was obtained from a grain processing plant in Xi’an, Shaanxi Province. Firstly, the RH was washed and then dried in an oven at 50 °C. Secondly, the dried RH was ground and passed through a 2 mm sieve. Finally. the RH powder was pyrolyzed in a tube furnace under N2 flow for 2 h at 550 °C with a heating rate of 5 °C/min [11]. The obtained black solid powder was labeled as RHBC (Scheme 1a). The surface morphologies were observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Zeiss Sigma 300, Oberkochen, Germany). The functional groups were determined using Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR, Nicolette is50, Thermo Fourier, Waltham, MA, USA).
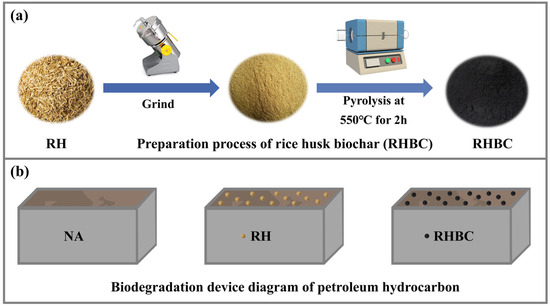
Scheme 1.
Schematic diagram of the preparation process of biochar (a) and the biodegradation device diagram of petroleum hydrocarbons (b).
2.3. Experimental Design
Firstly, three 2 kg soil samples were placed in three plastic boxes. Secondly, the first soil sample did not undergo any treatment, and therefore underwent natural attenuation (NA). A total of 0.05 g/g RH powder and RHBC were added to the second and third soil samples, respectively. Finally, the added material was mixed with the soil samples and the humidity was adjusted to 20%, and the humidity was kept during the biodegradation process (Scheme 1b). All soil samples were regularly stirred for oxygenation. The biodegradation experiment was carried out for 100 days and about 30 g soil samples were randomly obtained on days 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100, and then uniformly mixed. The collected soil samples were analyzed for residual petroleum hydrocarbons, petroleum-degrading bacteria, and dehydrogenase activity, etc.
2.4. Extraction and Determination of Petroleum Hydrocarbons
The content of total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPHs) was determined using the gravimetric method. Then, the 5.0 g soil was put into the extraction tank and extracted twice with n-hexane and acetone (1:1, v:v). Then, the solvent was blown off with N2 until the weight did not change. The content of individual n-alkanes was detected using gas chromatograph spectrometry (GC, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 7890A-5975C) [6]. The chromatographic column was HP-5MS (30.0 m × 250 μm, 0.25 μm). The initial temperature was first maintained at 50 °C for 2 min, then increased to 230 °C at a rate of 20 °C/min, and finally increased to 320 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min for 20 min. The gasification chamber temperature was 300 °C and the transmission line temperature was 320 °C. The carrier gas was He and the flow rate of carrier gas was 1.0 mL/min without shunt. The injection volume was 1 μL.
2.5. Measurement of Dehydrogenase Activity
Firstly, the 0.5 g soil was weighed into a 10 mL centrifuge tube, and then 2 mL of 1% TTC solution, 2 mL of 0.2 mol/L tris-HCl buffer (pH = 7.6), and 2 mL of 0.1 mol/L glucose solution were added in turn. Secondly, the soil was shaken upside down to no granular soil and cultured in a dark environment at 37 °C for 24 h. After the culture, 10 μL H2SO4 was added to stop the reaction, and then 5 mL of toluene was added to extract all TPF. Finally, the absorbance of the extract was measured at 492 nm, and the amount of TPF produced within 24 h was used to show the dehydrogenase activity [24,25].
2.6. Count of Petroleum-Degrading Bacteria
The petroleum-degrading bacteria (PDB) population was determined using the plate counting method [16]. The colony-forming unit (CFU/g soil) was the unit of the PDB population. The 5.0 g soil sample was mixed with 30 mL sterile water and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 μm filter membrane. The continuous dilution technique was used, and then each concentration containing liquid was coated on a plate containing petroleum medium. After 48 h of incubation at 37 °C, colony counting was performed on the plate.
2.7. TPHs Degradation Kinetics
The first-order kinetic model was used to describe the TPHs degradation data (Equation (1)). Based on the first-order kinetic model, the half-lives of TPHs degradation were calculated (Equation (2)).
where Ct is the content of TPHs at time t (mg/kg); C0 is the initial content of TPHs (mg/kg); k is the degradation rate constant of TPHs (d−1); t is the degradation time (day); t1/2 is the half-lives of the TPHs degradation (day).
Ct = C0·exp (−k·t)
t1/2 = ln (2)/k
2.8. Statistical Analysis
In this study, all experiments were performed in triplicate and the data were presented as the mean ± standard error. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) was calculated using SPSS 22.0 and p < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of RHBC Particles
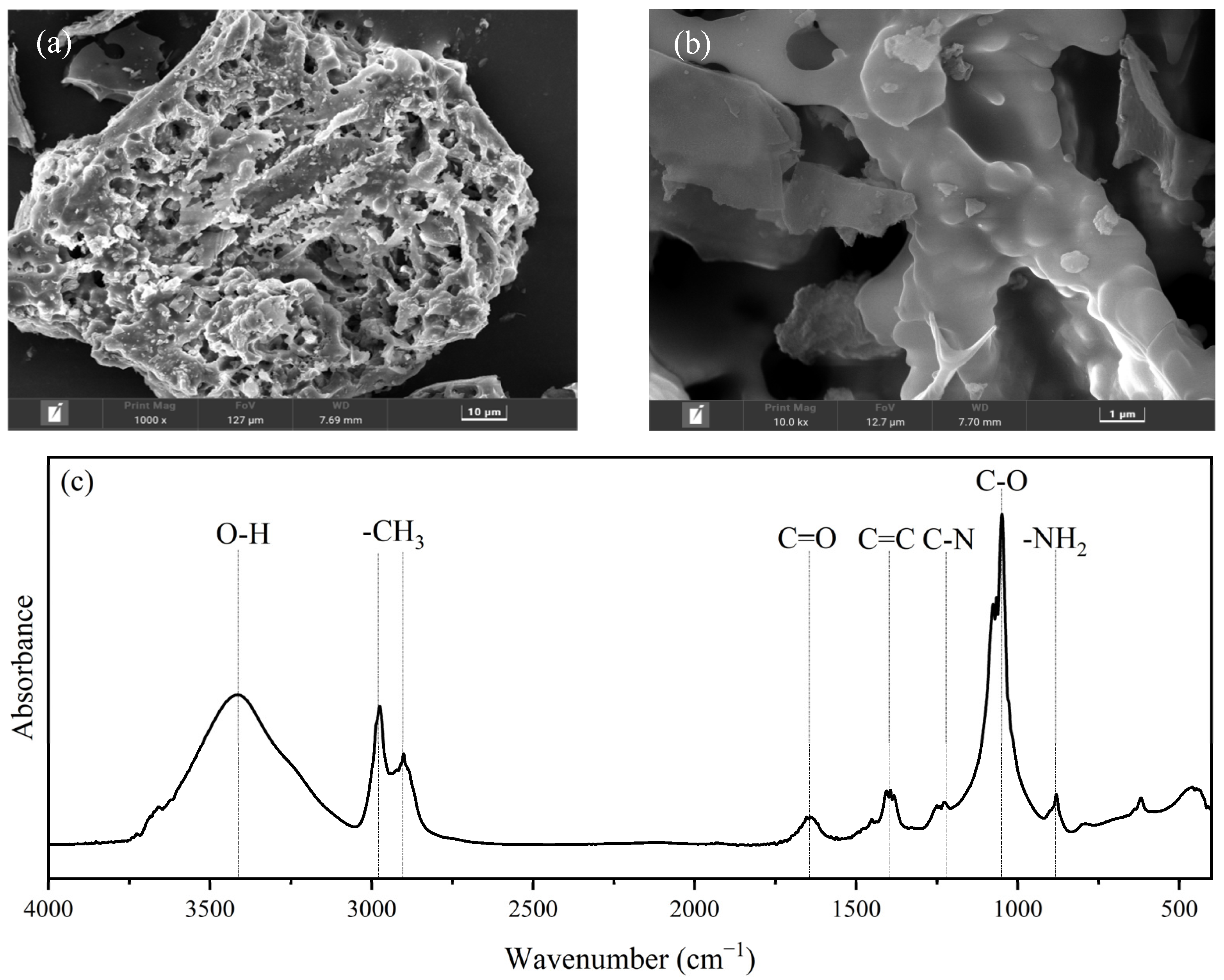
SEM was applied to determine the surface morphology and pore structure of biochar. As shown in Figure 1a, an RHBC particle with an irregular shape and porous structure was observed at a scale of 1000 times. Meanwhile, RHBC particles exhibited a smooth local surface at a scale of 10,000 times (Figure 1b). The porous pore structure of RHBC may be due to tendency of the thermal decomposition of organic components in rice husk, such as cellulose, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, to form pore structure in high temperature environment [22]. A FTIR spectrum was used to characterize the functional groups of RHBC. It can be seen from Figure 1c that the dominant functional groups of RHBC were the stretching vibration of O-H, C=O, aromatic C=C, C-O, and -NH2, as well as symmetric and antisymmetric stretching vibrations of -CH3 [6,26]. Mei et al. (2021) [22] also reported the existence of the above functional groups after rice straw was pyrolyzed at 700 °C.
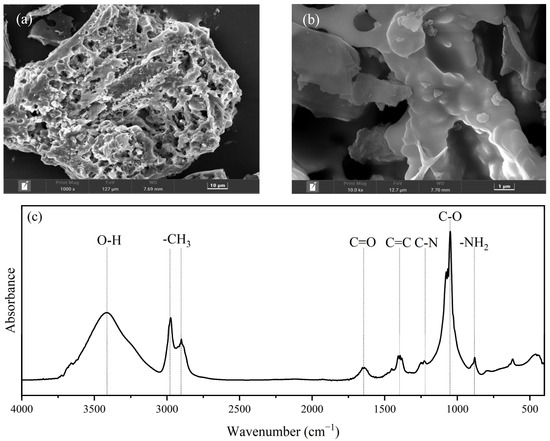
Figure 1.
SEM images (a,b) and FTIR spectrum (c) of RHBC.
As reported by previous studies, the high surface area and extensive porosity of biochar offered ample space for microbial growth-reproduction, creating a favorable micro-environment for hydrocarbon-degrading microorganisms [27]. This increased microbial biomass facilitated a more efficient breakdown of complex hydrocarbons. Additionally, the oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the biochar could improve the availability of essential nutrients and promote better microbial attachment. These functional groups also enhanced electron transfer processes and the stability of enzymes involved in degradation [28]. By adsorbing toxic byproducts and facilitating oxygen diffusion, biochar further supported a conducive environment for microbial activity. Together, these features of biochar contributed to a more effective and accelerated degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons, highlighting its potential as a valuable tool in bioremediation efforts.
3.2. Analysis of TPHs Degradation Kinetics
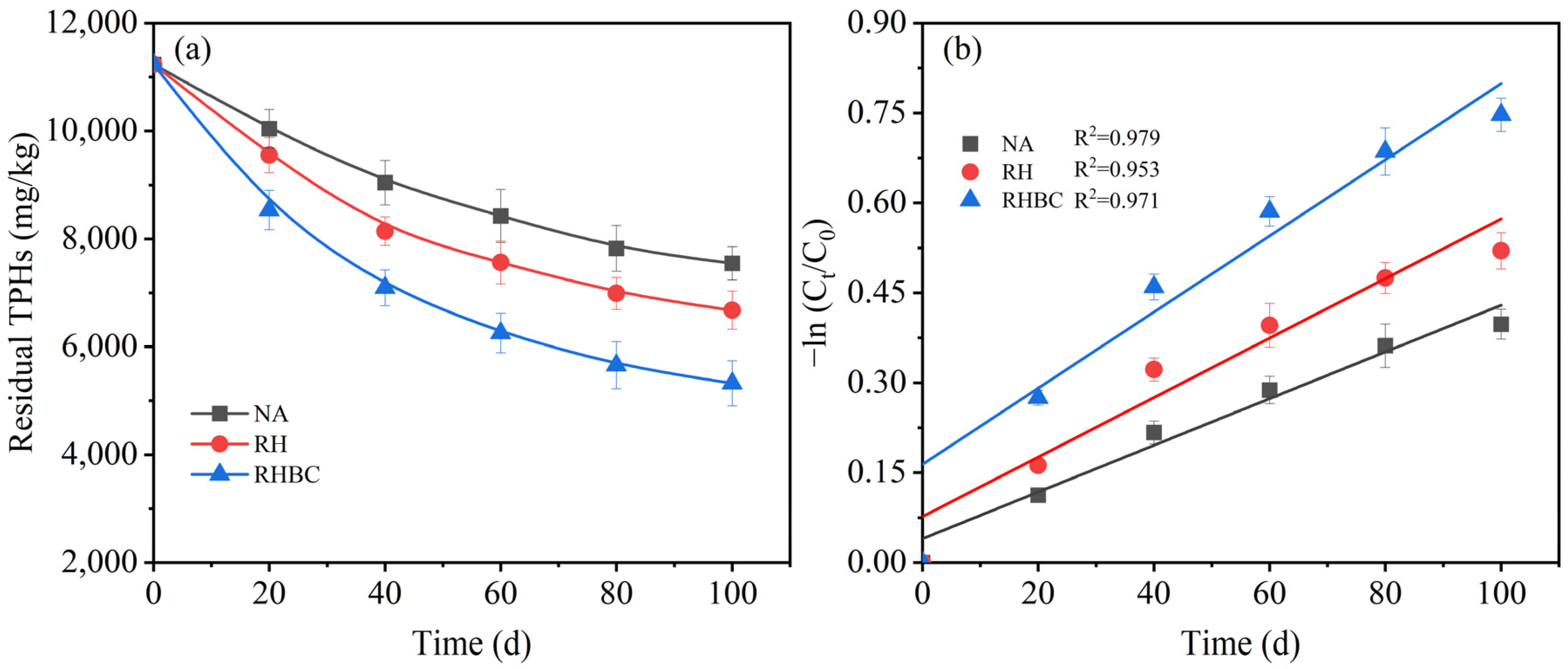
The residual amount of TPHs is shown in Figure 2a during biodegradation. As indicated, the residual TPHs amount in NA was 8425.3 mg/kg after 60 days of biodegradation. The addition of RH showed a promoting effect on the biodegradation of TPHs, with 7564.2 mg/kg of residual TPHs, equivalent to around 10.2% less than NA. Compared with RH, RHBC exhibited a higher promotion effect on TPHs biodegradation, with the residual TPHs reducing to 6254.6 mg/kg, equal to a reduction of approximately 17.3% more than RH. When the biodegradation time reached 100 days, the amount of residual TPHs in RHBC was 5323.5 mg/kg, which was 29.5 and 20.3% less than that of NA and RH, respectively. After biodegradation, the TPHs biodegradation amounts of NA, RH, and RHBC were 3688.2, 4557.9, and 5913.3 mg/kg, equivalent to the biodegradation efficiency of 32.8, 40.6, and 52.6%, respectively. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the addition of biochar can significantly enhance the biodegradation efficiency of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil, for example, alkanes, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and diesel oil [29]. It has been reported that the enhanced degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons was due to the addition of biochar, which could increase adsorption, improve soil permeability, improve soil–water distribution, enrich petroleum-degrading bacteria, etc. [30]. In addition, biochar also promoted the dissipation of petroleum in soil [31]. Furthermore, biochar produced at high temperatures contains stubborn carbon, which could stimulate microorganisms to degrade carbon substrates in petroleum [32]. Zhang et al. (2020) [33] reported that treating petroleum-contaminated soil with rice straw-derived biochar increased the petroleum biodegradation efficiency from 40 to 59%, attributed to a higher abundance of Acidobacteria-related genera compared to the control. Similarly, this study also increased TPHs degradation efficiency by around 20% by adding RHBC compared to NA.
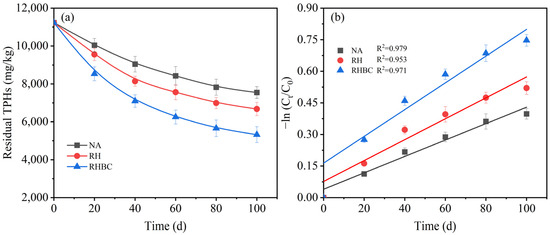
Figure 2.
Residual TPHs (a) and TPHs degradation kinetics (b) during biodegradation.
Moreover, the TPHs degradation kinetics under different systems were analyzed by employing a pseudo-first-order kinetic model. All R2 values obtained using linear fitting were greater than 0.9 (Figure 2b), indicating that the TPHs biodegradation was in good agreement with the pseudo-first-order kinetic model, which was consistent with the previous study [34]. Table 2 lists the dynamics equation equations, rate constants, and half-lives of different systems. As listed, the addition of RH increased the rate constants from 0.0039 to 0.0050 d−1 compared to NA, equal to an increase of 28.2%. At the same time, the half-life reduced from 167.5 to 122.6 d, which was 26.8% less than NA. In contrast, the higher rate constant and shorter half-life were achieved after adding RHBC. After the application of RHBC, the rate constant significantly rose to 0.064 d−1, which was about 1.6 and 1.3 times that of NA and RH, respectively. Meanwhile, the half-life notably descended to 83.3 d, only equivalent to 49.7 and 67.9% of NA and RH, respectively. Based on the analysis above, the application of RHBC could accelerate the rate of microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons and shorten the remediation time of contaminated soil.

Table 2.
Dynamics equation, rate constant, and half-life of TPHs biodegradation.
3.3. TPHs Degradation in Different Stages
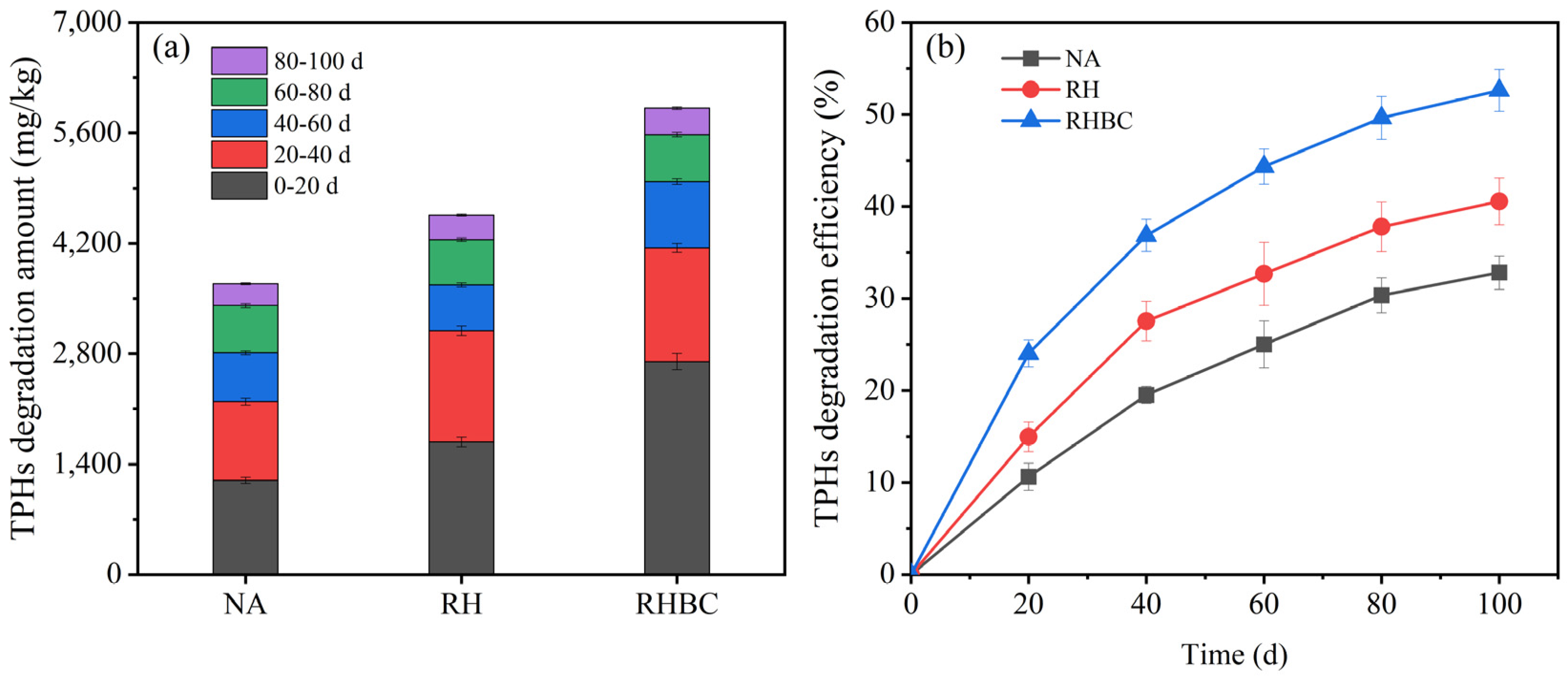
The biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons was divided into the following five stages: 0–20, 20–40, 40–60, 60–80, and 80–100 d (Figure 3a). During 0–20 d, the TPHs degradation amount in NA was 1195.2 mg/kg. Compared with NA, the TPHs removal amount in RH increased to 1682.5 mg/kg, which was equivalent to an increase of 40.8%. Obviously, the maximum TPHs degradation amount was obtained after adding RHBC and the corresponding value was 2701.0 mg/kg, which was approximately 126.0 and 60.5% more than NA and RH, respectively. Meanwhile, the TPHs degradation efficiency of NA, RH, and RHBC was 10.6, 15.0, and 24.0%, respectively (Figure 3b). At the stage of 20–40 d, the TPHs degradation amount of NA slightly decreased to 998.2 mg/kg. Similar decreasing trends in TPHs degradation amount could be found in RH and RHBC, and the corresponding degradation amounts were 1411.5, and 1440.5 mg/kg, respectively. In the first 40 d, the TPHs degradation amount of RHBC was 4141.5 mg/kg, equivalent to around 1.3 and 1.9 times that of NA and RH, respectively. Overall, the TPH biodegradation amount of all groups showed a decreasing trend with the extension of degradation time. When the biodegradation period was extended to 100 d, the total TPHs degradation amount of NA, RH, and RHBC was 3688.2, 4557.9, and 5913.3 mg/kg, corresponding to the biodegradation efficiency of 32.8, 40.6, and 52.6%, respectively (Figure 3b). It was worth noting that the TPHs biodegradation amount of all groups was dominantly concentrated in the first 40 d, accounting for more than 60% of the total degradation amount.
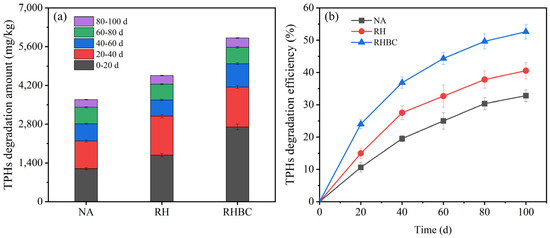
Figure 3.
TPHs degradation amount (a) and efficiency (b) during biodegradation.
Guo et al. (2022) [35] also reported an improvement of TPHs biodegradation after adding biochar derived from wheat bran. Previous studies have shown that biochar can be used as a biostimulator, which can change the physical and chemical properties of soil, provide nutrition and shelter for microorganisms, and thus enhance bioremediation [19,36]. Although the addition of RHBC enhanced the biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons, its effectiveness showed limitations based on the phase-specific data analysis. The presence of RHBC primarily improved the biodegradation efficiency during the first 40 days. In fact, the biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons is constrained by various factors, including the bioavailability of nutrients (for example, nitrogen and phosphorus) [37]. Initially, the availability of sufficient nutrients in conjunction with RHBC may have significantly boosted microbial activity, including growth rate and enzyme activity, thereby enhancing hydrocarbon degradation. As the incubation period extended, the depletion of readily available nutrients likely led to a decrease in the degradation rate of petroleum hydrocarbons. Additionally, the bioavailability of petroleum hydrocarbons is another limiting factor [38]. High bioavailability in the initial stages favors biodegradation, but decreased availability in later stages can restrict it. Therefore, the high degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons may rely on improvements in multiple factors, the incorporation of biochar potentially serving as an effective enhancement measure.
3.4. Degradation Amount of Individual n-Alkanes after Biodegradation
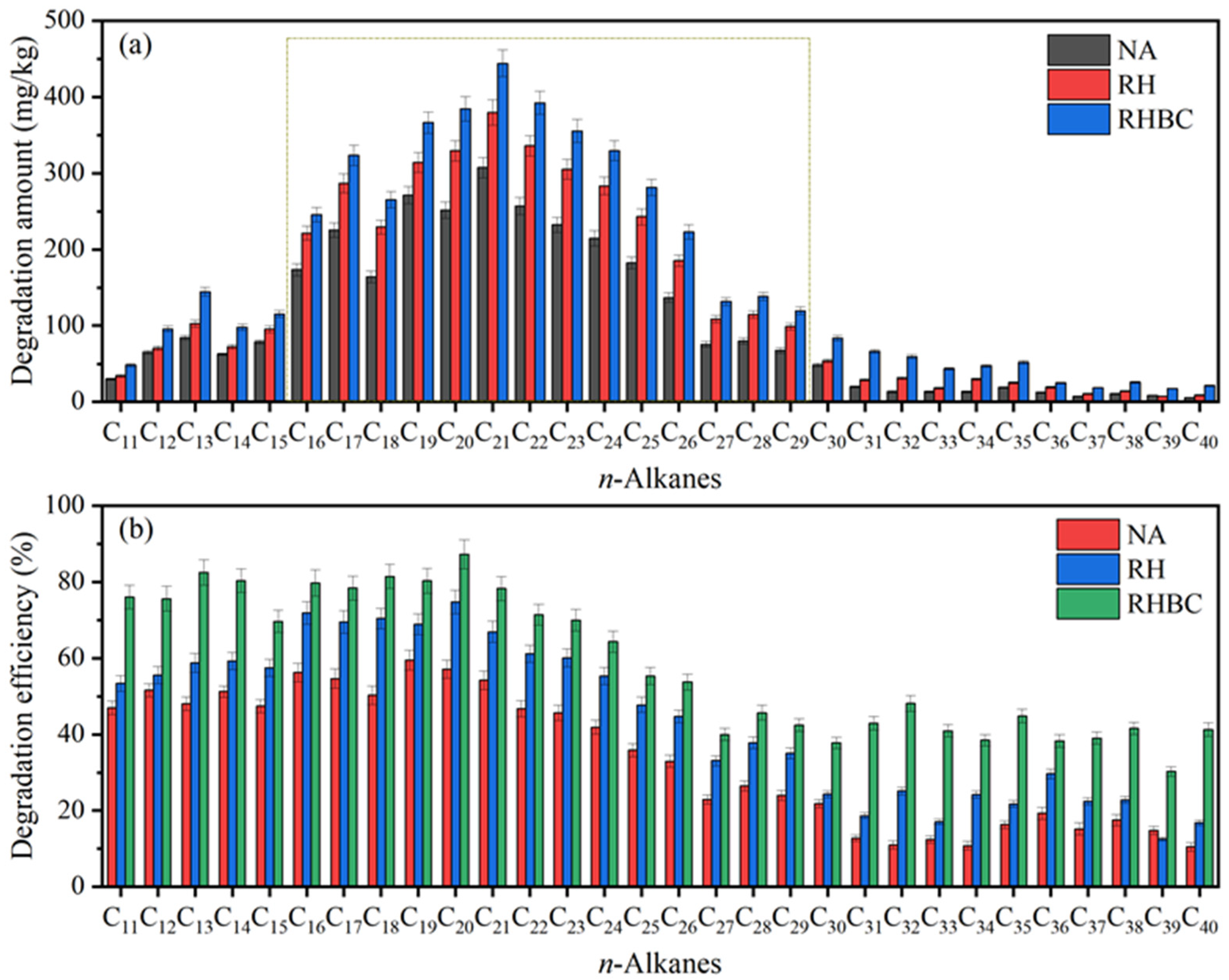
The initial content of n-alkanes C16–C29 (C16 represents n-alkanes with 16 carbons, namely n-Hexadecane) was 281.6~567.3 mg/kg, which was much higher than that of C11–C15 (63.5~175.1 mg/kg) and C30–C40 (47.4~221.4 mg/kg); thus, C16–C29 could be considered as the main component of n-alkanes. After biodegradation, the biodegradation amounts of C11–C15, C16–C29, and C30–C40 in NA were 29.8~84.1 mg/kg, 67.5~307.4 mg/kg, and 5.4~48.3 mg/kg, equal to a biodegradation efficiency of 46.9~51.6%, 23.1~59.5%, and 10.5~21.8% (Figure 4b), respectively. As expected, low molecular weight n-alkanes were more easily biodegraded than high molecular weight n-alkanes. Compared with NA, the biodegradation amounts of C11–C15, C16–C29, and C30–C40 in RS increased to 33.9~102.9 mg/kg, 98.7~379.6 mg/kg, and 7.3~53.8 mg/kg, which were equivalent to the increases of 3.9~10.7%, 9.4~20.2%, and 2.5~14.1%, respectively. In RHBC, the biodegradation amount of C11–C15, C16–C29, and C30–C40 significantly rose to 48.3~144.5 mg/kg, 119.5~444.2 mg/kg, and 17.5~83.6 mg/kg, respectively. Overall, the biodegradation efficiency of C11–C15, C16–C29, and C30–C40 in RHBC was up to 69.7~82.5%, 42.4~81.5%, and 30.2~48.1%, which was 22.3~34.5%, 17.1~30.2%, and 15.5~37.1% higher than that of NA, respectively. The results indicated that the application of RHBC enhanced the biodegradation of all individual n-alkanes, especially high molecular weight n-alkanes.
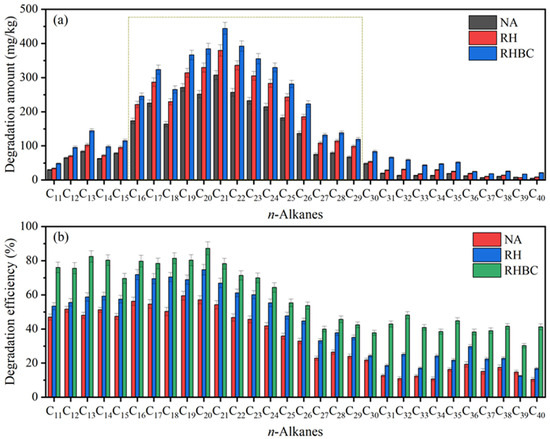
Figure 4.
Degradation amount (a) and efficiency (b) of individual n-alkanes after biodegradation.
Biochar has emerged as a promising agent to enhance the biodegradation of high molecular weight alkanes [39]. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to provide a stable habitat for microorganisms, thereby enriching the microbial community responsible for degrading complex hydrocarbons [40]. By adsorbing pollutants and supplying essential nutrients, biochar facilitates increased microbial growth and activity [41]. Moreover, biochar could improve enzyme stability and function, which are crucial for the breakdown of high molecular weight alkanes [42]. The porous structure of biochar also enhances oxygen availability and electron transfer, further boosting the biodegradation process [43]. Overall, the incorporation of biochar into bioremediation strategies not only accelerates the degradation of recalcitrant alkanes but also offers a sustainable approach to managing hydrocarbon contamination in soil and water environments. This makes biochar a valuable tool for improving the efficiency of bioremediation efforts targeting long-chain alkane pollutants. In this study, it could be found that the biochar formed using pyrolysis could significantly promote the degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by indigenous microorganisms compared with the original biomass.
3.5. Dynamic Changes in Enzyme Activity and Microbial Number
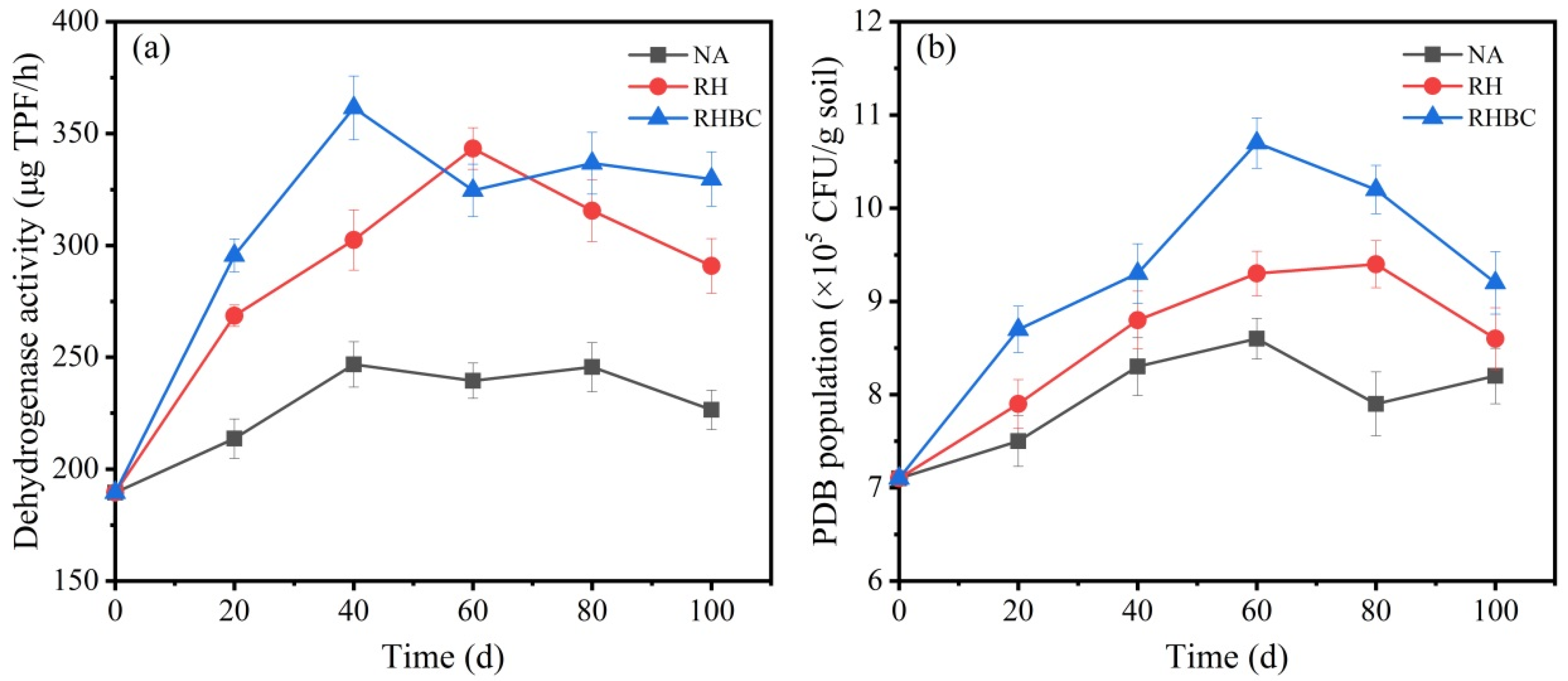
Generally, the biodegradation of organic pollutants is predominantly related to the enzymatic reaction in microorganisms. Therefore, the activity of the corresponding enzyme in the soil reflects the metabolic activity of the microorganisms to the target pollutant. It has been reported that the redox of oxygenase and peroxidase in microbial cells is the initial step of biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants [24]. Among many enzymes, dehydrogenase, an important oxidoreductase, plays an important role in the biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons [44]. Therefore, the dehydrogenase activity in soil presented the metabolic activity of microorganisms to petroleum hydrocarbons. Figure 5a shows the change in dehydrogenase in different systems during the biodegradation. It can be found that the dehydrogenase activity in all groups increased gradually in the initial stage, fluctuated up and down in the middle stage, and began to decrease in the final stage. On day 40, the dehydrogenase activity of RHBC reached a maximum of 361.5 μg TPF/h, which was 114.7 and 59.0 μg TPF/h higher than that of NA and RH, respectively. When the biodegradation time reached 60 d, the dehydrogenase activity of NA and RHBC slightly went down to 239.5 and 324.6 μg TPF/h, respectively. However, the dehydrogenase activity of RH significantly increased to 343.4 μg TPF/h on day 60. At the end of biodegradation, the dehydrogenase activity of NA, RH, and RHBC descended to 226.5, 290.9, and 329.7 μg TPF/h, respectively. Combined with Figure 3a and Figure 5a, it can be found that the change in dehydrogenase activity was consistent with the biodegradation trend in petroleum hydrocarbons. The results confirmed that the dehydrogenase activity in soil can well characterize the metabolic activity of microorganisms to petroleum hydrocarbons. The results suggested that the addition of biochar could increase soil dehydrogenase activity, thus promoting the biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. During biodegradation, the change in TPH degradation was very consistent with the change in dehydrogenase activity, which confirmed that petroleum hydrocarbons can be used as carbon and energy sources for soil bacteria [45]. Previous studies have shown that the enhancement of biochar on related enzymatic processes was attributed to several key factors: the provision of habitat and substrate, the improvement of soil aeration, and the concentration of nutrients promoted by its wide surface area and high porosity [46]. Additionally, biochar could adsorb toxic byproducts that might otherwise inhibit enzyme function, thus maintaining a more favorable biochemical environment [47]. By facilitating better nutrient and oxygen availability, biochar also supported optimal enzyme performance. Consequently, the incorporation of biochar into bioremediation systems not only boosted enzyme activity but also accelerated the overall degradation process of petroleum hydrocarbons, making it a valuable asset for effective environmental cleanup.
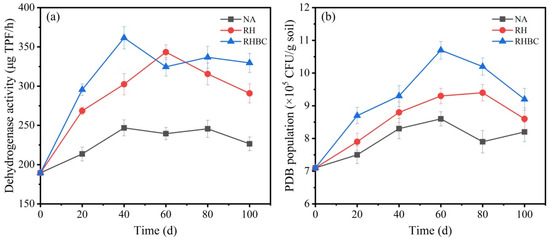
Figure 5.
Change in dehydrogenase activity (a) and PDB population (b) during biodegradation.
As the main body of biodegradation, the population of PDB can be used as an important indicator of TPHs degradation [48]. Thus, the PDB populations of all the groups were determined during biodegradation and are shown in Figure 5b. As indicated, PDB populations in all groups first showed a gradual increase and then slowly decreased, which was in harmony with a previous study [49]. The PDB populations in all systems almost peaked on day 60; the population value in RHBC was 10.7 × 105 CFU/g soil, equal to 24.4 and 15.1% more than NA and RHBC, respectively. When the biodegradation reached 100 d, the PDB populations of NA, RH, and RHBC decreased to 8.2 × 105, 8.6 × 105, and 9.6 × 105 CFU/g soil, respectively. As reported by a previous study, the increasing PDB populations have proved that indigenous microorganisms grow and reproduce on a large scale by consuming petroleum hydrocarbons [16]. In the early stage, the high bioavailability of petroleum hydrocarbons and nutrients in the soil led to a continuous increase in PDB populations. However, with the reduction of carbon sources and nutrients available to microorganisms, the PDB populations began to decline after reaching a peak [50]. In general, the introduction of biochar enhanced the growth and reproduction of microorganisms, which in turn promoted the remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil.
As reported, the porous structure and high surface area of biochar provided an ideal environment for microbial colonization, thereby increasing the counts of hydrocarbon-degrading microorganisms [27]. Liu et al. (2015) [51] reported that biochars derived from dairy manure and rice have promoted the growth of petroleum-degrading bacteria in paddy soil by up-regulating functional genes related to petroleum biodegradation. Kong et al. (2018) [52] also found that wheat straw biochar improved the relative abundance of PAHs-degrading bacteria as well as the biodegradability of PAHs in soil. Ye et al. (2019) [53] demonstrated that the incorporation of activated biochar enhanced microbial abundance and increased the ratio of optimized fungi-to-bacteria genes in petroleum-contaminated wetland soils. Additionally, the application of biochar to petroleum-contaminated upland soils altered the bacterial community structure and augmented the presence of petroleum-degrading bacteria such as Proteobacteria, thereby enhancing the contact between petroleum and petroleum-degraders [40]. According to the above analysis, it could be found that the addition of biochar could increase the relative abundance of petroleum-degrading bacteria, which also potentially explains why the addition of RHBC promoted the biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in this study.
4. Conclusions
This study focused on the effect of biochar application on the degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants in soil by indigenous bacteria. After 100 days of bioremediation, the TPHs biodegradation amounts of NA, RH, and RHBC were 3688.2, 4557.9, and 5913.3 mg/kg, corresponding to a biodegradation efficiency of 32.8, 40.6, and 52.6%, respectively. Compared with NA and RH, the biodegradation efficiency of C11–C15, C16–C29, and C30–C40 in RHBC increased to 69.7~82.5%, 42.4~81.5%, and 30.2~48.1%, equivalent to 12.2~34.5%, 6.9~31.2%, and 13.5~37.1% more than NA and RH, respectively. Meanwhile, the half-life of biodegradation in RHBC was shorted to 83.3 d, which was significantly lower than that of NA (167.5 d) and RH (122.6 d). Further investigation showed that RHBC could improve the dehydrogenase activity in soil and promote the growth and reproduction of PDB, which enhanced the bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. Compared with biomass raw materials, biochar formed using pyrolysis is a more promising biostimulator in improving the degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. and Y.Z.; methodology, Z.L. and R.Z.; software, Z.L., X.L. (Xiumin Li) and X.L. (Xuxiang Li); writing—original draft preparation, Z.L., X.L. (Xiumin Li) and Y.D.; writing—review and editing, Z.L. and X.L. (Xuxiang Li); funding acquisition, Y.Z. and Z.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Technology Innovation Center for Land Engineering and Human Settlements, Shaanxi Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd. and Xi’an Jiaotong University (2024WHZ0232 and 2021WHZ0092), the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2023-JC-QN-0343 and 2023-JC-QN-0360), and the Scientific Research Item of Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group (DJTD-2024-1 and DJTD-2022-5).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Technology Innovation Center for Land Engineering and Human Settlements by Shaanxi Land Engi-neering Construction Group Co., Ltd. and Xi’an Jiaotong University, School of Human Settlements and Civil Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, and Institute of Land Engineering and Technology, Shanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group, Xi’an, China. Special thanks go to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments in improving this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors were employed by the company Technology Innovation Center for Land Engineering and Human Settlements by Shaanxi Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd. and Xi’an Jiaotong University. Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, R were employed by the company Institute of Land Engineering and Technology, Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, M.; Ma, C.; Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.C.; Xu, H.N. Nutrient drip irrigation for refractory hydrocarbon removal and microbial community shift in a historically petroleum-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Upasani, V.N. Petroleum sludge polluted soil remediation: Integrated approach involving novel bacterial consortium and nutrient application. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.X.; Che, J.L.; Chen, X.; Tang, Z.W.; Liu, X. Mechanisms of biostimulant-enhanced biodegradation of PAHs and BTEX mixed contaminants in soil by native microbial consortium. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Zheng, X.; Oba, B.T.; Shen, C.B.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, Q.; Sun, L.N. Activating soil microbial community using bacillus and rhamnolipid to remediate TPH contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Teng, Y.; Ren, W.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Soil bacterial diversity and functionality are driven by plant species for enhancing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons dissipation in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z. Efficient oriented interfacial oxidation of petroleum hydrocarbons by functionalized Fe/N co-doped biochar-mediated heterogeneous Fenton for heavily contaminated soil remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.T.; Zhou, Q.X. Surfactants selectively reallocated the bacterial distribution in soil bioelectrochemical remediation of petroleum hydrocarbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, Y.; Su, R.; Liu, Z.; He, J.K.; Zhou, W.Z.; Gu, M.X.; Yan, M.L.; Li, Q. In situ synthesis of Fe-N co-doped carbonaceous nanocomposites using biogas residue as an effective persulfate activator for remediation of aged petroleum contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, J.; Lu, H.; Zhu, L.Z. Remediation of benzo[a]pyrene contaminated soils by moderate chemical oxidation coupled with microbial degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, F.; Shao, Z.; Wu, B.; Guo, S.H. Effects of thermal desorption on ecotoxicological characteristics of heavy petroleum-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z. Insight on efficiently oriented oxidation of petroleum hydrocarbons by redistribution of oxidant through inactivation of soil organic matter coupled with passivation of manganese minerals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil by petroleum-degrading bacteria immobilized on biochar. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35304–35311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wen, D.; Fu, R.B.; Feng, L.Y. Application of alkyl polyglycosides for enhanced bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil using Sphingomonas changbaiensis and Pseudomonas stutzeri. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banet, G.; Turaani, A.K.; Farber, R.; Armoza-Zvuloni, R.; Rotem, N.; Stavi, I.; Cahan, R. The effects of biostimulation and bioaugmentation on crude oil biodegradation in two adjacent terrestrial oil spills of different age, in a hyper-arid region. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, A.; Aydin, S.; Ince, B.; Ince, O. Reconstruction of bacterial community structure and variation for enhanced petroleum hydrocarbons degradation through biostimulation of oil contaminated soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdari, M.; Kariminia, H.; Rahmati, M.; Fazlollahi, F.; Polasko, A.; Mahendra, S.; Wilding, W.; Fletcher, T. Development of bioreactors for comparative study of natural attenuation, biostimulation, and bioaugmentation of petroleum-hydrocarbon contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, N.B.; Grotenhuis, T.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M. Impact of organic carbon and nutrients mobilized during chemical oxidation on subsequent bioremediation of a diesel-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2014, 97, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tan, X.J.; Yang, X.; Wan, C.L.; Lee, D. Enhancement of anaerobic degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by electron intermediate: Performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dike, C.C.; Khudur, L.S.; Hakeem, I.G.; Rani, A.; Shahsavari, E.; Surapaneni, A.; Shah, K.; Ball, A.S. Biosolids-derived biochar enhances the bioremediation of diesel-contaminated soil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108633. [Google Scholar]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Formicola, F.; Sbaffoni, S.; Milanese, C.; Franzetti, A.; Vaccari, M. Effect of biochar on petroleum hydrocarbon degradation and energy production in microbial electrochemical treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Ali, A.; Chen, A.L.; Zhang, Z.Q. Enhanced aqueous Cr(VI) removal using chitosan-modified magnetic biochars derived from bamboo residues. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Fan, S.S.; Xu, H.C. Effect of Fe-N modification on the properties of biochars and their adsorption behavior on tetracycline removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, S.; Yu, W.; Yuan, D.; Sun, L. The role of Fe3O4@biochar as electron shuttle in enhancing the biodegradation of gaseous para-xylene by aerobic surfactant secreted strains. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, L.; Hu, T.; Lv, R.; Wu, Y.C.; Chang, F.; Jia, F.A.; Gu, J. Succession of microbial communities and synergetic effects during bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil enhanced by chemical oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, P.F.; Zhang, A.N.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, C.X.; Yang, Z.Z.; Li, Z.H. Optimizing carbon sources regulation in the biochemical treatment systems for coal chemical wastewater: Aromatic compounds biodegradation and microbial response strategies. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Tang, J.C. Enhanced degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil by FeS@BC activated persulfate and its mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Niu, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, T. Effect of biochar-immobilized Sphingomonas sp. PJ2 on bioremediation of PAHs and bacterial community composition in saline soil. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gao, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.C.; Chen, R. Redox-based electron exchange capacity of biowaste-derived biochar accelerates syntrophic phenol oxidation for methanogenesis via direct interspecies electron transfer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dike, C.C.; Hakeem, I.G.; Rani, A.; Surapaneni, A.; Khudur, L.; Shah, K.; Ball, A.S. The co-application of biochar with bioremediation for the removal of petroleum hydrocarbons from contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnaf, K.M.; Puricelli, S.; Saponaro, S.; Werner, D. Effect of biochar on the fate of volatile petroleum hydrocarbons in an aerobic sandy soil. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2011, 126, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, N.; Wang, F.; Song, Y.; Bian, Y.; Shi, R.; Yang, X.; Gu, C.; Jiang, X. Mechanisms of biochar reducing the bioaccumulation of PAHs in rice from soil: Degradation stimulation vs. immobilization. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Durenkamp, M.; De Nobili, M.; Lin, Q.; Brookes, P.C. Short term soil priming effects and the mineralisation of biochar following its incorporation to soils of different pH. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2304–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, X.; Li, Y.; Han, L. Effect of pyrolysis temperature and correlation analysis on the yield and physicochemical properties of crop residue biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Jiang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wen, D.D.; Fu, T.Y.; Fu, R.B. Petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil bioremediation assisted by isolated bacterial consortium and sophorolipid. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, X.; Tang, J. Enhanced degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by immobilizing multiple bacteria on wheat bran biochar and its effect on greenhouse gas emission in saline-alkali soil. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Kumar, G.; Rene, E.R. Developments in biochar application for pesticide remediation: Current knowledge and future research directions. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, S.; Xu, Y.; Park, J.; Wang, J.J. Biochar-based materials as remediation strategy in petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil and water: Performances, mechanisms, and environmental impact. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 138, 350–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, N.B.; Langenhoff, A.A.M.; Lasso, D.H.; van der Zaan, B.; van Gaans, P.; Maphosa, F.; Smidt, H.; Grotenhuis, T.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M. Recovery of microbial diversity and activity during bioremediation following chemical oxidation of diesel contaminated soils. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 2751–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Bo, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yan, G.; Wu, Y.; Wong, C.; He, H. Converting waste lignin into nano-biochar as a renewable substitute of carbon black for reinforcing styrene-butadiene rubber. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Q.; Xu, M. Enhanced phenanthrene degradation in river sediments using a combination of biochar and nitrate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołtowski, M.; Hilber, I.; Bucheli, T.D.; Oleszczuk, P. Effect of steam activated biochar application to industrially contaminated soils on bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and ecotoxicity of soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W. Enhanced phytoremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil by biochar and urea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faheem, D.J.; Kim, S.H.; Hassan, M.A.; Irshad, S.; Bao, J. Application of biochar in advanced oxidation processes: Supportive, adsorptive, and catalytic role. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 37286–37312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margesin, R.; Zimmerbauer, A.; Schinner, F. Monitoring of bioremediation by soil biological activities. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, S.A.; Lamb, D.; Sarkar, B.; Seshadri, B.; Yu, R.; Tran, T.; O’Connor, J.; Rinklebe, J.; Kirkham, M.B.; Vo, H.; et al. Phosphorus application enhances alkane hydroxylase gene abundance in the rhizosphere of wild plants grown in petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Shen, B.; Liu, L. Insights into biochar and hydrochar production and applications: A review. Energy 2019, 171, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wei, C.; Qu, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, D. Strong binding of apolar hydrophobic organic contaminants by dissolved black carbon released from biochar: A mechanism of pseudomicelle partition and environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Castro, G.A.; Rodelas, B.; Perucha, C.; Laguna, J.; González-López, J.; Calvo, C. Bioremediation of diesel-polluted soil using biostimulation as post-treatment after oxidation with Fenton-like reagents: Assays in a pilot plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 445–446, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.F.; Chang, Y.C.; Chiou, W.T. Remediation of diesel-contaminated soil using in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) and the effects of common oxidants on the indigenous microbial community: A comparison study. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Deng, X.; Cui, Y.; Kong, F.X. Impact of chemical oxidation on indigenous bacteria and mobilization of nutrients and subsequent bioremediation of crude oil-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, P.; Sun, M.; Shen, G.; Shang, G. Effect of biochar amendment on PAH dissipation and indigenous degradation bacteria in contaminated soil. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Z. Biochar accelerates PAHs biodegradation in petroleum-polluted soil by biostimulation strategy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Liang, J.; Zhang, C.; Dai, J.; Xiong, W.; Song, B.; Wu, S.; Yu, J. The effects of activated biochar addition on remediation efficiency of co-composting with contaminated wetland soil. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 140, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).