Response of Summer Foxtail Millet Yield and Water Productivity to Water Supply in the North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Field Experiment
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Calculations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
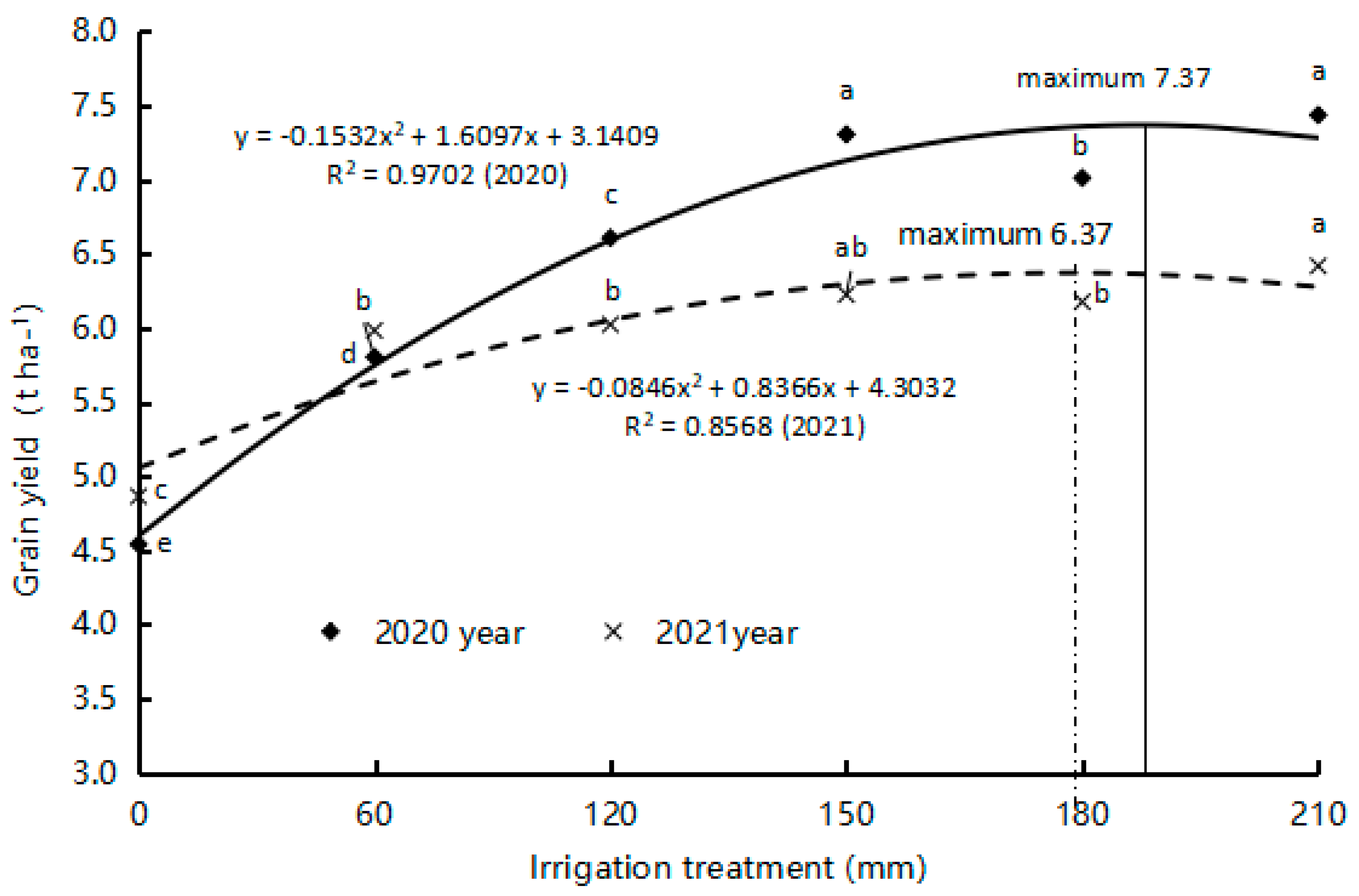
3.1. Yield, Biomass, Thousand Grain Weight, Abortive Grain Rate, and Panicle Weight
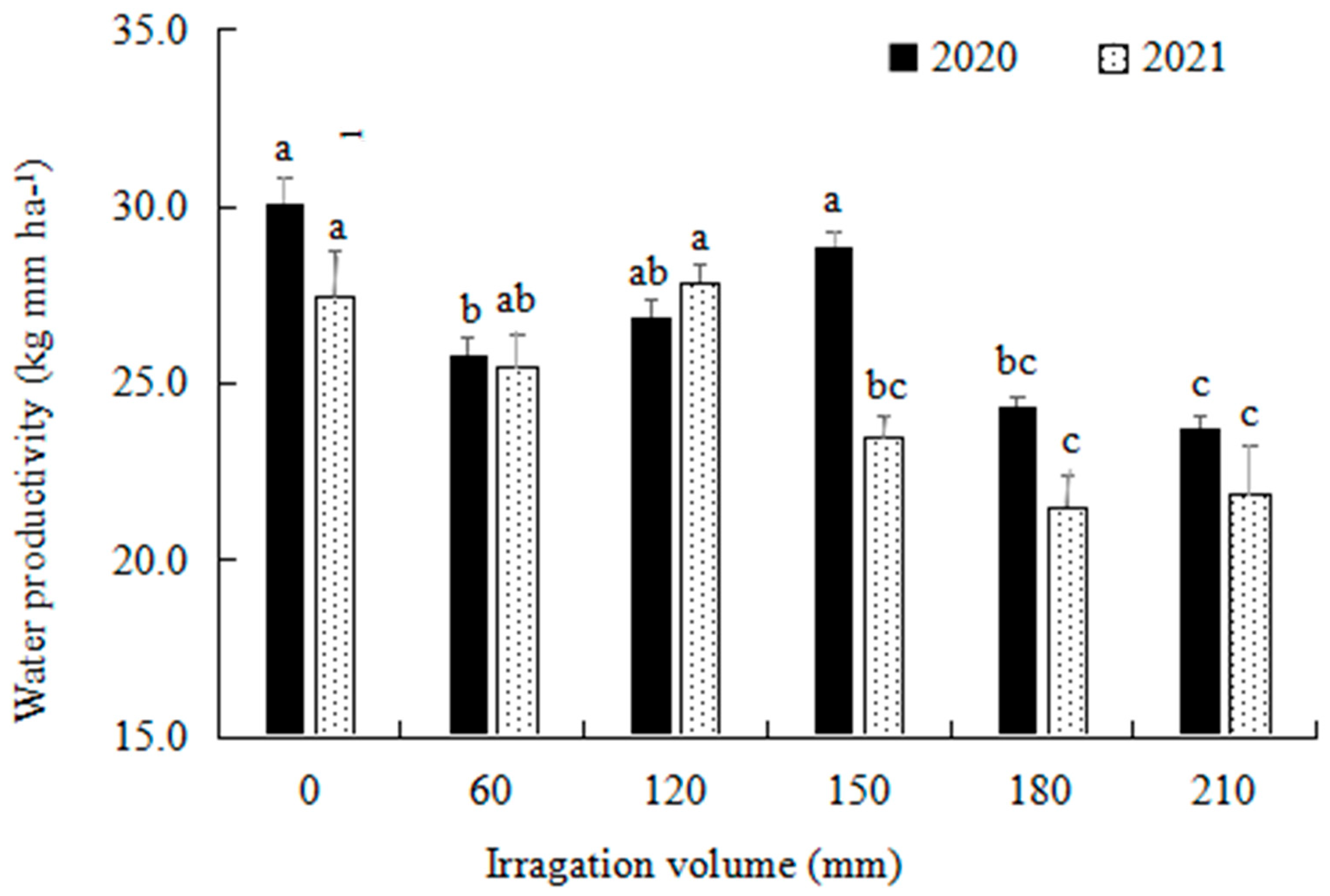
3.2. Water Productivity and Water Economic Benefit
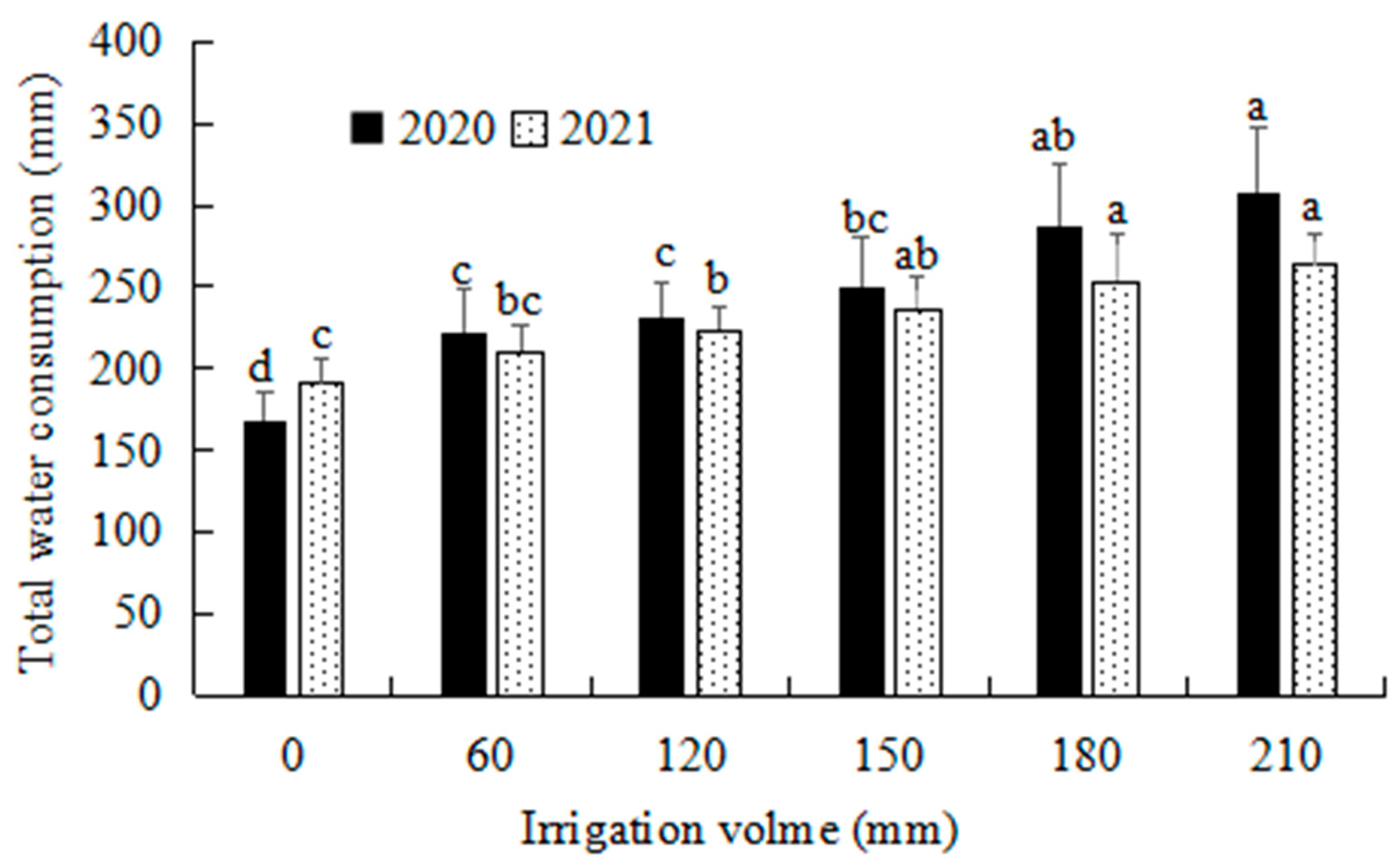
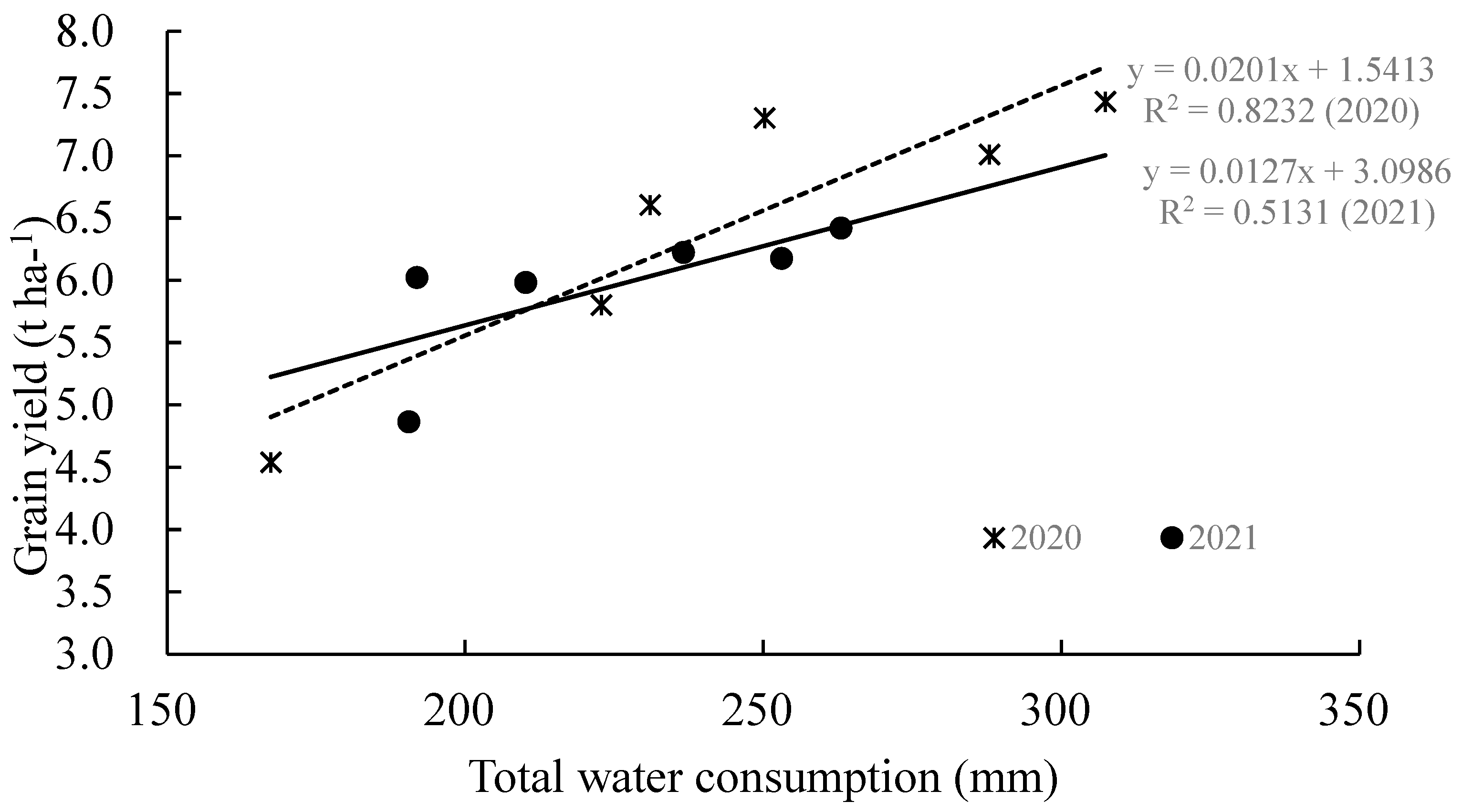
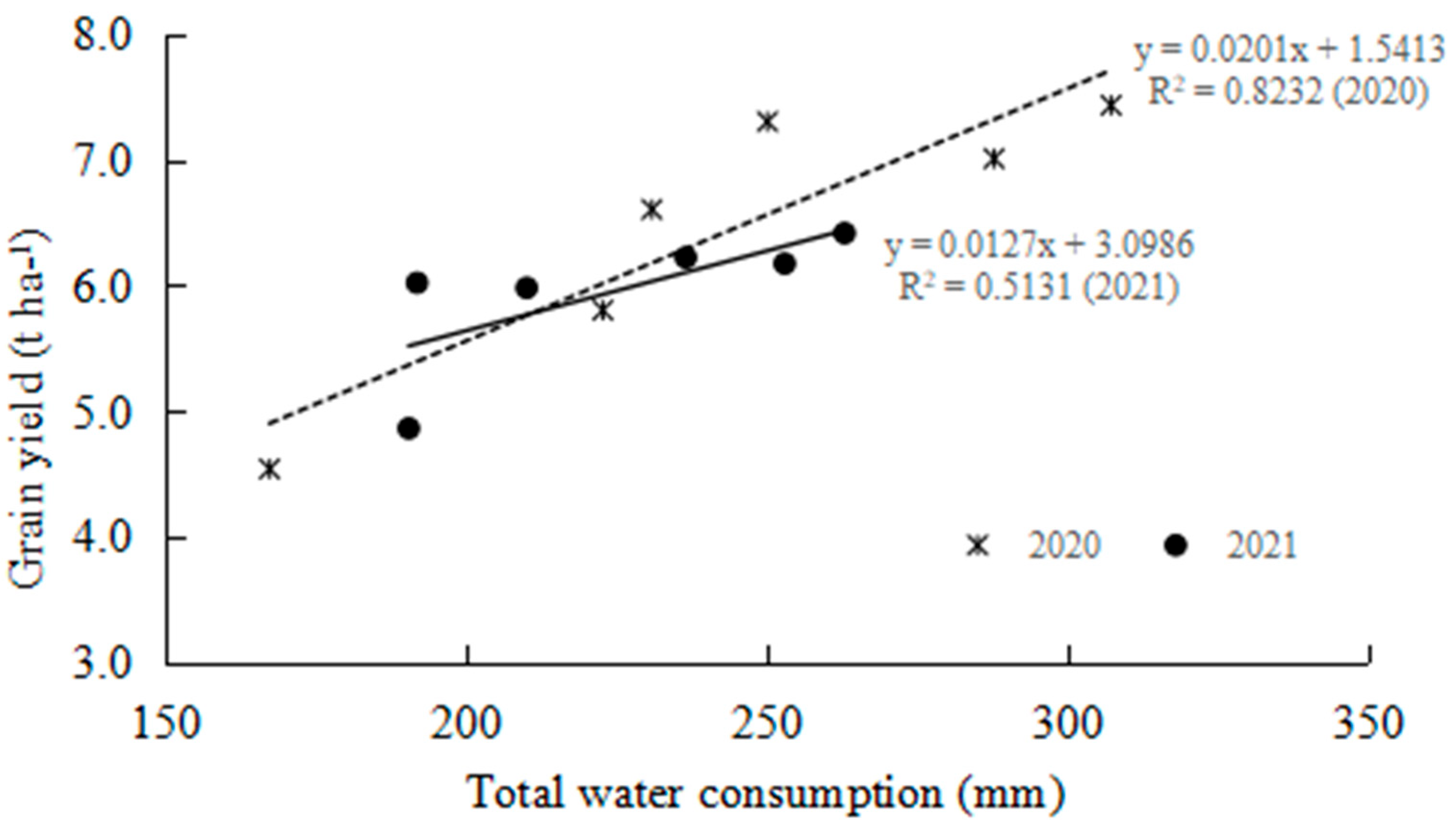
3.3. Water Reduction in Soil Storage, Total Water Consumption, and Yield Response Factor (Ky)
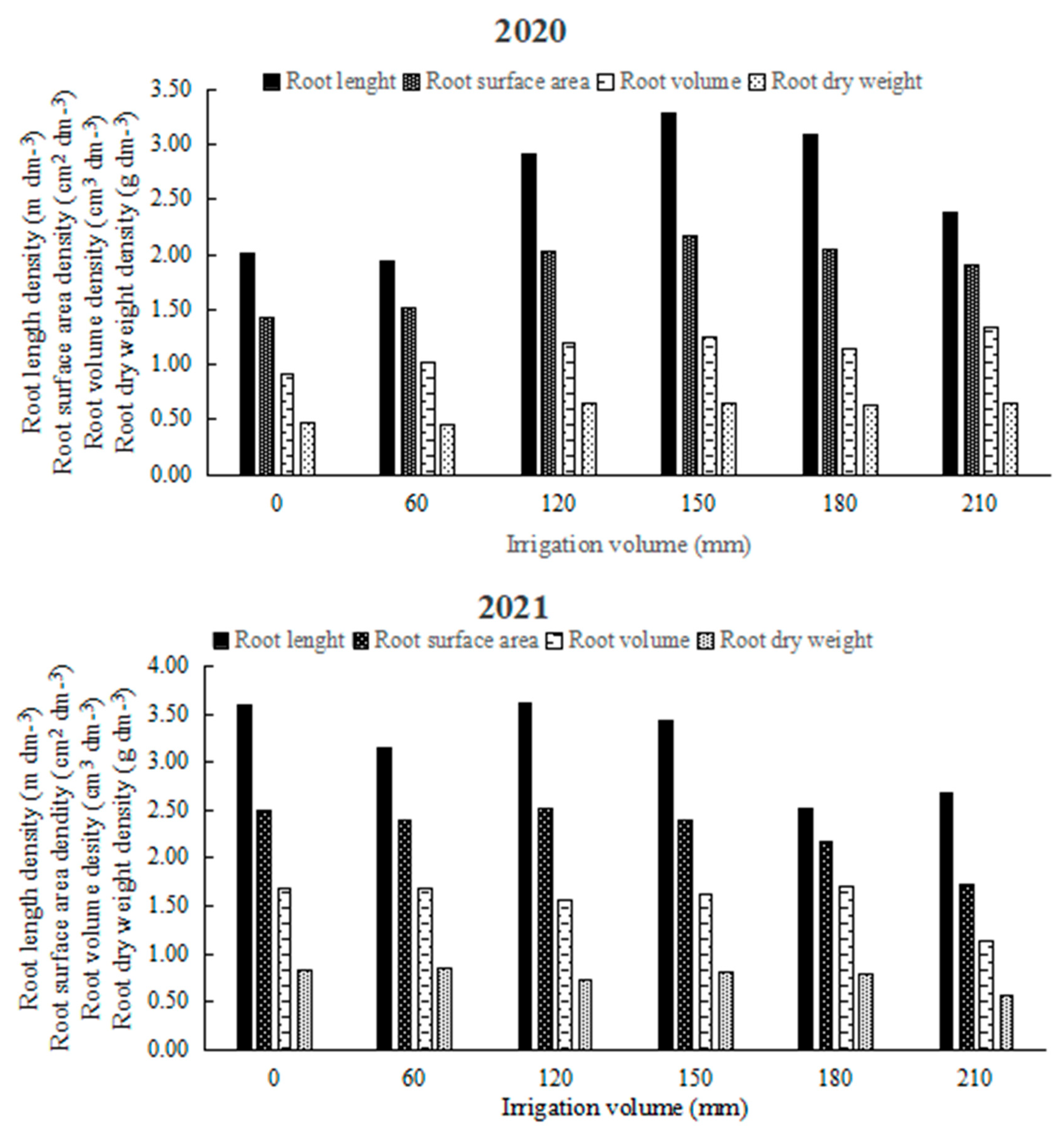
3.4. Root Traits
3.5. Grey Relational Analysis of Total Water Consumption
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, N.; Niranjan, K. Foxtail millet: Properties, processing, health benefits, and uses. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 34, 329–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wan, Z.; Perry, L.; Lu, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Xie, F.; Yu, J.; Cui, T.; et al. Early millet use in northern China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3726–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.S.; Hash, C.T.; Bidinger, F.R.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Howarth, C.J. Identification and utilization of quantitative trait loci to improve terminal drought tolerance in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R. Br.). In Workshop on Molecular Approaches for the Genetic Improvement of Cereals for Stable Production in Water-Limited Environments; Ribaut, J.M., Poland, D., Eds.; CIMMYT: Texcoco, Mexico, 1999; pp. 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, O.P.; Bhatnagar, S.K. Evaluation of indices for identification of pearl millet cultivars adapted to stress and non-stress conditions. Field Crops Res. 2001, 70, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.; Hu, H.; Shrestha, K.; Doust, A.N. Pearl millet response to drought: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1059574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, A. Water Management for Improving Pearl Millet Production under Irrigated Environment: A Review. Agric. Rev. 2021, 42, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Car, M.K.V. Advances in Irrigation Agronomy: Plantation Crops, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Onder, D.; Akiscan, Y.; Onder, S.; Mert, M. Effect of different irrigation water level on cotton yield and yield components. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Irmak, S.; Djaman, K.; Rudnick, D.R. Effect of full and limited irrigation amount and frequency on subsurface drip-irrigated maize evapotranspiration, yield, water use efficiency and yield response factors. Irrig. Sci. 2016, 34, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Shao, L. Water use efficiency and associated traits in winter wheat cultivars under moderate drought stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.M.; Schwartz, R.; McInnes, K.J.; Howell, T.; Morgan, C.L.S. Deficit irrigation effects on yield and yield components of grain sorghum. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Fu, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Soil moisture variation in relation to topography and land use in a hillslope catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2001, 240, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Khan, A.; Tan, D.; Luo, H. Rational water and nitrogen management improves root growth, increases yield and maintains water use efficiency of cotton under mulch drip irrigation. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sadras, V.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. Water use efficiency of dryland wheat in the Loess Plateau in response to soil and crop management. Field Crops Res. 2013, 151, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shao, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Responses of yield and water use efficiency to irrigation amount decided by pan evaporation for winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, F.; Zheng, X.; Gale, W.; Li, S. Effect of water saving management practices and nitrogen fertilizer rate on crop yield and water use efficiency in a winter wheat–summer maize cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2011, 122, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Zhou, D.X. Cultivation Technological Principles for Improving Water and Fertilizer Use Efficiency in Winter Wheat (Chinese); China Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, P.; Dong, S.; Zhao, B.; So, H.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Morphological and physiological characteristics of corn (Zea mays L.) roots from cultivars with different yield potentials. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 38, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.P.; Leskovar, D.I.; Crosby, K.M.; Volder, A.; Ibrahim, A. Root growth, yield, and fruit quality responses of reticulatus and inodorus melons (Cucumis melo L.) to deficit subsurface drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 136, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.H.; Plauborg, F.; Andersen, M.N.; Sepaskhah, A.R.; Jensen, C.R.; Hansen, S. Effects of irrigation strategies and soils on field grown potatoes: Root distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yang, P.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, W. Optimizing water and nitrogen management can enhance nitrogen heterogeneity and stimulate root foraging. Field Crops Res. 2023, 304, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Jie, F.; Zhang, R.; Meng, L. A generalized function of wheat’s root length density distributions. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Musick, J.; Stewart, B.A.; Dusek, D.A. Root growth and water uptake in winter wheat under deficit irrigation. Plant Soil 2003, 257, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Kong, L.; Zhen, T.; Xia, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Zheng, G. Grey relational analysis among yield of maize and major meteorological factors. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 10, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, B.; Meng, F. Quantitative analysis of the influence of meteorological factors at different growth stages on yield of winter wheat based on grey relational analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Grey Systems and Intelligent Services (GSIS), Stockholm, Sweden, 8–11 August 2017; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, E.; Guo, P. Grey relational analysis among yield of rice and meteorological factors during growth season in Henan. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 58–64, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]


| Treatments | 2020 | 2021 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass (t ha−1) | Thousand Grain Weight (g) | Abortive Grain Rate (%) | Panicle Dry Weight (t ha−1) | Biomass (t ha−1) | Thousand Grain Weight (g) | Abortive Grain Rate (%) | Panicle Dry Weight (t ha−1) | |
| I0 (CK) | 10.15 d | 2.88 b | 16.61 a | 6.18 c | 11.97 a | 2.84 b | 23.27 ab | 6.70 a |
| I1 | 12.47 b | 2.98 a | 14.68 ab | 6.84 b | 12.19 a | 2.96 a | 24.79 a | 6.62 a |
| I2 | 11.17 cd | 2.91 ab | 15.35 ab | 7.74 c | 11.44 a | 2.81 bc | 22.6 ab | 6.37 a |
| I3 | 11.87 bc | 2.95 ab | 13.86 bc | 8.10 ab | 12.21 a | 2.89 b | 22.12 b | 6.40 a |
| I4 | 12.85 ab | 2.95 ab | 13.47 bc | 7.76 b | 12.34 a | 2.82 b | 22.61 ab | 6.84 a |
| I5 | 13.92 a | 3.00 a | 12.50 c | 8.77 a | 11.54 a | 2.77 c | 24.44 ab | 6.32 a |
| Year | Irrigation Volume (mm) | Price of Water (RMB m−3) | Grain Yield (t ha−1) | Price of Millet (RMB m−3) | Economic Benefit (RMB ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 0 | 1 | 4.5 | 4 | 18,163.78 |
| 60 | 1 | 5.8 | 4 | 22,315.64 | |
| 120 | 1 | 6.6 | 4 | 24,627.46 | |
| 150 | 1 | 7.3 | 4 | 26,972.15 | |
| 180 | 1 | 7.0 | 4 | 25,347.75 | |
| 210 | 1 | 7.4 | 4 | 26,593.45 | |
| 2021 | 0 | 1 | 4.86 | 4 | 19,387.87 |
| 60 | 1 | 5.98 | 4 | 23,843.86 | |
| 120 | 1 | 6.02 | 4 | 23,993.36 | |
| 150 | 1 | 6.22 | 4 | 24,787.94 | |
| 180 | 1 | 6.18 | 4 | 24,599.17 | |
| 210 | 1 | 6.42 | 4 | 25,560.99 |
| Soil Depth | 2020 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I0 | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 | I5 | Mean | ||||||||
| GRG | CR | GRG | CR | GRG | CR | GRG | CR | GRG | CR | GRG | CR | GRG | CR | |
| 20 cm | 0.912 | 1 | 0.876 | 4 | 0.967 | 2 | 0.987 | 1 | 0.979 | 3 | 0.972 | 3 | 0.912 | 1 |
| 40 cm | 0.879 | 2 | 0.916 | 1 | 0.94 | 4 | 0.962 | 3 | 0.981 | 2 | 0.971 | 4 | 0.879 | 2 |
| 60 cm | 0.874 | 4 | 0.867 | 5 | 0.964 | 3 | 0.966 | 2 | 0.972 | 4 | 0.973 | 2 | 0.874 | 4 |
| 80 cm | 0.865 | 5 | 0.894 | 3 | 0.99 | 1 | 0.957 | 4 | 0.986 | 1 | 0.974 | 1 | 0.865 | 5 |
| 100 cm | 0.878 | 3 | 0.831 | 6 | 0.793 | 5 | 0.954 | 5 | 0.916 | 6 | 0.943 | 5 | 0.878 | 3 |
| 120 cm | 0.725 | 8 | 0.914 | 2 | 0.734 | 6 | 0.951 | 6 | 0.923 | 5 | 0.862 | 7 | 0.725 | 8 |
| 140 cm | 0.817 | 6 | 0.551 | 8 | 0.605 | 8 | 0.878 | 7 | 0.736 | 7 | 0.877 | 6 | 0.817 | 6 |
| 160 cm | 0.767 | 7 | 0.556 | 7 | 0.696 | 7 | 0.694 | 8 | 0.704 | 8 | 0.668 | 8 | 0.767 | 7 |
| 2021 | ||||||||||||||
| 20 cm | 0.833 | 3 | 0.921 | 1 | 0.941 | 1 | 0.920 | 1 | 0.960 | 1 | 0.793 | 5 | 0.678 | 1 |
| 40 cm | 0.818 | 7 | 0.890 | 3 | 0.887 | 2 | 0.879 | 2 | 0.935 | 4 | 0.857 | 3 | 0.653 | 2 |
| 60 cm | 0.829 | 4 | 0.895 | 2 | 0.842 | 4 | 0.862 | 3 | 0.941 | 3 | 0.896 | 1 | 0.626 | 4 |
| 80 cm | 0.822 | 6 | 0.735 | 8 | 0.828 | 5 | 0.841 | 4 | 0.955 | 2 | 0.875 | 2 | 0.602 | 6 |
| 100 cm | 0.854 | 2 | 0.826 | 6 | 0.750 | 7 | 0.783 | 5 | 0.924 | 5 | 0.572 | 8 | 0.629 | 3 |
| 120 cm | 0.891 | 1 | 0.803 | 7 | 0.475 | 8 | 0.658 | 8 | 0.884 | 6 | 0.856 | 4 | 0.606 | 5 |
| 140 cm | 0.826 | 5 | 0.827 | 5 | 0.87 | 3 | 0.728 | 6 | 0.585 | 8 | 0.692 | 7 | 0.576 | 7 |
| 160 cm | 0.728 | 8 | 0.84 | 4 | 0.795 | 6 | 0.664 | 7 | 0.645 | 7 | 0.722 | 6 | 0.557 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Lu, G.; Bai, C.; Ge, Y. Response of Summer Foxtail Millet Yield and Water Productivity to Water Supply in the North China Plain. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112468
Zhang W, Wang B, Liu B, Chen Z, Lu G, Bai C, Ge Y. Response of Summer Foxtail Millet Yield and Water Productivity to Water Supply in the North China Plain. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112468
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenying, Bianyin Wang, Binhui Liu, Zhaoyang Chen, Guanli Lu, Caihong Bai, and Yaoxiang Ge. 2025. "Response of Summer Foxtail Millet Yield and Water Productivity to Water Supply in the North China Plain" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112468
APA StyleZhang, W., Wang, B., Liu, B., Chen, Z., Lu, G., Bai, C., & Ge, Y. (2025). Response of Summer Foxtail Millet Yield and Water Productivity to Water Supply in the North China Plain. Agronomy, 15(11), 2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112468






