Changes in Rice Yield and Quality from 1994 to 2023 in Shanghai, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection of Shanghai Region State-Certified Rice Varieties from 1994 to 2023
2.2. Rice Yield, Growth Characteristics, and Quality Trait Description
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
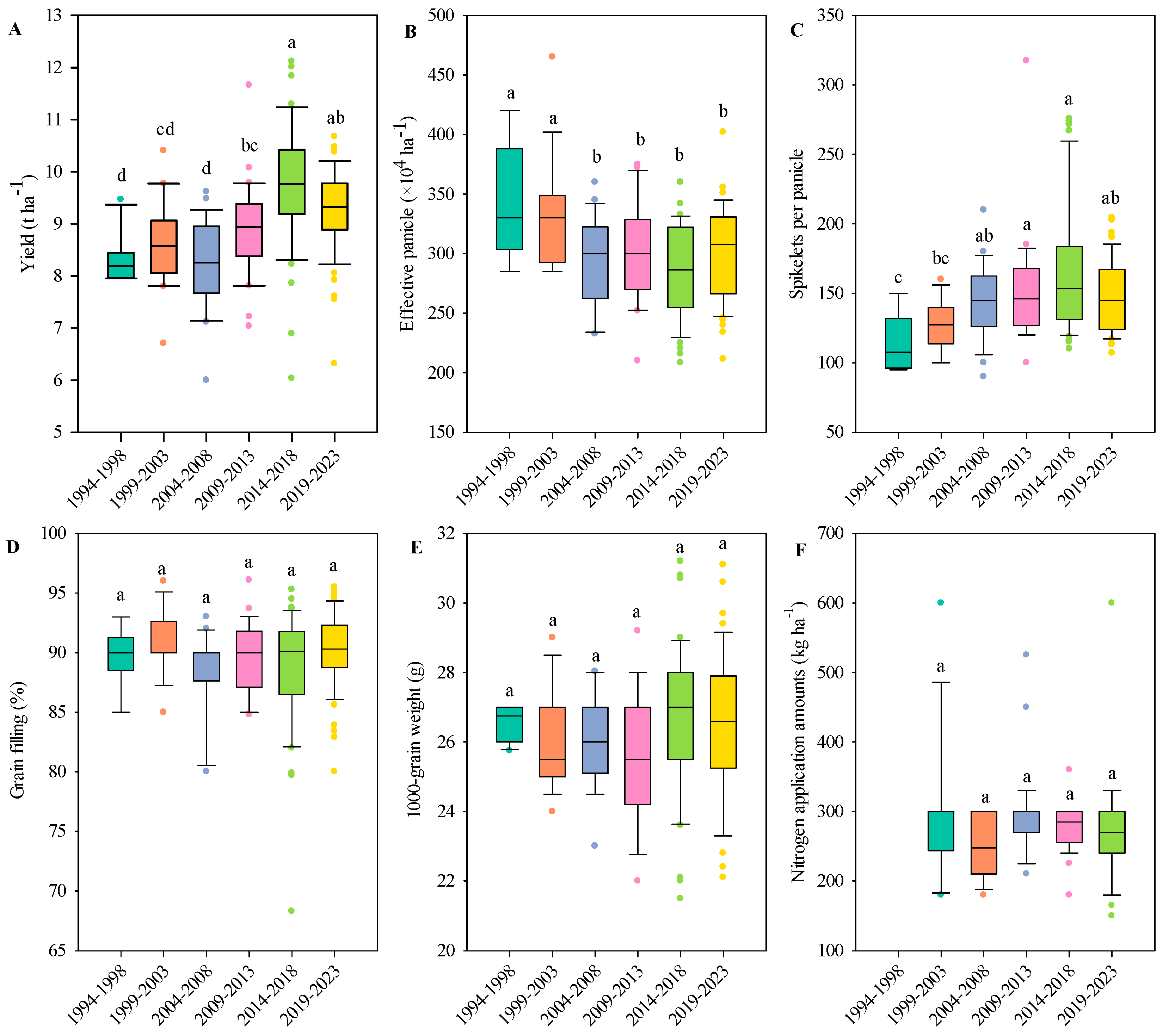
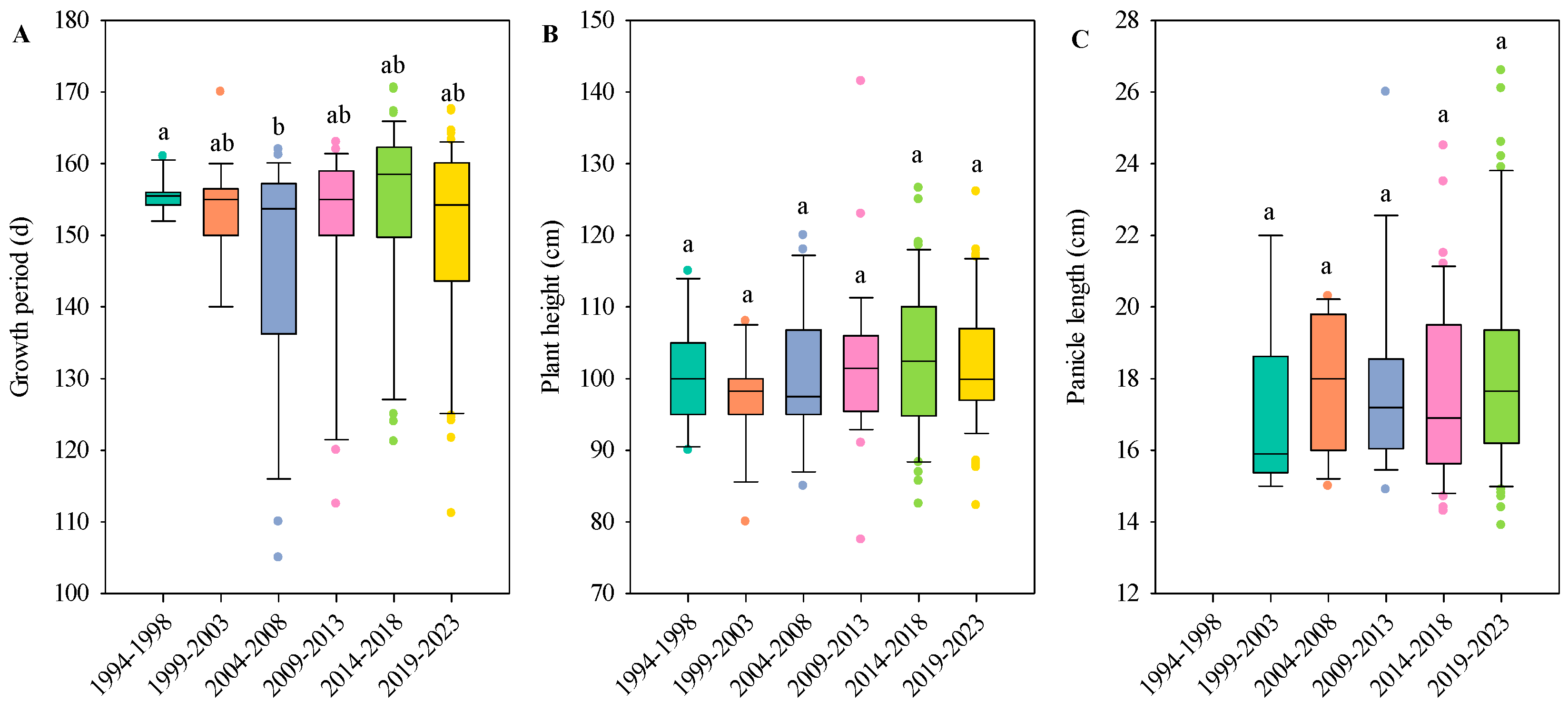
3.1. Variation Characteristics of Rice Yield from 1994 to 2023
3.2. Variation Characteristics of Rice Quality from 1994 to 2023
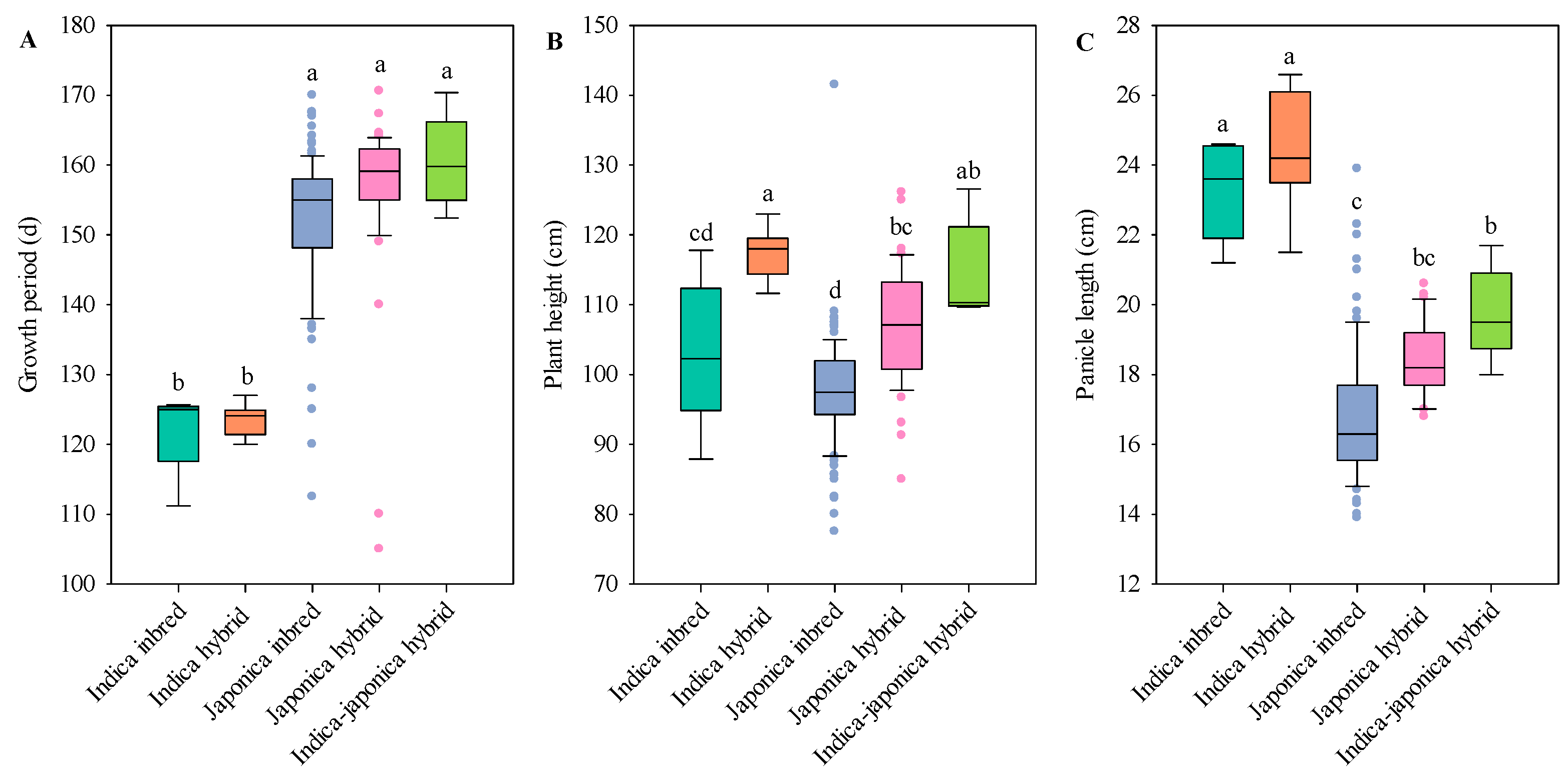
3.3. Changes in Rice Yield Between Different Variety Types in Past 30 Years
3.4. Changes in Rice Quality Between Different Variety Types in Past 30 Years
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Rice Yield and Quality in Past 30 Years
3.6. Stability of Different Types of Rice Varieties
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal Changes in Rice in Shanghai Region
4.2. Differences in Rice Types Traits in Shanghai Region
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. The dataset of main grain land changes in China over 1985–2020. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2024 National Grain Sowing Area, Total Output, and Yield Per Unit Are. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202412/t20241213_1957744.html (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Siddiq, E.A.; Vemireddy, L.R. Advances in genetics and breeding of rice: An overview. In Rice Improvement; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Lin, Q.B.; Wang, X.; Shao, J.L.; Ren, Y.L.; Liu, X.; Feng, M.; Li, S.; Sun, Q.; Luo, S.; et al. The DENSE AND ERECT PANICLE1-GRAIN NUMBER ASSOCIATED module enhances rice yield by repressing CYTOKININ OXIDASE 2 expression. Plant Cell 2025, 37, koae309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.G.; Meng, X.B.; Guo, H.Y.; Cheng, Q.; Jing, Y.H.; Chen, M.J.; Liu, G.F.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, J.Y.; et al. Targeting a gene regulatory element enhances rice grain yield by decoupling panicle number and size. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.Y.; Tan, X.M.; Yang, T.T.; Pan, X.H.; Zeng, Y.J.; Huang, S.; Shang, Q.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Y.H. Relation of cooked rice texture to starch structure and physicochemical properties under different nitrogen managements. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 295, 119882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Pan, Y.H.; Xia, X.Z.; Qing, D.J.; Chen, W.W.; Nong, B.X.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhou, W.Y.; Li, J.C.; Li, D.T.; et al. Molecular basis of genetic improvement for key rice quality traits in Southern China. Genomics 2023, 115, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.C.; Xing, Y.Z.; Mao, H.L.; Lu, T.T.; Han, B.; Xu, C.G.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.F. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, Z.C.; Liu, J.J.; Yu, L.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhu, S.H.; Shi, W.; Pan, C.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.H.; et al. Genetic improvement of eating and cooking quality of rice cultivars in southern China. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Xiong, R.Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Tan, X.M.; Pan, X.H.; Zeng, Y.J.; Huang, S.; Shang, Q.Y.; Xie, X.B.; Zhang, J.; et al. Grain yield improvement in high-quality rice varieties released in southern China from 2007 to 2017. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 986655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.H.; Tan, X.M.; Zeng, Y.J.; Xie, X.B.; Pan, X.H.; Shi, Q.H.; Zhang, J. Changes in the rice grain quality of different high-quality rice varieties released in southern China from 2007 to 2017. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 87, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.T.; Yu, J.H.; Chen, X.; Cao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, G.D.; Li, G.Y.; Xu, F.F.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, H.C.; et al. Differences in starch and protein composition, morphological and structure, and their impacts on eating quality of soft japonica rice under different light and nitrogen fertilizer conditions in southern China. Food Chem. 2025, 474, 143204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Li, X.; Jiang, S.K.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z.J. Discussion on strategy of grain quality improvement for super high yielding japonica rice in Northeast China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Q.; Groenigen, K.J.V.; Yang, H.Y.; Hungate, B.A.; Yang, B.; Tian, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Dong, W.J.; Huang, S.; Deng, A.X.; et al. Global warming and shifts in cropping systems together reduce China’s rice production. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 24, 100359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.X.; Tian, Y.; Xu, Q.S. Review of extension and analysis on current status of hybrid rice in China. Hybrid Rice 2016, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M. Application status, existing problems and countermeasures of high quality rice varieties in Jiangsu Province. China Rice 2020, 26, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.B.; Huang, J.L.; Cassman, K.; Laza, M.R.C.; Visperas, R.M.; Khush, G.S. The importance of maintenance breeding: A case study of the first miracle rice variety-IR8. Field Crops Res. 2010, 119, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.X.; Xiao, Z.W.; Li, X.; Cao, F.B.; Chen, J.N.; Ali, I.; Iqbal, A.; Wahab, A.; Huang, M. Stability differences of quality traits in high-quality hybrid rice. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.T.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Shang, L.Y.; Shang, C.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.B.; Huang, L.Y. Dense planting with reduced nitrogen input improves grain yield, protein quality, and resource use efficiency in hybrid rice. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yin, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.W.; Chu, G.; Xu, C.M.; Wang, D.Y.; Zhang, X.F. Effect of dense planting of hybrid rice on grain yield and solar radiation use in Southeastern China. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.P.; Ding, C.Q.; Zhang, G.H.; Hu, J.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, D.L.; Qian, Q.; Ren, D.Y. Genetic and environmental control of rice tillering. Crop J. 2023, 11, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, C.; Krishna, G.K.; Kapoor, R.T.; Mathur, K.; Dalal, M.; Singh, N.K.; Mohapatra, T.; Chinnusamy, V. Physiological analysis of source–sink relationship in rice genotypes with contrasting grain yields. Plants 2024, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.H.; Meng, T.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Dai, Q.G.; Zhang, H.C.; Yin, X.Y. Sink-source relationship during rice grain filling is associated with grain nitrogen concentration. Field Crops Res. 2018, 215, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Cui, J.H.; Gao, J.C.; Guo, L.Y.; Zhang, Q. Nitrogen fertilization application strategies improve yield of the rice cultivars with different yield types by regulating phytohormones. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.C.; Xu, X.P.; Zhang, J.J.; Huang, S.H.; He, P.; Zhou, W. Nitrogen balance acts an indicator for estimating thresholds of nitrogen input in rice paddies of China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.K.; Hu, R.; Han, T.F.; Zhang, W.F.; Hou, J.; Ren, K.Y. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer consumption and operation on rice yield and its components in China: A Meta-analysis. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2023, 37, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.T.; Yang, H.F.; Zeng, Y.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Xiong, R.Y.; Wu, L.M.; Zhang, B. Differences in the functional properties and starch structures of early/late season rice between the early and late seasons. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 105, 103460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.Y.; Tan, X.M.; Yang, T.T.; Wang, H.X.; Pan, X.H.; Zeng, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Y.H. Starch multiscale structure and physicochemical property alterations in high-quality indica rice quality and cooked rice texture under different nitrogen panicle fertilizer applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Yang, F.; Li, Q.P.; Zeng, Y.L.; Li, B.; Zhong, X.Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Differences in starch structural and physicochemical properties and texture characteristics of cooked rice between the main crop and ratoon rice. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 116, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.F.; Wan, X.Y.; Guo, T.; Jiang, L.; Zhai, H.Q.; Wan, J.M. Stability analysis of QTL for milling quality of rice (Oryza stativa L.) using CSSL population. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2007, 40, 2128–2135. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, C.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Z.J.; Chen, W.F. Effect of Rice Breeding Process on Improvement of Yield and Quality in China. Rice Sci. 2020, 27, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Daygon, V.D.; Mcnally, K.L.; Hamilton, R.S.; Xie, F.M.; Reinke, R.F.; Fitzgerald, M.A. Identification of stable QTLs causing chalk in rice grains in nine environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Xing, Y.; Yun, P.; Luo, L.; Yan, B.; Peng, B.; Xie, W.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; et al. Chalk5 encodes a vacuolar H(+)-translocating pyrophosphatase influencing grain chalkiness in rice. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoo, N.; Yu, C.; Park, C.S.; Baik, M.Y.; Park, I.M.; Cho, M.H.; Bhoo, S.H.; An, G.; Hahn, T.R.; Jeon, J.S. Knockout of a starch synthase gene OsSSIIIa/Flo5 causes white-core floury endosperm in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-P.; Pu, C.-H.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Hong, C.Y.; Chang, M.C.; Lin, Y.R. Three novel alleles of FLOURY ENDOSPERM2 (FLO2) confer dull grains with low amylose content in rice. Plant Sci. 2015, 266, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.N.; Chen, W.L.; Tao, L.; Hu, B.H.; Qu, G.L.; Tu, B.; Yuan, H.; Ma, B.T.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhu, X.B.; et al. GWC1 is essential for high grain quality in rice. Plant Sci. 2020, 296, 110497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Wei, X.H.; Sang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Zhu, C.R.; Lu, T.T.; Zhang, Z.W.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, G.M.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, L.T.; Liao, P.Q.; Wang, W.L.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.G.; et al. Excessive nitrogen application leads to lower rice yield and grain quality by inhibiting the grain filling of inferior grains. Agriculture 2022, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Yang, S.H.; Gong, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Gong, H.; Li, W.J.; Zhan, Q.L.; Cheng, B.Y.; Xia, J.H.; et al. Genomic analysis of hybrid rice varieties reveals numerous superior alleles that contribute to heterosis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Song, J.; Cui, Y.T.; Fan, H.H.; Tang, L.Q. Breeding and cultivation techniques of super-high yield, high-quality and early-maturity indica-japonica hybrid rice Zheyou 915. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci. 2024, 65, 2014–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Xu, Z.J.; Chen, W.F. Advances and prospects of super rice breeding in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.Y.; Zhen, X.D.; Chen, S.G.; Feng, Y.; Wu, W.M.; Shen, X.H.; Cheng, S.H. Breeding methodology and practice of super rice in China. Rice Sci. 2010, 17, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.M.; Tang, J.Y.; Zheng, J.K.; Chu, C.C. Exploration of rice yield potential: Decoding agronomic and physiological traits. Crop J. 2021, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.Y.; Tan, X.M.; Wang, H.X.; Pan, X.H.; Zeng, Y.J.; Zeng, Y.H. Optimized nitrogen fertilizer application strategy improves grain yield and quality of high-quality late indica rice under field ambient warming. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 154, 127091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Xu, J.K.; Huang, K.; Su, Y.; Tong, J.H.; Huang, Z.G.; Huang, C.; Wei, M.L.; Lin, W.H.; Xiao, L.T. Dynamic formation and transcriptional regulation mediated by phytohormones during chalkiness formation in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Du, Y.L.; Tian, X.Y.; Wang, Q.S.; Xiong, R.H.; Xu, G.C.; Yan, C.; Ding, Y.F. Effect of panicle nitrogen on grain filling characteristics of high-yielding rice cultivars. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 74, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.C.; Yuan, X.J.; Yan, F.J.; Xiang, K.H.; Wu, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.L.; He, L.M.; Fan, P.; Yang, Z.Y.; et al. Nitrogen Application Rate Affects the Accumulation of Carbohydrates in Functional Leaves and Grains to Improve Grain Filling and Reduce the Occurrence of Chalkiness. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 921130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Pei, Y.F.; Peng, J.; Wang, Z. An integrated strategy coordinating endogenous and exogenous approaches to alleviate crop lodging. Plant Stress 2023, 9, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, J.; Yang, R.; Cao, L.; Xiong, R. Changes in Rice Yield and Quality from 1994 to 2023 in Shanghai, China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030670
Wang H, Bai J, Zhao Q, Tang J, Yang R, Cao L, Xiong R. Changes in Rice Yield and Quality from 1994 to 2023 in Shanghai, China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030670
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haixia, Jianjiang Bai, Qi Zhao, Jianhao Tang, Ruifang Yang, Liming Cao, and Ruoyu Xiong. 2025. "Changes in Rice Yield and Quality from 1994 to 2023 in Shanghai, China" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030670
APA StyleWang, H., Bai, J., Zhao, Q., Tang, J., Yang, R., Cao, L., & Xiong, R. (2025). Changes in Rice Yield and Quality from 1994 to 2023 in Shanghai, China. Agronomy, 15(3), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030670





