Abstract
Strawberry anthracnose is becoming more important from a scientific and economic standpoint. The Colletotrichum spp. pathogen complex includes C. fragariae, C. gloeosporioides and C. acutatum. The aim was to use microsatellite (SSR) markers to assess the genetic diversity of Colletotrichum species. We used seven SSR primer pairs previously developed for the C. acutatum (3) and C. gloeosporioides (4) species. To analyze the genetic diversity of C. fragariae, it was discovered that SSR primer pairs created for C. gloeosporioides were helpful. SSR molecular markers were used in this study for the first time to identify the species of C. fragariae. The average polymorphism information content (PIC) value across all SSR primer pairs was 0.72, making them all informative. The most informative SSR primers were CG22 and CG30, with PIC values of 0.83 and 0.82, respectively. We believe these primers are suitable for the genetic diversity analysis of C. fragariae species. Therefore, the SSR primer pairs CG20 and CG30 are suggested for the genetic investigation of C. acutatum and C. gloeosporioides. A higher incidence of Colletotrichum spp. polymorphism in Lithuania can be linked to adaptation to survival in our environment, according to this study’s findings on the number of alleles and the degree of genetic diversity, which are higher than the results reported in the literature.
1. Introduction
Anthracnose, caused by the Colletotrichum spp. complex, including C. gloeosporioides, C. acutatum, and C. fragariae, stands out as one of the most significant diseases affecting strawberries globally. About 190 species comprise the Colletotrichum species complex [1,2]. Up to 80% of nursery plants can be infected by strawberry anthracnose (Colletotrichum spp.), reducing yield by more than 50% [3]. This genus ranks as the eighth most important group of pathogenic fungi globally, both scientifically and commercially [1,4,5]. Colletotrichum spp. is considered an inessential pathogen in regions with a warmer environment where the temperature is between 15 and 30 °C [6]. However, climate change, plants, and diseases spread more widely and are harder to control. Plant diseases are affected by rainfall, temperature, and leaf moisture [7]. As a result of climate change, pathogens can adjust in southern countries due to warmer temperature peaks [3]. The spread of strawberry diseases is also caused by climate change. The pathogenicity, diversity, and taxonomy of the Colletotrichum species complex affect the dissemination of the disease and the severity in regions where agrometeorological circumstances fluctuate [8,9]. In Lithuania, the climate conditions are moderate, which suggests that the presence of Colletotrichum spp. should be limited. The study carried out in Lithuania indicates that Colletotrichum spp. were not prevalent; however, due to climate change and its extremes, the disease is now frequently encountered. In order to understand the spread and resistance of a pathogen population, it is important to know its genetic diversity, which would help in understanding pathogens’ ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions [10]. Molecular methods facilitate the classification of fungal species [11]. Vieira et al. [12] investigated a collection of primers for the identification of Colletotrichum spp.; however, they could not identify efficient primers applicable to all Colletotrichum spp. complexes. Nevertheless, it was discovered that all Colletotrichum spp. complexes possess a minimum of three variable genes that could aid in species differentiation [12].
Identification of Colletotrichum spp. and analysis of genetic diversity are conducted using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) [13] and molecular markers, including random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) [14], amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) [15], and microsatellite simple sequence repeat (SSR) [10,16] methods. RAPD, RFLP and AFLP markers are dominant when only the presence of the dominant allele is visible; however, their reproducibility is not always reliable [17,18]. Microsatellites are codominant markers that allow the identification of all alleles at a single locus that represents the heterozygosity of the genotypes under study [19]. Although their development requires prior information about the DNA sequences, with SSR markers specific to certain pathogen species, genotypes, population structure, and genetic polymorphism can be more accurately identified [16]. SSR markers have more advantages than other DNA markers because of their high degree of polymorphism and heterozygosity. SSR markers are most used for studying genetic variation in fungi [20]. Colletotrichum spp. are characterized by high genetic variability. Therefore, molecular markers are superior to phenotypic markers to accurately assess the pathogen [20].
Colletotrichum spp. genetic diversity differs across regions: C. miaoliense with C. siamense is predominant in the island of Taiwan (Province in China) [21], but C. nymphaeae, C. godetiae, and C. fioriniae are predominant in the UK [22]; in addition, in the United states, C. nymphaeae predominates [23]. In China, the C. gloeosporioides complex of C. siamense, C. aenigma and C. fructicola dominates [24]. The species C. fragariae is mainly distributed in countries with a warm climate: Mexico [25], the United States of America [11,26,27], South America [28], Ethiopia [16], Tunisia [29] and Uruguay [11,27]. However, this species also spreads in harsher climates—in North America and Canada [30]. There are currently no data on the distribution of C. fragariae in Latvia and Estonia. Before this investigation, no species composition of Colletotrichum spp. had been identified in strawberries in Lithuania. Due to an insufficient understanding of the species composition of Colletotrichum spp. in strawberries, a decision was made to gather a collection of isolates from other host plants commonly cultivated in proximity to strawberries.
This study aimed to assess the genetic diversity of the Colletotrichum spp. pathogen complex in Lithuania with SSR markers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
Samples of strawberry flowers, leaves, stems, and fruit, both exhibiting and not exhibiting anthracnose (Colletotrichum spp.) symptoms, were gathered from commercial strawberry farms located in Kaunas, Panevezys, Siauliai, Radviliskis, and Klaipeda districts during the period from 2018 to 2020. In the comparison of genetic diversity among Colletotrichum spp., samples were collected from various sources, including weeds (stalks and orphaned stems), as well as apples, peaches, apricots, and cherries. Samples were stored a temperature of +4 °C until the extraction of single spores. In total, 250 samples were collected, but from them only 152 isolates were purified.
2.2. Preparation of Samples
Strawberry fragments and other samples lacking typical symptoms of rot associated with Colletotrichum spp. (excluding strawberry fruits) were crushed into 1–2 cm pieces, sterilized for 30 s. using a 70% ethanol solution, rinsed 3 times with distilled water, dried in laminar flow, and then transferred to Petri dishes containing potato dextrose agar (PDA, Liofilchem, Roseto degli Abruzzi, Italy) medium for a duration of 5–8 days at 25 °C. From 152 extracted isolates, purification of single-spore isolates was conducted. The evaluation of growing mycelium was conducted both visually and microscopically 40× magnification (Nikon Eclipse 80i, Tokyo, Japan), in accordance with cultural and morphological characteristics [31]. We evaluated the colonies’ appearance (colour, structure, texture and growth) and sporulation (presence of spores, shape and size). Single-spore isolates were maintained on Petri dishes at a temperature of +4 °C. For morphological identification, isolates were grown until 14 days post-inoculation (DPI). Finally, after mycelium evaluation, 69 isolates were chosen for further study, in which mycelium appearance and spore shape were attributed to Colletotrichum spp.
Genomic DNA from the 69 Colletotrichum spp. isolates (Table A1, Appendix A) was extracted using the Genomic DNA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania), according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania). DNA was stored at −20 °C in TE buffer until further investigation. The quantity and quality of DNA were measured with a NanoPhotometer® P300 (Implen, GmbH, Munich, Germany) spectrometer.
2.3. Identification of Samples
Colletotrichum spp. were identified with species-specific molecular primers. For C. acutatum identification, ITS4 (TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC) and CaInt2 (GGGGAAGCCTCTCGCGG) primers were chosen (amplifies ~590 bp). C. gloeosporioides and C. fragariae were identified with primers ITS1 (GCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG) and ITS4 (TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC) (amplifies ~590 bp) [13]. PCR amplifications were performed with a total volume of the reaction mixture of 25 µL, consisting of 1 µL of DNA (100 ng/μL), 0.5 μL 10 mM dNTP mix, 5 µL of 10X polymerase buffer (DreamTag) Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania), 1.5 µL 25 mM MgCl2, 0.2 μL of DNA polymerase (DreamTag, recombinant, 5 U/L) (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania), 15.8 µL water (Zymo Reseach, Irvine, CA, USA) and 0.5 µL of each primer. PCR amplification was performed in a Uno96 thermocycler (VWR International GmbH, Berkshire, UK) with conditions as follows: initial 4 min at +95 °C, 35 cycles consisting of 1 min at +95 °C, 30 s at +54 °C (with ITS4 and CaInt2 for C. acutatum) or 1 min +56 °C (with ITS1 and ITS4 C. gloeosporioides and C. fragaria), 1 min at +72 °C, and final 10 min at +72 °C [13].
Additionally, for C. gloeosporioides and C. fragariae separation, restriction by enzyme Bsh1236I was performed immediately after PCR; for C. gloeosporioides, we amplified two fragments, ~480 bp and 100 bp, and for C. fragariae, we amplified one ~590 bp fragment [12]. The restriction reaction was performed with a total volume of reaction mixture of 30 μL, including 17 μL water, 10 μL PCR product, 1 μL Bsh1236I (10 U/μL) restriction enzyme (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania), and 2 μL 10x reaction buffer (FastDigest) (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania), incubated at +37 °C for 16 h; after incubation, it was immediately inactivated at +80 °C. PCR amplification was performed in a thermocycler UNO96 (VWR International GmbH, Berkshire, UK). PCR amplification was repeated three times. The length of fragments was resolved on 1.5% agarose gel stained with Midori Green Direct dye (Nippon Genetics Europe, GmbH, Duren, Germany) and using GeneRuler 100 bp Plus DNA Ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania) as a marker.
2.4. Microsatellite Analysis
For microsatellite analysis, 50 isolates with good-quality DNA of Colletotrichum spp. were selected. In total, 14 polymorphic primers (7 primer pairs) for C. acutatum [10] and C. gloeosporioides [16] were used (Table 1). PCR amplification was repeated twice and performed in a total volume of the mixture of 10 μL, containing 1 μL of DNA, 1 µL of 10X polymerase buffer (DreamTag), 0.05 μL of DNA polymerase (DreamTag, recombinant, 5 U/L), 0.7 µL 25 mM MgCl2, 1 μL 10 mM dNTP mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania), 5.55 µL DNase/RNase-free water and 0.7 µL SSR primers. PCR amplification was performed with the following conditions: for C. acutatum: initial 1 min at +96 °C, 30 cycles consisting of 1 min at +94 °C, 1 min temperature for each primer in Table 1, and final 5 min at +72 °C [10]; for C. gloeosporioides: initial 3 min at +94 °C, 30 cycles consisting of 30 s at +94 °C, 1 min temperature for each primer in Table 2, 2 min 72 °C and final 10 min at +72 °C [16]. Capillary electrophoresis was performed with a Genetic Analyzer ABI 3130 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).

Table 1.
The SSR primer pairs.

Table 2.
Estimated microsatellite locus per 33 Colletotrichum spp. isolates.
The data were statistically analyzed using an ANOVA test with SAS Enterprise Guide, version 7.1 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). The figure’s standard error is marked as an error bar estimated for isolate growth rates. Scale bars are 10 μm. Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05) was used to determine differences among treatments. The parameters utilized for the assessment of SSR data include alleles per locus, expected heterozygosity (He), and observed heterozygosity (Ho), which were computed using the PowerMarker programme [32]. Cluster analysis was conducted using the Treecon v.1.3b programme [33].
3. Results
3.1. The Morphological Characteristics
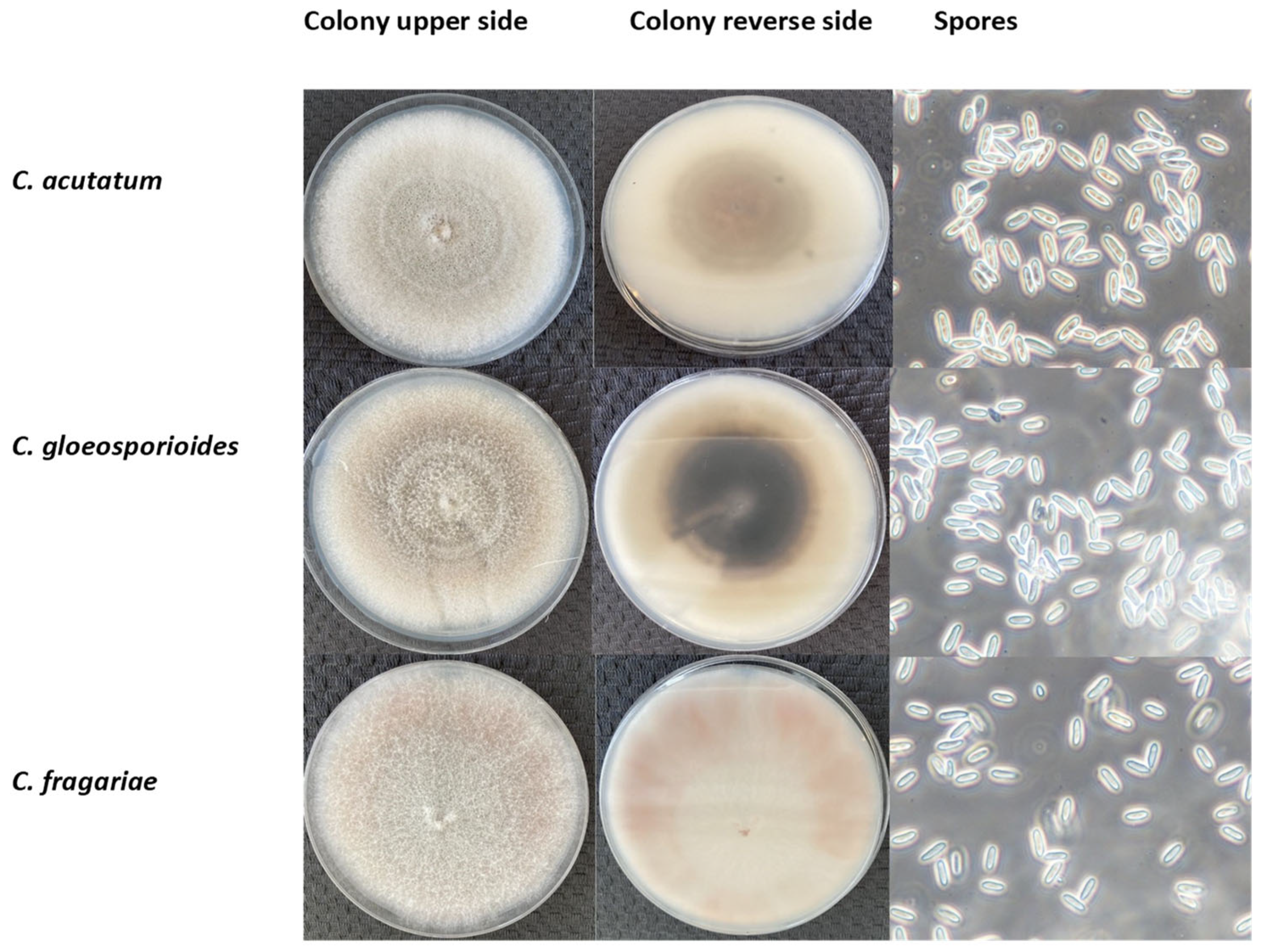
The morphological characteristics of C. acutatum, C. gloeosporioides, and C. fragariae are presented in Figure 1. The colonies’ appearance (colour, structure, and growth) on the Petri dish with the PDA medium was marginally different when comparing the upper and reverse images of the colonies (at least after 14 DPI), but it is challenging to identify the species visually. C. acutatum colonies had the lowest diameter (33.15 ± 1.44 mm), whereas C. fragariae isolation colonies grew the fastest and had the largest diameter (41.27 ± 1.14 mm). Compared to other species, the colony growth of C. gloeosporioides isolates was average (37.63 ± 1.76 mm). In addition, the C. fragariae isolates were light grey; C. acutatum isolates ranged in colour from white to grey and C. gloeosporioides isolates were dark grey.
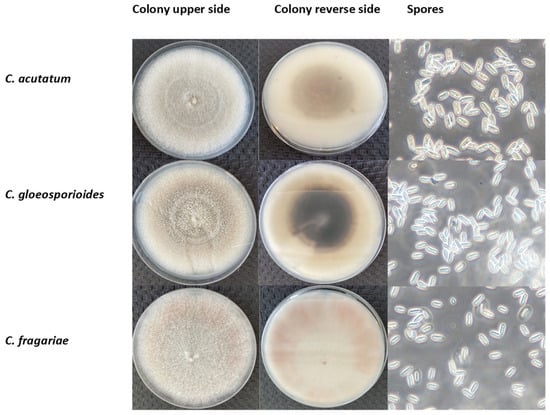
Figure 1.
The morphological features of C. acutatum, C. gloeosporioides and C. fragariae isolates after 14 days of inoculation. Scale bar = 10 μm.
3.2. Molecular Identification of Colletotrichum spp. and Distribution on Strawberry Parts
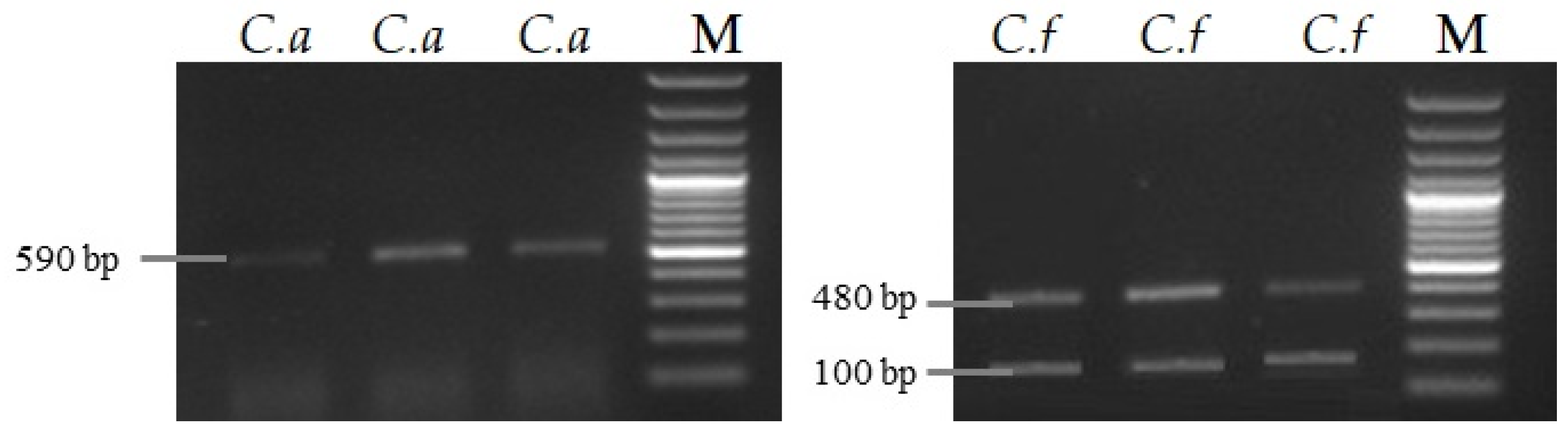
A group of 50 Colletotrichum spp. isolates were Analyzed with species-specific primers by PCR amplification. The results showed that with ITS4/CaInt2 primers, 15 isolates were identified as C. acutatum (~590 bp fragment) and C. fragariae, while C. gloeosporioides did not amplify any fragment. Analysis revealed that among 15 C. acutatum isolates, 12 were sourced from visually damaged strawberry fruits, with 2 from other plants (apricot and apple) and 1 from strawberry petioles. The restriction with Bsh1236I was performed to distinguish C. fragariae from C. gloeosporioides. Our results revealed that 15 isolates amplified two C. gloeosporioides specific segments (480 bp and 100 bp). Additionally, 20 isolates amplified a single fragment (590 bp)—C. fragariae (Figure 2). With ITS1/ITS4 primers, C. acutatum did not amplify any fragments.

Figure 2.
C. acutatum (590 bp) and C. fragariae (100 bp and 480 bp) PCR products after restriction. In the picture, C.a—C. acutatum; C.f—C. fragariae; M—marker.
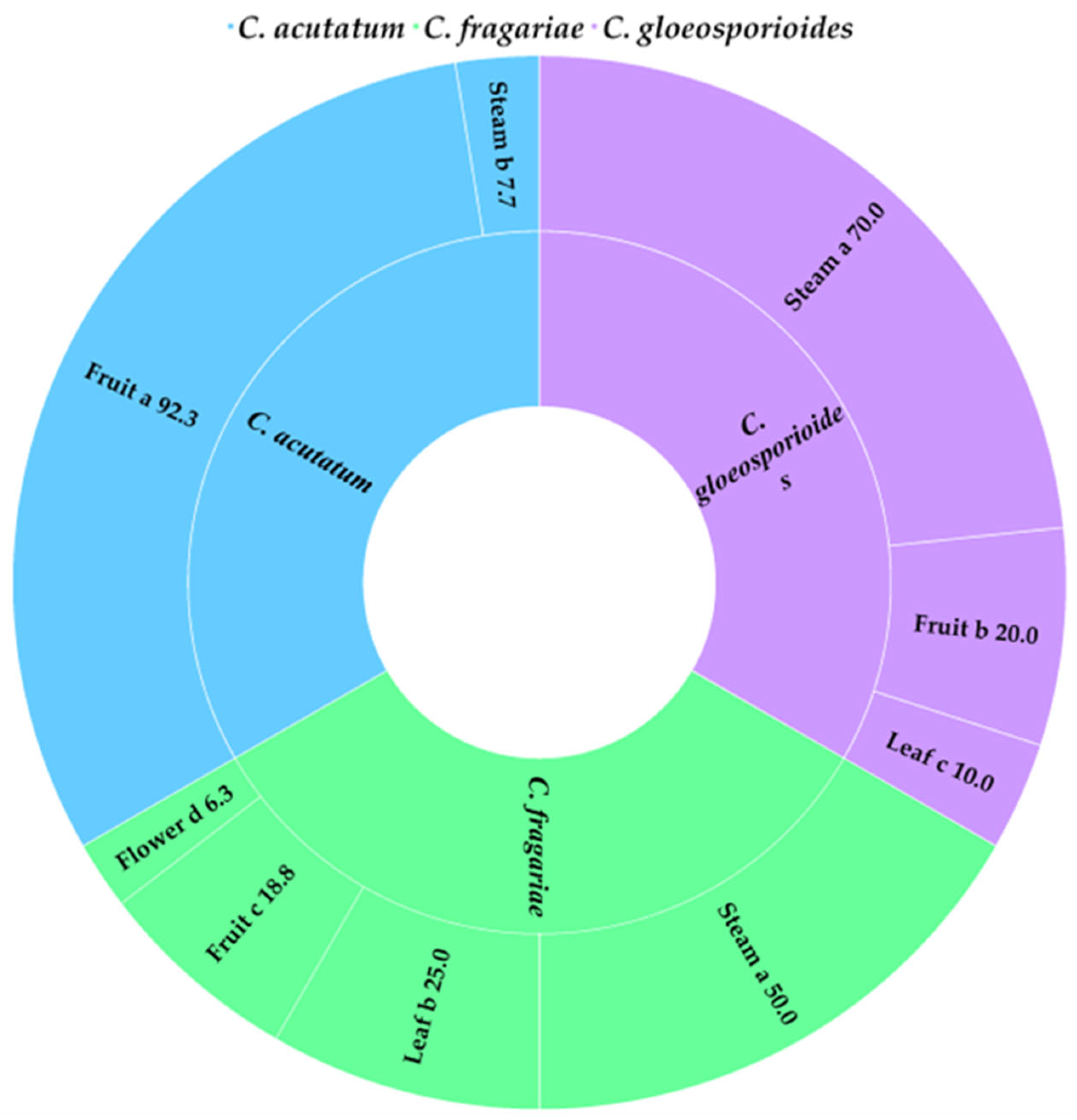
Colletotrichum spp. isolates were taken from different parts of the plant (Figure 3). Following the analysis of 50 DNA samples from Colletotrichum spp. isolates using the PCR method, all three species under investigation were identified: 15 samples of C. acutatum, 15 samples of C. gloeosporioides, and 20 samples of C. fragariae. C. fragariae isolates were extracted from all parts of the plant: strawberry stems (8), fruits (7) (strawberries (3), sour cherry (3), peach (1)), strawberry leaves (4), and strawberry flowers (1). In addition, C. gloeosporioides isolates were extracted from stems (8) (wild viola (1), strawberry (7)), strawberry fruits (4) and leaves (2) (common barnyard (1) and apple fruit (1)). The evaluation of the plant part from which C. acutatum was isolated revealed that the majority of those isolated were from fruits (strawberry (12), apple (1) and apricot (1)) and strawberry stems (1).
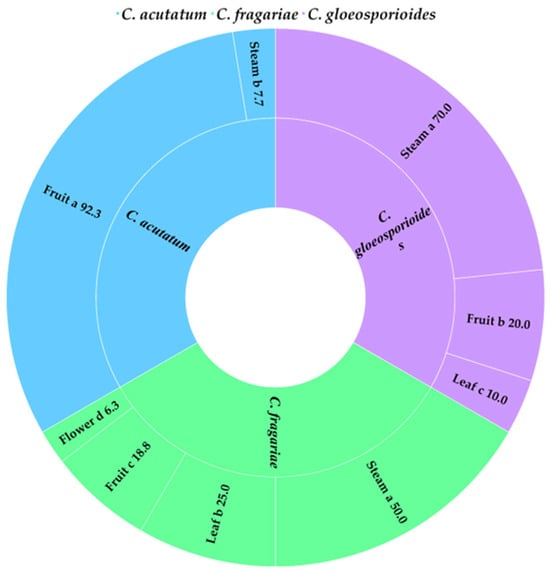
Figure 3.
The percent (%) distribution of C. acutatum, C. fragariae and C. gloeosporioides on different strawberry plant parts. The same letter indicates no significant differences between strawberry parts according to Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05).
3.3. Colletotrichum spp. Microsatellite Analysis
After microsatellite analysis of 50 Colletotrichum spp. samples, 33 showed reliable, repeatable results: 10 C. fragariae, 12 C. acutatum and 11 C. gloeosporioides isolates (Table A2, Appendix A). The SSR primer pairs designed for C. acutatum (CA13 and CA26 primers) amplified fragments for C. fragariae and C. gloeosporioides isolates. The CA13 primer pair amplified heterozygous fragments. However, the polymorphism was very low compared to other SSR primer pairs (Table 2). Primer CA16 was species-specific for C. acutatum, as only two out of ten C. fragariae and two out of eleven C. gloeosporioides isolate fragments were amplified. All primers developed for C. gloeosporioides species were suitable for C. acutatum polymorphism studies, as they were both heterozygous and polymorphic within C. acutatum species (Table A2, Appendix A). Based on the presence or absence of fragments, primers CG20, CG22, CG27 and CG30 were more suitable for the study of interspecies polymorphism in C. acutatum than in C. gloeosporioides, as the fragments were amplified at a lower frequency in samples of the latter species, with CG20 in nine, CG22 and CG27 in four, and CG30 in eight out of eleven isolates (Table A2, Appendix A). Meanwhile, for pathogens of the C. fragariae species, for which SSR markers have not been developed, CG22 and CG30 SSR primers can be used to study interspecies genetic diversity. Fragments were amplified with CG22 and CG30 SSR primers in many genotypes, and their polymorphism (according to the PIC value) was the largest (Table 2).
In total, 52 polymorphic alleles were identified (Table 2). The variation in the number of polymorphic alleles ranged from 4 to 11, with a mean value of 7.43 across different isolates. The CG22 microsatellite marker exhibited the highest polymorphism with a PIC value of 0.83, while the Ca13 marker showed the lowest polymorphism with a PIC value of 0.41. The observed heterozygosity (Ho) ranged from 0.97 to 1.0, yielding an average value of 1.00. The observed heterozygosity (He) values varied between 0.53 and 0.85, yielding an average of 0.76. In all investigated loci, the observed heterozygosity values exceeded the expected heterozygosity.
3.4. Genetic Diversity of Colletotrichum spp. Isolates
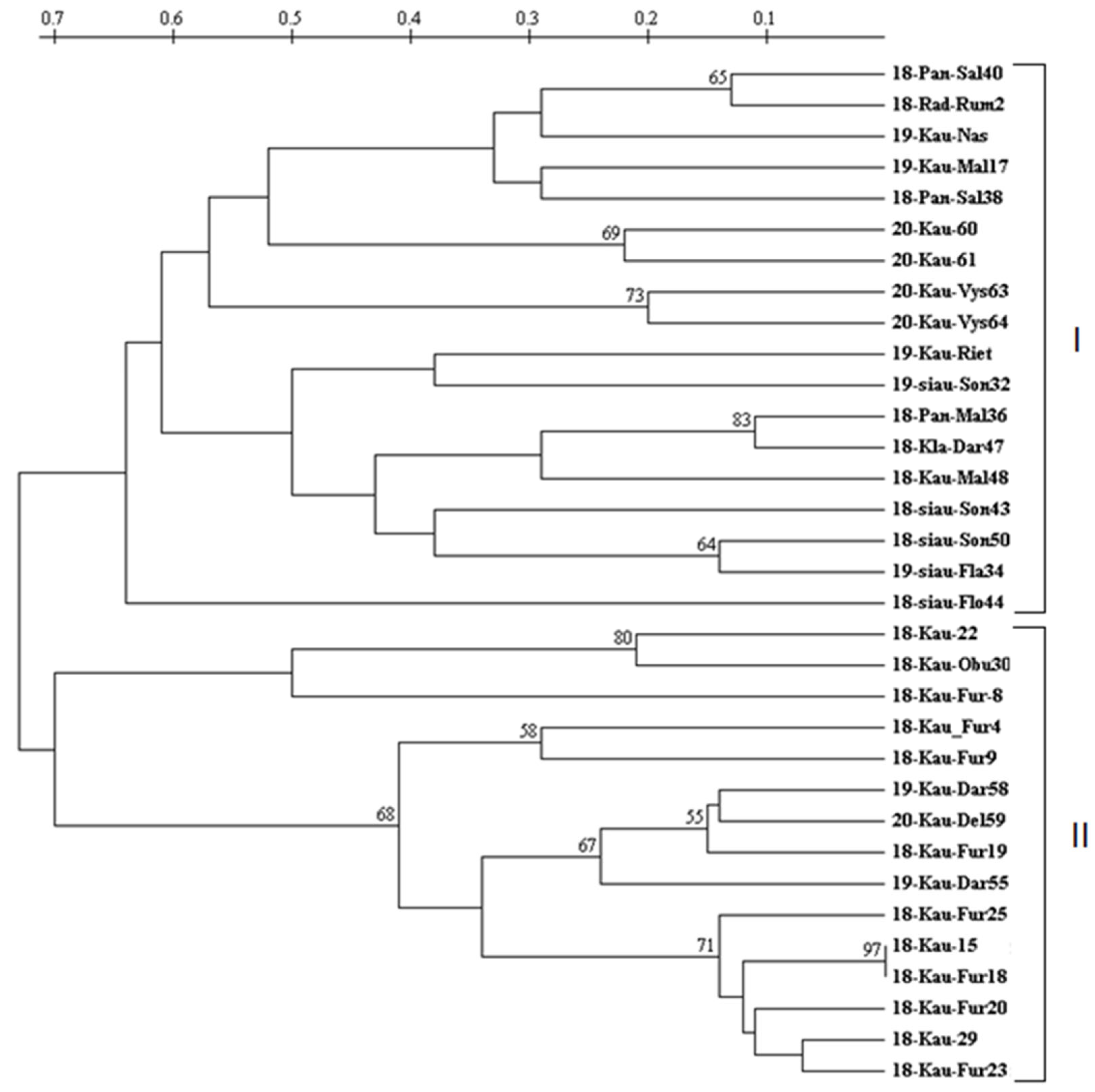
In order to determine the interspecific polymorphism of Colletotrichum species, a dendrogram was created with all C. gloeosporioides, C. fragariae, and C. acutatum isolates using seven SSR primer pairs (Figure 4). In the dendrogram, all 33 pathogens were grouped into two main groups. The first group included nine C. fragariae and nine C. gloeosporioides isolates. In this group, six C. fragariae isolates were statistically reliably separated into three separate subgroups: 18-Pan-Sal40 and 18-Rad-Rum2 (65% confidence), 20-Kau-60 and 20-Kau-61 (69%) and 18-siau-Son50 and 19-siau-Son43 (64%). Also, two isolates of C. gloeosporioides from cherry (20-Kau-Vys63 and 20-Kau-Vys64) and barnyard grass (19-Kau-Riet) were statistically reliably (73%) included in this group.

Figure 4.
Dendrogram illustrating the relationships among isolates of C. fragariae, C. acutatum, and C. gloeosporioides. The scale above the dendrogram represents genetic distances, as outlined by Nei and Li [34]. The values displayed above the dendrogram nodes represent bootstrap values exceeding 50%.
4. Discussion
Around 190 species comprise the Colletotrichum genus globally and cause plant diseases in different crops. Earlier studies on Colletotrichum species responsible for strawberry anthracnose were primarily based on morphological characteristics and single-gene identifications, which would have indicated species complexes rather than individual species [6]. Fruit, crown rot, and infections of the stolon, petioles, and leaves were all caused by C. acutatum, C. fragariae, and C. gloeosporioides [3,35,36]. However, C. acutatum primarily causes fruit rot, and C. fragariae causes crown rot and lesions in vegetative matter. Due to the species complex involved in strawberry anthracnose, these pathogens can attack various plant parts [37].
Morphological Colletotrichum spp. identification is rather difficult [13,38]. C. acutatum produces conidia with pointed tips, often pale and slow-growing. C. gloeosporioides features colonies that are often dark (melanized), cylindrical, and very quickly growing. Additionally, C. fragariae cannot be reliably separated from C. gloeosporioides sensu stricto [39]. However, Xie et al. [13] observed that the C. fragariae colony colour on PDA ranges from beige to dark grey, and C. gloeosporioides features dense colonies from white to dark olive-grey. In addition, C. acutatum, at 4–5 DPI, was white but over time turned greyish brown. Abera et al. [40] found that C. gloeosporioides colony colour ranges from white to grey and C. acutatum changes from creamy white to pinkish grey. Dembele et al. [41] observed that colony colour and spore morphology were not distinguished from different Colletotrichum spp. isolates, but also between origins. This confirms that Colletotrichum genus species are hard to distinguish visually.
In Lithuania, the Colletotrichum species complex consists of C. acutatum, C. gloeosporioides and C. fragariae. Our results show that in Lithuania, C. acutatum mainly cause strawberry fruit anthracnose, whereas C. gloeosporioides and C. fragariae affect the stems. Van Hemelrijck et al. [42] found that from all Colletotrichum spp. in Belgium, the most dominant is C. acutatum. However, genetic diversity differs in other regions, as C. siamense and C. miaoliense prevail in Taiwan [21], whereas C. fioriniae, C. godetia and C. nymphaea dominate in the UK [22]; in addition, C. nymphaea is also found in the United States [23]. In China, C. siamense, C. enigma, and C. fructicola as members of the C. gloeosporioides complex predominate [24].
A total of 50 Colletotrichum isolates from various agroecological regions were analyzed. For C. acutatum, three polymorphic microsatellite markers were utilized, while for C. gloeosporioides, four markers were employed. No markers for C. fragariae were detected in the literature. Consequently, primers specific to C. acutatum and C. gloeosporioides were utilized for this species. Moges et al. [16] indicated that we adjusted the annealing temperature: CG30 was modified from 50 to 47.9 °C, and CG20 was changed from 51 to 45 °C. The number of alleles generated with each primer pair ranged from 4 to 11, with an average of 7.43. In this study, the number of C. acutatum alleles ranged from 4 to 9 alleles. However, in other research, the number of alleles ranged from 3 to 6 [10] or from 1 to 3 [43].
Meanwhile, Moges et al.’s [16] study on C. gloeosporioides showed a predominance of alleles 8–9, whereas in this study, alleles 6–11 prevailed. This indicates a possible higher polymorphism of the species C. gloeosporioides in Lithuania, which can be associated with adaptation to the environment to survive in our conditions. However, different results were observed in Bahri et al.’s [29] study: C. gloeosporioides was dominated by only two alleles. This may have resulted in different electrophoresis methods, as fragments were separated with an accuracy of 1 bp in capillary electrophoresis, while in agarose gel, it was within 5–10 bp error limits. However, Penet et al. [44] found that C. gloeosporioides was dominated by alleles 2–29, with an average of 12.3.
The allele size ranges of CG22 and CG30 primer pairs were like those of Moges et al. [16]. However, the CG20 and CG27 primer pair’s allele size range showed differences from other research [16]. Allele size ranges with the CG27 primer pair were similar to those of Bahri et al. [29], but alleles showed only one fragment. Also, the allele size ranges obtained using primer pairs CG20, CG22, and CG30 were different from those of Bahri et al. [29]. In our studies, the allele size ranges obtained using Ca13 and Ca26 primer pairs were similar to those of Ciampi et al. [10]. Capillary electrophoresis was used in this study, which has a higher accuracy, while Bahri et al. [29] and Ciampi et al. [10] separated the fragments on an agarose gel with an accuracy of 5–10 bp. Studies have revealed that the allele size ranges obtained in this study indicate higher polymorphism.
In this study, the most informative microsatellite marker was CG22 (PIC value 0.83), and the least informative was Ca13 (PIC value 0.41). Compared with other studies, the highest PIC value was observed with CG22 (PIC 0.500) and the smallest was observed with CG20 (PIC 0.477) [29]. However, Moges et al. [16] reported that marker CG30 (PIC value 0.597) has the highest PIC value; the smallest PIC value was observed with CG22 at 0.552.
In this study, the Ho values analyzed were higher than those reported in other studies. Moges et al. [16] observed heterozygosity values of 0.018 for CG20, 0.000 for CG27, 0.006 for CG30, and 0.865 for CG22; Ciampi et al. [10] reported that Ho varied from 0.590 up to 0.093. Despite differences in Ho values, the He values were similar to those of Marulanda et al. [43]. Feres et al. [45] suggest that differences between He and Ho are due to the presence of null alleles, which mask heterozygous individuals with a single fragment, indicating low homozygosity.
5. Conclusions
The genetic diversity of the Colletotrichum spp. pathogen complex was studied using two C. acutatum and three selective C. gloeosporioides SSR primer pairs. C. gloeosporioides primer pairs were found to be suitable for these pathogens and C. fragariae genetic polymorphism analysis. Observed heterozygosity was higher than expected heterozygosity with all primer pairs. All SSR primer pairs studied were polymorphic and informative according to polymorphism information content. CG20 and CG30 were the most suitable for C. acutatum and C. gloeosporioides, and CG22 and CG30 were the most suitable for C. fragariae polymorphism analysis. Compared to the data presented in the literature, a higher number of alleles and greater genetic diversity were identified in this study, which may indicate a higher number of Colletotrichum spp. polymorphisms of isolates in Lithuania, which can be associated with adaptation to survival in our environmental conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M., N.R., B.F., V.V.-K., R.K. and A.V.; methodology, N.R. and B.F.; software, N.R., B.F., V.B., R.A. and I.M.; validation, A.M., N.R., B.F., R.A. and A.V.; formal analysis, N.R., B.F. and R.A.; investigation, A.M., N.R., V.V.-K., A.V. and R.K.; resources, A.M., N.R., A.V., B.F. and V.B.; data curation, A.M., N.R., B.F., I.M. and A.V.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M., N.R., B.F. and A.V.; writing—review and editing, A.M., B.F., N.R., V.B., R.A., I.M., V.V.-K., R.K. and A.V.; visualization, N.R., A.M., V.B., I.M., V.V.-K. and R.K.; supervision, A.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. This work was part of the PhD thesis of the first author, Armina Morkeliūnė; PhD program in Agricultural Sciences, Agronomy (A 001) at the Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry, Lithuania.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SSR | simple sequence repeat |
| PIC | polymorphism information content |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| RAPD | random amplified polymorphic DNA |
| RFLP | restricted-fragment-length polymorphism |
| AFLP | amplified-fragment-length polymorphism |
| LD | linear dichroism |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Colletotrichum spp. isolates used for DNA extraction.
Table A1.
Colletotrichum spp. isolates used for DNA extraction.
| Origin | Year | Host Plant | Isolate Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kaunas district, Babtai | 2018 | Strawberry | 13 |
| 2019 | 10 | ||
| 2020 | 3 | ||
| Panevezys district, Sodeliskiai village | 2018 | 4 | |
| 2019 | 3 | ||
| Panevezys district, Krekenava, | 2018 | 2 | |
| 2019 | 2 | ||
| Kaunas district, Labunava, | 2018 | 1 | |
| 2019 | 4 | ||
| Siauliai district, Bridai | 2018 | 1 | |
| 2019 | 4 | ||
| Siauliai district, Maniusiai village | 2018 | 3 | |
| 2019 | 2 | ||
| Radviliskis district, Velziai village | 2018 | 1 | |
| Prienai district, Klebiskis village | 2018 | 1 | |
| 2019 | 3 | ||
| Klaipeda district, Priekule | 2018 | 1 | |
| Kaunas district, Laumenai | 2020 | Sour Cherry | 2 |
| Kaunas district, Babtai | 2020 | Sour Cherry | 3 |
| Kaunas district, Vaisvydava | 2018 | Apple | 2 |
| Kaunas | 2020 | Apricots | 1 |
| 2020 | Peaches | 1 | |
| Kaunas district, Babtai | 2019 | Common barnyard | 1 |
| 2019 | Wild viola | 1 | |
| Total | 69 |

Table A2.
The profiles of the isolates of C. fragariae, C. gloeosporioides and C. acutatum using 7 SSR primer pairs.
Table A2.
The profiles of the isolates of C. fragariae, C. gloeosporioides and C. acutatum using 7 SSR primer pairs.
| Isolate | Primer Pair | Colletotrichum spp. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca13 | Ca16 | Ca26 | CG20 | CG22 | CG27 | CG30 | ||
| 18-Kau-Fur25 | 114:117 | 111:114 | 224:230 | 239:241 | 167:173 | 143:147 | C. fragariae | |
| 18-Kau-Mal48 | 114:117 | 223:229 | 143:147 | 153:154 | ||||
| 18-Pan-Mal36 | 114:117 | 223:229 | 179:184 | 143:147 | ||||
| 18-Pan-Sal40 | 114:117 | 224:230 | 187:189 | 150:156 | ||||
| 18-siau-Son50 | 114:117 | 223:229 | 187:189 | |||||
| 19-Kau-Mal17 | 114:117 | 224:230 | 143:147 | 154:156 | ||||
| 19-siau-Fla34 | 114:117 | 223:229 | 187:189 | 153:154 | ||||
| 20-Kau-60 | 114:117 | 98:100 | 223:230 | 161:163 | 154:156 | |||
| 20-Kau-61 | 114:117 | 223:229 | 161:163 | 154:156 | ||||
| 18-Rad-Rum2 | 114:117 | 224:230 | 187:189 | 154:156 | ||||
| 18-Kau_Fur4 | 114:117 | 111:1114 | 227:232 | 241:243 | 167:173 | 144:148 | 158:159 | C. acutatum |
| 18-Kau-15 | 114:117 | 111:1114 | 224:230 | 241:243 | 167:173 | 143:147 | 158:159 | |
| 18-Kau-22 | 114:117 | 98:100 | 224:230 | 241:243 | 161:163 | 143:147 | 149:150 | |
| 18-Kau-29 | 114:117 | 111:1114 | 224:230 | 237:239 | 167:173 | 143:147 | 158:159 | |
| 18-Kau-Fur18 | 114:117 | 111:1114 | 224:230 | 241:243 | 167:173 | 143:147 | 158:159 | |
| 18-Kau-Fur19 | 114:117 | 111:1114 | 224:230 | 238:240 | 167:173 | 158:159 | ||
| 18-Kau-Fur20 | 114:117 | 111:116 | 224:230 | 239:241 | 167:173 | 143:147 | 158:159 | |
| 18-Kau-Fur-8 | 98:100 | 227:232 | 241:243 | 161:163 | 144:148 | 149:150 | ||
| 18-Kau-Fur9 | 115:118 | 111:1114 | 224:230 | 241:243 | 167:173 | 144:148 | 158:159 | |
| 19-Kau-Dar55 | 114:117 | 111:1114 | 223:229 | 238:240 | 167:173 | 143:147 | 158:159 | |
| 19-Kau-Dar58 | 114:117 | 111:1114 | 224:231 | 238:240 | 167:173 | 142:146 | 158:159 | |
| 20-Kau-Del59 | 114:117 | 111:1114 | 224:230 | 238:240 | 167:173 | 142:146 | 158:159 | |
| 18-Kau-Fur23 | 114:117 | 111:1114 | 224:230 | 239:241 | 167:173 | 143:147 | 158:159 | C. gloeosporioides |
| 18-Kau-Obu30 | 114:117 | 98:100 | 224:230 | 239:241 | 191:193 | 143:147 | 149:150 | |
| 18-Kla-Dar47 | 114:117 | 223:229 | 239:241 | 179:184 | 143:147 | |||
| 18-Pan-Sal38 | 114:117 | 224:230 | 153:154 | |||||
| 18-siau-Flo44 | 114:117 | 236:237 | 187:189 | 159:159 | ||||
| 18-siau-Son43 | 114:117 | 223:229 | 237:239 | |||||
| 19-Kau-Nas | 114:117 | 224:230 | 156:158 | |||||
| 19-Kau-Riet | 114:117 | 223:229 | 241:243 | 142:146 | 153:154 | |||
| 19-siau-Son32 | 114:117 | 239:241 | 153:154 | |||||
| 20-Kau-Vys63 | 114:117 | 229:231 | ||||||
| 20-Kau-Vys64 | 114:117 | 229:231 | 154:156 | |||||
References
- Cannon, P.F.; Damm, U.; Johnston, P.R.; Weir, B.S. Colletotrichum—Current status and future directions. Stud. Mycol. 2012, 73, 181–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udayanga, D.; Manamgoda, D.S.; Liu, X.; Chukeatirote, E.; Hyde, K.D. What are the common anthracnose pathogens of tropical fruits? Fungal Divers. 2013, 61, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkeliūnė, A.; Rasiukevičiūtė, N.; Valiuškaitė, A. Pathogenicity of Colletotrichum acutatum to different strawberry cultivars and anthracnose control with essential oils. Zemdirb.-Agric. 2021, 108, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.; van Kan, J.A.L.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; di Pietro, A.; Spanu, P.D.; Rudd, J.J.; Dickman, M.; Kahmann, R.; Ellis, J.; et al. The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Xu, X.F.; Dai, D.J.; Shi, H.J.; Wang, H.D.; Zhang, C.Q. Differentiation in development of benzimidazole resistance in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides complex populations from strawberry and grape hosts. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2016, 45, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, R.S.; Huang, J.K.; Jin, B.C.; Yan, J.Y.; Li, X.H.; Hyde, K.D.; Bahkali, A.H.; Yin, S.L.; Zhang, G.Z. An account of Colletotrichum species associated with strawberry anthracnose in China based on morphology and molecular data. Mycosphere 2016, 7, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, K.A.; Nita, M.; Wolf, E.D.; Esker, P.D.; Gomez-Montano, L.; Sparks, A.H. Chapter 21—Plant pathogens as indicators of climate change. In Climate Change: Observed Impacts on Planet Earth, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 325–338. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, S.; Horowitz, S.; Sharon, A. Pathogenic and nonpathogenic lifestyle in Colletotrichum acutatum from strawberry and other plants. Phytopathology 2001, 91, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Quezada, G.D.; Esquivel, J.F.; Silva-Rojas, H.V.; Leyva-Mir, S.G.; de Garcia-Avila, C.J.; Noriega-Orozco, L.; Rivas-Valencia, P.; Ojeda-Barrios, D.; Melgoza-Castillo, A. Emerging plant diseases under a changing climate scenario: Threats to our global food supply. EJFA 2018, 30, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampi, M.B.; Baldauf, C.; Vigna, B.B.Z.; Souza, A.P.; Spósito, M.B.; Amorim, L. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in Colletotrichum acutatum, the causal agent of postbloom fruit drop on citrus. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2011, 3, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, M.; Peres, N.; Villani, S.; Schnabel, G. Managing Colletotrichum on Fruit Crops: A “Complex” Challenge. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2301–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, W.A.S.; Bezerra, P.A.; da Silva, A.C.; Silva Veloso, J.; Paz Saraiva Câmara, M.; Doyle, P.V. Optimal markers for the identification of Colletotrichum species. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2020, 143, 106694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Y.; Hu, D. Identification of Colletotrichum spp. isolated from strawberry in Zhejiang Province and Shanghai City, China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2010, 11, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, D.B.; de Medeiros, L.V.; de Medeiros, V.V.; Leão, M.P.C.; Camargo, L.E.A.; de Oliveira, N.T. Amplification of the cap20 pathogenicity gene and genetic characterization using different markers molecular in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides isolates. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2010, 53, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Cao, C.; Hu, J.; Shu, Q.; Finkeldey, R. Aflp analysis of resistance to Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in Camellia oleifera (Theaceae). Pak. J. Bot. 2019, 51, 2269–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moges, A.D.; Admassu, B.; Belew, D.; Yesuf, M.; Njuguna, J.; Kyalo, M.; Ghimire, S.R. Development of Microsatellite Markers and Analysis of Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides from Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliesaravičius, A.; Stanys, V. Žemės augalų biotechnologija, Enciklopedija; Agriculture Academy: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2005; p. 234. [Google Scholar]
- Sasnauskas, K. Genų Inžinerijos Pagrindai; Biotechnologijos Institutas: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2006; 238p. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, W.; Machray, G.; Provan, J. Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci. 1996, 1, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, N.N.; Mahiya-Farooq; Padder, B.A.; Shah, M.D.; Dar, M.S.; Nabi, A.; Bano, A.; Rasool, R.S.; Surma, S. Microsatellite mining in the genus Colletotrichum. Gene Rep. 2018, 13, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.C.; Hu, H.P.; Hung, T.H.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Wu, H.Y.; Tzean, S.S.; Chung, C.L.; Wang, Y.W. Diversity and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum species causing strawberry anthracnose in Taiwan and description of a new species, Colletotrichum miaoliense sp. nov. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroncelli, R.; Zapparata, A.; Thon, M.R.; Vannacci, G.; Sarrocco, S.; Holub, E.; Sukno, S.A.; Lane, C.R.; Sreenivasaprasad, S. Molecular Diversity of Anthracnose Pathogen Populations Associated with UK Strawberry Production Suggests Multiple Introductions of Three Different Colletotrichum Species. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.-Y.; Forcelini, B.B.; Peres, N.A. Anthracnose Fruit and Root Necrosis of Strawberry Are Caused by a Dominant Species Within the Colletotrichum acutatum Species Complex in the United States. Phytopathology® 2019, 109, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, Q.; Duan, K.; Song, L.; Zou, X.; Xu, X. Characterization and Fungicide Sensitivity of Colletotrichum Species Causing Strawberry Anthracnose in Eastern China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1960–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Silva, A.; García-Díaz, S.E.; Robles-Yerena, L.; Nava-Díaz, C.; Nieto-Ángel, D. First Report of Colletotrichum spp. in fruits of allspice (Pimenta dioica) in Veracruz, Mexico. Mex. J. Phytopathol. 2018, 36, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, E.; van der Scheer, H.A.T.; Lieten, F.; Dijkstra, J. Why is Colletotrichum acutatum a quarantine organism, and C. gloeosporioides and C. fragariae are not? Acta Hortic. 1997, 439, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaniz, S.; Hernández, L.; Damasco, D.; Mondino, P. First report of Colletotrichum acutatum and C. fragariae causing bitter rot of apple in Uruguay. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.S.C.; Canuto, R.d.S.; Santos, L.O.; Martins, R.N. Diseases of strawberry. (Doenças do morango.). Inf. Agropecu. 2005, 26, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bahri, B.A.; Saadani, M.; Mechichi, G.; Rouissi, W. Genetic diversity of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex associated with Citrus wither-tip of twigs in Tunisia using microsatellite markers. J. Phytopathol. 2019, 167, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnell, P.S.; Gubler, W.D. Taxonomy and morphology of Colletotrichum species pathogenic to strawberry. Mycologia 1992, 84, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Cai, L.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, J.Z.; Prihastuti, H. Colletotrichum: A catalogue of confusion. Fungal Divers. 2009, 39, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Muse, S.V. Power Marker: Integrated Analysis Environment for Genetic Marker Data. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Peer, Y.; De Wachter, R. TREECON for Windows: A software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Comput. Applic. Biosci. 1994, 9, 569–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Li, W.H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variations in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 5269–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debode, J.; Van Hemelrijck, W.; Xu, X.M.; Maes, M.; Creemers, P.; Heungens, K. Latent entry and spread of Colletotrichum acutatum (species complex) in strawberry fields. Plant Pathol. 2015, 64, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Hetman, B. Susceptibility of strawberry cultivars to Colletotrichum acutatum J. H. Simmonds. Acta Sci. Pol.-Hortoru 2016, 15, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Peres, N.A.; Timmer, L.W.; Adaskaveg, J.E.; Correll, J.C. Lifestyles of Colletotrichum acutatum. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Culebras, P.V.; Barrio, E.; García, M.; Querol, A. Identification of Colletotrichum species responsible for anthracnose of strawberry based on the internal transcribed spacers of the ribosomal region. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 189, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddie, A.G.; Martínez-Culebras, P.; Bridge, P.D.; García, M.D.; Querol, A.; Cannon, P.F.; Monte, E. Molecular characterization of Colletotrichum strains derived from strawberry. Mycol. Res. 1999, 103, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, A.; Lemessa, F.; Adunga, G. Morphological characteristics of Colletotrichum species associated with mango (Mangifera indica L.) in Southwest Ethiopia. Food Sci. Qual. Manag. 2016, 46, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Dembele, D.D.; Kamara, A.; Grechi, I.; Silué, N.; N’Goran, N.S.; Yéo, Y.S.; Rey, J.-Y.; Koné, D. Morphological characteristics and distribution of Colletotrichum isolates morphotypes infecting mango (Mangifera indica L.) in the north of Côte d’Ivoire. AJFAND 2020, 20, 15837–15856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemelrijck, W.; Debode, J.; Heungens, K.; Maes, M.; Creemers, P. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of Colletotrichum isolates from Belgian strawberry fields. Plant Pathol. 2010, 59, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marulanda, M.; Lopez, A.; Isaza, L.; Lopez, P. Microsatellite isolation and characterization for Colletotrichum spp, causal agent of anthracnose in Andean blackberry. GMR 2014, 13, 7673–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penet, L.; Briand, S.; Petro, D.; Bussière, F.; Guyader, S. Data on microsatellite markers in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides s.l., polymorphism levels and diversity range. Data Br. 2017, 12, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feres, J.M.; Martinez, M.L.; Martinez, C.A.; Mestriner, M.A.; Alzate-Marin, A.L. Transferability and characterization of nine microsatellite markers for the tropical tree species Tabebuia roseo alba. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).