Effects of Alfalfa–Grass Mixed Sowing on Grass Yield and Rhizosphere Soil Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Test Site
2.2. Test Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Measuring Indicators
2.5. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
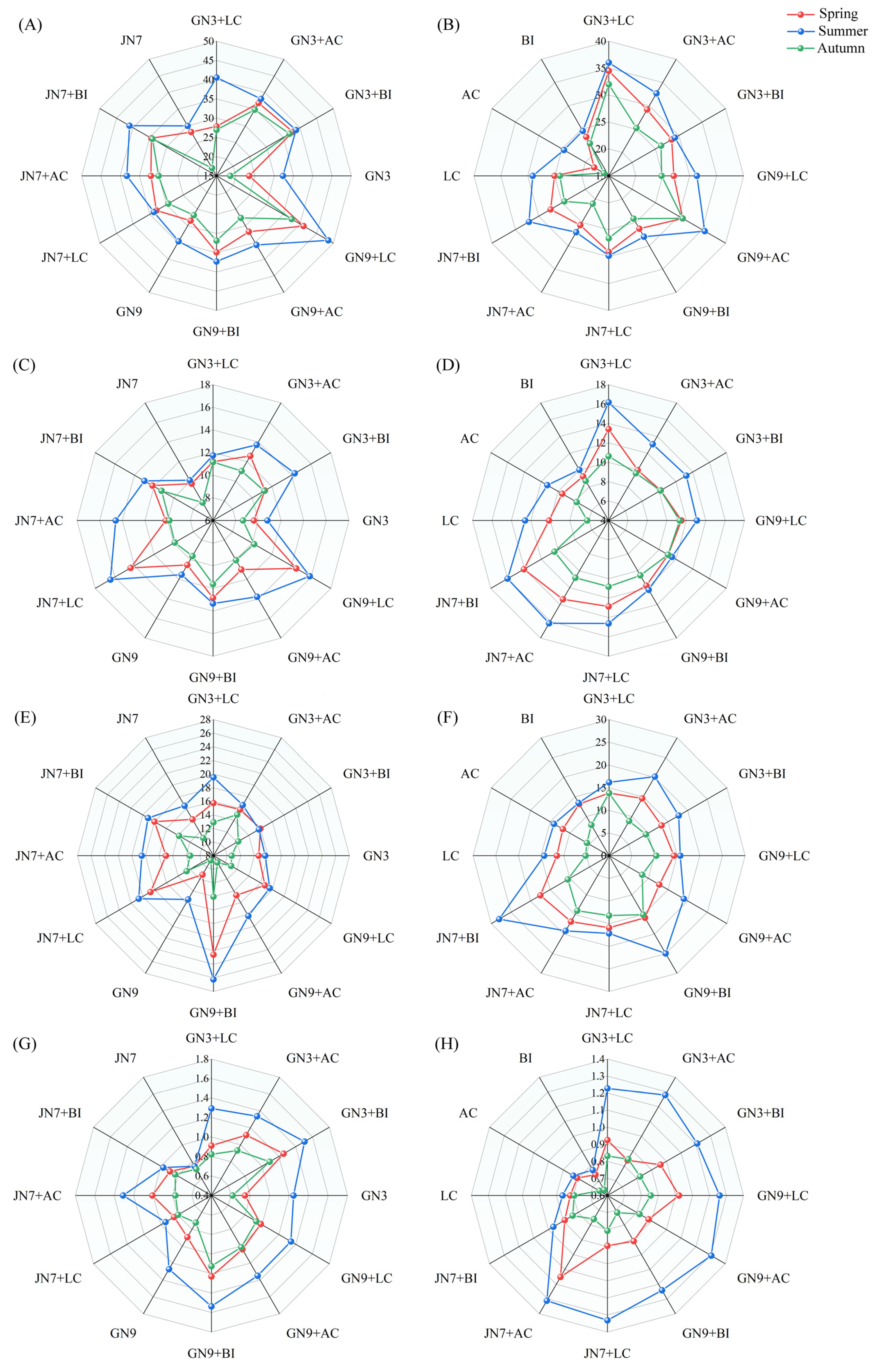
3.1. Seasonal Variation of Enzyme Activity in Rhizosphere Soil
3.2. Seasonal Variation of Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Biomass
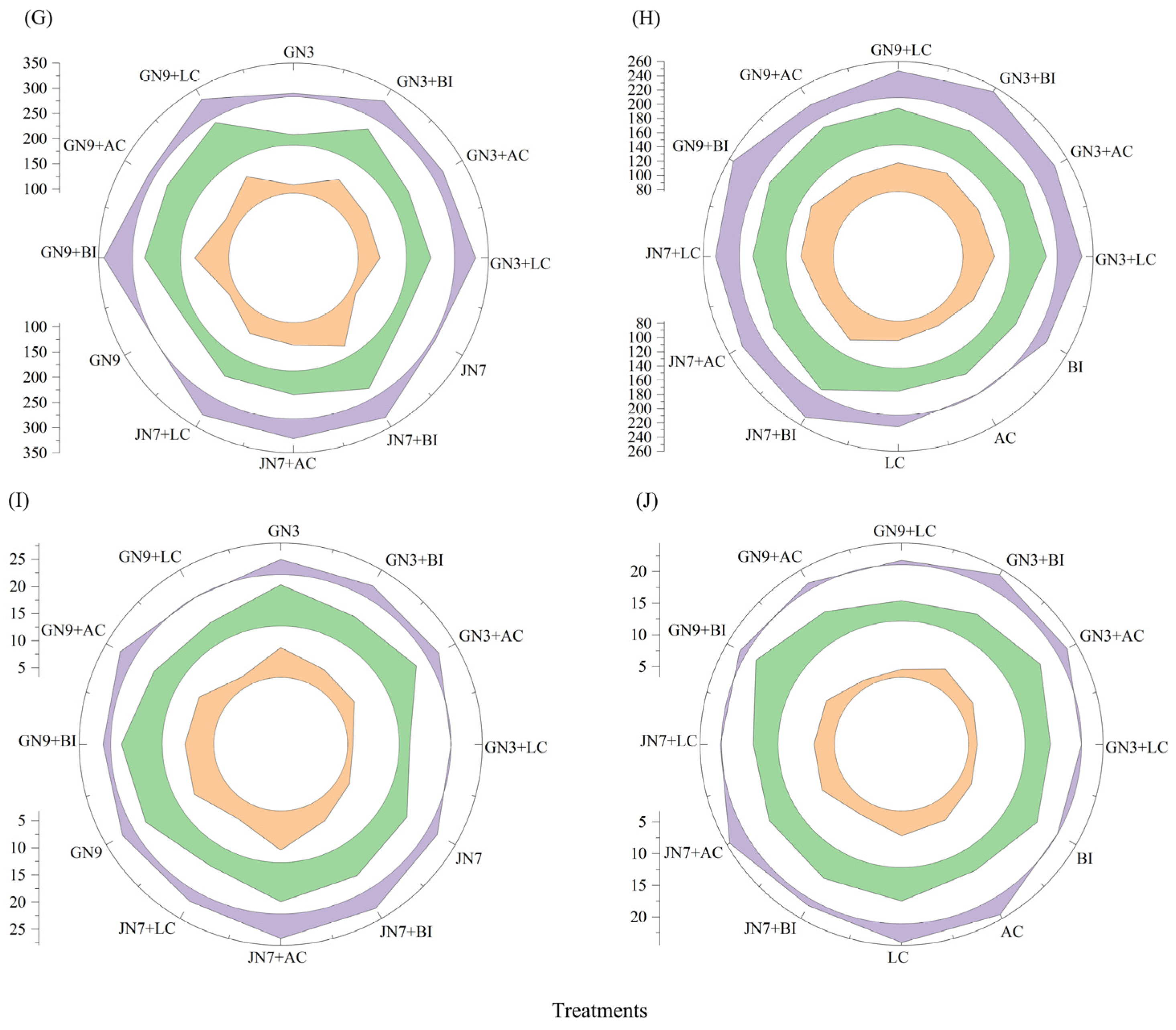
3.3. Changes in Hay Yield and Soil Nutrients Under Different Mixed Sowing Treatments
3.3.1. Forage Hay Yield
3.3.2. Rhizosphere Soil Nutrients
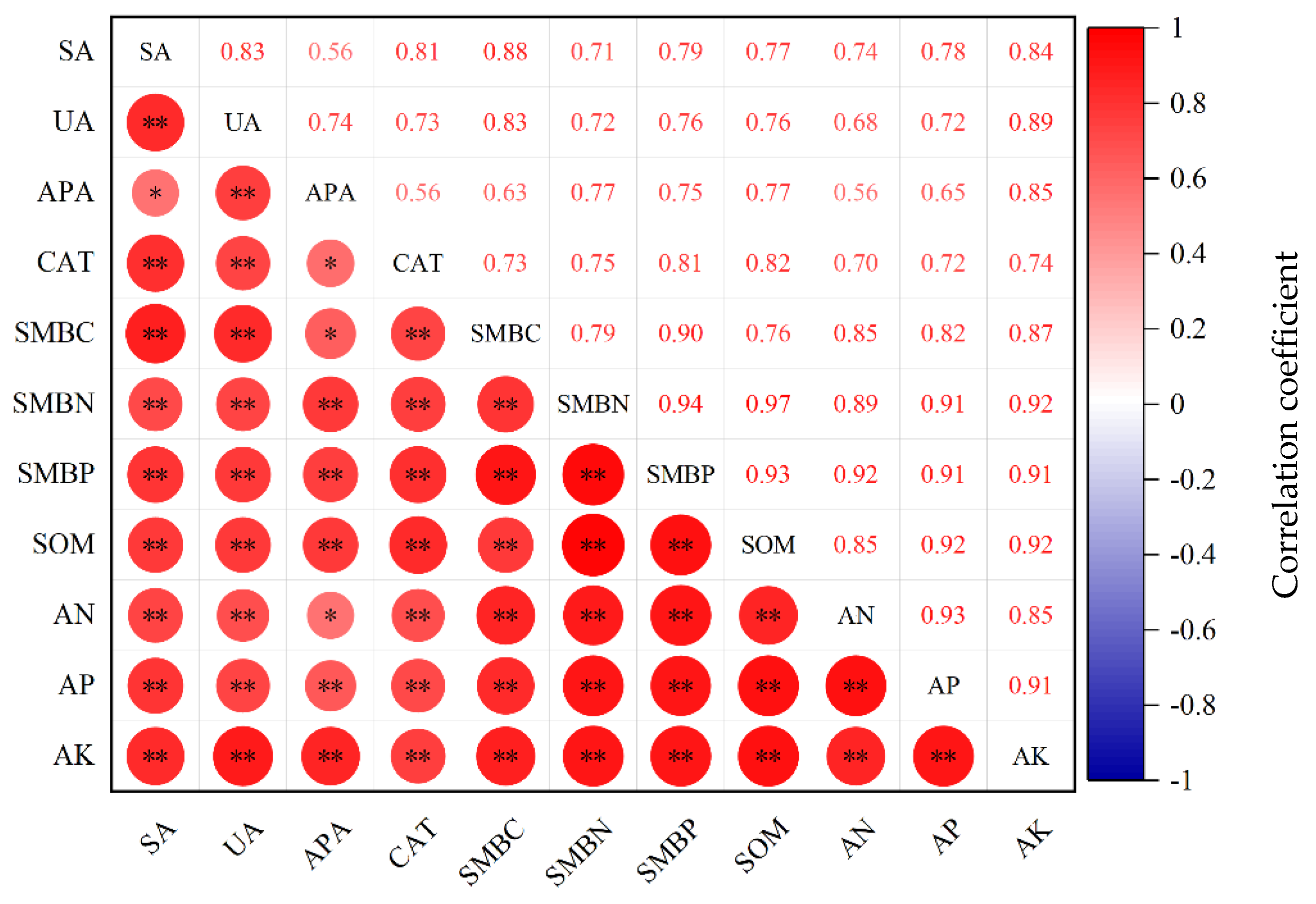
3.4. Correlation Analysis
3.5. Comprehensive Evaluation of Rhizosphere Soil
3.6. Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Legume–Gramineae Mixtures Grassland on Enzyme Activities in Rhizosphere Soil
4.2. Effects of Legume–Gramineae Mixed Grassland on Microbial Biomass in Rhizosphere Soil
4.3. Changes in Hay Yield and Soil Nutrients in Legume–Gramineae Mixed Grassland
4.4. Seasonal Changes in Soil Enzymes, Microbial Biomass, and Soil Nutrients in the Rhizosphere of Legume–Gramineae Mixed Grassland
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Y. Investigating the water, ecosystem, and agriculture nexus in three inland river basins of the arid Hexi Corridor, China, using integrated hydrological modeling. Hydrology 2025, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Ma, L.B.; Li, H.B.; Wang, X. Trends in the future evolution of rural settlements in oasis-desert areas under water use simulation scenarios: Take the Hexi Corridor region of China as an example. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2024, 248, 105110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Duan, Y.L.; Zhao, Z.X. Differences and spatial variations of plant leaf calorific value in deserts of the Hexi Corridor, Northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.M.; Zhong, Y.; Pan, C.C. Changes in soil nutrients and carbon properties in relation to grassland salinization. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 186, 012050. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Bai, Y.P.; Deng, X.Z.; Chen, J.C.; Hou, J.; Li, Z.H. Changes in livestock grazing efficiency incorporating grassland productivity: The case of Hulun Buir, China. Land 2020, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Liang, S.; Wu, X.H.; Zhong, Q.M.; Dong, S.K.; Wang, Y.F.; Yang, Z.F. Mitigating forage-livestock conflicts in China through economic structure transition. Cell Rep. Sustain. 2024, 1, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinyua, M.W.; Mucheru-Muna, M.W.; Bolo, P.; Kihara, J. Plant spatial configurations and their influences on phenological traits of cereal and legume crops under maize-based intercropping systems. J. Sustain. Agric. Environ. 2024, 3, 12110. [Google Scholar]
- Gintarė, Š.; Žydrė, K. The effect of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers on the quality of forage composed of various species of legumes in the northern part of a temperate climate zone. Plants 2023, 12, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, M.; Huguenin-Elie, O.; Lüscher, A. Multispecies for multifunctions: Combining four complementary species enhances multifunctionality of sown grassland. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3835. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen, J.; Askegaard, M.; Soegaard, K. Residual effect and nitrate leaching in grass-arable rotations: Effect of grassland proportion, sward type and fertilizer history. Soil Use Manag. 2008, 24, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.X.; Tewolde, H.; Liu, H.B.; Ren, T.Z.; Jiang, P.A.; Zhai, L.M.; Lei, B.K.; Lin, T.; Liu, E.K. Nitrogen uptake and transfer in broad bean and garlic strip intercropping systems. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhao, F.Y.; Sun, Z.X.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, C.; Cai, Q. Effects of Maize/Peanut intercropping on yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization under different nitrogen application rates. Agriculture 2024, 14, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.Y.; Yurkonis, K.A.; Wang, L.F.; Chang, J.C.; Vogeler, I.; Chen, D.M.; Liu, M.Q.; Yu, Q. Temporal stabilizing effects of species richness and seed arrangement on grassland biomass production. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, I.; Welty, A.; Blazewicz, S.; Bru, D.; Rouard, N.; Breuil, M.; Gessler, A.; Galiano, L.; Miranda, J.; Spor, A.; et al. Depth matters: Effects of precipitation regime on soil microbial activity upon rewetting of a plant-soil system. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Li, M.J.; Wu, J.C.; Pan, X.Y.; Gao, C.M.; Tang, D. Impact of combining long-term subsoiling and organic fertilizer on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen, soil enzyme activity, and water use of winter wheel. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 788651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, P.J.; Li, G.D.; Zhou, D.W. Grass-legume ratio can change soil carbon and nitrogen storage in a temperate steppe grassland. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 157, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.X.; Mu, L.; Yang, M.; Yang, H.M. Lucerne proportion regulates competitive uptake for nitrogen and phosphorus in lucerne and grass mixtures on the loess plateau of China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Wu, W.P.; Yang, H.M. Effects of legume–grass ratio on C and nutrients of root and soil in common vetch–oat mixture under fertilization. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.C.; Yiminijiang, A.; Li, R.X.; Wu, M.D.; Long, M.X.; Yang, P.Z.; He, S.B. Nutrient uptake and rhizosphere microbial community as related to yield advantage in broomcorn millet-alfalfa intercropping under different row configurations. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 2, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, A.; Samarappuli, D.; Berti, M. Alfalfa-grass mixtures in comparison to grass and alfalfa monocultures. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Li, C.H.; Zeng, T.R.; Xin, Y.F.; Chen, C.; Javed, H.H.; Yang, W.Y.; Yan, Y.H. Mixture composition influenced the biomass yield and nutritional quality of legume-grass pastures. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Z.W.; Yin, W.; Asibi, A.E.; Fan, Z.L.; Chai, Q.; Cao, W.D. Improving the sustainability of cropping systems via diversified planting in arid irrigation areas. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wang, H.; Xiu, W.M.; Zhao, J.N.; Liu, H.M.; Zhang, H.F.; Yang, D.L. Soil bacterial community composition is altered more by soil nutrient availability than pH following long-term nutrient addition in a temperate steppe. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 13, 1455891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurzhan, A.; Tian, H.; Nuralykyzy, B.; He, W. Soil enzyme activities and enzyme activity indices in long-term arsenic-contaminated soils. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2022, 55, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Bharti, P.; Das, A.; Kumar, S.; Rakshit, R. Assessment of soil specific enzyme activities in aggregates size actions: A case study from subtropical agro-ecosystem. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2024, 57, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Liu, X.C.; Boge, W.; Liu, X.P. Genome-wide association study identifies loci for salt tolerance during germination in autotetraploid alfalfa (Medicago sativa, L.) using genotyping-by-sequencing. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 28, 956. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, B.; Coulter, J.; Pagliari, P. Soil enzyme activity behavior after urea nitrogen application. Plants 2022, 11, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.H.; Gu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.H.; Huang, Q.R.; Shen, W.S. The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 511–522. [Google Scholar]
- Ngwenya, Z.D.; Mohammed, M.; Dakora, F.D. Monocropping and intercropping of maize with six food legumes at malkerns in eswatini: Their effects on plant growth, grain yield and N2 fixation, measured using the 15N natural abundance and ureide techniques. Orig. Pap. 2024, 92, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presti, E.L.; Badagliacca, G.; Custureri, I.M.G.; Preiti, G.; Santonoceto, C.; Bacchi, M.; Romeo, M.; Monti, M. The sowing ratio in legume intercropping regulates the facilitation of phosphorus uptake in wheat. Ital. J. Agron. 2024, 19, 100024. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.Y.; Guo, F.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, S.; Meng, J.J.; Li, X.G.; Wan, S.B. Single-seed sowing increased pod yield at a reduced seeding rate by improving root physiological state of Arachis hypogaea. J. Integr. Ative Agric. 2020, 19, 2095–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holatko, J.; Brtnicky, M.; Kintl, A.; Baltazar, T.; Malicek, O.; Mustafa, A.; Skladanka, J.; Kucerik, J.; Alamri, S.; Lochman, J.; et al. Effect of alfalfa-grass mixed culture and inoculation with Azotobacter and Rhizobium on soil biological properties and nutrient transformation activities. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 122, 103651. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.T.; Wang, L.F.; Liu, W.J.; Rihu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Forage mixed planting can effectively improve soil enzyme activity and microbial community structure and diversity in agro-pastoral interlacing arid zone. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 102, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.L.; Zhao, W.; Su, S.F.; Dong, Y.L.; Li, S.X. The changes of vegetation community characteristics led to the reconstruction of soil microbial communities and functions during the cultivation of degraded alpine meadows. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 4907–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.D.; Gu, D.Y.; Yang, H.T.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Zhan, N.B.; Cui, X.M. Effect of exogenous organic matter on phosphorus forms in middle-high fertility cinnamon soil. Plants 2024, 13, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Ncube, B.; Meyer, A.H.; Olatunji, O.S.; Mulidzi, R.; Lewu, F.B. Soil pH, nitrogen, phosphatase and urease activities in response to cover crop species, termination stage and termination method. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05980. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J.L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.T.; Li, C.N.; Han, J.R.; Yao, T. Inoculation of cold-adapted microbial consortium screened from alpine meadows promotes the growth of mixed grasses by changing soil properties and enzyme activity. Rhizosphere 2023, 28, 100782. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.H. The changes in anti-oxidant activity of roots in wintering period under single sowing of alfalfa and mixed sowing of alfalfa and Bromus inermis leyss. Asian Agric. Res. 2017, 2, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.F.; An, N. Effects of biochar and straw application on the physicochemical and biological properties of paddy soils in Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16531. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Chi, Y.K.; Song, S.Z. Important soil microbiota’s effects on plants and soils: A comprehensive 30-year systematic literature review. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1347745. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, N.J.; Suter, M.; Finn, J.A. Do belowground vertical niche differences between deep- and shallow-rooted species enhance resource uptake and drought resistance in grassland mixtures? Plant Soil 2015, 394, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.Q.; Liu, J.; Gao, L.H. Carbon mineralization in the soils under different cover crops and residue management in an intensive protected vegetable cultivation. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 127, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Deng, J.Q.; Wang, T.F.; Ni, W.; Feng, Q.; Lan, J. Effect of seeding options on interspecific competition in Oat (Avena sativa, L.)–Common Vetch (Vicia sativa, L.) forage crops. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Tahir, M.; Li, C.H.; Chen, C.; Xin, Y.F.; Zhang, G.J.; Cheng, M.J.; Yan, Y.H. Mixture of alfalfa, orchardgrass, and tall fescue produces greater biomass yield in southwest China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.L.; Gu, S.S.; Li, S.Z.; Shen, W.L.; Zhou, X.L.; Yu, H.; Ma, K.; Zhao, Y.G.; Wang, Y.C.; Zheng, H.; et al. Grass-legume mixtures enhance forage production via the bacterial community. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 338, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Wei, X.; Liu, H.P.; Li, J.Y.; Zhou, J.Q.; Kang, B.; Jiang, D.M.; Yan, Y.H. Mixed legume-grass seeding and nitrogen fertilizer input enhance forage yield and nutritional quality by improving the soil enzyme activities in Sichuan, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1176150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Chen, G.; Yang, Y.D.; Zeng, Z.H.; Hu, Y.G.; Zang, H.D. Sowing ratio determines forage yields and economic benefits of oat and common vetch intercropping. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Q.P.; Miao, F.H. Forage yield, competition, and economic indices of oat and common vetch intercrops in a semi-arid region. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 20, 1385296. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, G.X.; Shen, Q.R.; Cao, J.L. Nitrogen fixation and N transfer from peanut to rice cultivated in aerobic soil in an intercropping system and its effect on soil N fertility. Plant Soil 2004, 263, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Perotti, E.; Huguenin-Elie, O.; Meisser, M.; Dubois, S.; Probo, M.; Mariotte, P. Climatic, soil, and vegetation drivers of forage yield and quality differ across the first three growth cycles of intensively managed permanent grasslands. Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 122, 126194. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.H.; Li, B.B.; Tan, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.J.; Wang, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.K.; Li, J. Double advantages of nutrients and biotimulants derived from sewage sludge by alkaline thermal hydrolysis process for agricultural use: Quality promotion of soil and crop. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2307793. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F.; Liu, W.H.; Mi, W.B.; Ma, X.; Liu, K.Q.; Ju, Z.L.; Li, W. Legume-grass mixtures increase forage yield by improving soil quality in different ecological regions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1280771. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.Y.; Huan, H.; Zhang, W.J.; Wan, B.; Sun, J.M.; Tu, Z.P. Soil infiltration mechanisms under plant root disturbance in arid and semi-arid grasslands and the response of solute transport in rhizosphere soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.J.; Cao, Y.X.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.Z.; Peng, Y.Y.; Shao, Q.W.; Dan, Q.; Xu, Y.C.; Chen, X.Y.; Dang, P.; et al. Soil nutrients, enzyme activities, and microbial communities along a chronosequence of Chinese Fir plantations in subtropical China. Plants 2023, 12, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Ma, J.W.; Li, Y.J.; Shen, X.Y.; Xia, X.H. Microbial community and enzyme activity respond differently to seasonal and edaphic factors in forest and grassland ecosystems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 194, 105167. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Hu, J.Q.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chi, D.C. Effects of supplemental irrigation on water and nitrogen use, yield, and kernel quality of peanut under nitrogen-supplied conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.N.; Han, S.C.; Gao, J.L.; Yu, X.F.; Hu, S.P. Low-temperature corn straw-degrading bacterial agent and moisture effects on indigenous microbes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 5241–5255. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, T.L.; Augusto, L.; Tian, Y.; Wanek, W.; Fanin, N. Water availability is a stronger driver of soil microbial processing of organic nitrogen than tree species composition. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 71, 13350. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Shuang, Z.H.; Liu, X.L.; Yin, P.J.; Lan, T.Q.; Feng, D.J.; Yuan, J.C.; Kong, F.L. Soil amendment incorporation increases organic carbon by improving soil agglomerate and soil microbial biomass carbon in the alpine grassland. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 23, 13080. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Rong, Y.P.; Li, P.Z.; Liu, Y.L. Soil moisture drives the response of soil microbial nutrient limitation to N and P additions in an Inner Mongolian meadow steppe. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 120, 103601. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.Y.; Fang, F.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, S.Y.; Qiao, J.B.; Han, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Liu, W.Z. A mosaic pattern of apple orchards and farmland affects the distribution of soil water and nutrients in their adjacent areas on the Chinese Loess Plateau. CATENA 2024, 237, 107776. [Google Scholar]




| Cropping Patterns | Treatments |
|---|---|
| Single cropping | GN3, GN9, JN7, LC, AC, BI |
| Mixture cropping | GN3 + LC, GN3 + AC, GN3 + BI, GN9 + LC, GN9 + AC GN9 + BI, JN7 + LC, JN7 + AC, JN7 + BI |
| Treatments | The First Mowing/(kg/hm2) | The Second Mowing/(kg/hm2) | The Third Mowing/(kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GN3 + LC | 6020 ± 193.7 FG | 2743 ± 154.3 G | 2193 ± 95.6 F |
| GN3 + AC | 6548 ± 81.0 D | 3325 ± 82.5 E | 1999 ± 31.1 G |
| GN3 + BI | 7532 ± 71.2 BC | 4111 ± 202.8 C | 3000 ± 146.3 D |
| GN3 | 7667 ± 389.3 B | 5227 ± 202.1 A | 4350 ± 32.7 A |
| GN9 + LC | 7450 ± 313.2 BC | 3696 ± 73.7 D | 3830 ± 146.1 C |
| GN9 + AC | 6240 ± 29.9 EF | 3317 ± 74.3 E | 2442 ± 124.4 E |
| GN9 + BI | 8180 ± 154.4 A | 4104 ± 140.5 C | 3910 ± 47.3 C |
| GN9 | 8261 ± 80.7 A | 4974 ± 94.3 B | 4268 ± 192.5 AB |
| JN7 + LC | 5770 ± 221.1 G | 3462 ± 59.3 E | 3002 ± 31.2 D |
| JN7 + AC | 6474 ± 195.0 DE | 2497 ± 52.7 H | 2920 ± 50.6 D |
| JN7 + BI | 7307 ± 257.5 C | 3133 ± 56.9 F | 2454 ± 50.9 E |
| JN7 | 8060 ± 27.4 A | 5038 ± 77.2 B | 4119 ± 134.0 B |
| LC | 2464 ± 81.9 H | 997 ± 25.2 I | 506 ± 5.91 I |
| AC | 1277 ± 29.4 I | 428 ± 37.8 J | 277 ± 31.1 J |
| BI | 2463 ± 135.2 H | 819 ± 44.3 I | 666 ± 43.1 H |
| Treatments | Weighted Relevance Degree | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| GN3 + LC | 0.597 | 9 |
| GN3 + AC | 0.613 | 6 |
| GN3 + BI | 0.689 | 3 |
| GN3 | 0.548 | 11 |
| GN9 + LC | 0.719 | 2 |
| GN9 + AC | 0.604 | 8 |
| GN9 + BI | 0.744 | 1 |
| GN9 | 0.564 | 10 |
| JN7 + LC | 0.622 | 5 |
| JN7 + AC | 0.605 | 7 |
| JN7 + BI | 0.667 | 4 |
| JN7 | 0.523 | 12 |
| LC | 0.516 | 13 |
| AC | 0.485 | 15 |
| BI | 0.500 | 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Nan, L.; Wang, K. Effects of Alfalfa–Grass Mixed Sowing on Grass Yield and Rhizosphere Soil Characteristics. Agronomy 2025, 15, 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040830
Wu S, Nan L, Wang K. Effects of Alfalfa–Grass Mixed Sowing on Grass Yield and Rhizosphere Soil Characteristics. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):830. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040830
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Shiwen, Lili Nan, and Kun Wang. 2025. "Effects of Alfalfa–Grass Mixed Sowing on Grass Yield and Rhizosphere Soil Characteristics" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040830
APA StyleWu, S., Nan, L., & Wang, K. (2025). Effects of Alfalfa–Grass Mixed Sowing on Grass Yield and Rhizosphere Soil Characteristics. Agronomy, 15(4), 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040830






