Effects of Multi-Year Maize–Peanut Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on Rhizosphere Soil Properties and Root Morphological and Microbial Community Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
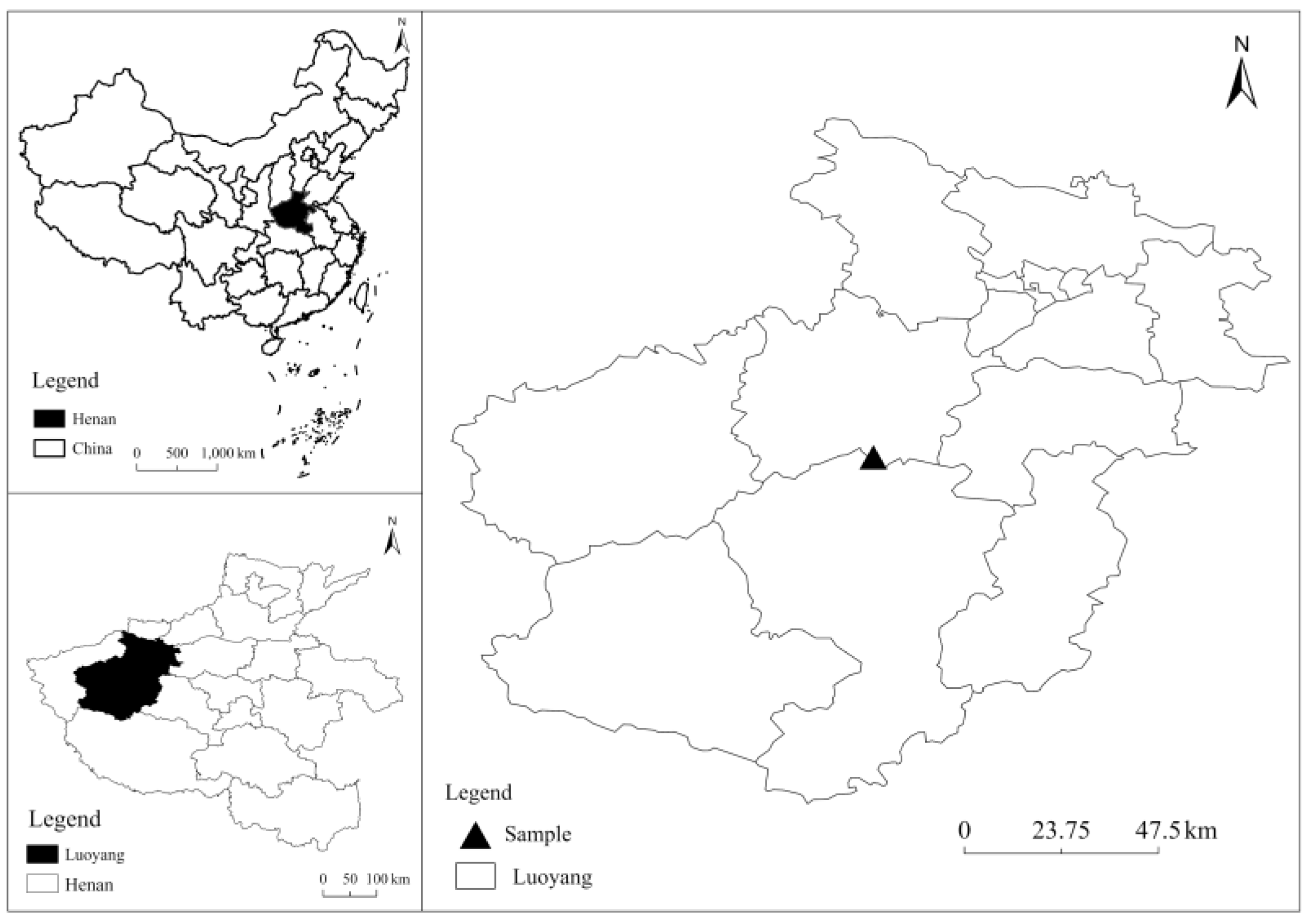
2.1. Experimental Site
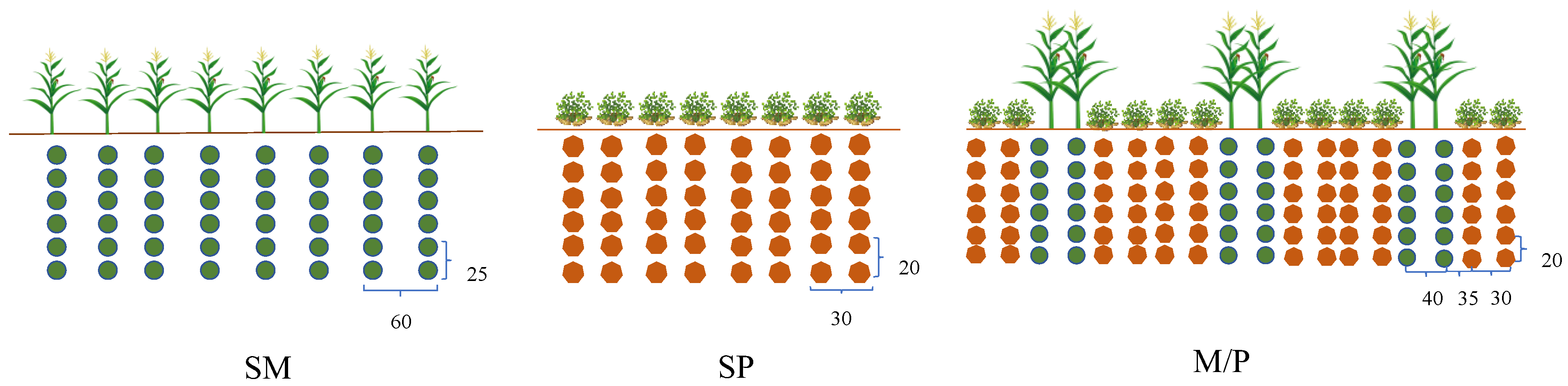
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Determination
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
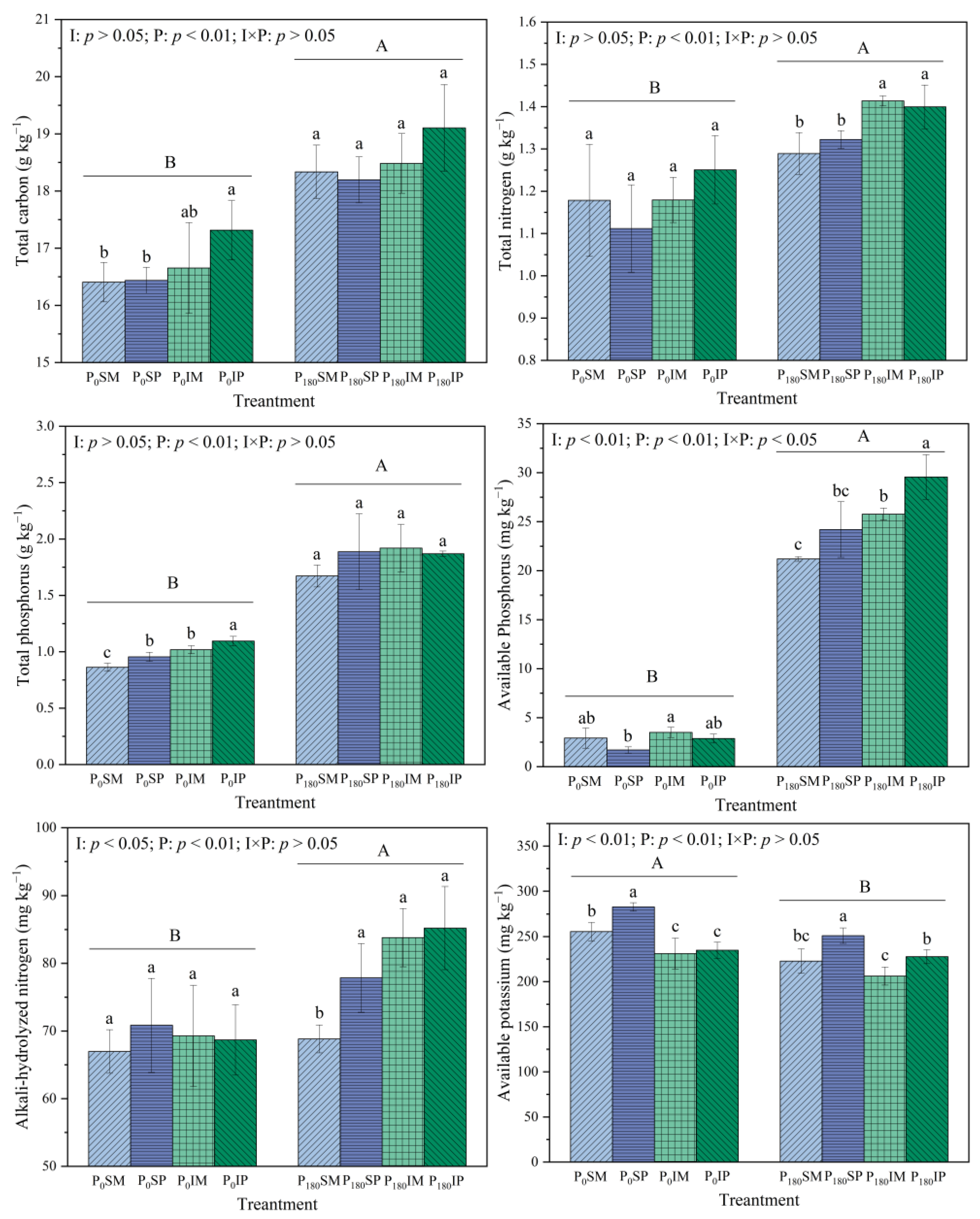
3.1. Effects of Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on the Basic Physicochemical Properties of Rhizosphere Soil
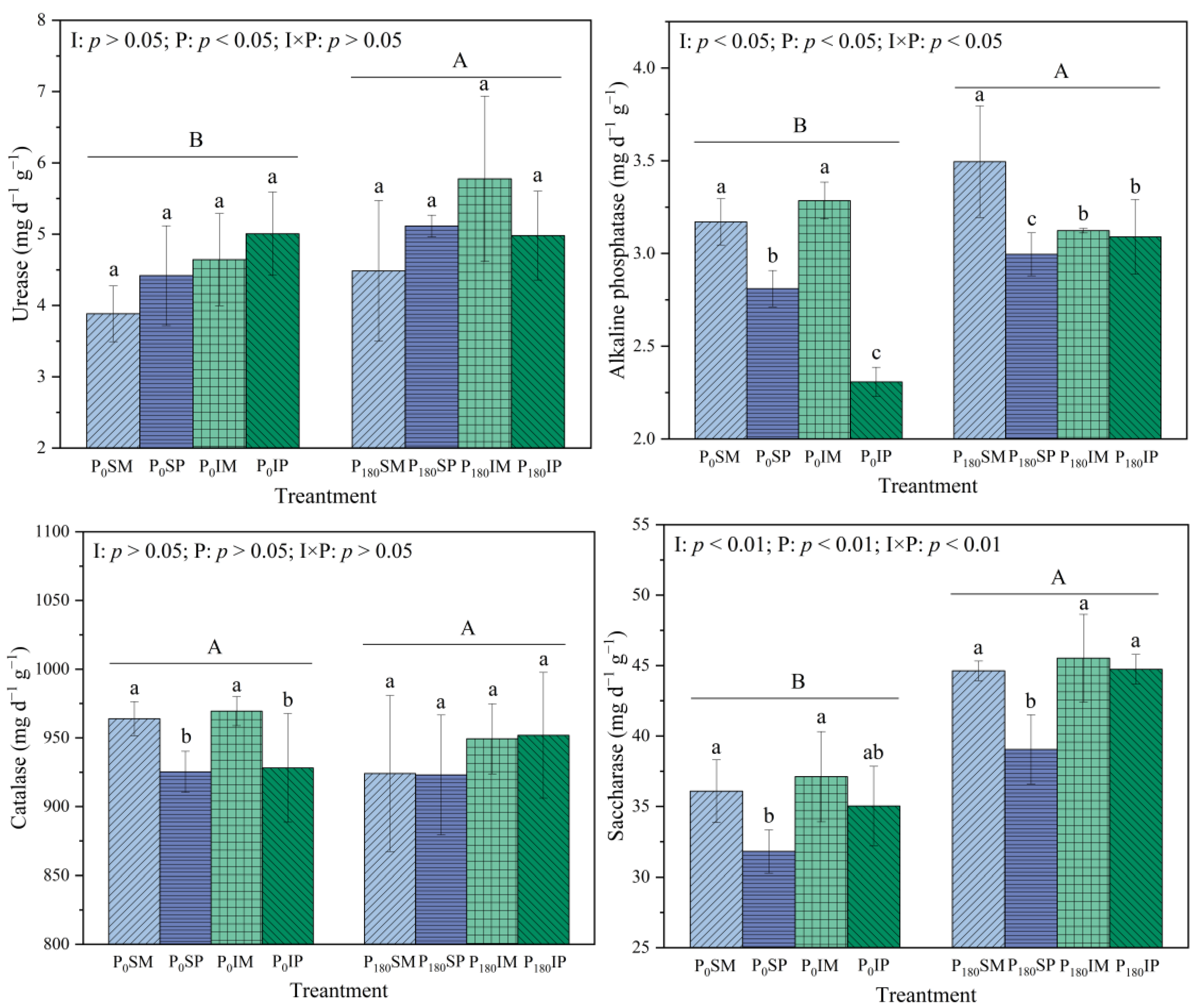
3.2. Effects of Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on the Enzyme Activity of Rhizosphere Soil
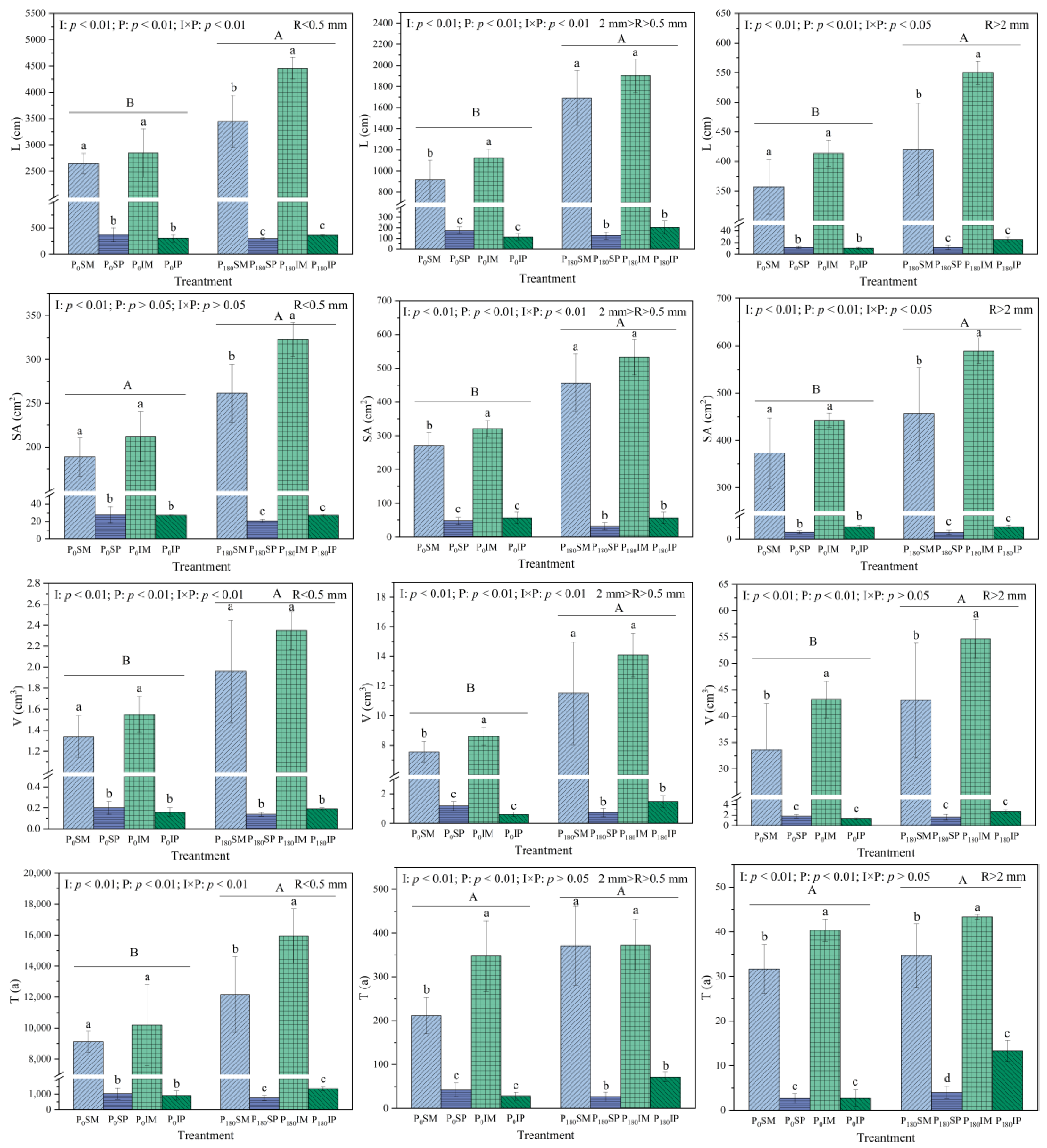
3.3. Effects of Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on the Root Morphological Characteristics of Maize and Peanut
3.4. Effects of Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on the Microbial Characteristics of Rhizosphere Soil
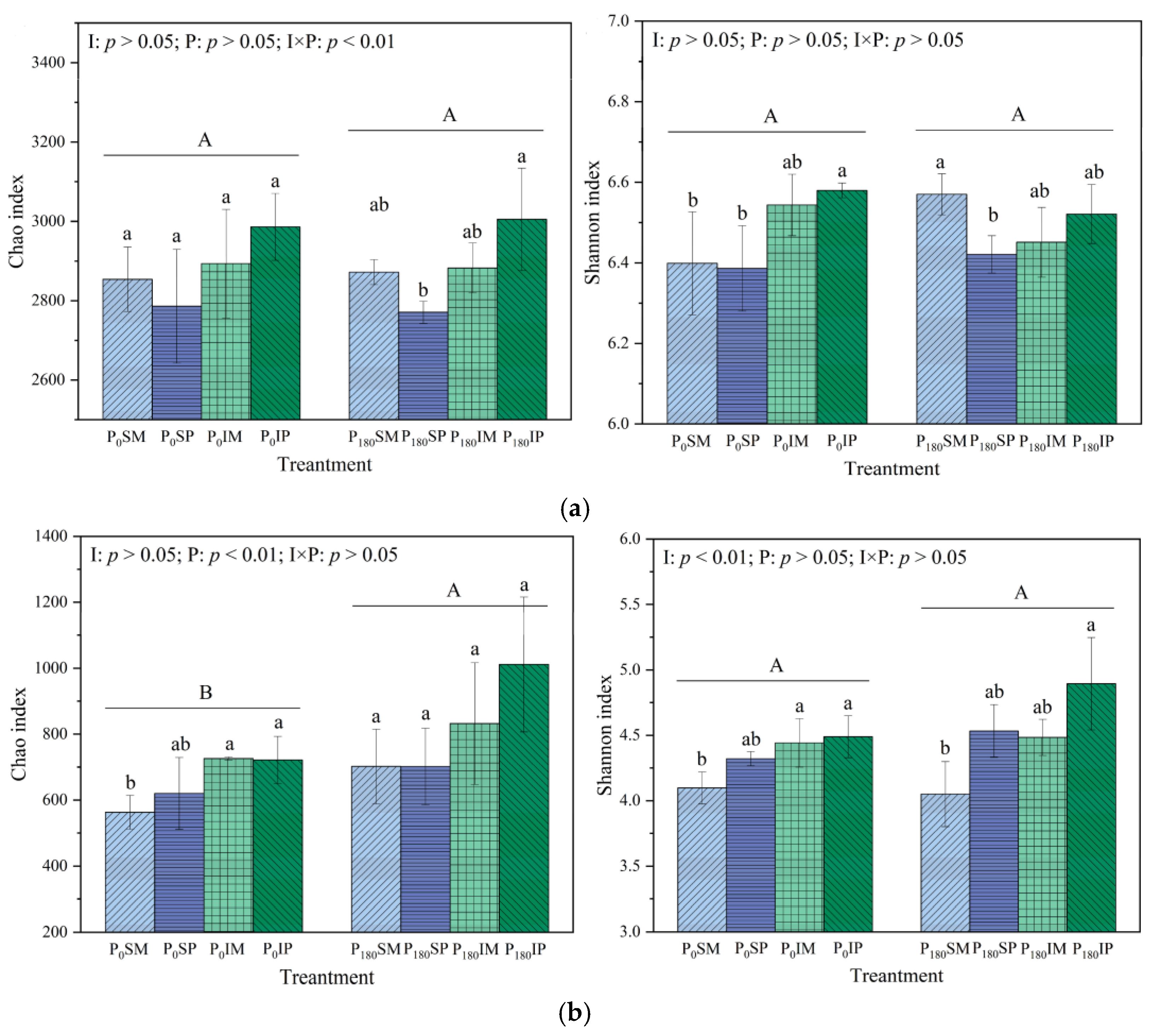
3.4.1. Effects of Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on Soil Microbial Diversity and Community Structure
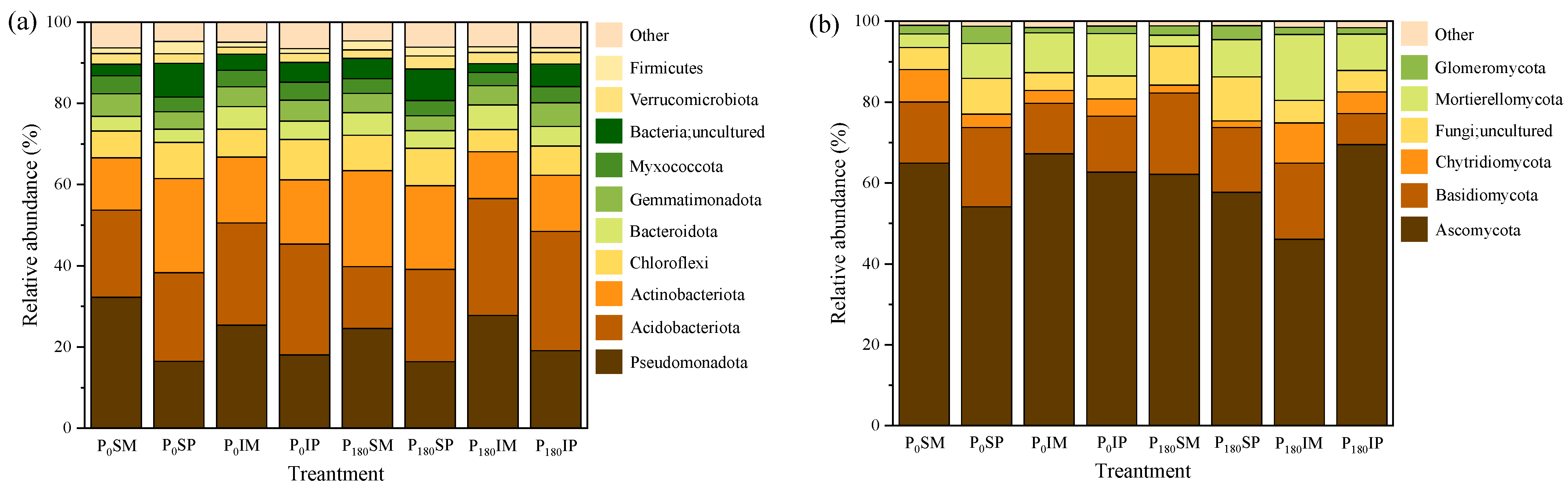
3.4.2. Effects of Intercropping and Phosphorus Fertilizer Application on Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community Composition
3.4.3. Effects of Intercropping and Phosphorus Fertilizer Application on Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community Co-Occurrence Networks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Bao, X.; Sun, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Tian, X.; et al. Long-term increased grain yield and soil fertility from intercropping. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 943–950. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, X.; Li, Z.; Sui, P.; Gao, W.; et al. The yield performance of maize-soybean intercropping in the North China Plain: From 172 sites empirical investigation. Field Crop Res. 2024, 315, 109467. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, E.; Carlsson, G.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H. Intercropping of grain legumes and cereals improves the use of soil N resources and reduces the requirement for synthetic fertilizer N: A global-scale analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2000, 40, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, N.; Wang, T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Rhizosphere bacteriome structure and functions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 836. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liao, D.; Rengel, Z.; Shen, J. Soil-plant-microbe interactions in the rhizosphere: Incremental amplification induced by localized fertilization. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2025, 12, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Taschen, E.; Amenc, L.; Tournier, E.; Deleporte, P.; Malagoli, P.; Fustec, J.; Bru, D.; Philippot, L.; Bernard, L. Cereal-legume intercropping modifies the dynamics of the active rhizospheric bacterial community. Rhizosphere 2017, 3, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, X.; Du, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Xiao, T.; Li, L.; et al. Maize-legume intercropping promote N uptake through changing the root spatial distribution, legume nodulation capacity, and soil N availability. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 1755–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Lai, H.; Su, H.; Chapman, S.; Li, Y.; Yao, H. Characterization of microbial communities assimilating rhizosphere-deposited carbon in a soybean/maize intercropping system using the DNA-SIP technique. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2024, 60, 927–939. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, X.; Qin, S.; Kang, Y. Legume-potato rotation affects soil physicochemical properties, enzyme activity, and rhizosphere metabolism in continuous potato cropping. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Dang, K.; Gong, X.; Feng, B. Effects of intercropping on rhizosphere microbial community structure and nutrient limitation in proso millet/mung bean intercropping system. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 122, 103646. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Shen, J.; van der Werf, W.; Zhang, F. Intercropping legumes and cereals increases phosphorus use efficiency; a meta-analysis. Plant Soil 2021, 460, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, S.; Cen, Z.; Dong, Y. Faba bean-wheat intercropping controls the occurrence of faba bean Fusarium wilt by improving the microecological environment of rhizosphere. Soil Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 123, 103685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdtner, U.; Spohn, M. Plant Species Interactions in the Rhizosphere Increase Maize N and P Acquisition and Maize Yields in Intercropping. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2022, 22, 3868–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshita, A.; Feng, Y.; Qian, R.; Wang, X.; Khan, W.; Gao, Y. Alfalfa and maize intercropping enhances soil nematode structure and food web complexity in low-nitrogen soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 186, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Chen, P.; Du, Q.; Pang, T.; Song, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, W.; Yong, T. Effects of maize-soybean relay intercropping on crop nutrient uptake and soil bacterial community. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2006–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Bezemer, T.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Li, L. Interspecific interactions between crops influence soil functional groups and networks in a maize/soybean intercropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 355, 108595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, H.; Vandana, S.; Sharma, S.; Pandey, R. Phosphorus Nutrition: Plant Growth in Response to Deficiency and Excess. In Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Lu, H.; Mao, C. Phosphate uptake and transport in plants: An elaborate regulatory system. Plant Cell Physiol. 2021, 62, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.; Terrer, C.; Pellegrini, A.; Ahlström, A.; van Lissa, C.; Zhao, X.; Xia, N.; Wu, X.; Jackson, B. Global patterns of terrestrial nitrogen and phosphorus limitation. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Lou, L.; Bai, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, N. Phosphorus deficiency is the main limiting factor for re-vegetation and soil microorganisms in Mu Us Sandy Land, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; Zheng, J.; Bai, W.; Gu, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; van der Werf, W. Maize/peanut intercropping increases land productivity: A meta-analysis. Field Crop. Res. 2021, 270, 108208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Feng, C.; Du, G.; Feng, L.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yang, J.; Li, C. Intercropping maize and peanut under semi-arid conditions is a zero-sum game. Field Crop Res. 2025, 326, 109833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hou, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, W.; Cai, J.; An, S. Long-term intercropping shaped soil bacterial microbiome composition and structure of maize fields in a semiarid region. Soil Till. Res. 2025, 247, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, N.; Wang, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, C.; Guo, D.; Zhang, F.; Jensen, E. The importance of aboveground and belowground interspecific interactions in determining crop growth and advantages of peanut/maize intercropping. Crop J. 2021, 9, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, Z.; Jiao, N.; Ma, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ning, T.; Zheng, B.; Liu, L.; Zhao, X.; Cong, W. Long-Term maize intercropping with peanut and phosphorus application maintains sustainable farmland productivity by improving soil aggregate stability and P availability. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Yang, T.; Xia, S.; Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Sun, R.; Gao, H.; Chu, H.; Ma, C. Soil depth exerts stronger impact on bacterial community than elevation in subtropical forests of Huangshan Mountain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agriculture Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dagnall, R.; Kirkbright, G.; West, T.; Wood, R. Multichannel atomic fluorescence and flame photometric determination of calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, potassium, and zinc in soil extracts. Anal. Chem. 1971, 43, 1765–1769. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Vivanco, J.; Shen, Q. The unseen rhizosphere root–soil–microbe interactions for crop production. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 37, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, P.; Feng, B. Responses of rhizosphere soil properties, enzyme activities and microbial diversity to intercropping patterns on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 195, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yu, N.; Zhao, S.; Kou, T.; Jiao, N. Effects of long-term maize-peanut Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on C-N-P Content and Stoichiometry in soil Aggregates. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mastro, F.; Brunetti, G.; Traversa, A.; Blagodatskaya, E. Fertilization promotes microbial growth and minimum tillage increases nutrient-acquiring enzyme activities in a semiarid agro-ecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 177, 104529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, Z.; Muhammad, I.; Chi, Y.; Zhou, X. Straw incorporation and nitrogen fertilization regulate soil quality, enzyme activities and maize crop productivity in dual maize cropping system. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 729. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, Q.; Yao, S.; Chen, Q.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H.; Li, C. Controlled-release phosphate fertilizer improves soil fertility and soybean productivity by regulating soil microbial diversity and composition and increasing enzyme activities. Field Crop Res. 2025, 325, 109836. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Liu, T.; Shen, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W. Effect of Maize (Zeal mays) and soybean (Glycine max) intercropping on yield and Root Development in Xinjiang, China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, L.; Yang, W. The plasticity of root distribution and nitrogen uptake contributes to recovery of maize growth at late growth stages in wheat/maize intercropping. Plant Soil 2020, 447, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Reich, P.; Trivedi, C.; Eldridge, D.; Abades, S.; Alfaro, F.; Bastida, F.; Berhe, A.; Cutler, N.; Gallardo, A. Multiple elements of soil biodiversity drive ecosystem functions across biomes. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 210–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, J.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; Luo, G. Crop rotation-driven changes in rhizosphere metabolite profiles regulate soil microbial diversity and functional capacity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 358, 108716. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, J.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; Yin, L.; Zhou, X.; Luo, G. Enhanced productivity of maize through intercropping is associated with community composition, core species, and network complexity of abundant microbiota in rhizosphere Soil. Geoderma 2024, 442, 116786. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Su, N.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, L.; Peng, J.; Rong, X.; Luo, G. Knowledge-based phosphorus input levels control the link between soil microbial diversity and ecosystem functions in paddy fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 28, 109352. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Ran, J.; Dong, L.; Du, Q.; Ji, M.; Yao, S.; Sun, Y.; Gong, C.; Hou, Q.; Gong, H.; et al. Aridity-driven shift in biodiversity-soil multifunctionality relationships. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5350. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Hu, X.; Liu, Q.; Yin, C. Soil fungi are more sensitive than bacteria to short-term plant interactions of Picea asperata and Abies faxoniana. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2021, 106, 103348. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Xu, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Soil microbial composition, diversity, and network stability in intercropping versus monoculture responded differently to drought. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 365, 108915. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Gao, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Phosphorus fertilizer input threshold shifts bacterial community structure and soil multifunctionality to maintain dryland wheat production. Soil Till. Res. 2024, 243, 106174. [Google Scholar]



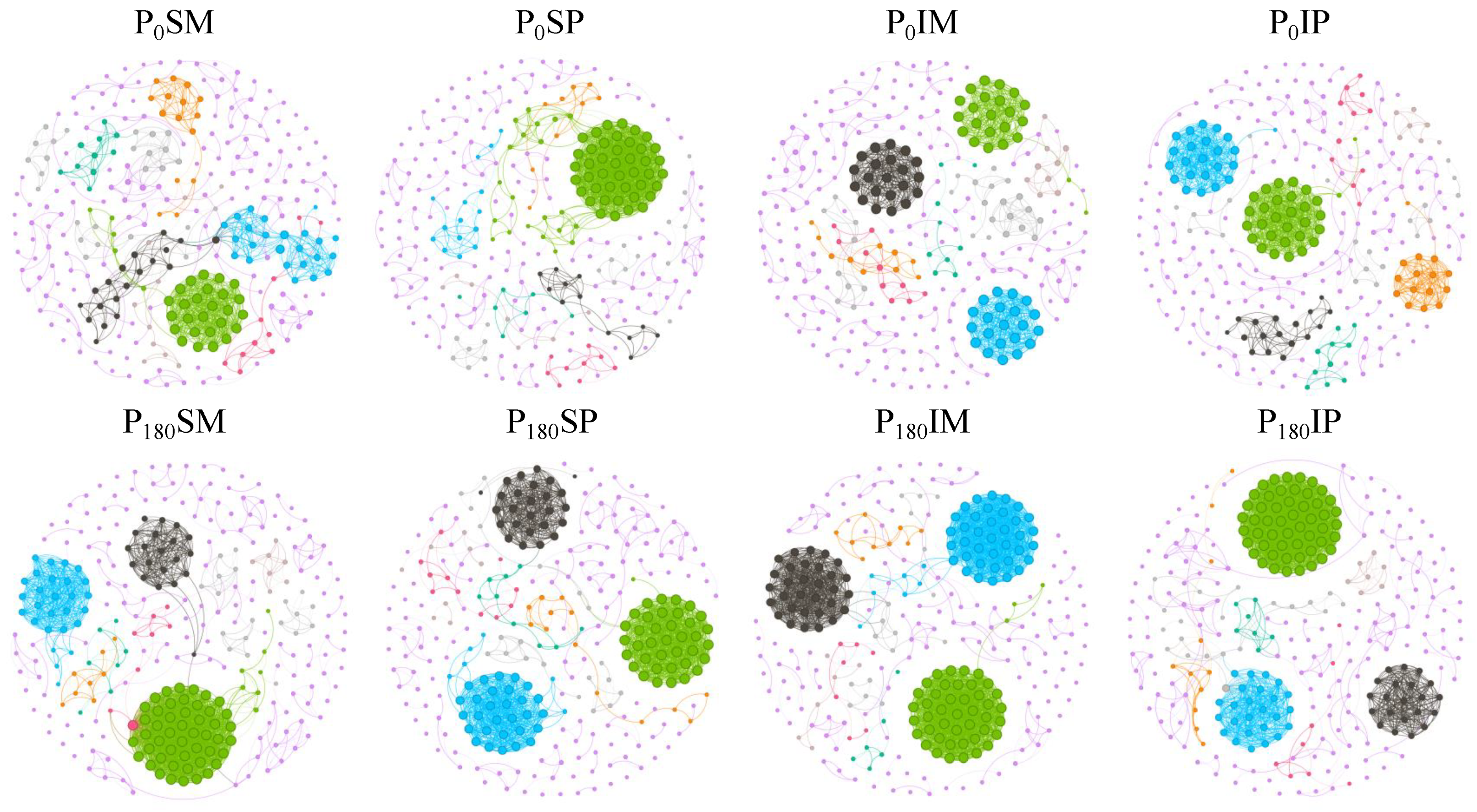
| Treatment | Node | Edge | Positive Correlative (%) | Negative Correlative (%) | Modularity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0SM | 281 | 506 | 44.40 | 55.60 | 1.306 |
| P0SP | 283 | 463 | 51.98 | 48.02 | 0.691 |
| P0IM | 281 | 517 | 65.18 | 34.82 | 1.964 |
| P0IP | 284 | 529 | 55.01 | 44.99 | 4.93 |
| P180SM | 289 | 581 | 53.61 | 46.39 | 3.144 |
| P180SP | 267 | 563 | 51.72 | 48.28 | 2.166 |
| P180IM | 282 | 608 | 55.83 | 44.17 | 4.137 |
| P180IP | 281 | 869 | 61.95 | 38.05 | 2.138 |
| Treatment | Node | Edge | Positive Correlative (%) | Negative Correlative (%) | Modularity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0SM | 277 | 926 | 76.72 | 23.28 | 0.519 |
| P0SP | 287 | 1023 | 90.55 | 9.45 | 0.531 |
| P0IM | 275 | 927 | 85.76 | 14.24 | 0.697 |
| P0IP | 281 | 1279 | 82.89 | 17.11 | 0.747 |
| P180SM | 276 | 1871 | 93.38 | 6.62 | 0.92 |
| P180SP | 273 | 1584 | 89.97 | 10.03 | 0.355 |
| P180IM | 265 | 2227 | 95.69 | 4.31 | 1.033 |
| P180IP | 273 | 2103 | 89.06 | 10.94 | 0.862 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, R.; Zan, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, S.; Kou, T.; Jiao, N. Effects of Multi-Year Maize–Peanut Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on Rhizosphere Soil Properties and Root Morphological and Microbial Community Characteristics. Agronomy 2025, 15, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040913
Ma R, Zan Z, Wang C, Zhao S, Kou T, Jiao N. Effects of Multi-Year Maize–Peanut Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on Rhizosphere Soil Properties and Root Morphological and Microbial Community Characteristics. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040913
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Rentian, Zhiman Zan, Chunli Wang, Shiwei Zhao, Taiji Kou, and Nianyuan Jiao. 2025. "Effects of Multi-Year Maize–Peanut Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on Rhizosphere Soil Properties and Root Morphological and Microbial Community Characteristics" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040913
APA StyleMa, R., Zan, Z., Wang, C., Zhao, S., Kou, T., & Jiao, N. (2025). Effects of Multi-Year Maize–Peanut Intercropping and Phosphorus Application on Rhizosphere Soil Properties and Root Morphological and Microbial Community Characteristics. Agronomy, 15(4), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040913






