Dosages of Biodegradable Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Microplastics Affect Soil Microbial Community, Function, and Metabolome in Plant–Soil System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil and Plant Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Plant Growth Evaluation
2.5. Soil DNA Extraction, Metagenomic Sequencing, and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.6. Non-Targeted Metabolome Detection for Soils and Data Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
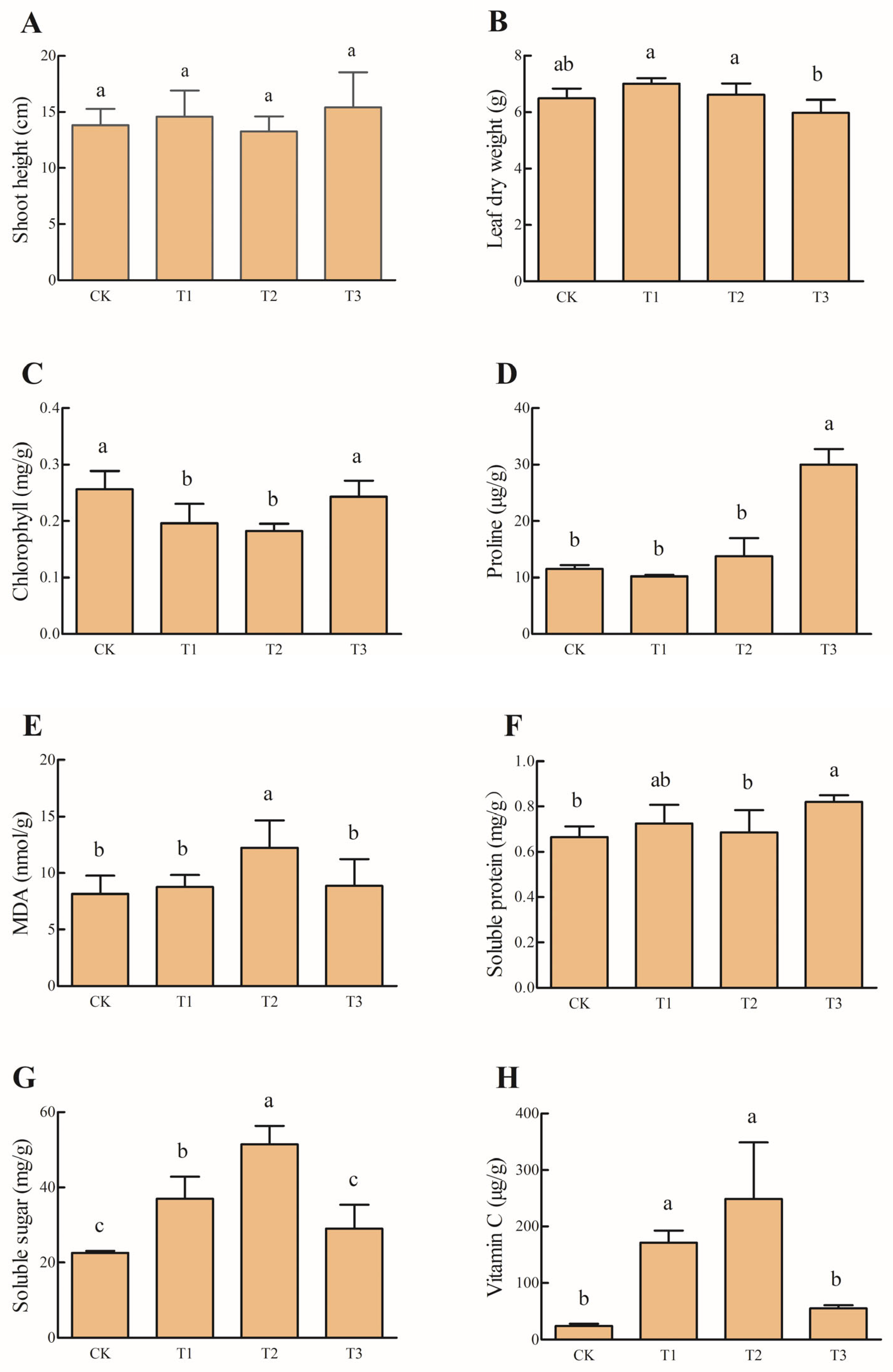
3.1. Effects of PBAT MP Concentration on Plant Growth
3.2. Effects of PBAT MP Concentration on Soil Properties
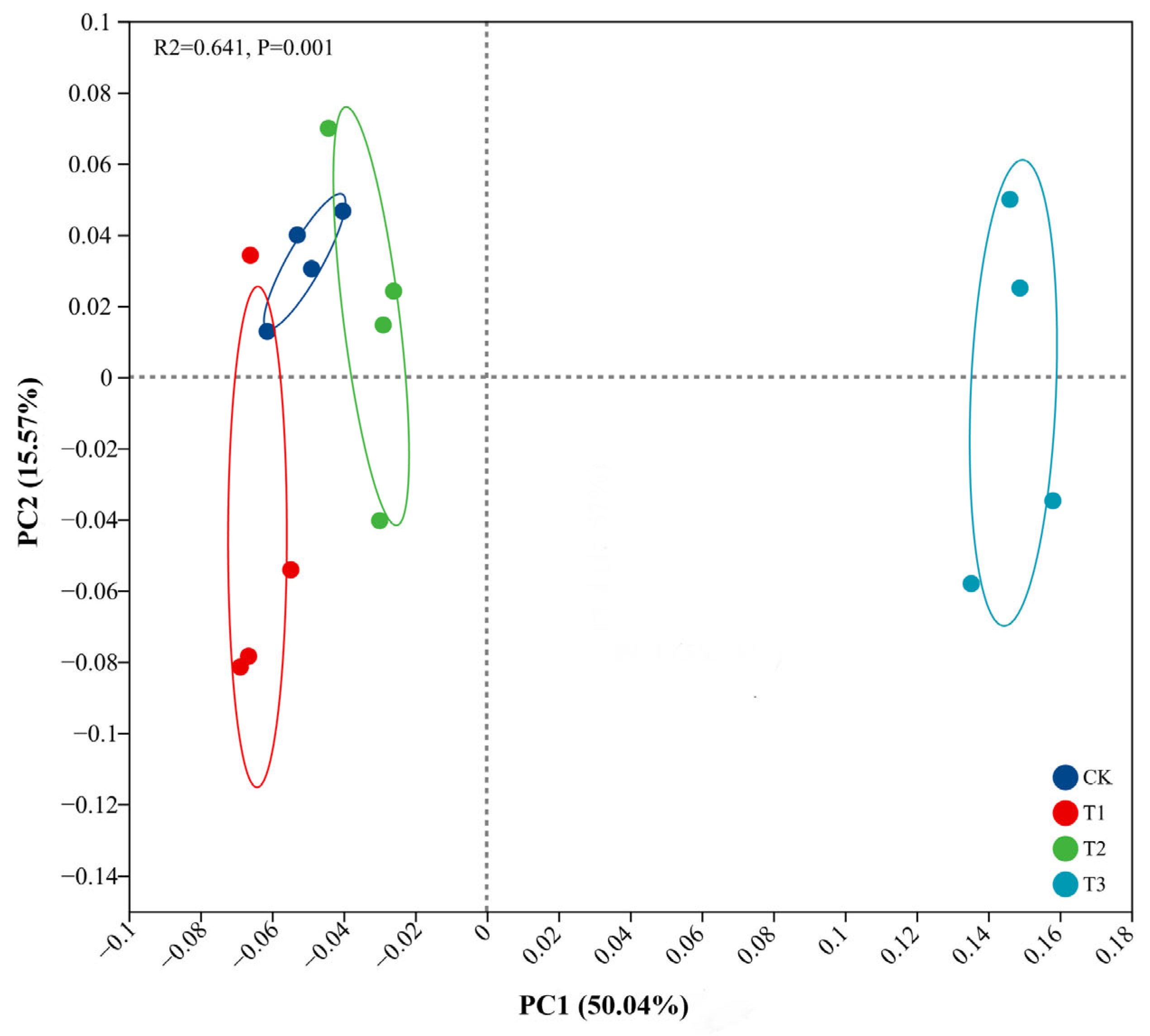
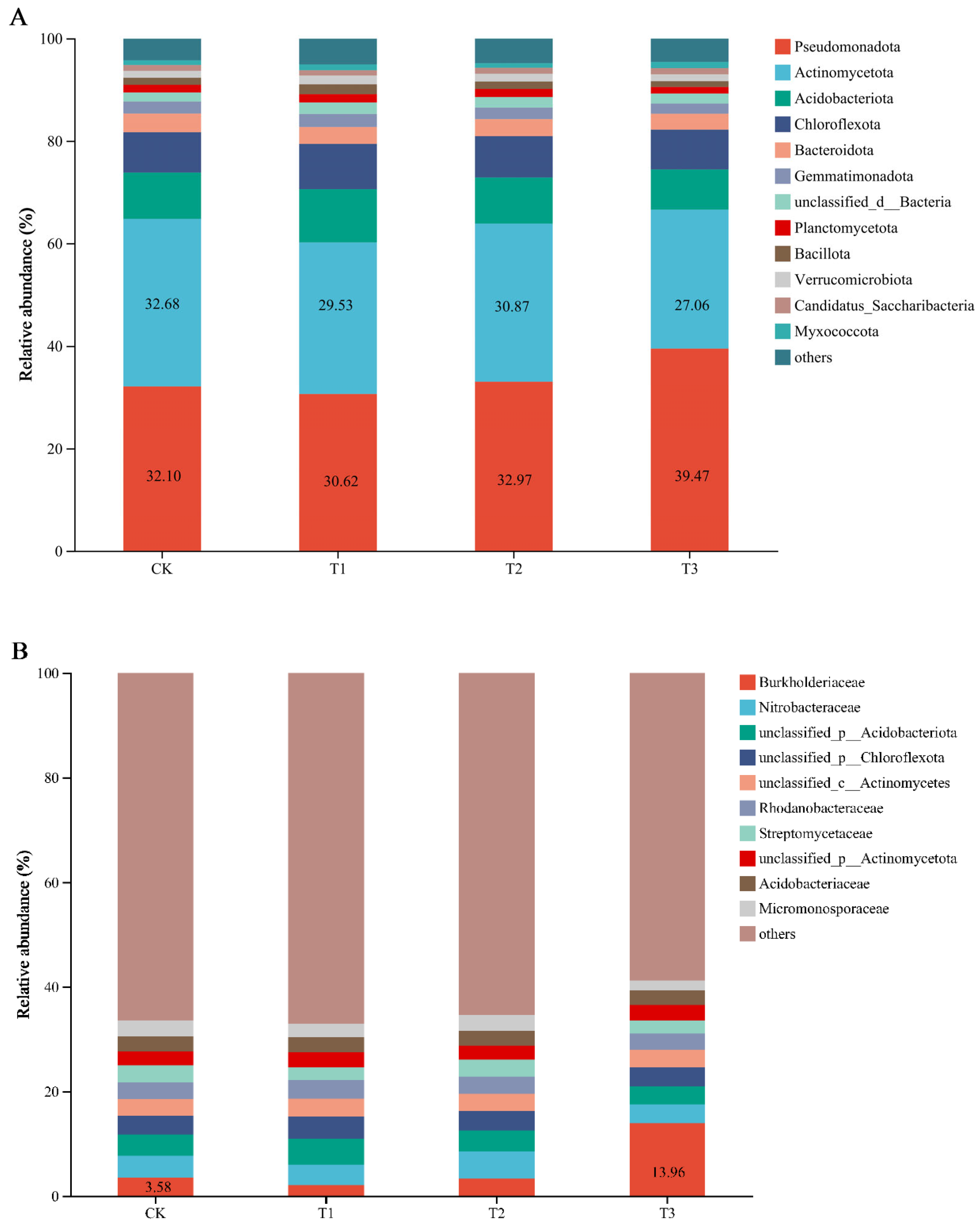
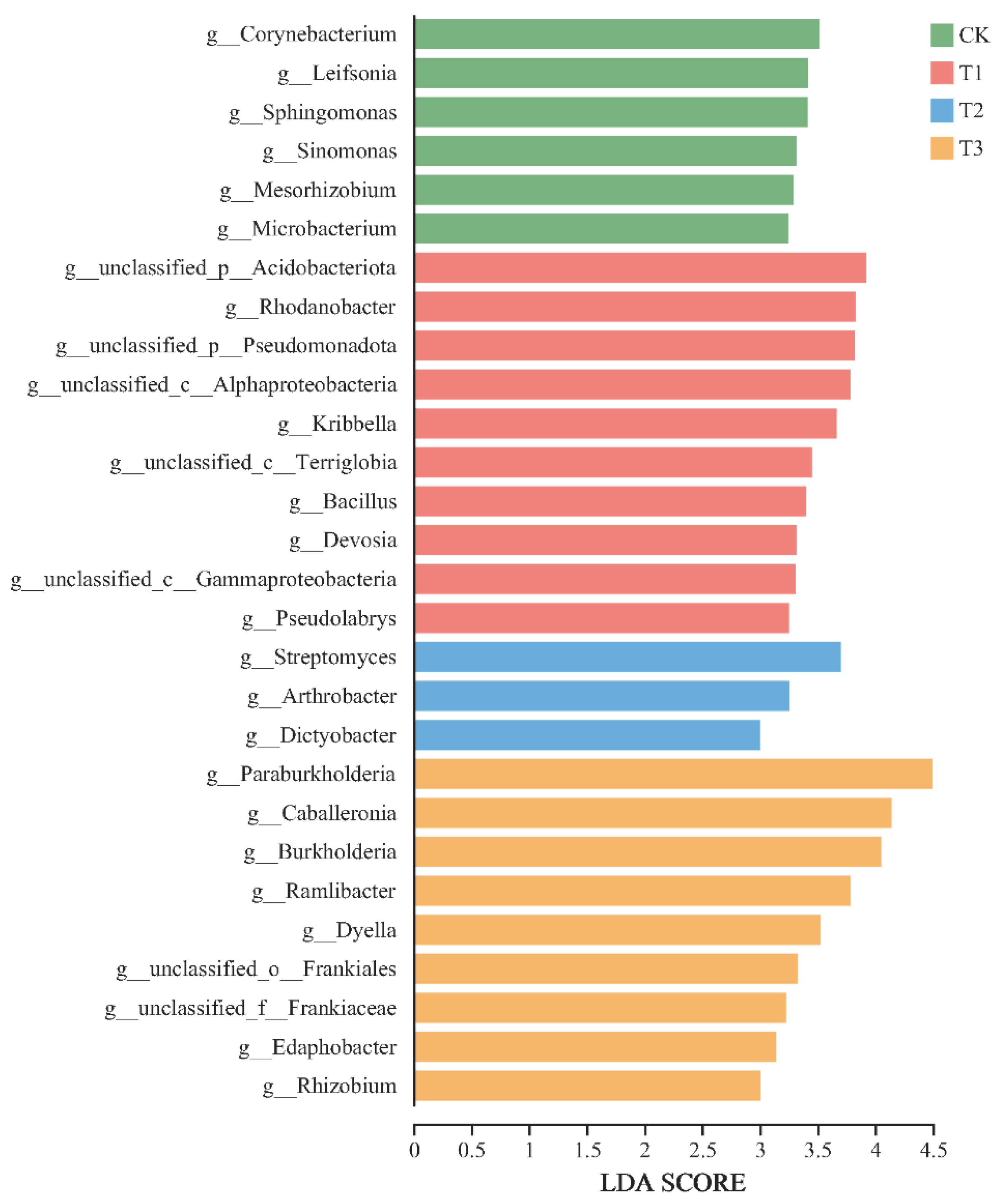
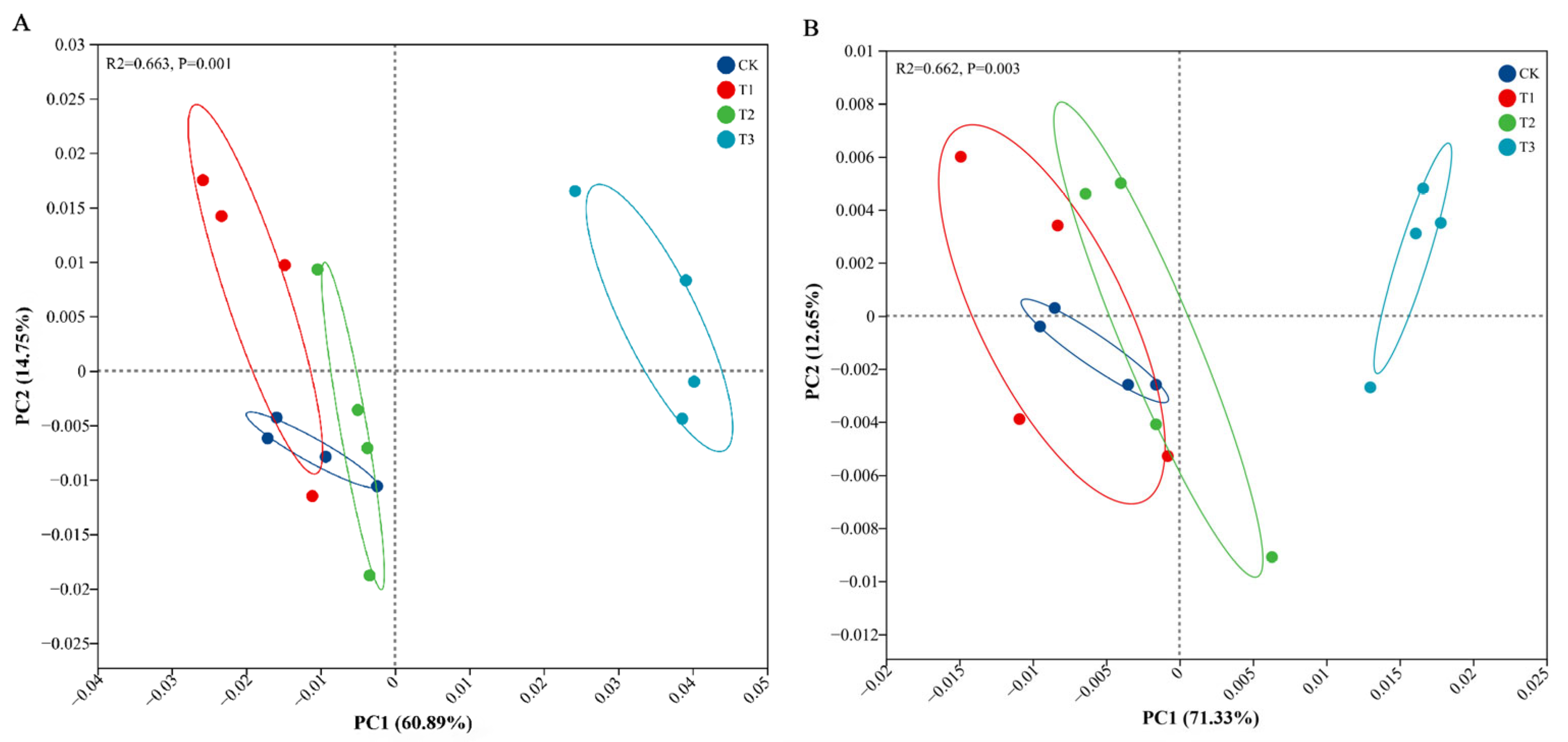
3.3. Soil Microbial Compositions and Diversity Under PBAT Addition
3.4. Response of Soil Microbial Function to PBAT
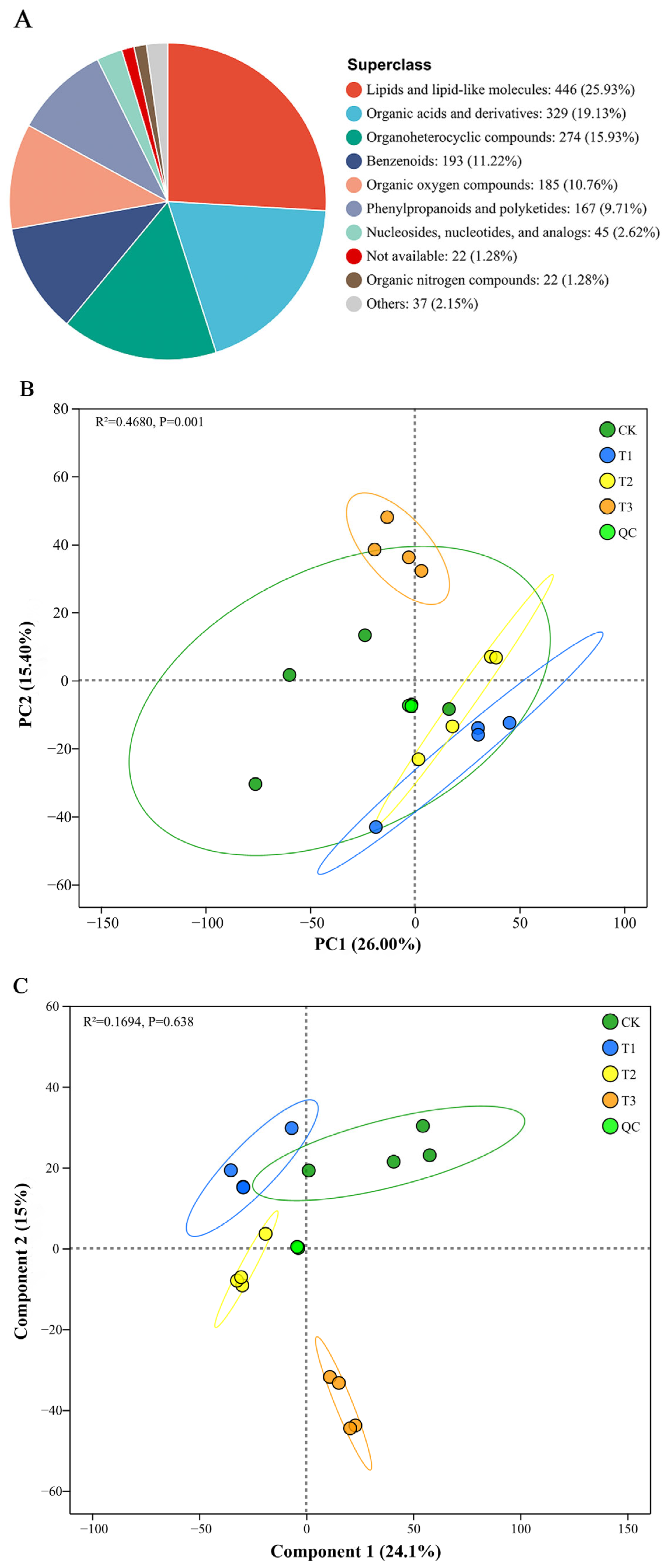
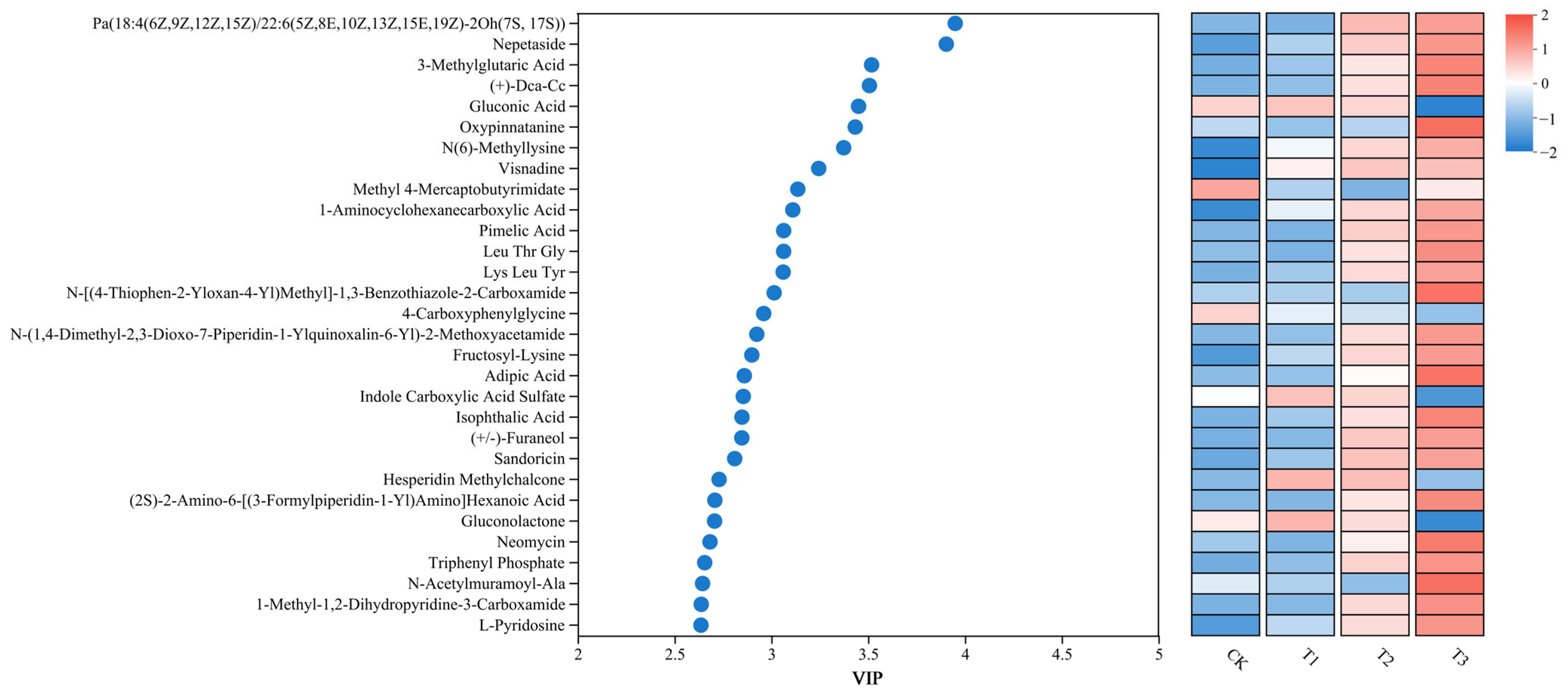
3.5. PBAT Dosages Altered Soil Metabolome Characteristics
3.6. Relationships Among Soil Properties, Microbial Communities, and Metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kader, M.A.; Senge, M.; Mojid, M.A.; Ito, K. Recent advances in mulching materials and methods for modifying soil environment. Soil Till. Res. 2017, 168, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Li, S.; Lü, X.T.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Schaeffer, S.; An, T.; Pei, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, J. Opposite effects of nitrogen fertilization and plastic film mulching on crop N and P stoichiometry in a temperate agroecosystem. J. Plant Ecol. 2019, 12, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.H.; Li, Y.N.; Xu, Y.B.; Zhou, C.M. Effects of mulches on water use in a winter wheat/summer maize rotation system in Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Land. 2018, 2, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Leng, X. Effect of biodegradable film mulching on crop yield, soil microbial and enzymatic activities, and optimal levels of irrigation and nitrogen fertilizer for the Zea mays crops in arid region. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, Z.; Wollmann, C.; Schaefer, M.; Buchmann, C.; David, J.; Tröger, J.; Muñoz, K.; Frör, O.; Schaumann, G.E. Plastic mulching in agriculture. Trading short-term agronomic benefits for long-term soil degradation? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Bank, M.S.; Dong, T.; Fang, J.K.; Leusch, F.D.L.; Rillig, M.C.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Xia, Y.; et al. The “Microplastome”—A holistic perspective to capture the real-world ecology of microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 4060–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbachu, O.; Jenkins, G.; Kaparaju, P.; Pratt, C. The rise of artificial soil carbon inputs: Reviewing microplastic pollution effects in the soil environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.Z.; Lu, W.X.; Shang, K.X. Comparative study on the properties and application of several biodegradable plastics. Chem. Fert. Des. 2020, 58, 1–3, 7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, F.V.; Luciana, S.C.; Rubia, F.G.; Liliane, M.F.L. An overview on properties and applications of poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)-PBAT based composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, E7–E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Kaur, S.; Baldwin, T.C.; Radecka, I.; Jiang, G.; Bretz, I.; Duale, K.; Adamus, G.; Kowalczuk, M. Effective control against broadleaf weed species provided by biodegradable PBAT/PLA mulch film embedded with the herbicide 2-Methyl-4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid (MCPA). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5360–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, N.; Bienaime, C.; Belloy, C.; Queneudec, M.; Silvestre, F.; Nava-Saucedo, J.E. Polymer biodegradation: Mechanisms and estimation techniques—A review. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastioli, C. Handbook of Biodegradable Polymers; Smithers Rapra Technology: Shrewsbury, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sintim, H.Y.; Bary, A.I.; Hayes, D.G.; Wadsworth, L.C.; Anunciado, M.B.; English, M.E.; Bandopadhyay, S.; Schaeffer, S.M.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Miles, C.A.; et al. In situ degradation of biodegradable plastic mulch films in compost and agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.X.; Chang, R.X.; Ren, Z.P.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.M.; Gao, M. Mature compost promotes biodegradable plastic degradation and reduces greenhouse gas emission during food waste composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.X.; Cao, Y.D.; Fan, L.W.; Xie, Y.L.; Zhou, X.Q.; Ren, Q.P.; Yang, X.F.; Gao, X.; Feng, Y.H. Degradation characteristics of polybutylene adipate terephthalic acid (PBAT) and its effect on soil physicochemical properties: A comparative study with several polyethylene (PE) mulch films. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Yu, H.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. A review on the occurrence and influence of biodegradable microplastics in soil ecosystems: Are biodegradable plastics substitute or threat? Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Flury, M.; Schaeffer, S.M.; Chang, Y.; Tao, Z.; Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Ding, F.; Wang, J. Agronomic performance of polyethylene and biodegradable plastic film mulches in a maize cropping system in a humid continental climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Zhang, L.; Dong, W.; Yan, C. Biodegradable plastic mulch films in agriculture: Feasibility and challenges. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintim, H.Y.; Bandopadhyay, S.; English, M.E.; Bary, A.I.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Schaeffer, S.M.; Miles, C.A.; Reganold, J.P.; Flury, M. Impacts of biodegradable plastic mulches on soil health. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 273, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.W.; Chadwick, D.R.; Zang, H.; Graf, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Greenfield, L.M.; Jones, D.L. Bioplastic (PHBV) addition to soil alters microbial community structure and negatively affects plant-microbial metabolic functioning in maize. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.H.; Liu, W.T.; Shi, R.Y.; Zeb, A.R.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.T.; Zheng, Z.Q.; Tang, J.C. Effects of polyethylene and polyactic acid microplastics on plant growth and bacterial community in the soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Feng, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, B. Microplastics effects on soil biota are dependent on their properties: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 178, 108940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, M.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H.; Ge, M.; Li, N.; Ning, Z.; Gao, W.; Fan, C.; et al. Molecular insights into effects of PBAT microplastics on latosol microbial diversity and DOM chemodiversity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 131076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.J.; Liu, J.X.; Han, S.Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, T.Q.; Xi, J.; Hou, L.J.; Lin, Y.B. Effect of conventional and biodegradable microplastics on the soil-soybean system: A perspective on rhizosphere microbial community and soil element cycling. Environ. Int. 2024, 190, 108781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.L.; Feng, X.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Cui, W.Z.; Sun, Y.H.; Zhang, S.W.; Wang, F.Y. Effects of microplastics and carbon nanotubes on soil geochemical properties and bacterial communities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Qu, C.S.; Bian, Y.R.; Gu, G.C.; Jiang, X.; Xin, J.; Song, Y. New insights into the responses of soil microorganism to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon stress by combining enzyme activity and sequencing analysis with metabolomics. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.B.; Heuberger, A.L.; Broeckling, C.D.; Jahn, C.E. Non-targeted metabolomics reveals sorghum rhizosphere-associated exudates are influenced by the belowground interaction of substrate and sorghum genotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Wang, Z.N.; Ma, Y.; Luo, J.Y.; Gao, X.K.; Ning, J.; Mei, X.D.; She, D.M. Influence of the neonicotinoid insecticide thiamethoxam on soil bacterial community composition and metabolic function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. World reference base for soil resources 2014, update 2015. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; Word Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, A.A.; Lau, C.W.; Till, J.; Kloas, W.; Lehmann, A.; Becher, R.; Rillig, M.C. Impacts of microplastics on the soil biophysical environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9656–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 1377-2007; Determination of pH in Soil. Agricultural Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Serrano-Ruiz, H.; Martin-Closas, L.; Pelacho, A.M. Impact of buried debris from agricultural biodegradable plastic mulches on two horticultural crop plants: Tomato and lettuce. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Wang, P.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, T.Q.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xi, J.; Hou, L.J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.Q.; et al. Negative effects of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) microplastics on Arabidopsis and its root-associated microbiome. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Yuan, X.Z.; Jia, Y.; Feng, L.J.; Zhu, F.P.; Dong, S.S.; Liu, J.; Kong, X.; Tian, H.; Duan, J.L.; et al. Differentially charged nanoplastics demonstrate distinct accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantis, L.J.; Adamczyk, S.; Velmala, S.M.; Adamczyk, B.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W.; Bosker, T. Comparing the impact of microplastics derived from a biodegradable and a conventional plastic mulch on plant performance. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Liu, C.; Yu, G.; Yu, J.; Lv, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Toxic effects of microplastics in plants depend more by their surface functional groups than just accumulation contents. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.; Liu, W.; Meng, L.; Wu, J.; Chao, L.; Zeb, A.; Sun, Y. Foliar-applied polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNPs) reduce the growth and nutritional quality of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Gholami, M.; Baninasab, B. Hydrogen peroxide-induced salt tolerance in relation to antioxidant systems in pistachio seedlings. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, J.P.; Saha, B.; Chowardhara, B.; Devi, S.S.; Borgohain, P.; Panda, S.K. Qualitative analysis of lipid peroxidation in plants under multiple stress through Schiff’s reagent: A histochemical approach. Bio-Protocol 2018, 8, e2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.J.; Teng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wen, D.; Gao, P.X.; Yan, D.; Yang, N. Biodegradable PBAT microplastics adversely affect pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) growth and the rhizosphere ecology: Focusing on rhizosphere microbial community composition, element metabolic potential, and root exudates. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, L. Mixing effect of polylactic acid microplastic and straw residue on soil property and ecological function. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aanderud, Z.T.; Saurey, S.; Ball, B.A.; Wall, D.H.; Barrett, J.E.; Muscarella, M.E.; Griffin, N.A.; Virginia, R.A.; Adams, B.J. Stoichiometric shifts in soil C:N:P promote bacterial taxa dominance, maintain biodiversity, and deconstruct community assemblages. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, J.A.; Purwadaria, T.; Yulandi, A.; Tan, W.A. Bacterial dynamics during the burial of starch-based bioplastic and oxo-low-density-polyethylene in compost soil. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Zou, G.Y.; Zuo, Q.; Li, C.Z.; Gu, J.L.; Kang, L.Y.; Ma, M.T.; Liang, K.Y.; Liu, D.S.; Du, L.F. Soil bacterial community and metabolism showed a more sensitive response to PBAT biodegradable mulch residues than that of LDPE mulch residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Teng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, W.J.; Wang, X.M.; Luo, Y.M.; Zhang, H.M.; Christie, P. Soil type driven change in microbial community affects poly(butylene adipate-coterephthalate) degradation potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4648–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Gu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Dai, Q.; Wang, G. Succession of soil bacterial communities and network patterns in response to conventional and biodegradable microplastics: A microcosmic study in Mollisol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.L.; Zhang, N.; Sun, B.; Liang, Y.T. Community structure of Burkholderiales and its diversity in typical maize rhizosphere soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 57, 975–985. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Paulitsch, F.; Delamuta, J.R.M.; Ribeiro, R.A.; da Silva Batista, J.S.; Hungria, M. Phylogeny of symbiotic genes reveals symbiovars within legume-nodulating Paraburkholderia species. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Malik, N.; Singh, S. Improved nutrient use efficiency increases plant growth of rice with the use of IAA-overproducing strains of endophytic Burkholderia cepacia strain RRE25. Micob. Ecol. 2013, 66, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.; Kumar, K.; Verma, A.; Verma, S.K. Seed inhabiting bacterial endophytes of maize promote seedling establishment and provide protection against fungal disease. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 255, 126926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Kang, S.C.; Maheshwari, D.K. Isolation of endophytic plant growth promoting Burkholderia sp. MSSP from root nodules of Mimosa pudica. Curr. Sci. 2005, 89, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Niu, S.; Xu, T.; Zhu, Y. Physiological, biochemical and proteomic insight into integrated strategies of an endophytic bacterium Burkholderia cenocepacia strain YG-3 response to cadmium stress. Metallomics 2019, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Duan, C.X.; Cao, N.; Ding, C.F.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Biodegradable and conventional microplastics exhibit distinct microbiome, functionality, and metabolome changes in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumilina, J.; Soboleva, A.; Abakumov, E.; Shtark, O.Y.; Zhukov, V.A.; Frolov, A. Signaling in legume-Rhizobia symbiosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athul, P.P.; Patra, R.K.; Sethi, D.; Panda, N.; Mukhi, S.K.; Padhan, K.; Sahoo, S.K.; Sahoo, T.R.; Mangaraj, S.; Pradhan, S.R.; et al. Efficient native strains of rhizobia improved nodulation and productivity of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under rainfed condition. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1048696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dissel, D.; Claessen, D.; van Wezel, G.P. Morphogenesis of Streptomyces in submerged cultures. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 89, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardes, M.B.; Dal’Rio, I.; Coelho, M.R.R.; Seldin, L. Response of sweet potato cultviars to Bacillus velezensis T149-19 and Bacillus safensis T052-76 used as biofertilizers. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, D.C.; Johnson, E.; Lewinson, O. ABC transporters: The power to change. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, A.M.; Cerulus, B.; Govers, S.K.; Perez-Samper, G.; Zhu, B.; Boogmans, S.; Xavier, J.B.; Verstrepen, K.J. Different levels of catabolite repression optimize growth in stable and variable environments. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.L.; Ossowicki, A.; Yang, X.M.; Lwanga, E.H.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Geissen, V.; Garbeva, P. Effects of plastic mulch film residues on wheat rhizosphere and soil properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zeng, X.B.; Huang, X.B. An overview on synthesis, properties and applications of poly(butylene-adipate-co-terephthalate)-PBAT. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2020, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kleeberg, I.; Welzel, K.; VandenHeuvel, J.; Müller, R.J.; Deckwer, W.D. Characterization of a new extracellular hydrolase from Thermobifida fusca degrading aliphatic-aromatic Copolyester. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.S.; Sehrawat, A.; Glick, B.R. The involvement of organic acids in soil fertility, plant health and environment sustainability. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D.; Li, S.; Yun, Y.L.; Li, J.P.; Sun, J.G.; Sun, G.W.; Feng, J.; Chen, Z.G.; Yang, L.F. The effect of controlling nitrogen by peptide fertilizer and reducing phosphorus fertilizer application on the growth of Yunyan 87. Hans J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 14, 931–939. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


| Treatment | CK | T1 | T2 | T3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.77 ± 0.05 a | 4.66 ± 0.05 a | 4.68 ± 0.08 a | 4.69 ± 0.07 a |
| OC (g/kg) | 28.16 ± 1.40 c | 29.30 ± 1.15 c | 38.87 ± 2.53 b | 82.59 ± 2.27 a |
| DOC (g/kg) | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 a | 0.10 ± 0.02 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 a |
| TN (g/kg) | 1.65 ± 0.07 ab | 1.69 ± 0.08 a | 1.55 ± 0.07 b | 1.59 ± 0.05 ab |
| TP (g/kg) | 0.88 ± 0.09 a | 0.89 ± 0.05 a | 0.67 ± 0.04 b | 0.87 ± 0.01 a |
| TK (g/kg) | 16.9 ± 1.78 a | 16.8 ± 0.48 a | 17.60 ± 1.31 a | 15.94 ± 0.84 a |
| AN (mg/kg) | 45.84 ± 1.69 b | 59.64 ± 8.43 a | 54.77 ± 8.19 ab | 50.33 ± 3.08 ab |
| AP (mg/kg) | 121.29 ± 4.52 a | 112.84 ± 4.49 b | 106.07 ± 3.26 c | 116.03 ± 4.64 b |
| AK (mg/kg) | 47.10 ± 4.90 a | 22.09 ± 4.92 bc | 14.51 ± 3.39 c | 26.34 ± 3.42 b |
| NH4+-N (mg/kg) | 4.56 ± 0.42 a | 0.79 ± 0.06 c | 0.42 ± 0.10 d | 2.18 ± 0.16 b |
| NO3−-N (mg/kg) | 7.49 ± 0.33 a | 6.07 ± 0.16 b | 5.98 ± 0.14 b | 7.01 ± 0.37 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Y.; Jia, X. Dosages of Biodegradable Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Microplastics Affect Soil Microbial Community, Function, and Metabolome in Plant–Soil System. Agronomy 2025, 15, 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040990
Fang Y, Lin C, Zhao J, Gao Y, Jia X. Dosages of Biodegradable Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Microplastics Affect Soil Microbial Community, Function, and Metabolome in Plant–Soil System. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):990. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040990
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Yu, Chenqiang Lin, Jie Zhao, Yuting Gao, and Xianbo Jia. 2025. "Dosages of Biodegradable Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Microplastics Affect Soil Microbial Community, Function, and Metabolome in Plant–Soil System" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040990
APA StyleFang, Y., Lin, C., Zhao, J., Gao, Y., & Jia, X. (2025). Dosages of Biodegradable Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Microplastics Affect Soil Microbial Community, Function, and Metabolome in Plant–Soil System. Agronomy, 15(4), 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040990





