Influence of Groundwater Depth on Salt Migration and Maize Growth in the Typical Irrigation Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
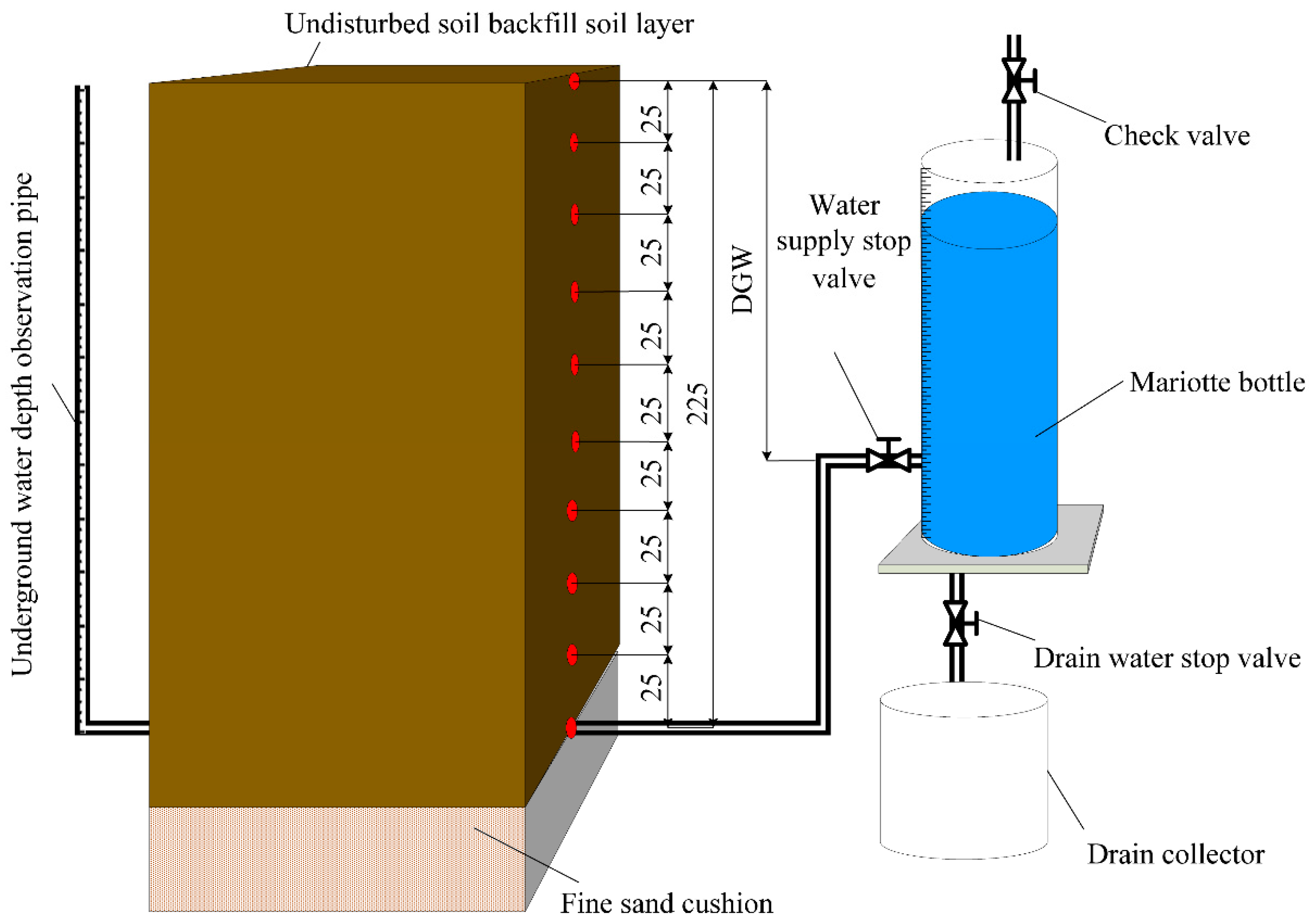
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Measurement Items and Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
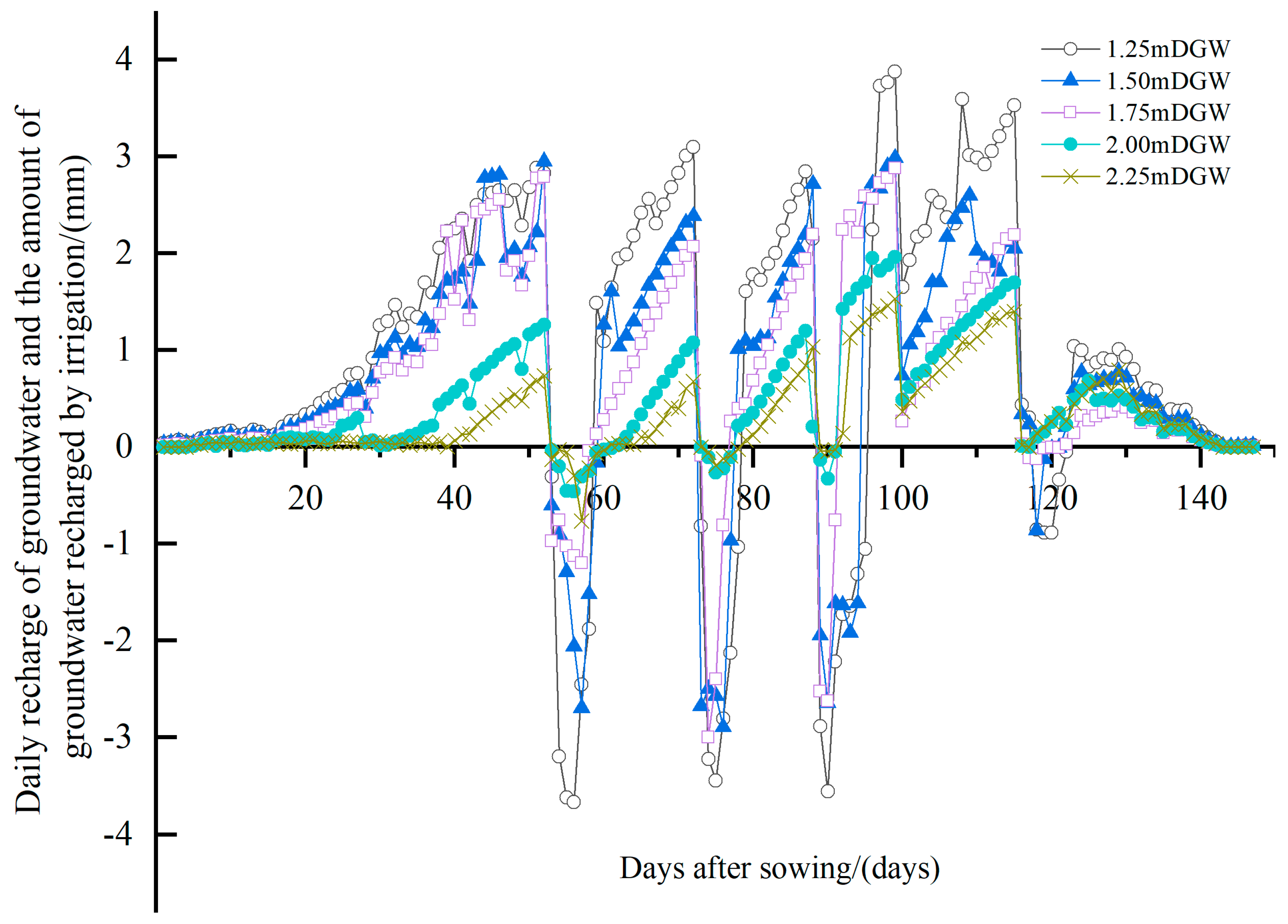
3.1. Influence of DGW on G_up and G_irr in Summer Maize Fields
3.2. Effect of Irrigation on Soil Electrical Conductivity Under Different DGWs
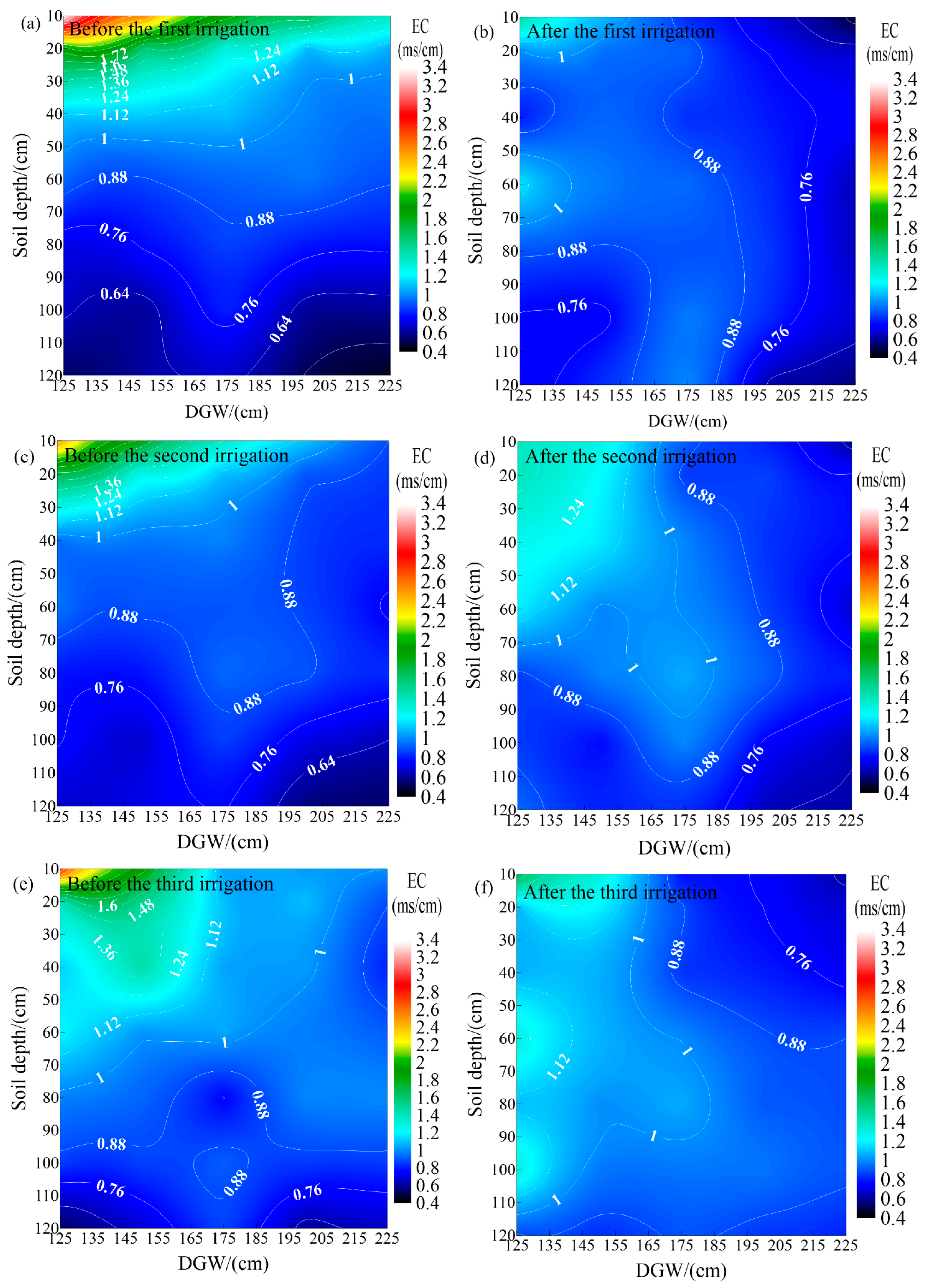
3.2.1. Effect of Irrigation on Soil Electrical Conductivity
3.2.2. Effect of Irrigation on the Leaching Effect of Soil Salinity at Different DGWs
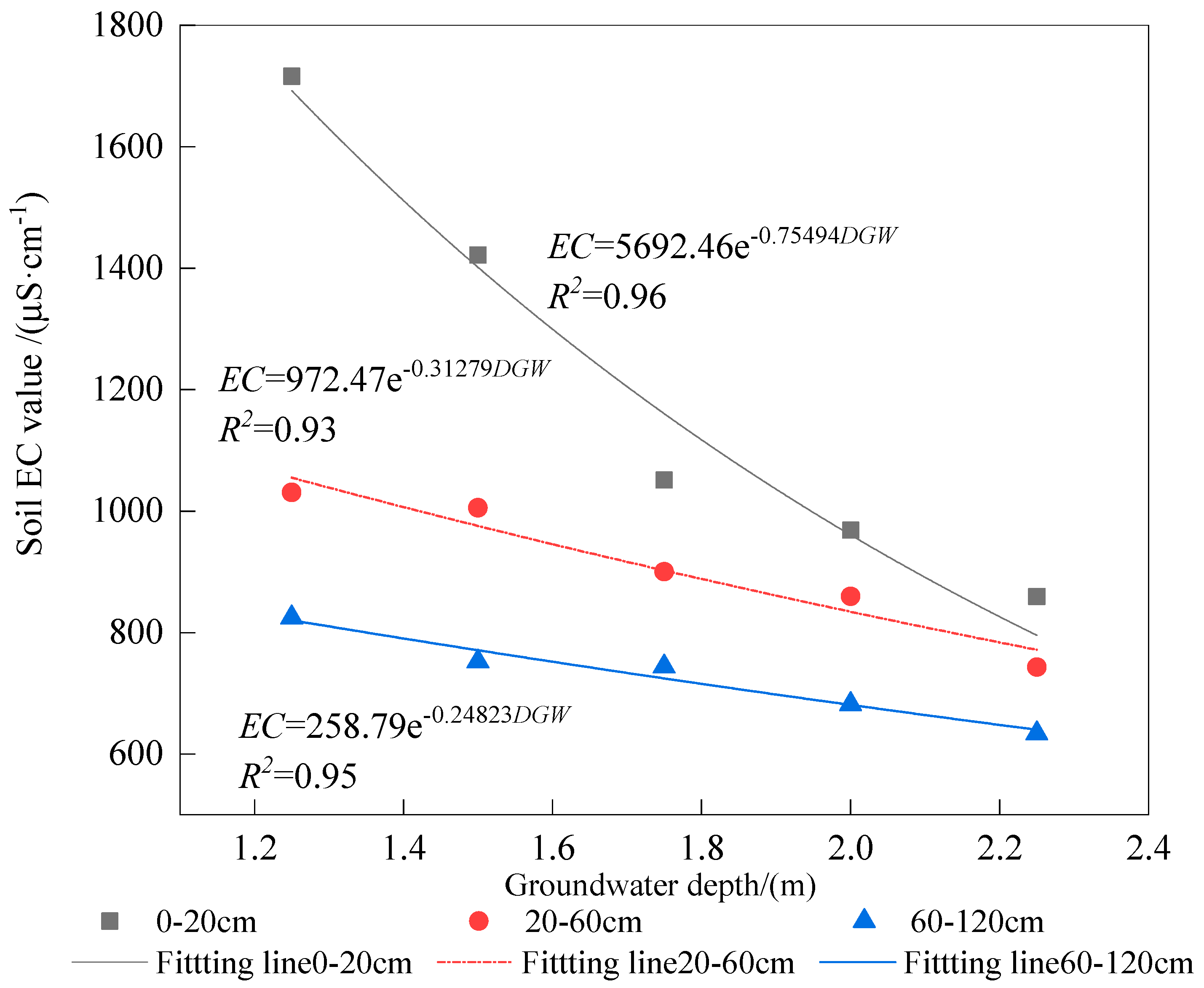
3.3. Effect of DGW on Soil EC
3.4. Effect of DGW on Maize Yield and WUE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, X.; Han, W.; Zhang, H.; Cui, J.; Ma, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, G. Estimating soil salinity under sunflower cover in the Hetao Irrigation District based on unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. The impacts of interannual climate variability and agricultural inputs on water footprint of crop production in an irrigation district of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Ren, Z.; Liao, J. Dynamics of carbon and water vapor fluxes in three typical ecosystems of Heihe River Basin, Northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.H.; Qu, Z.Y.; Pereira, L.S. Assessing the groundwater dynamics and impacts of water saving in the Hetao Irrigation District, Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, H.; Miao, Q.; Yang, S.; Hu, Z.; Hou, C.; Yu, C.; Yan, Y. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Variability and Coupling Relationship of Soil Water and Salt in Cultivated and Wasteland at Branch Canal Scale in the Hetao Irrigation District. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-T.; Wu, H.-Q.; Gu, H.-B.; Feng, G.-L.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, J.-D. Variability of Soil Salinity at Multiple Spatio-Temporal Scales and the Related Driving Factors in the Oasis Areas of Xinjiang, China. Pedosphere 2014, 24, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, H. Spatial and temporal mapping of groundwater salinity using ordinary kriging and indicator kriging: The case of Bafra Plain, Turkey. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 113, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Shannon, M.C.; Lesch, S.M. Timing of salinity stress affects rice growth and yield components. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 48, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Xu, X.; Engel, B.; Huang, Q.; Huo, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Han, W.; Huang, G. Modeling agro-hydrological processes and analyzing water use in a super-large irrigation district (Hetao) of arid upper Yellow River basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Feng, S. Study on relationship between soil salinization and groundwater table depth based on indicator Kriging. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng 2019, 35, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Vincent, B.; Bouarfa, S.; Vidal, A. On the effectiveness of dry drainage in soil salinity control. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2009, 52, 3328–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, B. Hydrochemistry characteristics of groundwater with the influence of spatial variability and water flow in Hetao Irrigation District, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 71150–71164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Wan, H.; Shang, S. A monthly distributed water and salt balance model in irrigated and non-irrigated lands of arid irrigation district with shallow groundwater table. J. Hydrol. 2023, 616, 12881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Wei, B.; Xu, X.; Engel, B.; Li, G.; Huang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, G. Analyzing spatiotemporal characteristics of soil salinity in arid irrigated agro-ecosystems using integrated approaches. Geoderma 2019, 356, 113935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, C.; Jiang, D.; Bailey, R.T.; Dong, J.; Zeng, W.; Huang, J. Water, Salt, and Ion Transport and Its Response to Water-Saving Irrigation in the Hetao Irrigation District Based on the SWAT-Salt Model. Agronomy 2024, 14, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Paredes, P.; Shi, H.; Ramos, T.; Tay, V.; Dai, L.; Pereira, L. Impacts of a shallow saline water table on maize evapotranspiration and groundwater contribution using static water table lysimeters and the dual Kc water balance model SIMDualKc. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 273, 107887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Liu, M.; Paredes, P.; Shi, H.; Feng, Z.; Lei, H.; Pereira, L.S. Salts dynamics in maize irrigation in the Hetao plateau using static water table lysimeters and HYDRUS-1D with focus on the autumn leaching irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Miao, Q.; Shi, H.; Feng, W.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Liu, M.; Sun, W.; Dai, L.; Liu, J. Simulation of water balance and irrigation strategy of typical sand-layered farmland in the Hetao Irrigation District, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 280, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Miao, Q.; Li, Z.; Akae, T. A Study on Water and Salt Transport, and Balance Analysis in Sand Dune–Wasteland–Lake Systems of Hetao Oases, Upper Reaches of the Yellow River Basin. Water 2020, 12, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Sun, C.; Pereira, L.S.; Ramos, T.B.; Huang, Q.; Hao, Y. Assessing the effects of water table depth on water use, soil salinity and wheat yield: Searching for a target depth for irrigated areas in the upper Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Pang, H.; Li, Y. Buried straw layer plus plastic mulching reduces soil salinity and increases sunflower yield in saline soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y. Impact of saline water irrigation on water use efficiency and soil salt accumulation for spring zmaize in arid regions of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 163, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, Z.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Shorafa, M.; Farahbakhsh, M. Using maize to evaluate the Mohammadi–Khataar (M–K) model as a salinity weighting function for the integral water capacity. Soil Res. 2022, 60, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Lv, X.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Shi, J. Impact of saline soil improvement measures on salt content in the abandonment-reclamation process. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Tan, X.; He, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, J.; Zhuang, W.; Liu, C. Transport of heat, water, and salts in freeze–thaw soils under flood irrigation: Experiment and simulation. J. Hydrol. 2025, 652, 132688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ao, C.; Zeng, W.; Srivastava, A.K.; Gaiser, T.; Wu, J.; Huang, J. Simulating water and salt transport in subsurface pipe drainage systems with HYDRUS-2D. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. Effects of irrigation frequency on transportation and accumulation regularity of greenhouse soil salt during different growth stages of pepper. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.L.; Cai, J.B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B.Z.; Huang, L.X. Responses of field evapotranspiration to the changes of cropping pattern and groundwater depth in large irrigation district of Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 188, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Meng, Q.; Li, L.; Bai, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, P.; Wang, T. Integrated deep vertical rotary tillage and subsurface pipe drainage techniques for sustainable soil salinization management and cotton production in arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 312, 109429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-J.; Feng, Q.; Li, F.-R.; Li, C.-S. A bidirectional model for simulating soil water flow and salt transport under mulched drip irrigation with saline water. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 146, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, N.; Hill, R.L.; Wu, S.; Dong, Q.g.; Ma, P. Effects of the combined application of biomaterial amendments and polyacrylamide on soil water and maize growth under deficit irrigation. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 99, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Huo, Z.; Adeloye, A.J. A sustainable irrigation water management framework coupling water-salt processes simulation and uncertain optimization in an arid area. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 231, 105994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gong, S.; Xu, D.; Sui, J.; Wu, Z.; Mo, Y. Effects of film mulching on evapotranspiration, yield and water use efficiency of a maize field with drip irrigation in Northeastern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 205, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, R. Evaluating the Effect of Groundwater Table on Summer Maize Growth Using the AquaCrop Model. Environ. Model. Assess. 2020, 25, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.; Feng, S.; Huang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, P. Effect of groundwater level depth and irrigation amount on water fluxes at the groundwater table and water use of wheat. Irrig. Drain. 2012, 61, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.-Y.; Kang, Y.-H.; Wan, S.-Q.; Hu, W. Soil Salinity Changes Under Cropping with Lycium barbarum L. and Irrigation with Saline-Sodic Water. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Layer (cm) | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Particle Size Distribution % | Soil Texture | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >0.05 mm | 0.002–0.05 mm | <0.002 mm | |||
| 0–10 | 1.46 | 17.27 | 75.15 | 7.58 | Silty loam |
| 10–20 | 1.44 | 15.03 | 76.20 | 8.77 | Silty loam |
| 20–40 | 1.52 | 20.60 | 73.23 | 6.17 | Silty loam |
| 40–60 | 1.56 | 26.04 | 66.44 | 7.52 | Silty loam |
| 60–80 | 1.53 | 22.41 | 70.72 | 6.87 | Silty loam |
| 80–100 | 1.53 | 22.51 | 70.67 | 6.82 | Silty loam |
| 100–120 | 1.55 | 24.45 | 67.48 | 8.07 | Silty loam |
| Treatment | 26 June 2020 | 17 July 2020 | 1 August 2020 | 30 August 2020 | Irrigation Times | Irrigation Quota |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilization and Irrigation (mm) | Irrigation (mm) | Fertilization and Irrigation (mm) | Irrigation (mm) | |||
| DGW1.25 m | 54 | 72 | 72 | 54 | 4 | 252 |
| DGW1.50 m | 54 | 72 | 72 | 54 | 4 | 252 |
| DGW1.75 m | 54 | 72 | 72 | 54 | 4 | 252 |
| DGW2.00 m | 54 | 72 | 72 | 54 | 4 | 252 |
| DGW2.25 m | 54 | 72 | 72 | 54 | 4 | 252 |
| Treatment | Period | Soil Depth/cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | 10–20 | 20–40 | 40–60 | 60–80 | 80–100 | 100–120 | ||
| DGW1.25 m | 1 d desalination rate after irrigation (%) | 58.1 | 49.3 | 30.6 | −26.1 | −28.4 | −15.7 | −42.0 |
| DGW1.50 m | 58.8 | 42.0 | 18.7 | −11.7 | −12.7 | −24.5 | −39.3 | |
| DGW1.75 m | 58.9 | 30.3 | 25.8 | −1.2 | −3.2 | −21.3 | −52.3 | |
| DGW2.00 m | 62.4 | 31.9 | 21.1 | 15.2 | −7.1 | −42.8 | −23.3 | |
| DGW2.25 m | 68.8 | 38.2 | 23.9 | 29.5 | 18.1 | −15.4 | −29.2 | |
| DGW1.25 m | 15 d desalination rate after irrigation (%) | 27.2 | 12.3 | 16.5 | −3.3 | −12.1 | −19.4 | −28.7 |
| DGW1.50 m | 28.8 | 21.3 | 15.7 | −2.8 | −1.4 | −12.6 | −17.4 | |
| DGW1.75 m | 29.1 | 16.7 | 12.0 | 3.3 | −8.0 | −6.8 | −16.4 | |
| DGW2.00 m | 35.4 | 17.4 | 13.7 | 10.6 | −14.1 | −20.9 | −11.2 | |
| DGW2.25 m | 38.6 | 20.3 | 14.7 | 17.8 | −6.3 | −7.2 | −22.8 | |
| DGW1.25 m | (%) Desalination rate after autumn harvest (%) | −80.9 | −80.4 | −91.4 | −86.1 | −76.5 | −52.9 | −63.2 |
| DGW1.50 m | −58.2 | −77.6 | −86.9 | −68.4 | −43.3 | −51.5 | −74.9 | |
| DGW1.75 m | −46.1 | −69.5 | −74.2 | −50.5 | −27.5 | −33.5 | −35.4 | |
| DGW2.00 m | −26.9 | −31.1 | −35.2 | −40.4 | −46.0 | −39.5 | −39.2 | |
| DGW2.25 m | −20.5 | −22.1 | −35.5 | −29.6 | −29.3 | −42.8 | −17.9 | |
| Treatments | Number of Grain | Grain Weight (g) | 100-Grain Weight (g) | Dry Matter (g) | Yield (kg/hm2) | Water Use Efficiency (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGW1.25 m | 393.40 b | 161.62 c | 33.65 ± 0.49 b | 156.34 ± 3.14 b | 9091.01 c | 2.17 ± 0.04 c |
| DGW1.50 m | 432.80 ab | 162.34 c | 34.03 ± 0.14 b | 188.02 ± 5.71 ab | 9131.63 c | 2.31 ± 0.19 c |
| DGW1.75 m | 436.40 ab | 176.04 c | 38.74 ± 0.39 a | 207.48 ± 5.92 ab | 10,357.35 b | 2.56 ± 0.13 b |
| DGW2.00 m | 444.40 ab | 192.38 b | 38.11 ± 0.45 a | 222.08 ± 5.42 a | 10,821.60 b | 2.72 ± 0.22 ab |
| DGW2.25 m | 457.40 a | 208.37 a | 39.20 ± 0.11 a | 228.36 ± 7.66 a | 11,720.70 a | 2.91 ± 0.20 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, L.; Miao, Q.; Shi, H.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, R.; Feng, W. Influence of Groundwater Depth on Salt Migration and Maize Growth in the Typical Irrigation Area. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051021
Dai L, Miao Q, Shi H, Feng Z, Li Y, Liu Y, Xu Y, Xu R, Feng W. Influence of Groundwater Depth on Salt Migration and Maize Growth in the Typical Irrigation Area. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051021
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Liping, Qingfeng Miao, Haibin Shi, Zhuangzhuang Feng, Yuxin Li, Yong Liu, Yongli Xu, Rigan Xu, and Weiying Feng. 2025. "Influence of Groundwater Depth on Salt Migration and Maize Growth in the Typical Irrigation Area" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051021
APA StyleDai, L., Miao, Q., Shi, H., Feng, Z., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Xu, Y., Xu, R., & Feng, W. (2025). Influence of Groundwater Depth on Salt Migration and Maize Growth in the Typical Irrigation Area. Agronomy, 15(5), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051021









