Rheological Characterization of Structural Stability for Black Soils from Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Investigated Sites of Soil Samples
2.2. Soil Properties
2.3. Rheological Tests
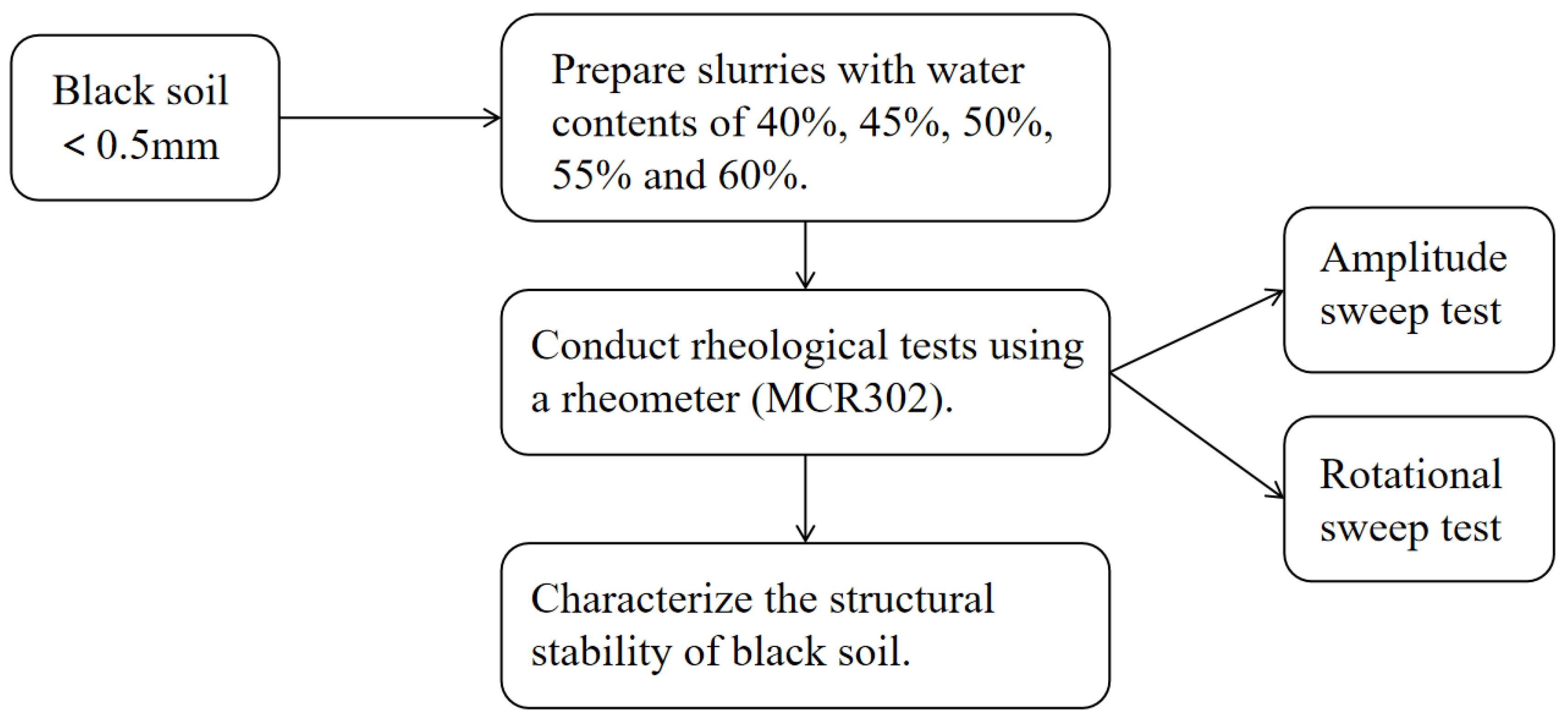
2.4. Technical Roadmap
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
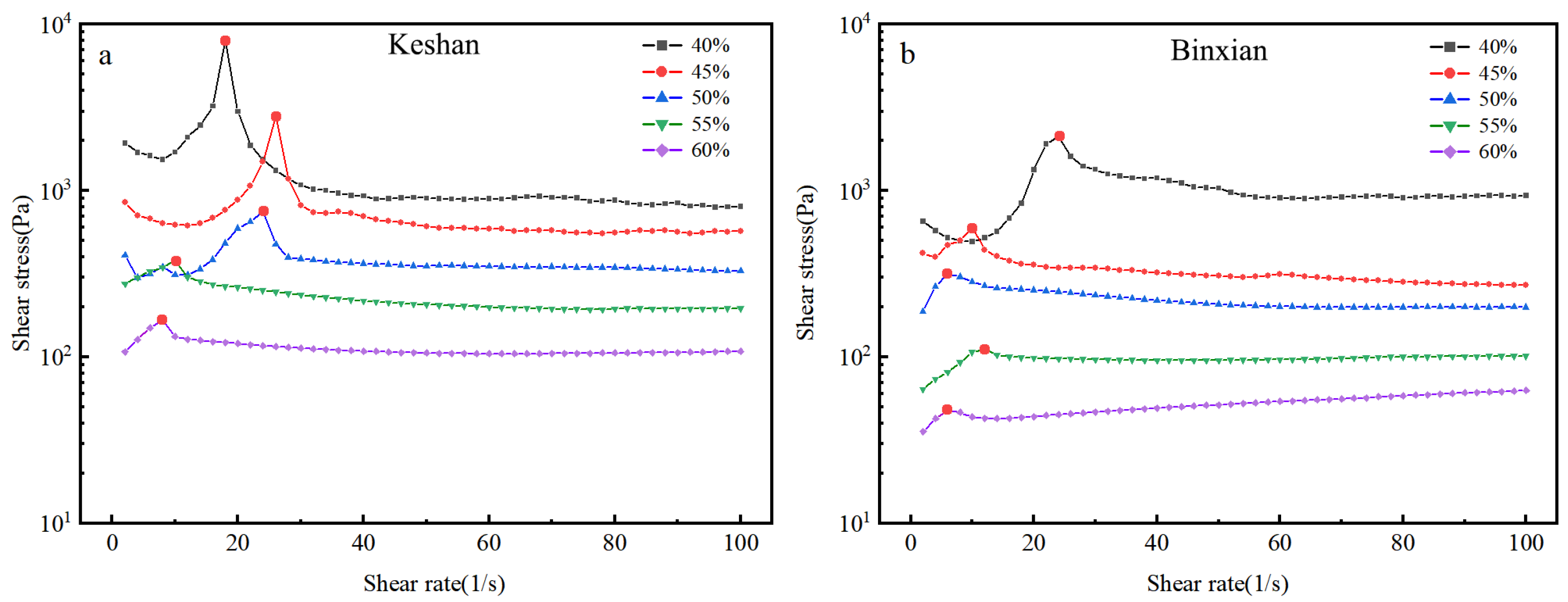
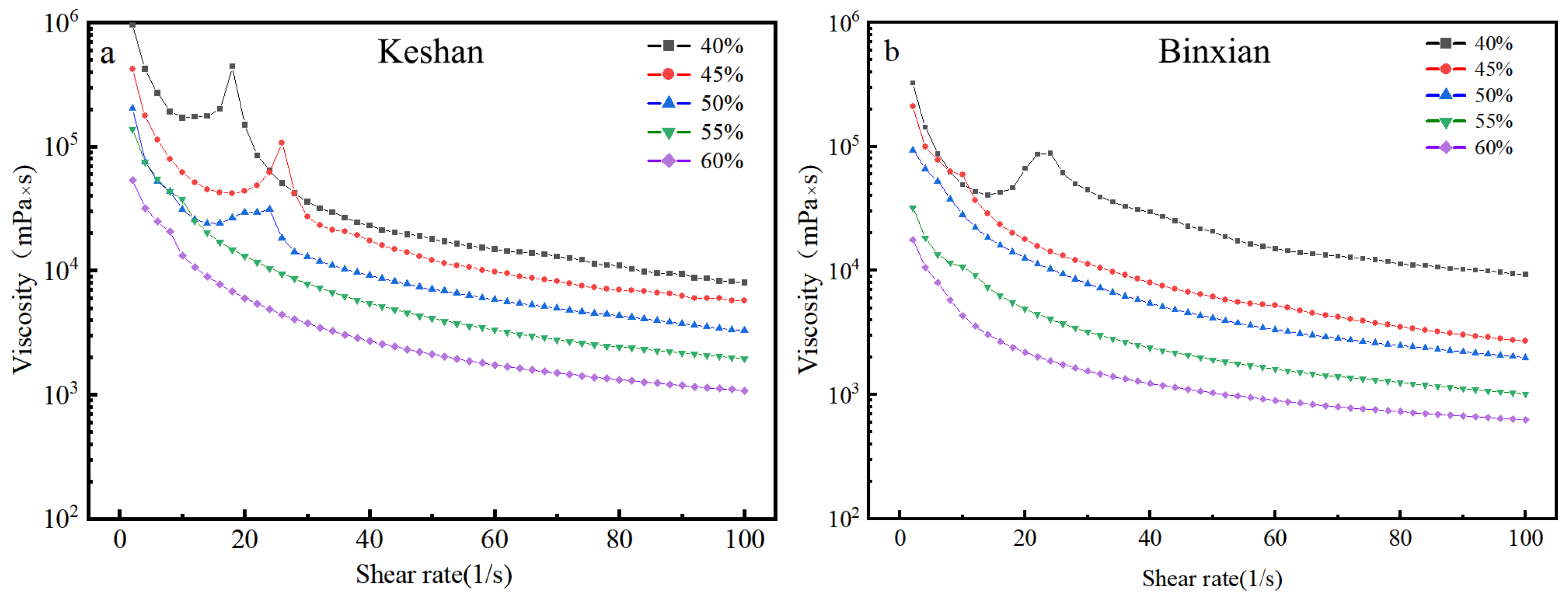
3.1. Flow and Viscosity Curves of the Soils
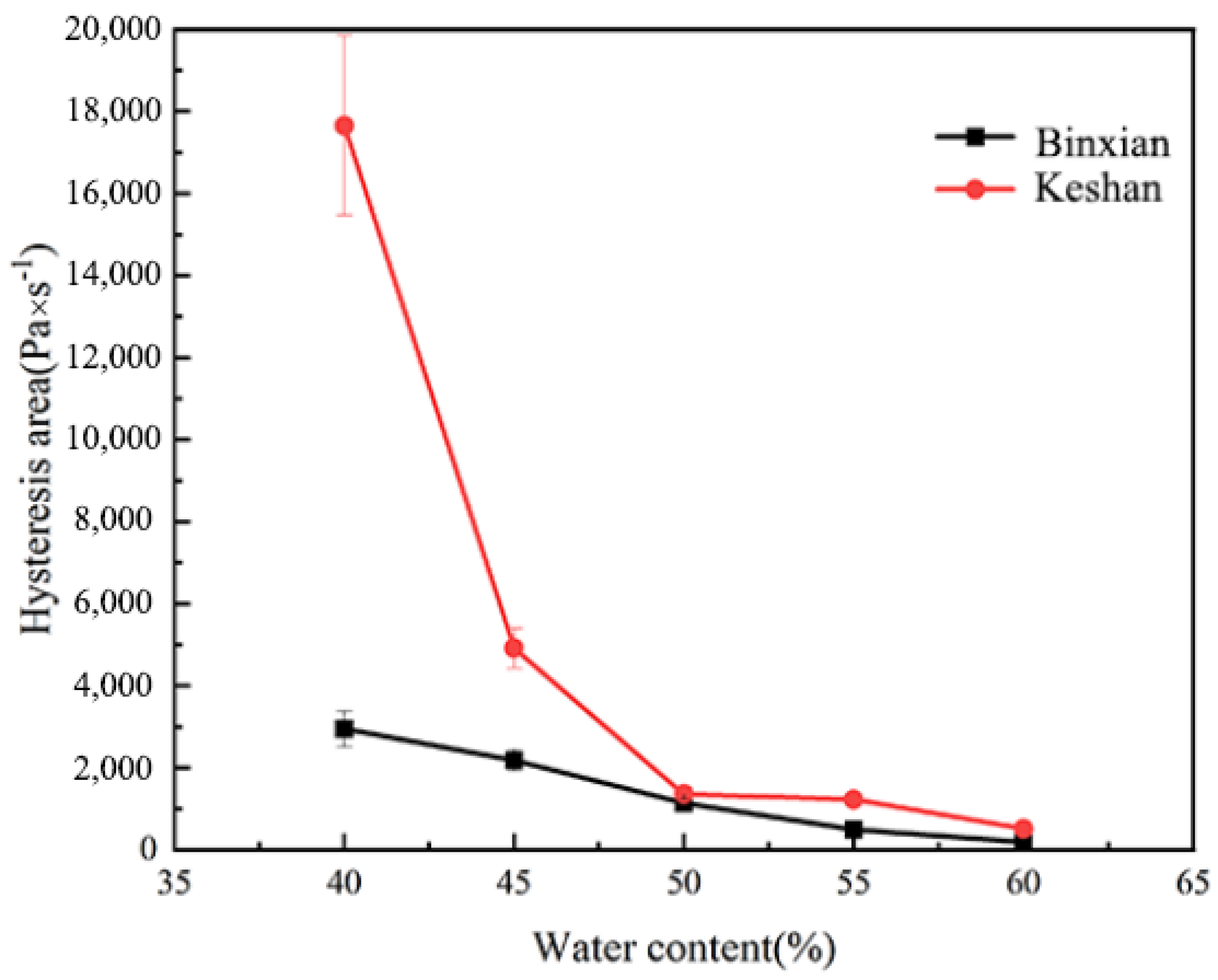
3.2. Hysteresis Curves of the Soils
3.3. Storage Modulus and Loss Modulus
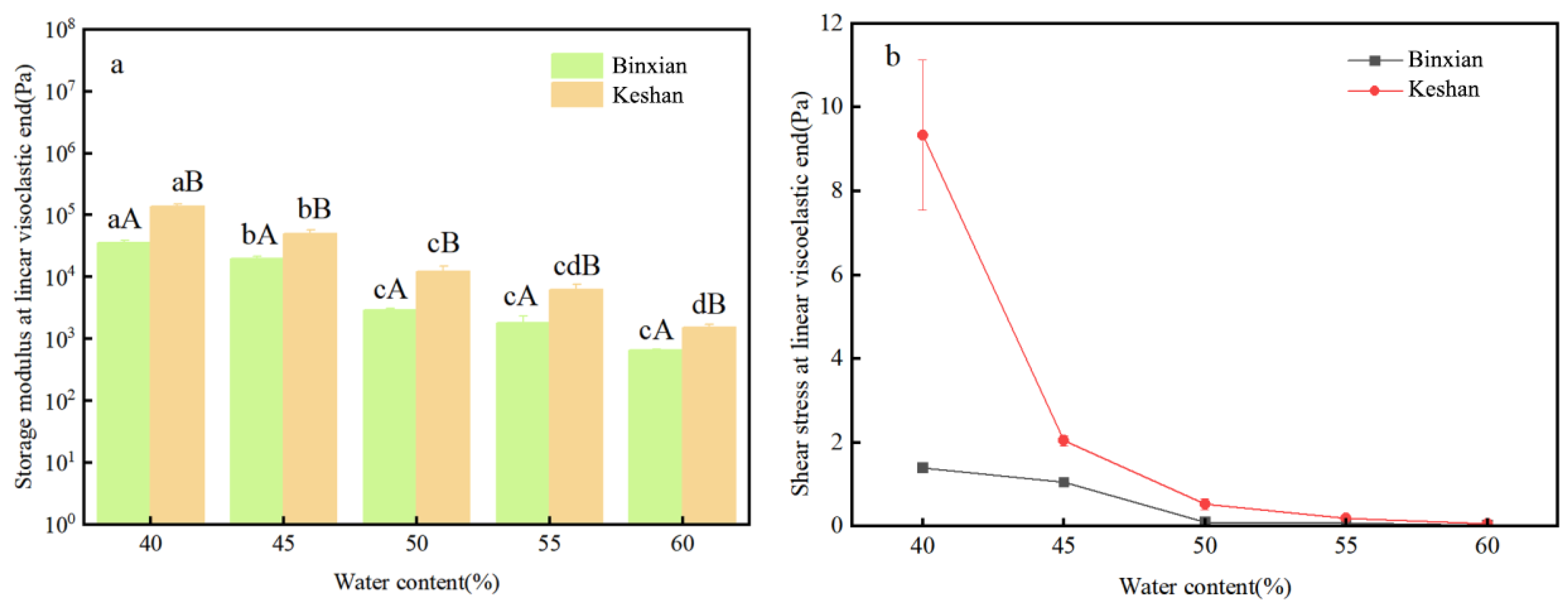
3.4. Rheological Parameters at the End of the Linear Viscoelastic Range
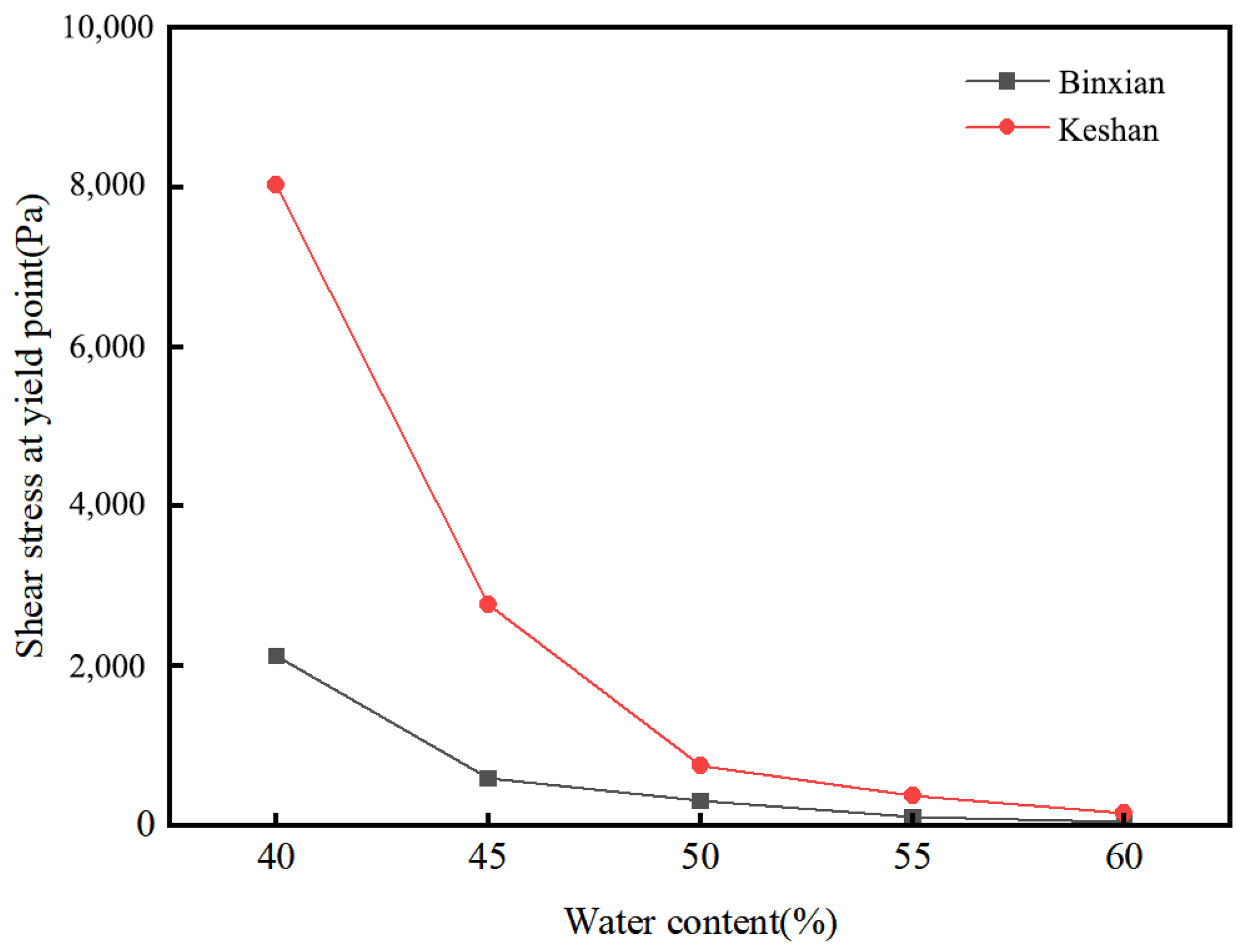
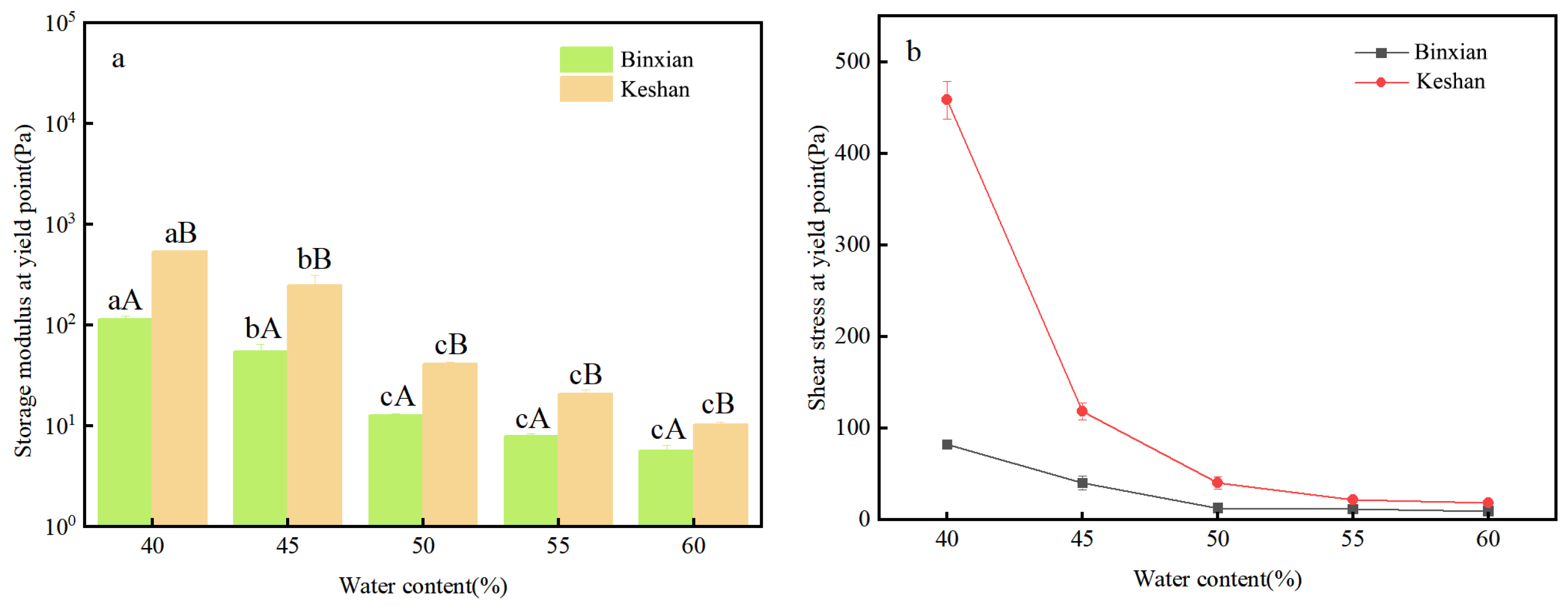
3.5. Rheological Parameters at the Yield Points
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, G.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, T.M.; Chen, J.M. Effects of artificial grassland establishment on soil nutrients and carbon properties in a black-soil-type degraded grassland. Plant Soil. 2010, 333, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Xu, X.R.; Pei, J.B. Current Situations of Black Soil Quality and Facing Opportunities and Challenges in Northeast China. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 695–701. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.N. Advances and Prospects of Soil Erosion Research in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- de Souza Machado, A.A.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C.; Hempel, S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics as an emerging threat to terrestrial ecosystems. Global. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Fan, H. Response mechanism of black soil structure to compound erosion forces in sloping farmland, Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 240, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhu, H.; Fu, W.; Shao, M. Responses of soil aggregate stability, erodibility and nutrient enrichment to simulated extreme heavy rainfall. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.F.; Ilavsky, J.; Jastrow, J.D.; Mayer, L.M.; Perfect, E.; Zhuang, J. Protection of organic carbon in soil microaggregates via restructuring of aggregate porosity and filling of pores with accumulating organic matter. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4725–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, P.; Yin, Z.; Li, A.; Zhou, X.; Qi, Z.; Wang, B. Soil Aggregates and Water Infiltration Performance of Different Water and Soil Conservation Measures on Phaeozems Sloping Farmland in Northeast China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, X.; Ihsan, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Effects of Straw and Plastic Film Mulching on Nitrogen Composition of Soil Aggregates in Dryland Wheat Field on the Loess Plateau. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 236–241. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Kuan, W.-X.; Wang, H.; Geng, R.; Wang, J.; Li, M. Variation in dissolved organic matter characteristics of soil aggregates in slip deposition zone with natural succession on a semiarid region. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 125040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ma, L.; Chen, P. Characteristics of aggregates with different particle sizes and their effects on slope erosion process in the Characteristics of aggregates with different particle sizes and their effects on slope erosion process in the rocky mountainous area of north China. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 32, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, C.-C.; Wang, E.-H. Mechanical properties of black soil after straw incorporation: Effect of straw mixing amount. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 2932–2938. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Baumgarten, W.; Horn, R. Assessing soil degradation by using a scale-spanning soil mechanical approach: A review. In Soil Degradation 1–61. Advances in Geoecology; Catena Verlag: Alde, Germany, 2013; Volume 42, ISBN 978-3-923381-59-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, W.; Ding, W.; Liu, K.; Qin, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Numerical study on the hydrodynamic properties of bentonite slurries with Herschel-Bulkley-Papanastasiou rheology model. Powder Technol. 2023, 419, 118375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, C.; Merola, M.C.; Álvarez-Romero, M.; Coppola, E.; Minale, M. Rheology of natural slurries involved in a rapid mudflow with different soil organic carbon content. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markgraf, W.; Horn, R. Scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive scan analyses and rheological investigations of South-Brazilian soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hu, F.; Xu, C. Study of the rheological behavior of pisha sandstone slurry based on dynamic oscillatory shear. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 45–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Johnston, C.T.; Sumner, M.E. Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3: Chemical Methods; Soil Science Society of America Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Romagnoli, M.; Leonelli, C.; Kamse, E.; Lassinantti Gualtieri, M. Rheology of geopolymer by DOE approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czibulya, Z.; Tombácz, E.; Szegi, T.; Michéli, E.; Zsolnay, Á. Standard state of soil dispersions for rheological measurements. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czibulya, Z.; Szegi, T.; Michéli, E.; Tombácz, E. Rheological Measurements for Indicating Structural Changes in selected Soil Catenas of European Experimental Fields. Int. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. Iran. 2014, 2, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, L.P.B.; de Queiroz, M.G.C.; da Nóbrega, A.F.; da Nóbrega, A.C.V.; de Souza, J.J.N.; Carneiro, A.M.P. Study of rheological properties of lime–metakaolin slurries. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 215, 106309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Du, W.; Liu, Z.; Hu, F. Effects of Pisha sandstone additions on microstructural stability of sandy soil in Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, M.; Kiranmai, P.; Garimella, S.M. Stability of fully developed pipe flow of a shear-thinning fluid that approximates the response of viscoplastic fluids. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2024, 19, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Ding, X.; Tao, Y.; Qu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Research on the flow around a circular cylinder near a wall for shear-thinning power-law fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid. 2024, 333, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto di Santolo, A.; Pellegrino, A.M.; Evangelista, A. Experimental study on the rheological behaviour of debris flow. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, C.; Bentz, J.; Schaumann, G.E. Intrinsic and model polymer hydrogel-induced soil structural stability of a silty sand soil as affected by soil moisture dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 154, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Shi, Y.; Qin, Y. Experiment on the rheological properties of tidal flat soil with moisture contentand standing time. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 190–198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Markgraf, W.; Watts, C.W.; Whalley, W.R.; Hrkac, T.; Horn, R. Influence of organic matter on rheological properties of soil. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 64, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro) aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögel-Knabner, I.; Guggenberger, G.; Kleber, M.; Kandeler, E.; Kalbitz, K.; Scheu, S.; Eusterhues, K.; Leinweber, P. Organo-mineral associations in temperate soils. Integrating biology, mineralogy, and organic matter chemistry. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2008, 171, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maček, M.; Mauko, A.; Mladenovič, A.; Majes, B.; Petkovšek, A. A comparison of methods used to characterize the soil specific surface area of clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 83–84, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markgraf, W.; Horn, R.; Peth, S. An approach to rheometry in soil mechanics—Structural changes in bentonite, clayey and silty soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 91, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Huang, Y. Rheological study on influence of mineral composition on viscoelastic properties of clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 187, 105493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, A.R.; Hashemi, A.M.; Herbert, S.J.; Asoodar, M.A. Interactive effects of tillage system and soil water content on aggregate size distribution for seedbed preparation in Fluvisols in southwest Iran. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 78, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Soils | SOM (−1) | CEC (−1) | SSA (−1) | pH | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.002 mm | 0.002–0.02 mm | 0.02–2 mm | |||||
| Keshan black soil | 49.9 | 23.4 | 66.5 | 5.88 | 35.5 | 25.4 | 39.1 |
| Binxian black soil | 28.9 | 21.3 | 58.6 | 6.32 | 32.9 | 24.7 | 42.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Zhou, L.; Yan, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, F. Rheological Characterization of Structural Stability for Black Soils from Northeast China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051050
Sun J, Zhou L, Yan Y, Xu C, Liu Z, Yu Z, Li J, Hu F. Rheological Characterization of Structural Stability for Black Soils from Northeast China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051050
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jian, Lin Zhou, Yuyang Yan, Chenyang Xu, Zhe Liu, Zhenghong Yu, Jiangwen Li, and Feinan Hu. 2025. "Rheological Characterization of Structural Stability for Black Soils from Northeast China" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051050
APA StyleSun, J., Zhou, L., Yan, Y., Xu, C., Liu, Z., Yu, Z., Li, J., & Hu, F. (2025). Rheological Characterization of Structural Stability for Black Soils from Northeast China. Agronomy, 15(5), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051050






