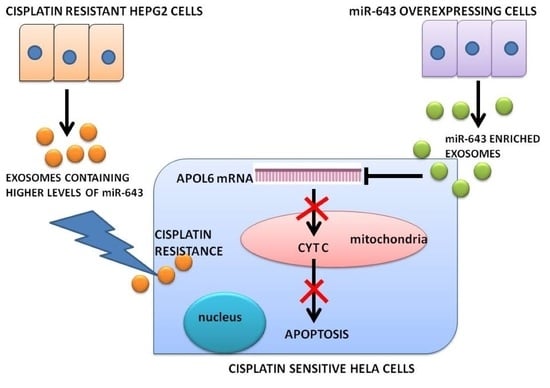
Horizontal Transfer of miR-643 from Cisplatin-Resistant Cells Confers Chemoresistance to Recipient Drug-Sensitive Cells by Targeting APOL6
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. XTT Viability Assay
2.3. Isolation of Exosomes from Culture Media
2.4. Isolation of Exosomal RNA and Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.5. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway and Gene Ontology (GO) Analysis
2.6. Prediction of miR-643 Target Gene and 3′UTR Analysis
2.7. mRNA Stability Assay
2.8. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.9. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR Analysis of Target Genes
- ACTIN sense primer—5′-CCAACCGCGAGAAGATGA-3′
- Anti-sense primer—5-CCAGAGGCGTACAGGGATAG-3′
- APOL6 sense primer—5-AGTGAGGCTGGTGTTGGTTT-3′
- Anti-sense primer—5′-CGTCTTGTAGCTCCACGTCTT-3′
2.10. Transfection of Cells
2.11. Western Blotting Analysis
2.12. Comet Assay
2.13. Cytoplasmic and Mitochondrial Fractionation
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression Levels and Target Prediction Analysis of Some Candidate miRNAs in Exosomes Released from Cp-r HepG2 Cells
3.2. KEGG Pathway and GO Analysis of Candidate miRNAs
3.3. Overexpression of miR-643 in Hela Cells
3.4. Exosomally Transferred miR-643 Can Modulate Cisplatin Sensitivity of Recipient Hela Cells
3.5. EXres Mediated Alteration in Cisplatin Resistance Involving APOL6
3.6. Ectopic Expression of miR-643 Can Reduce APOL6 Levels and Augments the Effect of EXres on APOL6 Levels
3.7. miR-643-Mediated, EXres-Dependent Alteration in Cisplatin Resistance Involve Reduced Apoptosis Resulting in Promotion of Cell Survival
3.8. Exosomes Enriched with miR-643 Reduces APOL6 Levels, Decreases Caspase Activity, and Promotes Cell Survival in Recipient Cells
3.9. miR-643-Mediated Promotion of Cell Survival and Cisplatin Resistance Is APOL6 Dependent
3.10. miR-643-Mediated Modulation of Cisplatin Resistance in Hela Cells Is Dependent on APOL6-Induced Release of Cytochrome C
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorr, R.T.; Fritz, W.L. Cancer Chemotherapy Handbook; Elsevier North-Holland, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Zahreddine, H.; Borden, K.L.B. Mechanisms and insights into drug resistance in cancer. Front. Pharm. 2013, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottesman, M.M. Mechanisms of Cancer Drug Resistance. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Multidrug resistance in cancer: Role of ATP–dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug resistance in cancer: An overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvakumaran, M.; A Pisarcik, D.; Bao, R.; Yeung, A.T.; Hamilton, T.C. Enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity by disturbing the nucleotide excision repair pathway in ovarian cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Indran, I.R.; Tufo, G.; Pervaiz, S.; Brenner, C. Recent advances in apoptosis, mitochondria and drug resistance in cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2011, 1807, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, X.; Sarmiento, C.; Tan, T.; Zhu, H. Regulation of multidrug resistance by microRNAs in anti-cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V. microRNAs. Cell 2001, 107, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhi, F.; Zhou, G.; Shao, N.; Xia, X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Xue, L.; Wang, S.; et al. miR-106a-5p Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Astrocytoma Cells and Promotes Apoptosis by Targeting FASTK. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ahmad, A.; Sarkar, F.H. The Role of MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer Migration, Invasion and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13414–13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Liu, H.-T.; Mei, J.; Ding, F.-B.; Xiao, H.-B.; Hu, F.-Q.; Hu, R.; Wang, M.-S. miR-106a promotes growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting PTEN. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 3827–3834. [Google Scholar]
- Edatt, L.; Maurya, A.K.; Raji, G.; Kunhiraman, H.; Kumar, S.V.B. MicroRNA106a regulates matrix metalloprotease 9 in a sirtuin-1 dependent mechanism. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 233, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, Z.H. Mechanisms of Action of Cancer Chemotherapeutic Agents: DNA-Interactive Alkylating Agents and Antitumour Platinum-Based Drugs. Cancer Handb. 2005, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharm. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Makino, T.; Masuzawa, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; Miyata, H.; Takiguchi, S.; Nakajima, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Matsuura, N.; Mori, M.; et al. Role of multidrug resistance protein 2 (MRP2) in chemoresistance and clinical outcome in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene 2011, 31, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishida, S.; Lee, J.; Thiele, D.J.; Herskowitz, I. Uptake of the anticancer drug cisplatin mediated by the copper transporter Ctr1 in yeast and mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14298–14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makin, G.; Hickman, J.A. Apoptosis and cancer chemotherapy. Cell Tissue Res. 2000, 301, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fraser, M.; Moll, U.M.; Basak, A.; Tsang, B.K. Akt-Mediated Cisplatin Resistance in Ovarian Cancer: Modulation of p53 Action on Caspase-Dependent Mitochondrial Death Pathway. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3126–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarin, N.; Engel, F.; Kalayda, G.V.; Mannewitz, M.; Cinatl, J., Jr.; Rothweiler, F.; Michaelis, M.; Saafan, H.; Ritter, C.A.; Jaehde, U.; et al. Cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells is associated with an abrogation of cisplatin-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovanovic, M.; Hengartner, M.O. miRNAs and apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6176–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raji, G.R.; Sruthi, T.; Edatt, L.; Haritha, K.; Shankar, S.; Kumar, V.S. Horizontal transfer of miR-106a/b from cisplatin resistant hepatocarcinoma cells can alter the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to cisplatin. Cell. Signal. 2017, 38, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Dong, C.; Ji, C. MicroRNA and drug resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.A.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 Is an Antiapoptotic Factor in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6029–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranji, N.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Bakhshandeh, B.; Karimipour, M.; Amanzadeh, A.; Azadmanesh, K. miR-17-92 cluster: An apoptosis inducer or proliferation enhancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 380, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhome, R.; Del Vecchio, F.; Lee, G.H.; Bullock, M.D.; Primrose, J.N.; Sayan, A.E.; Mirnezami, A.H. Exosomal microRNAs (exomiRs): Small molecules with a big role in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 420, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, C.; Rani, S.; O’Driscoll, L.; O’Brien, K.; O’Neill, A.; Prencipe, M.; Sheikh, R.; Webb, G.; McDermott, R.; Watson, W.; et al. Docetaxel-resistance in prostate cancer: Evaluating associated phenotypic changes and potential for resistance transfer via exosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Ren, Z.J.; Tang, J.H.; Yu, Q. Exosomal MicroRNA MiR-1246 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Drug Resistance by Targeting CCNG2 in Breast Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, C.L.A.; Co, N.-N.; Tsuruga, T.; Yeung, T.-L.; Kwan, S.-Y.; Leung, C.S.; Li, Y.; Lu, E.S.; Kwan, K.; Wong, K.-K.; et al. Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Xing, D.; Ren, D.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Peng, Z. MicroRNA-643 regulates the expression of ZEB1 and inhibits tumorigenesis in osteosarcoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5157–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longosorbello, G.S.A.; Saydam, G.; Banerjee, D.; Bertino, J.R. Cytotoxicity and Cell Growth Assays. In Cell Biology; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, J.; Huang, Z.; Peng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. A Novel Real-Time PCR Assay of microRNAs Using S-Poly(T), a Specific Oligo(dT) Reverse Transcription Primer with Excellent Sensitivity and Specificity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DiMauro, I.; Pearson, T.; Caporossi, D.; Jackson, M.J. A simple protocol for the subcellular fractionation of skeletal muscle cells and tissue. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Brenner, C.; Szabadkai, G.; Harel-Bellan, A.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Systems biology of cisplatin resistance: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.M.; Lippard, S.J. Cisplatin: From DNA damage to cancer chemotherapy. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2001, 67, 93–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, W.; Xiao, J.; Cao, B. The role of exosomes and “exosomal shuttle microRNA” in tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, M.D.R.; Pedro, A.; Lyden, D. Cancer Exosomes as Mediators of Drug Resistance. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2016, 1395, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, K.; Inoue, K.; Fujiwara, A.; Hatakeyama, K.; Kanto, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Muramatsu, K.; Fukuda, Y.; Ogura, S.-I.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Let-7 MicroRNA Family Is Selectively Secreted into the Extracellular Environment via Exosomes in a Metastatic Gastric Cancer Cell Line. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Xie, H.; Xu, Y.; Du, Q.; Zeng, H.; Su, B.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, X.; Chen, C.; et al. Expression of miR-150 and miR-3940-5p is reduced in non-small cell lung carcinoma and correlates with clinicopathological features. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 29, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Yu, S.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Ma, R.; Cao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, J. Exosomes: Decreased sensitivity of lung cancer A549 cells to cisplatin. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Pastuszyn, A.; Chien-an, A.H. Apolipoprotein L6, a Novel Proapoptotic Bcl-2 Homology 3–Only Protein, Induces Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2005, 3, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. The Bcl2 family: Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorrano, L.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Mechanisms of cytochrome c release by proapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raji, G.R.; Poyyakkara, A.; Krishnan, A.K.; Maurya, A.K.; Changmai, U.; Shankar, S.S.; Kumar, V.B.S. Horizontal Transfer of miR-643 from Cisplatin-Resistant Cells Confers Chemoresistance to Recipient Drug-Sensitive Cells by Targeting APOL6. Cells 2021, 10, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061341
Raji GR, Poyyakkara A, Krishnan AK, Maurya AK, Changmai U, Shankar SS, Kumar VBS. Horizontal Transfer of miR-643 from Cisplatin-Resistant Cells Confers Chemoresistance to Recipient Drug-Sensitive Cells by Targeting APOL6. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061341
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaji, Grace R., Aswini Poyyakkara, Anjali Kunhi Krishnan, Ashutosh Kumar Maurya, Udeshna Changmai, Sharath S. Shankar, and V. B. Sameer Kumar. 2021. "Horizontal Transfer of miR-643 from Cisplatin-Resistant Cells Confers Chemoresistance to Recipient Drug-Sensitive Cells by Targeting APOL6" Cells 10, no. 6: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061341
APA StyleRaji, G. R., Poyyakkara, A., Krishnan, A. K., Maurya, A. K., Changmai, U., Shankar, S. S., & Kumar, V. B. S. (2021). Horizontal Transfer of miR-643 from Cisplatin-Resistant Cells Confers Chemoresistance to Recipient Drug-Sensitive Cells by Targeting APOL6. Cells, 10(6), 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061341