Abstract
The metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptor family consists of group I receptors (mGlu1 and mGlu5) that are positively coupled to phospholipase-C and group II (mGlu2 and mGlu3) and III receptors (mGlu4-8) that are negatively coupled to adenylyl cyclase. Of these, mGlu5 has emerged as a key factor in the induction and maintenance of persistent (>24 h) forms of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Studies in freely behaving rodents have revealed that mGlu5 plays a pivotal role in the stabilisation of hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) that are tightly associated with the acquisition and retention of knowledge about spatial experience. In this review article we shall address the state of the art in terms of the role of mGlu5 in forms of hippocampal synaptic plasticity related to experience-dependent information storage and present evidence that normal mGlu5 function is central to these processes.
1. Introduction
Metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors comprise a family of G-protein coupled receptors that are present throughout the brain [1,2] and are highly expressed in the hippocampus [2]. They are specifically involved in the regulation of persistent (>24 h) forms of hippocampal synaptic plasticity, such as long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) [3,4,5,6,7,8], hippocampus-dependent learning [9,10,11,12,13,14,15].They also support hippocampal information transfer by means of neuronal oscillations [16,17] and the beneficial effects of environmental enrichment on hippocampal function [18].
Glutamate is the most abundant/primary neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and exerts its action by binding to ionotropic (iGlu) and metabotropic (mGlu) glutamate receptors [19,20,21,22,23]. In contrast to iGlu receptors, which are ligand-gated ion-channels, activation of mGlu receptors initiates G-protein-coupled signaling cascades. The mGlu receptors are subdivided into three groups, based on their biochemical coupling and signaling cascades [24].
Group I mGlu receptors, comprising mGlu1 and mGlu5 [25,26], are particularly important for enabling forms of hippocampal synaptic plasticity that persist for very long periods (>24 h) [27]. Group II (mGlu2 and 3), and group III mGlu receptors (mGlu 4–8) are negatively coupled to adenylyl cyclase [24] and mostly function as autoreceptors for glutamate [28,29,30,31,32], serving, for example, to lower excitability levels in the hippocampus [33]. Activation of these receptors raises the threshold for the induction of synaptic plasticity, or favours changes in synaptic strength that promote LTD [34,35,36,37].
Another differentiation of the separate mGlu receptor groups can be made based on their location of expression in the brain. Group I mGlu receptors are mainly expressed on postsynaptic sites [38,39,40], whereas group II and III mGlu receptors are mainly expressed presynaptically [41]. The expression of mGlu5 receptors is, correspondingly, mostly located postsynaptically and the highest expression can be found in the CA1 subregion of the hippocampus, whereas comparatively less expression of this receptor has been found in the dentate gyrus (DG) and the CA3 region [2,41].
Of the abovementioned family of mGlu receptors, mGlu5 stands out as being of particular importance for information processing and storage in the hippocampus relating to the acquisition and retention of long-term memory [27]. Furthermore, mGlu5 contributes to homeostatic brain function by means of the fine-tuning of synaptic plasticity [42]. For this reason, it is perhaps unsurprising that dysfunction of mGlu5 receptors is associated with several neurological diseases that impact specifically on hippocampal function, such as epilepsy [43,44,45], psychosis [46,47,48,49,50,51], Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59], Parkinson’s disease [60,61,62,63], Fragile X [64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72] and Rett Syndrome [73,74,75,76]. In fact, it has also been proposed that mGlu5 may be directly involved in the pathophysiology of these diseases. For example, the propagation of epileptiform activity by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) is supported by astrocytic mGlu5 receptor activation [77], and in AD, Aβ oligomers cause a shift of mGlu5 receptors towards the synapse, a process that may promote synaptotoxicity [78]. MGlu5 receptors also support the coupling of soluble amyloid-β oligomers and cellular prion protein [79] and, thus, directly impact synaptic plasticity. For example, it was reported that an mGlu5 receptor negative allosteric modulator rescued Aβ1-42-induced inhibition of LTP and prevented the induction of LTD in Aβ1-42 treated animals [80]. In Fragile X and Rett Syndrome, mGlu5 receptors directly interact with Fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) [64,75,78]. In light of these discoveries, mGlu5 receptors have been subjected to scrutiny as a promising target for the treatment of such diseases [53,57,81,82,83,84,85,86].
2. Contribution of mGlu5 to Persistent Forms of Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity
Persistent synaptic plasticity refers to long-lasting (>24 h) changes in synaptic transmission and is expressed in the form of LTP and LTD, both of which facilitate hippocampus-dependent spatial memory [87,88,89,90,91,92,93]. For this reason, these processes are typically investigated in freely behaving rats and mice [93]. MGlu5 is positively coupled to phospholipase C and activation of the receptor leads to the generation of inositol trisphospate (IP3) [24,94,95]. The binding of IP3 to receptors on the endoplasmic reticulum leads to release of calcium into the cytosol and subsequent activation of enzymes, such as protein kinase C (PKC), that are stimulated by intracellular Ca2+ elevations [96,97,98,99]. This supports a whole variety of biochemical signaling cascades that are conducive towards the maintenance of LTP and LTD for periods of hours and more [100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109]. For example, an increase in phosphorylation of protein F1, a substrate PKC, is directly related to long-term changes in synaptic enhancement [110]. Furthermore, activation of PKC results in the phosphorylation of the serine 818 residue of GluR1 (GluA1), a critical step that is required for LTP [103].
2.1. Contribution of mGlu5 to Long-Term Potentiation
In the hippocampus, LTP is typically induced in vivo via activation of NMDARs [111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120] although NMDAR-independent forms have also been described in behaving rodents [121,122]. Numerous studies have also described the necessity of mGlu5 receptors for the induction and maintenance of LTP in rodents in vivo [11,18,27,34,123,124]. Furthermore, activation of mGlu5 receptors, either with an agonist [125,126] or positive allosteric modulator (PAM), results in the enhancement of LTP [127,128,129,130]. It should be mentioned that not all hippocampal subregions display the same dependency of persistent LTP on mGlu5 receptors. Whereas perforant path (pp)–DG, mossy fiber (MF)–CA3 and Schaffer collateral (SC)–CA1 synapses require activation of mGlu5 to express LTP (>24 h) [3,5,11], associational commissural–CA3 synapses do not [3].
Following the induction of LTP, a first phase, called early-LTP (E-LTP, or short-term potentiation, STP) that lasts 2–3 h can be distinguished from late LTP (L-LTP) [131,132,133,134]. It is E-LTP/STP that typically depends on the activation of NMDARs [135,136,137,138]. The importance of mGlu5 receptors in this process has been shown in mGlu5 knock-out mice, where the NMDAR component of LTP is abolished [139]. In freely behaving rats, pharmacological antagonism of mGlu5 receptors dose-dependently impairs STP [11]. Mechanistically, mGlu5 receptor activation serves to potentiate NMDAR currents [140,141,142,143], a process that is dependent on intracellular Ca2+-release and PKC-activation [139,143,144].
NMDARs that support synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus are composed of GluN1, GluN2A and GluN2B subunits [145]. Whether glutamate binding to NMDARs results in LTP or LTD depends on the pattern of afferent stimulation [111,117], as well as on the subunit composition of the NMDAR, which switches from a high to low GluN2B/GluN2A ratio during development [146,147,148]. This change in ratio is dependent on activation of mGlu5 receptors. MGlu5 receptor knock-out mice, for example, show a deficiency in the activity-dependent switch from GluN2B to GluN2A in the hippocampus and visual cortex, and application of an mGlu5 receptor antagonist inhibits the sensitivity of EPSCs initiated by application of the GluN2B inhibitor ifenprodil [149]. The contribution of GluN2A and/or GluN2B to LTP and LTD depends on the frequency of postsynaptic depolarisation [150,151], as well as the pattern of impulses delivered by the afferent input [111]. Furthermore, the threshold for induction of GluN2B-dependent hippocampal LTD is lowered when mGlu5 is activated [152], and transgenic mice that lack mGlu5 fail to express NMDAR-dependent hippocampal LTP [139]. Thus, alterations in mGlu5 receptor function may alter the direction of change in frequency-dependent hippocampal synaptic plasticity, or even serve to hinder the induction of a specific form of synaptic plasticity.
The necessity of mGlu5 receptor activation for persistent forms of LTP has been described for perforant path–dentate gyrus, Schaffer collateral–CA1 and mossy fiber–CA3 synapses in mouse and rat hippocampi (Table 1, Figure 1) [3,5,11,153]. Sustained changes in synaptic efficacy (i.e., longer than 24 h) require protein synthesis [154,155,156], typically mediated by activation of immediate early genes (IEGs). Many signaling cascades that eventually lead to the activation of IEGs are dependent on mGlu5 receptor activation. For example, activation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMK) and the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 are crucial steps in the activation of the c-fos IEG [157], processes that are supported by activation of mGlu5 receptors [158]. Furthermore, mGlu5 receptor activation is involved in the modulation of other downstream targets, such as binding to the IEG, Homer 1a [159,160]. The interaction of Homer and Shank, two proteins of the postsynaptic density (PSD), result in morphological changes in dendritic spines [161] and to an association of group I mGlu receptors with the NMDAR signaling pathway [162,163]. Furthermore, increased levels of mGlu5 receptors and Homer1 proteins in Sin3aNH transgenic mice result in enhanced hippocampus-dependent memory and synaptic plasticity [164]. Another element in the mGlu5 receptor mediation of synaptic plasticity involves their interaction with PSD-95/Disk large/ZO-1 (PDZ) domains [165]. Tamalin, a PDZ domain-containing protein, is crucial for trafficking and cell surface expression of mGlu5 receptors [166]. Preventing the interaction of group I mGlu receptors and Tamalin impairs the expression of LTD, but not LTP, in the presence of an mGlu5 receptor agonist [7]. These results support the crucial role of PDZ-domain proteins in mGlu5 receptor mediated hippocampal LTD. Thus, the mechanistic regulation by the mGlu5 receptor of hippocampal synaptic plasticity extends beyond its biochemical coupling to phospholipase C and regulation of NMDAR function, but it is also enabled by its modulation of a variety of intracellular targets. The modulation by mGlu5 receptors of cell surface and intracellular targets related to the induction and maintenance of LTP, suggest, in turn, that perturbation of mGlu5 receptor activity will have profound effects on this form of persistent synaptic plasticity. This has been shown in a variety of studies using pharmacological antagonism, or transgenic deletion of mGlu5 receptors [3,8,11,16,127,153,167].

Table 1.
Summary of mGlu5 receptor contribution to short-term potentiation (STP), long-term potentiation (LTP), short-term depression (STD) and long-term depression (LTD) in the hippocampal perforant path–dentate gyrus (DG), mossy fiber–CA3 (MF-CA3), associational/commissural–CA3 (AC–CA3) or Schaffer collateral–CA1 (CA1) synapses in vivo and in vitro in rats or mice. KO: knock-out; NAM: negative allosteric modulators; PAM: positive allosteric modulators.
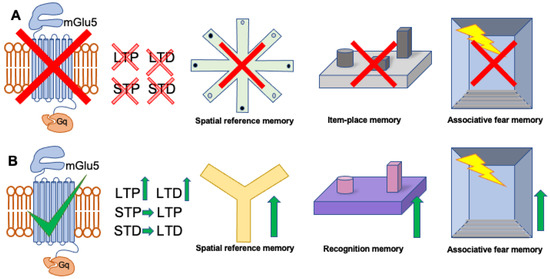
Figure 1.
Schema of the effects of pharmacological antagonism, or agonism, of mGlu5 receptors on hippocampal synaptic plasticity and hippocampus-dependent forms of learning and memory. (A) Pharmacological antagonism of mGlu5 receptors prevents the maintenance of both LTP and LTD. STP and STD are also impaired. Prior treatment with an mGlu5 receptor antagonist prevents spatial reference memory in paradigms such as the 8-arm radial maze, prevents effective item-place memory and disrupts associative fear memory. (B) Pharmacological activation of mGlu5 receptors strengthens and prolongs LTP and LTD and also facilitates short-term plasticity (STP, STD) into long-term plasticity (LTP, LTD respectively). Spatial learning in paradigms such as the Y-maze is enhanced, recognition memory is improved, as is associative fear memory. For relevant literature, see Table 1 and Table 2. The red cross signifies inhibition/impairment. The green tick signifies activation, and the green arrows signify enhancement.
2.2. Contribution of mGlu5 Receptors to Long-Term Depression
Hippocampal LTD is also significantly regulated by mGlu5. Initial studies reported that LTD could be induced by agonist activation of mGlu5 in hippocampal slice preparations [172]. Later, in vivo studies showed a more complex regulation of input-specific, experience-dependent LTD by mGlu5 receptors in the hippocampus of freely behaving rats and mice (Table 1, Figure 1, [3,4,5,123,169]). In this case, LTD was induced by patterned stimulation of afferent fibres within the hippocampus and the effects of pharmacological agonism, or antagonism of mGlu5 receptors was explored. Here, effects differ depending on the hippocampal subregion. For example, at pp–DG, SC–CA1 and AC–CA3 synapses, LTD depends on the activation of mGlu5 receptors. In contrast, LTD at MF–CA3 synapses does not require activation of this receptor [3]. Furthermore, hippocampal short-term depression (STD) is facilitated into persistent LTD by agonist activation of the receptors [123].
Interestingly, pharmacological antagonism of mGlu5 receptors prevents the induction, but not the persistency of LTD induced by high frequency stimulation of the perforant path both in vitro [168] and in vivo [5]. MGlu5 receptor antagonism results in a suppression of NMDAR currents and, thus, an inhibition of LTD [173]. Furthermore, it has been shown that mGlu5 knock-out mice fail to express LTD [172] and application of mGlu5 receptor antagonists impair both NMDAR-dependent [5] and independent forms of LTD [172,174,175,176,177]. In contrast, agonist activation of mGlu5 promotes the expression of persistent hippocampal LTD [3,4,7,169], a process that is likely to involve facilitation of currents through NMDARs that contain GluN2B [152].
3. Contribution of mGlu5 Receptors to Forms of Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity That Are Enabled by Spatial Experience
The hippocampus is an essential brain structure for the processing and encoding of spatial and associative representations of experience by means of long-term synaptic plasticity [87,93,178]. LTP and LTD are the cellular mechanisms that enable the storage of this kind of information [88,89,90,93,179,180]. Numerous studies have described the specific kinds of spatial information encoded by LTP and LTD, whereby a differentiation of the relative elements of spatial memory enabled by LTP and LTD has become evident. For example, LTP is expressed in response to the de novo acquisition of knowledge about a novel spatial environment [88,93,180,181,182,183,184,185], whereas LTD is facilitated upon the acquisition, or updating, of knowledge about discrete content features of an environment [4,88,89,90,180,186,187,188,189]. All hippocampal subfields reportedly show the same LTP-specific stimulus response related to novel spatial learning [88,180,186]. The facilitation of LTD in distinct hippocampal subfields and synaptic subcompartments, on the other hand, is triggered by different kinds of spatial content information. For example, whereas Schaffer collateral–CA1 and associational commissural–CA3 synapses respond, with LTD, to novel or changed configurations of discretely located spatial items [180,186], exposure of rodents to novel, or updated, configurations of highly visible landmark objects facilitates LTD at perforant path–DG and mossy fiber–CA3 synapses [180,186]. It is not only visuospatial cues that result in the expression of LTD, however, but spatial cues generated by odours, or sound, also facilitate synaptic plasticity and thus, enable the formation of spatial memories [169,190]. This suggests that, for the hippocampus, all sensory modalities may be able to generate salient sensory information that is integrated into associative records of experience by LTP, and spatial content representations by means of LTD. In other words, LTP creates representation templates that are refined and updated by LTD [191].
Numerous studies have shown that synaptic plasticity that occurs by spatial experience depends on the activation of mGlu5 receptors, that potentiating mGlu5 receptor function results in improved learning performance in spatial tasks and that antagonism of mGlu5 receptors decreases performance in spatial learning and working or reference memory (Table 2, Figure 1). The procurement of spatial content information, such as the acquisition, or updating, of knowledge about novel object-place configurations, or of spatial object recognition, is prevented in the hippocampal CA1 region during pharmacological antagonism of mGlu5 receptors [4,5]. LTD that is facilitated by this kind of learning experience is also inhibited [4,5]. Furthermore, a tight correlation between activation of mGlu5 receptors, successful induction of LTP and learning has been shown [9,11,16,124]. These results suggest that mGlu5 receptors are crucial for the expression of hippocampal LTD and LTP, as well as for the underlying acquisition of spatial information [4,5,11,192,193,194].

Table 2.
Summary of mGlu5 receptor contribution to hippocampal to hippocampus-dependent learningKO: knock-out; MWM: Morris water maze; NAM: negative allosteric modulators; PAM: positive allosteric modulators.
Table 2.
Summary of mGlu5 receptor contribution to hippocampal to hippocampus-dependent learningKO: knock-out; MWM: Morris water maze; NAM: negative allosteric modulators; PAM: positive allosteric modulators.
| Hippocampus-Dependent Learning Task | Species | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antagonist/NAM | |||
| object-place configuration | rat | LTD and memory inhibited | [5] |
| acquisition of novel environment | rat | impaired place field stability | [17] |
| acquisition of novel audiospatial cues | rat | LTD inhibited | [169] |
| eight-arm radial maze | rat | reference and working memory impaired | [11,16,124] |
| four-arm plus maze | rat | impairment of spontaneous alternation behaviour | [195] |
| Y-Maze spatial alternation task | rat | impairment of retention; no effect if antagonist applied immediately after training | [10] |
| T-Maze | rat | extinction of consolidated context impaired | [196] |
| working and reference memory | rat | impaired performance | [124] |
| inhibitory avoidance learning | rat | impairment in retention | [197] |
| extinction learning | rat | impaired extinction of consolidated information | [196] |
| fear conditioning | rat | impaired expression of contextual fear conditioning | [198] |
| fear conditioning | mouse | attenuation of cue-elicited freezing during fear conditioning | [199] |
| spatial object recognition | mouse | LTD and learning inhibited | [4] |
| environmental enrichment (EE) | mouse | impairment of EE-mediated LTP | [18] |
| Agonist/PAM | |||
| object recognition | rat | enhancement with low concentration of PAM | [200] |
| Y-maze spatial alternation task | rat | improvement in spatial alternation retention | [201] |
| T-maze | rat | enhanced memory abilities | [202] |
| MWM | mouse | enhanced learning and memory performance | [127] |
| MWM | mouse | impaired spatial learning | [203] |
| MWM | mouse | enhanced reversal learning | [204] |
| Barnes maze | mouse | improved performance during reversal training | [202] |
| fear extinction | mouse | enhanced fear extinction learning | |
| mGlu5 KO | |||
| MWM | mouse | impaired spatial learning | [153] |
| fear-conditioning | mouse | impaired processing of contextual information | [153] |
Novel, or constantly changing spatial and sensory stimuli within an environment, referred to as environmental enrichment, may help in preventing cognitive decline [205,206]. Environmental enrichment has also been reported to significantly improve hippocampal synaptic responses [207]. Interestingly, antagonism of mGlu5 receptors prevents enrichment-mediated improvement in synaptic plasticity, and environmental enrichment enhances mGlu5–Homer1a interactions [18,208], supporting a significant role for mGlu5 in the optimisation of cognitive performance. This possibility is, furthermore, supported by studies that show an upregulation of mGlu5 receptor expression after induction of synaptic plasticity, or hippocampus-dependent learning tasks [209,210]. As mentioned earlier, the hippocampus supports memory formation by integrating information from different sensory modalities and promoting learning-dependent synaptic plasticity that occurs in conjunction with this learning process [93,211]. These modalities comprise, for example, vision, hearing or olfaction [169,190,212,213,214,215] and all of these contribute to environmental enrichment. Here, also, mGlu5 receptors play a role. For example, receptor antagonism prevents the facilitation of hippocampal LTD that occurs in response to the novel exposure of freely behaving rats to audiospatial information [169].
The formation of a memory does not only depend on the expression of long-term synaptic plasticity but also on the creation of stable place fields [216,217] and the unhampered activity of network oscillations [171,178]. Here, too, mGlu5 receptors enable these mechanisms. Encoding of spatial memory by means of alterations in synaptic plasticity is supported by neuronal oscillations [218,219,220]. Oscillations in the hippocampus occur at theta (5–50 Hz) and gamma (30–100 Hz) frequencies, and their coupling supports the acquisition and retrieval of spatial information by means of synaptic potentiation [221,222]. Strikingly, mGlu5 receptors affect theta and gamma power: prolonged antagonism of mGlu5 receptors results in a suppression of theta and gamma activity in the dentate gyrus and subsequently leads to an inhibition of LTD [16,130]. In line with this, positive modulation with a PAM enhances LTP and leads to an increase in relative spectral and gamma power that precedes LTP [130]. Another facet of efficient cognitive performance comprises the suppression of memories and, specifically, of behaviors, that are no longer salient. The underlying process is termed extinction learning [223,224]. Here, too, mGlu5 plays a role, whereby receptor antagonism shifts extinction learning towards context-independent elements of spatial experience [196].
Spatial learning is also used as a behavioral assay to understand the mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of brain disease and disorders. In animal models of AD, performance in different spatial learning related tasks, such as the Barnes maze [225,226] or the water maze [227] is affected. Equivalent deficits in spatial learning can be found in transgenic models of Rett syndrome [228,229,230], Fragile X [231,232] and psychosis [233,234,235]. Strikingly, a dysfunction of mGlu5 receptors has been proposed to play a crucial role in these diseases. Furthermore, PAMs acting on mGlu5 receptors can reverse cognitive deficits and, thus, are under scrutiny as potential treatments for a variety of diseases involving learning-related disorders [127,200,236].
4. Conclusions
In summary, studies conducted in recent decades provide evidence for a key role for the mGlu5 receptor in the successful expression of persistent synaptic plasticity that, in turn, enables the effective acquisition and retention of spatial memory. Aberrations in mGlu5 receptor functionality, thus, affect not only LTP and LTD, but also cellular mechanisms that enable the formation of spatial representations and memories, both in humans and rodents [93,237,238]. Aspects that still remain unclear are, for example, the putative role of heteromeric mGlu receptors in hippocampal synaptic plasticity and experience-dependent information encoding. Chemogenetic approaches that allow the targeting of discrete populations of mGlu5 receptors should also help decipher the role of mGlu5 receptors in local networks that support cognition. Given the prominent role of mGlu5 receptors in a variety of diseases, this receptor holds promise as a potential target for pharmaceutical intervention. Although a vast amount of pre-clinical and basic research has been conducted to evaluate the function of mGlu5 receptors, the gap to clinical applications is still large [70,239,240] and see also: https://www.fraxa.org/fragile-x-clinical-trials-mglur-theory (accessed on 28 August 2022). Future research could help bridge this gap by dissecting the molecular mechanisms downstream of mGlu5 receptor activation, with the goal of understanding how these receptors contribute to diseases and, ultimately, of overcoming the challenge of transferring knowledge gained through basic research into clinically effective strategies.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) grant (SFB 1280/A04, project no.: 316803389).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ferraguti, F.; Shigemoto, R. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. Cell Tissue Res. 2006, 326, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, C.; Sesma, M.A.; McDonald, C.T.; O’Malley, K.; den Pol, A.N.V.; Olney, J.W. Distribution of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor MGluR5 Immunoreactivity in Rat Brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1995, 355, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagena, H.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. MGlu5 Acts as a Switch for Opposing Forms of Synaptic Plasticity at Mossy Fiber-CA3 and Commissural Associational-CA3 Synapses. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4999–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, J.J.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Endogenous Hippocampal LTD That Is Enabled by Spatial Object Recognition Requires Activation of NMDA Receptors and the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor, MGlu5. Hippocampus 2012, 23, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkirov, S.G.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Involvement of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor MGluR5 in NMDA Receptor-Dependent, Learning-Facilitated Long-Term Depression in CA1 Synapses. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Lim, Y.J.; Kumar, K.; Baby, N.; Pang, K.L.K.; Benoy, A.; Behnisch, T.; Sajikumar, S. Group III Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Gate Long-Term Potentiation and Synaptic Tagging/Capture in Rat Hippocampal Area CA2. elife 2020, 9, e55344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyman, S.; Braunewell, K.-H.; O’Connell, K.E.; Dev, K.K.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Inhibition of the Interaction Between Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and PDZ-Domain Proteins Prevents Hippocampal Long-Term Depression, but Not Long-Term Potentiation. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2019, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Lv, X.; Maksymetz, J.; Stansley, B.J.; Ghoshal, A.; Gogliotti, R.G.; Niswender, C.M.; Lindsley, C.W.; Conn, P.J. MGlu5 Positive Allosteric Modulators Facilitate Long-Term Potentiation via Disinhibition Mediated by MGlu5-Endocannabinoid Signaling. ACS Pharm. Transl. Sci. 2019, 2, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balschun, D.; Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Wagner, T.; Behnisch, T.; Reymann, K.G.; Wetzel, W. A Specific Role for Group I MGluRs in Hippocampal LTP and Hippocampus-Dependent Spatial Learning. Learn. Mem. 1999, 6, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balschun, D.; Wetzel, W. Inhibition of MGluR5 Blocks Hippocampal LTP in Vivo and Spatial Learning in Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 73, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naie, K.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Regulation by Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 of LTP in the Dentate Gyrus of Freely Moving Rats: Relevance for Learning and Memory Formation. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naie, K.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Investigations of the Protein Synthesis Dependency of MGluR-Induced Long-Term Depression in the Dentate Gyrus of Freely Moving Rats. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49 (Suppl. S1), 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinbilek, B.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Antagonism of Group III Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Results in Impairment of LTD but Not LTP in the Hippocampal CA1 Region, and Prevents Long-Term Spatial Memory. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinbilek, B.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. A Specific Role for Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Hippocampal Long-Term Depression and Spatial Memory. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleuca, A.E.; Alemà, G.S.; Casolini, P.; Barberis, I.; Ciabattoni, F.; Orlando, R.; Menna, L.D.; Iacovelli, L.; Scioli, M.R.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Changes in MGlu5 Receptor Signaling Are Associated with Associative Learning and Memory Extinction in Mice. Life 2022, 12, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikbaev, A.; Neyman, S.; Ngomba, R.T.; Conn, P.J.; Conn, J.; Nicoletti, F.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. MGluR5 Mediates the Interaction between Late-LTP, Network Activity, and Learning. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Place Field Stability Requires the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor, MGlu5. Hippocampus 2014, 24, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschler, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor, MGlu5, Mediates Enhancements of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation after Environmental Enrichment in Young and Old Mice. Neuropharmacology 2017, 115, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.L.; Westbrook, G.L. The Physiology of Excitatory Amino Acids in the Vertebrate Central Nervous System. Prog. Neurobiol. 1987, 28, 197–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepp, D.D.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Brain Function and Pathology. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1993, 14, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asztély, F.; Gustafsson, B. Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors. Mol. Neurobiol. 1996, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, M.; Heinemann, S. Cloned Glutamate Receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1994, 17, 31–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, S.; Nakajima, Y.; Masu, M.; Ueda, Y.; Nakahara, K.; Watanabe, D.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kawabata, S.; Okada, M. Glutamate Receptors: Brain Function and Signal Transduction. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1998, 26, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, P.J.; Pin, J.P. Pharmacology and Functions of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1997, 37, 205–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakami, R.; Katsuki, F.; Sugiyama, H. A Variant of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 5: An Evolutionally Conserved Insertion with No Termination Codon. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 194, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, C.; Gomeza, J.; Brabet, I.; Curry, K.; Bockaert, J.; Pin, J.P. Molecular, Functional, and Pharmacological Characterization of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Type 5 Splice Variants: Comparison with MGluR1. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 3970–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Role of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Persistent Forms of Hippocampal Plasticity and Learning. Neuropharmacology 2012, 66, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.W.; Cotman, C.W. Long-Term Potentiation of Guinea Pig Mossy Fiber Responses Is Not Blocked by N-Methyl D-Aspartate Antagonists. Neurosci. Lett. 1986, 70, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, H.; Shinozaki, H.; Yamamoto, C. Activation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Type 2/3 Suppresses Transmission at Rat Hippocampal Mossy Fibre Synapses. J. Physiol. 1996, 493 Pt 2, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macek, T.A.; Winder, D.G.; Gereau, R.W.; Ladd, C.O.; Conn, P.J. Differential Involvement of Group II and Group III MGluRs as Autoreceptors at Lateral and Medial Perforant Path Synapses. J. Neurophysiol. 1996, 76, 3798–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.Y.; Rusakov, D.A.; Kullmann, D.M. Activation of AMPA, Kainate, and Metabotropic Receptors at Hippocampal Mossy Fiber Synapses: Role of Glutamate Diffusion. Neuron 1998, 21, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.-B.; Castillo, P.E. Role of Glutamate Autoreceptors at Hippocampal Mossy Fiber Synapses. Neuron 2008, 60, 1082–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D. Group 1 and 2 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Play Differential Roles in Hippocampal Long-Term Depression and Long-Term Potentiation in Freely Moving Rats. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 3303–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Reymann, K.G. 1S,3R-ACPD Dose-Dependently Induces a Slow-Onset Potentiation in the Rat Hippocampal CA1 Region in Vivo. Neuropharmacology 1995, 34, 1103–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D. Group III Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Modulate Long-Term Depression in the Hippocampal CA1 Region of Two Rat Strains in Vivo. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausnitzer, J.; Kulla, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Role of the Group III Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor in LTP, Depotentiation and LTD in Dentate Gyrus of Freely Moving Rats. Neuropharmacology 2004, 46, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naie, K.; Gundimi, S.; Siegmund, H.; Heinemann, U.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Group III Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-Mediated, Chemically Induced Long-Term Depression Differentially Affects Cell Viability in the Hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 535, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baude, A.; Nusser, Z.; Roberts, J.D.; Mulvihill, E.; McIlhinney, R.A.; Somogyi, P. The Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor (MGluR1 Alpha) Is Concentrated at Perisynaptic Membrane of Neuronal Subpopulations as Detected by Immunogold Reaction. Neuron 1993, 11, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan, R.; Roberts, J.D.; Shigemoto, R.; Ohishi, H.; Somogyi, P. Differential Plasma Membrane Distribution of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors MGluR1 Alpha, MGluR2 and MGluR5, Relative to Neurotransmitter Release Sites. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1997, 13, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan, R.; Nusser, Z.; Roberts, J.D.; Shigemoto, R.; Somogyi, P. Perisynaptic Location of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors MGluR1 and MGluR5 on Dendrites and Dendritic Spines in the Rat Hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigemoto, R.; Kinoshita, A.; Wada, E.; Nomura, S.; Ohishi, H.; Takada, M.; Flor, P.J.; Neki, A.; Abe, T.; Nakanishi, S.; et al. Differential Presynaptic Localization of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtypes in the Rat Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 7503–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, P.; Isaac, M.; Slassi, A. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Modulators and Their Potential Therapeutic Applications. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2007, 17, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ure, J.; Baudry, M.; Perassolo, M. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and Epilepsy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 247, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldrich, R.X.; Chapman, A.G.; Sarro, G.D.; Meldrum, B.S. Glutamate Metabotropic Receptors as Targets for Drug Therapy in Epilepsy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 476, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicco, G.D.; Marzano, E.; Iacovelli, L.; Celli, R.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Nicoletti, F.; Ngomba, R.T.; Wall, M.J. Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-Mediated Long Term Depression Is Disrupted in the Hippocampus of WAG/Rij Rats Modelling Absence Epilepsy. Neuropharmacology 2021, 196, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, P.J.; Lindsley, C.W.; Jones, C.K. Activation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors as a Novel Approach for the Treatment of Schizophrenia. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niswender, C.M.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: Physiology, Pharmacology, and Disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 295–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovyk, V.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Time-Dependent Alterations in the Expression of NMDA Receptor Subunits along the Dorsoventral Hippocampal Axis in an Animal Model of Nascent Psychosis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardigan, J.D.; Huszar, S.L.; McNaughton, C.H.; Hutson, P.H.; Uslaner, J.M. MK-801 Produces a Deficit in Sucrose Preference That Is Reversed by Clozapine, d-Serine, and the Metabotropic Glutamate 5 Receptor Positive Allosteric Modulator CDPPB: Relevance to Negative Symptoms Associated with Schizophrenia? Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 95, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, C.R.; Veselinović, T.; Rajkumar, R.; Mauler, J.; Orth, L.; Ruch, A.; Ramkiran, S.; Heekeren, K.; Kawohl, W.; Wyss, C.; et al. MGluR5 Receptor Availability Is Associated with Lower Levels of Negative Symptoms and Better Cognition in Male Patients with Chronic Schizophrenia. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 2762–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matosin, N.; Fernandez-Enright, F.; Fung, S.J.; Lum, J.S.; Engel, M.; Andrews, J.L.; Huang, X.-F.; Weickert, C.S.; Newell, K.A. Alterations of MGluR5 and Its Endogenous Regulators Norbin, Tamalin and Preso1 in Schizophrenia: Towards a Model of MGluR5 Dysregulation. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 130, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, F.; Bockaert, J.; Collingridge, G.L.; Conn, P.J.; Ferraguti, F.; Schoepp, D.D.; Wroblewski, J.T.; Pin, J.P. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: From the Workbench to the Bedside. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 1017–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dhull, D.K.; Mishra, P.S. Therapeutic Potential of MGluR5 Targeting in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Belmonte, A.; Aguado, C.; Alfaro-Ruiz, R.; Albasanz, J.L.; Martín, M.; Moreno-Martínez, A.E.; Fukazawa, Y.; Luján, R. The Density of Group I MGlu5 Receptors Is Reduced along the Neuronal Surface of Hippocampal Cells in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Qin, S.; Xu, J.-T.; Duan, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Inhibition of the ISR Abrogates MGluR5-Dependent Long-Term Depression and Spatial Memory Deficits in a Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Transl. Psychiat. 2022, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elrahman, K.S.; Hamilton, A.; Albaker, A.; Ferguson, S.S.G. MGluR5 Contribution to Neuropathology in Alzheimer Mice Is Disease Stage-Dependent. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecca, A.P.; McDonald, J.W.; Michalak, H.R.; Godek, T.A.; Harris, J.E.; Pugh, E.A.; Kemp, E.C.; Chen, M.-K.; Salardini, A.; Nabulsi, N.B.; et al. PET Imaging of MGluR5 in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elrahman, K.S.; Albaker, A.; de Souza, J.M.; Ribeiro, F.M.; Schlossmacher, M.G.; Tiberi, M.; Hamilton, A.; Ferguson, S.S.G. Aβ Oligomers Induce Pathophysiological MGluR5 Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice in a Sex-Selective Manner. Sci. Signal 2020, 13, eabd2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elrahman, K.S.; Ferguson, S.S.G. Noncanonical Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 2021, 62, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastianutto, I.; Goyet, E.; Andreoli, L.; Font-Ingles, J.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Bouquier, N.; Jahannault-Talignani, C.; Moutin, E.; Menna, L.D.; Maslava, N.; et al. D1-MGlu5 Heteromers Mediate Noncanonical Dopamine Signaling in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1168–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-N.; Fan, J.-K.; Gu, L.; Yang, H.-M.; Zhan, S.-Q.; Zhang, H. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Inhibits α-Synuclein-Induced Microglia Inflammation to Protect from Neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turle-Lorenzo, N.; Breysse, N.; Baunez, C.; Amalric, M. Functional Interaction between MGlu 5 and NMDA Receptors in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, K.; Ko, J.K.-S.; Yung, K.K.-L. Roles of Glutamate Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, M.F.; Huber, K.M.; Warren, S.T. The MGluR Theory of Fragile X Mental Retardation. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassell, G.J.; Warren, S.T. Fragile X Syndrome: Loss of Local MRNA Regulation Alters Synaptic Development and Function. Neuron 2008, 60, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waung, M.W.; Huber, K.M. Protein Translation in Synaptic Plasticity: MGluR-LTD, Fragile X. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2009, 19, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dölen, G.; Carpenter, R.L.; Ocain, T.D.; Bear, M.F. Mechanism-Based Approaches to Treating Fragile X. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 127, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, D.D.; Bear, M.F. Toward Fulfilling the Promise of Molecular Medicine in Fragile X Syndrome. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalon, A.; Sidorov, M.; Ballard, T.M.; Ozmen, L.; Spooren, W.; Wettstein, J.G.; Jaeschke, G.; Bear, M.F.; Lindemann, L. Chronic Pharmacological MGlu5 Inhibition Corrects Fragile X in Adult Mice. Neuron 2012, 74, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppel, D.C.; McCamphill, P.K.; Senter, R.K.; Heynen, A.J.; Bear, M.F. MGluR5 Negative Modulators for Fragile X: Treatment Resistance and Persistence. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 718953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, M.; Petibon, Y.; Han, P.; Kuruppu, D.; Ma, C.; Yokell, D.; Neelamegam, R.; Normandin, M.D.; Fakhri, G.E.; Brownell, A.-L. In Vivo Imaging of MGlu5 Receptor Expression in Humans with Fragile X Syndrome towards Development of a Potential Biomarker. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brašić, J.R.; Goodman, J.A.; Nandi, A.; Russell, D.S.; Jennings, D.; Barret, O.; Martin, S.D.; Slifer, K.; Sedlak, T.; Mathur, A.K.; et al. Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein and Cerebral Expression of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 5 in Men with Fragile X Syndrome: A Pilot Study. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Li, H.; Chang, Q. MeCP2 Phosphorylation Is Required for Modulating Synaptic Scaling through MGluR5. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12841–12847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogliotti, R.G.; Senter, R.K.; Rook, J.M.; Ghoshal, A.; Zamorano, R.; Malosh, C.; Stauffer, S.R.; Bridges, T.M.; Bartolome, J.M.; Daniels, J.S.; et al. MGlu5 Positive Allosteric Modulation Normalizes Synaptic Plasticity Defects and Motor Phenotypes in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet 2016, 25, 1990–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wu, H.; Coronado, A.A.; de Laittre, E.; Osterweil, E.K.; Zhang, Y.; Bear, M.F. Negative Allosteric Modulation of MGluR5 Partially Corrects Pathophysiology in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 11946–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Mironov, S.L. CA1 Neurons Acquire Rett Syndrome Phenotype After Brief Activation of Glutamatergic Receptors: Specific Role of MGluR1/5. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Fellin, T.; Zhu, Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Auberson, Y.P.; Meaney, D.F.; Coulter, D.A.; Carmignoto, G.; Haydon, P.G. Enhanced Astrocytic Ca2+ Signals Contribute to Neuronal Excitotoxicity after Status Epilepticus. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10674–10684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, K.C.; Lacor, P.N.; Pitt, J.; Klein, W.L. Aβ Oligomer-Induced Synapse Degeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, J.W.; Kaufman, A.C.; Kostylev, M.; Heiss, J.K.; Stagi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kerrisk, M.E.; Vortmeyer, A.; Wisniewski, T.; Koleske, A.J.; et al. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Is a Coreceptor for Alzheimer Aβ Oligomer Bound to Cellular Prion Protein. Neuron 2013, 79, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.-W.; Nicoll, A.J.; Zhang, D.; Mably, A.J.; O’Malley, T.; Purro, S.A.; Terry, C.; Collinge, J.; Walsh, D.M.; Rowan, M.J. MGlu5 Receptors and Cellular Prion Protein Mediate Amyloid-β-Facilitated Synaptic Long-Term Depression in Vivo. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleva, R.M.; Olive, M.F. Positive Allosteric Modulators of Type 5 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (MGluR5) and Their Therapeutic Potential for the Treatment of CNS Disorders. Molecules 2011, 16, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenga, J.; Hayashi, S.; de Vrij, F.M.S.; Koekkoek, S.K.; van der Linde, H.C.; Nieuwenhuizen, I.; Song, C.; Buijsen, R.A.M.; Pop, A.S.; GomezMancilla, B.; et al. AFQ056, a New MGluR5 Antagonist for Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 42, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Grauer, S.; Kelley, C.; Navarra, R.; Graf, R.; Zhang, G.; Atkinson, P.J.; Popiolek, M.; Wantuch, C.; Khawaja, X.; et al. ADX47273 [S-(4-Fluoro-Phenyl)-{3-[3-(4-Fluoro-Phenyl)-[1,2,4]-Oxadiazol-5-Yl]-Piperidin-1-Yl}-Methanone]: A Novel Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5-Selective Positive Allosteric Modulator with Preclinical Antipsychotic-Like and Procognitive Activities. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 327, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musazzi, L. Targeting Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors for Rapid-Acting Antidepressant Drug Discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Dis. 2020, 16, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, S.H.; Jaeschke, G.; Wettstein, J.G.; Lindemann, L. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 as Drug Target for Fragile X Syndrome. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 20, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stansley, B.J.; Conn, P.J. The Therapeutic Potential of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Modulation for Schizophrenia. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 38, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Hippocampal Long-Term Depression: Master or Minion in Declarative Memory Processes? Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Hippocampal Long-Term Depression and Long-Term Potentiation Encode Different Aspects of Novelty Acquisition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8192–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacho, M.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. The Intriguing Contribution of Hippocampal Long-Term Depression to Spatial Learning and Long-Term Memory. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 806356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Braunewell, K.-H. Novelty Acquisition Is Associated with Induction of Hippocampal Long-Term Depression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8739–8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, J.R.; Heynen, A.J.; Shuler, M.G.; Bear, M.F. Learning Induces Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus. Science 2006, 313, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D. Item-Place Encoding Through Hippocampal Long-Term Depression. In Handbook of Object Novelty Recognition; Ennaceur, A., de Souza Silva, M., Eds.; Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 27, pp. 273–289. ISBN 9780128120125. [Google Scholar]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D. Learning-Related Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression; Byrne, H., John, Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 585–609. ISBN 978-0-12-805291-4. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, T.; Sugihara, H.; Nawa, H.; Shigemoto, R.; Mizuno, N.; Nakanishi, S. Molecular Characterization of a Novel Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor MGluR5 Coupled to Inositol Phosphate/Ca2+ Signal Transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 13361–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pin, J.P.; Duvoisin, R. The Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: Structure and Functions. Neuropharmacology 1995, 34, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, N.; Ritz, M.F.; Freyermuth, S.; Rogue, P.; Malviya, A.N. Stimulation of Nuclear Protein Kinase C Leads to Phosphorylation of Nuclear Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor and Accelerated Calcium Release by Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate from Isolated Rat Liver Nuclei. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, P.J.; Metzger, W.; Gaspers, L.D.; Thomas, A.P. Differential Regulation of Multiple Steps in Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Signaling by Protein Kinase C Shapes Hormone-Stimulated Ca2+ Oscillations. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 18519–18533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, R.F. 20 Years of Ins(1,4,5)P3, and 40 Years Before. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2003, 4, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, J.D. The Inositol Trisphosphate (IP3) Signal Transduction Pathway. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, tr3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Feng, D.P. Postsynaptic Protein Kinase C Essential to Induction and Maintenance of Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampal CA1 Region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2576–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.A.; Mizumori, S.J.Y.; Lovinger, D.M.; Sheu, F.-S.; Murakami, K.; Chan, S.Y.; Linden, D.J.; Nelson, R.B.; Routtenberg, A. Selective Decline in Protein F1 Phosphorylation in Hippocampus of Senescent Rats. Neurobiol. Aging 1988, 9, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovinger, D.M.; Colley, P.A.; Akers, R.F.; Nelson, R.B.; Routtenberg, A. Direct Relation of Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation to Phosphorylation of Membrane Protein F1, a Substrate for Membrane Protein Kinase C. Brain Res. 1986, 399, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Kang, M.-G.; Johnson, R.C.; Esteban, J.; Huganir, R.L.; Malinow, R. Synaptic Incorporation of AMPA Receptors during LTP Is Controlled by a PKC Phosphorylation Site on GluR1. Neuron 2006, 51, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, R.J.; Carpenter, D.O. A Comparison of the Roles of Protein Kinase C in Long-Term Potentiation in Rat Hippocampal Areas CA1 and CA3. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 25, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, E.M.; Vivar, C.; Camandola, S. Physiology and Pathology of Calcium Signaling in the Brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, R.F.; Lovinger, D.M.; Colley, P.A.; Linden, D.J.; Routtenberg, A. Translocation of Protein Kinase C Activity May Mediate Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation. Science 1986, 231, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klann, E.; Chen, S.J.; Sweatt, J.D. Mechanism of Protein Kinase C Activation during the Induction and Maintenance of Long-Term Potentiation Probed Using a Selective Peptide Substrate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8337–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenka, R.C.; Madison, D.V.; Nicoll, R.A. Potentiation of Synaptic Transmission in the Hippocampus by Phorbol Esters. Nature 1986, 321, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacktor, T.C.; Osten, P.; Valsamis, H.; Jiang, X.; Naik, M.U.; Sublette, E. Persistent Activation of the Zeta Isoform of Protein Kinase C in the Maintenance of Long-Term Potentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8342–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovinger, D.M.; Akers, R.F.; Nelson, R.B.; Barnes, C.A.; McNaughton, B.L.; Routtenberg, A. A Selective Increase in Phosphorylation of Protein F1, a Protein Kinase C Substrate, Directly Related to Three Day Growth of Long Term Synaptic Enhancement. Brain Res. 1985, 343, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.J.; Buschler, A.; Köhr, G.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Afferent Input Selects NMDA Receptor Subtype to Determine the Persistency of Hippocampal LTP in Freely Behaving Mice. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2016, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Reiser, M.; Pin, J.-P.; Wilsch, V.; Bockaert, J.; Reymann, K.G.; Riedel, G. Physiological and Pharmacological Profile Oftrans-Azetidine-2,4-Dicarboxylic Acid: Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Agonism and Effects on Long-Term Potentiation. Neuroscience 1996, 72, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy-Aksel, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Synaptic Strength at the Temporoammonic Input to the Hippocampal CA1 Region in Vivo Is Regulated by NMDA Receptors, Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. Neuroscience 2015, 309, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.C.; Mason, S.E. Effects of the NMDA Receptor/Channel Antagonists CPP and MK801 on Hippocampal Field Potentials and Long-Term Potentiation in Anesthetized Rats. Brain Res. 1988, 462, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.G. Synaptic Plasticity and Learning: Selective Impairment of Learning Rats and Blockade of Long-Term Potentiation in Vivo by the N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Antagonist AP5. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1989, 9, 3040–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.G.; Anderson, E.; Lynch, G.S.; Baudry, M. Selective Impairment of Learning and Blockade of Long-Term Potentiation by an N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Antagonist, AP5. Nature 1986, 319, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, S.; Gottschling, C.; Faissner, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Intrinsic Cellular and Molecular Properties of in Vivo Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity Are Altered in the Absence of Key Synaptic Matrix Molecules. Hippocampus 2017, 27, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschler, A.; Goh, J.J.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Frequency Dependency of NMDA Receptor-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampal CA1 Region of Freely Behaving Mice. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 2238–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarse, J.; Herlitze, S.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. The Requirement of BDNF for Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity Is Experience-Dependent. Hippocampus 2015, 26, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Bliss, T.V.P.; Dutrieux, G.; Laroche, S.; Errington, M.L. Induction and Duration of Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus of the Freely Moving Mouse. J. Neurosci. Meth. 1997, 75, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Braunewell, K.-H.; Reymann, K.G. Subtype-Specific Involvement of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Two Forms of Long-Term Potentiation in the Dentate Gyrus of Freely Moving Rats. Neuroscience 1998, 86, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrick, B.E.; Weinberger, S.B.; Martinez, J.L. Opioid Receptors Are Involved in an NMDA Receptor-Independent Mechanism of LTP Induction at Hippocampal Mossy Fiber-CA3 Synapses. Brain Res. Bull. 1991, 27, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyman, S.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 (MGluR1) and 5 (MGluR5) Regulate Late Phases of LTP and LTD in the Hippocampal CA1 Region in Vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Braunewell, K.-H. The Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor, MGluR5, Is a Key Determinant of Good and Bad Spatial Learning Performance and Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.S.; Raymond, C.R.; Abraham, W.C. Priming of Long-Term Potentiation Induced by Activation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Coupled to Phospholipase C. Hippocampus 1998, 8, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, C.R.; Thompson, V.L.; Tate, W.P.; Abraham, W.C. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Trigger Homosynaptic Protein Synthesis to Prolong Long-Term Potentiation. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, J.E.; Chen, Y.; Banko, J.L.; Sheffler, D.J.; Williams, R.; Telk, A.N.; Watson, N.L.; Xiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jones, P.J.; et al. MGluR5 Positive Allosteric Modulators Facilitate Both Hippocampal LTP and LTD and Enhance Spatial Learning. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 34, 2057–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, J.M.; Xiang, Z.; Lv, X.; Ghoshal, A.; Dickerson, J.W.; Bridges, T.M.; Johnson, K.A.; Foster, D.J.; Gregory, K.J.; Vinson, P.N.; et al. Biased MGlu5-Positive Allosteric Modulators Provide In Vivo Efficacy without Potentiating MGlu5 Modulation of NMDAR Currents. Neuron 2015, 86, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noetzel, M.J.; Gregory, K.J.; Vinson, P.N.; Manka, J.T.; Stauffer, S.R.; Lindsley, C.W.; Niswender, C.M.; Xiang, Z.; Conn, P.J. A Novel Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Positive Allosteric Modulator Acts at a Unique Site and Confers Stimulus Bias to MGlu5 Signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikbaev, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor, MGlu5, Regulates Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity and Is Required for Tetanisation-Triggered Changes in Theta and Gamma Oscillations. Neuropharmacology 2016, 115, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, M.; Lössner, B.; Ott, T. Anisomycin Blocks the Late Phase of Long-Term Potentiation in the Dentate Gyrus of Freely Moving Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 1984, 13, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, S.; Abraham, W.C. Inhibition of Protein Synthesis in the Dentate Gyrus, but Not the Entorhinal Cortex, Blocks Maintenance of Long-Term Potentiation in Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1989, 106, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthies, H.; Frey, U.; Reymann, K.; Krug, M.; Jork, R.; Schröeder, H. Different Mechanisms and Multiple Stages of LTP. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1990, 268, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, U.; Huang, Y.Y.; Kandel, E.R. Effects of CAMP Simulate a Late Stage of LTP in Hippocampal CA1 Neurons. Science 1993, 260, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, E.W.; Ganong, A.H.; Cotman, C.W. Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus Involves Activation of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptors. Brain Res. 1984, 323, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coan, E.J.; Collingridge, G.L. Characterization of an N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Component of Synaptic Transmission in Rat Hippocampal Slices. Neuroscience 1987, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collingridge, G.L.; Blake, J.F.; Brown, M.W.; Bashir, Z.I.; Ryan, E. Involvement of Excitatory Amino Acid Receptors in Long-Term Potentiation in the Schaffer Collateral-Commissural Pathway of Rat Hippocampal Slices. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1991, 69, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, M.F.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic Plasticity: LTP and LTD. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1994, 4, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Lu, Y.; Henderson, J.; Taverna, F.; Romano, C.; Abramow-Newerly, W.; Wojtowicz, J.M.; Roder, J. Selective Abolition of the NMDA Component of Long-Term Potentiation in Mice Lacking MGluR5. Learn. Mem. 1998, 5, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, H.; Hubert, G.W.; Smith, Y.; Levey, A.I.; Conn, P.J. Activation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Has Direct Excitatory Effects and Potentiates NMDA Receptor Currents in Neurons of the Subthalamic Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 7871–7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benquet, P.; Gee, C.E.; Gerber, U. Two Distinct Signaling Pathways Upregulate NMDA Receptor Responses via Two Distinct Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtypes. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9679–9686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, A.J.; Palmer, M.J.; Henley, J.M.; Collingridge, G.L.; Jane, D.E. (RS)-2-Chloro-5-Hydroxyphenylglycine (CHPG) Activates MGlu5, but Not MGlu1, Receptors Expressed in CHO Cells and Potentiates NMDA Responses in the Hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 1997, 36, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaioni, G.; Marino, M.J.; Valenti, O.; Traynelis, S.F.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors 1 and 5 Differentially Regulate CA1 Pyramidal Cell Function. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 5925–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attucci, S.; Carlà, V.; Mannaioni, G.; Moroni, F. Activation of Type 5 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Enhances NMDA Responses in Mice Cortical Wedges. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 132, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyoshi, K.; Masu, M.; Ishii, T.; Shigemoto, R.; Mizuno, N.; Nakanishi, S. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of the Rat NMDA Receptor. Nature 1991, 354, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monyer, H.; Burnashev, N.; Laurie, D.J.; Sakmann, B.; Seeburg, P.H. Developmental and Regional Expression in the Rat Brain and Functional Properties of Four NMDA Receptors. Neuron 1994, 12, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Cummings, J.; Roldan, L.A.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Changing Subunit Composition of Heteromeric NMDA Receptors during Development of Rat Cortex. Nature 1994, 368, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, N.; Petralia, R.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Blahos, J.; Hell, J.W.; Wenthold, R.J. A Developmental Change in NMDA Receptor-Associated Proteins at Hippocampal Synapses. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, J.A.; Ashby, M.C.; Sanz-Clemente, A.; Roche, K.W.; Isaac, J.T.R. MGluR5 and NMDA Receptors Drive the Experience- and Activity-Dependent NMDA Receptor NR2B to NR2A Subunit Switch. Neuron 2011, 70, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wong, T.P.; Pozza, M.F.; Lingenhoehl, K.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Auberson, Y.P.; Wang, Y.T. Role of NMDA Receptor Subtypes in Governing the Direction of Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. Science 2004, 304, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, P.V.; Johnson, B.E.; Moult, P.R.; Auberson, Y.P.; Brown, M.W.; Molnar, E.; Collingridge, G.L.; Bashir, Z.I. Differential Roles of NR2A and NR2B-Containing NMDA Receptors in Cortical Long-Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7821–7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Riordan, K.J.; Hu, N.-W.; Rowan, M.J. Physiological Activation of MGlu5 Receptors Supports the Ion Channel Function of NMDA Receptors in Hippocampal LTD Induction in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.M.; Jia, Z.; Janus, C.; Henderson, J.T.; Gerlai, R.; Wojtowicz, J.M.; Roder, J.C. Mice Lacking Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Show Impaired Learning and Reduced CA1 Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) but Normal CA3 LTP. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, U.; Krug, M.; Reymann, K.G.; Matthies, H. Anisomycin, an Inhibitor of Protein Synthesis, Blocks Late Phases of LTP Phenomena in the Hippocampal CA1 Region in Vitro. Brain Res. 1988, 452, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Kulla, A.; Frey, J.U. Requirement of Translation but Not Transcription for the Maintenance of Long-Term Depression in the CA1 Region of Freely Moving Rats. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8572–8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagena, H.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Differentiation in the Protein Synthesis-Dependency of Persistent Synaptic Plasticity in Mossy Fiber and Associational/Commissural CA3 Synapses in Vivo. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavigelli, M.; Dolfi, F.; Claret, F.X.; Karin, M. Induction of C-Fos Expression through JNK-Mediated TCF/Elk-1 Phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 5957–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, Y.-J.I.; Kumar, V.; O’Malley, K.L. Intracellular Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 (MGluR5) Activates Signaling Cascades Distinct from Cell Surface Counterparts. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35827–35838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakeman, P.R.; Lanahan, A.A.; O’Brien, R.; Roche, K.; Barnes, C.A.; Huganir, R.L.; Worley, P.F. Homer: A Protein That Selectively Binds Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. Nature 1997, 386, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.C.; Xiao, B.; Yuan, J.P.; Lanahan, A.A.; Leoffert, K.; Li, M.; Linden, D.J.; Worley, P.F. Homer Binds a Novel Proline-Rich Motif and Links Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors with IP3 Receptors. Neuron 1998, 21, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, C.; Piëch, V.; Wilson, N.R.; Passafaro, M.; Liu, G.; Sheng, M. Regulation of Dendritic Spine Morphology and Synaptic Function by Shank and Homer. Neuron 2001, 31, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.C.; Xiao, B.; Naisbitt, S.; Yuan, J.P.; Petralia, R.S.; Brakeman, P.; Doan, A.; Aakalu, V.K.; Lanahan, A.A.; Sheng, M.; et al. Coupling of MGluR/Homer and PSD-95 Complexes by the Shank Family of Postsynaptic Density Proteins. Neuron 1999, 23, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naisbitt, S.; Kim, E.; Tu, J.C.; Xiao, B.; Sala, C.; Valtschanoff, J.; Weinberg, R.J.; Worley, P.F.; Sheng, M. Shank, a Novel Family of Postsynaptic Density Proteins That Binds to the NMDA Receptor/PSD-95/GKAP Complex and Cortactin. Neuron 1999, 23, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridi, M.; Schoch, H.; Florian, C.; Poplawski, S.G.; Banerjee, A.; Hawk, J.D.; Porcari, G.S.; Lejards, C.; Hahn, C.-G.; Giese, K.-P.; et al. Transcriptional Corepressor SIN3A Regulates Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity via Homer1/MGluR5 Signaling. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e92385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugi, T.; Oyama, T.; Muto, T.; Nakanishi, S.; Morikawa, K.; Jingami, H. Crystal Structures of Autoinhibitory PDZ Domain of Tamalin: Implications for Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Trafficking Regulation. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 2192–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, J.; Kimura, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Soda, T.; Shigemoto, R.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakanishi, S. Tamalin, a PDZ Domain-Containing Protein, Links a Protein Complex Formation of Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and the Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor Cytohesins. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, Z.A.; Collett, V.J.; Conquet, F.; Jia, Z.; van der Putten, H.; Collingridge, G.L. The Regulation of Hippocampal LTP by the Molecular Switch, a Form of Metaplasticity, Requires MGlu5 Receptors. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49 (Suppl. S1), 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naie, K.; Tsanov, M.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Enable Two Distinct Forms of Long-Term Depression in the Rat Dentate Gyrus in Vivo. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, B.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Hippocampal Long-Term Depression Is Facilitated by the Acquisition and Updating of Memory of Spatial Auditory Content and Requires MGlu5 Activation. Neuropharmacology 2016, 115, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, W.; Cammalleri, M.; Sanna, P.P. The Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Is Necessary for Late-Phase Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampal CA1 Region. Brain Res. 2004, 1022, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, D.T.; Li, Y.; Takagi, S.; Presti, K.T.; Ramikie, T.S.; Rook, J.M.; Jones, C.K.; Lindsley, C.W.; Conn, P.J.; Bolshakov, V.Y.; et al. An MGlu5-Positive Allosteric Modulator Rescues the Neuroplasticity Deficits in a Genetic Model of NMDA Receptor Hypofunction in Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol 2016, 41, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.M.; Roder, J.C.; Bear, M.F. Chemical Induction of MGluR5- and Protein Synthesis-Dependent Long-Term Depression in Hippocampal Area CA1. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harney, S.C.; Rowan, M.; Anwyl, R. Long-Term Depression of NMDA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Transmission Is Dependent on Activation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors and Is Altered to Long-Term Potentiation by Low Intracellular Calcium Buffering. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparini, F.; Lingenhöhl, K.; Stoehr, N.; Flor, P.J.; Heinrich, M.; Vranesic, I.; Biollaz, M.; Allgeier, H.; Heckendorn, R.; Urwyler, S.; et al. 2-Methyl-6-(Phenylethynyl)-Pyridine (MPEP), a Potent, Selective and Systemically Active MGlu5 Receptor Antagonist. Neuropharmacology 1999, 38, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faas, G.C.; Adwanikar, H.; Gereau, R.W.; Saggau, P. Modulation of Presynaptic Calcium Transients by Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Activation: A Differential Role in Acute Depression of Synaptic Transmission and Long-Term Depression. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6885–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; You, J.-L.; Wu, M.-Y.; Hsu, K.-S. Rap1-Induced P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation Facilitates AMPA Receptor Trafficking via the GDI·Rab5 Complex Potential Role in (S)-3,5-Dihydroxyphenylglycine-Induced Long Term Depression. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12286–12292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-C.; Hsu, K.-S. Sustained Activation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases Mediate the Expression of (S)-3,5-Dihydroxyphenylglycine-Induced Long-Term Depression in the Hippocampal CA1 Region. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, T.V.; Collingridge, G.L. A Synaptic Model of Memory: Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus. Nature 1993, 361, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunewell, K.-H.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Long-Term Depression: A Cellular Basis for Learning? Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 12, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagena, H.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Learning-Facilitated Synaptic Plasticity at CA3 Mossy Fiber and Commissural-Associational Synapses Reveals Different Roles in Information Processing. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercerón-Martínez, D.; Almaguer-Melian, W.; Bergado, J.A. Basolateral Amygdala Stimulation plus Water Maze Training Restore Dentate Gyrus LTP and Improve Spatial Learning and Memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 417, 113589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Park, P.; Baek, G.-C.; Sim, S.-E.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, Y.; Ahn, S.-H.; Lim, C.-S.; Lee, Y.-S.; Collingridge, G.L.; et al. Effects of PI3Kβ Overexpression in the Hippocampus on Synaptic Plasticity and Spatial Learning. Mol. Brain 2014, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.D.; Jones, F.L.; Derrick, B.E. Novel Environments Enhance the Induction and Maintenance of Long-Term Potentiation in the Dentate Gyrus. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6497–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Cullen, W.K.; Anwyl, R.; Rowan, M.J. Dopamine-Dependent Facilitation of LTP Induction in Hippocampal CA1 by Exposure to Spatial Novelty. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Mercado, D.; Dieguez, D.; Barea-Rodriguez, E.J. Brief Novelty Exposure Facilitates Dentate Gyrus LTP in Aged Rats. Hippocampus 2008, 18, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. The Hippocampal CA1 Region and Dentate Gyrus Differentiate between Environmental and Spatial Feature Encoding through Long-Term Depression. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashby, D.M.; Floresco, S.B.; Phillips, A.G.; McGirr, A.; Seamans, J.K.; Wang, Y.T. LTD Is Involved in the Formation and Maintenance of Rat Hippocampal CA1 Place-Cell Fields. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki-Hamada, S.; Ayumu, F.; Satoh, S.; Iwai, T.; Oka, J.-I. GLP-2 Restores Impairments in Spatial Working Memory and Hippocampal LTD via the MEK/ERK Pathway in Juvenile-Onset Diabetes Rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 406, 113235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-P.; Lee, C.-T.; Hou, W.-H.; Lin, M.-S.; Lai, H.-L.; Chien, C.-L.; Chang, C.; Cheng, P.-L.; Lien, C.-C.; Chern, Y. Type VI Adenylyl Cyclase Negatively Regulates GluN2B-Mediated LTD and Spatial Reversal Learning. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, M.A.E.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Spatial Olfactory Learning Facilitates Long-Term Depression in the Hippocampus. Hippocampus 2013, 23, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagena, H.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. MGLU Receptors. Recept 2017, 31, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Z.K.; Ganella, D.E.; Dick, A.L.W.; Duncan, J.R.; Ong-Palsson, E.; Bathgate, R.A.D.; Kim, J.H.; Lawrence, A.J. Spatial Learning Requires MGlu5 Signalling in the Dorsal Hippocampus. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, G.; Platt, B.; Micheau, J. Glutamate Receptor Function in Learning and Memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 140, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyi, A.; Schachtman, T.R.; Christoffersen, G.R.J. The Role of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in Learning and Memory Processes. Drug News Perspect. 2005, 18, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayoun, H.; Stefani, M.R.; Adams, B.W.; Tamagan, G.D.; Moghaddam, B. Functional Interaction Between NMDA and MGlu5 Receptors: Effects on Working Memory, Instrumental Learning, Motor Behaviors, and Dopamine Release. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004, 29, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, M.A.E.; Güntürkün, O.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. The Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor, MGlu5, Is Required for Extinction Learning That Occurs in the Absence of a Context Change. Hippocampus 2014, 25, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyi, A.; Serfozo, P.; Shelat, P.B.; Dopheide, M.M.; Coulibaly, A.P.; Schachtman, T.R. Differential Roles of Hippocampal Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors 1 and 5 in Inhibitory Avoidance Learning. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2007, 88, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gravius, A.; Barberi, C.; Schäfer, D.; Schmidt, W.J.; Danysz, W. The Role of Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Acquisition and Expression of Contextual and Auditory Fear Conditioning in Rats—A Comparison. Neuropharmacology 2006, 51, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handford, C.E.; Tan, S.; Lawrence, A.J.; Kim, J.H. The Effect of the MGlu5 Negative Allosteric Modulator MTEP and NMDA Receptor Partial Agonist D-Cycloserine on Pavlovian Conditioned Fear. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uslaner, J.M.; Parmentier-Batteur, S.; Flick, R.B.; Surles, N.O.; Lam, J.S.H.; McNaughton, C.H.; Jacobson, M.A.; Hutson, P.H. Dose-Dependent Effect of CDPPB, the MGluR5 Positive Allosteric Modulator, on Recognition Memory Is Associated with GluR1 and CREB Phosphorylation in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balschun, D.; Zuschratter, W.; Wetzel, W. Allosteric Enhancement of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Function Promotes Spatial Memory. Neuroscience 2006, 142, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.W.; Walker, J.M.; Klakotskaia, D.; Will, M.J.; Serfozo, P.; Simonyi, A.; Schachtman, T.R. Effects of a Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Positive Allosteric Modulator, CDPPB, on Spatial Learning Task Performance in Rodents. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2013, 99, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckler, T.; Oliveira, A.F.M.; Dyck, C.V.; Craenendonck, H.V.; Mateus, A.M.A.; Langlois, X.; Lesage, A.S.J.; Prickaerts, J. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 Blockade Impairs Acquisition and Retention in a Spatial Water Maze Task. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 164, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Kraniotis, S.; He, Q.; Marshall, J.J.; Nomura, T.; Stauffer, S.R.; Lindsley, C.W.; Conn, P.J.; Contractor, A. Potentiating MGluR5 Function with a Positive Allosteric Modulator Enhances Adaptive Learning. Learn. Mem. 2013, 20, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T.Y.C.; Hannan, A.J. Enhancement of Cognitive Function in Models of Brain Disease through Environmental Enrichment and Physical Activity. Neuropharmacology 2013, 64, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.; Holloway, J.; Holtkamp, C.C.M.; Larsson, A.; Hartman, L.C.; Pearce, R.; Scherman, B.; Johansson, S.; Thomas, P.W.; Wareing, L.A.; et al. Effects of Multi-sensory Stimulation for People with Dementia. J. Adv. Nurs. 2003, 43, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschler, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Brief Environmental Enrichment Elicits Metaplasticity of Hippocampal Synaptic Potentiation in Vivo. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, G.P.; Olin, A.; O’Riordan, K.; Hullinger, R.; Burger, C. Environmental Enrichment Improves Hippocampal Function in Aged Rats by Enhancing Learning and Memory, LTP, and MGluR5-Homer1c Activity. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Ngomba, R.T.; Storto, M.; Kulla, A.; Catania, M.V.; Chiechio, S.; Rampello, L.; Passarelli, F.; Capece, A.; Reymann, K.G.; et al. An Increased Expression of the MGlu5 Receptor Protein Following LTP Induction at the Perforant Path-Dentate Gyrus Synapse in Freely Moving Rats. Neuropharmacology 2003, 44, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, G.; Casabona, G.; Platt, B.; Macphail, E.M.; Nicoletti, F. Fear Conditioning-Induced Time- and Subregion-Specific Increase in Expression of MGlu5 Receptor Protein in Rat Hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D. Regulation of Hippocampal Information Encoding by Metabotopic Glutamate Receptors. Neuroforum 2018, 24, A121–A126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Passive Spatial Perception Facilitates the Expression of Persistent Hippocampal Long-Term Depression. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 22, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, D.; Feldmann, M.; Shchyglo, O.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity, Spatial Memory, and Neurotransmitter Receptor Expression Are Profoundly Altered by Gradual Loss of Hearing Ability. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 23, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Spatial Olfactory Learning Contributes to Place Field Formation in the Hippocampus. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsanov, M.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Visual Cortex Plasticity Evokes Excitatory Alterations in the Hippocampus. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2009, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keefe, J.; Dostrovsky, J. The Hippocampus as a Spatial Map. Preliminary Evidence from Unit Activity in the Freely-Moving Rat. Brain Res. 1971, 34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knierim, J.; Kudrimoti, H.; McNaughton, B. Place Cells, Head Direction Cells, and the Learning of Landmark Stability. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axmacher, N.; Mormann, F.; Fernández, G.; Elger, C.E.; Fell, J. Memory Formation by Neuronal Synchronization. Brain Res. Rev. 2006, 52, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düzel, E.; Penny, W.D.; Burgess, N. Brain Oscillations and Memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyhus, E.; Curran, T. Functional Role of Gamma and Theta Oscillations in Episodic Memory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikbaev, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Hippocampal Network Activity Is Transiently Altered by Induction of Long-Term Potentiation in the Dentate Gyrus of Freely Behaving Rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2007, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikbaev, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Relationship of Hippocampal Theta and Gamma Oscillations to Potentiation of Synaptic Transmission. Front. Neurosci. 2008, 2, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouton, M.E. Context and Behavioral Processes in Extinction. Learn. Mem. 2004, 11, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Maren, S. Hippocampal Involvement in Contextual Modulation of Fear Extinction. Hippocampus 2007, 17, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiserer, R.S.; Harrison, F.E.; Syverud, D.C.; McDonald, M.P. Impaired Spatial Learning in the APPSwe + PSEN1ΔE9 Bigenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Genes Brain Behav. 2007, 6, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.M.; Fowler, S.W.; Miller, D.K.; Sun, A.Y.; Weisman, G.A.; Wood, W.G.; Sun, G.Y.; Simonyi, A.; Schachtman, T.R. Spatial Learning and Memory Impairment and Increased Locomotion in a Transgenic Amyloid Precursor Protein Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 222, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkeviciene, R.; Banerjee, P.; Tanila, H. Memantine Improves Spatial Learning in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 311, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, P.; Levenson, J.M.; Battaglia, F.; Atkinson, R.; Teague, R.; Antalffy, B.; Armstrong, D.; Arancio, O.; Sweatt, J.D.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Learning and Memory and Synaptic Plasticity Are Impaired in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, S.E.; Mou, X.; Zoghbi, H.Y.; Ji, D. Impaired Spatial Memory Codes in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome. Elife 2018, 7, e31451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, H.A.; Pozzo-Miller, L. The Role of MeCP2 in Learning and Memory. Learn. Mem. 2019, 26, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.J.; Asafo-Adjei, P.K.; Arnold, H.M.; Brown, R.E.; Bauchwitz, R.P. A Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of the Fmr1-tm1Cgr Fragile X Mouse. Genes Brain Behav. 2004, 3, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Murthy, A.C.; Zhang, L.; Johnson, E.B.; Schaller, E.G.; Allan, A.M.; Zhao, X. Inhibition of GSK3β Improves Hippocampus-Dependent Learning and Rescues Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet 2012, 21, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlichman, R.S.; Luminais, S.N.; White, S.L.; Rudnick, N.D.; Ma, N.; Dow, H.C.; Kreibich, A.S.; Abel, T.; Brodkin, E.S.; Hahn, C.-G.; et al. Neuregulin 1 Transgenic Mice Display Reduced Mismatch Negativity, Contextual Fear Conditioning and Social Interactions. Brain Res. 2009, 1294, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Kasai, A.; Mizuno, M.; Fengyi, L.; Shintani, N.; Maeda, S.; Yokoyama, M.; Ozaki, M.; Nawa, H. Phenotypic Characterization of Transgenic Mice Overexpressing Neuregulin-1. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deakin, I.H.; Nissen, W.; Law, A.J.; Lane, T.; Kanso, R.; Schwab, M.H.; Nave, K.-A.; Lamsa, K.P.; Paulsen, O.; Bannerman, D.M.; et al. Transgenic Overexpression of the Type I Isoform of Neuregulin 1 Affects Working Memory and Hippocampal Oscillations but Not Long-Term Potentiation. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, N.E.; Morisot, N.; Girardon, S.; Millan, M.J.; Loiseau, F. Enhancement of Social Novelty Discrimination by Positive Allosteric Modulators at Metabotropic Glutamate 5 Receptors: Adolescent Administration Prevents Adult-Onset Deficits Induced by Neonatal Treatment with Phencyclidine. Psychopharmacology 2013, 225, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenbaum, H. On the Integration of Space, Time, and Memory. Neuron 2017, 95, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, A.J.; Doeller, C.F. Plasticity of Hippocampal Memories in Humans. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 43, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksymetz, J.; Moran, S.P.; Conn, P.J. Targeting Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors for Novel Treatments of Schizophrenia. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montana, M.C.; Gereau, R.W. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors as Targets for Analgesia: Antagonism, Activation, and Allosteric Modulation. Curr. Pharm. Biotechno. 2011, 12, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).